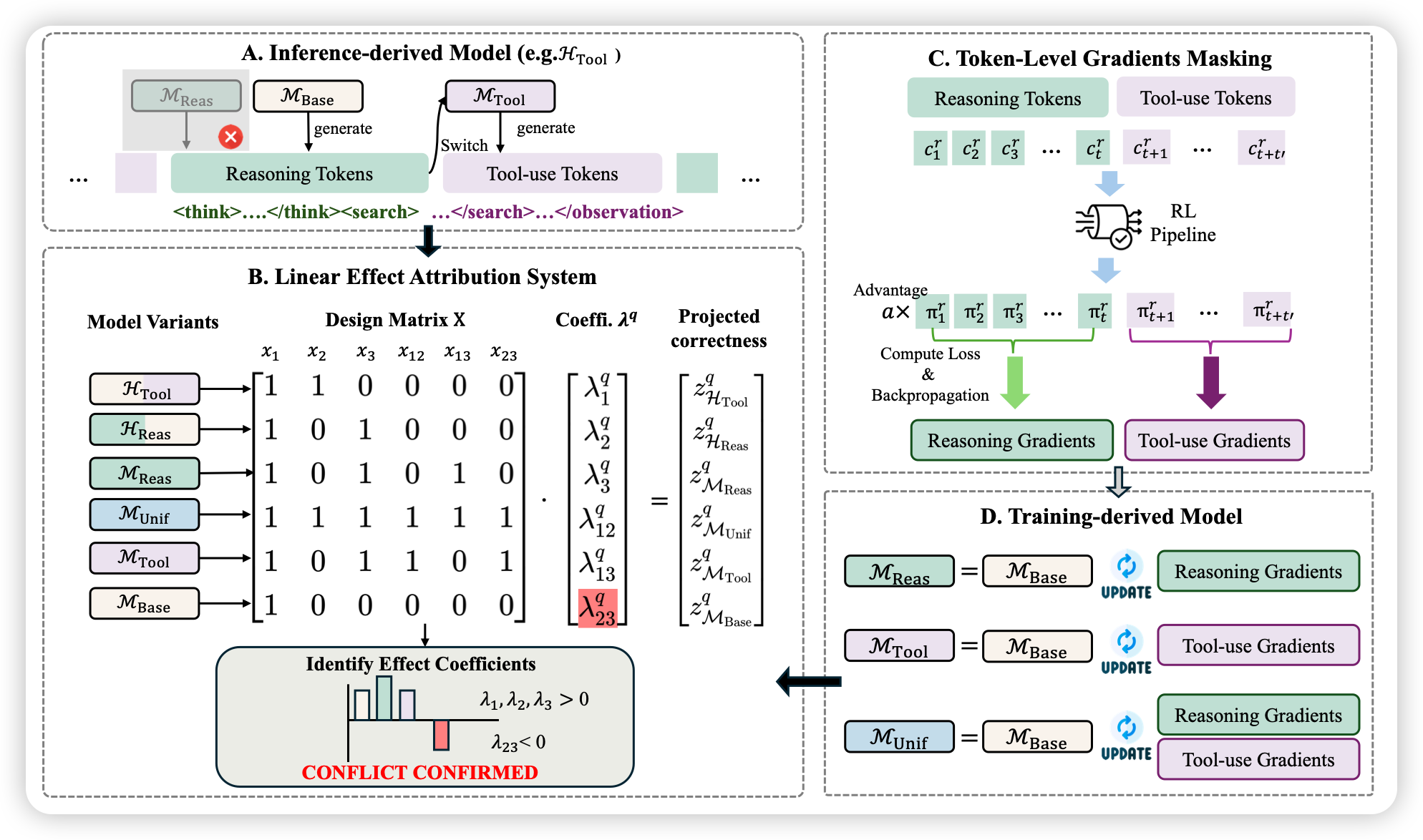
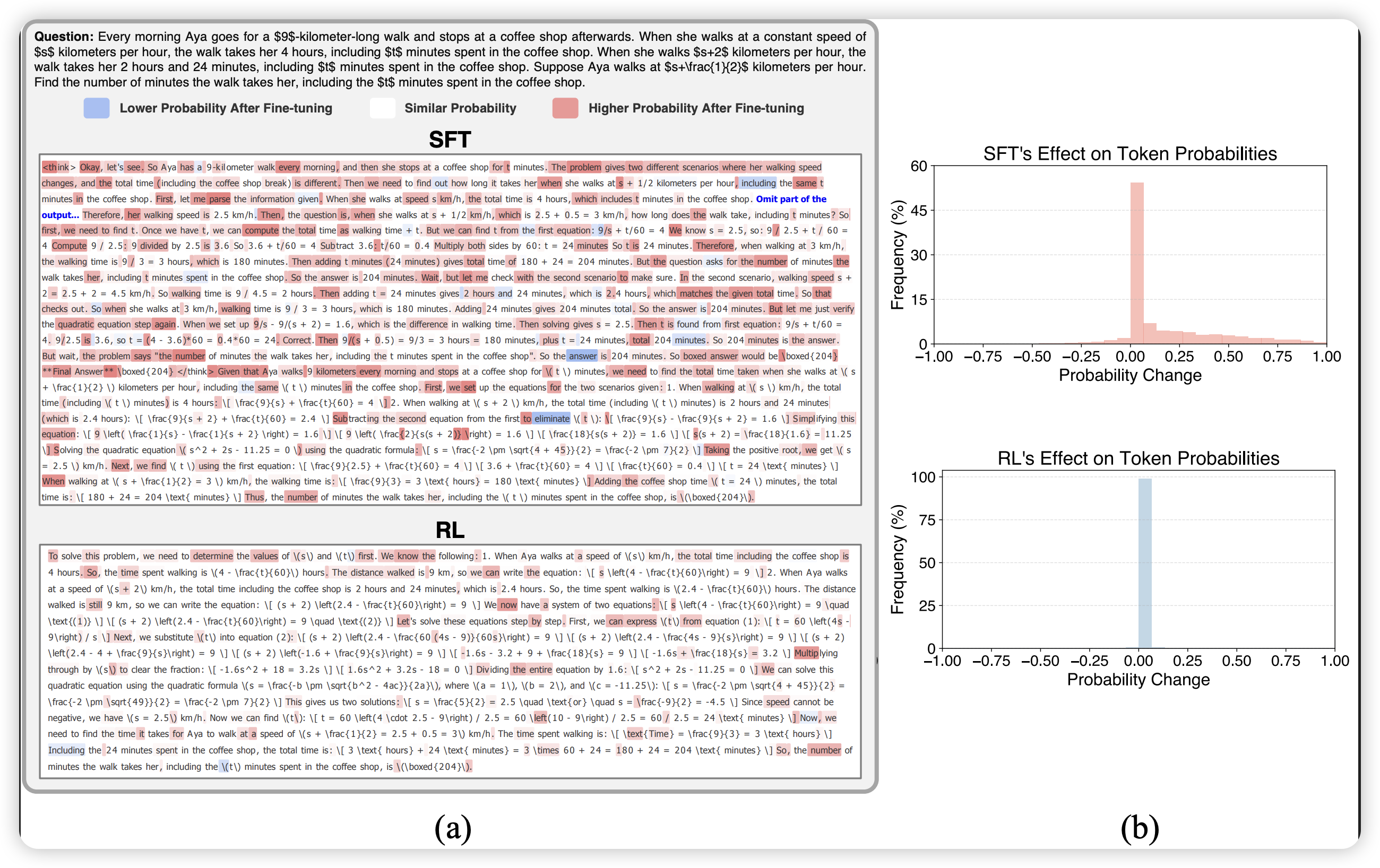
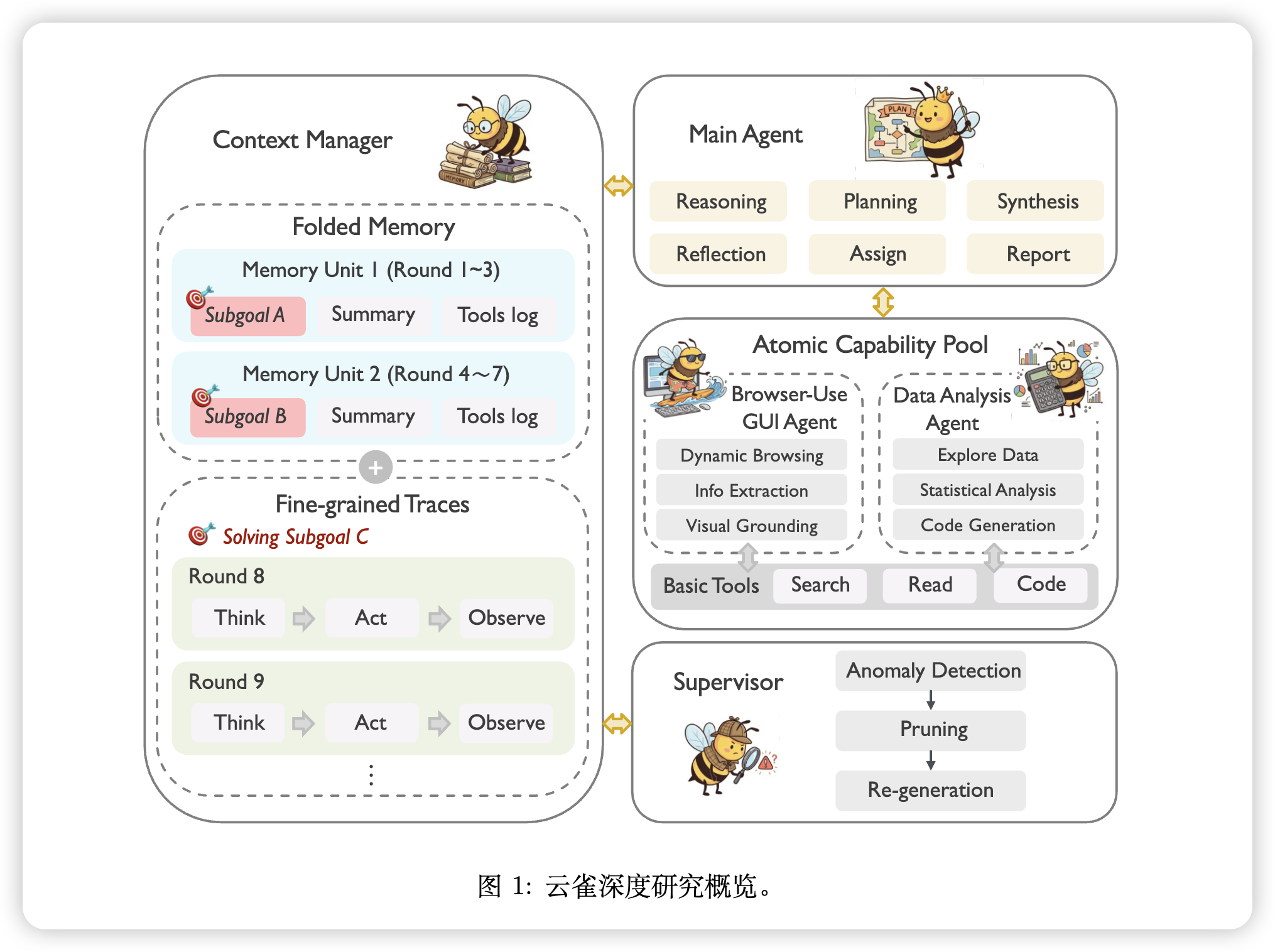
本篇博文主要内容为 2026-01-07 从Arxiv.org论文网站获取的最新论文列表,自动更新,按照NLP、CV、ML、AI、IR五个大方向区分,若需要邮件定时接收,请在评论区留下你的邮箱号。
说明:每日论文数据从Arxiv.org获取,每天早上12:00左右定时自动更新。
友情提示: 如何您需要邮箱接收每日论文数据,请在评论处留下你的邮箱。
目录
概览 (2026-01-07)
今日共更新474篇论文,其中:
- 自然语言处理共108篇(Computation and Language (cs.CL))
- 人工智能共154篇(Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI))
- 计算机视觉共80篇(Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV))
- 机器学习共105篇(Machine Learning (cs.LG))
自然语言处理
[NLP-0] Automated Semantic Rules Detection (ASRD) for Emergent Communication Interpretation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多智能体系统中涌现通信(emergent communication)的可解释性问题,即如何理解自主智能体在未受显式编程的情况下自发形成的通信策略。解决方案的关键在于提出一种自动化语义规则检测(Automated Semantic Rules Detection, ASRD)算法,该算法能够从训练于不同数据集上的智能体在Lewis博弈中交换的消息中提取相关模式,并将这些模式与输入数据的具体属性建立关联,从而显著简化对涌现语言的后续分析。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03254
作者: Bastien Vanderplaetse,Xavier Siebert,Stéphane Dupont
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:The field of emergent communication within multi-agent systems examines how autonomous agents can independently develop communication strategies, without explicit programming, and adapt them to varied environments. However, few studies have focused on the interpretability of emergent languages. The research exposed in this paper proposes an Automated Semantic Rules Detection (ASRD) algorithm, which extracts relevant patterns in messages exchanged by agents trained with two different datasets on the Lewis Game, which is often studied in the context of emergent communication. ASRD helps at the interpretation of the emergent communication by relating the extracted patterns to specific attributes of the input data, thereby considerably simplifying subsequent analysis.
zh
[NLP-1] STReason er: Empowering LLM s for Spatio-Temporal Reasoning in Time Series via Spatial-Aware Reinforcement Learning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决时间序列中时空推理(spatio-temporal reasoning)能力不足的问题,即现有方法多关注预测准确性而忽视对时间动态、空间依赖性和文本上下文的显式融合与推理。其关键解决方案是提出STReasoner框架,该框架通过整合时间序列数据、图结构信息和文本语义,使大语言模型(LLM)能够进行显式的多模态推理;同时引入S-GRPO强化学习算法,专门奖励因利用空间信息带来的性能提升,从而增强空间感知逻辑。实验表明,STReasoner在保持极低计算成本(仅为商业模型的0.004倍)的情况下,实现17%至135%的平均准确率提升,并具备良好的现实数据泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03248
作者: Juntong Ni,Shiyu Wang,Ming Jin,Qi He,Wei Jin
机构: Emory University (埃默里大学); Griffith University (格里菲斯大学); Microsoft (微软)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: preprint, we release our code publicly at this https URL
Abstract:Spatio-temporal reasoning in time series involves the explicit synthesis of temporal dynamics, spatial dependencies, and textual context. This capability is vital for high-stakes decision-making in systems such as traffic networks, power grids, and disease propagation. However, the field remains underdeveloped because most existing works prioritize predictive accuracy over reasoning. To address the gap, we introduce ST-Bench, a benchmark consisting of four core tasks, including etiological reasoning, entity identification, correlation reasoning, and in-context forecasting, developed via a network SDE-based multi-agent data synthesis pipeline. We then propose STReasoner, which empowers LLM to integrate time series, graph structure, and text for explicit reasoning. To promote spatially grounded logic, we introduce S-GRPO, a reinforcement learning algorithm that rewards performance gains specifically attributable to spatial information. Experiments show that STReasoner achieves average accuracy gains between 17% and 135% at only 0.004X the cost of proprietary models and generalizes robustly to real-world data.
zh
[NLP-2] Multi-RADS Synthetic Radiology Report Dataset and Head-to-Head Benchmarking of 41 Open-Weight and Proprietary Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决放射学风险评估系统(RADS)自动化分配难题,其核心挑战在于指南复杂性、输出格式限制以及跨不同RADS框架和模型规模的基准测试不足。解决方案的关键在于构建了一个由放射科医生验证的合成多RADS基准数据集(RXL-RADSet),包含1600份涵盖10种RADS标准(如BI-RADS、LI-RADS等)的合成影像报告,并通过两阶段放射科医生审核确保质量;同时对比了41个量化的小语言模型(SLMs,参数范围0.135B–32B)与专有模型GPT-5.2在固定引导提示下的性能表现,发现大尺寸SLMs(20–32B参数)在引导提示下可接近专有模型性能,但高复杂度RADS仍存在准确率差距。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03232
作者: Kartik Bose,Abhinandan Kumar,Raghuraman Soundararajan,Priya Mudgil,Samonee Ralmilay,Niharika Dutta,Manphool Singhal,Arun Kumar,Saugata Sen,Anurima Patra,Priya Ghosh,Abanti Das,Amit Gupta,Ashish Verma,Dipin Sudhakaran,Ekta Dhamija,Himangi Unde,Ishan Kumar,Krithika Rangarajan,Prerna Garg,Rachel Sequeira,Sudhin Shylendran,Taruna Yadav,Tej Pal,Pankaj Gupta
机构: Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India 160012; Tata Medical Center, Kolkata, India 700156; All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Kalyani, India 741245; National Cancer Institute, Jhajjar, India 124105; Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India 221005; Aster Malabar Institute of Medical Sciences, Kerala, India 670621; All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India 110029; Tata Main Hospital, Mumbai, India 400012; Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute and Research Centre, Delhi, India 110085; Baby Memorial Hospital, Kerala, India 670621; All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Jodhpur, India 342005
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Background: Reporting and Data Systems (RADS) standardize radiology risk communication but automated RADS assignment from narrative reports is challenging because of guideline complexity, output-format constraints, and limited benchmarking across RADS frameworks and model sizes. Purpose: To create RXL-RADSet, a radiologist-verified synthetic multi-RADS benchmark, and compare validity and accuracy of open-weight small language models (SLMs) with a proprietary model for RADS assignment. Materials and Methods: RXL-RADSet contains 1,600 synthetic radiology reports across 10 RADS (BI-RADS, CAD-RADS, GB-RADS, LI-RADS, Lung-RADS, NI-RADS, O-RADS, PI-RADS, TI-RADS, VI-RADS) and multiple modalities. Reports were generated by LLMs using scenario plans and simulated radiologist styles and underwent two-stage radiologist verification. We evaluated 41 quantized SLMs (12 families, 0.135-32B parameters) and GPT-5.2 under a fixed guided prompt. Primary endpoints were validity and accuracy; a secondary analysis compared guided versus zero-shot prompting. Results: Under guided prompting GPT-5.2 achieved 99.8% validity and 81.1% accuracy (1,600 predictions). Pooled SLMs (65,600 predictions) achieved 96.8% validity and 61.1% accuracy; top SLMs in the 20-32B range reached ~99% validity and mid-to-high 70% accuracy. Performance scaled with model size (inflection between 1B and =10B) and declined with RADS complexity primarily due to classification difficulty rather than invalid outputs. Guided prompting improved validity (99.2% vs 96.7%) and accuracy (78.5% vs 69.6%) compared with zero-shot. Conclusion: RXL-RADSet provides a radiologist-verified multi-RADS benchmark; large SLMs (20-32B) can approach proprietary-model performance under guided prompting, but gaps remain for higher-complexity schemes.
zh
[NLP-3] MalruleLib: Large-Scale Executable Misconception Reasoning with Step Traces for Modeling Student Thinking in Mathematics
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决学生在数学学习中系统性错误(malrule)的建模与预测问题,即如何从单一错误解答中推断出学生的误解,并准确预测其在不同题型变体下的后续错误反应。解决方案的关键在于提出 MalruleLib——一个基于学习科学和数学教育研究构建的框架,它将已知的误解转化为可执行的程序(executable procedures),并结合参数化的问题模板(parameterized problem templates)生成正确推理与错误推理的双路径步骤追踪(dual-path traces)。该框架支持大规模、可控的监督学习与评估,使模型能够在跨模板情境下更准确地识别和预测学生的真实误解,从而为教育人工智能提供诊断与反馈的基础基础设施。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03217
作者: Xinghe Chen,Naiming Liu,Shashank Sonkar
机构: Rice University (莱斯大学); University of Central Florida (中佛罗里达大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Student mistakes in mathematics are often systematic: a learner applies a coherent but wrong procedure and repeats it across contexts. We introduce MalruleLib, a learning-science-grounded framework that translates documented misconceptions into executable procedures, drawing on 67 learning-science and mathematics education sources, and generates step-by-step traces of malrule-consistent student work. We formalize a core student-modeling problem as Malrule Reasoning Accuracy (MRA): infer a misconception from one worked mistake and predict the student’s next answer under cross-template rephrasing. Across nine language models (4B-120B), accuracy drops from 66% on direct problem solving to 40% on cross-template misconception prediction. MalruleLib encodes 101 malrules over 498 parameterized problem templates and produces paired dual-path traces for both correct reasoning and malrule-consistent student reasoning. Because malrules are executable and templates are parameterizable, MalruleLib can generate over one million instances, enabling scalable supervision and controlled evaluation. Using MalruleLib, we observe cross-template degradations of 10-21%, while providing student step traces improves prediction by 3-15%. We release MalruleLib as infrastructure for educational AI that models student procedures across contexts, enabling diagnosis and feedback that targets the underlying misconception.
zh
[NLP-4] Fine-tuning Small Language Models as Efficient Enterprise Search Relevance Labelers
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决企业搜索中高质量标注数据获取困难的问题,这一问题限制了相关模型的训练与优化。其解决方案的关键在于利用大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)生成合成数据,并通过三阶段流程构建高质、低成本的领域特定相关性标注数据集:首先以种子文档生成真实感的企业查询;其次使用BM25检索难负样本以增强训练多样性;最后由教师LLM赋予相关性评分,进而将知识蒸馏至小型语言模型(Small Language Models, SLMs),从而获得性能媲美甚至超越教师模型的紧凑相关性标签器。该方法在保证标注质量的同时显著提升吞吐量(17倍)和成本效益(19倍),适用于企业级检索系统的规模化离线评估与迭代。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03211
作者: Yue Kang,Zhuoyi Huang,Benji Schussheim,Diana Licon,Dina Atia,Shixing Cao,Jacob Danovitch,Kunho Kim,Billy Norcilien,Jonah Karpman,Mahmound Sayed,Mike Taylor,Tao Sun,Pavel Metrikov,Vipul Agarwal,Chris Quirk,Ye-Yi Wang,Nick Craswell,Irene Shaffer,Tianwei Chen,Sulaiman Vesal,Soundar Srinivasan
机构: Microsoft(微软); Amazon(亚马逊)
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:In enterprise search, building high-quality datasets at scale remains a central challenge due to the difficulty of acquiring labeled data. To resolve this challenge, we propose an efficient approach to fine-tune small language models (SLMs) for accurate relevance labeling, enabling high-throughput, domain-specific labeling comparable or even better in quality to that of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs). To overcome the lack of high-quality and accessible datasets in the enterprise domain, our method leverages on synthetic data generation. Specifically, we employ an LLM to synthesize realistic enterprise queries from a seed document, apply BM25 to retrieve hard negatives, and use a teacher LLM to assign relevance scores. The resulting dataset is then distilled into an SLM, producing a compact relevance labeler. We evaluate our approach on a high-quality benchmark consisting of 923 enterprise query-document pairs annotated by trained human annotators, and show that the distilled SLM achieves agreement with human judgments on par with or better than the teacher LLM. Furthermore, our fine-tuned labeler substantially improves throughput, achieving 17 times increase while also being 19 times more cost-effective. This approach enables scalable and cost-effective relevance labeling for enterprise-scale retrieval applications, supporting rapid offline evaluation and iteration in real-world settings.
zh
[NLP-5] UltraLogic: Enhancing LLM Reasoning through Large-Scale Data Synthesis and Bipolar Float Reward
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在复杂通用推理任务中面临的瓶颈问题,即多步逻辑推理、规划与验证能力不足的问题。现有方法如基于可验证奖励的强化学习(Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards, RLVR)受限于缺乏大规模、高质量且难度分级的数据集。为此,作者提出UltraLogic框架,其核心创新在于通过代码驱动的求解方法(Code-based Solving methodology)将问题的逻辑内核与其自然语言表达解耦,从而实现高质量数据的自动化生成;同时引入双极浮点奖励机制(Bipolar Float Reward, BFR),利用分级惩罚有效区分完全正确与存在逻辑缺陷的回答,缓解二值奖励稀疏性和非负奖励陷阱问题,并结合难度匹配策略显著提升训练效率,引导模型收敛至全局逻辑最优解。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03205
作者: Yile Liu,Yixian Liu,Zongwei Li,Yufei Huang,Xinhua Feng,Zhichao Hu,Jinglu Hu,Jianfeng Yan,Fengzong Lian,Yuhong Liu
机构: Hunyuan, Tencent; Waseda University
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 19 pages, 6 figures, 7 tables
Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in natural language processing , complex general-purpose reasoning requiring multi-step logic, planning, and verification remains a critical bottleneck. Although Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has succeeded in specific domains , the field lacks large-scale, high-quality, and difficulty-calibrated data for general reasoning. To address this, we propose UltraLogic, a framework that decouples the logical core of a problem from its natural language expression through a Code-based Solving methodology to automate high-quality data production. The framework comprises hundreds of unique task types and an automated calibration pipeline across ten difficulty levels. Furthermore, to mitigate binary reward sparsity and the Non-negative Reward Trap, we introduce the Bipolar Float Reward (BFR) mechanism, utilizing graded penalties to effectively distinguish perfect responses from those with logical flaws. Our experiments demonstrate that task diversity is the primary driver for reasoning enhancement , and that BFR, combined with a difficulty matching strategy, significantly improves training efficiency, guiding models toward global logical optima.
zh
[NLP-6] DIP: Dynamic In-Context Planner For Diffusion Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决扩散语言模型(Diffusion Language Models, DLMs)在处理长上下文时因双向注意力机制导致的计算开销过大问题。传统方法需将所有示例一次性放入提示(prompt)中,随着上下文长度增长,推理效率显著下降。解决方案的关键在于发现扩散生成范式允许在生成过程中动态调整上下文,基于此提出动态上下文规划器(Dynamic In-Context Planner, DIP),通过在生成阶段动态选择并插入示例,而非预先固定全部示例,从而在保持生成质量的同时实现最高达12.9倍的推理加速(相比标准推理)和1.17倍的KV缓存增强推理加速。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03199
作者: Yang Li,Han Meng,Chenan Wang,Haipeng Chen
机构: College of William & Mary (威廉与玛丽学院)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 4 pages
Abstract:Diffusion language models (DLMs) have shown strong potential for general natural language tasks with in-context examples. However, due to the bidirectional attention mechanism, DLMs incur substantial computational cost as context length increases. This work addresses this issue with a key discovery: unlike the sequential generation in autoregressive language models (ARLMs), the diffusion generation paradigm in DLMs allows \textitefficient dynamic adjustment of the context during generation. Building on this insight, we propose \textbfDynamic \textbfIn-Context \textbfPlanner (DIP), a context-optimization method that dynamically selects and inserts in-context examples during generation, rather than providing all examples in the prompt upfront. Results show DIP maintains generation quality while achieving up to 12.9 \times inference speedup over standard inference and 1.17 \times over KV cache-enhanced inference.
zh
[NLP-7] X-MuTeST: A Multilingual Benchmark for Explainable Hate Speech Detection and A Novel LLM -consulted Explanation Framework AAAI2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决社交媒体中仇恨言论检测在准确性和可解释性方面的挑战,尤其针对资源匮乏的印地语(Indic languages)等语言。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一种新颖的可解释性引导训练框架 X-MuTeST(eXplainable Multilingual haTe Speech deTection),该框架融合了大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的高层语义推理与传统注意力增强技术,并通过提供词级人工标注理由(rationale)来指导模型训练。具体而言,X-MuTeST 通过计算原始文本与一元组、二元组和三元组的预测概率差异生成解释,并将 LLM 解释与 X-MuTeST 解释进行联合,从而提升模型性能与可解释性;实验表明,引入人类理由不仅能增强分类准确率,还能优化注意力机制,显著改善解释的合理性(如 Token-F1、IOU-F1)和忠实性(如 Comprehensiveness 和 Sufficiency)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03194
作者: Mohammad Zia Ur Rehman,Sai Kartheek Reddy Kasu,Shashivardhan Reddy Koppula,Sai Rithwik Reddy Chirra,Shwetank Shekhar Singh,Nagendra Kumar
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Accepted in the proceedings of AAAI 2026
Abstract:Hate speech detection on social media faces challenges in both accuracy and explainability, especially for underexplored Indic languages. We propose a novel explainability-guided training framework, X-MuTeST (eXplainable Multilingual haTe Speech deTection), for hate speech detection that combines high-level semantic reasoning from large language models (LLMs) with traditional attention-enhancing techniques. We extend this research to Hindi and Telugu alongside English by providing benchmark human-annotated rationales for each word to justify the assigned class label. The X-MuTeST explainability method computes the difference between the prediction probabilities of the original text and those of unigrams, bigrams, and trigrams. Final explanations are computed as the union between LLM explanations and X-MuTeST explanations. We show that leveraging human rationales during training enhances both classification performance and explainability. Moreover, combining human rationales with our explainability method to refine the model attention yields further improvements. We evaluate explainability using Plausibility metrics such as Token-F1 and IOU-F1 and Faithfulness metrics such as Comprehensiveness and Sufficiency. By focusing on under-resourced languages, our work advances hate speech detection across diverse linguistic contexts. Our dataset includes token-level rationale annotations for 6,004 Hindi, 4,492 Telugu, and 6,334 English samples. Data and code are available on this https URL
zh
[NLP-8] MemRL: Self-Evolving Agents via Runtime Reinforcement Learning on Episodic Memory
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在持续学习过程中面临的“稳定性-可塑性困境”问题:即如何在不引发灾难性遗忘的前提下,使模型能够通过自身经验不断进化以适应新任务。传统方法如微调计算成本高且易遗忘旧知识,而现有基于记忆的方案依赖被动语义匹配,常检索到噪声信息。解决方案的关键在于提出MemRL框架,其核心是将冻结的LLM推理能力与可塑的记忆模块分离,并采用两阶段检索机制——首先按语义相关性筛选候选记忆,再基于学习到的Q值(utility)进行优选;这些Q值通过环境反馈以试错方式持续优化,从而实现对高价值策略的有效识别与利用,最终在无需更新模型权重的情况下实现运行时的持续性能提升。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03192
作者: Shengtao Zhang,Jiaqian Wang,Ruiwen Zhou,Junwei Liao,Yuchen Feng,Weinan Zhang,Ying Wen,Zhiyu Li,Feiyu Xiong,Yutao Qi,Bo Tang,Muning Wen
机构: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); Xidian University (西安电子科技大学); National University of Singapore (新加坡国立大学); Shanghai Innovation Institute; MemTensor (Shanghai) Technology Co., Ltd. (MemTensor(上海)科技有限公司); University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 23 pages, 11 figures
Abstract:The hallmark of human intelligence is the ability to master new skills through Constructive Episodic Simulation-retrieving past experiences to synthesize solutions for novel tasks. While Large Language Models possess strong reasoning capabilities, they struggle to emulate this self-evolution: fine-tuning is computationally expensive and prone to catastrophic forgetting, while existing memory-based methods rely on passive semantic matching that often retrieves noise. To address these challenges, we propose MemRL, a framework that enables agents to self-evolve via non-parametric reinforcement learning on episodic memory. MemRL explicitly separates the stable reasoning of a frozen LLM from the plastic, evolving memory. Unlike traditional methods, MemRL employs a Two-Phase Retrieval mechanism that filters candidates by semantic relevance and then selects them based on learned Q-values (utility). These utilities are continuously refined via environmental feedback in an trial-and-error manner, allowing the agent to distinguish high-value strategies from similar noise. Extensive experiments on HLE, BigCodeBench, ALFWorld, and Lifelong Agent Bench demonstrate that MemRL significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. Our analysis experiments confirm that MemRL effectively reconciles the stability-plasticity dilemma, enabling continuous runtime improvement without weight updates.
zh
[NLP-9] Maximizing Local Entropy Where It Matters: Prefix-Aware Localized LLM Unlearning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)中敏感知识遗忘问题,即在确保模型对特定敏感信息的生成能力被有效移除的同时,尽可能保留其通用性能。现有方法通常对响应中的所有token进行全局不确定性强化,导致不必要的性能下降和优化范围扩展至无关区域。解决方案的关键在于提出PALU(Prefix-Aware Localized Unlearning)框架,其核心是基于时空维度上的局部熵最大化目标:首先发现仅抑制敏感前缀即可切断因果生成链路;其次表明仅对top-k logits进行平滑处理即可在关键子空间内最大化不确定性。这一机制使PALU能够避免在整个词汇表和参数空间上冗余优化,从而最小化对模型整体性能的附带损害,并显著提升遗忘效果与通用性能的平衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03190
作者: Naixin Zhai,Pengyang Shao,Binbin Zheng,Fei Shen,Long Bai,Xun Yang
机构: University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学); National University of Singapore (新加坡国立大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Machine unlearning aims to forget sensitive knowledge from Large Language Models (LLMs) while maintaining general utility. However, existing approaches typically treat all tokens in a response indiscriminately and enforce uncertainty over the entire vocabulary. This global treatment results in unnecessary utility degradation and extends optimization to content-agnostic regions. To address these limitations, we propose PALU (Prefix-Aware Localized Unlearning), a framework driven by a local entropy maximization objective across both temporal and vocabulary dimensions. PALU reveals that (i) suppressing the sensitive prefix alone is sufficient to sever the causal generation link, and (ii) flattening only the top- k logits is adequate to maximize uncertainty in the critical subspace. These findings allow PALU to avoid redundant optimization across the full vocabulary and parameter space while minimizing collateral damage to general model performance. Extensive experiments validate that PALU achieves superior forgetting efficacy and utility preservation compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
zh
[NLP-10] Multi-Modal Data-Enhanced Foundation Models for Prediction and Control in Wireless Networks: A Survey
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决无线网络管理中复杂任务处理能力不足的问题,尤其是如何利用基础模型(Foundation Models, FMs)提升对多模态数据的 contextual 信息理解能力,并增强预测与控制类任务的智能化水平。其解决方案的关键在于:首先,通过引入多模态基础模型(Multi-modal Foundation Models),实现对无线网络中异构数据(如文本、图像、信号特征等)的统一建模与语义理解;其次,从数据集构建和方法论两个维度推动面向无线场景的专用基础模型开发,从而支撑更通用、高效的AI代理在无线网络中的部署与应用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03181
作者: Han Zhang,Mohammad Farzanullah,Mohammad Ghassemi,Akram Bin Sediq,Ali Afana,Melike Erol-Kantarci
机构: University of Ottawa (渥太华大学); Ericsson (爱立信)
类目: Networking and Internet Architecture (cs.NI); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 5 figures, 7 tables, IEEE COMST
Abstract:Foundation models (FMs) are recognized as a transformative breakthrough that has started to reshape the future of artificial intelligence (AI) across both academia and industry. The integration of FMs into wireless networks is expected to enable the development of general-purpose AI agents capable of handling diverse network management requests and highly complex wireless-related tasks involving multi-modal data. Inspired by these ideas, this work discusses the utilization of FMs, especially multi-modal FMs in wireless networks. We focus on two important types of tasks in wireless network management: prediction tasks and control tasks. In particular, we first discuss FMs-enabled multi-modal contextual information understanding in wireless networks. Then, we explain how FMs can be applied to prediction and control tasks, respectively. Following this, we introduce the development of wireless-specific FMs from two perspectives: available datasets for development and the methodologies used. Finally, we conclude with a discussion of the challenges and future directions for FM-enhanced wireless networks.
zh
[NLP-11] Can Embedding Similarity Predict Cross-Lingual Transfer? A Systematic Study on African Languages
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决低资源非洲语言在自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing, NLP)系统构建中面临的跨语言迁移(cross-lingual transfer)难题,尤其是缺乏可靠的方法来选择最优源语言的问题。其解决方案的关键在于系统性评估五种嵌入相似性度量方法在816次跨语言迁移实验中的预测性能,发现余弦差距(cosine gap)和基于检索的指标(P@1、CSLS)具有稳定的预测能力(相关系数 ρ = 0.4–0.6),而中心核对齐(CKA)则几乎无预测价值(ρ ≈ 0.1)。此外,研究揭示了模型间相关性方向可能因聚合不同模型而出现辛普森悖论(Simpson’s Paradox),强调必须针对每个具体模型进行验证,从而为源语言选择提供了可操作的实证依据,并指出嵌入相似性指标与URIEL语言类型学特征具有相当的预测效力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03168
作者: Tewodros Kederalah Idris,Prasenjit Mitra,Roald Eiselen
机构: Carnegie Mellon University Africa (卡内基梅隆大学非洲校区); North-West University (西北大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 13 pages, 1 figure, 19 tables
Abstract:Cross-lingual transfer is essential for building NLP systems for low-resource African languages, but practitioners lack reliable methods for selecting source languages. We systematically evaluate five embedding similarity metrics across 816 transfer experiments spanning three NLP tasks, three African-centric multilingual models, and 12 languages from four language families. We find that cosine gap and retrieval-based metrics (P@1, CSLS) reliably predict transfer success ( \rho = 0.4-0.6 ), while CKA shows negligible predictive power ( \rho \approx 0.1 ). Critically, correlation signs reverse when pooling across models (Simpson’s Paradox), so practitioners must validate per-model. Embedding metrics achieve comparable predictive power to URIEL linguistic typology. Our results provide concrete guidance for source language selection and highlight the importance of model-specific analysis.
zh
[NLP-12] WebAnchor: Anchoring Agent Planning to Stabilize Long-Horizon Web Reasoning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)在长程网络信息检索任务中因规划能力不足而导致的性能瓶颈问题,特别是现有强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)方法未能有效处理“计划锚定”(plan anchor)现象——即初始推理步骤对后续行为具有显著影响。解决方案的关键在于提出一种两阶段强化学习框架 Anchor-GRPO:第一阶段通过自对弈经验与人工校准生成细粒度规则,优化首步规划;第二阶段利用稀疏奖励确保执行过程与初始计划对齐,从而实现稳定且高效的工具调用。此设计有效分离了规划与执行阶段,显著提升了任务成功率和工具使用效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03164
作者: Yu Xinmiao,Zhang Liwen,Feng Xiaocheng,Jiang Yong,Qin Bing,Xie Pengjun,Zhou Jingren
机构: Tongyi Lab, Alibaba Group (通义实验室,阿里巴巴集团)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large Language Model(LLM)-based agents have shown strong capabilities in web information seeking, with reinforcement learning (RL) becoming a key optimization paradigm. However, planning remains a bottleneck, as existing methods struggle with long-horizon strategies. Our analysis reveals a critical phenomenon, plan anchor, where the first reasoning step disproportionately impacts downstream behavior in long-horizon web reasoning tasks. Current RL algorithms, fail to account for this by uniformly distributing rewards across the trajectory. To address this, we propose Anchor-GRPO, a two-stage RL framework that decouples planning and execution. In Stage 1, the agent optimizes its first-step planning using fine-grained rubrics derived from self-play experiences and human calibration. In Stage 2, execution is aligned with the initial plan through sparse rewards, ensuring stable and efficient tool usage. We evaluate Anchor-GRPO on four benchmarks: BrowseComp, BrowseComp-Zh, GAIA, and XBench-DeepSearch. Across models from 3B to 30B, Anchor-GRPO outperforms baseline GRPO and First-step GRPO, improving task success and tool efficiency. Notably, WebAnchor-30B achieves 46.0% pass@1 on BrowseComp and 76.4% on GAIA. Anchor-GRPO also demonstrates strong scalability, getting higher accuracy as model size and context length increase.
zh
[NLP-13] Prompt-Counterfactual Explanations for Generative AI System Behavior
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)系统中 prompt 输入与输出特性之间因果关系的可解释性问题,即明确哪些输入特征会导致模型产生特定输出行为(如毒性、负面情绪或政治偏见)。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种适用于非确定性生成式 AI 系统的灵活框架,该框架基于对抗性解释(counterfactual explanations)思想,结合下游分类器对输出特性的识别能力,设计出 prompt-counterfactual explanations (PCEs) 算法,从而实现对 prompt 变化如何影响输出特性的定量分析和可视化解释。此方法不仅支持提示工程优化以抑制不良输出,还可增强红队测试效果,提升生成式 AI 的透明度与可控性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03156
作者: Sofie Goethals,Foster Provost,João Sedoc
机构: University of Antwerp (安特卫普大学); NYU Stern School of Business (纽约大学斯特恩商学院)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注:
Abstract:As generative AI systems become integrated into real-world applications, organizations increasingly need to be able to understand and interpret their behavior. In particular, decision-makers need to understand what causes generative AI systems to exhibit specific output characteristics. Within this general topic, this paper examines a key question: what is it about the input -the prompt- that causes an LLM-based generative AI system to produce output that exhibits specific characteristics, such as toxicity, negative sentiment, or political bias. To examine this question, we adapt a common technique from the Explainable AI literature: counterfactual explanations. We explain why traditional counterfactual explanations cannot be applied directly to generative AI systems, due to several differences in how generative AI systems function. We then propose a flexible framework that adapts counterfactual explanations to non-deterministic, generative AI systems in scenarios where downstream classifiers can reveal key characteristics of their outputs. Based on this framework, we introduce an algorithm for generating prompt-counterfactual explanations (PCEs). Finally, we demonstrate the production of counterfactual explanations for generative AI systems with three case studies, examining different output characteristics (viz., political leaning, toxicity, and sentiment). The case studies further show that PCEs can streamline prompt engineering to suppress undesirable output characteristics and can enhance red-teaming efforts to uncover additional prompts that elicit undesirable outputs. Ultimately, this work lays a foundation for prompt-focused interpretability in generative AI: a capability that will become indispensable as these models are entrusted with higher-stakes tasks and subject to emerging regulatory requirements for transparency and accountability.
zh
[NLP-14] Decoupling the Effect of Chain-of-Thought Reasoning : A Human Label Variation Perspective
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI (Generative AI) 中长链式思维(Chain-of-Thought, CoT)在处理具有人类标签变异性(Human Label Variation)的任务时,其对概率模糊性建模能力不足的问题。传统基于 CoT 的大语言模型(LLM)擅长单答案任务的推理,但难以捕捉和表达人类标注中的不确定性分布。解决方案的关键在于通过系统性的解耦实验(Cross-CoT 实验),将推理文本的影响与模型内在先验(intrinsic priors)分离,发现了一个“解耦机制”:CoT 决定了最终预测的准确性(贡献 99% 方差),而模型先验则主导了分布结构的排序(贡献超 80%)。这表明,尽管 CoT 能有效提升最优选项的选择精度,却无法精细校准复杂任务中所需的分布级不确定性建模。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03154
作者: Beiduo Chen,Tiancheng Hu,Caiqi Zhang,Robert Litschko,Anna Korhonen,Barbara Plank
机构: MaiNLP, Center for Information and Language Processing, LMU Munich, Germany (慕尼黑大学信息与语言处理中心); Munich Center for Machine Learning (MCML), Munich, Germany (慕尼黑机器学习中心); Language Technology Lab, University of Cambridge, United Kingdom (剑桥大学语言技术实验室)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 19 pages, 10 figures
Abstract:Reasoning-tuned LLMs utilizing long Chain-of-Thought (CoT) excel at single-answer tasks, yet their ability to model Human Label Variation–which requires capturing probabilistic ambiguity rather than resolving it–remains underexplored. We investigate this through systematic disentanglement experiments on distribution-based tasks, employing Cross-CoT experiments to isolate the effect of reasoning text from intrinsic model priors. We observe a distinct “decoupled mechanism”: while CoT improves distributional alignment, final accuracy is dictated by CoT content (99% variance contribution), whereas distributional ranking is governed by model priors (over 80%). Step-wise analysis further shows that while CoT’s influence on accuracy grows monotonically during the reasoning process, distributional structure is largely determined by LLM’s intrinsic priors. These findings suggest that long CoT serves as a decisive LLM decision-maker for the top option but fails to function as a granular distribution calibrator for ambiguous tasks.
zh
[NLP-15] Self-Verification is All You Need To Pass The Japanese Bar Examination
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在高专业性、结构化考试中难以稳定达到可靠性能的问题,特别是针对日本律师资格考试这一极具挑战性的基准任务。该考试不仅要求复杂的法律推理能力,还依赖于多命题联合评分的严格格式规范。现有方法虽通过将题目分解为简单真假判断提升表现,但未在原始考试格式和评分体系下进行系统评估,因而无法验证其是否真正具备考试级能力。本文的关键解决方案是构建一个忠实还原原考试格式与评分规则的新数据集,并训练一种自验证(self-verification)模型,使其在不改变原始问题结构或评分标准的前提下,首次实现超过官方及格线的性能表现。实验证明,该方法优于多代理推理和基于分解的监督策略,凸显了格式忠实监督与一致性验证的重要性,表明精心设计的单模型架构可在高风险专业推理任务中超越复杂系统。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03144
作者: Andrew Shin
机构: Keio University (庆应义塾大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: this https URL
Abstract:Despite rapid advances in large language models (LLMs), achieving reliable performance on highly professional and structured examinations remains a significant challenge. The Japanese bar examination is a particularly demanding benchmark, requiring not only advanced legal reasoning but also strict adherence to complex answer formats that involve joint evaluation of multiple propositions. While recent studies have reported improvements by decomposing such questions into simpler true–false judgments, these approaches have not been systematically evaluated under the original exam format and scoring scheme, leaving open the question of whether they truly capture exam-level competence. In this paper, we present a self-verification model trained on a newly constructed dataset that faithfully replicates the authentic format and evaluation scale of the exam. Our model is able to exceed the official passing score when evaluated on the actual exam scale, marking the first demonstration, to our knowledge, of an LLM passing the Japanese bar examination without altering its original question structure or scoring rules. We further conduct extensive comparisons with alternative strategies, including multi-agent inference and decomposition-based supervision, and find that these methods fail to achieve comparable performance. Our results highlight the importance of format-faithful supervision and consistency verification, and suggest that carefully designed single-model approaches can outperform more complex systems in high-stakes professional reasoning tasks. Our dataset and codes are publicly available.
zh
[NLP-16] Accurate Table Question Answering with Accessible LLM s ICDE
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决在表格问答(Table Question Answering, TQA)任务中,如何利用小型开源权重大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)实现高质量、低成本的答案生成问题。传统方法依赖于昂贵的商用大模型(如GPT-4),而小型开放模型因提示复杂度高、推理能力弱,在TQA性能上存在显著下降。解决方案的关键在于提出Orchestra——一种多智能体协同框架,通过将复杂任务分解为多个简单子任务,并由不同LLM代理按分层结构协作完成,从而降低单个代理所需处理的提示复杂度,提升输出可靠性。实验表明,Orchestra在多个基准测试中显著优于现有方法,甚至在Qwen2.5-14B等小模型上接近GPT-4的性能,验证了其高效性和可行性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03137
作者: Yangfan Jiang,Fei Wei,Ergute Bao,Yaliang Li,Bolin Ding,Yin Yang,Xiaokui Xiao
机构: Tongyi Lab, Alibaba Group (通义实验室,阿里巴巴集团); University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学); Zhejiang University (浙江大学); Tsinghua University (清华大学)
类目: Databases (cs.DB); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: accepted for publication in the Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE) 2026
Abstract:Given a table T in a database and a question Q in natural language, the table question answering (TQA) task aims to return an accurate answer to Q based on the content of T. Recent state-of-the-art solutions leverage large language models (LLMs) to obtain high-quality answers. However, most rely on proprietary, large-scale LLMs with costly API access, posing a significant financial barrier. This paper instead focuses on TQA with smaller, open-weight LLMs that can run on a desktop or laptop. This setting is challenging, as such LLMs typically have weaker capabilities than large proprietary models, leading to substantial performance degradation with existing methods. We observe that a key reason for this degradation is that prior approaches often require the LLM to solve a highly sophisticated task using long, complex prompts, which exceed the capabilities of small open-weight LLMs. Motivated by this observation, we present Orchestra, a multi-agent approach that unlocks the potential of accessible LLMs for high-quality, cost-effective TQA. Orchestra coordinates a group of LLM agents, each responsible for a relatively simple task, through a structured, layered workflow to solve complex TQA problems – akin to an orchestra. By reducing the prompt complexity faced by each agent, Orchestra significantly improves output reliability. We implement Orchestra on top of AgentScope, an open-source multi-agent framework, and evaluate it on multiple TQA benchmarks using a wide range of open-weight LLMs. Experimental results show that Orchestra achieves strong performance even with small- to medium-sized models. For example, with Qwen2.5-14B, Orchestra reaches 72.1% accuracy on WikiTQ, approaching the best prior result of 75.3% achieved with GPT-4; with larger Qwen, Llama, or DeepSeek models, Orchestra outperforms all prior methods and establishes new state-of-the-art results across all benchmarks. Comments: accepted for publication in the Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE) 2026 Subjects: Databases (cs.DB); Computation and Language (cs.CL) Cite as: arXiv:2601.03137 [cs.DB] (or arXiv:2601.03137v1 [cs.DB] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.03137 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[NLP-17] Limited Linguistic Diversity in Embodied AI Datasets
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前视觉-语言-动作(Vision-Language-Action, VLA)模型训练与评估数据集中语言特征缺乏系统性描述的问题。其关键解决方案在于对多个广泛使用的VLA语料库进行系统的数据集审计,从词汇多样性、重复度与重叠率、语义相似性以及句法复杂度等互补维度量化指令语言的特性,揭示现有数据集普遍依赖高度重复、模板化的命令且结构变化有限,从而为更细致的数据集报告、更合理的数据选择及有针对性的语言覆盖扩展策略提供依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03136
作者: Selma Wanna,Agnes Luhtaru,Jonathan Salfity,Ryan Barron,Juston Moore,Cynthia Matuszek,Mitch Pryor
机构: Los Alamos National Laboratory (洛斯阿拉莫斯国家实验室); Institute of Computer Science, University of Tartu (塔尔图大学计算机科学研究所); Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Texas at Austin (德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校机械工程系); University of Maryland, Baltimore County (马里兰大学巴尔的摩县分校)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注:
Abstract:Language plays a critical role in Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, yet the linguistic characteristics of the datasets used to train and evaluate these systems remain poorly documented. In this work, we present a systematic dataset audit of several widely used VLA corpora, aiming to characterize what kinds of instructions these datasets actually contain and how much linguistic variety they provide. We quantify instruction language along complementary dimensions-including lexical variety, duplication and overlap, semantic similarity, and syntactic complexity. Our analysis shows that many datasets rely on highly repetitive, template-like commands with limited structural variation, yielding a narrow distribution of instruction forms. We position these findings as descriptive documentation of the language signal available in current VLA training and evaluation data, intended to support more detailed dataset reporting, more principled dataset selection, and targeted curation or augmentation strategies that broaden language coverage.
zh
[NLP-18] Improving Indigenous Language Machine Translation with Synthetic Data and Language-Specific Preprocessing
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决低资源土著语言在神经机器翻译(Neural Machine Translation, NMT)中因缺乏平行语料库而导致的性能瓶颈问题。其核心解决方案是通过高容量多语言翻译模型生成合成句对,以扩充人工精选的平行数据集,并在此基础上微调多语言mBART模型。关键创新在于结合合成数据增强与语言特定的预处理策略(如拼写规范化和抗噪过滤),从而显著提升瓜拉尼语–西班牙语和克丘亚语–西班牙语翻译任务中的chrF++得分,同时揭示了通用预处理方法在高度黏着语言(如艾马拉语)上的局限性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03135
作者: Aashish Dhawan,Christopher Driggers-Ellis,Christan Grant,Daisy Zhe Wang
机构: University of Florida (佛罗里达大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Low-resource indigenous languages often lack the parallel corpora required for effective neural machine translation (NMT). Synthetic data generation offers a practical strategy for mitigating this limitation in data-scarce settings. In this work, we augment curated parallel datasets for indigenous languages of the Americas with synthetic sentence pairs generated using a high-capacity multilingual translation model. We fine-tune a multilingual mBART model on curated-only and synthetically augmented data and evaluate translation quality using chrF++, the primary metric used in recent AmericasNLP shared tasks for agglutinative languages. We further apply language-specific preprocessing, including orthographic normalization and noise-aware filtering, to reduce corpus artifacts. Experiments on Guarani–Spanish and Quechua–Spanish translation show consistent chrF++ improvements from synthetic data augmentation, while diagnostic experiments on Aymara highlight the limitations of generic preprocessing for highly agglutinative languages. Subjects: Computation and Language (cs.CL) Cite as: arXiv:2601.03135 [cs.CL] (or arXiv:2601.03135v1 [cs.CL] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.03135 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[NLP-19] he Anatomy of Conversational Scams: A Topic-Based Red Teaming Analysis of Multi-Turn Interactions in LLM s
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在多轮对话中因增强的说服性代理能力(persuasive agentic capabilities)而引入的新风险,尤其是单轮安全评估无法捕捉的多轮欺骗性交互(multi-turn conversational scams)问题。解决方案的关键在于构建了一个受控的LLM-to-LLM模拟框架,在多轮诈骗场景下系统性地评估八个最先进的英文和中文模型,通过分析对话结果、标注攻击策略、防御响应及失败模式,揭示了诈骗交互中的重复升级规律以及防御机制以验证和延迟为核心,并指出交互失败主要源于安全护栏激活与角色不稳定性,从而确立多轮交互安全性为LLM行为的一个关键且独立维度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03134
作者: Xiangzhe Yuan,Zhenhao Zhang,Haoming Tang,Siying Hu
机构: University of Iowa (爱荷华大学); City University of Hong Kong (香港城市大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:As LLMs gain persuasive agentic capabilities through extended dialogues, they introduce novel risks in multi-turn conversational scams that single-turn safety evaluations fail to capture. We systematically study these risks using a controlled LLM-to-LLM simulation framework across multi-turn scam scenarios. Evaluating eight state-of-the-art models in English and Chinese, we analyze dialogue outcomes and qualitatively annotate attacker strategies, defensive responses, and failure modes. Results reveal that scam interactions follow recurrent escalation patterns, while defenses employ verification and delay mechanisms. Furthermore, interactional failures frequently stem from safety guardrail activation and role instability. Our findings highlight multi-turn interactional safety as a critical, distinct dimension of LLM behavior.
zh
[NLP-20] Automatic Prompt Engineering with No Task Cues and No Tuning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决数据库表中晦涩列名扩展(Cryptic Column Name Expansion, CNE)这一关键但研究匮乏的任务,该任务对于表格数据的搜索、访问与理解至关重要。现有方法通常依赖复杂的调参或明确的任务提示,而本文提出了一种无需调参且不依赖显式任务线索的自动提示工程(Automatic Prompt Engineering)系统,其核心创新在于设计简洁且高效的提示生成机制,在英语和德语两种语言的数据集上均表现出与现有方法相当的效果,首次实现了非英语场景下自动提示工程在CNE任务中的应用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03130
作者: Faisal Chowdhury,Nandana Mihindukulasooriya,Niharika S D’Souza,Horst Samulowitz,Neeru Gupta,Tomasz Hanusiak,Michal Kapitonow
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:This paper presents a system for automatic prompt engineering that is much simpler in both design and application and yet as effective as the existing approaches. It requires no tuning and no explicit clues about the task. We evaluated our approach on cryptic column name expansion (CNE) in database tables, a task which is critical for tabular data search, access, and understanding and yet there has been very little existing work. We evaluated on datasets in two languages, English and German. This is the first work to report on the application of automatic prompt engineering for the CNE task. To the best of our knowledge, this is also the first work on the application of automatic prompt engineering for a language other than English.
zh
[NLP-21] oxiGAN: Toxic Data Augmentation via LLM -Guided Directional Adversarial Generation EACL2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决毒性语言数据增强中难以实现可控且类别特异性的扩充问题,这在提升毒性分类模型鲁棒性方面至关重要,但受限于监督信号不足和分布偏斜。其解决方案的关键在于提出ToxiGAN框架,该框架结合对抗生成与大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)提供的语义引导,通过两阶段定向训练策略缓解GAN类方法常见的模式崩溃(mode collapse)和语义漂移(semantic drift)问题,并创新性地利用LLM生成的中性文本作为语义“压载物”(semantic ballast),动态选择中性样本以提供平衡的语义约束,同时显式优化毒性样本与其偏离,强化类别特定的对比信号,从而显著提升分类性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03121
作者: Peiran Li,Jan Fillies,Adrian Paschke
机构: Freie Universität Berlin (柏林自由大学); Fraunhofer-Institut für Offene Kommunikationssysteme (弗劳恩霍夫开放通信系统研究所); Institut für Angewandte Informatik (应用信息学研究所); Stanford University (斯坦福大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: This paper has been accepted to the main conference of EACL 2026
Abstract:Augmenting toxic language data in a controllable and class-specific manner is crucial for improving robustness in toxicity classification, yet remains challenging due to limited supervision and distributional skew. We propose ToxiGAN, a class-aware text augmentation framework that combines adversarial generation with semantic guidance from large language models (LLMs). To address common issues in GAN-based augmentation such as mode collapse and semantic drift, ToxiGAN introduces a two-step directional training strategy and leverages LLM-generated neutral texts as semantic ballast. Unlike prior work that treats LLMs as static generators, our approach dynamically selects neutral exemplars to provide balanced guidance. Toxic samples are explicitly optimized to diverge from these exemplars, reinforcing class-specific contrastive signals. Experiments on four hate speech benchmarks show that ToxiGAN achieves the strongest average performance in both macro-F1 and hate-F1, consistently outperforming traditional and LLM-based augmentation methods. Ablation and sensitivity analyses further confirm the benefits of semantic ballast and directional training in enhancing classifier robustness.
zh
[NLP-22] Discovering and Causally Validating Emotion-Sensitive Neurons in Large Audio-Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决现代大音频语言模型(Large Audio-Language Models, LALMs)中情感信息内部编码机制不明确的问题,即缺乏对情感敏感神经元(Emotion-Sensitive Neurons, ESNs)的因果性理解。解决方案的关键在于首次在三个主流开源模型(Qwen2.5-Omni、Kimi-Audio 和 Audio Flamingo 3)中开展基于神经元层面的可解释性研究,通过频率、熵、幅度和对比度等不同选择策略识别ESNs,并利用推理时干预(inference-time interventions)验证其功能:消融实验显示特定情感的神经元被移除会显著降低对应情感的识别准确率,而放大这些神经元则能增强目标情感的预测倾向,且效果随干预强度系统性变化。这一方法为理解LALMs中的情感决策提供了因果证据,并揭示了靶向神经元干预作为可控情感行为调控的有效手段。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03115
作者: Xiutian Zhao,Björn Schuller,Berrak Sisman
机构: Center for Language and Speech Processing (CLSP), Johns Hopkins University (约翰霍普金斯大学); Group on Language, Audio & Music (GLAM), Imperial College London (帝国理工学院)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS)
备注: 16 pages, 6 figures
Abstract:Emotion is a central dimension of spoken communication, yet, we still lack a mechanistic account of how modern large audio-language models (LALMs) encode it internally. We present the first neuron-level interpretability study of emotion-sensitive neurons (ESNs) in LALMs and provide causal evidence that such units exist in Qwen2.5-Omni, Kimi-Audio, and Audio Flamingo 3. Across these three widely used open-source models, we compare frequency-, entropy-, magnitude-, and contrast-based neuron selectors on multiple emotion recognition benchmarks. Using inference-time interventions, we reveal a consistent emotion-specific signature: ablating neurons selected for a given emotion disproportionately degrades recognition of that emotion while largely preserving other classes, whereas gain-based amplification steers predictions toward the target emotion. These effects arise with modest identification data and scale systematically with intervention strength. We further observe that ESNs exhibit non-uniform layer-wise clustering with partial cross-dataset transfer. Taken together, our results offer a causal, neuron-level account of emotion decisions in LALMs and highlight targeted neuron interventions as an actionable handle for controllable affective behaviors.
zh
[NLP-23] One Sample to Rule Them All: Extreme Data Efficiency in RL Scaling
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)训练中对高数量高质量样本的依赖问题,即现有方法通常需要数千甚至更多样本才能实现性能提升。其解决方案的关键在于提出“博学学习”(polymath learning)框架,通过设计单个具有多学科特征的训练样本,显著提升模型在多个领域(如物理、化学、生物)中的推理能力。研究表明,样本的质量与结构设计比单纯增加数据量更为关键,从而推动从“数据规模导向”向“样本工程导向”的范式转变。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03111
作者: Yiyuan Li,Zhen Huang,Yanan Wu,Weixun Wang,Xuefeng Li,Yijia Luo,Wenbo Su,Bo Zheng,Pengfei Liu
机构: Taobao & Tmall Group of Alibaba (淘宝与天猫集团); Shanghai Jiaotong Univeristy (上海交通大学); GAIR (通用人工智能研究中心)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:The reasoning ability of large language models (LLMs) can be unleashed with reinforcement learning (RL) (OpenAI, 2024; DeepSeek-AI et al., 2025a; Zeng et al., 2025). The success of existing RL attempts in LLMs usually relies on high-quality samples of thousands or beyond. In this paper, we challenge fundamental assumptions about data requirements in RL for LLMs by demonstrating the remarkable effectiveness of one-shot learning. Specifically, we introduce polymath learning, a framework for designing one training sample that elicits multidisciplinary impact. We present three key findings: (1) A single, strategically selected math reasoning sample can produce significant performance improvements across multiple domains, including physics, chemistry, and biology with RL; (2) The math skills salient to reasoning suggest the characteristics of the optimal polymath sample; and (3) An engineered synthetic sample that integrates multidiscipline elements outperforms training with individual samples that naturally occur. Our approach achieves superior performance to training with larger datasets across various reasoning benchmarks, demonstrating that sample quality and design, rather than quantity, may be the key to unlock enhanced reasoning capabilities in language models. Our results suggest a shift, dubbed as sample engineering, toward precision engineering of training samples rather than simply increasing data volume.
zh
[NLP-24] Who Laughs with Whom? Disentangling Influential Factors in Humor Preferences across User Clusters and LLM s
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在评估幽默时面临的个体与文化差异性问题,即用户对幽默的偏好具有高度异质性,导致难以建立统一的评价标准。其解决方案的关键在于:首先通过聚类分析用户投票日志识别出具有相似幽默偏好的用户群体(user clusters),并利用Bradley-Terry-Luce模型估计各群体在可解释偏好因子上的权重;其次,通过提示LLM选择更有趣的回应来获取其偏好判断,并发现LLM的偏好模式可映射到特定用户集群;最后,借助角色提示(persona prompting)技术,可引导LLM的偏好向目标用户集群靠拢,从而实现对LLM幽默理解能力的可控调节。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03103
作者: Soichiro Murakami,Hidetaka Kamigaito,Hiroya Takamura,Manabu Okumura
机构: CyberAgent( CyberAgent); Nara Institute of Science and Technology(奈良科学技术大学院大学); Institute of Science Tokyo(东京科学研究所)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Humor preferences vary widely across individuals and cultures, complicating the evaluation of humor using large language models (LLMs). In this study, we model heterogeneity in humor preferences in Oogiri, a Japanese creative response game, by clustering users with voting logs and estimating cluster-specific weights over interpretable preference factors using Bradley-Terry-Luce models. We elicit preference judgments from LLMs by prompting them to select the funnier response and found that user clusters exhibit distinct preference patterns and that the LLM results can resemble those of particular clusters. Finally, we demonstrate that, by persona prompting, LLM preferences can be directed toward a specific cluster. The scripts for data collection and analysis will be released to support reproducibility.
zh
[NLP-25] ATLAS: Adaptive Test-Time Latent Steering with External Verifiers for Enhancing LLM s Reasoning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决现有生成式 AI(Generative AI)在推理过程中因采用固定干预策略和静态干预强度而导致的鲁棒性不足问题,即在不同任务实例中容易出现过度或不足的引导(over- or under-steering),从而影响推理准确性和效率。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一种名为 ATLAS(Adaptive Test-time Latent Steering)的动态测试时潜空间引导框架,该框架通过引入一个轻量级外部潜变量验证器(latent verifier),在推理阶段实时评估中间隐藏状态的质量,并据此自适应地决定是否以及以何种强度执行潜空间干预,实现每个样本、每一步的精细化控制,同时保持极低的计算开销。实验表明,ATLAS 在多个数学推理基准上均优于基线方法,在提升准确率的同时显著降低测试阶段的 token 消耗。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03093
作者: Tuc Nguyen,Thai Le
机构: Indiana University (印第安纳大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 12 pages, 3 figures
Abstract:Recent work on activation and latent steering has demonstrated that modifying internal representations can effectively guide large language models (LLMs) toward improved reasoning and efficiency without additional training. However, most existing approaches rely on fixed steering policies and static intervention strengths, which limit their robustness across problem instances and often result in over- or under-steering. We propose Adaptive Test-time Latent Steering, called (ATLAS), a task- specific framework that dynamically controls steering decisions at inference time using an external, lightweight latent verifier. Given intermediate hidden states, the verifier predicts the quality of ongoing reasoning and adaptively selects whether and how strongly to apply steering, enabling per-example and per-step adjustment with minimal overhead. To our knowledge, ATLAS is the first method to integrate learned latent verification into test-time steering for enhancing LLMs reasoning. Experiments on multiple mathematical reasoning benchmarks show that ATLAS consistently outperforms both vanilla decoding and fixed steering baselines, achieving higher accuracy while substantially reducing test-time token usage. These results demonstrate that verifier-guided latent adaptation provides an effective and scalable mechanism for controlling reasoning efficiency without sacrificing solution quality. All source code will be publicly available.
zh
[NLP-26] Grad-ELLM : Gradient-based Explanations for Decoder-only LLM s
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)因黑箱特性导致的透明性与忠实性(faithfulness)不足的问题。现有输入归因方法多为模型无关(model-agnostic),未针对解码器-only 的 Transformer 架构进行优化,因而难以准确刻画各输入 token 对输出的贡献。其解决方案的关键在于提出 Grad-ELLM,一种基于梯度的归因方法,通过聚合输出 logit 相对于注意力层的梯度所反映的通道重要性(channel importance)与注意力图所体现的空间重要性(spatial importance),在无需修改模型架构的前提下,在每个生成步骤中生成高保真度的热力图(heatmap)。此外,作者还设计了两个改进的忠实性指标 π-Soft-NC 和 π-Soft-NS,通过控制扰动时保留的信息量实现更公平的比较,实验表明 Grad-ELLM 在情感分类、问答和开放式生成任务中均显著优于现有方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03089
作者: Xin Huang,Antoni B. Chan
机构: City University of Hong Kong (香港城市大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across diverse tasks, yet their black-box nature raises concerns about transparency and faithfulness. Input attribution methods aim to highlight each input token’s contributions to the model’s output, but existing approaches are typically model-agnostic, and do not focus on transformer-specific architectures, leading to limited faithfulness. To address this, we propose Grad-ELLM, a gradient-based attribution method for decoder-only transformer-based LLMs. By aggregating channel importance from gradients of the output logit with respect to attention layers and spatial importance from attention maps, Grad-ELLM generates heatmaps at each generation step without requiring architectural modifications. Additionally, we introduce two faithfulneses metrics \pi -Soft-NC and \pi -Soft-NS, which are modifications of Soft-NC/NS that provide fairer comparisons by controlling the amount of information kept when perturbing the text. We evaluate Grad-ELLM on sentiment classification, question answering, and open-generation tasks using different models. Experiment results show that Grad-ELLM consistently achieves superior faithfulness than other attribution methods.
zh
[NLP-27] Audit Me If You Can: Query-Efficient Active Fairness Auditing of Black-Box LLM s ACL
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决黑箱大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在不同人口群体中存在系统性偏见的问题,以及现有公平性审计方法因查询访问资源密集而难以高效实施的挑战。解决方案的关键在于将公平性审计建模为对目标公平指标(如ΔAUC)的不确定性估计问题,并提出BAFA(Bounded Active Fairness Auditor),通过维护与已查询得分一致的代理模型版本空间,利用约束经验风险最小化计算公平指标的置信区间,再结合主动查询选择策略逐步缩小区间以降低估计误差。该方法显著减少了达到预定误差阈值所需的查询次数(最多减少40倍),同时提升了性能稳定性与一致性,支持对LLMs进行持续、高效的独立公平性评估。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03087
作者: David Hartmann,Lena Pohlmann,Lelia Hanslik,Noah Gießing,Bettina Berendt,Pieter Delobelle
机构: Weizenbaum Institut Berlin; Technische Universität Berlin; FIZ Karlsruhe; KU Leuven; Aleph Alpha
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注: Submitted to ACL ARR 2026
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit systematic biases across demographic groups. Auditing is proposed as an accountability tool for black-box LLM applications, but suffers from resource-intensive query access. We conceptualise auditing as uncertainty estimation over a target fairness metric and introduce BAFA, the Bounded Active Fairness Auditor for query-efficient auditing of black-box LLMs. BAFA maintains a version space of surrogate models consistent with queried scores and computes uncertainty intervals for fairness metrics (e.g., \Delta AUC) via constrained empirical risk minimisation. Active query selection narrows these intervals to reduce estimation error. We evaluate BAFA on two standard fairness dataset case studies: \textscCivilComments and \textscBias-in-Bios, comparing against stratified sampling, power sampling, and ablations. BAFA achieves target error thresholds with up to 40 \times fewer queries than stratified sampling (e.g., 144 vs 5,956 queries at \varepsilon=0.02 for \textscCivilComments) for tight thresholds, demonstrates substantially better performance over time, and shows lower variance across runs. These results suggest that active sampling can reduce resources needed for independent fairness auditing with LLMs, supporting continuous model evaluations.
zh
[NLP-28] Learning to Diagnose and Correct Moral Errors: Towards Enhancing Moral Sensitivity in Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决如何提升大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的道德敏感性(moral sensitivity)问题,即让模型能够识别并响应道德上良善或危险的输入,并纠正道德错误。其解决方案的关键在于提出两种实用的语用推理(pragmatic inference)方法,这些方法不依赖于对语义多样且复杂的表面形式建模,而是基于推理负载(inferential loads)提供一种原则性的设计框架,从而统一地增强LLMs在道德情境下的感知与响应能力。实证结果表明,该方法在多个与道德相关的基准测试中均表现出优异性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03079
作者: Bocheng Chen,Han Zi,Xi Chen,Xitong Zhang,Kristen Johnson,Guangliang Liu
机构: University of Mississippi(密西西比大学); Northeastern University(东北大学); Nanyang Technological University(南洋理工大学); Michigan State University(密歇根州立大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Moral sensitivity is fundamental to human moral competence, as it guides individuals in regulating everyday behavior. Although many approaches seek to align large language models (LLMs) with human moral values, how to enable them morally sensitive has been extremely challenging. In this paper, we take a step toward answering the question: how can we enhance moral sensitivity in LLMs? Specifically, we propose two pragmatic inference methods that faciliate LLMs to diagnose morally benign and hazardous input and correct moral errors, whereby enhancing LLMs’ moral sensitivity. A central strength of our pragmatic inference methods is their unified perspective: instead of modeling moral discourses across semantically diverse and complex surface forms, they offer a principled perspective for designing pragmatic inference procedures grounded in their inferential loads. Empirical evidence demonstrates that our pragmatic methods can enhance moral sensitivity in LLMs and achieves strong performance on representative morality-relevant benchmarks.
zh
[NLP-29] Do LLM s Encode Functional Importance of Reasoning Tokens?
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型在生成复杂任务推理链时存在的计算成本高、难以定位功能相关推理步骤的问题。现有方法如概率采样、启发式规则或前沿模型监督虽能压缩推理链长度,但缺乏对模型内部是否编码了token级功能重要性的诊断能力。其解决方案的关键在于提出“贪婪剪枝”(greedy pruning)方法,这是一种保持似然不变的删除机制,通过迭代移除在特定目标下对模型似然影响最小的推理token,从而获得可控长度的推理链。实验表明,基于剪枝推理链训练的学生模型在相同长度下优于前沿模型监督的压缩基线,且注意力分数可有效预测剪枝优先级,揭示了模型内部存在非平凡的功能重要性结构。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03066
作者: Janvijay Singh,Dilek Hakkani-Tür
机构: University of Illinois Urbana Champaign (伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 20 pages, 8 figures, 2 tables
Abstract:Large language models solve complex tasks by generating long reasoning chains, achieving higher accuracy at the cost of increased computational cost and reduced ability to isolate functionally relevant reasoning. Prior work on compact reasoning shortens such chains through probabilistic sampling, heuristics, or supervision from frontier models, but offers limited insight into whether models internally encode token-level functional importance for answer generation. We address this gap diagnostically and propose greedy pruning, a likelihood-preserving deletion procedure that iteratively removes reasoning tokens whose removal minimally degrades model likelihood under a specified objective, yielding length-controlled reasoning chains. We evaluate pruned reasoning in a distillation framework and show that students trained on pruned chains outperform a frontier-model-supervised compression baseline at matched reasoning lengths. Finally, our analysis reveals systematic pruning patterns and shows that attention scores can predict greedy pruning ranks, further suggesting that models encode a nontrivial functional importance structure over reasoning tokens.
zh
[NLP-30] Detecting Hallucinations in Retrieval-Augmented Generation via Semantic-level Internal Reasoning Graph
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决基于大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)的检索增强生成(Retrieval-augmented generation, RAG)系统中依然存在的忠实性幻觉(faithfulness hallucination)问题。现有检测方法要么忽略模型内部推理过程,要么对这些特征处理粗糙,导致判别器难以有效学习。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于语义级内部推理图(semantic-level internal reasoning graph)的方法:首先将逐层相关性传播(layer-wise relevance propagation)算法从词元层面扩展至语义层面,构建基于归因向量的内部推理图,从而更准确地刻画模型推理中的语义依赖关系;其次设计了一个基于小型预训练语言模型的通用框架,利用LLM推理中的依赖信息进行训练与幻觉检测,并通过动态阈值调整正确样本的通过率,显著提升了检测性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03052
作者: Jianpeng Hu,Yanzeng Li,Jialun Zhong,Wenfa Qi,Lei Zou
机构: Wangxuan Institute of Computer Technology, Peking University (北京大学王选计算机研究所); Institute of Artificial Intelligence and Future Networks, Beijing Normal University (北京师范大学人工智能与未来网络研究院)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:The Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) system based on Large language model (LLM) has made significant progress. It can effectively reduce factuality hallucinations, but faithfulness hallucinations still exist. Previous methods for detecting faithfulness hallucinations either neglect to capture the models’ internal reasoning processes or handle those features coarsely, making it difficult for discriminators to learn. This paper proposes a semantic-level internal reasoning graph-based method for detecting faithfulness hallucination. Specifically, we first extend the layer-wise relevance propagation algorithm from the token level to the semantic level, constructing an internal reasoning graph based on attribution vectors. This provides a more faithful semantic-level representation of dependency. Furthermore, we design a general framework based on a small pre-trained language model to utilize the dependencies in LLM’s reasoning for training and hallucination detection, which can dynamically adjust the pass rate of correct samples through a threshold. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves better overall performance compared to state-of-the-art baselines on RAGTruth and Dolly-15k.
zh
[NLP-31] mporal Graph Network: Hallucination Detection in Multi-Turn Conversation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决对话系统中多轮对话场景下产生的幻觉(Hallucination)检测问题,尤其关注上下文变化和矛盾信息导致的生成错误。其解决方案的关键在于将整个对话表示为时间图(temporal graph),其中每个对话回合作为节点,并通过两种连接方式构建边:共享实体边(shared-entity edges)用于连接提及相同实体的回合,以及时间边(temporal edges)用于连接连续对话回合。利用消息传递机制更新节点嵌入,使相关信息在图结构中流动,再通过注意力池化整合上下文感知的节点嵌入形成统一向量,最终由分类器判断是否存在幻觉及其类型。该方法不仅提升了检测性能,还借助注意力机制提供决策解释性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03051
作者: Vidhi Rathore,Sambu Aneesh,Himanshu Singh
机构: IIIT Hyderabad (印度信息学院海得拉巴分校)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Hallucinations can be produced by conversational AI systems, particularly in multi-turn conversations where context changes and contradictions may eventually surface. By representing the entire conversation as a temporal graph, we present a novel graph-based method for detecting dialogue-level hallucinations. Our framework models each dialogue as a node, encoding it using a sentence transformer. We explore two different ways of connectivity: i) shared-entity edges, which connect turns that refer to the same entities; ii) temporal edges, which connect contiguous turns in the conversation. Message-passing is used to update the node embeddings, allowing flow of information between related nodes. The context-aware node embeddings are then combined using attention pooling into a single vector, which is then passed on to a classifier to determine the presence and type of hallucinations. We demonstrate that our method offers slightly improved performance over existing methods. Further, we show the attention mechanism can be used to justify the decision making process. The code and model weights are made available at: this https URL.
zh
[NLP-32] Lil: Less is Less When Applying Post-Training Sparse-Attention Algorithms in Long-Decode Stage
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)在大规模部署时推理效率低下问题,特别是针对解码阶段(decode stage)因稀疏注意力(sparse attention)机制引入的信息损失导致的端到端复杂度上升问题。研究发现,稀疏注意力虽能降低时间与内存复杂度,但常引发“信息丢失”现象,从而迫使模型生成更长序列以补偿语义完整性,形成“少即是少”(Less is Less, Lil)效应。解决方案的关键在于提出一种早期停止算法(early-stopping algorithm),通过动态检测稀疏解码过程中信息损失超过信息增益的阈值点,实现对冗余token的提前终止,从而在保持精度损失小于2%的前提下,最多减少90%的token消耗。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03043
作者: Junhao Hu,Fangze Li,Mingtao Xu,Feifan Meng,Shiju Zhao,Tiancheng Hu,Ting Peng,Anmin Liu,Wenrui Huang,Chenxu Liu,Ziyue Hua,Tao Xie
机构: Peking University (北京大学); Key Lab of HCST (PKU), MOE (教育部); Nanjing University (南京大学); Tencent (腾讯)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate strong capabilities across a wide range of complex tasks and are increasingly deployed at scale, placing significant demands on inference efficiency. Prior work typically decomposes inference into prefill and decode stages, with the decode stage dominating total latency. To reduce time and memory complexity in the decode stage, a line of work introduces sparse-attention algorithms. In this paper, we show, both empirically and theoretically, that sparse attention can paradoxically increase end-to-end complexity: information loss often induces significantly longer sequences, a phenomenon we term ``Less is Less’’ (Lil). To mitigate the Lil problem, we propose an early-stopping algorithm that detects the threshold where information loss exceeds information gain during sparse decoding. Our early-stopping algorithm reduces token consumption by up to 90% with a marginal accuracy degradation of less than 2% across reasoning-intensive benchmarks.
zh
[NLP-33] BaseCal: Unsupervised Confidence Calibration via Base Model Signals
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决后训练大语言模型(Post-trained LLMs, PoLLMs)普遍存在的严重过自信问题,即其输出的概率置信度不可靠,从而削弱用户对模型结果的信任。解决方案的关键在于利用未经过后训练的基线模型(base LLM)作为校准参考,提出两种无监督、可插拔的校准方法:BaseCal-ReEval通过将PoLLM生成的响应重新输入到base LLM中获取平均概率作为置信度;而更高效的BaseCal-Proj则训练一个轻量级投影层,将PoLLM的最终层隐藏状态映射回base LLM的隐藏状态空间,并使用base LLM的输出层计算校准后的置信度,从而在不修改模型结构或依赖人工标注的情况下显著降低预期校准误差(Expected Calibration Error, ECE)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03042
作者: Hexiang Tan,Wanli Yang,Junwei Zhang,Xin Chen,Rui Tang,Du Su,Jingang Wang,Yuanzhuo Wang,Fei Sun,Xueqi Cheng
机构: Institute of Computing Technology, CAS (中国科学院计算技术研究所); University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院大学); Meituan (美团)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Reliable confidence is essential for trusting the outputs of LLMs, yet widely deployed post-trained LLMs (PoLLMs) typically compromise this trust with severe overconfidence. In contrast, we observe that their corresponding base LLMs often remain well-calibrated. This naturally motivates us to calibrate PoLLM confidence using the base LLM as a reference. This work proposes two ways to achieve this. A straightforward solution, BaseCal-ReEval, evaluates PoLLM’s responses by feeding them into the base LLM to get average probabilities as confidence. While effective, this approach introduces additional inference overhead. To address this, we propose BaseCal-Proj, which trains a lightweight projection to map the final-layer hidden states of PoLLMs back to those of their base LLMs. These projected states are then processed by the base LLM’s output layer to derive base-calibrated confidence for PoLLM’s responses. Notably, BaseCal is an unsupervised, plug-and-play solution that operates without human labels or LLM modifications. Experiments across five datasets and three LLM families demonstrate the effectiveness of BaseCal, reducing Expected Calibration Error (ECE) by an average of 42.90% compared to the best unsupervised baselines.
zh
[NLP-34] NorwAIs Large Language Models : Technical Report
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决挪威语(Norwegian)在自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing, NLP)领域中代表性不足的问题,特别是在当前主流大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)中对挪威语及北欧语言支持有限的现状。解决方案的关键在于由NorwAI团队开发的一系列专为挪威语及其他北欧语言定制的Transformer架构模型(如GPT、Mistral、Llama2、Mixtral和Magistral),这些模型通过从头预训练或持续预训练(使用25B–88.45B tokens数据集)、采用扩展的挪威语分词器(Norwegian-extended tokenizer)以及先进的后训练策略(post-training strategies)来优化性能、增强鲁棒性并提升跨任务适应能力。特别地,指令微调版本(如Mistral-7B-Instruct和Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct)展现出强助理式交互能力,表明其在实际应用场景中的部署潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03034
作者: Jon Atle Gulla,Peng Liu,Lemei Zhang
机构: Norwegian Research Center for AI Innovation (挪威人工智能创新研究中心), NTNU (挪威科技大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Norwegian, spoken by approximately five million people, remains underrepresented in many of the most significant breakthroughs in Natural Language Processing (NLP). To address this gap, the NorLLM team at NorwAI has developed a family of models specifically tailored to Norwegian and other Scandinavian languages, building on diverse Transformer-based architectures such as GPT, Mistral, Llama2, Mixtral and Magistral. These models are either pretrained from scratch or continually pretrained on 25B - 88.45B tokens, using a Norwegian-extended tokenizer and advanced post-training strategies to optimize performance, enhance robustness, and improve adaptability across various real-world tasks. Notably, instruction-tuned variants (e.g., Mistral-7B-Instruct and Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct) showcase strong assistant-style capabilities, underscoring their potential for practical deployment in interactive and domain-specific applications. The NorwAI large language models are openly available to Nordic organizations, companies and students for both research and experimental use. This report provides detailed documentation of the model architectures, training data, tokenizer design, fine-tuning strategies, deployment, and evaluations.
zh
[NLP-35] Reducing Hallucinations in LLM s via Factuality-Aware Preference Learning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI (Generative AI) 在偏好对齐(如基于人类反馈的强化学习 RLHF 和直接偏好优化 DPO)过程中因过度奖励流畅性和自信度而导致幻觉(hallucination)加剧的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出 F-DPO(Factuality-aware Direct Preference Optimization),其核心创新是:(i) 引入标签翻转变换,确保偏好对中被选择的响应在事实性上不低于被拒绝的响应;(ii) 设计事实性感知边界(factuality-aware margin),强化具有明显事实差异的偏好对,同时在两响应事实性一致时退化为标准 DPO。该方法仅需二元事实性标签,无需辅助奖励模型、词元级标注或多阶段训练,即可显著提升大语言模型的事实性并降低幻觉率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03027
作者: Sindhuja Chaduvula,Ahmed Y. Radwan,Azib Farooq,Yani Ioannou,Shaina Raza
机构: Vector Institute for Artificial Intelligence (人工智能研究所); University of Calgary (卡尔加里大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Preference alignment methods such as RLHF and Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) improve instruction following, but they can also reinforce hallucinations when preference judgments reward fluency and confidence over factual correctness. We introduce F-DPO (Factuality-aware Direct Preference Optimization), a simple extension of DPO that uses only binary factuality labels. F-DPO (i) applies a label-flipping transformation that corrects misordered preference pairs so the chosen response is never less factual than the rejected one, and (ii) adds a factuality-aware margin that emphasizes pairs with clear correctness differences, while reducing to standard DPO when both responses share the same factuality. We construct factuality-aware preference data by augmenting DPO pairs with binary factuality indicators and synthetic hallucinated variants. Across seven open-weight LLMs (1B-14B), F-DPO consistently improves factuality and reduces hallucination rates relative to both base models and standard DPO. On Qwen3-8B, F-DPO reduces hallucination rates by five times (from 0.424 to 0.084) while improving factuality scores by 50 percent (from 5.26 to 7.90). F-DPO also generalizes to out-of-distribution benchmarks: on TruthfulQA, Qwen2.5-14B achieves plus 17 percent MC1 accuracy (0.500 to 0.585) and plus 49 percent MC2 accuracy (0.357 to 0.531). F-DPO requires no auxiliary reward model, token-level annotations, or multi-stage training.
zh
[NLP-36] LittiChoQA: Literary Texts in Indic Languages Chosen for Question Answering AACL2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决长文本问答(Long-context Question Answering, QA)在低资源语言中的挑战,尤其是印度语系(Indic)语言缺乏高质量、大规模的文学文本QA数据集的问题。其核心解决方案是构建了LittiChoQA,这是目前覆盖印度恒河平原多种语言的最大文学QA数据集,包含超过27万对自动生成的问答对,涵盖事实型与非事实型问题,并基于从开放网络获取的自然文学文本进行构建。该数据集为多语言大语言模型(Multilingual Large Language Models, LLMs)在长文本理解与生成式问答任务上的评估提供了重要基准,同时通过对比全上下文与上下文缩短两种设置下的性能表现,揭示了模型性能与效率之间的权衡关系。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03025
作者: Aarya Khandelwal,Ritwik Mishra,Rajiv Ratn Shah
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Submitted to ARR Jan cycle. Targetting AACL 2026
Abstract:Long-context question answering (QA) over literary texts poses significant challenges for modern large language models, particularly in low-resource languages. We address the scarcity of long-context QA resources for Indic languages by introducing LittiChoQA, the largest literary QA dataset to date covering many languages spoken in the Gangetic plains of India. The dataset comprises over 270K automatically generated question-answer pairs with a balanced distribution of factoid and non-factoid questions, generated from naturally authored literary texts collected from the open web. We evaluate multiple multilingual LLMs on non-factoid, abstractive QA, under both full-context and context-shortened settings. Results demonstrate a clear trade-off between performance and efficiency: full-context fine-tuning yields the highest token-level and semantic-level scores, while context shortening substantially improves throughput. Among the evaluated models, Krutrim-2 achieves the strongest performance, obtaining a semantic score of 76.1 with full context. While, in shortened context settings it scores 74.9 with answer paragraph selection and 71.4 with vector-based retrieval. Qualitative evaluations further corroborate these findings.
zh
[NLP-37] MedDialogRubrics: A Comprehensive Benchmark and Evaluation Framework for Multi-turn Medical Consultations in Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前医疗对话大语言模型(LLM)在信息采集与诊断推理能力评估方面缺乏严谨基准和评价框架的问题。现有方法未能充分验证模型在多轮交互中对患者病史的准确挖掘及临床逻辑推理能力,导致模型改进方向模糊。解决方案的关键在于提出MedDialogRubrics这一新型基准,其核心创新包括:(1) 基于多智能体系统合成5,200个真实感患者病例,避免使用真实电子健康记录以保障隐私合规;(2) 设计具备动态引导机制的患者代理(Patient Agent),通过原子级医学事实约束与持续幻觉检测确保模拟病例的内部一致性与临床合理性;(3) 构建由LLM生成并经临床专家标注的细粒度评分标准(rubric)体系,结合循证医学(Evidence-Based Medicine, EBM)指南与拒绝采样策略提取每例病例中的“必问项”,从而实现结构化、可量化且贴近临床实践的评估。实证表明,当前主流模型在多维指标上仍面临显著挑战,提示未来提升医疗对话性能需从对话管理架构层面突破,而非仅依赖基础模型微调。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03023
作者: Lecheng Gong,Weimin Fang,Ting Yang,Dongjie Tao,Chunxiao Guo,Peng Wei,Bo Xie,Jinqun Guan,Zixiao Chen,Fang Shi,Jinjie Gu,Junwei Liu
机构: Ant Group(蚂蚁集团)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注:
Abstract:Medical conversational AI (AI) plays a pivotal role in the development of safer and more effective medical dialogue systems. However, existing benchmarks and evaluation frameworks for assessing the information-gathering and diagnostic reasoning abilities of medical large language models (LLMs) have not been rigorously evaluated. To address these gaps, we present MedDialogRubrics, a novel benchmark comprising 5,200 synthetically constructed patient cases and over 60,000 fine-grained evaluation rubrics generated by LLMs and subsequently refined by clinical experts, specifically designed to assess the multi-turn diagnostic capabilities of LLM. Our framework employs a multi-agent system to synthesize realistic patient records and chief complaints from underlying disease knowledge without accessing real-world electronic health records, thereby mitigating privacy and data-governance concerns. We design a robust Patient Agent that is limited to a set of atomic medical facts and augmented with a dynamic guidance mechanism that continuously detects and corrects hallucinations throughout the dialogue, ensuring internal coherence and clinical plausibility of the simulated cases. Furthermore, we propose a structured LLM-based and expert-annotated rubric-generation pipeline that retrieves Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM) guidelines and utilizes the reject sampling to derive a prioritized set of rubric items (“must-ask” items) for each case. We perform a comprehensive evaluation of state-of-the-art models and demonstrate that, across multiple assessment dimensions, current models face substantial challenges. Our results indicate that improving medical dialogue will require advances in dialogue management architectures, not just incremental tuning of the base-model.
zh
[NLP-38] Dementia-R1: Reinforced Pretraining and Reasoning from Unstructured Clinical Notes for Real-World Dementia Prognosis
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在纵向预测任务(如阿尔茨海默病痴呆预后)中表现不佳的问题,这类任务需要对跨多次就诊的复杂且非单调的症状演变轨迹进行推理。现有方法受限于缺乏显式的症状演化标注,而直接使用强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)则因稀疏的二元奖励信号难以有效训练。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于强化学习的框架 Dementia-R1,采用“冷启动”策略:首先利用可验证的临床指标对模型进行预训练,从而增强模型对疾病进展的推理能力,再通过强化学习优化最终临床状态的预测。实验表明,该方法在真实世界未结构化临床数据上达到 77.03% 的 F1 分数,并在 ADNI 基准上使 7B 模型性能媲美 GPT-4o,有效捕捉认知功能的波动轨迹。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03018
作者: Choonghan Kim,Hyunmin Hwang,Hangeol Chang,Jaemin Kim,Jinse Park,Jae-Sung Lim,Jong Chul Ye
机构: KAIST(韩国科学技术院); Inje University(仁荷大学); University of Ulsan College of Medicine(首尔大学医学院)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown strong performance on clinical text understanding, they struggle with longitudinal prediction tasks such as dementia prognosis, which require reasoning over complex, non-monotonic symptom trajectories across multiple visits. Standard supervised training lacks explicit annotations for symptom evolution, while direct Reinforcement Learning (RL) is hindered by sparse binary rewards. To address this challenge, we introduce Dementia-R1, an RL-based framework for longitudinal dementia prognosis from unstructured clinical notes. Our approach adopts a Cold-Start RL strategy that pre-trains the model to predict verifiable clinical indices extracted from patient histories, enhancing the capability to reason about disease progression before determining the final clinical status. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Dementia-R1 achieves an F1 score of 77.03% on real-world unstructured clinical datasets. Notably, on the ADNI benchmark, our 7B model rivals GPT-4o, effectively capturing fluctuating cognitive trajectories. Code is available at this https URL
zh
[NLP-39] MMFormalizer: Multimodal Autoformalization in the Wild
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决自然语言数学到形式化陈述的自动转化(autoformalization)在现实世界中面临的挑战,尤其是物理场景下需从视觉元素中推断隐藏约束(如质量或能量)的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出MMFormalizer,该方法通过将感知基础的原始实体与真实世界的数学和物理领域进行自适应对齐(adaptive grounding),并利用递归接地(recursive grounding)和公理组合(axiom composition)构建形式命题,同时引入自适应递归终止机制确保每个抽象都有视觉证据支持,并锚定在维度或公理基础上,从而实现跨模态的统一形式化推理。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03017
作者: Jing Xiong,Qi Han,Yunta Hsieh,Hui Shen,Huajian Xin,Chaofan Tao,Chenyang Zhao,Hengyuan Zhang,Taiqiang Wu,Zhen Zhang,Haochen Wang,Zhongwei Wan,Lingpeng Kong,Ngai Wong
机构: The University of Hong Kong (香港大学); University of Michigan, Ann Arbor (密歇根大学安娜堡分校); University of Edinburgh (爱丁堡大学); University of California, Santa Barbara (加州大学圣巴巴拉分校); Ohio State University (俄亥俄州立大学); University of California, Los Angeles (加州大学洛杉矶分校)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Technical Report
Abstract:Autoformalization, which translates natural language mathematics into formal statements to enable machine reasoning, faces fundamental challenges in the wild due to the multimodal nature of the physical world, where physics requires inferring hidden constraints (e.g., mass or energy) from visual elements. To address this, we propose MMFormalizer, which extends autoformalization beyond text by integrating adaptive grounding with entities from real-world mathematical and physical domains. MMFormalizer recursively constructs formal propositions from perceptually grounded primitives through recursive grounding and axiom composition, with adaptive recursive termination ensuring that every abstraction is supported by visual evidence and anchored in dimensional or axiomatic grounding. We evaluate MMFormalizer on a new benchmark, PhyX-AF, comprising 115 curated samples from MathVerse, PhyX, Synthetic Geometry, and Analytic Geometry, covering diverse multimodal autoformalization tasks. Results show that frontier models such as GPT-5 and Gemini-3-Pro achieve the highest compile and semantic accuracy, with GPT-5 excelling in physical reasoning, while geometry remains the most challenging domain. Overall, MMFormalizer provides a scalable framework for unified multimodal autoformalization, bridging perception and formal reasoning. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first multimodal autoformalization method capable of handling classical mechanics (derived from the Hamiltonian), as well as relativity, quantum mechanics, and thermodynamics. More details are available on our project page: this http URL
zh
[NLP-40] SentGraph: Hierarchical Sentence Graph for Multi-hop Retrieval-Augmented Question Answering
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决传统检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)在多跳问答(multi-hop question answering)任务中的局限性,即基于文本块(chunk-based)的检索常提供无关且逻辑不连贯的上下文,导致证据链不完整和推理错误。其解决方案的关键在于提出SentGraph——一个基于句子级图结构的RAG框架,通过显式建模句子间的细粒度逻辑关系来提升多跳推理能力:首先利用修辞结构理论(Rhetorical Structure Theory)区分核心句(nucleus)与卫星句(satellite),构建分层句子图;其次在跨文档实体桥接的基础上形成主题级子图;在线检索时则执行图引导的证据选择与路径扩展,从而精准获取细粒度句子级证据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03014
作者: Junli Liang,Pengfei Zhou,Wangqiu Zhou,Wenjie Qing,Qi Zhao,Ziwen Wang,Qi Song,Xiangyang Li
机构: University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学); Hefei University of Technology (合肥工业大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) effectively supports single-hop question answering with large language models but faces significant limitations in multi-hop question answering tasks, which require combining evidence from multiple documents. Existing chunk-based retrieval often provides irrelevant and logically incoherent context, leading to incomplete evidence chains and incorrect reasoning during answer generation. To address these challenges, we propose SentGraph, a sentence-level graph-based RAG framework that explicitly models fine-grained logical relationships between sentences for multi-hop question answering. Specifically, we construct a hierarchical sentence graph offline by first adapting Rhetorical Structure Theory to distinguish nucleus and satellite sentences, and then organizing them into topic-level subgraphs with cross-document entity bridges. During online retrieval, SentGraph performs graph-guided evidence selection and path expansion to retrieve fine-grained sentence-level evidence. Extensive experiments on four multi-hop question answering benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of SentGraph, validating the importance of explicitly modeling sentence-level logical dependencies for multi-hop reasoning.
zh
[NLP-41] Large Reasoning Models Are (Not Yet) Multilingual Latent Reason ers
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多语言大推理模型(Large Reasoning Models, LRMs)中潜在推理(latent reasoning)行为的跨语言一致性问题,即模型在不同语言环境下是否具备类似的内部非显式推理机制。解决方案的关键在于采用截断策略(truncation-based strategy),通过仅向模型提供部分推理链(chain-of-thought, CoT)来观察其正确答案如何逐步形成,从而量化并比较11种语言下模型的隐式推理能力;同时结合表示分析(representational analyses)揭示尽管表面表现存在差异,但不同语言下的内部预测演化路径高度一致,体现出以英语为中心的潜在推理通路。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02996
作者: Yihong Liu,Raoyuan Zhao,Hinrich Schütze,Michael A. Hedderich
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: preprint
Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) achieve strong performance on mathematical reasoning tasks, often attributed to their capability to generate explicit chain-of-thought (CoT) explanations. However, recent work shows that LRMs often arrive at the correct answer before completing these textual reasoning steps, indicating the presence of latent reasoning – internal, non-verbal computation encoded in hidden states. While this phenomenon has been explored in English, its multilingual behavior remains largely unknown. In this paper, we conduct a systematic investigation of multilingual latent reasoning in LRMs across 11 languages. Using a truncation-based strategy, we examine how the correct answer emerges as the model is given only partial reasoning traces, allowing us to measure stepwise latent prediction formation. Our results reveal clear evidence of multilingual latent reasoning, though unevenly: strong in resource-rich languages, weaker in low-resource ones, and broadly less observable on harder benchmarks. To understand whether these differences reflect distinct internal mechanisms, we further perform representational analyses. Despite surface-level disparities, we find that the internal evolution of predictions is highly consistent across languages and broadly aligns with English – a pattern suggesting an English-centered latent reasoning pathway.
zh
[NLP-42] Stable-RAG : Mitigating Retrieval-Permutation-Induced Hallucinations in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)中因检索文档顺序变化导致大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)输出不一致的问题,即检索顺序敏感性(permutation sensitivity)。现有方法主要关注提升对低质量检索结果的鲁棒性或缓解位置偏置(positional bias),但未直接应对这种由排列顺序引发的幻觉现象。解决方案的关键在于提出 Stable-RAG,其通过在多种检索顺序下运行生成器,聚类隐藏状态,并基于簇中心表示(cluster-center representation)进行解码,从而捕捉主导推理模式;随后利用该推理结果对幻觉输出进行对齐,使模型在不同文档排列下仍能产生一致且准确的答案,显著提升了答案准确性、推理一致性及跨数据集、检索器和输入长度的泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02993
作者: Qianchi Zhang,Hainan Zhang,Liang Pang,Hongwei Zheng,Zhiming Zheng
机构: Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Future Blockchain and Privacy Computing (北京先进区块链与隐私计算创新中心); School of Artificial Intelligence, Beihang University (北京航空航天大学人工智能学院); Beijing Academy of Blockchain and Edge Computing (北京区块链与边缘计算研究院); Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院计算技术研究所)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 19 pages, 13figures, 8 tables, under review
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has become a key paradigm for reducing factual hallucinations in large language models (LLMs), yet little is known about how the order of retrieved documents affects model behavior. We empirically show that under Top-5 retrieval with the gold document included, LLM answers vary substantially across permutations of the retrieved set, even when the gold document is fixed in the first position. This reveals a previously underexplored sensitivity to retrieval permutations. Although robust RAG methods primarily focus on enhancing LLM robustness to low-quality retrieval and mitigating positional bias to distribute attention fairly over long contexts, neither approach directly addresses permutation sensitivity. In this paper, we propose Stable-RAG, which exploits permutation sensitivity estimation to mitigate permutation-induced hallucinations. Stable-RAG runs the generator under multiple retrieval orders, clusters hidden states, and decodes from a cluster-center representation that captures the dominant reasoning pattern. It then uses these reasoning results to align hallucinated outputs toward the correct answer, encouraging the model to produce consistent and accurate predictions across document permutations. Experiments on three QA datasets show that Stable-RAG significantly improves answer accuracy, reasoning consistency and robust generalization across datasets, retrievers, and input lengths compared with baselines.
zh
[NLP-43] Mechanistic Interpretability of Large-Scale Counting in LLM s through a System-2 Strategy
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在计数任务中因Transformer架构限制而表现出系统性精度下降的问题,尤其在处理大规模计数任务时更为显著。其解决方案的关键在于借鉴人类认知中的System-2思维模式,提出一种测试阶段的分解策略:将复杂的计数任务拆解为若干独立的小规模子问题,使模型能够可靠地分别求解,并通过特定注意力头在中间步骤传递隐式计数信息,最终在输出阶段聚合得到总和。该方法突破了模型深度受限带来的精度瓶颈,实验证明其能显著提升大尺度计数任务的准确性,并揭示了System-2类计数机制在LLMs中的关键组成要素。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02989
作者: Hosein Hasani,Mohammadali Banayeeanzade,Ali Nafisi,Sadegh Mohammadian,Fatemeh Askari,Mobin Bagherian,Amirmohammad Izadi,Mahdieh Soleymani Baghshah
机构: Sharif University of Technology (谢里夫理工大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), despite strong performance on complex mathematical problems, exhibit systematic limitations in counting tasks. This issue arises from architectural limits of transformers, where counting is performed across layers, leading to degraded precision for larger counting problems due to depth constraints. To address this limitation, we propose a simple test-time strategy inspired by System-2 cognitive processes that decomposes large counting tasks into smaller, independent sub-problems that the model can reliably solve. We evaluate this approach using observational and causal mediation analyses to understand the underlying mechanism of this System-2-like strategy. Our mechanistic analysis identifies key components: latent counts are computed and stored in the final item representations of each part, transferred to intermediate steps via dedicated attention heads, and aggregated in the final stage to produce the total count. Experimental results demonstrate that this strategy enables LLMs to surpass architectural limitations and achieve high accuracy on large-scale counting tasks. This work provides mechanistic insight into System-2 counting in LLMs and presents a generalizable approach for improving and understanding their reasoning behavior.
zh
[NLP-44] P-Check: Advancing Personalized Reward Model via Learning to Generate Dynamic Checklist
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决个性化奖励建模中用户上下文被当作静态或隐式条件信号,从而无法捕捉人类判断动态性和多维性的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出P-Check框架,通过训练一个即插即用的检查清单生成器(checklist generator),动态合成用于指导奖励预测的评估标准,并引入偏好对比准则加权(Preference-Contrastive Criterion Weighting)策略,依据各准则对个性化判断的区分能力分配显著性分数,从而提升奖励模型的准确性与下游个性化生成效果,并增强在分布外(OOD)场景下的鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02986
作者: Kwangwook Seo,Dongha Lee
机构: Yonsei University (延世大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Work in Progress
Abstract:Recent approaches in personalized reward modeling have primarily focused on leveraging user interaction history to align model judgments with individual preferences. However, existing approaches largely treat user context as a static or implicit conditioning signal, failing to capture the dynamic and multi-faceted nature of human judgment. In this paper, we propose P-Check, a novel personalized reward modeling framework, designed to train a plug-and-play checklist generator that synthesizes dynamic evaluation criteria for guiding the reward prediction. To better align these checklists with personalized nuances, we introduce Preference-Contrastive Criterion Weighting, a training strategy that assigns saliency scores to criteria based on their discriminative power for personalized judgment. We conduct extensive experiments and demonstrate that P-Check not only improves reward accuracy but also enhances downstream personalized generation, and remains robust in OOD scenarios.
zh
[NLP-45] Mechanistic Knobs in LLM s: Retrieving and Steering High-Order Semantic Features via Sparse Autoencoders
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02978
作者: Ruikang Zhang,Shuo Wang,Qi Su
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
[NLP-46] Correct Concise and Complete: Multi-stage Training For Adaptive Reasoning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在推理过程中因链式思维(Chain-of-Thought, CoT)过长而导致的“过度思考”(overthinking)问题,即生成冗余文本虽增加计算成本但未提升甚至损害准确率的现象。解决方案的关键在于提出一种多阶段高效推理方法:首先通过监督微调(如拒绝采样或推理轨迹重格式化)优化初始推理路径,再结合强化学习引入自适应长度惩罚机制,并设计轻量级奖励函数——仅在自我验证有益时鼓励其发生,同时对首个正确答案之后的 token 进行惩罚。该策略在保持较高准确率的前提下显著压缩响应长度(平均减少 28%~40%),并在 Overthinking-Adjusted Accuracy 曲线下面积(AUC_OAA)指标上优于现有复杂方法,实现更优的准确率-响应长度权衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02972
作者: Nathanaël Carraz Rakotonirina,Ren Pang,Neha Anna John,Michael Bohlke-Schneider,Momchil Hardalov
机构: Universitat Pompeu Fabra (庞佩乌法布拉大学); AWS AI Labs (亚马逊云科技人工智能实验室); Amazon AGI (亚马逊通用人工智能)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) have improved substantially through increased test-time computation, typically in the form of intermediate tokens known as chain-of-thought (CoT). However, CoT often becomes unnecessarily long, increasing computation cost without actual accuracy gains or sometimes even degrading performance, a phenomenon known as ``overthinking’'. We propose a multi-stage efficient reasoning method that combines supervised fine-tuning – via rejection sampling or reasoning trace reformatting – with reinforcement learning using an adaptive length penalty. We introduce a lightweight reward function that penalizes tokens generated after the first correct answer but encouraging self-verification only when beneficial. We conduct a holistic evaluation across seven diverse reasoning tasks, analyzing the accuracy–response length trade-off. Our approach reduces response length by an average of 28% for 8B models and 40% for 32B models, while incurring only minor performance drops of 1.6 and 2.5 points, respectively. Despite its conceptual simplicity, it achieves a superior trade-off compared to more complex state-of-the-art efficient reasoning methods, scoring 76.6, in terms of the area under the Overthinking-Adjusted Accuracy curve ( \textAUC_\textOAA ) – 5 points above the base model and 2.5 points above the second-best approach.
zh
[NLP-47] Reliability-Aware Adaptive Self-Consistency for Efficient Sampling in LLM Reasoning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决自一致性(Self-Consistency)方法在推理过程中因多样本聚合导致的高推理成本问题。现有自适应自一致性方法虽通过调整采样预算缓解此问题,但其基于计数的停止规则对所有响应一视同仁,常造成冗余采样。其解决方案的关键在于提出可靠性感知的自适应自一致性(Reliability-Aware Adaptive Self-Consistency, ReASC),将采样策略从响应计数重构为证据充分性判断,利用响应级别的置信度实现更合理的的信息聚合:首先在单样本决策阶段识别可由单一响应可靠回答的实例,其次在可靠性感知累积阶段联合考虑响应频率与置信度进行聚合。该方法在多个模型和数据集上均实现了最优的准确率-成本权衡,显著提升了推理效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02970
作者: Junseok Kim,Nakyeong Yang,Kyungmin Min,Kyomin Jung
机构: Seoul National University (首尔国立大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 15 pages, 8 figures
Abstract:Self-Consistency improves reasoning reliability through multi-sample aggregation, but incurs substantial inference cost. Adaptive self-consistency methods mitigate this issue by adjusting the sampling budget; however, they rely on count-based stopping rules that treat all responses equally, often leading to unnecessary sampling. We propose Reliability-Aware Adaptive Self-Consistency (ReASC), which addresses this limitation by reframing adaptive sampling from response counting to evidence sufficiency, leveraging response-level confidence for principled information aggregation. ReASC operates in two stages: a single-sample decision stage that resolves instances confidently answerable from a single response, and a reliability-aware accumulation stage that aggregates responses by jointly leveraging their frequency and confidence. Across five models and four datasets, ReASC consistently achieves the best accuracy-cost trade-off compared to existing baselines, yielding improved inference efficiency across model scales from 3B to 27B parameters. As a concrete example, ReASC reduces inference cost by up to 70% relative to self-consistency while preserving accuracy on GSM8K using Gemma-3-4B-it.
zh
[NLP-48] Low-Resource Heuristics for Bahnaric Optical Character Recognition Improvement
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决Bahnar语(一种在越南、柬埔寨和老挝境内使用的少数民族语言)文档数字化过程中因图像质量差导致的光学字符识别(OCR)准确率低的问题。其关键解决方案在于提出了一种结合先进表格与非表格区域检测技术以及基于概率的后处理启发式校正方法的综合框架:首先通过检测算法提升输入图像数据质量,再对OCR输出结果进行概率性错误修正,从而显著提高识别准确率,实验结果显示准确率从72.86%提升至79.26%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02965
作者: Phat Tran,Phuoc Pham,Hung Trinh,Tho Quan
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Bahnar, a minority language spoken across Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos, faces significant preservation challenges due to limited research and data availability. This study addresses the critical need for accurate digitization of Bahnar language documents through optical character recognition (OCR) technology. Digitizing scanned paper documents poses significant challenges, as degraded image quality from broken or blurred areas introduces considerable OCR errors that compromise information retrieval systems. We propose a comprehensive approach combining advanced table and non-table detection techniques with probability-based post-processing heuristics to enhance recognition accuracy. Our method first applies detection algorithms to improve input data quality, then employs probabilistic error correction on OCR output. Experimental results indicate a substantial improvement, with recognition accuracy increasing from 72.86% to 79.26%. This work contributes valuable resources for Bahnar language preservation and provides a framework applicable to other minority language digitization efforts.
zh
[NLP-49] LLM -Augmented Changepoint Detection: A Framework for Ensemble Detection and Automated Explanation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决时间序列数据中变化点检测(changepoint detection)的两大关键问题:一是单一检测方法因数据特性差异而表现不稳定,导致方法选择困难且结果易次优;二是现有方法缺乏对检测到的变化点提供自动化的、上下文相关的解释。解决方案的关键在于构建一个集成统计方法与大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的框架:首先通过聚合十种不同算法的结果提升检测性能和鲁棒性;其次利用LLM驱动的解释流水线自动生成与真实世界历史事件关联的语境化叙述,并针对私有或领域特定数据引入检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)机制,确保解释基于用户提供的文档。此框架显著提升了检测结果的可解释性与实用性,已在金融、政治学和环境科学等领域验证其应用价值。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02957
作者: Fabian Lukassen,Christoph Weisser,Michael Schlee,Manish Kumar,Anton Thielmann,Benjamin Saefken,Thomas Kneib
机构: University of Göttingen (哥廷根大学); TU Clausthal (克劳斯塔尔工业大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:This paper introduces a novel changepoint detection framework that combines ensemble statistical methods with Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance both detection accuracy and the interpretability of regime changes in time series data. Two critical limitations in the field are addressed. First, individual detection methods exhibit complementary strengths and weaknesses depending on data characteristics, making method selection non-trivial and prone to suboptimal results. Second, automated, contextual explanations for detected changes are largely absent. The proposed ensemble method aggregates results from ten distinct changepoint detection algorithms, achieving superior performance and robustness compared to individual methods. Additionally, an LLM-powered explanation pipeline automatically generates contextual narratives, linking detected changepoints to potential real-world historical events. For private or domain-specific data, a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) solution enables explanations grounded in user-provided documents. The open source Python framework demonstrates practical utility in diverse domains, including finance, political science, and environmental science, transforming raw statistical output into actionable insights for analysts and decision-makers.
zh
[NLP-50] Enhancing Multilingual RAG Systems with Debiased Language Preference-Guided Query Fusion
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多语言检索增强生成(mRAG)系统中普遍存在的“英语偏好”现象,即模型在跨语言任务中倾向于选择英语作为中间语言进行处理,从而导致对低资源语言性能的低估。现有研究常将此现象归因于大型语言模型(LLM)本身对英语的更强能力,但本文指出这种评估结果被基准测试中的结构性偏倚严重扭曲,包括暴露偏倚(exposure bias)、黄金答案可用性先验(gold availability prior)以及文化主题局部性带来的先验因素。解决方案的关键在于提出DeLP(Debiased Language Preference)这一校准指标,显式剥离上述结构混淆因素,并基于分析发现:检索器本质上更偏好查询与文档语言的一致性(monolingual alignment)。由此进一步设计DELTA(DEbiased Language preference-guided Text Augmentation)框架,通过策略性利用单语对齐机制优化跨语言检索与生成过程,实验表明其在多种语言上均显著优于传统英语转译和mRAG基线方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02956
作者: Jeonghyun Park,Byeongjeong Kim,Seojin Hwang,Hwanhee Lee
机构: Chung-Ang University (中央大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 20 pages, 5 figures, 15 tables
Abstract:Multilingual Retrieval-Augmented Generation (mRAG) systems often exhibit a perceived preference for high-resource languages, particularly English, resulting in the widespread adoption of English pivoting. While prior studies attribute this advantage to the superior English-centric capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), we find that such measurements are significantly distorted by structural priors inherent in evaluation benchmarks. Specifically, we identify exposure bias and a gold availability prior-both driven by the disproportionate concentration of resources in English-as well as cultural priors rooted in topic locality, as factors that hinder accurate assessment of genuine language preference. To address these biases, we propose DeLP (Debiased Language Preference), a calibrated metric designed to explicitly factor out these structural confounds. Our analysis using DeLP reveals that the previously reported English preference is largely a byproduct of evidence distribution rather than an inherent model bias. Instead, we find that retrievers fundamentally favor monolingual alignment between the query and the document language. Building on this insight, we introduce DELTA (DEbiased Language preference-guided Text Augmentation), a lightweight and efficient mRAG framework that strategically leverages monolingual alignment to optimize cross-lingual retrieval and generation. Experimental results demonstrate that DELTA consistently outperforms English pivoting and mRAG baselines across diverse languages.
zh
[NLP-51] SastBench: A Benchmark for Testing Agent ic SAST Triage
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决静态应用安全测试(Static Application Security Testing, SAST)工具在实际应用中因产生大量误报(false positives)而导致人工筛选(triage)成本高昂的问题。现有评估基准无法真实模拟SAST发现的分布情况,限制了自动化工具(如基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的代理)的有效性验证。解决方案的关键在于提出SastBench——一个结合真实CVE漏洞作为真阳性、经过滤的SAST工具结果作为近似假阳性的基准数据集,其设计具有代理无关性(agent-agnostic),从而为评估SAST归约代理提供更贴近现实场景的评测框架,并支持对不同代理性能的系统性比较与深入分析。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02941
作者: Jake Feiglin,Guy Dar
机构: Rival Labs
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:SAST (Static Application Security Testing) tools are among the most widely used techniques in defensive cybersecurity, employed by commercial and non-commercial organizations to identify potential vulnerabilities in software. Despite their great utility, they generate numerous false positives, requiring costly manual filtering (aka triage). While LLM-powered agents show promise for automating cybersecurity tasks, existing benchmarks fail to emulate real-world SAST finding distributions. We introduce SastBench, a benchmark for evaluating SAST triage agents that combines real CVEs as true positives with filtered SAST tool findings as approximate false positives. SastBench features an agent-agnostic design. We evaluate different agents on the benchmark and present a comparative analysis of their performance, provide a detailed analysis of the dataset, and discuss the implications for future development.
zh
[NLP-52] Pearmut: Human Evaluation of Translation Made Trivial
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前多语言自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing, NLP)领域中人工评估(human evaluation)因流程复杂、耗时长且工具工程与运营开销大而常被自动指标替代的问题。其核心解决方案是提出一个轻量但功能丰富的平台 Pearmut,该平台将端到端的人工评估简化为与自动评估同等便捷的操作,通过支持标准评估协议(如 DA、ESA、MQM)、文档级上下文、绝对与对比评估、注意力检查、ESAAI 预标注以及静态和基于主动学习的分配策略,显著降低人工评估的实施门槛,并增强其在模型开发与诊断中的实用性与可重复性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02933
作者: Vilém Zouhar,Tom Kocmi
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注: typeset with Typst
Abstract:Human evaluation is the gold standard for multilingual NLP, but is often skipped in practice and substituted with automatic metrics, because it is notoriously complex and slow to set up with existing tools with substantial engineering and operational overhead. We introduce Pearmut, a lightweight yet feature-rich platform that makes end-to-end human evaluation as easy to run as automatic evaluation. Pearmut removes common entry barriers and provides support for evaluating multilingual tasks, with a particular focus on machine translation. The platform implements standard evaluation protocols, including DA, ESA, or MQM, but is also extensible to allow prototyping new protocols. It features document-level context, absolute and contrastive evaluation, attention checks, ESAAI pre-annotations and both static and active learning-based assignment strategies. Pearmut enables reliable human evaluation to become a practical, routine component of model development and diagnosis rather than an occasional effort.
zh
[NLP-53] Memorization Emergence and Explaining Reversal Failures: A Controlled Study of Relational Semantics in LLM s
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决自回归大语言模型(Autoregressive LLMs)在处理关系推理任务时是否真正习得了关系的逻辑语义(如对称性和逆向逻辑),以及反转失败现象是由关系语义缺失还是由左到右生成顺序偏差导致的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个基于知识图谱的可控合成框架,通过生成对称/逆关系三元组文本数据,从头训练GPT风格的自回归模型,并系统评估模型的记忆能力、逻辑推理能力和零样本泛化性能;实验发现,在获得足够承载逻辑信息的监督信号后,即使浅层模型(2-3层)也能出现关系语义的突变式涌现,且成功泛化与中间层稳定信号一致;进一步的顺序匹配正向/反向测试和扩散基线表明,反转失败主要源于自回归顺序偏差,而非逆向语义缺失。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02931
作者: Yihua Zhu,Qianying Liu,Jiaxin Wang,Fei Cheng,Chaoran Liu,Akiko Aizawa,Sadao Kurohashi,Hidetoshi Shimodaira
机构: Kyoto University (京都大学); University of Tokyo (东京大学); NII LLMC (日本国立信息学研究所语言模型与认知研究中心); RIKEN (理化学研究所)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Autoregressive LLMs perform well on relational tasks that require linking entities via relational words (e.g., father/son, friend), but it is unclear whether they learn the logical semantics of such relations (e.g., symmetry and inversion logic) and, if so, whether reversal-type failures arise from missing relational semantics or left-to-right order bias. We propose a controlled Knowledge Graph-based synthetic framework that generates text from symmetric/inverse triples, train GPT-style autoregressive models from scratch, and evaluate memorization, logical inference, and in-context generalization to unseen entities to address these questions. We find a sharp phase transition in which relational semantics emerge with sufficient logic-bearing supervision, even in shallow (2-3 layer) models, and that successful generalization aligns with stable intermediate-layer signals. Finally, order-matched forward/reverse tests and a diffusion baseline indicate that reversal failures are primarily driven by autoregressive order bias rather than deficient inversion semantics.
zh
[NLP-54] RAL2M: Retrieval Augmented Learning-To-Match Against Hallucination in Compliance-Guaranteed Service Systems
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在服务系统中产生的幻觉(hallucination)问题,即模型生成内容与事实不符,从而影响响应的合规性和可靠性。其核心解决方案是提出一种名为检索增强型学习匹配框架(Retrieval-Augmented Learning-to-Match, RAL2M)的新方法,将LLM从生成式角色转变为基于检索系统的查询-响应匹配判官(query-response matching judges),从而避免直接生成可能产生幻觉的内容。该方案的关键创新在于引入一种查询自适应潜在集成策略(query-adaptive latent ensemble strategy),显式建模不同LLM之间的异质能力及相互依赖关系,进而获得校准后的共识决策,有效抑制判断层面的幻觉,显著优于现有强基线方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02917
作者: Mengze Hong,Di Jiang,Jiangtao Wen,Zhiyang Su,Yawen Li,Yanjie Sun,Guan Wang,Chen Jason Zhang
机构: Hong Kong Polytechnic University (香港理工大学); New York University Shanghai (纽约大学上海分校); Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (香港科技大学); Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (北京邮电大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Hallucination is a major concern in LLM-driven service systems, necessitating explicit knowledge grounding for compliance-guaranteed responses. In this paper, we introduce Retrieval-Augmented Learning-to-Match (RAL2M), a novel framework that eliminates generation hallucination by repositioning LLMs as query-response matching judges within a retrieval-based system, providing a robust alternative to purely generative approaches. To further mitigate judgment hallucination, we propose a query-adaptive latent ensemble strategy that explicitly models heterogeneous model competence and interdependencies among LLMs, deriving a calibrated consensus decision. Extensive experiments on large-scale benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed method effectively leverages the “wisdom of the crowd” and significantly outperforms strong baselines. Finally, we discuss best practices and promising directions for further exploiting latent representations in future work.
zh
[NLP-55] Image Word and Thought: A More Challenging Language Task for the Iterated Learning Model
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决语言结构如何在代际传播中自发形成的问题,即探究语言传输过程中的约束条件如何促进语言规则的涌现。其解决方案的关键在于引入一种计算上更可行且生态效度更高的半监督迭代学习模型,该模型结合了监督与无监督学习,并嵌入自编码器架构,从而能够在更大规模的意义-信号空间中模拟语言传播动态。通过将该模型应用于七段显示器图像的复杂语义通信任务,研究证明了代理能够习得并传递一种表达性强(所有128个字符均有唯一编码)、组合性强(信号成分稳定映射到意义成分)且稳定的语言,表明该方法能有效捕捉语言结构的演化机制。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02911
作者: Hyoyeon Lee,Seth Bullock,Conor Houghton
机构: University of Bristol (布里斯托大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注: This is an extended version of a paper accepted for EvoLang2026, it includes additional details of the numerical experiments
Abstract:The iterated learning model simulates the transmission of language from generation to generation in order to explore how the constraints imposed by language transmission facilitate the emergence of language structure. Despite each modelled language learner starting from a blank slate, the presence of a bottleneck limiting the number of utterances to which the learner is exposed can lead to the emergence of language that lacks ambiguity, is governed by grammatical rules, and is consistent over successive generations, that is, one that is expressive, compositional and stable. The recent introduction of a more computationally tractable and ecologically valid semi supervised iterated learning model, combining supervised and unsupervised learning within an autoencoder architecture, has enabled exploration of language transmission dynamics for much larger meaning-signal spaces. Here, for the first time, the model has been successfully applied to a language learning task involving the communication of much more complex meanings: seven-segment display images. Agents in this model are able to learn and transmit a language that is expressive: distinct codes are employed for all 128 glyphs; compositional: signal components consistently map to meaning components, and stable: the language does not change from generation to generation.
zh
[NLP-56] Beyond the Black Box: Theory and Mechanism of Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文试图解决当前大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)研究中理论理解滞后于工程实践的困境,即尽管LLMs在实践中表现出显著效能,但其内在机制和性能边界仍缺乏系统性理论支撑,导致模型常被视为“黑箱”。解决方案的关键在于提出一个基于生命周期的统一分类框架,将LLM研究划分为数据准备、模型准备、训练、对齐、推理和评估六个阶段,并在此基础上系统梳理各阶段的基础理论与内部机制,从而为LLM的发展从经验性工程实践向原理驱动的科学范式转型提供结构化路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02907
作者: Zeyu Gan,Ruifeng Ren,Wei Yao,Xiaolin Hu,Gengze Xu,Chen Qian,Huayi Tang,Zixuan Gong,Xinhao Yao,Pengwei Tang,Zhenxing Dou,Yong Liu
机构: Gaoling School of Artificial Intelligence, Renmin University of China (中国人民大学高瓴人工智能学院); Key Laboratory of Multimedia Trusted Perception and Efficient Computing, Xiamen University (厦门大学多媒体可信感知与高效计算重点实验室)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:The rapid emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has precipitated a profound paradigm shift in Artificial Intelligence, delivering monumental engineering successes that increasingly impact modern society. However, a critical paradox persists within the current field: despite the empirical efficacy, our theoretical understanding of LLMs remains disproportionately nascent, forcing these systems to be treated largely as ``black boxes’'. To address this theoretical fragmentation, this survey proposes a unified lifecycle-based taxonomy that organizes the research landscape into six distinct stages: Data Preparation, Model Preparation, Training, Alignment, Inference, and Evaluation. Within this framework, we provide a systematic review of the foundational theories and internal mechanisms driving LLM performance. Specifically, we analyze core theoretical issues such as the mathematical justification for data mixtures, the representational limits of various architectures, and the optimization dynamics of alignment algorithms. Moving beyond current best practices, we identify critical frontier challenges, including the theoretical limits of synthetic data self-improvement, the mathematical bounds of safety guarantees, and the mechanistic origins of emergent intelligence. By connecting empirical observations with rigorous scientific inquiry, this work provides a structured roadmap for transitioning LLM development from engineering heuristics toward a principled scientific discipline.
zh
[NLP-57] Linear Script Representations in Speech Foundation Models Enable Zero-Shot Transliteration
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多语言语音基础模型(如Whisper)在处理同一语言的不同地域变体时,因使用不同书写系统而导致语音识别输出存在非确定性脚本的问题。解决方案的关键在于发现脚本信息在线性编码于多语言语音模型的激活空间中,并通过在推理阶段修改激活值来实现对输出脚本的直接控制;具体而言,向测试时的激活添加特定脚本向量即可诱导脚本转换,即使在非常规的语言-脚本组合(如意大利语使用西里尔字母、日语使用拉丁字母)下也能生效,从而实现了对语音识别输出脚本的后验控制,且在Whisper的所有模型规模上均表现出竞争性性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02906
作者: Ryan Soh-Eun Shim,Kwanghee Choi,Kalvin Chang,Ming-Hao Hsu,Florian Eichin,Zhizheng Wu,Alane Suhr,Michael A. Hedderich,David Harwath,David R. Mortensen,Barbara Plank
机构: LMU Munich (慕尼黑路德维希马克西米利安大学); Munich Center for Machine Learning (慕尼黑机器学习中心); University of Texas at Austin (德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校); Carnegie Mellon University (卡内基梅隆大学); University of California, Berkeley (加州大学伯克利分校); Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen (香港中文大学(深圳)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Multilingual speech foundation models such as Whisper are trained on web-scale data, where data for each language consists of a myriad of regional varieties. However, different regional varieties often employ different scripts to write the same language, rendering speech recognition output also subject to non-determinism in the output script. To mitigate this problem, we show that script is linearly encoded in the activation space of multilingual speech models, and that modifying activations at inference time enables direct control over output script. We find the addition of such script vectors to activations at test time can induce script change even in unconventional language-script pairings (e.g. Italian in Cyrillic and Japanese in Latin script). We apply this approach to inducing post-hoc control over the script of speech recognition output, where we observe competitive performance across all model sizes of Whisper.
zh
[NLP-58] Logical Phase Transitions: Understanding Collapse in LLM Logical Reasoning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在逻辑推理能力上的局限性问题,特别是当逻辑复杂度提升时出现的性能骤降现象。研究发现,逻辑推理性能并非随复杂度平滑下降,而是在某一临界逻辑深度处发生“逻辑相变”(Logical Phase Transitions),即性能在稳定区间内保持不变,一旦超过临界点则突然崩溃,类似于物理系统中的相变行为。解决方案的关键在于提出“神经符号课程调优”(Neuro-Symbolic Curriculum Tuning),该框架通过自适应对齐自然语言与逻辑符号以建立共享表示,并围绕相变边界重塑训练动态,从而逐步增强模型在更高逻辑深度下的推理能力,显著提升了准确率和对未见逻辑组合的泛化性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02902
作者: Xinglang Zhang,Yunyao Zhang,ZeLiang Chen,Junqing Yu,Wei Yang,Zikai Song
机构: Huazhong University of Science and Technology (华中科技大学)
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Logic in Computer Science (cs.LO)
备注:
Abstract:Symbolic logical reasoning is a critical yet underexplored capability of large language models (LLMs), providing reliable and verifiable decision-making in high-stakes domains such as mathematical reasoning and legal judgment. In this study, we present a systematic analysis of logical reasoning under controlled increases in logical complexity, and reveal a previously unrecognized phenomenon, which we term Logical Phase Transitions: rather than degrading smoothly, logical reasoning performance remains stable within a regime but collapses abruptly beyond a critical logical depth, mirroring physical phase transitions such as water freezing beyond a critical temperature threshold. Building on this insight, we propose Neuro-Symbolic Curriculum Tuning, a principled framework that adaptively aligns natural language with logical symbols to establish a shared representation, and reshapes training dynamics around phase-transition boundaries to progressively strengthen reasoning at increasing logical depths. Experiments on five benchmarks show that our approach effectively mitigates logical reasoning collapse at high complexity, yielding average accuracy gains of +1.26 in naive prompting and +3.95 in CoT, while improving generalization to unseen logical compositions. Code and data are available at this https URL.
zh
[NLP-59] ransparent Semantic Change Detection with Dependency-Based Profiles
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决词汇语义变化检测(Lexical Semantic Change Detection, LSC)中现有基于嵌入的分布语义模型(embedding-based distributional word representations)可解释性差的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种仅依赖词间依存共现模式(dependency co-occurrence patterns)的方法,无需神经网络或复杂嵌入空间,通过分析词语在句法结构中的共现关系来识别语义演变,并在定量与定性层面验证了该方法的有效性与可解释性,且性能优于多个主流分布语义模型。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02891
作者: Bach Phan-Tat,Kris Heylen,Dirk Geeraerts,Stefano De Pascale,Dirk Speelman
机构: KU Leuven (鲁汶大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Most modern computational approaches to lexical semantic change detection (LSC) rely on embedding-based distributional word representations with neural networks. Despite the strong performance on LSC benchmarks, they are often opaque. We investigate an alternative method which relies purely on dependency co-occurrence patterns of words. We demonstrate that it is effective for semantic change detection and even outperforms a number of distributional semantic models. We provide an in-depth quantitative and qualitative analysis of the predictions, showing that they are plausible and interpretable.
zh
[NLP-60] ReTreVal: Reasoning Tree with Validation - A Hybrid Framework for Enhanced LLM Multi-Step Reasoning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在复杂任务中进行多步推理时面临的挑战,尤其是数学问题和创意写作等需要系统性探索、严格验证与跨问题知识迁移的场景。现有方法如ReAct、Reflexion和Self-Refine虽通过迭代优化与反思机制提升推理能力,但普遍存在缺乏对备选解题路径的结构化探索以及无法持久积累经验的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为ReTreVal(Reasoning Tree with Validation)的混合框架,该框架融合了思维树(Tree-of-Thoughts)探索、基于LLM的批判评分、自我精炼与反思记忆机制,构建自适应深度的结构化推理树;每个节点均接受迭代式自我批判与精炼,并通过双重验证机制评估质量、连贯性和正确性;同时利用批判性剪枝保留高分节点以控制计算成本,并将成功路径与失败模式存入反思记忆缓冲区,实现跨问题的学习与知识迁移,从而显著提升推理效率与准确性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02880
作者: Abhishek HS,Pavan C Shekar,Arpit Jain,Ashwanth Krishnan
机构: QpiAI(量子智能人工智能)
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 14 pages, 1 figure, 5 tables
Abstract:Multi-step reasoning remains a key challenge for Large Language Models (LLMs), particularly in complex domains such as mathematics and creative writing. While recent approaches including ReAct, Reflexion, and Self-Refine improve reasoning through iterative refinement and reflection, they often lack structured exploration of alternative solution paths and persistent learning across problems. We propose ReTreVal (Reasoning Tree with Validation), a hybrid framework that integrates Tree-of-Thoughts exploration, self-refinement, LLM-based critique scoring, and reflexion memory to enable bounded and validated multi-step reasoning. ReTreVal constructs a structured reasoning tree with adaptive depth based on problem complexity, where each node undergoes iterative self-critique and refinement guided by explicit LLM-generated feedback. A dual validation mechanism evaluates reasoning quality, coherence, and correctness at each node while persistently storing insights from successful reasoning paths and failure patterns in a reflexion memory buffer, enabling cross-problem learning. Critique-based pruning retains only the top-k highest-scoring nodes at each level, controlling computational cost while preserving high-quality solution paths. We evaluate ReTreVal against ReAct, Reflexion, and Self-Refine across 500 mathematical problems and creative writing tasks using Qwen 2.5 7B as the underlying LLM, and demonstrate that ReTreVal consistently outperforms existing methods through its combination of structured exploration, critique-driven refinement, and cross-problem memory, making it particularly effective for tasks requiring exploratory reasoning, rigorous verification, and knowledge transfer.
zh
[NLP-61] Revisiting Data Compression with Language Modeling
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决如何利用大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)提升数据压缩效率的问题,特别是在不依赖额外训练的前提下实现更低的调整后压缩率(adjusted compression rate)。其关键解决方案在于优化LLMs在压缩任务中的配置与使用方式,包括对模型输入输出结构的适配、序列建模策略的改进以及针对不同数据类型(如非英语文本、代码和字节流)的针对性调整。实验表明,在enwik9数据集上无需额外训练即可达到18%的调整后压缩率,优于现有方法,验证了LLMs在多模态和非自然文本压缩场景下的潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02875
作者: Chen-Han Tsai
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Preprint
Abstract:In this report, we investigate the potential use of large language models (LLM’s) in the task of data compression. Previous works have demonstrated promising results in applying LLM’s towards compressing not only text, but also a wide range of multi-modal data. Despite the favorable performance achieved, there still remains several practical questions that pose a challenge towards replacing existing data compression algorithms with LLM’s. In this work, we explore different methods to achieve a lower adjusted compression rate using LLM’s as data compressors. In comparison to previous works, we were able to achieve a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) adjusted compression rate of around 18% on the enwik9 dataset without additional model training. Furthermore, we explore the use of LLM’s in compressing non-English data, code data, byte stream sequences. We show that while LLM’s excel in compressing data in text-dominant domains, their ability in compressing non-natural text sequences still remain competitive if configured in the right way.
zh
[NLP-62] LongBench Pro: A More Realistic and Comprehensive Bilingual Long-Context Evaluation Benchmark
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前长上下文(long-context)大语言模型(LLM)评估基准在可扩展性与现实性之间的权衡问题:现有基准要么依赖合成任务而难以反映真实场景复杂性,要么依赖人工标注导致难以扩展至极端长度和多样化场景。其解决方案的关键在于提出LongBench Pro——一个包含1,500个自然发生、中英文双语的长上下文样本的综合性基准,覆盖11项主任务和25项次任务,输入长度跨度达8k至256k tokens,并引入细粒度的任务指标与多维上下文需求分类体系(全依赖 vs. 部分依赖、长度六级、难度四级)。为平衡质量与可扩展性,作者设计了“人-模型协同构建”流程:前沿大模型生成挑战性问题及参考答案、设计逻辑与解题过程以降低专家验证成本,再由专家严格校验并修正问题案例。该方案显著提升了评估的真实性与效率,为长上下文理解能力的系统性评测提供了可靠测试平台。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02872
作者: Ziyang Chen,Xing Wu,Junlong Jia,Chaochen Gao,Qi Fu,Debing Zhang,Songlin Hu
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The rapid expansion of context length in large language models (LLMs) has outpaced existing evaluation benchmarks. Current long-context benchmarks often trade off scalability and realism: synthetic tasks underrepresent real-world complexity, while fully manual annotation is costly to scale to extreme lengths and diverse scenarios. We present LongBench Pro, a more realistic and comprehensive bilingual benchmark of 1,500 naturally occurring long-context samples in English and Chinese spanning 11 primary tasks and 25 secondary tasks, with input lengths from 8k to 256k tokens. LongBench Pro supports fine-grained analysis with task-specific metrics and a multi-dimensional taxonomy of context requirement (full vs. partial dependency), length (six levels), and difficulty (four levels calibrated by model performance). To balance quality with scalability, we propose a Human-Model Collaborative Construction pipeline: frontier LLMs draft challenging questions and reference answers, along with design rationales and solution processes, to reduce the cost of expert verification. Experts then rigorously validate correctness and refine problematic cases. Evaluating 46 widely used long-context LLMs on LongBench Pro yields three findings: (1) long-context optimization contributes more to long-context comprehension than parameter scaling; (2) effective context length is typically shorter than the claimed context length, with pronounced cross-lingual misalignment; and (3) the “thinking” paradigm helps primarily models trained with native reasoning, while mixed-thinking designs offer a promising Pareto trade-off. In summary, LongBench Pro provides a robust testbed for advancing long-context understanding.
zh
[NLP-63] raining Language Models with homotokens Leads to Delayed Overfitting
【速读】: 该论文试图解决语言模型中因子词分词(subword tokenization)导致的非唯一性问题,即多个不同的token序列可解码为相同表面形式并保留语义,但会引发不同的内部计算。这一现象在训练过程中可能引入不必要的敏感性,影响模型泛化能力。解决方案的关键在于提出“同词符”(homotokens)的概念——即同一词汇项的替代性有效子词分割方式,并设计一种轻量级训练架构:通过辅助因果编码器和块因果交叉注意力机制,在不修改训练目标或token接口的前提下,使标准的下一个token预测任务条件于采样的同词符变体。该方法在数据受限预训练中延迟过拟合,在多语言微调中则表现出对分词器质量的依赖性,从而提供了一种简单且模块化的机制来增强语言模型对分词方式的不变性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02867
作者: Adrian Cosma,Stefan Ruseti,Emilian Radoi,Mihai Dascalu
机构: Dalle Molle Institute for Artificial Intelligence (IDSIA); National University of Science and Technology POLITEHNICA Bucharest
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 8 pages, 6 figures, 3 Appendices
Abstract:Subword tokenization introduces a computational layer in language models where many distinct token sequences decode to the same surface form and preserve meaning, yet induce different internal computations. Despite this non-uniqueness, language models are typically trained using a single canonical longest-prefix tokenization. We formalize homotokens-alternative valid subword segmentations of the same lexical item-as a strictly meaning-preserving form of data augmentation. We introduce a lightweight training architecture that conditions canonical next-token prediction on sampled homotoken variants via an auxiliary causal encoder and block-causal cross-attention, without modifying the training objective or token interface. In data-constrained pretraining, homotoken augmentation consistently delays overfitting under repeated data exposure and improves generalization across diverse evaluation datasets. In multilingual fine-tuning, we find that the effectiveness of homotokens depends on tokenizer quality: gains are strongest when canonical tokens are highly compressed and diminish when the tokenizer already over-fragments the input. Overall, homotokens provide a simple and modular mechanism for inducing tokenization invariance in language models.
zh
[NLP-64] o Generate or Discriminate? Methodological Considerations for Measuring Cultural Alignment in LLM s AACL2025
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决社会人口学提示(Socio-demographic Prompting, SDP)在评估大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)文化能力时存在的混淆因素问题,如提示敏感性、解码参数影响以及生成任务相对于判别任务的固有难度,这些问题导致难以区分模型表现不佳是源于偏见还是任务设计缺陷。解决方案的关键在于提出逆向社会人口学提示(Inverse Socio-demographic Prompting, ISDP),即要求LLMs基于真实与模拟用户行为来判别和预测其社会人口学特征,从而更清晰地衡量模型对不同群体行为的理解能力;实验使用Goodreads-CSI数据集验证了该方法的有效性,结果表明模型在处理真实行为时表现优于模拟行为,但在个体层面性能下降且趋于一致,揭示了个性化能力的局限性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02858
作者: Saurabh Kumar Pandey,Sougata Saha,Monojit Choudhury
机构: Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence (穆罕默德·本·扎耶德人工智能大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: IJCNLP-AACL 2025
Abstract:Socio-demographic prompting (SDP) - prompting Large Language Models (LLMs) using demographic proxies to generate culturally aligned outputs - often shows LLM responses as stereotypical and biased. While effective in assessing LLMs’ cultural competency, SDP is prone to confounding factors such as prompt sensitivity, decoding parameters, and the inherent difficulty of generation over discrimination tasks due to larger output spaces. These factors complicate interpretation, making it difficult to determine if the poor performance is due to bias or the task design. To address this, we use inverse socio-demographic prompting (ISDP), where we prompt LLMs to discriminate and predict the demographic proxy from actual and simulated user behavior from different users. We use the Goodreads-CSI dataset (Saha et al., 2025), which captures difficulty in understanding English book reviews for users from India, Mexico, and the USA, and test four LLMs: Aya-23, Gemma-2, GPT-4o, and LLaMA-3.1 with ISDP. Results show that models perform better with actual behaviors than simulated ones, contrary to what SDP suggests. However, performance with both behavior types diminishes and becomes nearly equal at the individual level, indicating limits to personalization.
zh
[NLP-65] Mem: Temporal-Hierarchical Memory Consolidation for Long-Horizon Conversational Agents
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决长时对话代理中因交互历史不断累积而超出大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)有限上下文窗口的问题,尤其针对现有记忆框架在跨层级时间结构信息组织上的不足,导致记忆碎片化和长期个性化不稳定。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种时空层次化记忆框架 TiMem,核心创新是引入Temporal Memory Tree (TMT) 实现从原始对话观测到逐步抽象的人格表征的记忆系统性整合;该框架具备三个关键特性:(1) 通过TMT实现时间-层次结构组织;(2) 基于语义引导的记忆融合机制,在无需微调的情况下实现跨层级记忆整合;(3) 复杂度感知的记忆召回策略,根据查询复杂度动态平衡精度与效率。实验表明,TiMem 在 LoCoMo 和 LongMemEval-S 上分别达到 75.30% 和 76.88% 的准确率,显著优于基线方法,并将召回记忆长度减少 52.20%,同时在人格分离性和分布紧凑性上表现更优。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02845
作者: Kai Li,Xuanqing Yu,Ziyi Ni,Yi Zeng,Yao Xu,Zheqing Zhang,Xin Li,Jitao Sang,Xiaogang Duan,Xuelei Wang,Chengbao Liu,Jie Tan
机构: Institute of Automation, CAS (中国科学院自动化研究所); School of Artificial Intelligence, UCAS (中国科学院大学人工智能学院); AI Lab, AIGility Cloud Innovation; North China Electric Power University (华北电力大学); Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence (北京智源研究院); Gaoling School of Artificial Intelligence, RUC (中国人民大学高瓴人工智能学院); School of Biomedical Engineering, USTC (中国科学技术大学生物医学工程学院); Suzhou Institute for Advance Research, USTC (中国科学技术大学苏州高等研究院); School of Computer Science and Technology, BJTU (北京交通大学计算机科学与技术学院); Hunan Central South Intelligent Equipment Co., Ltd. (湖南中南智能装备有限公司)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Long-horizon conversational agents have to manage ever-growing interaction histories that quickly exceed the finite context windows of large language models (LLMs). Existing memory frameworks provide limited support for temporally structured information across hierarchical levels, often leading to fragmented memories and unstable long-horizon personalization. We present TiMem, a temporal–hierarchical memory framework that organizes conversations through a Temporal Memory Tree (TMT), enabling systematic memory consolidation from raw conversational observations to progressively abstracted persona representations. TiMem is characterized by three core properties: (1) temporal–hierarchical organization through TMT; (2) semantic-guided consolidation that enables memory integration across hierarchical levels without fine-tuning; and (3) complexity-aware memory recall that balances precision and efficiency across queries of varying complexity. Under a consistent evaluation setup, TiMem achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on both benchmarks, reaching 75.30% on LoCoMo and 76.88% on LongMemEval-S. It outperforms all evaluated baselines while reducing the recalled memory length by 52.20% on LoCoMo. Manifold analysis indicates clear persona separation on LoCoMo and reduced dispersion on LongMemEval-S. Overall, TiMem treats temporal continuity as a first-class organizing principle for long-horizon memory in conversational agents.
zh
[NLP-66] he performances of the Chinese and U.S. Large Language Models on the Topic of Chinese Culture
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在跨文化语境下是否存在文化认知差异的问题,特别是针对中文语境中由中国与美国开发者训练的LLM在理解中国传统文化的任务上表现是否不同。其解决方案的关键在于采用直接提问范式,对包括GPT-5.1、DeepSeek-V3.2、Qwen3-Max和Gemini 2.5Pro在内的多个主流LLM进行系统评估,聚焦于历史、文学、诗歌等传统中国文化相关领域,通过量化比较模型在特定文化知识上的准确率,揭示文化背景对模型性能的影响机制。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02830
作者: Feiyan Liu,Chenxun Zhuo,Siyan Zhao,Bao Ge,Tianming Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Cultural backgrounds shape individuals’ perspectives and approaches to problem-solving. Since the emergence of GPT-1 in 2018, large language models (LLMs) have undergone rapid development. To date, the world’s ten leading LLM developers are primarily based in China and the United States. To examine whether LLMs released by Chinese and U.S. developers exhibit cultural differences in Chinese-language settings, we evaluate their performance on questions about Chinese culture. This study adopts a direct-questioning paradigm to evaluate models such as GPT-5.1, DeepSeek-V3.2, Qwen3-Max, and Gemini2.5Pro. We assess their understanding of traditional Chinese culture, including history, literature, poetry, and related domains. Comparative analyses between LLMs developed in China and the U.S. indicate that Chinese models generally outperform their U.S. counterparts on these tasks. Among U.S.-developed models, Gemini 2.5Pro and GPT-5.1 achieve relatively higher accuracy. The observed performance differences may potentially arise from variations in training data distribution, localization strategies, and the degree of emphasis on Chinese cultural content during model development.
zh
[NLP-67] Punctuation-aware Hybrid Trainable Sparse Attention for Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决长序列建模中密集注意力(dense attention)因二次计算复杂度而难以扩展的问题,以及现有稀疏注意力方法在块选择过程中依赖粗粒度语义表示导致块内语义边界模糊、关键信息丢失的局限性。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种原生可训练的稀疏注意力框架——标点感知混合稀疏注意力(Punctuation-aware Hybrid Sparse Attention, PHSA),通过引入标点符号作为语义边界锚点,设计双分支聚合机制融合全局语义与标点增强的边界特征,在几乎不增加计算开销的前提下保留核心语义结构,并结合极端稀疏性自适应训练与推理策略,确保在极低激活率下模型行为稳定,从而显著提升长序列建模效果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02819
作者: Junxiang Qiu,Shuo Wang,Zhengsu Chen,Hengheng Zhang,Jinda Lu,Changcheng Li,Qi Tian
机构: University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学); Huawei Inc. (华为公司)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Attention serves as the fundamental mechanism for long-context modeling in large language models (LLMs), yet dense attention becomes structurally prohibitive for long sequences due to its quadratic complexity. Consequently, sparse attention has received increasing attention as a scalable alternative. However, existing sparse attention methods rely on coarse-grained semantic representations during block selection, which blur intra-block semantic boundaries and lead to the loss of critical information. To address this issue, we propose \textbfPunctuation-aware \textbfHybrid \textbfSparse \textbfAttention \textbf(PHSA), a natively trainable sparse attention framework that leverages punctuation tokens as semantic boundary anchors. Specifically, (1) we design a dual-branch aggregation mechanism that fuses global semantic representations with punctuation-enhanced boundary features, preserving the core semantic structure while introducing almost no additional computational overhead; (2) we introduce an extreme-sparsity-adaptive training and inference strategy that stabilizes model behavior under very low token activation ratios; Extensive experiments on general benchmarks and long-context evaluations demonstrate that PHSA consistently outperforms dense attention and state-of-the-art sparse attention baselines, including InfLLM v2. Specifically, for the 0.6B-parameter model with 32k-token input sequences, PHSA can reduce the information loss by 10.8% at a sparsity ratio of 97.3%.
zh
[NLP-68] HAL: Inducing Human-likeness in LLM s with Alignment
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前语言模型在人机交互中难以准确定义、测量和优化“对话类人性”(conversational human-likeness)的问题。传统方法依赖模型规模扩展或广义监督训练,缺乏对类人行为的精准对齐。解决方案的关键在于提出Human Aligning LLMs (HAL) 框架,其核心是通过对比对话数据提取可解释的显式对话特征,并将其融合为一个紧凑的标量奖励得分,作为透明的信号用于标准偏好优化方法进行对齐。该方法可在不损害模型整体性能的前提下,提升模型的类人对话表现,且因基于可解释特征,支持对齐过程的可观测性和异常诊断。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02813
作者: Masum Hasan,Junjie Zhao,Ehsan Hoque
机构: University of Rochester (罗切斯特大学)
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Conversational human-likeness plays a central role in human-AI interaction, yet it has remained difficult to define, measure, and optimize. As a result, improvements in human-like behavior are largely driven by scale or broad supervised training, rather than targeted alignment. We introduce Human Aligning LLMs (HAL), a framework for aligning language models to conversational human-likeness using an interpretable, data-driven reward. HAL derives explicit conversational traits from contrastive dialogue data, combines them into a compact scalar score, and uses this score as a transparent reward signal for alignment with standard preference optimization methods. Using this approach, we align models of varying sizes without affecting their overall performance. In large-scale human evaluations, models aligned with HAL are more frequently perceived as human-like in conversation. Because HAL operates over explicit, interpretable traits, it enables inspection of alignment behavior and diagnosis of unintended effects. More broadly, HAL demonstrates how soft, qualitative properties of language–previously outside the scope for alignment–can be made measurable and aligned in an interpretable and explainable way.
zh
[NLP-69] Stratified Hazard Sampling: Minimal-Variance Event Scheduling for CTMC/DTMC Discrete Diffusion and Flow Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决基于连续时间马尔可夫链(CTMC)或离散时间马尔可夫链(DTMC)的离散生成模型在推理阶段因独立伯努利(或类别)采样导致的编辑数量与时机方差过大问题,从而引发如欠编辑(残留噪声)或过编辑(级联不必要的替换)等典型失败模式,降低生成结果的可复现性。解决方案的关键在于提出分层风险采样(Stratified Hazard Sampling, SHS),其核心思想是将每个 token 的编辑建模为由累积风险(CTMC)或累积跳跃质量(DTMC)驱动的事件,并通过分层方式放置这些事件:对每个位置仅需一个随机相位,当累积风险跨越等距阈值时触发编辑。此方法在不改变每次跳跃的目标分布的前提下,保持期望编辑次数不变,同时实现无偏整数估计量中最小可能方差(上界为 1/4),有效提升了生成稳定性与一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02799
作者: Seunghwan Jang,SooJean Han
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Work in progress. Feedback welcome
Abstract:CTMC/DTMC-based discrete generative models, including uniform-noise discrete diffusion (e.g., D3PM/CTDD) and discrete flow matching, enable non-autoregressive sequence generation by repeatedly replacing tokens through a time-inhomogeneous Markov process. Inference is typically implemented with step-based simulation: each token decides to jump via independent Bernoulli (or categorical) draws at every discretization step. Under uniform-noise initialization, where self-correction requires multiple edits per position, these independent decisions induce substantial variance in both the number and timing of edits, leading to characteristic failure modes such as under-editing (residual noise) or over-editing (cascading unnecessary substitutions), decreasing reproducibility. We propose Stratified Hazard Sampling (SHS), a drop-in and hyperparameter-free inference principle for any sampler that admits a stay-vs.-replace decomposition. SHS models per-token edits as events driven by cumulative hazard (CTMC) or cumulative jump mass (DTMC) and places events by stratifying this cumulative quantity: with a single random phase per position, a token jumps whenever its accumulated hazard crosses unit-spaced thresholds. This preserves the expected number of jumps while achieving the minimum possible variance among unbiased integer estimators (bounded by 1/4), without altering per-jump destination sampling and thus retaining multimodality. We also introduce a phase-allocation variant for blacklist-style lexical constraints that prioritizes early edits at high-risk positions to mitigate late-masking artifacts. Comments: Work in progress. Feedback welcome Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computation and Language (cs.CL) ACMclasses: I.2.6; I.2.7 Cite as: arXiv:2601.02799 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2601.02799v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02799 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[NLP-70] MiMo-V2-Flash Technical Report
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大模型在推理效率与性能之间难以平衡的问题,尤其是在保持强推理能力的同时实现高效推理和可扩展的后训练优化。其核心解决方案是提出MiMo-V2-Flash——一个基于混合专家(Mixture-of-Experts, MoE)架构的模型,通过引入混合注意力机制(将滑动窗口注意力Sliding Window Attention, SWA与全局注意力交织,比例为5:1),显著提升长序列处理效率;同时采用多教师在线蒸馏(Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation, MOPD)框架,在后训练阶段利用领域专业化教师模型提供细粒度奖励信号,使学生模型精准掌握专家知识;此外,创新性地将多标记预测(Multi-Token Prediction, MTP)作为推测解码(speculative decoding)的草稿模型,借助三层MTP结构实现最高3.6的接受长度和2.6倍的解码加速,从而在仅使用DeepSeek-V3.2和Kimi-K2约一半至三分之一参数的情况下达到相当甚至更优的性能表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02780
作者: Bangjun Xiao,Bingquan Xia,Bo Yang,Bofei Gao,Bowen Shen,Chen Zhang,Chenhong He,Chiheng Lou,Fuli Luo,Gang Wang,Gang Xie,Hailin Zhang,Hanglong Lv,Hanyu Li,Heyu Chen,Hongshen Xu,Houbin Zhang,Huaqiu Liu,Jiangshan Duo,Jianyu Wei,Jiebao Xiao,Jinhao Dong,Jun Shi,Junhao Hu,Kainan Bao,Kang Zhou,Lei Li,Liang Zhao,Linghao Zhang,Peidian Li,Qianli Chen,Shaohui Liu,Shihua Yu,Shijie Cao,Shimao Chen,Shouqiu Yu,Shuo Liu,Tianling Zhou,Weijiang Su,Weikun Wang,Wenhan Ma,Xiangwei Deng,Bohan Mao,Bowen Ye,Can Cai,Chenghua Wang,Chengxuan Zhu,Chong Ma,Chun Chen,Chunan Li,Dawei Zhu,Deshan Xiao,Dong Zhang,Duo Zhang,Fangyue Liu,Feiyu Yang,Fengyuan Shi,Guoan Wang,Hao Tian,Hao Wu,Heng Qu,Hongfei Yi,Hongxu An,Hongyi Guan,Xing Zhang,Yifan Song,Yihan Yan,Yihao Zhao,Yingchun Lai,Yizhao Gao,Yu Cheng,Yuanyuan Tian,Yudong Wang,Zhen Tang,Zhengju Tang,Zhengtao Wen,Zhichao Song,Zhixian Zheng,Zihan Jiang,Jian Wen,Jiarui Sun,Jiawei Li,Jinlong Xue,Jun Xia,Kai Fang,Menghang Zhu,Nuo Chen,Qian Tu,Qihao Zhang,Qiying Wang,Rang Li,Rui Ma,Shaolei Zhang,Shengfan Wang,Shicheng Li,Shuhao Gu,Shuhuai Ren,Sirui Deng,Tao Guo,Tianyang Lu
机构: Xiaomi(小米)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 31 pages, technical report
Abstract:We present MiMo-V2-Flash, a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model with 309B total parameters and 15B active parameters, designed for fast, strong reasoning and agentic capabilities. MiMo-V2-Flash adopts a hybrid attention architecture that interleaves Sliding Window Attention (SWA) with global attention, with a 128-token sliding window under a 5:1 hybrid ratio. The model is pre-trained on 27 trillion tokens with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), employing a native 32k context length and subsequently extended to 256k. To efficiently scale post-training compute, MiMo-V2-Flash introduces a novel Multi-Teacher On-Policy Distillation (MOPD) paradigm. In this framework, domain-specialized teachers (e.g., trained via large-scale reinforcement learning) provide dense and token-level reward, enabling the student model to perfectly master teacher expertise. MiMo-V2-Flash rivals top-tier open-weight models such as DeepSeek-V3.2 and Kimi-K2, despite using only 1/2 and 1/3 of their total parameters, respectively. During inference, by repurposing MTP as a draft model for speculative decoding, MiMo-V2-Flash achieves up to 3.6 acceptance length and 2.6x decoding speedup with three MTP layers. We open-source both the model weights and the three-layer MTP weights to foster open research and community collaboration.
zh
[NLP-71] EComStage: Stage-wise and Orientation-specific Benchmarking for Large Language Models in E-commerce
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决现有基准测试仅关注大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)代理是否成功完成最终任务,而忽视了在复杂决策过程中至关重要的中间推理阶段的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出EComStage——一个统一的、面向电商场景的分阶段评估基准,涵盖感知(Perception,理解用户意图)、规划(Planning,制定行动方案)和执行(Action,实施决策)三个核心推理阶段,并通过7个代表性任务对LLM代理进行细粒度评估。该基准不仅覆盖客户导向场景,还纳入商家导向任务(如促销管理、内容审核与运营支持),且所有样本均经人工标注与质量验证,从而为真实电商环境中LLM代理的设计与优化提供可操作的精细化洞见。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02752
作者: Kaiyan Zhao,Zijie Meng,Zheyong Xie,Jin Duan,Yao Hu,Zuozhu Liu,Shaosheng Cao
机构: The University of Tokyo (东京大学); Zhejiang University (浙江大学); Xiaohongshu Inc. (小红书公司)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: preprint
Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents are increasingly deployed in e-commerce applications to assist customer services in tasks such as product inquiries, recommendations, and order management. Existing benchmarks primarily evaluate whether these agents successfully complete the final task, overlooking the intermediate reasoning stages that are crucial for effective decision-making. To address this gap, we propose EComStage, a unified benchmark for evaluating agent-capable LLMs across the comprehensive stage-wise reasoning process: Perception (understanding user intent), Planning (formulating an action plan), and Action (executing the decision). EComStage evaluates LLMs through seven separate representative tasks spanning diverse e-commerce scenarios, with all samples human-annotated and quality-checked. Unlike prior benchmarks that focus only on customer-oriented interactions, EComStage also evaluates merchant-oriented scenarios, including promotion management, content review, and operational support relevant to real-world applications. We evaluate a wide range of over 30 LLMs, spanning from 1B to over 200B parameters, including open-source models and closed-source APIs, revealing stage/orientation- specific strengths and weaknesses. Our results provide fine-grained, actionable insights for designing and optimizing LLM-based agents in real-world e-commerce settings.
zh
[NLP-72] Window-based Membership Inference Attacks Against Fine-tuned Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前针对大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的成员推理攻击(Membership Inference Attacks, MIAs)普遍依赖全局信号(如平均损失)而导致对记忆特征敏感度不足的问题。现有方法因采用全局平均策略,弱化了训练数据在局部上下文中的细微记忆痕迹,从而限制了攻击效果。论文提出的关键解决方案是WBC(Window-Based Comparison),其核心在于利用局部上下文中的记忆信号:通过滑动窗口机制在文本序列上进行多尺度分析,每个窗口基于目标模型与参考模型的损失差异生成二值投票,再通过对几何间隔分布的窗口尺寸进行集成聚合,有效捕获从词级别到短语级别的记忆模式。实验表明,该方法显著优于现有基线,在多个数据集上实现更高的AUC得分及低假阳性阈值下的检测率提升2–3倍,揭示了局部证据聚合相较于全局平均更具优越性,暴露了微调后LLMs存在的关键隐私风险。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02751
作者: Yuetian Chen,Yuntao Du,Kaiyuan Zhang,Ashish Kundu,Charles Fleming,Bruno Ribeiro,Ninghui Li
机构: Purdue University (普渡大学); Cisco Research (思科研究院); Cisco Systems (思科系统)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR)
备注: Code is available at [ this https URL ]( this https URL ). This arXiv version corresponds to the accepted paper and includes the full experimental results
Abstract:Most membership inference attacks (MIAs) against Large Language Models (LLMs) rely on global signals, like average loss, to identify training data. This approach, however, dilutes the subtle, localized signals of memorization, reducing attack effectiveness. We challenge this global-averaging paradigm, positing that membership signals are more pronounced within localized contexts. We introduce WBC (Window-Based Comparison), which exploits this insight through a sliding window approach with sign-based aggregation. Our method slides windows of varying sizes across text sequences, with each window casting a binary vote on membership based on loss comparisons between target and reference models. By ensembling votes across geometrically spaced window sizes, we capture memorization patterns from token-level artifacts to phrase-level structures. Extensive experiments across eleven datasets demonstrate that WBC substantially outperforms established baselines, achieving higher AUC scores and 2-3 times improvements in detection rates at low false positive thresholds. Our findings reveal that aggregating localized evidence is fundamentally more effective than global averaging, exposing critical privacy vulnerabilities in fine-tuned LLMs.
zh
[NLP-73] SYNAPSE: Empowering LLM Agents with Episodic-Semantic Memory via Spreading Activation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在长期代理记忆(long-term agentic memory)中因静态向量相似性检索导致的“断连”问题,即传统检索增强方法难以有效捕捉复杂时序和多跳推理任务中的动态关联。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为Synapse的统一记忆架构,该架构受认知科学启发,将记忆建模为一个动态图结构,通过激活扩散机制(spreading activation)而非预计算链接来实现语义相关性,同时引入侧向抑制(lateral inhibition)与时间衰减(temporal decay)机制以动态突出相关子图并抑制干扰信息。进一步地,该方案采用三重混合检索策略(Triple Hybrid Retrieval),融合几何嵌入与基于激活的图遍历,从而显著提升复杂时序和多跳推理能力,在LoCoMo基准测试中优于现有最优方法,有效缓解了“上下文隧道效应”(Contextual Tunneling)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02744
作者: Hanqi Jiang,Junhao Chen,Yi Pan,Ling Chen,Weihang You,Yifan Zhou,Ruidong Zhang,Yohannes Abate,Tianming Liu
机构: University of Georgia (佐治亚大学); University of Tennessee, Knoxville (田纳西大学诺克斯维尔分校)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at generalized reasoning, standard retrieval-augmented approaches fail to address the disconnected nature of long-term agentic memory. To bridge this gap, we introduce Synapse (Synergistic Associative Processing Semantic Encoding), a unified memory architecture that transcends static vector similarity. Drawing from cognitive science, Synapse models memory as a dynamic graph where relevance emerges from spreading activation rather than pre-computed links. By integrating lateral inhibition and temporal decay, the system dynamically highlights relevant sub-graphs while filtering interference. We implement a Triple Hybrid Retrieval strategy that fuses geometric embeddings with activation-based graph traversal. Comprehensive evaluations on the LoCoMo benchmark show that Synapse significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in complex temporal and multi-hop reasoning tasks, offering a robust solution to the “Contextual Tunneling” problem. Our code and data will be made publicly available upon acceptance.
zh
[NLP-74] Language Hierarchization Provides the Optimal Solution to Human Working Memory Limits
【速读】: 该论文试图解决的问题是:为何人类语言具有层级结构(hierarchical structure)这一普遍现象。其解决方案的关键在于提出并验证了一个基于工作记忆容量(working memory capacity, WMC)的最优性假设——即语言的层级化组织能够最有效地适应人类有限的工作记忆资源。研究通过构建一个量化语言处理机制与WMC匹配程度的似然函数,发现最大似然估计(maximum likelihood estimate, MLE)对应于单位数的均值;计算模拟和自然语言分析表明,相较于线性处理方式,层级处理在长序列条件下显著更优地控制MLE值,使其始终处于人类WMC限制内,并呈现出与儿童WMC发展相一致的收敛模式。这从认知加工效率角度揭示了层级结构对语言演化和习得的根本意义。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02740
作者: Luyao Chen,Weibo Gao,Junjie Wu,Jinshan Wu,Angela D. Friederici
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Applications (stat.AP)
备注:
Abstract:Language is a uniquely human trait, conveying information efficiently by organizing word sequences in sentences into hierarchical structures. A central question persists: Why is human language hierarchical? In this study, we show that hierarchization optimally solves the challenge of our limited working memory capacity. We established a likelihood function that quantifies how well the average number of units according to the language processing mechanisms aligns with human working memory capacity (WMC) in a direct fashion. The maximum likelihood estimate (MLE) of this function, tehta_MLE, turns out to be the mean of units. Through computational simulations of symbol sequences and validation analyses of natural language sentences, we uncover that compared to linear processing, hierarchical processing far surpasses it in constraining the tehta_MLE values under the human WMC limit, along with the increase of sequence/sentence length successfully. It also shows a converging pattern related to children’s WMC development. These results suggest that constructing hierarchical structures optimizes the processing efficiency of sequential language input while staying within memory constraints, genuinely explaining the universal hierarchical nature of human language.
zh
[NLP-75] Mitigating Prompt-Induced Hallucinations in Large Language Models via Structured Reasoning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)中由提示诱导引发的幻觉问题(hallucination),即模型在生成回答时产生与事实不符或缺乏依据的内容。其解决方案的关键在于构建一种改进的知识蒸馏链式模型(knowledge distillation chain-style model),通过引入代码模块来引导知识图谱(knowledge graph)的探索,并将代码作为思维链(chain-of-thought)提示的一部分,从而形成外部知识输入,为模型提供更准确、结构化的信息。这一设计有效约束了模型的推理过程,显著提升了推理准确性与结果可验证性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02739
作者: Jinbo Hao,Kai Yang,Qingzhen Su,Yang Chen,Yifan Li,Chao Jiang
机构: Jiangsu Ocean University (江苏海洋大学); Soochow University (苏州大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:To address hallucination issues in large language models (LLMs), this paper proposes a method for mitigating prompt-induced hallucinations. Building on a knowledge distillation chain-style model, we introduce a code module to guide knowledge-graph exploration and incorporate code as part of the chain-of-thought prompt, forming an external knowledge input that provides more accurate and structured information to the model. Based on this design, we develop an improved knowledge distillation chain-style model and leverage it to analyze and constrain the reasoning process of LLMs, thereby improving inference accuracy. We empirically evaluate the proposed approach using GPT-4 and LLaMA-3.3 on multiple public datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that incorporating code modules significantly enhances the model’s ability to capture contextual information and effectively mitigates prompt-induced hallucinations. Specifically, HIT@1, HIT@3, and HIT@5 improve by 15.64%, 13.38%, and 13.28%, respectively. Moreover, the proposed method achieves HIT@1, HIT@3, and HIT@5 scores exceeding 95% across several evaluation settings. These results indicate that the proposed approach substantially reduces hallucination behavior while improving the accuracy and verifiability of large language models.
zh
[NLP-76] me-Scaling Is What Agents Need Now
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在深度语义推理能力上的不足,尤其是在复杂问题求解中缺乏系统性、可扩展的时序推理机制的问题。早期模型虽能生成流畅文本,但难以实现稳定且高效的逻辑推理;尽管Chain-of-Thought(CoT)和Tree-of-Thought(ToT)等提示技术通过显式化中间步骤拓展了推理路径,仍存在搜索不完整与效率低下的局限。为此,论文提出“时间缩放”(Time-Scaling)作为核心解决方案——即通过架构设计引入扩展的时间路径,使智能体能够在动态时间内进行更深层次的问题空间探索、策略自适应调整以及元认知控制,从而在不显著增加静态参数规模的前提下,逼近人类在有限认知资源下进行序列化推理的能力。其关键在于将显式的时序推理管理置于智能体架构的核心位置,推动从单一感知-决策范式向闭环“感知-决策-行动”认知代理的演进。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02714
作者: Zhi Liu,Guangzhi Wang
机构: CareerInternational Research Team
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Early artificial intelligence paradigms exhibited separated cognitive functions: Neural Networks focused on “perception-representation,” Reinforcement Learning on “decision-making-behavior,” and Symbolic AI on “knowledge-reasoning.” With Transformer-based large models and world models, these paradigms are converging into cognitive agents with closed-loop “perception-decision-action” capabilities. Humans solve complex problems under limited cognitive resources through temporalized sequential reasoning. Language relies on problem space search for deep semantic reasoning. While early large language models (LLMs) could generate fluent text, they lacked robust semantic reasoning capabilities. Prompting techniques like Chain-of-Thought (CoT) and Tree-of-Thought (ToT) extended reasoning paths by making intermediate steps explicit. Recent models like DeepSeek-R1 enhanced performance through explicit reasoning trajectories. However, these methods have limitations in search completeness and efficiency. This highlights the need for “Time-Scaling”–the systematic extension and optimization of an agent’s ability to unfold reasoning over time. Time-Scaling refers to architectural design utilizing extended temporal pathways, enabling deeper problem space exploration, dynamic strategy adjustment, and enhanced metacognitive control, paralleling human sequential reasoning under cognitive constraints. It represents a critical frontier for enhancing deep reasoning and problem-solving without proportional increases in static model parameters. Advancing intelligent agent capabilities requires placing Time-Scaling principles at the forefront, positioning explicit temporal reasoning management as foundational. Subjects: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02714 [cs.AI] (or arXiv:2601.02714v1 [cs.AI] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02714 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[NLP-77] Adversarial Question Answering Robustness: A Multi-Level Error Analysis and Mitigation Study
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式问答(Question Answering, QA)系统在标准基准测试(如SQuAD)中表现优异,但在面对对抗样本时仍存在脆弱性的问题。其核心挑战在于如何提升模型在对抗环境下的鲁棒性,同时不牺牲干净数据上的性能。解决方案的关键在于:首先通过五种互补的分类方案进行多层次错误分析,识别出否定混淆(negation confusion)和实体替换(entity substitution)为主要失败模式;其次,通过系统性实验确定80%干净数据与20%对抗数据混合训练为最优比例;最后,引入基于命名实体识别(Named Entity Recognition, NER)引导的对比学习策略(Entity-Aware contrastive learning),显著缩小了干净数据与对抗数据之间的性能差距,在AddSent数据集上达到89.89%的精确匹配(Exact Match, EM)得分,实现了94.9%的对抗差距闭合,首次将详尽的语言学错误分析与NER指导的对比学习相结合,有效提升了QA模型的对抗鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02700
作者: Agniv Roy Choudhury,Vignesh Ponselvan Rajasingh
机构: University of Texas at Austin (德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Question answering (QA) systems achieve impressive performance on standard benchmarks like SQuAD, but remain vulnerable to adversarial examples. This project investigates the adversarial robustness of transformer models on the AddSent adversarial dataset through systematic experimentation across model scales and targeted mitigation strategies. We perform comprehensive multi-level error analysis using five complementary categorization schemes, identifying negation confusion and entity substitution as the primary failure modes. Through systematic evaluation of adversarial fine-tuning ratios, we identify 80% clean + 20% adversarial data as optimal. Data augmentation experiments reveal a capacity bottleneck in small models. Scaling from ELECTRA-small (14M parameters) to ELECTRA-base (110M parameters) eliminates the robustness-accuracy trade-off, achieving substantial improvements on both clean and adversarial data. We implement three targeted mitigation strategies, with Entity-Aware contrastive learning achieving best performance: 89.89% AddSent Exact Match (EM) and 90.73% SQuAD EM, representing 94.9% closure of the adversarial gap. To our knowledge, this is the first work integrating comprehensive linguistic error analysis with Named Entity Recognition (NER)-guided contrastive learning for adversarial QA, demonstrating that targeted mitigation can achieve near-parity between clean and adversarial performance.
zh
[NLP-78] Boosting Accuracy and Interpretability in Multilingual Hate Speech Detection Through Layer Freezing and Explainable AI
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多语言环境下情感分析(Sentiment Analysis)与仇恨言论检测(Hate Speech Detection)任务中模型性能与可解释性不足的问题。其解决方案的关键在于采用三种基于Transformer的预训练模型(BERT-base-multilingual-cased、RoBERTa-base 和 XLM-RoBERTa-base,其中前八层冻结),在英语、韩语、日语、汉语和法语五种语言上进行评估,并引入局部可解释模型无关解释(LIME)框架以增强模型决策过程的透明度,从而提升多语言文本分类系统的有效性与可解释性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02697
作者: Meysam Shirdel Bilehsavar,Negin Mahmoudi,Mohammad Jalili Torkamani,Kiana Kiashemshaki
机构: University of South Carolina (南卡罗来纳大学); Stevens Institute of Technology (斯蒂文斯理工学院); University of Nebraska-Lincoln (内布拉斯加林肯大学); Bowling Green State University (鲍林格林州立大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 19 pages, 7 figures
Abstract:Sentiment analysis focuses on identifying the emotional polarity expressed in textual data, typically categorized as positive, negative, or neutral. Hate speech detection, on the other hand, aims to recognize content that incites violence, discrimination, or hostility toward individuals or groups based on attributes such as race, gender, sexual orientation, or religion. Both tasks play a critical role in online content moderation by enabling the detection and mitigation of harmful or offensive material, thereby contributing to safer digital environments. In this study, we examine the performance of three transformer-based models: BERT-base-multilingual-cased, RoBERTa-base, and XLM-RoBERTa-base with the first eight layers frozen, for multilingual sentiment analysis and hate speech detection. The evaluation is conducted across five languages: English, Korean, Japanese, Chinese, and French. The models are compared using standard performance metrics, including accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score. To enhance model interpretability and provide deeper insight into prediction behavior, we integrate the Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME) framework, which highlights the contribution of individual words to the models decisions. By combining state-of-the-art transformer architectures with explainability techniques, this work aims to improve both the effectiveness and transparency of multilingual sentiment analysis and hate speech detection systems.
zh
[NLP-79] EvoRoute: Experience-Driven Self-Routing LLM Agent Systems
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决复杂代理型人工智能系统(Agentic AI Systems)在执行多轮任务时面临的“代理系统三难困境”(Agent System Trilemma),即在追求最优性能、最小化经济成本和确保快速任务完成之间存在的内在矛盾。解决方案的关键在于提出EvoRoute——一种自演化模型路由范式,它通过利用不断扩展的历史经验知识库,在每一步动态选择帕累托最优的大型语言模型(LLM)骨干网络,平衡准确性、效率与资源消耗,并借助环境反馈持续优化自身的决策策略。实验表明,EvoRoute可显著降低执行成本(最高达80%)和延迟(超过70%),同时维持或提升系统性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02695
作者: Guibin Zhang,Haiyang Yu,Kaiming Yang,Bingli Wu,Fei Huang,Yongbin Li,Shuicheng Yan
机构: National University of Singapore (新加坡国立大学); Tongyi Lab (通义实验室)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注:
Abstract:Complex agentic AI systems, powered by a coordinated ensemble of Large Language Models (LLMs), tool and memory modules, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities on intricate, multi-turn tasks. However, this success is shadowed by prohibitive economic costs and severe latency, exposing a critical, yet underexplored, trade-off. We formalize this challenge as the \textbfAgent System Trilemma: the inherent tension among achieving state-of-the-art performance, minimizing monetary cost, and ensuring rapid task completion. To dismantle this trilemma, we introduce EvoRoute, a self-evolving model routing paradigm that transcends static, pre-defined model assignments. Leveraging an ever-expanding knowledge base of prior experience, EvoRoute dynamically selects Pareto-optimal LLM backbones at each step, balancing accuracy, efficiency, and resource use, while continually refining its own selection policy through environment feedback. Experiments on challenging agentic benchmarks such as GAIA and BrowseComp+ demonstrate that EvoRoute, when integrated into off-the-shelf agentic systems, not only sustains or enhances system performance but also reduces execution cost by up to 80% and latency by over 70% .
zh
[NLP-80] Iterative Structured Pruning for Large Language Models with Multi-Domain Calibration
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)因规模不断增长而带来的实际部署难题,包括计算开销大、内存占用高和推理延迟长等问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种新型的结构化剪枝(structured pruning)框架,通过引入混合多域校准集(hybrid multi-domain calibration set)与迭代校准策略(iterative calibration strategy),有效识别并移除冗余通道,从而在保持与标准硬件加速器兼容性的前提下实现显著压缩,同时最小化模型性能损失。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02674
作者: Guangxin Wu,Hao Zhang,Zhang Zhibin,Jiafeng Guo,Xueqi Cheng
机构: Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院计算技术研究所); University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院大学); School of Advanced Interdisciplinary Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院大学交叉学科研究院)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 10 pages
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success across a wide spectrum of natural language processing tasks. However, their ever-growing scale introduces significant barriers to real-world deployment, including substantial computational overhead, memory footprint, and inference latency. While model pruning presents a viable solution to these challenges, existing unstructured pruning techniques often yield irregular sparsity patterns that necessitate specialized hardware or software support. In this work, we explore structured pruning, which eliminates entire architectural components and maintains compatibility with standard hardware accelerators. We introduce a novel structured pruning framework that leverages a hybrid multi-domain calibration set and an iterative calibration strategy to effectively identify and remove redundant channels. Extensive experiments on various models across diverse downstream tasks show that our approach achieves significant compression with minimal performance degradation.
zh
[NLP-81] Extracting books from production language models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)在版权法领域中的一个核心争议问题:大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)是否会在训练过程中“记忆”(memorize)其训练数据,并且这些被记忆的数据能否从模型输出中被提取出来。这一问题直接关系到LLM在使用受版权保护文本作为训练数据时可能引发的法律风险。论文的关键解决方案在于设计了一种两阶段提取方法:第一阶段通过初步探测(包括必要时使用Best-of-N(BoN)越狱技术)测试是否存在可提取性;第二阶段则采用迭代续写提示(iterative continuation prompts)尝试系统性地恢复整本书籍内容。作者在四个主流生产级LLM(Claude 3.7 Sonnet、GPT-4.1、Gemini 2.5 Pro 和 Grok 3)上验证了该方法的有效性,结果表明即使存在模型级和系统级安全机制,仍存在显著的版权文本提取风险,尤其在部分模型中可实现近乎原文还原(如nv-recall达95.8%)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02671
作者: Ahmed Ahmed,A. Feder Cooper,Sanmi Koyejo,Percy Liang
机构: Stanford University (斯坦福大学); Yale University (耶鲁大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: We ran experiments from mid-August to mid-September 2025, notified affected providers shortly after, and now make our findings public after a 90-day disclosure window
Abstract:Many unresolved legal questions over LLMs and copyright center on memorization: whether specific training data have been encoded in the model’s weights during training, and whether those memorized data can be extracted in the model’s outputs. While many believe that LLMs do not memorize much of their training data, recent work shows that substantial amounts of copyrighted text can be extracted from open-weight models. However, it remains an open question if similar extraction is feasible for production LLMs, given the safety measures these systems implement. We investigate this question using a two-phase procedure: (1) an initial probe to test for extraction feasibility, which sometimes uses a Best-of-N (BoN) jailbreak, followed by (2) iterative continuation prompts to attempt to extract the book. We evaluate our procedure on four production LLMs – Claude 3.7 Sonnet, GPT-4.1, Gemini 2.5 Pro, and Grok 3 – and we measure extraction success with a score computed from a block-based approximation of longest common substring (nv-recall). With different per-LLM experimental configurations, we were able to extract varying amounts of text. For the Phase 1 probe, it was unnecessary to jailbreak Gemini 2.5 Pro and Grok 3 to extract text (e.g, nv-recall of 76.8% and 70.3%, respectively, for Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone), while it was necessary for Claude 3.7 Sonnet and GPT-4.1. In some cases, jailbroken Claude 3.7 Sonnet outputs entire books near-verbatim (e.g., nv-recall=95.8%). GPT-4.1 requires significantly more BoN attempts (e.g., 20X), and eventually refuses to continue (e.g., nv-recall=4.0%). Taken together, our work highlights that, even with model- and system-level safeguards, extraction of (in-copyright) training data remains a risk for production LLMs.
zh
[NLP-82] Multi-Turn Jailbreaking of Aligned LLM s via Lexical Anchor Tree Search
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前对抗性越狱攻击(jailbreak attack)中存在的高资源消耗与查询效率低下问题,即现有方法通常依赖攻击者大语言模型(attacker LLM)生成难以解释的随机前缀文本,并需大量查询才能实现高成功率(ASR)。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种无需 attacker LLM 的 Lexical Anchor Tree Search (LATS) 方法,通过纯 lexical anchor 注入机制,在多轮对话中以广度优先树搜索方式逐步向良性提示注入目标攻击词,从而在极低查询预算(平均仅约6.4次)下实现对最新GPT、Claude和Llama模型的97–100% ASR,凸显了对话结构作为潜在攻击面的价值及高效攻击的可能性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02670
作者: Devang Kulshreshtha,Hang Su,Chinmay Hegde,Haohan Wang
机构: Amazon(亚马逊); New York University (纽约大学); University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Most jailbreak methods achieve high attack success rates (ASR) but require attacker LLMs to craft adversarial queries and/or demand high query budgets. These resource limitations make jailbreaking expensive, and the queries generated by attacker LLMs often consist of non-interpretable random prefixes. This paper introduces Lexical Anchor Tree Search (), addressing these limitations through an attacker-LLM-free method that operates purely via lexical anchor injection. LATS reformulates jailbreaking as a breadth-first tree search over multi-turn dialogues, where each node incrementally injects missing content words from the attack goal into benign prompts. Evaluations on AdvBench and HarmBench demonstrate that LATS achieves 97-100% ASR on latest GPT, Claude, and Llama models with an average of only ~6.4 queries, compared to 20+ queries required by other methods. These results highlight conversational structure as a potent and under-protected attack surface, while demonstrating superior query efficiency in an era where high ASR is readily achievable. Our code will be released to support reproducibility.
zh
[NLP-83] owards Comprehensive Stage-wise Benchmarking of Large Language Models in Fact-Checking
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在事实核查系统中评估过于聚焦于单一的声明验证环节,而忽视了完整的事实核查流程(包括声明提取、证据检索与推理判断)所带来的局限性问题。这种狭隘的评估方式无法揭示LLMs在系统性推理错误、事实盲区及鲁棒性方面的深层缺陷。其解决方案的关键在于提出FactArena——一个全自动的竞技场式评估框架,通过三个核心组件实现全流程、分阶段的基准测试:(i) 基于LLM驱动的事实核查流程,标准化声明分解、工具增强的证据检索与基于理由的结论预测;(ii) 基于统一参考指南的竞技场式评判机制,确保异构裁判代理间的无偏一致性比较;(iii) 基于竞技场引导的声明演化模块,自适应生成更具挑战性和语义可控的新声明,以探测LLMs在固定种子数据之外的事实鲁棒性。该框架实现了对16个主流LLMs的稳定且可解释的排序,并揭示了静态声明验证准确率与端到端事实核查能力之间的显著差异,为LLMs事实推理能力的诊断和可靠部署提供了可扩展、可信的新范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02669
作者: Hongzhan Lin,Zixin Chen,Zhiqi Shen,Ziyang Luo,Zhen Ye,Jing Ma,Tat-Seng Chua,Guandong Xu
机构: Hong Kong Baptist University (香港浸会大学); Salesforce AI Research; The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (香港科技大学); National University of Singapore (新加坡国立大学); The Education University of Hong Kong (香港教育大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 17 pages, 21 figures, 7 tables
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world fact-checking systems, yet existing evaluations focus predominantly on claim verification and overlook the broader fact-checking workflow, including claim extraction and evidence retrieval. This narrow focus prevents current benchmarks from revealing systematic reasoning failures, factual blind spots, and robustness limitations of modern LLMs. To bridge this gap, we present FactArena, a fully automated arena-style evaluation framework that conducts comprehensive, stage-wise benchmarking of LLMs across the complete fact-checking pipeline. FactArena integrates three key components: (i) an LLM-driven fact-checking process that standardizes claim decomposition, evidence retrieval via tool-augmented interactions, and justification-based verdict prediction; (ii) an arena-styled judgment mechanism guided by consolidated reference guidelines to ensure unbiased and consistent pairwise comparisons across heterogeneous judge agents; and (iii) an arena-driven claim-evolution module that adaptively generates more challenging and semantically controlled claims to probe LLMs’ factual robustness beyond fixed seed data. Across 16 state-of-the-art LLMs spanning seven model families, FactArena produces stable and interpretable rankings. Our analyses further reveal significant discrepancies between static claim-verification accuracy and end-to-end fact-checking competence, highlighting the necessity of holistic evaluation. The proposed framework offers a scalable and trustworthy paradigm for diagnosing LLMs’ factual reasoning, guiding future model development, and advancing the reliable deployment of LLMs in safety-critical fact-checking applications.
zh
[NLP-84] When Do Tools and Planning Help LLM s Think? A Cost- and Latency-Aware Benchmark
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决现代大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在推理过程中如何有效利用工具与规划策略以提升任务性能的问题,尤其是在复杂现实场景中平衡准确性与计算成本的挑战。其解决方案的关键在于设计并评估一种“计划-执行-重规划”(plan–execute–replan)代理架构,该架构基于LangChain和LangGraph框架,集成任务特定工具(如DBpedia SPARQL查询、维基百科检索及主题网络搜索),并与单次提示(one-shot)基线进行对比。实验表明,在事件中心问答(Event-QA)任务中,工具增强配置显著提升准确率(GPT-4o从47.5%提升至67.5%),但代价是端到端延迟增加近两个数量级;而在Reddit ChangeMyView(CMV)任务中,单一提示方法表现更优,说明工具调度并非普适解法,需根据任务特性与资源约束进行精细化权衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02663
作者: Subha Ghoshal,Ali Al-Bustami
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Modern large language models (LLMs) increasingly rely on inference-time planning and external tools to improve reasoning. We benchmark this behavior on two real-world settings: event-centric question answering over graph-structured knowledge (Event-QA) and persuasive response generation in Reddit ChangeMyView (CMV). Using LangChain and LangGraph, we compare a one-shot baseline against a plan–execute–replan agent equipped with task-specific tools (DBpedia SPARQL/lookup/schema exploration, Wikipedia-focused retrieval, and topical web search). We evaluate on 60 examples each from Event-QA and CMV (3 splits of 20), and report both mean end-to-end latency and per-example token cost estimates. We evaluate GPT-4o and GPT-4o-mini under identical workflows and report accuracy and end-to-end latency. On Event-QA, the best tool-augmented configuration improves accuracy (e.g., 47.5% \rightarrow 67.5% for GPT-4o) while increasing latency by orders of magnitude ( \sim 8s \rightarrow \sim 317s per example). On CMV, one-shot prompting is strongest (e.g., GPT-4o-mini achieves 75% at \sim 6s), and planning+search increases latency substantially without consistent gains. However, complex multi-tool orchestration exposes failure modes where the smaller model degrades. Overall, the findings highlight the need for task-specific, cost-aware choices of both model size and agent/tooling complexity.
zh
[NLP-85] Empirical Comparison of Encoder-Based Language Models and Feature-Based Supervised Machine Learning Approaches to Automated Scoring of Long Essays
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决编码器-only 语言模型在处理长文本(如长篇作文)时面临的性能挑战,尤其是在自动化评分任务中的表现瓶颈。其关键解决方案是构建一种基于嵌入的集成模型(ensemble-of-embeddings model),该模型融合多个预训练语言模型(如 BERT、RoBERTa、DistilBERT 和 DeBERTa)的文本表示,并使用梯度提升分类器(Gradient-Boosted Decision Trees)作为集成策略,从而显著优于单一语言模型在长作文评分任务上的表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02659
作者: Kuo Wang,Haowei Hua,Pengfei Yan,Hong Jiao,Dan Song
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 22 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables, presented at National Council on Measurement in Education 2025
Abstract:Long context may impose challenges for encoder-only language models in text processing, specifically for automated scoring of essays. This study trained several commonly used encoder-based language models for automated scoring of long essays. The performance of these trained models was evaluated and compared with the ensemble models built upon the base language models with a token limit of 512?. The experimented models include BERT-based models (BERT, RoBERTa, DistilBERT, and DeBERTa), ensemble models integrating embeddings from multiple encoder models, and ensemble models of feature-based supervised machine learning models, including Gradient-Boosted Decision Trees, eXtreme Gradient Boosting, and Light Gradient Boosting Machine. We trained, validated, and tested each model on a dataset of 17,307 essays, with an 80%/10%/10% split, and evaluated model performance using Quadratic Weighted Kappa. This study revealed that an ensemble-of-embeddings model that combines multiple pre-trained language model representations with gradient-boosting classifier as the ensemble model significantly outperforms individual language models at scoring long essays.
zh
[NLP-86] Prioritized Replay for RL Post-training
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)后训练阶段中,如何高效选择训练问题以提升学习信号质量的问题。传统课程学习(curriculum learning)策略通常优先安排简单任务,但可能无法充分挖掘具有潜力的中等难度问题;而本文提出了一种基于问题级别的优先级调度框架,其关键在于设计了一个由模型驱动的优先级评分机制,该评分基于经验成功率统计,自动识别出既非始终成功也非始终失败的问题——这类问题能为GRPO(Generalized Reward Policy Optimization)方法提供更强的学习信号。该方案无需预定义难度层级、辅助预测器或外部标签,实现了持续自适应的数据选择过程,并通过堆结构采样与周期性重测机制缓解饥饿(starvation)和遗忘(forgetting)问题,从而在不依赖人工干预的前提下,使数据选取直接对齐GRPO训练动态,提升了训练效率与可扩展性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02648
作者: Mehdi Fatemi
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:We introduce a problem-level prioritization framework for RL post-training of large language models. Building on insights from prioritized replay in deep RL, as well as prior observations that rollouts with intermediate success rates tend to produce stronger learning signals under methods such as GRPO, our approach selects problems according to a simple, model-driven priority score derived from empirical success statistics. In contrast to conventional curriculum strategies that emphasize easier tasks early in training, the resulting schedule naturally focuses training on problems that are neither consistently solved nor consistently failed, while deprioritizing those that contribute little gradient information. The method yields a continuously adapting and automatic prioritization process that requires no predefined difficulty tiers, auxiliary predictors, or external labels. We further introduce lightweight mechanisms for practical deployment, including heap-based prioritized sampling and periodic retesting of solved and unsolved problems to mitigate starvation and forgetting. Overall, the approach offers a principled and scalable alternative to manually designed curricula while aligning data selection directly with the dynamics of GRPO-based post-training.
zh
[NLP-87] Improved Evidence Extraction for Document Inconsistency Detection with LLM s
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)在文档不一致性检测中的证据提取问题,即不仅判断文档是否存在不一致内容,更关键的是精准识别并提供支持不一致性的句子证据。其解决方案的核心在于提出了一套新的综合性证据提取指标,并设计了一个“删除与重试”(redact-and-retry)框架,结合约束过滤机制,显著优于直接提示(direct prompting)方法,从而提升了基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的文档不一致性检测性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02627
作者: Nelvin Tan,Yaowen Zhang,James Asikin Cheung,Fusheng Liu,Yu-Ching Shih,Dong Yang
机构: American Express (美国运通)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 10 pages, 6 figures
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are becoming useful in many domains due to their impressive abilities that arise from large training datasets and large model sizes. However, research on LLM-based approaches to document inconsistency detection is relatively limited. There are two key aspects of document inconsistency detection: (i) classification of whether there exists any inconsistency, and (ii) providing evidence of the inconsistent sentences. We focus on the latter, and introduce new comprehensive evidence-extraction metrics and a redact-and-retry framework with constrained filtering that substantially improves LLM-based document inconsistency detection over direct prompting. We back our claims with promising experimental results.
zh
[NLP-88] Chronicals: A High-Performance Framework for LLM Fine-Tuning with 3.51x Speedup over Unsloth
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)微调过程中因内存瓶颈导致的训练效率低下问题,特别是针对7B参数模型在A100-40GB显存限制下难以完成全量微调的挑战。其核心解决方案是提出一个名为Chronicals的开源训练框架,通过四项协同优化实现显著加速:(1) 使用融合Triton内核减少75%内存流量,包括RMSNorm、SwiGLU和QK-RoPE的高效融合;(2) 引入Cut Cross-Entropy机制,将logit存储从5GB降至135MB,基于在线softmax计算;(3) 提出LoRA+方法,依据梯度幅度分析推导出adapter矩阵间理论上的16倍差异学习率;(4) 采用Best-Fit Decreasing序列打包策略,恢复因填充浪费的60–75%计算资源。这些技术共同使全量微调速度提升至Unsloth的3.51倍,LoRA微调速度提升至4.10倍,并纠正了现有基准中未实际训练的问题,提供了完整的数学证明与开源实现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02609
作者: Arjun S. Nair
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
备注: 61 pages, 25 figures, open-source framework available at this https URL and pip install chronicals
Abstract:Large language model fine-tuning is bottlenecked by memory: a 7B parameter model requires 84GB–14GB for weights, 14GB for gradients, and 56GB for FP32 optimizer states–exceeding even A100-40GB capacity. We present Chronicals, an open-source training framework achieving 3.51x speedup over Unsloth through four synergistic optimizations: (1) fused Triton kernels eliminating 75% of memory traffic via RMSNorm (7x), SwiGLU (5x), and QK-RoPE (2.3x) fusion; (2) Cut Cross-Entropy reducing logit memory from 5GB to 135MB through online softmax computation; (3) LoRA+ with theoretically-derived 16x differential learning rates between adapter matrices; and (4) Best-Fit Decreasing sequence packing recovering 60-75% of compute wasted on padding. On Qwen2.5-0.5B with A100-40GB, Chronicals achieves 41,184 tokens/second for full fine-tuning versus Unsloth’s 11,736 tokens/second (3.51x). For LoRA at rank 32, we reach 11,699 tokens/second versus Unsloth MAX’s 2,857 tokens/second (4.10x). Critically, we discovered that Unsloth’s reported 46,000 tokens/second benchmark exhibited zero gradient norms–the model was not training. We provide complete mathematical foundations: online softmax correctness proofs, FlashAttention IO complexity bounds O(N^2 d^2 M^-1), LoRA+ learning rate derivations from gradient magnitude analysis, and bin-packing approximation guarantees. All implementations, benchmarks, and proofs are available at this https URL with pip installation via this https URL. Comments: 61 pages, 25 figures, open-source framework available at this https URL and pip install chronicals Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Machine Learning (stat.ML) MSC classes: 68T05 ACMclasses: I.2.6; I.2.7 Cite as: arXiv:2601.02609 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2601.02609v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02609 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[NLP-89] Scalable Construction of a Lung Cancer Knowledge Base: Profiling Semantic Reasoning in LLM s
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生物医学领域中大型语言模型(LLM)性能受限于训练数据语义质量的问题,尤其是在肺癌这一对精准性和可解释性要求极高的子领域。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个结构化、大规模且具备噪声感知能力的肺癌知识库,通过开放信息抽取(OpenIE)技术从许可宽松的开放获取文献中自动提取(主语,关系,宾语)三元组,并结合命名实体识别(NER)增强生物医学相关性,最终用于微调T5模型。实验证明,该方法显著提升了模型在语义一致性和生成质量上的表现,为低成本、可扩展地提升生物医学自然语言处理(NLP)提供了有效路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02604
作者: Cesar Felipe Martínez Cisneros,Jesús Ulises Quiroz Bautista,Claudia Anahí Guzmán Solano,Bogdan Kaleb García Rivera,Iván García Pacheco,Yalbi Itzel Balderas Martínez,Kolawole John Adebayoc,Ignacio Arroyo Fernández
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: \c{opyright} 2025 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media, including reprinting/republishing this material for advertising or promotional purposes, creating new collective works, for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or reuse of any copyrighted component of this work in other works
Abstract:The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into biomedical research offers new opportunities for domainspecific reasoning and knowledge representation. However, their performance depends heavily on the semantic quality of training data. In oncology, where precision and interpretability are vital, scalable methods for constructing structured knowledge bases are essential for effective fine-tuning. This study presents a pipeline for developing a lung cancer knowledge base using Open Information Extraction (OpenIE). The process includes: (1) identifying medical concepts with the MeSH thesaurus; (2) filtering open-access PubMed literature with permissive licenses (CC0); (3) extracting (subject, relation, object) triplets using OpenIE method; and (4) enriching triplet sets with Named Entity Recognition (NER) to ensure biomedical relevance. The resulting triplet sets provide a domain-specific, large-scale, and noise-aware resource for fine-tuning LLMs. We evaluated T5 models finetuned on this dataset through Supervised Semantic Fine-Tuning. Comparative assessments with ROUGE and BERTScore show significantly improved performance and semantic coherence, demonstrating the potential of OpenIE-derived resources as scalable, low-cost solutions for enhancing biomedical NLP.
zh
[NLP-90] FlowPlan-G2P: A Structured Generation Framework for Transforming Scientific Papers into Patent Descriptions
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决将科学论文转化为专利说明书时面临的挑战,尤其是由于两者在修辞风格和法律要求上的显著差异,导致传统黑箱式文本生成方法难以满足结构化推理与法律合规性需求。其解决方案的关键在于提出FlowPlan-G2P框架,该框架模拟专家撰写者的认知流程,将任务分解为三个阶段:(1) 概念图诱导(Concept Graph Induction),通过类专家推理提取技术实体及其关系并构建有向图;(2) 段落与章节规划(Paragraph and Section Planning),将概念图重组为符合标准专利结构的语义簇;(3) 图条件生成(Graph-Conditioned Generation),基于特定章节子图和定制提示生成合法合规的段落。此结构化方法显著提升了逻辑连贯性和法律合规性,为论文到专利的生成任务提供了新范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02589
作者: Kris W Pan,Yongmin Yoo
机构: Amazon(亚马逊); Macquarie University(麦考瑞大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Over 3.5 million patents are filed annually, with drafting patent descriptions requiring deep technical and legal expertise. Transforming scientific papers into patent descriptions is particularly challenging due to their differing rhetorical styles and stringent legal requirements. Unlike black-box text-to-text approaches that struggle to model structural reasoning and legal constraints, we propose FlowPlan-G2P, a novel framework that mirrors the cognitive workflow of expert drafters by reformulating this task into three stages: (1) Concept Graph Induction, extracting technical entities and relationships into a directed graph via expert-like reasoning; (2) Paragraph and Section Planning, reorganizing the graph into coherent clusters aligned with canonical patent sections; and (3) Graph-Conditioned Generation, producing legally compliant paragraphs using section-specific subgraphs and tailored prompts. Experiments demonstrate that FlowPlan-G2P significantly improves logical coherence and legal compliance over end-to-end LLM baselines. Our framework establishes a new paradigm for paper-to-patent generation and advances structured text generation for specialized domains.
zh
[NLP-91] Reconstructing Item Characteristic Curves using Fine-Tuned Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决传统评估项目参数(如难度和区分度)确定方法依赖昂贵实地测试以收集学生作答数据进行项目反应理论(Item Response Theory, IRT)校准的问题。其解决方案的关键在于利用大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)通过微调来隐式建模这些心理测量属性,具体而言是基于离散的能力描述符生成对多项选择题的模拟作答,并重构正确作答概率与学生能力之间的关系,从而生成合成的项目特征曲线(Item Characteristic Curves, ICCs),进而估计IRT参数。该方法在Grade 6英语语言艺术(ELA)项目和BEA 2024共享任务数据集上的实验表明,其性能可媲美或优于基线方法,尤其在建模项目区分度方面表现突出。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02580
作者: Christopher Ormerod
机构: Cambium Assessment (Cambium评估)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 19 pages, 5 tables, 3 figures
Abstract:Traditional methods for determining assessment item parameters, such as difficulty and discrimination, rely heavily on expensive field testing to collect student performance data for Item Response Theory (IRT) calibration. This study introduces a novel approach that implicitly models these psychometric properties by fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs) to simulate student responses across a spectrum of latent abilities. Leveraging the Qwen-3 dense model series and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), we train models to generate responses to multiple choice questions conditioned on discrete ability descriptors. We reconstruct the probability of a correct response as a function of student ability, effectively generating synthetic Item Characteristic Curves (ICCs) to estimate IRT parameters. Evaluation on a dataset of Grade 6 English Language Arts (ELA) items and the BEA 2024 Shared Task dataset demonstrates that this method competes with or outperforms baseline approaches. This simulation-based technique seems particularly effective at modeling item discrimination.
zh
[NLP-92] DataParasite Enables Scalable and Repurposable Online Data Curation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决计算社会科学中数据集构建依赖异构在线来源时面临的劳动密集、成本高且难以复现的问题。现有方法在利用大语言模型进行网络代理搜索和结构化提取方面虽有进展,但普遍存在不透明、灵活性差或不适合科学数据整理的缺陷。解决方案的关键在于提出一个名为DataParasite的开源模块化流水线,其将表格类整理任务分解为独立的实体级搜索,通过轻量级配置文件定义并由通用的任务无关Python脚本执行;更重要的是,该流水线可通过自然语言指令直接适配新任务(包括无预定义实体列表的任务),从而显著提升可扩展性与复用性。实验表明,DataParasite在多个典型任务(如教职招聘历史、精英死亡事件、政治生涯轨迹)中均实现高精度,并使数据收集成本降低一个数量级。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02578
作者: Mengyi Sun(Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
备注:
Abstract:Many questions in computational social science rely on datasets assembled from heterogeneous online sources, a process that is often labor-intensive, costly, and difficult to reproduce. Recent advances in large language models enable agentic search and structured extraction from the web, but existing systems are frequently opaque, inflexible, or poorly suited to scientific data curation. Here we introduce DataParasite, an open-source, modular pipeline for scalable online data collection. DataParasite decomposes tabular curation tasks into independent, entity-level searches defined through lightweight configuration files and executed through a shared, task-agnostic python script. Crucially, the same pipeline can be repurposed to new tasks, including those without predefined entity lists, using only natural-language instructions. We evaluate the pipeline on multiple canonical tasks in computational social science, including faculty hiring histories, elite death events, and political career trajectories. Across tasks, DataParasite achieves high accuracy while reducing data-collection costs by an order of magnitude relative to manual curation. By lowering the technical and labor barriers to online data assembly, DataParasite provides a practical foundation for scalable, transparent, and reusable data curation in computational social science and beyond.
zh
[NLP-93] Fact-Checking with Large Language Models via Probabilistic Certainty and Consistency
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在生成事实性内容时存在的幻觉问题(hallucination),即模型输出与真实信息不符的现象。现有事实核查方法通常无差别地检索外部证据,忽略了模型自身的内部知识,并可能引入无关噪声,且缺乏针对模型推理中特定不确定性进行精准干预的机制。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为概率确定性与一致性(Probabilistic Certainty and Consistency, PCC)的框架,通过联合建模LLM的概率确定性和推理一致性来量化其对事实的置信度。基于此置信信号,PCC设计了一种自适应验证策略:当模型对某命题具有高置信度时直接作答,对不确定或不一致的命题触发目标检索,对高度模糊的情况则启动深度搜索。该置信度引导的路由机制确保仅在必要时调用检索,从而提升效率与可靠性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02574
作者: Haoran Wang,Maryam Khalid,Qiong Wu,Jian Gao,Cheng Cao
机构: Emory University (埃默里大学); Amazon.com (亚马逊)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in applications requiring factual accuracy, yet their outputs often contain hallucinated responses. While fact-checking can mitigate these errors, existing methods typically retrieve external evidence indiscriminately, overlooking the model’s internal knowledge and potentially introducing irrelevant noise. Moreover, current systems lack targeted mechanisms to resolve specific uncertainties in the model’s reasoning. Inspired by how humans fact-check, we argue that LLMs should adaptively decide whether to rely on internal knowledge or initiate retrieval based on their confidence in a given claim. We introduce Probabilistic Certainty and Consistency (PCC), a framework that estimates factual confidence by jointly modeling an LLM’s probabilistic certainty and reasoning consistency. These confidence signals enable an adaptive verification strategy: the model answers directly when confident, triggers targeted retrieval when uncertain or inconsistent, and escalates to deep search when ambiguity is high. Our confidence-guided routing mechanism ensures that retrieval is invoked only when necessary, improving both efficiency and reliability. Extensive experiments across three challenging benchmarks show that PCC achieves better uncertainty quantification than verbalized confidence and consistently outperforms strong LLM-based fact-checking baselines. Furthermore, we demonstrate that PCC generalizes well across various LLMs.
zh
[NLP-94] LoRA-Drop: Temporal LoRA Decoding for Efficient LLM Inference
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决自回归大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在推理阶段因逐 token 解码导致的计算瓶颈问题,即每次生成新 token 时通常需遍历全部 Transformer 层,造成高延迟和资源消耗。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种无需路由网络、兼容标准键值缓存(KV caching)的插件式推理框架 LoRA-Drop:通过施加时间维度上的计算调度策略,在大多数解码步骤中选择性地跳过部分中间层,仅利用低秩适配(LoRA)对前一 token 的隐藏状态进行修正;同时定期执行完整模型以防止误差累积(称为“刷新”步骤)。此方法可在不显著牺牲准确性的前提下,实现高达 2.6 倍的加速与 45–55% 的 KV 缓存占用减少,且存在一个稳定的安全调度区间,可兼顾性能与效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02569
作者: Hossein Rajabzadeh,Maryam Dialameh,Chul B. Park,Il-Min Kim,Hyock Ju Kwon
机构: University of Waterloo (滑铁卢大学); University of Toronto (多伦多大学); Queen’s University (皇后大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Autoregressive large language models (LLMs) are bottlenecked by sequential decoding, where each new token typically requires executing all transformer layers. Existing dynamic-depth and layer-skipping methods reduce this cost, but often rely on auxiliary routing mechanisms or incur accuracy degradation when bypassed layers are left uncompensated. We present \textbfLoRA-Drop, a plug-and-play inference framework that accelerates decoding by applying a \emphtemporal compute schedule to a fixed subset of intermediate layers: on most decoding steps, selected layers reuse the previous-token hidden state and apply a low-rank LoRA correction, while periodic \emphrefresh steps execute the full model to prevent drift. LoRA-Drop requires no routing network, is compatible with standard KV caching, and can reduce KV-cache footprint by skipping KV updates in droppable layers during LoRA steps and refreshing periodically. Across \textbfLLaMA2-7B, \textbfLLaMA3-8B, \textbfQwen2.5-7B, and \textbfQwen2.5-14B, LoRA-Drop achieves up to \textbf2.6 \times faster decoding and \textbf45–55% KV-cache reduction while staying within \textbf0.5 percentage points (pp) of baseline accuracy. Evaluations on reasoning (GSM8K, MATH, BBH), code generation (HumanEval, MBPP), and long-context/multilingual benchmarks (LongBench, XNLI, XCOPA) identify a consistent \emphsafe zone of scheduling configurations that preserves quality while delivering substantial efficiency gains, providing a simple path toward adaptive-capacity inference in LLMs. Codes are available at this https URL.
zh
[NLP-95] Compressed code: the hidden effects of quantization and distillation on programming tokens
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在代码生成任务中,其分词级别(token-level)机制在压缩模型中的理解不足问题。研究发现,现有方法对编程语言在LLM分词器中的编码方式、词汇分布与关键字覆盖模式缺乏系统性分析,且优化技术(如量化、蒸馏、模型缩放和任务特定微调)对分词表示及代码生成质量的影响尚不明确。论文的关键解决方案在于提出一种新颖的“冷启动概率分析”方法,无需显式提示即可揭示模型行为;并通过全面的概率分布分析和评估指标,系统评估不同优化策略对token级表示与代码生成质量的影响,从而提供可实证验证的优化指导原则,为生产环境中高效部署压缩模型提供了理论支持与实践依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02563
作者: Viacheslav Siniaev,Iaroslav Chelombitko,Aleksey Komissarov
机构: National Sun Yat-Sen University (国立中山大学); DataSpike; aglabx; Neapolis University Pafos (尼奥波利斯大学帕福斯分校); Meta (Meta)
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Programming Languages (cs.PL)
备注: 18 pages, 1 figure and 6 tables
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional code generation capabilities, yet their token-level mechanisms remain underexplored, particularly in compressed models. Through systematic analysis of programming language token representations, we characterize how programming languages are encoded in LLM tokenizers by analyzing their vocabulary distribution and keyword coverage patterns. We introduce a novel cold-start probability analysis method that provides insights into model behavior without requiring explicit prompts. Additionally, we present a comprehensive evaluation of how different model optimization techniques - including quantization, distillation, model scaling, and task-specific fine-tuning - affect token-level representations and code generation quality. Our experiments, supported by comprehensive probability distribution analysis and evaluation metrics, reveal critical insights into token-level behavior and provide empirically-validated guidelines for maintaining code generation quality under various optimization constraints. These findings advance both theoretical understanding of LLM code generation and practical implementation of optimized models in production environments.
zh
[NLP-96] ModeX: Evaluator-Free Best-of-N Selection for Open-Ended Generation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在开放任务中从多个随机生成结果中选择高质量输出的难题,尤其在缺乏标准答案的情况下,传统方法如Best-of-N和自一致性(self-consistency)依赖外部评估器、奖励模型或精确字符串匹配投票,限制了其适用性和效率。解决方案的关键在于提出一种无需评估器的Best-of-N选择框架——模式提取(Mode Extraction, ModeX),其核心思想是通过构建候选生成文本的相似性图并递归应用谱聚类(spectral clustering),识别出代表语义共识的模态输出(modal output),从而实现对开放文本生成的鲁棒选择。进一步地,作者还提出了高效版本ModeX–Lite,引入早期剪枝策略以提升计算效率,在文本摘要、代码生成和数学推理等开放任务中均显著优于标准单路径与多路径基线方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02535
作者: Hyeong Kyu Choi,Sharon Li
机构: University of Wisconsin-Madison(威斯康星大学麦迪逊分校)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Selecting a single high-quality output from multiple stochastic generations remains a fundamental challenge for large language models (LLMs), particularly in open-ended tasks where no canonical answer exists. While Best-of-N and self-consistency methods show that aggregating multiple generations can improve performance, existing approaches typically rely on external evaluators, reward models, or exact string-match voting, limiting their applicability and efficiency. We propose Mode Extraction (ModeX), an evaluator-free Best-of-N selection framework that generalizes majority voting to open-ended text generation by identifying the modal output representing the dominant semantic consensus among generated texts. ModeX constructs a similarity graph over candidate generations and recursively applies spectral clustering to select a representative centroid, without requiring additional inference or auxiliary models. We further instantiate this selection principle as ModeX–Lite, an improved version of ModeX with early pruning for efficiency. Across open-ended tasks–including text summarization, code generation, and mathematical reasoning–our approaches consistently outperform standard single- and multi-path baselines, providing a computationally efficient solution for robust open-ended text generation. Code is released in this https URL.
zh
[NLP-97] Losses that Cook: Topological Optimal Transport for Structured Recipe Generation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决烹饪食谱生成中因标准训练目标(如交叉熵损失)仅关注文本流畅性而导致的成分准确性、时间温度精度及步骤连贯性不足的问题。其关键解决方案是引入多种复合目标函数,尤其是提出一种新的拓扑损失(topological loss),将食材列表表示为嵌入空间中的点云,并最小化预测与真实食材之间的差异;同时结合Dice损失提升时间和温度的精确度,以及混合损失在数量和时间上的协同优化,从而显著改善食谱生成在成分级和动作级指标上的表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02531
作者: Mattia Ottoborgo,Daniele Rege Cambrin,Paolo Garza
机构: Trustpilot; Politecnico di Torino
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Cooking recipes are complex procedures that require not only a fluent and factual text, but also accurate timing, temperature, and procedural coherence, as well as the correct composition of ingredients. Standard training procedures are primarily based on cross-entropy and focus solely on fluency. Building on RECIPE-NLG, we investigate the use of several composite objectives and present a new topological loss that represents ingredient lists as point clouds in embedding space, minimizing the divergence between predicted and gold ingredients. Using both standard NLG metrics and recipe-specific metrics, we find that our loss significantly improves ingredient- and action-level metrics. Meanwhile, the Dice loss excels in time/temperature precision, and the mixed loss yields competitive trade-offs with synergistic gains in quantity and time. A human preference analysis supports our finding, showing our model is preferred in 62% of the cases.
zh
[NLP-98] Dynamic Quantization Error Propagation in Encoder-Decoder ASR Quantization
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决在内存受限的边缘设备上运行自动语音识别(Automatic Speech Recognition, ASR)模型时,因层间后训练量化(layer-wise post-training quantization)导致的误差累积问题,尤其是在编码器-解码器架构中表现尤为显著。现有方法如量化误差传播(Quantization Error Propagation, QEP)由于ASR模型结构的异质性(编码器处理声学特征、解码器生成文本)而效果不佳。解决方案的关键在于提出细粒度Alpha动态量化误差传播机制(Fine-grained Alpha for Dynamic Quantization Error Propagation, FADE),该机制能够自适应地调控跨层误差校正与局部量化之间的权衡,从而显著提升模型稳定性并降低平均词错误率(Word Error Rate, WER)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02455
作者: Xinyu Wang,Yajie Luo,Yihong Wu,Liheng Ma,Ziyu Zhao,Jingrui Tian,Lei Ding,Yufei Cui,Xiao-Wen Chang
机构: McGill University (麦吉尔大学); Tsinghua University (清华大学); Peking University (北京大学); Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学)
类目: ound (cs.SD); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS)
备注: 9 pages, 4 figures, 3 tables
Abstract:Running Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models on memory-constrained edge devices requires efficient compression. While layer-wise post-training quantization is effective, it suffers from error accumulation, especially in encoder-decoder architectures. Existing solutions like Quantization Error Propagation (QEP) are suboptimal for ASR due to the model’s heterogeneity, processing acoustic features in the encoder while generating text in the decoder. To address this, we propose Fine-grained Alpha for Dynamic Quantization Error Propagation (FADE), which adaptively controls the trade-off between cross-layer error correction and local quantization. Experiments show that FADE significantly improves stability by reducing performance variance across runs, while simultaneously surpassing baselines in mean WER.
zh
[NLP-99] PCEval: A Benchmark for Evaluating Physical Computing Capabilities of Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在物理计算(Physical Computing)场景下,尤其是在硬件约束条件下,其在逻辑与物理层面协同设计能力尚未被系统评估的问题。当前LLMs在软件开发中表现优异,但在涉及电路设计、硬件交互和实际布线等物理实现环节时,缺乏可靠的自动化评估机制。解决方案的关键在于提出首个面向物理计算的自动评估基准——\textscPCEval,该框架可在仿真环境中对LLMs生成电路逻辑与物理布板的能力进行端到端、无需人工介入的量化评估,从而首次实现了对LLMs在硬件实现约束下推理能力的可复现、自动验证的实证分析。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02404
作者: Inpyo Song,Eunji Jeon,Jangwon Lee
机构: Sungkyunkwan University (成均馆大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Code and Dataset available at this https URL
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across various domains, including software development, education, and technical assistance. Among these, software development is one of the key areas where LLMs are increasingly adopted. However, when hardware constraints are considered-for instance, in physical computing, where software must interact with and control physical hardware -their effectiveness has not been fully explored. To address this gap, we introduce \textscPCEval (Physical Computing Evaluation), the first benchmark in physical computing that enables a fully automatic evaluation of the capabilities of LLM in both the logical and physical aspects of the projects, without requiring human assessment. Our evaluation framework assesses LLMs in generating circuits and producing compatible code across varying levels of project complexity. Through comprehensive testing of 13 leading models, \textscPCEval provides the first reproducible and automatically validated empirical assessment of LLMs’ ability to reason about fundamental hardware implementation constraints within a simulation environment. Our findings reveal that while LLMs perform well in code generation and logical circuit design, they struggle significantly with physical breadboard layout creation, particularly in managing proper pin connections and avoiding circuit errors. \textscPCEval advances our understanding of AI assistance in hardware-dependent computing environments and establishes a foundation for developing more effective tools to support physical computing education.
zh
[NLP-100] WearVox: An Egocentric Multichannel Voice Assistant Benchmark for Wearables
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前语音助手在可穿戴设备(如AI眼镜)场景下性能评估缺乏真实性和复杂性的问题,特别是针对第一人称视角音频(egocentric audio)受运动干扰、噪声影响、快速微交互以及设备定向语音与背景对话难以区分等挑战。现有基准测试多基于干净或通用对话音频,无法反映实际使用环境的复杂性。解决方案的关键在于提出首个专门面向可穿戴场景的基准测试集WearVox,其包含3,842条多通道第一人称音频记录,覆盖五类典型任务(如搜索引导问答、工具调用等),并配有丰富元数据以支持细粒度分析。实验表明,多数实时语音大语言模型(SLLMs)在WearVox上的准确率仅为29%–59%,且在户外嘈杂环境中性能显著下降,凸显了该基准的真实性与挑战性;进一步对比单通道与多通道输入的模型表现,验证了空间音频线索对提升环境噪声鲁棒性和设备定向语音识别能力的重要性,从而确立了多通道音频输入作为增强上下文感知语音助手性能的核心策略。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02391
作者: Zhaojiang Lin,Yong Xu,Kai Sun,Jing Zheng,Yin Huang,Surya Teja Appini,Krish Narang,Renjie Tao,Ishan Kapil Jain,Siddhant Arora,Ruizhi Li,Yiteng Huang,Kaushik Patnaik,Wenfang Xu,Suwon Shon,Yue Liu,Ahmed A Aly,Anuj Kumar,Florian Metze,Xin Luna Dong
机构: Meta(Meta)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Sound (cs.SD); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS)
备注:
Abstract:Wearable devices such as AI glasses are transforming voice assistants into always-available, hands-free collaborators that integrate seamlessly with daily life, but they also introduce challenges like egocentric audio affected by motion and noise, rapid micro-interactions, and the need to distinguish device-directed speech from background conversations. Existing benchmarks largely overlook these complexities, focusing instead on clean or generic conversational audio. To bridge this gap, we present WearVox, the first benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate voice assistants in realistic wearable scenarios. WearVox comprises 3,842 multi-channel, egocentric audio recordings collected via AI glasses across five diverse tasks including Search-Grounded QA, Closed-Book QA, Side-Talk Rejection, Tool Calling, and Speech Translation, spanning a wide range of indoor and outdoor environments and acoustic conditions. Each recording is accompanied by rich metadata, enabling nuanced analysis of model performance under real-world constraints. We benchmark leading proprietary and open-source speech Large Language Models (SLLMs) and find that most real-time SLLMs achieve accuracies on WearVox ranging from 29% to 59%, with substantial performance degradation on noisy outdoor audio, underscoring the difficulty and realism of the benchmark. Additionally, we conduct a case study with two new SLLMs that perform inference with single-channel and multi-channel audio, demonstrating that multi-channel audio inputs significantly enhance model robustness to environmental noise and improve discrimination between device-directed and background speech. Our results highlight the critical importance of spatial audio cues for context-aware voice assistants and establish WearVox as a comprehensive testbed for advancing wearable voice AI research.
zh
[NLP-101] LLM -as-evaluator in Strategy Research: A Normative Variance-Aware Protocol
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)在战略研究中作为文本评估工具时存在的可靠性问题,尤其是其评估结果的不稳定性对研究推断有效性的潜在威胁。解决方案的关键在于提出一套全面的方法论协议,该协议具备方差感知性(variance-aware)、规范性(normative)和可审计性(auditable)特征,并提供灵活的实施指南,包括预注册和透明报告策略,从而将LLM驱动的文本评估从当前的临时做法提升为严谨、可操作且可审计的测量方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02370
作者: Arnaldo Camuffo,Alfonso Gambardella,Saeid Kazemi,Jakub Malachowski,Abhinav Pandey
机构: Bocconi University (博科尼大学)
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 61 pages, 16 pages for appendix
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are becoming essential tools for strategy scholars who need to evaluate text corpora at scale. This paper provides a systematic analysis of the reliability of LLM-as-evaluator in strategy research. After classifying the typical ways in which LLMs can be deployed for evaluation purposes in strategy research, we draw on the specialised AI literature to analyse their properties as measurement instruments. Our empirical analysis reveals substantial instability in LLMs’ evaluation output, stemming from multiple factors: the specific phrasing of prompts, the context provided, sampling procedures, extraction methods, and disagreements across different models. We quantify these effects and demonstrate how this unreliability can compromise the validity of research inferences drawn from LLM-generated evaluations. To address these challenges, we develop a comprehensive protocol that is variance-aware, normative, and auditable. We provide practical guidance for flexible implementation of this protocol, including approaches to preregistration and transparent reporting. By establishing these methodological standards, we aim to elevate LLM-based evaluation of business text corpora from its current ad hoc status to a rigorous, actionable, and auditable measurement approach suitable for scholarly research.
zh
[NLP-102] Cross-Platform Digital Discourse Analysis of the Israel-Hamas Conflict: Sentiment Topics and Event Dynamics
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决数字平台上冲突叙事的生成、传播与对抗机制问题,尤其关注以色列-巴勒斯坦冲突中不同社交媒体平台(Telegram、Twitter/X 和 Reddit)如何塑造和扩散政治话语。其关键解决方案在于构建了一个多平台、符合FAIR原则的数据集,并开发了一套集成分析管道,融合了主题建模(LDA与BERTopic)、基于Transformer的情感与情绪分析模型以及垃圾信息过滤技术,从而系统性地识别主导议题、情感动态及宣传策略,揭示各平台因功能特性差异而形成的叙事扩散路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02367
作者: Despoina Antonakaki,Sotiris Ioannidis
机构: Institute of Computer Science, Foundation for Research and Technology (希腊国家研究基金会计算机科学研究所); Technical University of Crete (克里特理工学院)
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Social and Information Networks (cs.SI)
备注:
Abstract:The Israeli-Palestinian conflict remains one of the most polarizing geopolitical issues, with the October 2023 escalation intensifying online debate. Social media platforms, particularly Telegram, have become central to real-time news sharing, advocacy, and propaganda. In this study, we analyze Telegram, Twitter/X, and Reddit to examine how conflict narratives are produced, amplified, and contested across different digital spheres. Building on our previous work on Telegram discourse during the 2023 escalation, we extend the analysis longitudinally and cross-platform using an updated dataset spanning October 2023 to mid-2025. The corpus includes more than 187,000 Telegram messages, 2.1 million Reddit comments, and curated Twitter/X posts. We combine Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), BERTopic, and transformer-based sentiment and emotion models to identify dominant themes, emotional dynamics, and propaganda strategies. Telegram channels provide unfiltered, high-intensity documentation of events; Twitter/X amplifies frames to global audiences; and Reddit hosts more reflective and deliberative discussions. Our findings reveal persistent negative sentiment, strong coupling between humanitarian framing and solidarity expressions, and platform-specific pathways for the diffusion of pro-Palestinian and pro-Israeli narratives. This paper offers three contributions: (1) a multi-platform, FAIR-compliant dataset on the Israel-Hamas war, (2) an integrated pipeline combining topic modeling, sentiment and emotion analysis, and spam filtering for large-scale conflict discourse, and (3) empirical insights into how platform affordances and affective publics shape the evolution of digital conflict communication.
zh
[NLP-103] FUSE : Failure-aware Usage of Subagent Evidence for MultiModal Search and Recommendation ICDM
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多模态创意助手在任务分解与子代理(subagent)协作过程中因检索质量不佳而导致的系统失效问题,尤其关注用户意图理解、内容类型选择、候选结果召回(recall)及排序准确性等关键环节的性能瓶颈。其核心解决方案是提出FUSE框架,通过引入一种紧凑的“基座设计表示”(Grounded Design Representation, GDR),将原始图像提示替换为结构化的JSON格式元素(如图像、文本、形状、图标等),从而显著降低图像传输与处理成本;同时,FUSE采用七种上下文预算策略进行优化,其中“上下文压缩”(Context Compression)被证明在所有流水线阶段均表现最优,实现了93.3%的意图准确率、86.8%的路由成功率、99.4%的召回率和88.5%的NDCG@5,验证了战略性上下文摘要优于全面或极简情境化方法的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02365
作者: Tushar Vatsa,Vibha Belavadi,Priya Shanmugasundaram,Suhas Suresha,Dewang Sultania
机构: Adobe Inc.(Adobe公司)
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: ICDM MMSR 2025: Workshop on Multimodal Search and Recommendations
Abstract:Multimodal creative assistants decompose user goals and route tasks to subagents for layout, styling, retrieval, and generation. Retrieval quality is pivotal, yet failures can arise at several stages: understanding user intent, choosing content types, finding candidates (recall), or ranking results. Meanwhile, sending and processing images is costly, making naive multimodal approaches impractical. We present FUSE: Failure-aware Usage of Subagent Evidence for MultiModal Search and Recommendation. FUSE replaces most raw-image prompting with a compact Grounded Design Representation (GDR): a selection aware JSON of canvas elements (image, text, shape, icon, video, logo), structure, styles, salient colors, and user selection provided by the Planner team. FUSE implements seven context budgeting strategies: comprehensive baseline prompting, context compression, chain-of-thought reasoning, mini-shot optimization, retrieval-augmented context, two-stage processing, and zero-shot minimalism. Finally, a pipeline attribution layer monitors system performance by converting subagent signals into simple checks: intent alignment, content-type/routing sanity, recall health (e.g., zero-hit and top-match strength), and ranking displacement analysis. We evaluate the seven context budgeting variants across 788 evaluation queries from diverse users and design templates (refer Figure 3). Our systematic evaluation reveals that Context Compression achieves optimal performance across all pipeline stages, with 93.3% intent accuracy, 86.8% routing success(with fallbacks), 99.4% recall, and 88.5% NDCG@5. This approach demonstrates that strategic context summarization outperforms both comprehensive and minimal contextualization strategies.
zh
[NLP-104] WIST: Training-free and Label-free Short Text Clustering through Iterative Vector Updating with LLM s
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决商业场景中短文本聚类问题,特别是在缺乏标注数据和未知簇数量的情况下,如何高效、准确地对用户意图进行聚类。其核心挑战在于传统方法通常依赖于对比学习或标签信息,而实际应用中这些条件难以满足。解决方案的关键在于提出一种无需训练且不依赖标签的迭代向量更新方法:首先基于代表性文本构建稀疏向量,随后通过大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)引导进行迭代优化,从而提升聚类质量。该方法具有模型无关性、低资源消耗和良好的可扩展性,适用于任意嵌入器(embedder)、小型LLM及多种聚类算法,显著提升了在真实世界部署中的实用性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.06747
作者: I-Fan Lin,Faegheh Hasibi,Suzan Verberne
机构: Leiden University (莱顿大学); Radboud University (奈梅亨大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a training-free and label-free method for short text clustering that can be used on top of any existing embedder. In the context of customer-facing chatbots, companies are dealing with large amounts of user utterances that need to be clustered according to their intent. In these commercial settings, no labeled data is typically available, and the number of clusters is not known. Our method is based on iterative vector updating: it constructs sparse vectors based on representative texts, and then iteratively refines them through LLM guidance. Our method achieves comparable or superior results to state-of-the-art methods that use contrastive learning, but without assuming prior knowledge of clusters or labels. Experiments on diverse datasets and smaller LLMs show that our method is model agnostic and can be applied to any embedder, with relatively small LLMs, and different clustering methods. We also show that our method scales to large datasets, reducing the computational cost of the LLM. These low-resource, adaptable settings and the scalability of our method make it more aligned with real-world scenarios than existing clustering methods.
zh
[NLP-105] DNACHUNKER: Learnable Tokenization for DNA Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决DNA语言模型中因固定tokenization策略导致性能受限的问题,即传统方法将DNA序列划分为等长片段时,难以适应序列中功能区域的异质性与变异敏感性。解决方案的关键在于提出DNACHUNKER,其核心创新是集成可学习的动态DNA分块机制(dynamic DNA tokenization mechanism),并以掩码语言建模方式进行训练。该机制基于H-Net提出的动态分块方法,使模型能够自动学习将DNA序列分割为变长片段:在功能重要区域(如启动子和外显子)使用更小的chunk以保留细节,在重复或冗余区域使用更大的chunk以提升效率,从而增强对DNA序列变异的鲁棒性并更好地捕捉生物语法结构。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03019
作者: Taewon Kim,Jihwan Shin,Hyomin Kim,Youngmok Jung,Jonhoon Lee,Won-Chul Lee,Insu Han,Sungsoo Ahn
机构: Korea Academic Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST); INOCRAS
类目: Genomics (q-bio.GN); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:DNA language models have emerged as powerful tools for decoding the complex language of DNA sequences. However, the performance of these models is heavily affected by their tokenization strategy, i.e., a method used to parse DNA sequences into a shorter sequence of chunks. In this work, we propose DNACHUNKER, which integrates a learnable dynamic DNA tokenization mechanism and is trained as a masked language model. Adopting the dynamic chunking procedure proposed by H-Net, our model learns to segment sequences into variable-length chunks. This dynamic chunking offers two key advantages: it’s resilient to shifts and mutations in the DNA, and it allocates more detail to important functional areas. We demonstrate the performance of DNACHUNKER by training it on the human reference genome (HG38) and testing it on the Nucleotide Transformer and Genomic benchmarks. Further ablative experiments reveal that DNACHUNKER learns tokenization that grasps biological grammar and uses smaller chunks to preserve detail in important functional elements such as promoters and exons, while using larger chunks for repetitive, redundant regions.
zh
[NLP-106] Hierarchical temporal receptive windows and zero-shot timescale generalization in biologically constrained scale-invariant deep networks
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大脑认知如何在嵌套时间尺度上整合信息的问题,尤其是神经网络中局部回路的时间常数异质性与皮层层级时间感知窗口(Temporal Receptive Windows, TRWs)之间的矛盾。其关键解决方案是基于尺度不变的海马体时间细胞(scale-invariant hippocampal time cells)构建生物约束的深度网络模型,通过训练一个前馈结构(SITHCon)发现层级TRWs可自然涌现,进而将此类归纳偏置提炼为一种生物合理且受限的循环神经网络架构(SITH-RNN)。该架构仅用极少参数即可实现快速学习,并在零样本情况下泛化至分布外的时间尺度,表明大脑可能采用尺度不变的序列先验——即“事件发生的时间”编码机制,使具备此类先验的递归网络更适于描述人类认知过程。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02618
作者: Aakash Sarkar,Marc W. Howard
机构: 未知
类目: Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE)
备注:
Abstract:Human cognition integrates information across nested timescales. While the cortex exhibits hierarchical Temporal Receptive Windows (TRWs), local circuits often display heterogeneous time constants. To reconcile this, we trained biologically constrained deep networks, based on scale-invariant hippocampal time cells, on a language classification task mimicking the hierarchical structure of language (e.g., ‘letters’ forming ‘words’). First, using a feedforward model (SITHCon), we found that a hierarchy of TRWs emerged naturally across layers, despite the network having an identical spectrum of time constants within layers. We then distilled these inductive priors into a biologically plausible recurrent architecture, SITH-RNN. Training a sequence of architectures ranging from generic RNNs to this restricted subset showed that the scale-invariant SITH-RNN learned faster with orders-of-magnitude fewer parameters, and generalized zero-shot to out-of-distribution timescales. These results suggest the brain employs scale-invariant, sequential priors - coding “what” happened “when” - making recurrent networks with such priors particularly well-suited to describe human cognition.
zh
[NLP-107] Detecting and Mitigating Treatment Leakage in Text-Based Causal Inference: Distillation and Sensitivity Analysis
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决文本作为混杂变量代理时存在的“治疗泄漏”(treatment leakage)问题,即文本中既包含未观测混杂因素的信息,又含有预测处理状态的信号,从而导致因果估计出现后处理偏差。解决方案的关键在于提出四种文本蒸馏方法——基于相似性的片段移除、远监督分类、显著特征移除和迭代零空间投影——这些方法旨在在保留混杂变量信息的同时消除与处理状态相关的预测性内容,从而实现偏倚最小化与混杂控制之间的最优平衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02400
作者: Adel Daoud,Richard Johansson,Connor T. Jerzak
机构: Linköping University (林雪平大学); Chalmers University of Technology (查尔姆斯理工大学); University of Texas at Austin (德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校)
类目: Econometrics (econ.EM); Computation and Language (cs.CL); General Economics (econ.GN); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
备注:
Abstract:Text-based causal inference increasingly employs textual data as proxies for unobserved confounders, yet this approach introduces a previously undertheorized source of bias: treatment leakage. Treatment leakage occurs when text intended to capture confounding information also contains signals predictive of treatment status, thereby inducing post-treatment bias in causal estimates. Critically, this problem can arise even when documents precede treatment assignment, as authors may employ future-referencing language that anticipates subsequent interventions. Despite growing recognition of this issue, no systematic methods exist for identifying and mitigating treatment leakage in text-as-confounder applications. This paper addresses this gap through three contributions. First, we provide formal statistical and set-theoretic definitions of treatment leakage that clarify when and why bias occurs. Second, we propose four text distillation methods – similarity-based passage removal, distant supervision classification, salient feature removal, and iterative nullspace projection – designed to eliminate treatment-predictive content while preserving confounder information. Third, we validate these methods through simulations using synthetic text and an empirical application examining International Monetary Fund structural adjustment programs and child mortality. Our findings indicate that moderate distillation optimally balances bias reduction against confounder retention, whereas overly stringent approaches degrade estimate precision.
zh
计算机视觉
[CV-0] Muses: Designing Composing Generating Nonexistent Fantasy 3D Creatures without Training
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前3D生物形态生成中因复杂部件级操控和域外生成能力有限而导致的现实感不足与结构不一致问题(incoherent 3D assets)。现有方法依赖部件感知优化、人工组装或2D图像生成,难以实现高质量、结构合理的三维生物体创建。解决方案的关键在于引入3D骨骼(3D skeleton)作为基础表示,将3D内容创作形式化为结构感知的设计-组合-生成流程:首先通过图约束推理构建具有合理布局与尺度的创意3D骨骼;随后在结构化的潜在空间中基于体素进行部件整合;最后在骨骼约束下采用图像引导的外观建模生成风格一致且和谐的纹理。此方法实现了无需训练即可生成逼真、语义对齐的幻想3D生物体,并具备灵活编辑潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03256
作者: Hexiao Lu,Xiaokun Sun,Zeyu Cai,Hao Guo,Ying Tai,Jian Yang,Zhenyu Zhang
机构: Nanjing University (南京大学); China Agricultural University (中国农业大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Project page: this https URL
Abstract:We present Muses, the first training-free method for fantastic 3D creature generation in a feed-forward paradigm. Previous methods, which rely on part-aware optimization, manual assembly, or 2D image generation, often produce unrealistic or incoherent 3D assets due to the challenges of intricate part-level manipulation and limited out-of-domain generation. In contrast, Muses leverages the 3D skeleton, a fundamental representation of biological forms, to explicitly and rationally compose diverse elements. This skeletal foundation formalizes 3D content creation as a structure-aware pipeline of design, composition, and generation. Muses begins by constructing a creatively composed 3D skeleton with coherent layout and scale through graph-constrained reasoning. This skeleton then guides a voxel-based assembly process within a structured latent space, integrating regions from different objects. Finally, image-guided appearance modeling under skeletal conditions is applied to generate a style-consistent and harmonious texture for the assembled shape. Extensive experiments establish Muses’ state-of-the-art performance in terms of visual fidelity and alignment with textual descriptions, and potential on flexible 3D object editing. Project page: this https URL.
zh
[CV-1] InfiniDepth: Arbitrary-Resolution and Fine-Grained Depth Estimation with Neural Implicit Fields
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有深度估计方法在离散图像网格上预测深度所带来的局限性,这些方法难以扩展至任意输出分辨率并阻碍几何细节的恢复。其解决方案的关键在于提出InfiniDepth,将深度表示为神经隐式场(neural implicit fields),并通过一个简单而有效的局部隐式解码器实现对连续二维坐标的深度查询,从而支持任意分辨率和细粒度的深度估计。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03252
作者: Hao Yu,Haotong Lin,Jiawei Wang,Jiaxin Li,Yida Wang,Xueyang Zhang,Yue Wang,Xiaowei Zhou,Ruizhen Hu,Sida Peng
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); Li Auto (理想汽车); Shenzhen University (深圳大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 19 pages, 13 figures
Abstract:Existing depth estimation methods are fundamentally limited to predicting depth on discrete image grids. Such representations restrict their scalability to arbitrary output resolutions and hinder the geometric detail recovery. This paper introduces InfiniDepth, which represents depth as neural implicit fields. Through a simple yet effective local implicit decoder, we can query depth at continuous 2D coordinates, enabling arbitrary-resolution and fine-grained depth estimation. To better assess our method’s capabilities, we curate a high-quality 4K synthetic benchmark from five different games, spanning diverse scenes with rich geometric and appearance details. Extensive experiments demonstrate that InfiniDepth achieves state-of-the-art performance on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks across relative and metric depth estimation tasks, particularly excelling in fine-detail regions. It also benefits the task of novel view synthesis under large viewpoint shifts, producing high-quality results with fewer holes and artifacts.
zh
[CV-2] A Versatile Multimodal Agent for Multimedia Content Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前生成式 AI (Generative AI) 模型在真实应用场景中难以实现多模态内容端到端生成的问题,尤其是面对复杂任务时,现有模型通常仅能作为单一模块使用,无法有效整合图像、视频、音频及文本等多种模态输入与输出。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个名为 MultiMedia-Agent 的代理系统,该系统通过构建数据生成流水线、内容创作工具库以及偏好对齐评估指标来支撑复杂内容生成;特别地,引入技能习得理论优化训练数据的筛选与代理训练过程,并采用两阶段相关性策略(自相关与模型偏好相关)进行计划优化,最终通过三阶段微调方法(基础计划微调、成功计划微调和偏好优化)提升代理性能,从而显著增强多模态内容生成的质量与一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03250
作者: Daoan Zhang,Wenlin Yao,Xiaoyang Wang,Yebowen Hu,Jiebo Luo,Dong Yu
机构: University of Rochester (罗切斯特大学); Tencent AI Lab, Bellevue (腾讯人工智能实验室); University of Central Florida (中佛罗里达大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:With the advancement of AIGC (AI-generated content) technologies, an increasing number of generative models are revolutionizing fields such as video editing, music generation, and even film production. However, due to the limitations of current AIGC models, most models can only serve as individual components within specific application scenarios and are not capable of completing tasks end-to-end in real-world applications. In real-world applications, editing experts often work with a wide variety of images and video inputs, producing multimodal outputs – a video typically includes audio, text, and other elements. This level of integration across multiple modalities is something current models are unable to achieve effectively. However, the rise of agent-based systems has made it possible to use AI tools to tackle complex content generation tasks. To deal with the complex scenarios, in this paper, we propose a MultiMedia-Agent designed to automate complex content creation. Our agent system includes a data generation pipeline, a tool library for content creation, and a set of metrics for evaluating preference alignment. Notably, we introduce the skill acquisition theory to model the training data curation and agent training. We designed a two-stage correlation strategy for plan optimization, including self-correlation and model preference correlation. Additionally, we utilized the generated plans to train the MultiMedia-Agent via a three stage approach including base/success plan finetune and preference optimization. The comparison results demonstrate that the our approaches are effective and the MultiMedia-Agent can generate better multimedia content compared to novel models.
zh
[CV-3] LTX-2: Efficient Joint Audio-Visual Foundation Model
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前文本到视频扩散模型在生成视频时缺乏音频信息的问题,即视频内容缺少语义、情感和氛围等由音频提供的关键线索。其解决方案的关键在于提出LTX-2——一个开源的统一音频视觉生成基础模型,采用异构双流Transformer架构(14B参数视频流与5B参数音频流),通过双向跨模态注意力层与时间位置嵌入实现音视频同步,并引入模态感知的无分类器引导(modality-CFG)机制提升音视频对齐精度与可控性,从而在保证高保真度的同时显著降低计算成本。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03233
作者: Yoav HaCohen,Benny Brazowski,Nisan Chiprut,Yaki Bitterman,Andrew Kvochko,Avishai Berkowitz,Daniel Shalem,Daphna Lifschitz,Dudu Moshe,Eitan Porat,Eitan Richardson,Guy Shiran,Itay Chachy,Jonathan Chetboun,Michael Finkelson,Michael Kupchick,Nir Zabari,Nitzan Guetta,Noa Kotler,Ofir Bibi,Ori Gordon,Poriya Panet,Roi Benita,Shahar Armon,Victor Kulikov,Yaron Inger,Yonatan Shiftan,Zeev Melumian,Zeev Farbman
机构: Lightricks
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Recent text-to-video diffusion models can generate compelling video sequences, yet they remain silent – missing the semantic, emotional, and atmospheric cues that audio provides. We introduce LTX-2, an open-source foundational model capable of generating high-quality, temporally synchronized audiovisual content in a unified manner. LTX-2 consists of an asymmetric dual-stream transformer with a 14B-parameter video stream and a 5B-parameter audio stream, coupled through bidirectional audio-video cross-attention layers with temporal positional embeddings and cross-modality AdaLN for shared timestep conditioning. This architecture enables efficient training and inference of a unified audiovisual model while allocating more capacity for video generation than audio generation. We employ a multilingual text encoder for broader prompt understanding and introduce a modality-aware classifier-free guidance (modality-CFG) mechanism for improved audiovisual alignment and controllability. Beyond generating speech, LTX-2 produces rich, coherent audio tracks that follow the characters, environment, style, and emotion of each scene – complete with natural background and foley elements. In our evaluations, the model achieves state-of-the-art audiovisual quality and prompt adherence among open-source systems, while delivering results comparable to proprietary models at a fraction of their computational cost and inference time. All model weights and code are publicly released.
zh
[CV-4] UniCorn: Towards Self-Improving Unified Multimodal Models through Self-Generated Supervision
【速读】:该论文旨在解决统一多模态模型(Unified Multimodal Models, UMMs)在跨模态理解与高质量生成之间存在的“传导性失语症”(Conduction Aphasia)问题,即模型虽能准确理解多模态输入,却难以将其转化为忠实且可控的生成结果。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为UniCorn的自监督改进框架,通过将单一UMM划分为三个协同角色——提议者(Proposer)、求解者(Solver)和裁判者(Judge),利用自我对弈(self-play)机制生成高质量交互,并采用认知模式重构(cognitive pattern reconstruction)技术将隐式理解提炼为显式的生成信号,从而实现无需外部数据或教师监督的端到端自提升。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03193
作者: Ruiyan Han,Zhen Fang,XinYu Sun,Yuchen Ma,Ziheng Wang,Yu Zeng,Zehui Chen,Lin Chen,Wenxuan Huang,Wei-Jie Xu,Yi Cao,Feng Zhao
机构: USTC (中国科学技术大学); FDU (复旦大学); ECNU (华东师范大学); CUHK (香港中文大学); NJU (南京大学); SUDA (苏州大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:While Unified Multimodal Models (UMMs) have achieved remarkable success in cross-modal comprehension, a significant gap persists in their ability to leverage such internal knowledge for high-quality generation. We formalize this discrepancy as Conduction Aphasia, a phenomenon where models accurately interpret multimodal inputs but struggle to translate that understanding into faithful and controllable synthesis. To address this, we propose UniCorn, a simple yet elegant self-improvement framework that eliminates the need for external data or teacher supervision. By partitioning a single UMM into three collaborative roles: Proposer, Solver, and Judge, UniCorn generates high-quality interactions via self-play and employs cognitive pattern reconstruction to distill latent understanding into explicit generative signals. To validate the restoration of multimodal coherence, we introduce UniCycle, a cycle-consistency benchmark based on a Text to Image to Text reconstruction loop. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniCorn achieves comprehensive and substantial improvements over the base model across six general image generation benchmarks. Notably, it achieves SOTA performance on TIIF(73.8), DPG(86.8), CompBench(88.5), and UniCycle while further delivering substantial gains of +5.0 on WISE and +6.5 on OneIG. These results highlight that our method significantly enhances T2I generation while maintaining robust comprehension, demonstrating the scalability of fully self-supervised refinement for unified multimodal intelligence.
zh
[CV-5] AnatomiX an Anatomy-Aware Grounded Multimodal Large Language Model for Chest X-Ray Interpretation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前多模态医学大语言模型在胸部X光片解读中面临的空间推理与解剖学理解不足的问题,尤其是现有定位(grounding)技术难以建立真正的解剖对应关系,导致医学领域内错误的解剖认知。解决方案的关键在于提出AnatomiX,一个专为解剖结构精准定位设计的多任务多模态大语言模型;其核心创新是采用两阶段架构:第一阶段识别解剖结构并提取特征,第二阶段利用大语言模型完成包括短语定位、报告生成、视觉问答和图像理解等下游任务,从而显著提升解剖合理性与跨任务性能,在解剖定位、短语定位、定位诊断和定位描述等任务上相较现有方法提升超25%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03191
作者: Anees Ur Rehman Hashmi,Numan Saeed,Christoph Lippert
机构: Hasso Plattner Institute (哈索普拉特纳研究所); MBZUAI (穆罕默德·本·扎耶德人工智能大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Multimodal medical large language models have shown impressive progress in chest X-ray interpretation but continue to face challenges in spatial reasoning and anatomical understanding. Although existing grounding techniques improve overall performance, they often fail to establish a true anatomical correspondence, resulting in incorrect anatomical understanding in the medical domain. To address this gap, we introduce AnatomiX, a multitask multimodal large language model explicitly designed for anatomically grounded chest X-ray interpretation. Inspired by the radiological workflow, AnatomiX adopts a two stage approach: first, it identifies anatomical structures and extracts their features, and then leverages a large language model to perform diverse downstream tasks such as phrase grounding, report generation, visual question answering, and image understanding. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that AnatomiX achieves superior anatomical reasoning and delivers over 25% improvement in performance on anatomy grounding, phrase grounding, grounded diagnosis and grounded captioning tasks compared to existing approaches. Code and pretrained model are available at this https URL
zh
[CV-6] DiffBench Meets DiffAgent : End-to-End LLM -Driven Diffusion Acceleration Code Generation AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决扩散模型(Diffusion Models)在实际部署中因多步推理过程导致的计算开销过大问题,以及如何有效组合多种模型加速技术这一关键挑战。解决方案的核心在于提出一个由大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)驱动的自动化加速代码生成与评估框架——DiffAgent,其通过闭环工作流实现策略优化:包含规划模块、调试模块和代码生成模块,并引入遗传算法从执行环境中提取性能反馈以指导后续代码迭代优化,从而显著提升扩散模型加速策略的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03178
作者: Jiajun jiao,Haowei Zhu,Puyuan Yang,Jianghui Wang,Ji Liu,Ziqiong Liu,Dong Li,Yuejian Fang,Junhai Yong,Bin Wang,Emad Barsoum
机构: 1. University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学); 2. Shenzhen Institute of Artificial Intelligence and Robotics for Society (深圳人工智能与机器人研究院); 3. Tsinghua University (清华大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted to AAAI 2026
Abstract:Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in image and video generation. However, their inherently multiple step inference process imposes substantial computational overhead, hindering real-world deployment. Accelerating diffusion models is therefore essential, yet determining how to combine multiple model acceleration techniques remains a significant challenge. To address this issue, we introduce a framework driven by large language models (LLMs) for automated acceleration code generation and evaluation. First, we present DiffBench, a comprehensive benchmark that implements a three stage automated evaluation pipeline across diverse diffusion architectures, optimization combinations and deployment scenarios. Second, we propose DiffAgent, an agent that generates optimal acceleration strategies and codes for arbitrary diffusion models. DiffAgent employs a closed-loop workflow in which a planning component and a debugging component iteratively refine the output of a code generation component, while a genetic algorithm extracts performance feedback from the execution environment to guide subsequent code refinements. We provide a detailed explanation of the DiffBench construction and the design principles underlying DiffAgent. Extensive experiments show that DiffBench offers a thorough evaluation of generated codes and that DiffAgent significantly outperforms existing LLMs in producing effective diffusion acceleration strategies.
zh
[CV-7] LSP-DETR: Efficient and Scalable Nuclei Segmentation in Whole Slide Images
【速读】:该论文旨在解决全切片图像(Whole-Slide Images, WSI)中细胞核实例分割的精度与可扩展性问题,现有方法依赖于基于图像块(patch-based)处理和昂贵的后处理步骤,导致上下文信息丢失且计算效率低下。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种端到端的LSP-DETR框架,该框架采用线性复杂度的轻量级Transformer架构,能够直接处理更大尺度图像而无需额外计算开销;同时,通过将细胞核表示为星凸多边形(star-convex polygons),并引入一种新颖的径向距离损失函数(radial distance loss),使重叠细胞核的分割自然涌现,无需显式的重叠标注或手工后处理步骤,从而在保证高精度的同时显著提升效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03163
作者: Matěj Pekár,Vít Musil,Rudolf Nenutil,Petr Holub,Tomáš Brázdil
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Precise and scalable instance segmentation of cell nuclei is essential for computational pathology, yet gigapixel Whole-Slide Images pose major computational challenges. Existing approaches rely on patch-based processing and costly post-processing for instance separation, sacrificing context and efficiency. We introduce LSP-DETR (Local Star Polygon DEtection TRansformer), a fully end-to-end framework that uses a lightweight transformer with linear complexity to process substantially larger images without additional computational cost. Nuclei are represented as star-convex polygons, and a novel radial distance loss function allows the segmentation of overlapping nuclei to emerge naturally, without requiring explicit overlap annotations or handcrafted post-processing. Evaluations on PanNuke and MoNuSeg show strong generalization across tissues and state-of-the-art efficiency, with LSP-DETR being over five times faster than the next-fastest leading method. Code and models are available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-8] Unified Thinker: A General Reasoning Modular Core for Image Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式AI在高保真图像合成中面临的逻辑密集型指令遵循能力不足的问题,即存在持续的“推理-执行差距”(reasoning–execution gap)。当前开源模型在复杂任务上的表现显著落后于闭源系统(如Nano Banana),其根源在于缺乏可执行的推理机制。解决方案的关键在于提出一种任务无关的推理架构——Unified Thinker,该架构将推理模块(Thinker)与图像生成器(Generator)解耦,形成一个可插拔的统一规划核心,从而实现无需重新训练整个生成模型即可对推理能力进行模块化升级。进一步地,通过两阶段训练范式:首先构建结构化的规划接口,再利用强化学习基于像素级反馈优化策略,使计划更注重视觉正确性而非仅文本合理性,从而显著提升图像生成的质量与逻辑一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03127
作者: Sashuai Zhou,Qiang Zhou,Jijin Hu,Hanqing Yang,Yue Cao,Junpeng Ma,Yinchao Ma,Jun Song,Tiezheng Ge,Cheng Yu,Bo Zheng,Zhou Zhao
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); Alibaba Group (阿里巴巴集团); Nanjing University (南京大学); Fudan University (复旦大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Despite impressive progress in high-fidelity image synthesis, generative models still struggle with logic-intensive instruction following, exposing a persistent reasoning–execution gap. Meanwhile, closed-source systems (e.g., Nano Banana) have demonstrated strong reasoning-driven image generation, highlighting a substantial gap to current open-source models. We argue that closing this gap requires not merely better visual generators, but executable reasoning: decomposing high-level intents into grounded, verifiable plans that directly steer the generative process. To this end, we propose Unified Thinker, a task-agnostic reasoning architecture for general image generation, designed as a unified planning core that can plug into diverse generators and workflows. Unified Thinker decouples a dedicated Thinker from the image Generator, enabling modular upgrades of reasoning without retraining the entire generative model. We further introduce a two-stage training paradigm: we first build a structured planning interface for the Thinker, then apply reinforcement learning to ground its policy in pixel-level feedback, encouraging plans that optimize visual correctness over textual plausibility. Extensive experiments on text-to-image generation and image editing show that Unified Thinker substantially improves image reasoning and generation quality.
zh
[CV-9] LeafLife: An Explainable Deep Learning Framework with Robustness for Grape Leaf Disease Recognition
【速读】:该论文旨在解决葡萄叶片病害的精准识别问题,以支持农民做出科学的田间管理决策,从而提升作物产量与品质。其关键解决方案在于采用预训练深度卷积神经网络模型(InceptionV3 和 Xception)对9,032张葡萄叶图像进行分类,其中Xception模型在70%训练、20%验证和10%测试的数据划分下达到96.23%的准确率,显著优于InceptionV3;同时引入对抗训练(Adversarial Training)增强模型鲁棒性,并结合梯度加权类激活映射(Grad-CAM)生成热力图可视化病灶区域,提高模型可解释性;最终通过Streamlit框架部署Web应用,实现病害分类结果与置信度的直观展示,形成端到端的智能诊断系统。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03124
作者: B. M. Shahria Alam,Md. Nasim Ahmed
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 4 pages, 8 figures, 2025 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Information, Communication and Systems (SPICSCON)
Abstract:Plant disease diagnosis is essential to farmers’ management choices because plant diseases frequently lower crop yield and product quality. For harvests to flourish and agricultural productivity to boost, grape leaf disease detection is important. The plant disease dataset contains grape leaf diseases total of 9,032 images of four classes, among them three classes are leaf diseases, and the other one is healthy leaves. After rigorous pre-processing dataset was split (70% training, 20% validation, 10% testing), and two pre-trained models were deployed: InceptionV3 and Xception. Xception shows a promising result of 96.23% accuracy, which is remarkable than InceptionV3. Adversarial Training is used for robustness, along with more transparency. Grad-CAM is integrated to confirm the leaf disease. Finally deployed a web application using Streamlit with a heatmap visualization and prediction with confidence level for robust grape leaf disease classification.
zh
[CV-10] xt-Guided Layer Fusion Mitigates Hallucination in Multimodal LLM s
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)中视觉表征利用不足与视觉误导性幻觉(visually ungrounded hallucinations)的问题。现有方法通常仅使用冻结视觉编码器的单一高层特征,忽视了其多层次的视觉线索,并且多数缓解策略仅作用于文本侧,未能充分利用视觉特征的层次结构。论文提出的关键解决方案是TGIF(Text-Guided Inter-layer Fusion),它将视觉编码器的不同层视为深度卷积“专家”,并基于输入提示动态预测一个查询相关的视觉特征融合方案,实现轻量级、无需更新视觉编码器的层次感知融合,从而增强视觉 grounding 效果并减少幻觉。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03100
作者: Chenchen Lin,Sanbao Su,Rachel Luo,Yuxiao Chen,Yan Wang,Marco Pavone,Fei Miao
机构: University of Connecticut (康涅狄格大学); NVIDIA (英伟达); Stanford University (斯坦福大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) typically rely on a single late-layer feature from a frozen vision encoder, leaving the encoder’s rich hierarchy of visual cues under-utilized. MLLMs still suffer from visually ungrounded hallucinations, often relying on language priors rather than image evidence. While many prior mitigation strategies operate on the text side, they leave the visual representation unchanged and do not exploit the rich hierarchy of features encoded across vision layers. Existing multi-layer fusion methods partially address this limitation but remain static, applying the same layer mixture regardless of the query. In this work, we introduce TGIF (Text-Guided Inter-layer Fusion), a lightweight module that treats encoder layers as depth-wise “experts” and predicts a prompt-dependent fusion of visual features. TGIF follows the principle of direct external fusion, requires no vision-encoder updates, and adds minimal overhead. Integrated into LLaVA-1.5-7B, TGIF provides consistent improvements across hallucination, OCR, and VQA benchmarks, while preserving or improving performance on ScienceQA, GQA, and MMBench. These results suggest that query-conditioned, hierarchy-aware fusion is an effective way to strengthen visual grounding and reduce hallucination in modern MLLMs.
zh
[CV-11] LesionTABE: Equitable AI for Skin Lesion Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI 在皮肤科临床应用中因肤色偏见导致的公平性问题,即现有诊断模型在深色皮肤上的表现显著低于浅色皮肤。解决方案的关键在于提出 LesionTABE 框架,该框架结合对抗去偏(adversarial debiasing)与皮肤病学特定的基础模型嵌入(dermatology-specific foundation model embeddings),从而在多个涵盖恶性与炎症性病变的数据集上实现公平性指标提升超过 25%,同时保持或提高整体诊断准确率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03090
作者: Rocio Mexia Diaz,Yasmin Greenway,Petru Manescu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Submitted to IEEE ISBI 2026
Abstract:Bias remains a major barrier to the clinical adoption of AI in dermatology, as diagnostic models underperform on darker skin tones. We present LesionTABE, a fairness-centric framework that couples adversarial debiasing with dermatology-specific foundation model embeddings. Evaluated across multiple datasets covering both malignant and inflammatory conditions, LesionTABE achieves over a 25% improvement in fairness metrics compared to a ResNet-152 baseline, outperforming existing debiasing methods while simultaneously enhancing overall diagnostic accuracy. These results highlight the potential of foundation model debiasing as a step towards equitable clinical AI adoption.
zh
[CV-12] Understanding Multi-Agent Reasoning with Large Language Models for Cartoon VQA
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)在处理风格化卡通图像时的视觉问答(Visual Question Answering, VQA)任务中存在的挑战,尤其是对夸张视觉抽象和叙事驱动上下文的理解不足问题。现有大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)主要基于自然图像训练,在面对卡通图像时表现受限。解决方案的关键在于提出一种多智能体大语言模型(multi-agent LLM)框架,由三个专业化代理协同工作:视觉代理(visual agent)、语言代理(language agent)和批评代理(critic agent),通过整合视觉线索与叙事上下文实现结构化推理,从而提升在卡通图像上的多模态推理能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03073
作者: Tong Wu,Thanet Markchom
机构: University of Reading (雷丁大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Visual Question Answering (VQA) for stylised cartoon imagery presents challenges, such as interpreting exaggerated visual abstraction and narrative-driven context, which are not adequately addressed by standard large language models (LLMs) trained on natural images. To investigate this issue, a multi-agent LLM framework is introduced, specifically designed for VQA tasks in cartoon imagery. The proposed architecture consists of three specialised agents: visual agent, language agent and critic agent, which work collaboratively to support structured reasoning by integrating visual cues and narrative context. The framework was systematically evaluated on two cartoon-based VQA datasets: Pororo and Simpsons. Experimental results provide a detailed analysis of how each agent contributes to the final prediction, offering a deeper understanding of LLM-based multi-agent behaviour in cartoon VQA and multimodal inference.
zh
[CV-13] Fine-Grained Generalization via Structuralizing Concept and Feature Space into Commonality Specificity and Confounding AAAI26
【速读】:该论文旨在解决细粒度领域泛化(Fine-Grained Domain Generalization, FGDG)中的性能下降问题,其核心挑战在于细粒度识别任务中类间差异细微而类内变化显著,导致模型在域迁移时对细粒度特征过度敏感,从而抑制关键特征并降低泛化能力。解决方案的关键在于提出概念-特征结构化泛化(Concept-Feature Structuralized Generalization, CFSG)模型,该模型将概念空间与特征空间显式解耦为三类结构化组件:共性(common)、特异性(specific)和混淆性(confounding)部分,并引入自适应机制动态调整各组件比例以应对不同强度的分布偏移,同时在最终预测中为每对组件分配显式权重,从而实现多粒度结构化知识的有效融合与利用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03056
作者: Zhen Wang,Jiaojiao Zhao,Qilong Wang,Yongfeng Dong,Wenlong Yu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted in AAAI26
Abstract:Fine-Grained Domain Generalization (FGDG) presents greater challenges than conventional domain generalization due to the subtle inter-class differences and relatively pronounced intra-class variations inherent in fine-grained recognition tasks. Under domain shifts, the model becomes overly sensitive to fine-grained cues, leading to the suppression of critical features and a significant drop in performance. Cognitive studies suggest that humans classify objects by leveraging both common and specific attributes, enabling accurate differentiation between fine-grained categories. However, current deep learning models have yet to incorporate this mechanism effectively. Inspired by this mechanism, we propose Concept-Feature Structuralized Generalization (CFSG). This model explicitly disentangles both the concept and feature spaces into three structured components: common, specific, and confounding segments. To mitigate the adverse effects of varying degrees of distribution shift, we introduce an adaptive mechanism that dynamically adjusts the proportions of common, specific, and confounding components. In the final prediction, explicit weights are assigned to each pair of components. Extensive experiments on three single-source benchmark datasets demonstrate that CFSG achieves an average performance improvement of 9.87% over baseline models and outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods by an average of 3.08%. Additionally, explainability analysis validates that CFSG effectively integrates multi-granularity structured knowledge and confirms that feature structuralization facilitates the emergence of concept structuralization.
zh
[CV-14] IBISAgent : Reinforcing Pixel-Level Visual Reasoning in MLLM s for Universal Biomedical Object Referring and Segmentation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前医学多模态大语言模型(Medical MLLMs)在像素级理解任务中面临的两大挑战:一是现有分割方法引入隐式分割标记并需同时微调MLLM与外部像素解码器,易导致灾难性遗忘且泛化能力弱;二是多数方法依赖单次推理,缺乏迭代优化能力,难以生成高质量分割结果。解决方案的关键在于提出一种新型代理型多模态大语言模型IBISAgent,其将分割重构为以视觉为中心的多步决策过程,使模型能够生成交错的推理链与基于文本的点击动作、调用分割工具,并在不修改架构的前提下生成高精度掩码。通过在掩码图像特征上进行多步视觉推理,IBISAgent天然支持掩码精炼,显著提升像素级视觉推理能力。此外,设计了两阶段训练框架——冷启动监督微调与面向细粒度奖励的代理强化学习,进一步增强模型在复杂医学指代和推理分割任务中的鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03054
作者: Yankai Jiang,Qiaoru Li,Binlu Xu,Haoran Sun,Chao Ding,Junting Dong,Yuxiang Cai,Xuhong Zhang,Jianwei Yin
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (上海人工智能实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Recent research on medical MLLMs has gradually shifted its focus from image-level understanding to fine-grained, pixel-level comprehension. Although segmentation serves as the foundation for pixel-level understanding, existing approaches face two major challenges. First, they introduce implicit segmentation tokens and require simultaneous fine-tuning of both the MLLM and external pixel decoders, which increases the risk of catastrophic forgetting and limits generalization to out-of-domain scenarios. Second, most methods rely on single-pass reasoning and lack the capability to iteratively refine segmentation results, leading to suboptimal performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel agentic MLLM, named IBISAgent, that reformulates segmentation as a vision-centric, multi-step decision-making process. IBISAgent enables MLLMs to generate interleaved reasoning and text-based click actions, invoke segmentation tools, and produce high-quality masks without architectural modifications. By iteratively performing multi-step visual reasoning on masked image features, IBISAgent naturally supports mask refinement and promotes the development of pixel-level visual reasoning capabilities. We further design a two-stage training framework consisting of cold-start supervised fine-tuning and agentic reinforcement learning with tailored, fine-grained rewards, enhancing the model’s robustness in complex medical referring and reasoning segmentation tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that IBISAgent consistently outperforms both closed-source and open-source SOTA methods. All datasets, code, and trained models will be released publicly.
zh
[CV-15] On the Intrinsic Limits of Transformer Image Embeddings in Non-Solvable Spatial Reasoning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉 Transformer (Vision Transformer, ViT) 在空间推理任务(如心理旋转)中系统性失效的问题,尽管其在语义识别方面表现优异。解决方案的关键在于从计算复杂性理论出发,将空间理解建模为保持变换群代数结构的同态映射(Group Homomorphism),并证明对于非可解群(如三维旋转群 SO(3)),此类结构保持嵌入的计算下界为 Word Problem 问题,属于 NC¹-完全类;而常深度 ViT 在多项式精度下仅能实现 TC⁰ 计算能力。基于 TC⁰ ⊂neq NC¹ 的假设,作者确立了常深度 ViT 在表达非可解空间结构上的根本局限性,并通过潜空间探测验证了随着组合深度增加,ViT 表征会出现结构性坍缩。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03048
作者: Siyi Lyu,Quan Liu,Feng Yan
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computational Complexity (cs.CC)
备注:
Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) excel in semantic recognition but exhibit systematic failures in spatial reasoning tasks such as mental rotation. While often attributed to data scale, we propose that this limitation arises from the intrinsic circuit complexity of the architecture. We formalize spatial understanding as learning a Group Homomorphism: mapping image sequences to a latent space that preserves the algebraic structure of the underlying transformation group. We demonstrate that for non-solvable groups (e.g., the 3D rotation group \mathrmSO(3) ), maintaining such a structure-preserving embedding is computationally lower-bounded by the Word Problem, which is \mathsfNC^1 -complete. In contrast, we prove that constant-depth ViTs with polynomial precision are strictly bounded by \mathsfTC^0 . Under the conjecture \mathsfTC^0 \subsetneq \mathsfNC^1 , we establish a complexity boundary: constant-depth ViTs fundamentally lack the logical depth to efficiently capture non-solvable spatial structures. We validate this complexity gap via latent-space probing, demonstrating that ViT representations suffer a structural collapse on non-solvable tasks as compositional depth increases.
zh
[CV-16] Motion Blur Robust Wheat Pest Damage Detection with Dynamic Fuzzy Feature Fusion
【速读】:该论文旨在解决由相机抖动引起的运动模糊(motion blur)导致的边缘侧目标检测性能下降问题,尤其是传统方法在抑制模糊时易丢失判别性结构,或采用全图恢复策略增加延迟、限制在资源受限设备上的部署。其核心解决方案是提出动态模糊鲁棒卷积金字塔(DFRCP),作为YOLOv11的即插即用增强模块:通过融合大尺度与中尺度特征并保留原始表示,引入动态鲁棒切换单元(Dynamic Robust Switch units)以自适应注入模糊特征来强化全局感知;模糊特征由多尺度特征旋转与非线性插值合成,并经透明卷积学习内容自适应权衡原始与模糊线索。此外,设计CUDA并行旋转与插值核避免边界溢出,实现超过400倍加速,使方案具备边缘部署可行性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03046
作者: Han Zhang,Yanwei Wang,Fang Li,Hongjun Wang
机构: Changji College (昌吉学院); Shandong University (山东大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Motion blur caused by camera shake produces ghosting artifacts that substantially degrade edge side object detection. Existing approaches either suppress blur as noise and lose discriminative structure, or apply full image restoration that increases latency and limits deployment on resource constrained devices. We propose DFRCP, a Dynamic Fuzzy Robust Convolutional Pyramid, as a plug in upgrade to YOLOv11 for blur robust detection. DFRCP enhances the YOLOv11 feature pyramid by combining large scale and medium scale features while preserving native representations, and by introducing Dynamic Robust Switch units that adaptively inject fuzzy features to strengthen global perception under jitter. Fuzzy features are synthesized by rotating and nonlinearly interpolating multiscale features, then merged through a transparency convolution that learns a content adaptive trade off between original and fuzzy cues. We further develop a CUDA parallel rotation and interpolation kernel that avoids boundary overflow and delivers more than 400 times speedup, making the design practical for edge deployment. We train with paired supervision on a private wheat pest damage dataset of about 3,500 images, augmented threefold using two blur regimes, uniform image wide motion blur and bounding box confined rotational blur. On blurred test sets, YOLOv11 with DFRCP achieves about 10.4 percent higher accuracy than the YOLOv11 baseline with only a modest training time overhead, reducing the need for manual filtering after data collection.
zh
[CV-17] Flow Matching and Diffusion Models via PointNet for Generating Fluid Fields on Irregular Geometries
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在不规则几何域上预测流体流动变量(如速度场、压力场及升力/阻力)时,传统方法因依赖规则网格投影或复杂图神经网络结构而导致的精度不足与噪声问题。其解决方案的关键在于将PointNet引入流匹配(Flow Matching)和扩散模型(Diffusion Models)中,构建两种新型生成式几何深度学习框架——Flow Matching PointNet 和 Diffusion PointNet。这些框架直接在点云表示的计算域上操作,避免了像素化带来的信息失真,并通过单一的PointNet架构实现几何条件编码,无需额外的辅助网络,从而简化模型结构并提升预测精度与鲁棒性,尤其在处理不完整几何输入时表现更优。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03030
作者: Ali Kashefi
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computational Physics (physics.comp-ph)
备注:
Abstract:We present two novel generative geometric deep learning frameworks, termed Flow Matching PointNet and Diffusion PointNet, for predicting fluid flow variables on irregular geometries by incorporating PointNet into flow matching and diffusion models, respectively. In these frameworks, a reverse generative process reconstructs physical fields from standard Gaussian noise conditioned on unseen geometries. The proposed approaches operate directly on point-cloud representations of computational domains (e.g., grid vertices of finite-volume meshes) and therefore avoid the limitations of pixelation used to project geometries onto uniform lattices. In contrast to graph neural network-based diffusion models, Flow Matching PointNet and Diffusion PointNet do not exhibit high-frequency noise artifacts in the predicted fields. Moreover, unlike such approaches, which require auxiliary intermediate networks to condition geometry, the proposed frameworks rely solely on PointNet, resulting in a simple and unified architecture. The performance of the proposed frameworks is evaluated on steady incompressible flow past a cylinder, using a geometric dataset constructed by varying the cylinder’s cross-sectional shape and orientation across samples. The results demonstrate that Flow Matching PointNet and Diffusion PointNet achieve more accurate predictions of velocity and pressure fields, as well as lift and drag forces, and exhibit greater robustness to incomplete geometries compared to a vanilla PointNet with the same number of trainable parameters.
zh
[CV-18] SA-ResGS: Self-Augmented Residual 3D Gaussian Splatting for Next Best View Selection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决主动场景重建中Next-Best-View (NBV) 选择的不确定性量化不稳定以及监督信号不足的问题,尤其在稀疏和远基线视角下,传统方法易导致高不确定性区域学习信号弱、训练不稳定性增加。其解决方案的关键在于提出Self-Augmented Residual 3D Gaussian Splatting (SA-ResGS),通过两种核心机制实现:一是基于物理引导的视图选择策略,利用训练视图与光栅化外推视图之间的三角测量生成自增强点云(SA-Points),提升场景覆盖率估计效率;二是引入专为3D Gaussian Splatting设计的残差学习监督机制,结合不确定性驱动过滤与dropout及硬负样本挖掘启发的采样策略,增强高不确定性高斯点的梯度传播,从而改善模型训练稳定性和不确定性估计准确性。此方案还隐式缓解了宽基线探索与稀疏视图模糊性之间的冲突,提升了NBV规划的鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03024
作者: Kim Jun-Seong,Tae-Hyun Oh,Eduardo Pérez-Pellitero,Youngkyoon Jang
机构: POSTECH(浦项科技大学); KAIST(韩国科学技术院); Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab(华为诺亚方舟实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:We propose Self-Augmented Residual 3D Gaussian Splatting (SA-ResGS), a novel framework to stabilize uncertainty quantification and enhancing uncertainty-aware supervision in next-best-view (NBV) selection for active scene reconstruction. SA-ResGS improves both the reliability of uncertainty estimates and their effectiveness for supervision by generating Self-Augmented point clouds (SA-Points) via triangulation between a training view and a rasterized extrapolated view, enabling efficient scene coverage estimation. While improving scene coverage through physically guided view selection, SA-ResGS also addresses the challenge of under-supervised Gaussians, exacerbated by sparse and wide-baseline views, by introducing the first residual learning strategy tailored for 3D Gaussian Splatting. This targeted supervision enhances gradient flow in high-uncertainty Gaussians by combining uncertainty-driven filtering with dropout- and hard-negative-mining-inspired sampling. Our contributions are threefold: (1) a physically grounded view selection strategy that promotes efficient and uniform scene coverage; (2) an uncertainty-aware residual supervision scheme that amplifies learning signals for weakly contributing Gaussians, improving training stability and uncertainty estimation across scenes with diverse camera distributions; (3) an implicit unbiasing of uncertainty quantification as a consequence of constrained view selection and residual supervision, which together mitigate conflicting effects of wide-baseline exploration and sparse-view ambiguity in NBV planning. Experiments on active view selection demonstrate that SA-ResGS outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in both reconstruction quality and view selection robustness.
zh
[CV-19] ReCCur: A Recursive Corner-Case Curation Framework for Robust Vision-Language Understanding in Open and Edge Scenarios
【速读】:该论文旨在解决真实世界中罕见或极端场景(即corner cases)难以规模化构建高质量标注数据的问题,这类场景常导致系统失效,但传统方法受限于网络数据噪声大、标签脆弱以及边缘部署无法进行大规模重训练等挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种低计算开销的递归式异常案例精炼框架ReCCur,通过多智能体递归流水线实现:首先利用视觉-语言模型(VLM)进行大规模数据采集与过滤,并结合轻量级人工抽检确保图像、描述和关键词三模态一致性;其次采用专家混合知识蒸馏策略,融合多种编码器(如CLIP、DINOv2、BEiT)进行kNN投票与双置信度激活及不确定性采样,逐步收敛至高精度标签集;最后引入基于区域证据的对抗性标注机制,由提案者(多粒度区域与语义线索)与验证者(全局与局部链式一致性)协同生成可解释标签并形成闭环优化。该方法在消费级GPU上即可运行,显著提升标签纯度与可分离性,且仅需极少人工干预,为资源受限环境下的下游训练与评估提供实用基础。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03011
作者: Yihan Wei,Shenghai Yuan,Tianchen Deng,Boyang Lou,Enwen Hu
机构: Nanyang Technological University (南洋理工大学); Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (北京邮电大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注:
Abstract:Corner cases are rare or extreme scenarios that drive real-world failures, but they are difficult to curate at scale: web data are noisy, labels are brittle, and edge deployments preclude large retraining. We present ReCCur (Recursive Corner-Case Curation), a low-compute framework that converts noisy web imagery into auditable fine-grained labels via a multi-agent recursive pipeline. First, large-scale data acquisition and filtering expands a domain vocabulary with a vision-language model (VLM), crawls the web, and enforces tri-modal (image, description, keyword) consistency with light human spot checks to yield refined candidates. Next, mixture-of-experts knowledge distillation uses complementary encoders (e.g., CLIP, DINOv2, BEiT) for kNN voting with dual-confidence activation and uncertainty sampling, converging to a high-precision set. Finally, region-evidence VLM adversarial labeling pairs a proposer (multi-granularity regions and semantic cues) with a validator (global and local chained consistency) to produce explainable labels and close the loop. On realistic corner-case scenarios (e.g., flooded-car inspection), ReCCur runs on consumer-grade GPUs, steadily improves purity and separability, and requires minimal human supervision, providing a practical substrate for downstream training and evaluation under resource constraints. Code and dataset will be released.
zh
[CV-20] owards Efficient 3D Object Detection for Vehicle-Infrastructure Collaboration via Risk-Intent Selection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决车辆-基础设施协同感知(Vehicle-Infrastructure Collaborative Perception, VICP)中通信带宽与特征冗余之间的权衡问题,尤其针对现有方法依赖空间压缩或静态置信度图导致非关键背景区域特征无效传输的瓶颈。解决方案的关键在于提出一种交互感知的“风险-意图选择性检测”(Risk-intent Selective detection, RiSe)框架,其核心创新包括:基于势场理论构建的潜在场-轨迹相关模型(Potential Field-Trajectory Correlation Model, PTCM),用于定量评估运动学风险;以及利用自车运动先验的意图驱动区域预测模块(Intention-Driven Area Prediction Module, IDAPM),主动预测并筛选对决策至关重要的鸟瞰图(Bird’s-Eye-View, BEV)区域。通过融合这两个模块,RiSe实现了仅在高交互区域传输高保真特征的语义选择性融合机制,有效充当特征去噪器,在DeepAccident数据集上将通信量降至全特征共享的0.71%,同时保持最先进的检测精度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03001
作者: Li Wang,Boqi Li,Hang Chen,Xingjian Wu,Yichen Wang,Jiewen Tan,Xinyu Zhang,Huaping Liu
机构: Beijing Institute of Technology (北京理工大学); Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology (重庆创新中心,北京理工大学); Wuhan University of Technology (武汉理工大学); University of Michigan (密歇根大学); Sun Yat-Sen University (中山大学); Harbin Institute of Technology (哈尔滨工业大学); University of California, Irvine (加州大学欧文分校); Tsinghua University (清华大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Vehicle-Infrastructure Collaborative Perception (VICP) is pivotal for resolving occlusion in autonomous driving, yet the trade-off between communication bandwidth and feature redundancy remains a critical bottleneck. While intermediate fusion mitigates data volume compared to raw sharing, existing frameworks typically rely on spatial compression or static confidence maps, which inefficiently transmit spatially redundant features from non-critical background regions. To address this, we propose Risk-intent Selective detection (RiSe), an interaction-aware framework that shifts the paradigm from identifying visible regions to prioritizing risk-critical ones. Specifically, we introduce a Potential Field-Trajectory Correlation Model (PTCM) grounded in potential field theory to quantitatively assess kinematic risks. Complementing this, an Intention-Driven Area Prediction Module (IDAPM) leverages ego-motion priors to proactively predict and filter key Bird’s-Eye-View (BEV) areas essential for decision-making. By integrating these components, RiSe implements a semantic-selective fusion scheme that transmits high-fidelity features only from high-interaction regions, effectively acting as a feature denoiser. Extensive experiments on the DeepAccident dataset demonstrate that our method reduces communication volume to 0.71% of full feature sharing while maintaining state-of-the-art detection accuracy, establishing a competitive Pareto frontier between bandwidth efficiency and perception performance.
zh
[CV-21] From Memorization to Creativity: LLM as a Designer of Novel Neural-Architectures
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在神经网络架构设计中缺乏自主导航能力的问题,即如何在保证结构语法正确性、提升性能指标的同时实现结构新颖性。其核心挑战在于将LLM从文本生成任务扩展至可执行的、具有实际性能反馈的架构合成过程。解决方案的关键在于构建一个闭环合成框架:通过将代码导向型LLM嵌入到包含验证、低 fidelity 性能评估(单轮次准确率)、MinHash-Jaccard结构去重机制的迭代流程中,使模型基于执行反馈持续优化;同时采用参数高效微调方法LoRA对高绩效且新颖的架构进行prompt-code对的迭代训练,从而让模型逐步内化经验性的架构先验知识。实验表明,该方法显著提升了有效生成率和初始性能表现,并成功挖掘出455个原始数据集中未见的高性能架构,证明了LLM可通过非文本奖励信号实现对架构空间的自主探索与优化。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02997
作者: Waleed Khalid,Dmitry Ignatov,Radu Timofte
机构: Computer Vision Lab, CAIDAS & IFI, University of Würzburg (维尔茨堡大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel in program synthesis, yet their ability to autonomously navigate neural architecture design–balancing syntactic reliability, performance, and structural novelty–remains underexplored. We address this by placing a code-oriented LLM within a closed-loop synthesis framework, analyzing its evolution over 22 supervised fine-tuning cycles. The model synthesizes PyTorch convolutional networks which are validated, evaluated via low-fidelity performance signals (single-epoch accuracy), and filtered using a MinHash-Jaccard criterion to prevent structural redundancy. High-performing, novel architectures are converted into prompt-code pairs for iterative fine-tuning via parameter-efficient LoRA adaptation, initialized from the LEMUR dataset. Across cycles, the LLM internalizes empirical architectural priors, becoming a robust generator. The valid generation rate stabilizes at 50.6 percent (peaking at 74.5 percent), while mean first-epoch accuracy rises from 28.06 percent to 50.99 percent, and the fraction of candidates exceeding 40 percent accuracy grows from 2.04 percent to 96.81 percent. Analyses confirm the model moves beyond replicating existing motifs, synthesizing 455 high-performing architectures absent from the original corpus. By grounding code synthesis in execution feedback, this work provides a scalable blueprint for transforming stochastic generators into autonomous, performance-driven neural designers, establishing that LLMs can internalize empirical, non-textual rewards to transcend their training data.
zh
[CV-22] owards Faithful Reasoning in Comics for Small MLLM s
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)在漫画视觉问答(Comic-based Visual Question Answering, CVQA)任务中因符号抽象、叙事逻辑和幽默理解等复杂特性而导致的性能瓶颈问题,尤其是小规模多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在使用传统思维链(Chain-of-Thought, CoT)提示时表现下降的问题。其核心挑战在于标准CoT在CVQA中存在状态纠缠(state entanglement)、虚假转移(spurious transitions)和探索效率低下等问题,尤其对资源受限的小模型影响显著。解决方案的关键在于提出一种新颖的漫画推理框架,通过模块化CoT生成与基于GRPO(Generalized Reward Policy Optimization)的强化学习微调相结合,并引入一种结构化奖励机制,从而提升小模型在CVQA及其他以幽默和抽象推理为核心的视觉任务中的推理忠实度与迁移能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02991
作者: Chengcheng Feng,Haojie Yin,Yucheng Jin,Kaizhu Huang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Comic-based visual question answering (CVQA) poses distinct challenges to multimodal large language models (MLLMs) due to its reliance on symbolic abstraction, narrative logic, and humor, which differ from conventional VQA tasks. Although Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting is widely used to enhance MLLM reasoning, surprisingly, its direct application to CVQA often degrades performance, especially in small-scale models. Our theoretical and empirical analyses reveal that standard CoT in CVQA suffers from state entanglement, spurious transitions, and exploration inefficiency, with small models particularly vulnerable in resource-constrained settings. To address these issues, we propose a novel comic reasoning framework, designed to produce more faithful and transferable reasoning chains in small MLLMs. Specifically, our framework combines modular CoT generation with GRPO-based reinforcement fine-tuning and a novel structured reward. Beyond comic VQA, we further evaluate our approach on a broader class of humor-centric and abstract visual reasoning tasks, including meme understanding and editorial cartoon interpretation. Across five challenging benchmarks, our 3B model outperforms state-of-the-art methods, and plug-in experiments yield an additional average improvement of \mathbf12.1% across different MLLMs.
zh
[CV-23] ULS: Data-driven Model Adaptation Enhances Lesion Segmentation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学影像中全身病变(lesion)自动分割的准确性与效率问题,尤其针对基于点击点(click-point)引导的体积兴趣区域(VOI)内病变分割任务。原有Universal Lesion Segmentation (ULS)模型虽已具备跨部位病变识别能力,但受限于训练数据规模和输入图像尺寸,存在精度不足与推理速度较慢的问题。解决方案的关键在于:一是引入多个新公开数据集以增强模型泛化能力;二是采用更小的输入图像尺寸,在保证性能的前提下显著提升推理速度;三是通过持续的数据驱动更新与临床验证机制,确保模型在真实医疗场景中的鲁棒性和实用性。实验表明,改进后的ULS+在Dice分数和对点击点位置变化的稳定性上均显著优于原版模型,并在ULS23 Challenge测试集上排名第一。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02988
作者: Rianne Weber,Niels Rocholl,Max de Grauw,Mathias Prokop,Ewoud Smit,Alessa Hering
机构: Radboud University Medical Center (奈梅亨大学医学中心)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted for publication at BVM 2026 (Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin), peer-reviewed conference paper
Abstract:In this study, we present ULS+, an enhanced version of the Universal Lesion Segmentation (ULS) model. The original ULS model segments lesions across the whole body in CT scans given volumes of interest (VOIs) centered around a click-point. Since its release, several new public datasets have become available that can further improve model performance. ULS+ incorporates these additional datasets and uses smaller input image sizes, resulting in higher accuracy and faster inference. We compared ULS and ULS+ using the Dice score and robustness to click-point location on the ULS23 Challenge test data and a subset of the Longitudinal-CT dataset. In all comparisons, ULS+ significantly outperformed ULS. Additionally, ULS+ ranks first on the ULS23 Challenge test-phase leaderboard. By maintaining a cycle of data-driven updates and clinical validation, ULS+ establishes a foundation for robust and clinically relevant lesion segmentation models. Comments: Accepted for publication at BVM 2026 (Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin), peer-reviewed conference paper Subjects: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02988 [cs.CV] (or arXiv:2601.02988v1 [cs.CV] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02988 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[CV-24] LAMS-Edit: Latent and Attention Mixing with Schedulers for Improved Content Preservation in Diffusion-Based Image and Style Editing
【速读】:该论文旨在解决扩散模型在文本到图像编辑(Text-to-Image editing)中面临的两个核心挑战:一是如何在保持原始内容不变的前提下准确应用编辑指令,二是如何有效处理真实图像的编辑任务。解决方案的关键在于提出LAMS-Edit框架,其核心创新是利用图像逆过程(inversion process)中提取的中间状态——包括潜在表示(latent representations)和注意力图(attention maps)——在生成过程中通过加权插值进行融合,且该融合由调度器(scheduler)控制。这种Latent and Attention Mixing with Schedulers(LAMS)机制与Prompt-to-Prompt(P2P)方法结合,实现了高精度区域掩码编辑和基于LoRA的风格迁移能力,从而在内容保留与编辑效果之间取得良好平衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02987
作者: Wingwa Fu,Takayuki Okatani
机构: Tohoku University (东北大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Text-to-Image editing using diffusion models faces challenges in balancing content preservation with edit application and handling real-image editing. To address these, we propose LAMS-Edit, leveraging intermediate states from the inversion process–an essential step in real-image editing–during edited image generation. Specifically, latent representations and attention maps from both processes are combined at each step using weighted interpolation, controlled by a scheduler. This technique, Latent and Attention Mixing with Schedulers (LAMS), integrates with Prompt-to-Prompt (P2P) to form LAMS-Edit–an extensible framework that supports precise editing with region masks and enables style transfer via LoRA. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LAMS-Edit effectively balances content preservation and edit application.
zh
[CV-25] VTONQA: A Multi-Dimensional Quality Assessment Dataset for Virtual Try-on
【速读】:该论文旨在解决图像驱动的虚拟试衣(Virtual Try-On, VTON)生成图像中存在的质量评估难题,特别是现有模型常出现服装扭曲和人体不一致等伪影问题,导致难以可靠地衡量生成结果的质量。解决方案的关键在于构建首个面向VTON的多维质量评估数据集VTONQA,该数据集包含11种代表性VTON模型生成的8,132张图像及对应24,396条平均意见得分(Mean Opinion Scores, MOS),覆盖服装贴合度、身体适配性和整体质量三个维度。基于此数据集,论文进一步对VTON模型与多种图像质量评估(Image Quality Assessment, IQA)指标进行了基准测试,揭示了现有方法的局限性,并验证了VTONQA在推动感知一致性评价方面的价值。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02945
作者: Xinyi Wei,Sijing Wu,Zitong Xu,Yunhao Li,Huiyu Duan,Xiongkuo Min,Guangtao Zhai
机构: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:With the rapid development of e-commerce and digital fashion, image-based virtual try-on (VTON) has attracted increasing attention. However, existing VTON models often suffer from artifacts such as garment distortion and body inconsistency, highlighting the need for reliable quality evaluation of VTON-generated images. To this end, we construct VTONQA, the first multi-dimensional quality assessment dataset specifically designed for VTON, which contains 8,132 images generated by 11 representative VTON models, along with 24,396 mean opinion scores (MOSs) across three evaluation dimensions (i.e., clothing fit, body compatibility, and overall quality). Based on VTONQA, we benchmark both VTON models and a diverse set of image quality assessment (IQA) metrics, revealing the limitations of existing methods and highlighting the value of the proposed dataset. We believe that the VTONQA dataset and corresponding benchmarks will provide a solid foundation for perceptually aligned evaluation, benefiting both the development of quality assessment methods and the advancement of VTON models.
zh
[CV-26] HybridSolarNet: A Lightweight and Explainable EfficientNet-CBAM Architecture for Real-Time Solar Panel Fault Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决太阳能板系统人工巡检效率低、成本高且易出错的问题,提出一种适用于无人机(UAV)实时监测的轻量化、高精度故障检测模型。其关键解决方案是设计了HybridSolarNet模型,该模型融合了EfficientNet-B0与卷积块注意力模块(Convolutional Block Attention Module, CBAM),通过引入焦点损失(focal loss)缓解类别不平衡问题,并采用余弦退火(cosine annealing)优化训练过程;同时采用“分割-增强”协议避免评估偏差,最终在Kaggle太阳能板图像竞赛数据集上实现了92.37% ± 0.41的平均准确率和54.9 FPS的推理速度,显著优于VGG19等基线模型,且仅需16.3 MB存储空间,具备边缘计算部署可行性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02928
作者: Md. Asif Hossain,G M Mota-Tahrin Tayef,Nabil Subhan
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 5 page , 6 figures
Abstract:Manual inspections for solar panel systems are a tedious, costly, and error-prone task, making it desirable for Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) based monitoring. Though deep learning models have excellent fault detection capabilities, almost all methods either are too large and heavy for edge computing devices or involve biased estimation of accuracy due to ineffective learning techniques. We propose a new solar panel fault detection model called HybridSolarNet. It integrates EfficientNet-B0 with Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM). We implemented it on the Kaggle Solar Panel Images competition dataset with a tight split-before-augmentation protocol. It avoids leakage in accuracy estimation. We introduced focal loss and cosine annealing. Ablation analysis validates that accuracy boosts due to added benefits from CBAM (+1.53%) and that there are benefits from recognition of classes with imbalanced samples via focal loss. Overall average accuracy on 5-fold stratified cross-validation experiments on the given competition dataset topped 92.37% +/- 0.41 and an F1-score of 0.9226 +/- 0.39 compared to baselines like VGG19, requiring merely 16.3 MB storage, i.e., 32 times less. Its inference speed measured at 54.9 FPS with GPU support makes it a successful candidate for real-time UAV implementation. Moreover, visualization obtained from Grad-CAM illustrates that HybridSolarNet focuses on actual locations instead of irrelevant ones.
zh
[CV-27] PrismVAU: Prompt-Refined Inference System for Multimodal Video Anomaly Understanding WACV2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视频异常理解(Video Anomaly Understanding, VAU)任务中现有方法依赖昂贵标注、复杂训练流程及高推理开销的问题,这些问题限制了其在真实场景中的实用性。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种轻量且高效的系统PrismVAU,该系统仅使用一个现成的多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Model, MLLM),通过两个互补阶段实现异常评分、解释与提示优化:首先利用文本锚点计算帧级异常分数,随后通过系统和用户提示对异常进行上下文建模;整个过程采用弱监督自动提示工程(Automatic Prompt Engineering, APE)框架优化文本锚点与提示,从而在无需指令微调、帧级标注或外部模块的情况下,实现高效率与可解释性的VAU能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02927
作者: Iñaki Erregue,Kamal Nasrollahi,Sergio Escalera
机构: Universitat de Barcelona(巴塞罗那大学); Computer Vision Center(计算机视觉中心); Aalborg University(奥尔堡大学); Milestone Systems
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: This paper has been accepted to the 6th Workshop on Real-World Surveillance: Applications and Challenges (WACV 2025)
Abstract:Video Anomaly Understanding (VAU) extends traditional Video Anomaly Detection (VAD) by not only localizing anomalies but also describing and reasoning about their context. Existing VAU approaches often rely on fine-tuned multimodal large language models (MLLMs) or external modules such as video captioners, which introduce costly annotations, complex training pipelines, and high inference overhead. In this work, we introduce PrismVAU, a lightweight yet effective system for real-time VAU that leverages a single off-the-shelf MLLM for anomaly scoring, explanation, and prompt optimization. PrismVAU operates in two complementary stages: (1) a coarse anomaly scoring module that computes frame-level anomaly scores via similarity to textual anchors, and (2) an MLLM-based refinement module that contextualizes anomalies through system and user prompts. Both textual anchors and prompts are optimized with a weakly supervised Automatic Prompt Engineering (APE) framework. Extensive experiments on standard VAD benchmarks demonstrate that PrismVAU delivers competitive detection performance and interpretable anomaly explanations – without relying on instruction tuning, frame-level annotations, and external modules or dense processing – making it an efficient and practical solution for real-world applications.
zh
[CV-28] DCG ReID: Disentangling Collaboration and Guidance Fusion Representations for Multi-modal Vehicle Re-Identification
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态车辆再识别(Multi-modal Vehicle Re-Identification, Multi-modal Vehicle ReID)中因模态质量分布不确定性导致的融合冲突问题,即在模态间存在固有差异时,现有方法采用统一融合模型处理所有数据,忽略了平衡与非平衡质量分布下不同的融合需求,从而难以同时保证类内一致性与模态间异质性之间的解耦。解决方案的关键在于提出一种解耦协作与引导融合表示框架(DCG-ReID),其核心包括:(1) 动态置信度解耦加权机制(Dynamic Confidence-based Disentangling Weighting, DCDW),通过交互式模态置信度动态调整三模态贡献,构建无干扰的解耦融合框架;(2) 场景自适应融合策略:针对平衡质量分布设计协作融合模块(Collaboration Fusion Module, CFM)以挖掘成对共识特征提升类内一致性;针对不平衡分布设计引导融合模块(Guidance Fusion Module, GFM)通过差异化放大主导模态优势并引导辅助模态挖掘互补判别信息,缓解模态间分歧,增强多模态联合决策性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02924
作者: Aihua Zheng,Ya Gao,Shihao Li,Chenglong Li,Jin Tang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Multi-modal vehicle Re-Identification (ReID) aims to leverage complementary information from RGB, Near Infrared (NIR), and Thermal Infrared (TIR) modalities to retrieve the same vehicle. The challenges of multi-modal vehicle ReID arise from the uncertainty of modality quality distribution induced by inherent discrepancies across modalities, resulting in distinct conflicting fusion requirements for data with balanced and unbalanced quality distributions. Existing methods handle all multi-modal data within a single fusion model, overlooking the different needs of the two data types and making it difficult to decouple the conflict between intra-class consistency and inter-modal heterogeneity. To this end, we propose Disentangle Collaboration and Guidance Fusion Representations for Multi-modal Vehicle ReID (DCG-ReID). Specifically, to disentangle heterogeneous quality-distributed modal data without mutual interference, we first design the Dynamic Confidence-based Disentangling Weighting (DCDW) mechanism: dynamically reweighting three-modal contributions via interaction-derived modal confidence to build a disentangled fusion framework. Building on DCDW, we develop two scenario-specific fusion strategies: (1) for balanced quality distributions, Collaboration Fusion Module (CFM) mines pairwise consensus features to capture shared discriminative information and boost intra-class consistency; (2) for unbalanced distributions, Guidance Fusion Module (GFM) implements differential amplification of modal discriminative disparities to reinforce dominant modality advantages, guide auxiliary modalities to mine complementary discriminative info, and mitigate inter-modal divergence to boost multi-modal joint decision performance. Extensive experiments on three multi-modal ReID benchmarks (WMVeID863, MSVR310, RGBNT100) validate the effectiveness of our method. Code will be released upon acceptance.
zh
[CV-29] Zoom-IQA: Image Quality Assessment with Reliable Region-Aware Reasoning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有基于视觉语言模型(Vision Language Model, VLM)的图像质量评估(Image Quality Assessment, IQA)方法在推理可靠性上的不足,即模型难以有效融合视觉与文本线索,导致生成的质量描述和评分缺乏准确性与一致性。解决方案的关键在于提出Zoom-IQA,通过显式模拟人类认知行为——不确定性感知、区域推理和迭代优化——构建一个两阶段训练框架:首先在Grounded-Rationale-IQA(GR-IQA)数据集上进行监督微调(Supervised Fine-Tuning, SFT),使模型能够将评估锚定在关键图像区域;其次采用强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)并引入KL-Coverage正则项以稳定策略探索、防止推理多样性崩溃,并结合渐进重采样策略缓解标注偏差。该设计显著提升了IQA模型的鲁棒性、可解释性和泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02918
作者: Guoqiang Liang,Jianyi Wang,Zhonghua Wu,Shangchen Zhou
机构: S-Lab, Nanyang Technological University (南洋理工大学); SenseTime Research (商汤科技)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Project Page: this https URL
Abstract:Image Quality Assessment (IQA) is a long-standing problem in computer vision. Previous methods typically focus on predicting numerical scores without explanation or provide low-level descriptions lacking precise scores. Recent reasoning-based vision language models (VLMs) have shown strong potential for IQA, enabling joint generation of quality descriptions and scores. However, we notice that existing VLM-based IQA methods tend to exhibit unreliable reasoning due to their limited capability of integrating visual and textual cues. In this work, we introduce Zoom-IQA, a VLM-based IQA model to explicitly emulate key cognitive behaviors: uncertainty awareness, region reasoning, and iterative refinement. Specifically, we present a two-stage training pipeline: 1) supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on our Grounded-Rationale-IQA (GR-IQA) dataset to teach the model to ground its assessments in key regions; and 2) reinforcement learning (RL) for dynamic policy exploration, primarily stabilized by our KL-Coverage regularizer to prevent reasoning and scoring diversity collapse, and supported by a Progressive Re-sampling Strategy to mitigate annotation bias. Extensive experiments show that Zoom-IQA achieves improved robustness, explainability, and generalization. The application to downstream tasks, such as image restoration, further demonstrates the effectiveness of Zoom-IQA.
zh
[CV-30] A-Prompting: Enhancing Video Large Language Models for Dense Video Captioning via Temporal Anchors WACV2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前视频大语言模型(VideoLLMs)在未剪辑视频中难以精确定位事件边界的问题,导致生成的描述无法准确对齐时间片段。其解决方案的关键在于提出TA-Prompting方法,通过引入时序锚点(Temporal Anchors)来学习精确的事件定位,并引导VideoLLMs实现时序感知的视频事件理解;同时,在推理阶段采用事件连贯采样策略(event coherent sampling),从任意数量的事件中选择具有足够时序一致性和跨模态相似性的caption序列,从而提升密集视频字幕生成与时间理解任务的性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02908
作者: Wei-Yuan Cheng,Kai-Po Chang,Chi-Pin Huang,Fu-En Yang,Yu-Chiang Frank Wang
机构: National Taiwan University (台湾大学); NVIDIA (英伟达)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 8 pages for main paper (exclude citation pages), 6 pages for appendix, totally 10 figures 7 tables and 2 algorithms. The paper is accepted by WACV 2026
Abstract:Dense video captioning aims to interpret and describe all temporally localized events throughout an input video. Recent state-of-the-art methods leverage large language models (LLMs) to provide detailed moment descriptions for video data. However, existing VideoLLMs remain challenging in identifying precise event boundaries in untrimmed videos, causing the generated captions to be not properly grounded. In this paper, we propose TA-Prompting, which enhances VideoLLMs via Temporal Anchors that learn to precisely localize events and prompt the VideoLLMs to perform temporal-aware video event understanding. During inference, in order to properly determine the output caption sequence from an arbitrary number of events presented within a video, we introduce an event coherent sampling strategy to select event captions with sufficient coherence across temporal events and cross-modal similarity with the given video. Through extensive experiments on benchmark datasets, we show that our TA-Prompting is favorable against state-of-the-art VideoLLMs, yielding superior performance on dense video captioning and temporal understanding tasks including moment retrieval and temporalQA.
zh
[CV-31] owards Agnostic and Holistic Universal Image Segmentation with Bit Diffusion
【速读】:该论文旨在解决通用图像分割(universal image segmentation)问题,特别是克服传统基于掩码(mask-based)框架的局限性,实现无需依赖掩码即可进行整体性分割的方法。其核心解决方案是提出一种基于扩散模型(diffusion model)的框架,通过关键改进提升离散数据下的分割性能:包括引入位置感知的调色板(location-aware palette)并采用二维灰度编码(2D gray code ordering)以增强空间信息表达;在输出层添加tanh激活函数以适配离散数据特性;优化扩散参数时采用sigmoid损失加权策略和x-prediction预测方式,显著优于其他变体。尽管当前模型尚未超越领先的掩码架构,但已显著缩小性能差距,并首次引入了可解释的不确定性建模能力,为未来结合大规模预训练或提示引导条件(promptable conditioning)提供了可行路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02881
作者: Jakob Lønborg Christensen,Morten Rieger Hannemose,Anders Bjorholm Dahl,Vedrana Andersen Dahl
机构: Technical University of Denmark(丹麦技术大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted at NLDL 26
Abstract:This paper introduces a diffusion-based framework for universal image segmentation, making agnostic segmentation possible without depending on mask-based frameworks and instead predicting the full segmentation in a holistic manner. We present several key adaptations to diffusion models, which are important in this discrete setting. Notably, we show that a location-aware palette with our 2D gray code ordering improves performance. Adding a final tanh activation function is crucial for discrete data. On optimizing diffusion parameters, the sigmoid loss weighting consistently outperforms alternatives, regardless of the prediction type used, and we settle on x-prediction. While our current model does not yet surpass leading mask-based architectures, it narrows the performance gap and introduces unique capabilities, such as principled ambiguity modeling, that these models lack. All models were trained from scratch, and we believe that combining our proposed improvements with large-scale pretraining or promptable conditioning could lead to competitive models.
zh
[CV-32] Breaking Self-Attention Failure: Rethinking Query Initialization for Infrared Small Target Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决红外小目标检测(Infrared Small Target Detection, IRSTD)中因信噪比低、目标尺寸小及背景复杂导致的检测性能下降问题,尤其针对基于DETR(Detection Transformer)的方法在IRSTD任务中表现不佳的现象。研究表明,这是由于自注意力机制下目标相关特征被强背景特征淹没,造成查询初始化不可靠和定位不准。解决方案的关键在于提出SEF-DETR框架,其核心创新包括:频域引导的局部块筛选(Frequency-guided Patch Screening, FPS)用于构建目标相关密度图以抑制背景主导特征;动态嵌入增强(Dynamic Embedding Enhancement, DEE)实现多尺度的目标感知特征强化;以及可靠性一致性感知融合(Reliability-Consistency-aware Fusion, RCF)通过空间-频率一致性约束进一步优化对象查询,从而显著提升红外小目标的检测鲁棒性与准确性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02837
作者: Yuteng Liu,Duanni Meng,Maoxun Yuan,Xingxing Wei
机构: Beihang University (北京航空航天大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Infrared small target detection (IRSTD) faces significant challenges due to the low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), small target size, and complex cluttered backgrounds. Although recent DETR-based detectors benefit from global context modeling, they exhibit notable performance degradation on IRSTD. We revisit this phenomenon and reveal that the target-relevant embeddings of IRST are inevitably overwhelmed by dominant background features due to the self-attention mechanism, leading to unreliable query initialization and inaccurate target localization. To address this issue, we propose SEF-DETR, a novel framework that refines query initialization for IRSTD. Specifically, SEF-DETR consists of three components: Frequency-guided Patch Screening (FPS), Dynamic Embedding Enhancement (DEE), and Reliability-Consistency-aware Fusion (RCF). The FPS module leverages the Fourier spectrum of local patches to construct a target-relevant density map, suppressing background-dominated features. DEE strengthens multi-scale representations in a target-aware manner, while RCF further refines object queries by enforcing spatial-frequency consistency and reliability. Extensive experiments on three public IRSTD datasets demonstrate that SEF-DETR achieves superior detection performance compared to state-of-the-art methods, delivering a robust and efficient solution for infrared small target detection task.
zh
[CV-33] DGA-Net: Enhancing SAM with Depth Prompting and Graph-Anchor Guidance for Camouflaged Object Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决伪装目标检测(Camouflaged Object Detection, COD)中深度线索利用不充分的问题,现有方法多依赖稀疏提示(如点或框),难以有效捕捉场景的几何结构信息。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种新颖的“深度提示”(depth prompting)范式,通过两个核心模块实现:一是跨模态图增强(Cross-modal Graph Enhancement, CGE)模块,用于在异构图中融合RGB语义与深度几何信息,生成统一的引导信号;二是锚点引导细化(Anchor-Guided Refinement, AGR)模块,通过构建全局锚点并建立非局部传播路径,将深层引导信息直接传递至浅层特征,缓解特征层次中的信息衰减问题,从而提升分割精度与一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02831
作者: Yuetong Li,Qing Zhang,Yilin Zhao,Gongyang Li,Zeming Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:To fully exploit depth cues in Camouflaged Object Detection (COD), we present DGA-Net, a specialized framework that adapts the Segment Anything Model (SAM) via a novel ``depth prompting" paradigm. Distinguished from existing approaches that primarily rely on sparse prompts (e.g., points or boxes), our method introduces a holistic mechanism for constructing and propagating dense depth prompts. Specifically, we propose a Cross-modal Graph Enhancement (CGE) module that synthesizes RGB semantics and depth geometric within a heterogeneous graph to form a unified guidance signal. Furthermore, we design an Anchor-Guided Refinement (AGR) module. To counteract the inherent information decay in feature hierarchies, AGR forges a global anchor and establishes direct non-local pathways to broadcast this guidance from deep to shallow layers, ensuring precise and consistent segmentation. Quantitative and qualitative experimental results demonstrate that our proposed DGA-Net outperforms the state-of-the-art COD methods.
zh
[CV-34] SketchThinker-R1: Towards Efficient Sketch-Style Reasoning in Large Multimodal Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大规模多模态模型在执行长序列推理时带来的高计算开销问题(如token消耗增加和响应时间延长),从而影响推理效率。其核心解决方案是受人类“草图式推理”(sketch-style reasoning)启发,提出SketchThinker-R1框架,通过三个关键阶段实现:首先在Sketch-Mode Cold Start阶段将标准长推理转化为草图式推理并微调基础模型以获得初始能力;其次训练SketchJudge奖励模型来显式评估推理过程并给予草图式推理更高评分;最后在SketchJudge监督下进行强化学习,进一步提升模型的草图式推理泛化能力。实验表明,该方法可在不牺牲最终答案准确性的前提下,降低超过64%的推理token成本,并且定性分析显示草图式推理更聚焦于关键线索。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02825
作者: Ruiyang Zhang,Dongzhan Zhou,Zhedong Zheng
机构: University of Macau (澳门大学); Shanghai AI Laboratory (上海人工智能实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 28 pages, 11 figures
Abstract:Despite the empirical success of extensive, step-by-step reasoning in large multimodal models, long reasoning processes inevitably incur substantial computational overhead, i.e., in terms of higher token costs and increased response time, which undermines inference efficiency. In contrast, humans often employ sketch-style reasoning: a concise, goal-directed cognitive process that prioritizes salient information and enables efficient problem-solving. Inspired by this cognitive efficiency, we propose SketchThinker-R1, which incentivizes sketch-style reasoning ability in large multimodal models. Our method consists of three primary stages. In the Sketch-Mode Cold Start stage, we convert standard long reasoning process into sketch-style reasoning and finetune base multimodal model, instilling initial sketch-style reasoning capability. Next, we train SketchJudge Reward Model, which explicitly evaluates thinking process of model and assigns higher scores to sketch-style reasoning. Finally, we conduct Sketch-Thinking Reinforcement Learning under supervision of SketchJudge to further generalize sketch-style reasoning ability. Experimental evaluation on four benchmarks reveals that our SketchThinker-R1 achieves over 64% reduction in reasoning token cost without compromising final answer accuracy. Qualitative analysis further shows that sketch-style reasoning focuses more on key cues during problem solving.
zh
[CV-35] opology-aware Pathological Consistency Matching for Weakly-Paired IHC Virtual Staining
【速读】:该论文旨在解决免疫组织化学(Immunohistochemical, IHC)染色在临床应用中因流程复杂、耗时且成本高昂而难以广泛使用的问题,同时针对虚拟染色(HE-to-IHC)中由于相邻切片作为标签导致的弱配对数据、空间错位和局部形变阻碍监督学习效果的挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种拓扑感知框架,包含两个核心机制:一是拓扑一致性匹配(Topology-aware Consistency Matching, TACM),通过图对比学习与拓扑扰动来学习鲁棒的匹配模式以保障结构一致性;二是病理一致性约束匹配(Topology-constrained Pathological Matching, TCPM),基于节点重要性对齐病理阳性区域以增强病理一致性。该方法在多个基准和染色任务上均显著优于现有技术,生成质量更高且更具临床相关性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02806
作者: Mingzhou Jiang,Jiaying Zhou,Nan Zeng,Mickael Li,Qijie Tang,Chao He,Huazhu Fu,Honghui He
机构: Guangdong Research Center of Polarization Imaging and Measurement Engineering Technology; Shenzhen Key Laboratory for Minimal Invasive Medical Technologies; Institute of Biopharmaceutical and Health Engineering; Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School; Tsinghua University; Department of Engineering Science; University of Oxford; Institute of High Performance Computing (IHPC); Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining provides crucial molecular characterization of tissue samples and plays an indispensable role in the clinical examination and diagnosis of cancers. However, compared with the commonly used Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) staining, IHC staining involves complex procedures and is both time-consuming and expensive, which limits its widespread clinical use. Virtual staining converts HE images to IHC images, offering a cost-effective alternative to clinical IHC staining. Nevertheless, using adjacent slides as ground truth often results in weakly-paired data with spatial misalignment and local deformations, hindering effective supervised learning. To address these challenges, we propose a novel topology-aware framework for HE-to-IHC virtual staining. Specifically, we introduce a Topology-aware Consistency Matching (TACM) mechanism that employs graph contrastive learning and topological perturbations to learn robust matching patterns despite spatial misalignments, ensuring structural consistency. Furthermore, we propose a Topology-constrained Pathological Matching (TCPM) mechanism that aligns pathological positive regions based on node importance to enhance pathological consistency. Extensive experiments on two benchmarks across four staining tasks demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, achieving superior generation quality with higher clinical relevance.
zh
[CV-36] StableDPT: Temporal Stable Monocular Video Depth Estimation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决单图像单目深度估计(Monocular Depth Estimation, MDE)模型应用于视频序列时产生的显著时间不稳定性和闪烁伪影问题。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种名为StableDPT的新架构,其核心创新是通过在Dense Prediction Transformer(DPT)头部引入可训练的时序模块,利用高效的交叉注意力机制整合整个视频序列中关键帧的信息,从而捕捉全局上下文和帧间关系,提升深度预测的时空一致性。此外,该方法还设计了一种新颖的推理策略,避免了传统重叠窗口方法导致的尺度错位和冗余计算,实现了更高效、稳定的视频深度估计。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02793
作者: Ivan Sobko,Hayko Riemenschneider,Markus Gross,Christopher Schroers
机构: ETH Zürich (苏黎世联邦理工学院); DisneyResearch|Studios (迪士尼研究工作室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Applying single image Monocular Depth Estimation (MDE) models to video sequences introduces significant temporal instability and flickering artifacts. We propose a novel approach that adapts any state-of-the-art image-based (depth) estimation model for video processing by integrating a new temporal module - trainable on a single GPU in a few days. Our architecture StableDPT builds upon an off-the-shelf Vision Transformer (ViT) encoder and enhances the Dense Prediction Transformer (DPT) head. The core of our contribution lies in the temporal layers within the head, which use an efficient cross-attention mechanism to integrate information from keyframes sampled across the entire video sequence. This allows the model to capture global context and inter-frame relationships leading to more accurate and temporally stable depth predictions. Furthermore, we propose a novel inference strategy for processing videos of arbitrary length avoiding the scale misalignment and redundant computations associated with overlapping windows used in other methods. Evaluations on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate improved temporal consistency, competitive state-of-the-art performance and on top 2x faster processing in real-world scenarios.
zh
[CV-37] xtile IR: A Bidirectional Intermediate Representation for Physics-Aware Fashion CAD
【速读】:该论文旨在解决时尚设计中制造可行性、物理仿真与生命周期评估(LCA)之间长期割裂的问题,即当前工具链缺乏统一的语义桥梁,导致设计师需在不同阶段反复迭代,难以同时优化可持续性、可制造性和美学表现。解决方案的关键在于提出一种双向中间表示——Textile IR,它通过七层验证阶梯(Verification Ladder)将CAD、物理仿真和LCA集成到一个连贯的约束满足框架中,使设计变更能够实时反馈至材料选择、结构合理性与环境影响估算,并以场景图(scene-graph)形式实现对服装的结构化程序式操作,从而在早期识别并量化不确定性传播,避免因物理原型阶段才发现冲突而造成的资源浪费。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02792
作者: Petteri Teikari,Neliana Fuenmayor
机构: Open Mode(Open Mode)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 20 pages, 8 figures, SI Technologies and Practices (Fashion Practice)
Abstract:We introduce Textile IR, a bidirectional intermediate representation that connects manufacturing-valid CAD, physics-based simulation, and lifecycle assessment for fashion design. Unlike existing siloed tools where pattern software guarantees sewable outputs but understands nothing about drape, and physics simulation predicts behaviour but cannot automatically fix patterns, Textile IR provides the semantic glue for integration through a seven-layer Verification Ladder – from cheap syntactic checks (pattern closure, seam compatibility) to expensive physics validation (drape simulation, stress analysis). The architecture enables bidirectional feedback: simulation failures suggest pattern modifications; material substitutions update sustainability estimates in real time; uncertainty propagates across the pipeline with explicit confidence bounds. We formalise fashion engineering as constraint satisfaction over three domains and demonstrate how Textile IR’s scene-graph representation enables AI systems to manipulate garments as structured programs rather than pixel arrays. The framework addresses the compound uncertainty problem: when measurement errors in material testing, simulation approximations, and LCA database gaps combine, sustainability claims become unreliable without explicit uncertainty tracking. We propose six research priorities and discuss deployment considerations for fashion SMEs where integrated workflows reduce specialised engineering requirements. Key contribution: a formal representation that makes engineering constraints perceptible, manipulable, and immediately consequential – enabling designers to navigate sustainability, manufacturability, and aesthetic tradeoffs simultaneously rather than discovering conflicts after costly physical prototyping.
zh
[CV-38] DreamStyle: A Unified Framework for Video Stylization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视频风格化(Video Stylization)任务中因单一风格条件输入导致的应用范围受限,以及由于高质量数据集缺乏引发的风格不一致性和时间闪烁问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个统一框架DreamStyle,支持文本引导、风格图像引导和首帧引导三种风格条件输入,并通过精心设计的数据清洗流程获取高质量配对视频数据;此外,基于基础Image-to-Video (I2V)模型并采用针对特定标记的低秩适应(LoRA with token-specific up matrices)训练策略,有效减少不同条件标记之间的混淆,从而在风格一致性与视频质量上显著优于现有方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02785
作者: Mengtian Li,Jinshu Chen,Songtao Zhao,Wanquan Feng,Pengqi Tu,Qian He
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Github Page: this https URL
Abstract:Video stylization, an important downstream task of video generation models, has not yet been thoroughly explored. Its input style conditions typically include text, style image, and stylized first frame. Each condition has a characteristic advantage: text is more flexible, style image provides a more accurate visual anchor, and stylized first frame makes long-video stylization feasible. However, existing methods are largely confined to a single type of style condition, which limits their scope of application. Additionally, their lack of high-quality datasets leads to style inconsistency and temporal flicker. To address these limitations, we introduce DreamStyle, a unified framework for video stylization, supporting (1) text-guided, (2) style-image-guided, and (3) first-frame-guided video stylization, accompanied by a well-designed data curation pipeline to acquire high-quality paired video data. DreamStyle is built on a vanilla Image-to-Video (I2V) model and trained using a Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) with token-specific up matrices that reduces the confusion among different condition tokens. Both qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate that DreamStyle is competent in all three video stylization tasks, and outperforms the competitors in style consistency and video quality.
zh
[CV-39] EarthVL: A Progressive Earth Vision-Language Understanding and Generation Framework
【速读】:该论文旨在解决地球视觉(Earth vision)在地物关系推理(object-relational reasoning)方面的不足,从而提升对遥感场景的全面理解能力。现有研究虽在地理空间目标识别上取得进展,但缺乏对物体间语义关联的深入建模,限制了其在城市规划等复杂应用中的表现。解决方案的关键在于提出一个渐进式的地球视觉-语言理解与生成框架,包含两个核心组件:一是多任务数据集 EarthVLSet,涵盖10.9k张亚米级遥感图像、地表覆盖掩码及761.5k条文本配对数据(支持多项选择和开放式视觉问答任务);二是语义引导的网络 EarthVLNet,通过三个阶段逐步实现语义分割、关系推理与综合理解:第一阶段基于土地覆盖分割生成对象语义,第二阶段利用像素级语义引导的大语言模型(LLM)进行关系推理与知识总结以生成答案。此外,文中引入数值差异损失(numerical difference loss)动态添加差异惩罚项,有效缓解不同对象统计特性带来的偏差问题。实验表明,该方法在语义分割、多项选择和开放式VQA三类基准任务中均优于现有方案,并揭示了分割特征对跨数据集VQA性能的稳定增益、视觉编码器对多项选择任务更敏感、以及开放式任务需更强视觉与语言解码器协同优化等未来方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02783
作者: Junjue Wang,Yanfei Zhong,Zihang Chen,Zhuo Zheng,Ailong Ma,Liangpei Zhang
机构: Wuhan University (武汉大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Earth vision has achieved milestones in geospatial object recognition but lacks exploration in object-relational reasoning, limiting comprehensive scene understanding. To address this, a progressive Earth vision-language understanding and generation framework is proposed, including a multi-task dataset (EarthVLSet) and a semantic-guided network (EarthVLNet). Focusing on city planning applications, EarthVLSet includes 10.9k sub-meter resolution remote sensing images, land-cover masks, and 761.5k textual pairs involving both multiple-choice and open-ended visual question answering (VQA) tasks. In an object-centric way, EarthVLNet is proposed to progressively achieve semantic segmentation, relational reasoning, and comprehensive understanding. The first stage involves land-cover segmentation to generate object semantics for VQA guidance. Guided by pixel-wise semantics, the object awareness based large language model (LLM) performs relational reasoning and knowledge summarization to generate the required answers. As for optimization, the numerical difference loss is proposed to dynamically add difference penalties, addressing the various objects’ statistics. Three benchmarks, including semantic segmentation, multiple-choice, and open-ended VQA demonstrated the superiorities of EarthVLNet, yielding three future directions: 1) segmentation features consistently enhance VQA performance even in cross-dataset scenarios; 2) multiple-choice tasks show greater sensitivity to the vision encoder than to the language decoder; and 3) open-ended tasks necessitate advanced vision encoders and language decoders for an optimal performance. We believe this dataset and method will provide a beneficial benchmark that connects ‘‘image-mask-text’’, advancing geographical applications for Earth vision.
zh
[CV-40] AbductiveMLLM : Boosting Visual Abductive Reasoning Within MLLM s AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉归纳推理(Visual Abductive Reasoning, VAR)任务中大型多模态语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在因果推断能力上的不足问题,即MLLMs难以像人类一样从不完整视觉观测中推导出最可能的解释。解决方案的关键在于提出一种双组件协同架构——AbductiveMLLM,其核心机制包括:1)REASONER模块在语义域内通过盲源大语言模型探索广泛解释空间,并基于跨模态因果对齐筛选出视觉上一致的假设,再以目标先验形式引导MLLM推理;2)IMAGINER模块模拟人类图像思维,利用文本到图像扩散模型以输入视频和REASONER输出嵌入为条件“想象”与语义解释匹配的可视化场景,从而增强MLLM的上下文感知能力。两个模块端到端联合训练,显著提升了VAR任务中的因果一致性与推理性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02771
作者: Boyu Chang,Qi Wang,Xi Guo,Zhixiong Nan,Yazhou Yao,Tianfei Zhou
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted by AAAI 2026 as Oral. Code: this https URL
Abstract:Visual abductive reasoning (VAR) is a challenging task that requires AI systems to infer the most likely explanation for incomplete visual observations. While recent MLLMs develop strong general-purpose multimodal reasoning capabilities, they fall short in abductive inference, as compared to human beings. To bridge this gap, we draw inspiration from the interplay between verbal and pictorial abduction in human cognition, and propose to strengthen abduction of MLLMs by mimicking such dual-mode behavior. Concretely, we introduce AbductiveMLLM comprising of two synergistic components: REASONER and IMAGINER. The REASONER operates in the verbal domain. It first explores a broad space of possible explanations using a blind LLM and then prunes visually incongruent hypotheses based on cross-modal causal alignment. The remaining hypotheses are introduced into the MLLM as targeted priors, steering its reasoning toward causally coherent explanations. The IMAGINER, on the other hand, further guides MLLMs by emulating human-like pictorial thinking. It conditions a text-to-image diffusion model on both the input video and the REASONER’s output embeddings to “imagine” plausible visual scenes that correspond to verbal explanation, thereby enriching MLLMs’ contextual grounding. The two components are trained jointly in an end-to-end manner. Experiments on standard VAR benchmarks show that AbductiveMLLM achieves state-of-the-art performance, consistently outperforming traditional solutions and advanced MLLMs.
zh
[CV-41] ClearAIR: A Human-Visual-Perception-Inspired All-in-One Image Restoration AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前全功能图像复原(All-in-One Image Restoration, AiOIR)方法因过度依赖退化特定表示而导致的过平滑和伪影问题。解决方案的关键在于受人类视觉感知(Human Visual Perception, HVP)启发,提出了一种分层、由粗到细的复原策略:首先利用多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Model, MLLM)驱动的图像质量评估(Image Quality Assessment, IQA)模型进行全局评价,通过跨模态理解更准确刻画复合退化;其次引入区域感知与任务识别管道,借助语义交叉注意力生成粗粒度语义提示,并通过退化感知模块隐式捕捉局部退化特征以实现精准修复;最后设计内部线索重用机制,在自监督框架下挖掘图像自身内在信息,显著提升细节恢复能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02763
作者: Xu Zhang,Huan Zhang,Guoli Wang,Qian Zhang,Lefei Zhang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted to AAAI 2026. Project page: this https URL
Abstract:All-in-One Image Restoration (AiOIR) has advanced significantly, offering promising solutions for complex real-world degradations. However, most existing approaches rely heavily on degradation-specific representations, often resulting in oversmoothing and artifacts. To address this, we propose ClearAIR, a novel AiOIR framework inspired by Human Visual Perception (HVP) and designed with a hierarchical, coarse-to-fine restoration strategy. First, leveraging the global priority of early HVP, we employ a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM)-based Image Quality Assessment (IQA) model for overall evaluation. Unlike conventional IQA, our method integrates cross-modal understanding to more accurately characterize complex, composite degradations. Building upon this overall assessment, we then introduce a region awareness and task recognition pipeline. A semantic cross-attention, leveraging semantic guidance unit, first produces coarse semantic prompts. Guided by this regional context, a degradation-aware module implicitly captures region-specific degradation characteristics, enabling more precise local restoration. Finally, to recover fine details, we propose an internal clue reuse mechanism. It operates in a self-supervised manner to mine and leverage the intrinsic information of the image itself, substantially enhancing detail restoration. Experimental results show that ClearAIR achieves superior performance across diverse synthetic and real-world datasets.
zh
[CV-42] AnyDepth: Depth Estimation Made Easy
【速读】:该论文旨在解决单目深度估计(monocular depth estimation)中模型效率低、泛化能力弱的问题,尤其针对现有方法对大规模数据集和复杂解码器(如DPT)的高度依赖。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个轻量级且以数据为中心的框架:首先采用DINOv3作为视觉编码器提取高质量密集特征;其次设计了结构简洁的Simple Depth Transformer(SDT)解码器,通过单路径特征融合与上采样机制替代复杂的跨尺度融合,显著降低计算开销(参数减少约85%-89%)并提升精度;同时提出基于质量的样本过滤策略,有效剔除有害样本,在压缩数据规模的同时提升训练质量。实验表明,该框架在五个基准测试中优于DPT,凸显了模型设计与数据质量协同优化对实现高效且泛化能力强的零样本深度估计的重要性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02760
作者: Zeyu Ren,Zeyu Zhang,Wukai Li,Qingxiang Liu,Hao Tang
机构: The University of Melbourne (墨尔本大学); Peking University (北京大学); Shanghai University of Engineering Science (上海工程技术大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Monocular depth estimation aims to recover the depth information of 3D scenes from 2D images. Recent work has made significant progress, but its reliance on large-scale datasets and complex decoders has limited its efficiency and generalization ability. In this paper, we propose a lightweight and data-centric framework for zero-shot monocular depth estimation. We first adopt DINOv3 as the visual encoder to obtain high-quality dense features. Secondly, to address the inherent drawbacks of the complex structure of the DPT, we design the Simple Depth Transformer (SDT), a compact transformer-based decoder. Compared to the DPT, it uses a single-path feature fusion and upsampling process to reduce the computational overhead of cross-scale feature fusion, achieving higher accuracy while reducing the number of parameters by approximately 85%-89%. Furthermore, we propose a quality-based filtering strategy to filter out harmful samples, thereby reducing dataset size while improving overall training quality. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks demonstrate that our framework surpasses the DPT in accuracy. This work highlights the importance of balancing model design and data quality for achieving efficient and generalizable zero-shot depth estimation. Code: this https URL. Website: this https URL.
zh
[CV-43] owards Zero-Shot Point Cloud Registration Across Diverse Scales Scenes and Sensor Setups ICCV2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决基于深度学习的点云配准方法在零样本(zero-shot)场景下泛化能力不足的问题,具体表现为:(a) 固定的手动设定超参数(如体素大小、搜索半径)无法适应不同尺度环境;(b) 学习得到的关键点检测器跨域迁移性能差;© 绝对坐标加剧了不同数据集间的尺度不一致。解决方案的关键在于提出 BUFFER-X 框架,其核心创新包括:(a) 通过几何自举(geometric bootstrapping)实现超参数自动估计,(b) 引入分布感知的最远点采样(distribution-aware farthest point sampling)替代学习型关键点检测器以提升跨域适应性,© 采用局部坐标归一化(patch-level coordinate normalization)确保尺度一致性,并结合分层多尺度匹配策略提取局部、中程和全局感受野中的对应关系,从而实现无需训练即可在多种场景(包括异构LiDAR传感器间)有效配准。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02759
作者: Hyungtae Lim,Minkyun Seo,Luca Carlone,Jaesik Park
机构: Massachusetts Institute of Technology (麻省理工学院); Seoul National University (首尔国立大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注: 18 pages, 15 figures. Extended version of our ICCV 2025 highlight paper [ arXiv:2503.07940 ]. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2503.07940
Abstract:Some deep learning-based point cloud registration methods struggle with zero-shot generalization, often requiring dataset-specific hyperparameter tuning or retraining for new environments. We identify three critical limitations: (a) fixed user-defined parameters (e.g., voxel size, search radius) that fail to generalize across varying scales, (b) learned keypoint detectors exhibit poor cross-domain transferability, and © absolute coordinates amplify scale mismatches between datasets. To address these three issues, we present BUFFER-X, a training-free registration framework that achieves zero-shot generalization through: (a) geometric bootstrapping for automatic hyperparameter estimation, (b) distribution-aware farthest point sampling to replace learned detectors, and © patch-level coordinate normalization to ensure scale consistency. Our approach employs hierarchical multi-scale matching to extract correspondences across local, middle, and global receptive fields, enabling robust registration in diverse environments. For efficiency-critical applications, we introduce BUFFER-X-Lite, which reduces total computation time by 43% (relative to BUFFER-X) through early exit strategies and fast pose solvers while preserving accuracy. We evaluate on a comprehensive benchmark comprising 12 datasets spanning object-scale, indoor, and outdoor scenes, including cross-sensor registration between heterogeneous LiDAR configurations. Results demonstrate that our approach generalizes effectively without manual tuning or prior knowledge of test domains. Code: this https URL.
zh
[CV-44] D3R-DETR: DETR with Dual-Domain Density Refinement for Tiny Object Detection in Aerial Images
【速读】:该论文旨在解决遥感图像中微小目标检测(tiny object detection)的难题,尤其是针对主流基于Transformer的检测器在训练收敛慢和查询-目标匹配不准确的问题。其关键解决方案是提出D³R-DETR模型,该模型引入双域密度精炼机制(Dual-Domain Density Refinement),通过融合空间域与频域信息来优化低层特征图,利用其丰富的细节生成更精确的目标密度图,从而引导模型实现对微小目标的精准定位。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02747
作者: Zixiao Wen,Zhen Yang,Xianjie Bao,Lei Zhang,Xiantai Xiang,Wenshuai Li,Yuhan Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Abstract:Detecting tiny objects plays a vital role in remote sensing intelligent interpretation, as these objects often carry critical information for downstream applications. However, due to the extremely limited pixel information and significant variations in object density, mainstream Transformer-based detectors often suffer from slow convergence and inaccurate query-object matching. To address these challenges, we propose D ^3 R-DETR, a novel DETR-based detector with Dual-Domain Density Refinement. By fusing spatial and frequency domain information, our method refines low-level feature maps and utilizes their rich details to predict more accurate object density map, thereby guiding the model to precisely localize tiny objects. Extensive experiments on the AI-TOD-v2 dataset demonstrate that D ^3 R-DETR outperforms existing state-of-the-art detectors for tiny object detection.
zh
[CV-45] Unveiling and Bridging the Functional Perception Gap in MLLM s: Atomic Visual Alignment and Hierarchical Evaluation via PET-Bench
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在功能成像(functional imaging)领域中存在的“功能性感知鸿沟”问题,即现有视觉编码器无法独立于解剖结构先验来解析功能示踪剂分布,导致对正电子发射断层扫描(Positron Emission Tomography, PET)图像的误判。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为原子级视觉对齐(Atomic Visual Alignment, AVA)的微调策略,该策略通过强制模型先掌握低层级的功能性感知先验,再进行高层级诊断推理,从而将原本易产生链式思维(Chain-of-Thought, CoT)幻觉的推理机制转化为基于视觉证据的可靠推断工具,显著提升诊断准确性达14.83%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02737
作者: Zanting Ye,Xiaolong Niu,Xuanbin Wu,Xu Han,Shengyuan Liu,Jing Hao,Zhihao Peng,Hao Sun,Jieqin Lv,Fanghu Wang,Yanchao Huang,Hubing Wu,Yixuan Yuan,Habib Zaidi,Arman Rahmim,Yefeng Zheng,Lijun Lu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 9 pages, 6 figures, 6 tables
Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in tasks such as abnormality detection and report generation for anatomical modalities, their capability in functional imaging remains largely unexplored. In this work, we identify and quantify a fundamental functional perception gap: the inability of current vision encoders to decode functional tracer biodistribution independent of morphological priors. Identifying Positron Emission Tomography (PET) as the quintessential modality to investigate this disconnect, we introduce PET-Bench, the first large-scale functional imaging benchmark comprising 52,308 hierarchical QA pairs from 9,732 multi-site, multi-tracer PET studies. Extensive evaluation of 19 state-of-the-art MLLMs reveals a critical safety hazard termed the Chain-of-Thought (CoT) hallucination trap. We observe that standard CoT prompting, widely considered to enhance reasoning, paradoxically decouples linguistic generation from visual evidence in PET, producing clinically fluent but factually ungrounded diagnoses. To resolve this, we propose Atomic Visual Alignment (AVA), a simple fine-tuning strategy that enforces the mastery of low-level functional perception prior to high-level diagnostic reasoning. Our results demonstrate that AVA effectively bridges the perception gap, transforming CoT from a source of hallucination into a robust inference tool and improving diagnostic accuracy by up to 14.83%. Code and data are available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-46] Omni2Sound: Towards Unified Video-Text-to-Audio Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决统一模型在视频到音频(V2A)、文本到音频(T2A)及视频-文本联合到音频(VT2A)生成任务中面临的两大基础挑战:一是高质量、强跨模态对齐(视觉-音频-文本,V-A-T)的音频描述数据稀缺,导致多模态条件间语义冲突;二是跨任务与同任务内部的竞争关系,表现为V2A与T2A性能存在负向权衡,以及VT2A任务中模态偏倚问题。解决方案的关键在于两个核心创新:其一,构建大规模高质量数据集SoundAtlas(470k样本),通过新型智能体流水线(agentic pipeline)实现视觉语言压缩以缓解多模态大模型(MLLM)的视觉偏倚、采用“初级-高级代理交接”机制降低5倍训练成本,并结合后验过滤确保标注忠实性,从而提供语义丰富且时序精确的V-A-T对齐音频描述;其二,提出Omni2Sound统一扩散模型,设计三阶段多任务渐进式训练策略,将跨任务竞争转化为联合优化目标,有效缓解VT2A中的模态偏倚,同时保持音视频对齐与离屏音频生成的真实性。最终,在VGGSound-Omni基准上验证了Omni2Sound在单一模型中实现三项任务的SOTA性能,展现出优异的泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02731
作者: Yusheng Dai,Zehua Chen,Yuxuan Jiang,Baolong Gao,Qiuhong Ke,Jun Zhu,Jianfei Cai
机构: Tsinghua University (清华大学); Monash University (莫纳什大学); Shengshu AI (盛疏AI)
类目: ound (cs.SD); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Multimedia (cs.MM)
备注:
Abstract:Training a unified model integrating video-to-audio (V2A), text-to-audio (T2A), and joint video-text-to-audio (VT2A) generation offers significant application flexibility, yet faces two unexplored foundational challenges: (1) the scarcity of high-quality audio captions with tight A-V-T alignment, leading to severe semantic conflict between multimodal conditions, and (2) cross-task and intra-task competition, manifesting as an adverse V2A-T2A performance trade-off and modality bias in the VT2A task. First, to address data scarcity, we introduce SoundAtlas, a large-scale dataset (470k pairs) that significantly outperforms existing benchmarks and even human experts in quality. Powered by a novel agentic pipeline, it integrates Vision-to-Language Compression to mitigate visual bias of MLLMs, a Junior-Senior Agent Handoff for a 5 times cost reduction, and rigorous Post-hoc Filtering to ensure fidelity. Consequently, SoundAtlas delivers semantically rich and temporally detailed captions with tight V-A-T alignment. Second, we propose Omni2Sound, a unified VT2A diffusion model supporting flexible input modalities. To resolve the inherent cross-task and intra-task competition, we design a three-stage multi-task progressive training schedule that converts cross-task competition into joint optimization and mitigates modality bias in the VT2A task, maintaining both audio-visual alignment and off-screen audio generation faithfulness. Finally, we construct VGGSound-Omni, a comprehensive benchmark for unified evaluation, including challenging off-screen tracks. With a standard DiT backbone, Omni2Sound achieves unified SOTA performance across all three tasks within a single model, demonstrating strong generalization across benchmarks with heterogeneous input conditions. The project page is at this https URL.
zh
[CV-47] HOLO: Homography-Guided Pose Estimator Network for Fine-Grained Visual Localization on SD Maps
【速读】:该论文旨在解决标准分辨率(Standard-Definition, SD)地图上的视觉定位问题,现有基于回归的方法因忽视内在几何先验(geometric priors),导致训练效率低下且定位精度受限。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于单应性(homography)引导的姿态估计网络,通过将地面视角特征投影至鸟瞰图(Bird’s-Eye-View, BEV)域并强制与地图特征进行语义对齐,构建满足单应性约束的输入对;进而利用单应性关系指导特征融合,并将姿态输出限制在有效可行区域内,从而显著提升训练效率和定位精度。该方法首次将BEV语义推理与单应性学习统一用于图像到地图的视觉定位,同时具备跨分辨率输入支持能力,增强了模型灵活性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02730
作者: Xuchang Zhong,Xu Cao,Jinke Feng,Hao Fang
机构: Beijing Institute of Technology (北京理工大学); University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Visual localization on standard-definition (SD) maps has emerged as a promising low-cost and scalable solution for autonomous driving. However, existing regression-based approaches often overlook inherent geometric priors, resulting in suboptimal training efficiency and limited localization accuracy. In this paper, we propose a novel homography-guided pose estimator network for fine-grained visual localization between multi-view images and standard-definition (SD) maps. We construct input pairs that satisfy a homography constraint by projecting ground-view features into the BEV domain and enforcing semantic alignment with map features. Then we leverage homography relationships to guide feature fusion and restrict the pose outputs to a valid feasible region, which significantly improves training efficiency and localization accuracy compared to prior methods relying on attention-based fusion and direct 3-DoF pose regression. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to unify BEV semantic reasoning with homography learning for image-to-map localization. Furthermore, by explicitly modeling homography transformations, the proposed framework naturally supports cross-resolution inputs, enhancing model flexibility. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art visual localization methods. Code and pretrained models will be publicly released to foster future research.
zh
[CV-48] Foreground-Aware Dataset Distillation via Dynamic Patch Selection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统数据蒸馏方法在处理大规模深度模型训练时存在的计算开销高、内存受限以及生成图像不真实、缺乏结构信息等问题,尤其是非优化类方法因固定patch选择策略导致关键目标信息丢失的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种前景感知的数据蒸馏方法,通过引入Grounded SAM2模型识别图像中的前景对象并计算每张图像的前景占据率,进而设定类别级patch选择阈值;在此基础上设计了一种双路径动态patch选择机制:当前景占比高时直接保留整图,否则从候选patch中选取最具信息量的局部区域,从而在减少冗余背景内容的同时有效保留主要目标的关键语义信息,显著提升蒸馏数据的代表性和跨架构鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02727
作者: Longzhen Li,Guang Li,Ren Togo,Keisuke Maeda,Takahiro Ogawa,Miki Haseyama
机构: Hokkaido University (北海道大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a foreground-aware dataset distillation method that enhances patch selection in a content-adaptive manner. With the rising computational cost of training large-scale deep models, dataset distillation has emerged as a promising approach for constructing compact synthetic datasets that retain the knowledge of their large original counterparts. However, traditional optimization-based methods often suffer from high computational overhead, memory constraints, and the generation of unrealistic, noise-like images with limited architectural generalization. Recent non-optimization methods alleviate some of these issues by constructing distilled data from real image patches, but the used rigid patch selection strategies can still discard critical information about the main objects. To solve this problem, we first leverage Grounded SAM2 to identify foreground objects and compute per-image foreground occupancy, from which we derive a category-wise patch decision threshold. Guided by these thresholds, we design a dynamic patch selection strategy that, for each image, either selects the most informative patch from multiple candidates or directly resizes the full image when the foreground dominates. This dual-path mechanism preserves more key information about the main objects while reducing redundant background content. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks show that the proposed method consistently improves distillation performance over existing approaches, producing more informative and representative distilled datasets and enhancing robustness across different architectures and image compositions.
zh
[CV-49] Loop Closure using AnyLoc Visual Place Recognition in DPV-SLAM
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉SLAM(Simultaneous Localization and Mapping,同步定位与地图构建)系统中回环闭合(loop closure)性能不足的问题,尤其是在复杂环境下的准确性和鲁棒性问题。其解决方案的关键在于用基于学习的视觉场景识别方法AnyLoc替代传统的词袋模型(Bag of Visual Words, BoVW)回环检测方法,并引入一种自适应机制以动态调整相似度阈值,从而减少对人工调参的依赖。AnyLoc利用深度特征表示,相比BoVW所依赖的手工设计特征,能更有效地应对不同视角和光照条件下的图像检索任务,显著提升了回环闭合的准确性与系统整体稳定性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02723
作者: Wenzheng Zhang,Kazuki Adachi,Yoshitaka Hara,Sousuke Nakamura
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted at IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration(SII) 2026. 6 pages, 14 figures
Abstract:Loop closure is crucial for maintaining the accuracy and consistency of visual SLAM. We propose a method to improve loop closure performance in DPV-SLAM. Our approach integrates AnyLoc, a learning-based visual place recognition technique, as a replacement for the classical Bag of Visual Words (BoVW) loop detection method. In contrast to BoVW, which relies on handcrafted features, AnyLoc utilizes deep feature representations, enabling more robust image retrieval across diverse viewpoints and lighting conditions. Furthermore, we propose an adaptive mechanism that dynamically adjusts similarity threshold based on environmental conditions, removing the need for manual tuning. Experiments on both indoor and outdoor datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms the original DPV-SLAM in terms of loop closure accuracy and robustness. The proposed method offers a practical and scalable solution for enhancing loop closure performance in modern SLAM systems.
zh
[CV-50] Robust Mesh Saliency GT Acquisition in VR via View Cone Sampling and Geometric Smoothing
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前3D mesh显著性标注(saliency ground truth, GT)获取方法存在的两大问题:一是现有方法沿用2D图像处理范式,忽视了3D几何拓扑结构与2D图像阵列的本质差异;二是虚拟现实(VR)眼动追踪流水线依赖单射线采样和欧氏平滑,导致纹理注意力干扰及跨间隙信号泄露。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种鲁棒框架:首先引入视锥采样(view cone sampling, VCS)策略,通过高斯分布的射线束模拟人类中央凹感受野,提升复杂拓扑下的采样鲁棒性;其次设计混合流形-欧氏约束扩散(hybrid Manifold-Euclidean constrained diffusion, HCD)算法,融合流形测地线约束与欧氏尺度,确保显著性传播在拓扑一致性下进行,从而有效缓解“拓扑短路”和混叠效应,实现更贴近自然人类感知的3D注意力获取。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02721
作者: Guoquan Zheng,Jie Hao,Huiyu Duan,Yongming Han,Liang Yuan,Dong Zhang,Guangtao Zhai
机构: 1. University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学); 2. Tsinghua University (清华大学); 3. Peking University (北京大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Multimedia (cs.MM)
备注:
Abstract:Reliable 3D mesh saliency ground truth (GT) is essential for human-centric visual modeling in virtual reality (VR). However, current 3D mesh saliency GT acquisition methods are generally consistent with 2D image methods, ignoring the differences between 3D geometry topology and 2D image array. Current VR eye-tracking pipelines rely on single ray sampling and Euclidean smoothing, triggering texture attention and signal leakage across gaps. This paper proposes a robust framework to address these limitations. We first introduce a view cone sampling (VCS) strategy, which simulates the human foveal receptive field via Gaussian-distributed ray bundles to improve sampling robustness for complex topologies. Furthermore, a hybrid Manifold-Euclidean constrained diffusion (HCD) algorithm is developed, fusing manifold geodesic constraints with Euclidean scales to ensure topologically-consistent saliency propagation. By mitigating “topological short-circuits” and aliasing, our framework provides a high-fidelity 3D attention acquisition paradigm that aligns with natural human perception, offering a more accurate and robust baseline for 3D mesh saliency research.
zh
[CV-51] CAMO: Category-Agnostic 3D Motion Transfer from Monocular 2D Videos
【速读】:该论文旨在解决从单目2D视频到3D资产的运动迁移问题,该问题因姿态歧义性和目标形状多样性而极具挑战性,传统方法通常依赖于类别特定的参数化模板。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一种无类别限制(category-agnostic)的框架CAMO,该框架采用形态参数化的刚性3D高斯泼溅(articulated 3D Gaussian splatting)模型,并结合密集语义对应关系,通过优化联合适应形状与姿态,从而有效缓解形状-姿态歧义性,实现对多样化目标网格的视觉保真运动迁移。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02716
作者: Taeyeon Kim,Youngju Na,Jumin Lee,Minhyuk Sung,Sung-Eui Yoon
机构: KAIST
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Project website: this https URL
Abstract:Motion transfer from 2D videos to 3D assets is a challenging problem, due to inherent pose ambiguities and diverse object shapes, often requiring category-specific parametric templates. We propose CAMO, a category-agnostic framework that transfers motion to diverse target meshes directly from monocular 2D videos without relying on predefined templates or explicit 3D supervision. The core of CAMO is a morphology-parameterized articulated 3D Gaussian splatting model combined with dense semantic correspondences to jointly adapt shape and pose through optimization. This approach effectively alleviates shape-pose ambiguities, enabling visually faithful motion transfer for diverse categories. Experimental results demonstrate superior motion accuracy, efficiency, and visual coherence compared to existing methods, significantly advancing motion transfer in varied object categories and casual video scenarios.
zh
[CV-52] GRRE: Leverag ing G-Channel Removed Reconstruction Error for Robust Detection of AI-Generated Images
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)图像检测中普遍存在的泛化能力不足问题,即现有检测方法在面对未见过的生成模型所产图像时准确率显著下降。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于通道移除重建误差(G-channel Removed Reconstruction Error, GRRE)的新范式:通过移除图像的绿色(G)通道并进行重建,发现真实图像与AI生成图像在此过程中的重建误差存在显著差异,从而利用这一差异实现对AI生成图像的鲁棒检测。该方法在多个生成模型上均表现出优异的跨模型泛化性能和抗扰动能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02709
作者: Shuman He,Xiehua Li,Xioaju Yang,Yang Xiong,Keqin Li
机构: Hunan University (湖南大学); State University of New York at New Paltz (纽约州立大学新帕尔兹分校)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:The rapid progress of generative models, particularly diffusion models and GANs, has greatly increased the difficulty of distinguishing synthetic images from real ones. Although numerous detection methods have been proposed, their accuracy often degrades when applied to images generated by novel or unseen generative models, highlighting the challenge of achieving strong generalization. To address this challenge, we introduce a novel detection paradigm based on channel removal reconstruction. Specifically, we observe that when the green (G) channel is removed from real images and reconstructed, the resulting reconstruction errors differ significantly from those of AI-generated images. Building upon this insight, we propose G-channel Removed Reconstruction Error (GRRE), a simple yet effective method that exploits this discrepancy for robust AI-generated image detection. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GRRE consistently achieves high detection accuracy across multiple generative models, including those unseen during training. Compared with existing approaches, GRRE not only maintains strong robustness against various perturbations and post-processing operations but also exhibits superior cross-model generalization. These results highlight the potential of channel-removal-based reconstruction as a powerful forensic tool for safeguarding image authenticity in the era of generative AI.
zh
[CV-53] DreamLoop: Controllable Cinemagraph Generation from a Single Photograph
【速读】:该论文旨在解决从单张静态图像中可控生成具有无缝循环运动的景像画(cinemagraph)的问题。现有方法受限于简单的低频运动,且仅适用于水、烟等重复纹理的特定场景;而大规模视频扩散模型因缺乏针对景像画约束的专门数据与设计,难以生成高质量、可控制的循环动画。解决方案的关键在于提出DreamLoop框架,通过在通用视频扩散模型上引入两个训练目标——时间桥接(temporal bridging)和运动条件化(motion conditioning),实现灵活控制。推理阶段利用输入图像同时作为首帧和末帧条件以强制循环一致性,通过静态轨迹条件保持背景静止,并结合用户指定的目标对象运动路径实现对动画轨迹与时序的直观控制,从而首次实现了对一般场景下高质量景像画的可控生成。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02646
作者: Aniruddha Mahapatra,Long Mai,Cusuh Ham,Feng Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Project Page: this https URL
Abstract:Cinemagraphs, which combine static photographs with selective, looping motion, offer unique artistic appeal. Generating them from a single photograph in a controllable manner is particularly challenging. Existing image-animation techniques are restricted to simple, low-frequency motions and operate only in narrow domains with repetitive textures like water and smoke. In contrast, large-scale video diffusion models are not tailored for cinemagraph constraints and lack the specialized data required to generate seamless, controlled loops. We present DreamLoop, a controllable video synthesis framework dedicated to generating cinemagraphs from a single photo without requiring any cinemagraph training data. Our key idea is to adapt a general video diffusion model by training it on two objectives: temporal bridging and motion conditioning. This strategy enables flexible cinemagraph generation. During inference, by using the input image as both the first- and last- frame condition, we enforce a seamless loop. By conditioning on static tracks, we maintain a static background. Finally, by providing a user-specified motion path for a target object, our method provides intuitive control over the animation’s trajectory and timing. To our knowledge, DreamLoop is the first method to enable cinemagraph generation for general scenes with flexible and intuitive controls. We demonstrate that our method produces high-quality, complex cinemagraphs that align with user intent, outperforming existing approaches.
zh
[CV-54] Shallow- and Deep-fake Image Manipulation Localization Using Vision Mamba and Guided Graph Neural Network
【速读】:该论文旨在解决图像伪造定位问题,即在浅层伪造(shallowfake)图像和深层伪造(deepfake)图像中精准识别篡改区域。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一种结合视觉Mamba网络(Vision Mamba)与新型引导图神经网络(Guided Graph Neural Network, G-GNN)的深度学习架构:首先利用Vision Mamba提取能清晰描述篡改区域边界特征的地图,再通过G-GNN模块增强篡改像素与真实像素之间的区分度,从而实现对两类伪造图像的高精度定位。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02566
作者: Junbin Zhang,Hamid Reza Tohidypour,Yixiao Wang,Panos Nasiopoulos
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Under review for journal publication
Abstract:Image manipulation localization is a critical research task, given that forged images may have a significant societal impact of various aspects. Such image manipulations can be produced using traditional image editing tools (known as “shallowfakes”) or advanced artificial intelligence techniques (“deepfakes”). While numerous studies have focused on image manipulation localization on either shallowfake images or deepfake videos, few approaches address both cases. In this paper, we explore the feasibility of using a deep learning network to localize manipulations in both shallow- and deep-fake images, and proposed a solution for such purpose. To precisely differentiate between authentic and manipulated pixels, we leverage the Vision Mamba network to extract feature maps that clearly describe the boundaries between tampered and untouched regions. To further enhance this separation, we propose a novel Guided Graph Neural Network (G-GNN) module that amplifies the distinction between manipulated and authentic pixels. Our evaluation results show that our proposed method achieved higher inference accuracy compared to other state-of-the-art methods.
zh
[CV-55] Normalized Conditional Mutual Information Surrogate Loss for Deep Neural Classifiers
【速读】:该论文旨在解决深度神经网络(DNN)分类器训练中传统交叉熵(Cross-Entropy, CE)损失函数在某些任务上性能提升受限的问题。其核心挑战在于如何设计一种更具信息论意义且能更直接优化模型准确率的替代损失函数。解决方案的关键在于提出一种新的信息论代理损失——归一化条件互信息(Normalized Conditional Mutual Information, NCMI),并发现模型的NCMI与其分类准确率呈反比关系;基于此洞察,作者进一步设计了一种交替优化算法以高效最小化NCMI,在图像识别和全切片显微图像(Whole-Slide Imaging, WSI)分型等基准测试中显著优于现有损失函数,同时计算开销与CE相当,展现出良好的实用性和竞争力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02543
作者: Linfeng Ye,Zhixiang Chi,Konstantinos N. Plataniotis,En-hui Yang
机构: University of Waterloo (滑铁卢大学); University of Toronto (多伦多大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Information Theory (cs.IT)
备注: 8 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel information theoretic surrogate loss; normalized conditional mutual information (NCMI); as a drop in alternative to the de facto cross-entropy (CE) for training deep neural network (DNN) based classifiers. We first observe that the model’s NCMI is inversely proportional to its accuracy. Building on this insight, we introduce an alternating algorithm to efficiently minimize the NCMI. Across image recognition and whole-slide imaging (WSI) subtyping benchmarks, NCMI-trained models surpass state of the art losses by substantial margins at a computational cost comparable to that of CE. Notably, on ImageNet, NCMI yields a 2.77% top-1 accuracy improvement with ResNet-50 comparing to the CE; on CAMELYON-17, replacing CE with NCMI improves the macro-F1 by 8.6% over the strongest baseline. Gains are consistent across various architectures and batch sizes, suggesting that NCMI is a practical and competitive alternative to CE.
zh
[CV-56] MovieRecapsQA: A Multimodal Open-Ended Video Question-Answering Benchmark
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有视频问答(VideoQA)基准在多模态推理能力上的不足,特别是难以评估开放性自由回答的问题,以及缺乏对视频与对话线索协同理解的挑战。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个全新的开放性多模态VideoQA基准——MovieRecapsQA,该基准基于电影回顾视频(movie recap videos),通过同步的视觉(回顾视频)和文本(总结摘要)模态提供结构化输入,并生成约8.2K个与电影字幕对齐的问答对,同时提供用于参考-free评估的事实依据。这一设计首次明确提供了输入内容的显式文本上下文,从而支持更精确、细粒度的模型性能分析,尤其适用于测试模型从视频中提取事实信息的能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02536
作者: Shaden Shaar,Bradon Thymes,Sirawut Chaixanien,Claire Cardie,Bharath Hariharan
机构: Cornell University (康奈尔大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Understanding real-world videos such as movies requires integrating visual and dialogue cues to answer complex questions. Yet existing VideoQA benchmarks struggle to capture this multimodal reasoning and are largely not open-ended, given the difficulty of evaluating free-form answers. In this paper, we introduce a novel open-ended multi-modal VideoQA benchmark, MovieRecapsQA created using movie recap videos–a distinctive type of YouTube content that summarizes a film by presenting its key events through synchronized visual (recap video) and textual (recap summary) modalities. Using the recap summary, we generate \approx 8.2 K question-answer (QA) pairs (aligned with movie-subtitles) and provide the necessary “facts” needed to verify an answer in a reference-free manner. To our knowledge, this is the first open-ended VideoQA benchmark that supplies explicit textual context of the input (video and/or text); which we use for evaluation. Our benchmark provides videos of multiple lengths (i.e., recap-segments, movie-segments) and categorizations of questions (by modality and type) to enable fine-grained analysis. We evaluate the performance of seven state-of-the-art MLLMs using our benchmark and observe that: 1) visual-only questions remain the most challenging; 2) models default to textual inputs whenever available; 3) extracting factually accurate information from video content is still difficult for all models; and 4) proprietary and open-source models perform comparably on video-dependent questions.
zh
[CV-57] CT Scans As Video: Efficient Intracranial Hemorrhage Detection Using Multi-Object Tracking
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在边缘设备上对体积医学影像(如CT)进行自动化分析时,因3D卷积神经网络(3D Convolutional Neural Networks, CNNs)高内存与计算需求而导致的效率瓶颈问题。其核心解决方案是将三维CT数据重构为序列视频流(video-viewpoint paradigm),从而在保持2D检测高效性的同时引入3D空间上下文信息;具体而言,采用YOLO系列Nano版本中mAP@50最高的模型作为切片级检测骨干,并结合ByteTrack算法实现z轴方向上的解剖一致性追踪;此外,通过混合推理策略和时空一致性滤波器缓解视频跟踪器的初始化延迟问题,有效区分真实病灶与瞬态预测噪声,最终在独立测试集上将颅内出血(Intracranial Hemorrhage, ICH)检测精度从0.703提升至0.779,同时维持高敏感性,为资源受限环境下的实时患者分诊提供可扩展方案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02521
作者: Amirreza Parvahan,Mohammad Hoseyni,Javad Khoramdel,Amirhossein Nikoofard
机构: K. N. Toosi University of Technology (K. N. 托osi理工大学); Tarbiat Modares University (Tarbiat Modares 大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Automated analysis of volumetric medical imaging on edge devices is severely constrained by the high memory and computational demands of 3D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). This paper develops a lightweight computer vision framework that reconciles the efficiency of 2D detection with the necessity of 3D context by reformulating volumetric Computer Tomography (CT) data as sequential video streams. This video-viewpoint paradigm is applied to the time-sensitive task of Intracranial Hemorrhage (ICH) detection using the Hemorica dataset. To ensure operational efficiency, we benchmarked multiple generations of the YOLO architecture (v8, v10, v11 and v12) in their Nano configurations, selecting the version with the highest mAP@50 to serve as the slice-level backbone. A ByteTrack algorithm is then introduced to enforce anatomical consistency across the z -axis. To address the initialization lag inherent in video trackers, a hybrid inference strategy and a spatiotemporal consistency filter are proposed to distinguish true pathology from transient prediction noise. Experimental results on independent test data demonstrate that the proposed framework serves as a rigorous temporal validator, increasing detection Precision from 0.703 to 0.779 compared to the baseline 2D detector, while maintaining high sensitivity. By approximating 3D contextual reasoning at a fraction of the computational cost, this method provides a scalable solution for real-time patient prioritization in resource-constrained environments, such as mobile stroke units and IoT-enabled remote clinics.
zh
[CV-58] PatchAlign3D: Local Feature Alignment for Dense 3D Shape understanding ATC
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前3D基础模型在全局任务(如检索、分类)上表现优异,但在局部部件级推理(如3D部件分割)上迁移能力差的问题。现有方法依赖多视角渲染与语言模型(Language Model, LM)提示工程来实现密集预测,存在计算开销大、对文本描述敏感且未充分利用3D几何结构等缺陷。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种仅含编码器的3D模型,直接从点云输入中生成与语言对齐的patch-level特征表示;通过两阶段预训练策略:首先将来自视觉编码器(如DINOv2)的稠密2D特征蒸馏至3D patch,再利用多正例对比学习目标将这些patch嵌入与部件级文本嵌入对齐,从而实现无需测试时多视角渲染的快速单次前向推理,并在多个3D部件分割基准上显著优于基于渲染和前馈结构的方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02457
作者: Souhail Hadgi,Bingchen Gong,Ramana Sundararaman,Emery Pierson,Lei Li,Peter Wonka,Maks Ovsjanikov
机构: École polytechnique (巴黎综合理工学院); University of Virginia (弗吉尼亚大学); KAUST (沙特阿卜杜拉国王科技大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Project website: this https URL
Abstract:Current foundation models for 3D shapes excel at global tasks (retrieval, classification) but transfer poorly to local part-level reasoning. Recent approaches leverage vision and language foundation models to directly solve dense tasks through multi-view renderings and text queries. While promising, these pipelines require expensive inference over multiple renderings, depend heavily on large language-model (LLM) prompt engineering for captions, and fail to exploit the inherent 3D geometry of shapes. We address this gap by introducing an encoder-only 3D model that produces language-aligned patch-level features directly from point clouds. Our pre-training approach builds on existing data engines that generate part-annotated 3D shapes by pairing multi-view SAM regions with VLM captioning. Using this data, we train a point cloud transformer encoder in two stages: (1) distillation of dense 2D features from visual encoders such as DINOv2 into 3D patches, and (2) alignment of these patch embeddings with part-level text embeddings through a multi-positive contrastive objective. Our 3D encoder achieves zero-shot 3D part segmentation with fast single-pass inference without any test-time multi-view rendering, while significantly outperforming previous rendering-based and feed-forward approaches across several 3D part segmentation benchmarks. Project website: this https URL
zh
[CV-59] Dont Mind the Gaps: Implicit Neural Representations for Resolution-Agnostic Retinal OCT Analysis
【速读】:该论文旨在解决光学相干断层扫描(Optical Coherence Tomography, OCT)图像因切片间距过大导致的各向异性问题,以及由此引发的2D分割方法在相邻B-scan间结果不一致、3D表面不连续的问题。同时,传统卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Networks, CNNs)受限于训练数据分辨率,难以适配不同成像协议的图像。解决方案的关键在于引入隐式神经表示(Implicit Neural Representations, INRs),其以坐标为输入,具备分辨率无关特性,从而能够处理各向异性数据并实现跨分辨率泛化。论文提出两种基于INRs的框架:一是利用横断面(en-face)模态信息进行B-scan插值,保留结构连续性;二是构建分辨率无关的视网膜图谱,支持无需严格数据格式要求的通用分析。二者均通过群体训练提升形状建模能力,并可在未见病例中实现稳定预测,显著改善了OCT图像的三维密集分析能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02447
作者: Bennet Kahrs,Julia Andresen,Fenja Falta,Monty Santarossa,Heinz Handels,Timo Kepp
机构: University of Heidelberg (海德堡大学); German Cancer Research Center (德国癌症研究中心); University Medical Center Heidelberg (海德堡大学医学中心)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Extended journal version of the proceedings paper “Bridging Gaps in Retinal Imaging: Fusing OCT and SLO Information with Implicit Neural Representations for Improved Interpolation and Segmentation” from the German Conference on Medical Image Computing (BVM 2025; DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-47422-5_24 ). Under review for a MELBA Special Issue. Minor revision resubmitted; decision pending
Abstract:Routine clinical imaging of the retina using optical coherence tomography (OCT) is performed with large slice spacing, resulting in highly anisotropic images and a sparsely scanned retina. Most learning-based methods circumvent the problems arising from the anisotropy by using 2D approaches rather than performing volumetric analyses. These approaches inherently bear the risk of generating inconsistent results for neighboring B-scans. For example, 2D retinal layer segmentations can have irregular surfaces in 3D. Furthermore, the typically used convolutional neural networks are bound to the resolution of the training data, which prevents their usage for images acquired with a different imaging protocol. Implicit neural representations (INRs) have recently emerged as a tool to store voxelized data as a continuous representation. Using coordinates as input, INRs are resolution-agnostic, which allows them to be applied to anisotropic data. In this paper, we propose two frameworks that make use of this characteristic of INRs for dense 3D analyses of retinal OCT volumes. 1) We perform inter-B-scan interpolation by incorporating additional information from en-face modalities, that help retain relevant structures between B-scans. 2) We create a resolution-agnostic retinal atlas that enables general analysis without strict requirements for the data. Both methods leverage generalizable INRs, improving retinal shape representation through population-based training and allowing predictions for unseen cases. Our resolution-independent frameworks facilitate the analysis of OCT images with large B-scan distances, opening up possibilities for the volumetric evaluation of retinal structures and pathologies.
zh
[CV-60] A Spatio-Temporal Deep Learning Approach For High-Resolution Gridded Monsoon Prediction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决印度夏季风(Indian Summer Monsoon, ISM)长期预测中缺乏空间细节的问题,传统方法通常仅预测季节平均值,难以满足区域级资源管理需求。解决方案的关键在于将格点化的季风预测重构为一个时空计算机视觉任务:将多变量的前期大气和海洋场视为多通道图像序列,形成类似视频的输入张量,并基于85年ERA5再分析数据与印度气象局(IMD)降水数据,采用卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)架构学习从五个月前期(1–5月)到后续季风期高分辨率降雨格局的复杂映射关系。该框架能够分别输出四个季风月(6–9月)及整个季节的精细化降水预测,从而实现对季内与季节尺度气候趋势的有效预估。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02445
作者: Parashjyoti Borah,Sanghamitra Sarkar,Ranjan Phukan
机构: Indian Institute of Information Technology Guwahati (印度信息技术学院古瓦哈蒂分校)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 8 pages, 3 figures, 2 Tables, to be submitted to “IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing”
Abstract:The Indian Summer Monsoon (ISM) is a critical climate phenomenon, fundamentally impacting the agriculture, economy, and water security of over a billion people. Traditional long-range forecasting, whether statistical or dynamical, has predominantly focused on predicting a single, spatially-averaged seasonal value, lacking the spatial detail essential for regional-level resource management. To address this gap, we introduce a novel deep learning framework that reframes gridded monsoon prediction as a spatio-temporal computer vision task. We treat multi-variable, pre-monsoon atmospheric and oceanic fields as a sequence of multi-channel images, effectively creating a video-like input tensor. Using 85 years of ERA5 reanalysis data for predictors and IMD rainfall data for targets, we employ a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-based architecture to learn the complex mapping from the five-month pre-monsoon period (January-May) to a high-resolution gridded rainfall pattern for the subsequent monsoon season. Our framework successfully produces distinct forecasts for each of the four monsoon months (June-September) as well as the total seasonal average, demonstrating its utility for both intra-seasonal and seasonal outlooks.
zh
[CV-61] Evaluating the Diagnostic Classification Ability of Multimodal Large Language Models : Insights from the Osteoarthritis Initiative
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在特定疾病影像分类任务中表现不稳定的问题,尤其是针对膝骨关节炎(Knee Osteoarthritis, OA)X光片的诊断分类。尽管MLLMs在医学视觉问答(Medical Visual Question Answering, VQA)和报告生成方面展现出潜力,但其在疾病特异性分类任务中的可靠性仍不足。研究通过系统性消融实验,评估了视觉编码器、连接模块和大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)在不同训练策略下的贡献,发现:仅训练视觉编码器即可超越完整MLLM流水线的分类准确率;对LLM进行微调并未带来显著提升,而基于小规模、类别均衡数据集(500张图像)的LoRA微调效果优于大规模但类别不平衡的数据集(5778张图像)。关键结论是,在需要高置信度的临床诊断场景中,LLM更适合作为解释工具或报告生成器,而非主分类器,因此应优先优化视觉编码器并注重数据集的质量与平衡性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02443
作者: Li Wang,Xi Chen,XiangWen Deng,HuaHui Yi,ZeKun Jiang,Kang Li,Jian Li
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
备注:
Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) show promising performance on medical visual question answering (VQA) and report generation, but these generation and explanation abilities do not reliably transfer to disease-specific classification. We evaluated MLLM architectures on knee osteoarthritis (OA) radiograph classification, which remains underrepresented in existing medical MLLM benchmarks, even though knee OA affects an estimated 300 to 400 million people worldwide. Through systematic ablation studies manipulating the vision encoder, the connector, and the large language model (LLM) across diverse training strategies, we measured each component’s contribution to diagnostic accuracy. In our classification task, a trained vision encoder alone could outperform full MLLM pipelines in classification accuracy and fine-tuning the LLM provided no meaningful improvement over prompt-based guidance. And LoRA fine-tuning on a small, class-balanced dataset (500 images) gave better results than training on a much larger but class-imbalanced set (5,778 images), indicating that data balance and quality can matter more than raw scale for this task. These findings suggest that for domain-specific medical classification, LLMs are more effective as interpreters and report generators rather than as primary classifiers. Therefore, the MLLM architecture appears less suitable for medical image diagnostic classification tasks that demand high certainty. We recommend prioritizing vision encoder optimization and careful dataset curation when developing clinically applicable systems.
zh
[CV-62] Understanding Pure Textual Reasoning for Blind Image Quality Assessment
【速读】:该论文旨在解决盲图像质量评估(Blind Image Quality Assessment, BIQA)中文本信息如何贡献于质量预测以及文本对评分相关图像内容的表征能力究竟有多大的问题。其解决方案的关键在于从信息流视角出发,通过对比现有BIQA模型与三种设计用于学习图像-文本-评分关系的新范式——思维链(Chain-of-Thought)、自一致性(Self-Consistency)和自编码器(Autoencoder)——来系统分析文本在质量预测中的作用机制。实验表明,仅使用文本信息时现有模型性能显著下降;而自一致性范式能有效缩小图像条件与文本条件预测之间的差距(PLCC/SRCC差异降至0.02/0.03),揭示了提升文本推理能力以增强BIQA性能的核心路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02441
作者: Yuan Li,Shin’ya Nishida
机构: Kyoto University (京都大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Code available at this https URL . This work is under review
Abstract:Textual reasoning has recently been widely adopted in Blind Image Quality Assessment (BIQA). However, it remains unclear how textual information contributes to quality prediction and to what extent text can represent the score-related image contents. This work addresses these questions from an information-flow perspective by comparing existing BIQA models with three paradigms designed to learn the image-text-score relationship: Chain-of-Thought, Self-Consistency, and Autoencoder. Our experiments show that the score prediction performance of the existing model significantly drops when only textual information is used for prediction. Whereas the Chain-of-Thought paradigm introduces little improvement in BIQA performance, the Self-Consistency paradigm significantly reduces the gap between image- and text-conditioned predictions, narrowing the PLCC/SRCC difference to 0.02/0.03. The Autoencoder-like paradigm is less effective in closing the image-text gap, yet it reveals a direction for further optimization. These findings provide insights into how to improve the textual reasoning for BIQA and high-level vision tasks.
zh
[CV-63] WebGym: Scaling Training Environments for Visual Web Agents with Realistic Tasks
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前视觉网页智能体(Visual Web Agent)训练中因网站非平稳性和多样性导致的泛化能力不足问题,即现有小规模或人工构造的任务集难以支持鲁棒策略学习。其解决方案的关键在于构建了目前最大规模的开源环境WebGym,包含近30万项基于评分标准(rubric-based evaluation)的多样化真实网页任务,并采用简单的强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)训练范式——利用代理自身交互轨迹(rollouts)作为训练数据,以任务奖励为反馈信号指导策略优化。此外,通过开发高吞吐量异步轨迹采样系统,实现4–5倍的采样效率提升,并系统性扩展任务集的广度、深度与规模,从而显著提升模型在未见网站上的性能表现,验证了大规模真实场景数据对视觉网页智能体泛化能力的关键作用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02439
作者: Hao Bai,Alexey Taymanov,Tong Zhang,Aviral Kumar,Spencer Whitehead
机构: Microsoft(微软); UIUC(伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校); CMU(卡内基梅隆大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:We present WebGym, the largest-to-date open-source environment for training realistic visual web agents. Real websites are non-stationary and diverse, making artificial or small-scale task sets insufficient for robust policy learning. WebGym contains nearly 300,000 tasks with rubric-based evaluations across diverse, real-world websites and difficulty levels. We train agents with a simple reinforcement learning (RL) recipe, which trains on the agent’s own interaction traces (rollouts), using task rewards as feedback to guide learning. To enable scaling RL, we speed up sampling of trajectories in WebGym by developing a high-throughput asynchronous rollout system, designed specifically for web agents. Our system achieves a 4-5x rollout speedup compared to naive implementations. Second, we scale the task set breadth, depth, and size, which results in continued performance improvement. Fine-tuning a strong base vision-language model, Qwen-3-VL-8B-Instruct, on WebGym results in an improvement in success rate on an out-of-distribution test set from 26.2% to 42.9%, significantly outperforming agents based on proprietary models such as GPT-4o and GPT-5-Thinking that achieve 27.1% and 29.8%, respectively. This improvement is substantial because our test set consists only of tasks on websites never seen during training, unlike many other prior works on training visual web agents.
zh
[CV-64] AP-ViTs: Task-Adaptive Pruning for On-Device Deployment of Vision Transformers
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在隐私保护的移动计算场景下,如何实现任务定制化的视觉Transformer(Vision Transformer, ViT)剪枝问题。现有方法要么生成单一剪枝模型无法适配设备异构性,要么依赖设备本地数据微调,难以满足资源受限和隐私约束条件。解决方案的关键在于提出TAP-ViTs框架:首先通过高斯混合模型(Gaussian Mixture Model, GMM)构建设备级任务特征代理数据集——各设备仅上传GMM参数至云端,云端据此从公共数据中筛选分布一致的样本形成任务代表性度量数据集;进而设计双粒度重要性评估策略,联合衡量复合神经元重要性和自适应层重要性,从而实现细粒度、任务感知的个性化剪枝,且无需访问原始本地数据,兼顾隐私保护与模型效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02437
作者: Zhibo Wang,Zuoyuan Zhang,Xiaoyi Pang,Qile Zhang,Xuanyi Hao,Shuguo Zhuo,Peng Sun
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); Hunan University (湖南大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have demonstrated strong performance across a wide range of vision tasks, yet their substantial computational and memory demands hinder efficient deployment on resource-constrained mobile and edge devices. Pruning has emerged as a promising direction for reducing ViT complexity. However, existing approaches either (i) produce a single pruned model shared across all devices, ignoring device heterogeneity, or (ii) rely on fine-tuning with device-local data, which is often infeasible due to limited on-device resources and strict privacy constraints. As a result, current methods fall short of enabling task-customized ViT pruning in privacy-preserving mobile computing settings. This paper introduces TAP-ViTs, a novel task-adaptive pruning framework that generates device-specific pruned ViT models without requiring access to any raw local data. Specifically, to infer device-level task characteristics under privacy constraints, we propose a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM)-based metric dataset construction mechanism. Each device fits a lightweight GMM to approximate its private data distribution and uploads only the GMM parameters. Using these parameters, the cloud selects distribution-consistent samples from public data to construct a task-representative metric dataset for each device. Based on this proxy dataset, we further develop a dual-granularity importance evaluation-based pruning strategy that jointly measures composite neuron importance and adaptive layer importance, enabling fine-grained, task-aware pruning tailored to each device’s computational budget. Extensive experiments across multiple ViT backbones and datasets demonstrate that TAP-ViTs consistently outperforms state-of-the-art pruning methods under comparable compression ratios.
zh
[CV-65] NitroGen: An Open Foundation Model for Generalist Gaming Agents
【速读】:该论文旨在解决通用游戏智能体(generalist gaming agents)在跨游戏场景中缺乏泛化能力的问题,即如何让模型从大量多样化游戏中学习到可迁移的视觉-动作策略。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个大规模、多游戏的视觉-动作基础模型NitroGen,该模型基于4万小时跨1000余款游戏的 gameplay 视频数据训练而成,核心创新包括:(1)通过自动提取公开 gameplay 视频中的玩家操作构建互联网规模的视频-动作数据集(internet-scale video-action dataset);(2)设计一个多游戏基准环境以量化模型的跨游戏泛化性能;(3)采用大规模行为克隆(behavior cloning)训练统一的视觉-动作模型(unified vision-action model)。该方法显著提升了模型在未见过的游戏中的任务成功率,相对从头训练模型最高提升52%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02427
作者: Loïc Magne,Anas Awadalla,Guanzhi Wang,Yinzhen Xu,Joshua Belofsky,Fengyuan Hu,Joohwan Kim,Ludwig Schmidt,Georgia Gkioxari,Jan Kautz,Yisong Yue,Yejin Choi,Yuke Zhu,Linxi “Jim” Fan
机构: NVIDIA(英伟达); Stanford University (斯坦福大学); California Institute of Technology (加州理工学院); University of Chicago (芝加哥大学); University of Texas at Austin (德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 16 pages, 7 figures
Abstract:We introduce NitroGen, a vision-action foundation model for generalist gaming agents that is trained on 40,000 hours of gameplay videos across more than 1,000 games. We incorporate three key ingredients: 1) an internet-scale video-action dataset constructed by automatically extracting player actions from publicly available gameplay videos, 2) a multi-game benchmark environment that can measure cross-game generalization, and 3) a unified vision-action model trained with large-scale behavior cloning. NitroGen exhibits strong competence across diverse domains, including combat encounters in 3D action games, high-precision control in 2D platformers, and exploration in procedurally generated worlds. It transfers effectively to unseen games, achieving up to 52% relative improvement in task success rates over models trained from scratch. We release the dataset, evaluation suite, and model weights to advance research on generalist embodied agents.
zh
[CV-66] Watch Wider and Think Deeper: Collaborative Cross-modal Chain-of-Thought for Complex Visual Reasoning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态推理中现有思维链(Chain-of-Thought)方法在跨模态场景下的两个关键问题:一是对单一粗粒度图像区域的过度依赖,二是连续推理步骤之间的语义碎片化。其解决方案的核心在于提出CoCoT(Collaborative Cross-modal Thought)框架,包含两项关键技术:(1) 动态多区域定位(Dynamic Multi-Region Grounding),根据问题自适应地检测最相关的图像区域;(2) 关系感知推理(Relation-Aware Reasoning),通过迭代对齐视觉线索实现多区域协同,构建连贯且逻辑一致的推理链条。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02422
作者: Wenting Lu,Didi Zhu,Tao Shen,Donglin Zhu,Ayong Ye,Chao Wu
机构: Fujian Normal University (福建师范大学); Zhejiang University (浙江大学); Zhejiang Normal University (浙江师范大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Multi-modal reasoning requires the seamless integration of visual and linguistic cues, yet existing Chain-of-Thought methods suffer from two critical limitations in cross-modal scenarios: (1) over-reliance on single coarse-grained image regions, and (2) semantic fragmentation between successive reasoning steps. To address these issues, we propose the CoCoT (Collaborative Coross-modal Thought) frame- work, built upon two key innovations: a) Dynamic Multi-Region Grounding to adaptively detect the most relevant image regions based on the question, and b) Relation-Aware Reasoning to enable multi-region collaboration by iteratively align- ing visual cues to form a coherent and logical chain of thought. Through this approach, we construct the CoCoT-70K dataset, comprising 74,691 high-quality samples with multi-region annotations and structured reasoning chains. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CoCoT significantly enhances complex visual rea- soning, achieving an average accuracy improvement of 15.4% on LLaVA-1.5 and 4.0% on Qwen2-VL across six challenging benchmarks. The data and code are available at: this https URL.
zh
[CV-67] Multimodal Sentiment Analysis based on Multi-channel and Symmetric Mutual Promotion Feature Fusion
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态情感分析(Multimodal Sentiment Analysis)中因单模态特征提取不充分以及现有方法忽视模态间差异而导致的特征融合效果不佳的问题。其解决方案的关键在于:首先,通过多通道特征提取策略增强视觉和听觉模态内部的特征表示能力;其次,提出对称互促进(Symmetric Mutual Promotion, SMP)的跨模态特征融合机制,该机制结合对称交叉注意力与自注意力机制,实现模态间有用信息的有效交换与上下文建模,从而强化模态间的协同作用;最终,将模态内特征与融合后的跨模态特征进行整合,充分利用模态间信息的互补性并考虑特征差异,显著提升情感识别性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02415
作者: Wangyuan Zhu,Jun Yu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Multimodal sentiment analysis is a key technology in the fields of human-computer interaction and affective computing. Accurately recognizing human emotional states is crucial for facilitating smooth communication between humans and machines. Despite some progress in multimodal sentiment analysis research, numerous challenges remain. The first challenge is the limited and insufficiently rich features extracted from single modality data. Secondly, most studies focus only on the consistency of inter-modal feature information, neglecting the differences between features, resulting in inadequate feature information fusion. In this paper, we first extract multi-channel features to obtain more comprehensive feature information. We employ dual-channel features in both the visual and auditory modalities to enhance intra-modal feature representation. Secondly, we propose a symmetric mutual promotion (SMP) inter-modal feature fusion method. This method combines symmetric cross-modal attention mechanisms and self-attention mechanisms, where the cross-modal attention mechanism captures useful information from other modalities, and the self-attention mechanism models contextual information. This approach promotes the exchange of useful information between modalities, thereby strengthening inter-modal interactions. Furthermore, we integrate intra-modal features and inter-modal fused features, fully leveraging the complementarity of inter-modal feature information while considering feature information differences. Experiments conducted on two benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our proposed method.
zh
[CV-68] MIAR: Modality Interaction and Alignment Representation Fuison for Multimodal Emotion
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态情感识别(Multimodal Emotion Recognition, MER)中因模态间分布差异显著、贡献度不均以及跨文本模型特征泛化能力不足所导致的性能瓶颈问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为模态交互与对齐表示(Modality Interaction and Alignment Representation, MIAR)的新架构:该架构通过特征交互机制生成能表征各模态全局信息的特征令牌(feature tokens),从而实现跨模态信息提取;同时,利用对比学习和归一化策略对不同模态进行对齐,提升模型在多样化文本特征下的鲁棒性与泛化能力。实验结果表明,MIAR在CMU-MOSI和CMU-MOSEI两个基准数据集上优于现有最优方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02414
作者: Jichao Zhu,Jun Yu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Multimodal Emotion Recognition (MER) aims to perceive human emotions through three modes: language, vision, and audio. Previous methods primarily focused on modal fusion without adequately addressing significant distributional differences among modalities or considering their varying contributions to the task. They also lacked robust generalization capabilities across diverse textual model features, thus limiting performance in multimodal scenarios. Therefore, we propose a novel approach called Modality Interaction and Alignment Representation (MIAR). This network integrates contextual features across different modalities using a feature interaction to generate feature tokens to represent global representations of this modality extracting information from other modalities. These four tokens represent global representations of how each modality extracts information from others. MIAR aligns different modalities using contrastive learning and normalization strategies. We conduct experiments on two benchmarks: CMU-MOSI and CMU-MOSEI datasets, experimental results demonstrate the MIAR outperforms state-of-the-art MER methods.
zh
[CV-69] Expert-Guided Explainable Few-Shot Learning with Active Sample Selection for Medical Image Analysis ALT
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学图像分析中两个关键问题:标注数据稀缺与模型可解释性不足,二者均限制了生成式 AI (Generative AI) 在临床环境中的部署。解决方案的核心在于提出双框架方法:一是专家引导的可解释少样本学习(EGxFSL),通过放射科医生定义的感兴趣区域(Region-of-Interest, ROI)作为空间监督信号,结合Grad-CAM-based Dice损失与原型分类联合优化,实现可解释的少样本学习;二是可解释性引导的主动学习(xGAL),在样本获取阶段同时考虑预测不确定性与注意力区域错位程度,形成以可解释性驱动训练和样本选择的闭环系统。该方案在BraTS、VinDr-CXR和SIIM-COVID-19等多个数据集上显著优于非引导基线,并在极低数据量下仍保持高精度,验证了其在跨模态任务中的泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02409
作者: Longwei Wang,Ifrat Ikhtear Uddin,KC Santosh
机构: University of South Dakota (南达科他大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted for publication in IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2025
Abstract:Medical image analysis faces two critical challenges: scarcity of labeled data and lack of model interpretability, both hindering clinical AI deployment. Few-shot learning (FSL) addresses data limitations but lacks transparency in predictions. Active learning (AL) methods optimize data acquisition but overlook interpretability of acquired samples. We propose a dual-framework solution: Expert-Guided Explainable Few-Shot Learning (EGxFSL) and Explainability-Guided AL (xGAL). EGxFSL integrates radiologist-defined regions-of-interest as spatial supervision via Grad-CAM-based Dice loss, jointly optimized with prototypical classification for interpretable few-shot learning. xGAL introduces iterative sample acquisition prioritizing both predictive uncertainty and attention misalignment, creating a closed-loop framework where explainability guides training and sample selection synergistically. On the BraTS (MRI), VinDr-CXR (chest X-ray), and SIIM-COVID-19 (chest X-ray) datasets, we achieve accuracies of 92%, 76%, and 62%, respectively, consistently outperforming non-guided baselines across all datasets. Under severe data constraints, xGAL achieves 76% accuracy with only 680 samples versus 57% for random sampling. Grad-CAM visualizations demonstrate guided models focus on diagnostically relevant regions, with generalization validated on breast ultrasound confirming cross-modality applicability.
zh
[CV-70] Self-Supervised Masked Autoencoders with Dense-Unet for Coronary Calcium Removal in limited CT Data
【速读】:该论文旨在解决冠状动脉钙化在CT血管成像(CTA)中产生的伪影问题,此类伪影严重干扰管腔狭窄的诊断。传统基于深度卷积神经网络(DCNN)的方法如Dense-Unet虽能在图像修复(inpainting)中发挥作用,但通常依赖大量标注数据,在医学领域难以获取。为此,作者提出了一种新的自监督学习框架Dense-MAE,其关键创新在于引入了类似Masked Autoencoders(MAE)的思想,通过随机遮蔽血管腔的3D体素块并训练Dense-Unet重建缺失几何结构,从而迫使编码器在无需人工标注的情况下学习动脉拓扑的高层特征表示。实验表明,使用该预训练策略获得的权重初始化模型,在少量样本场景下显著提升了去钙化精度与狭窄评估性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02392
作者: Mo Chen
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 6 pages, in Chinese language, 2 figures
Abstract:Coronary calcification creates blooming artifacts in Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA), severely hampering the diagnosis of lumen stenosis. While Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (DCNNs) like Dense-Unet have shown promise in removing these artifacts via inpainting, they often require large labeled datasets which are scarce in the medical domain. Inspired by recent advancements in Masked Autoencoders (MAE) for 3D point clouds, we propose \textbfDense-MAE, a novel self-supervised learning framework for volumetric medical data. We introduce a pre-training strategy that randomly masks 3D patches of the vessel lumen and trains the Dense-Unet to reconstruct the missing geometry. This forces the encoder to learn high-level latent features of arterial topology without human annotation. Experimental results on clinical CTA datasets demonstrate that initializing the Calcium Removal network with our MAE-based weights significantly improves inpainting accuracy and stenosis estimation compared to training from scratch, specifically in few-shot scenarios.
zh
[CV-71] ransformers self-organize like newborn visual systems when trained in prenatal worlds
【速读】:该论文试图解决的核心问题是:生成式 AI(如Transformer)与大脑在学习机制上是否存在共性,即它们是否遵循相同的通用学习原则。传统研究受限于训练数据的差异——大脑依赖于出生前的生物可塑性输入(如视网膜波),而Transformer通常基于大规模非生物合理的文本或图像数据进行训练。为验证两者学习机制的相似性,作者提出关键解决方案:模拟胎儿期视觉输入(使用视网膜波生成器)并采用自监督时序学习策略对Transformer进行训练。实验结果表明,模型在适应这种“产前视觉世界”后,其内部结构自发演化出与新生儿视觉系统一致的特征:早期层对边缘敏感、后期层对形状敏感、且感受野随层次递增。这一发育收敛现象表明,无论生物或人工系统,在面对相同初始感知输入时,均能自发形成类似的层级表征结构,揭示了大脑与Transformer可能共享基本的学习动力学和拟合原则。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03117
作者: Lalit Pandey,Samantha M. W. Wood,Justin N. Wood
机构: Indiana University Bloomington (印第安纳大学布卢明顿分校)
类目: Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Do transformers learn like brains? A key challenge in addressing this question is that transformers and brains are trained on fundamentally different data. Brains are initially “trained” on prenatal sensory experiences (e.g., retinal waves), whereas transformers are typically trained on large datasets that are not biologically plausible. We reasoned that if transformers learn like brains, then they should develop the same structure as newborn brains when exposed to the same prenatal data. To test this prediction, we simulated prenatal visual input using a retinal wave generator. Then, using self-supervised temporal learning, we trained transformers to adapt to those retinal waves. During training, the transformers spontaneously developed the same structure as newborn visual systems: (1) early layers became sensitive to edges, (2) later layers became sensitive to shapes, and (3) the models developed larger receptive fields across layers. The organization of newborn visual systems emerges spontaneously when transformers adapt to a prenatal visual world. This developmental convergence suggests that brains and transformers learn in common ways and follow the same general fitting principles.
zh
[CV-72] DiT-JSCC: Rethinking Deep JSCC with Diffusion Transformers and Semantic Representations
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式联合信源信道编码(Generative Joint Source-Channel Coding, GJSCC)中因重建导向型编码器与生成式解码器之间存在根本性不匹配而导致的语义一致性不足问题,尤其在极端无线信道条件(如超低带宽和低信噪比)下表现尤为明显。其解决方案的关键在于提出DiT-JSCC架构:通过设计一个语义-细节双分支编码器(semantics-detail dual-branch encoder),自然地与粗到细条件扩散Transformer(conditional Diffusion Transformer, DiT)解码器协同学习,从而优先保障语义一致性;同时引入一种基于Kolmogorov复杂度启发的无需训练的自适应带宽分配策略,进一步提升传输效率,重新定义了生成式解码时代的信息价值概念。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03112
作者: Kailin Tan,Jincheng Dai,Sixian Wang,Guo Lu,Shuo Shao,Kai Niu,Wenjun Zhang,Ping Zhang
机构: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (北京邮电大学); Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); University of Shanghai for Science and Technology (上海理工大学)
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 14pages, 14figures, 2tables
Abstract:Generative joint source-channel coding (GJSCC) has emerged as a new Deep JSCC paradigm for achieving high-fidelity and robust image transmission under extreme wireless channel conditions, such as ultra-low bandwidth and low signal-to-noise ratio. Recent studies commonly adopt diffusion models as generative decoders, but they frequently produce visually realistic results with limited semantic consistency. This limitation stems from a fundamental mismatch between reconstruction-oriented JSCC encoders and generative decoders, as the former lack explicit semantic discriminability and fail to provide reliable conditional cues. In this paper, we propose DiT-JSCC, a novel GJSCC backbone that can jointly learn a semantics-prioritized representation encoder and a diffusion transformer (DiT) based generative decoder, our open-source project aims to promote the future research in GJSCC. Specifically, we design a semantics-detail dual-branch encoder that aligns naturally with a coarse-to-fine conditional DiT decoder, prioritizing semantic consistency under extreme channel conditions. Moreover, a training-free adaptive bandwidth allocation strategy inspired by Kolmogorov complexity is introduced to further improve the transmission efficiency, thereby indeed redefining the notion of information value in the era of generative decoding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DiT-JSCC consistently outperforms existing JSCC methods in both semantic consistency and visual quality, particularly in extreme regimes.
zh
[CV-73] Lesion Segmentation in FDG-PET/CT Using Swin Transformer U-Net 3D: A Robust Deep Learning Framework
【速读】:该论文旨在解决正电子发射断层扫描/计算机断层扫描(PET/CT)图像中病灶自动分割的准确性与效率问题,这对于癌症诊断和治疗规划至关重要。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于Swin Transformer的3D U-Net架构(SwinUNet3D),通过引入移位窗口自注意力机制(shifted window self-attention)增强全局上下文建模能力,并结合U-Net式的跳跃连接(skip connections)保留精细解剖结构信息,从而在保持高精度的同时提升推理速度。实验表明,该方法在AutoPET III FDG数据集上显著优于传统3D U-Net,在Dice系数(0.88)和交并比(IoU 0.78)上均有大幅提升,同时对小尺寸和不规则病灶的检测表现更优,且减少了假阳性结果,提升了PET/CT融合质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02864
作者: Shovini Guha,Dwaipayan Nandi
机构: 未知
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 8 pages, 3 figures, 3 tables
Abstract:Accurate and automated lesion segmentation in Positron Emission Tomography / Computed Tomography (PET/CT) imaging is essential for cancer diagnosis and therapy planning. This paper presents a Swin Transformer UNet 3D (SwinUNet3D) framework for lesion segmentation in Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography / Computed Tomography (FDG-PET/CT) scans. By combining shifted window self-attention with U-Net style skip connections, the model captures both global context and fine anatomical detail. We evaluate SwinUNet3D on the AutoPET III FDG dataset and compare it against a baseline 3D U-Net. Results show that SwinUNet3D achieves a Dice score of 0.88 and IoU of 0.78, surpassing 3D U-Net (Dice 0.48, IoU 0.32) while also delivering faster inference times. Qualitative analysis demonstrates improved detection of small and irregular lesions, reduced false positives, and more accurate PET/CT fusion. While the framework is currently limited to FDG scans and trained under modest GPU resources, it establishes a strong foundation for future multi-tracer, multi-center evaluations and benchmarking against other transformer-based architectures. Overall, SwinUNet3D represents an efficient and robust approach to PET/CT lesion segmentation, advancing the integration of transformer-based models into oncology imaging workflows.
zh
[CV-74] Annealed Langevin Posterior Sampling (ALPS): A Rapid Algorithm for Image Restoration with Multiscale Energy Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决成像领域逆问题(inverse problems in imaging)中模型对高效推理、不确定性量化及合理概率推理的需求,传统能量模型(Energy-Based Models, EBMs)虽具备可解释的能量景观和组合结构优势,但存在计算成本高与训练不稳定的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种快速蒸馏策略,将预训练扩散模型的优势迁移至多尺度EBM框架中,从而实现高效采样并保留基于势函数(potential-based)框架的可解释性与组合性;进一步地,利用EBM的组合特性设计了退火朗之万后验采样算法(Annealed Langevin Posterior Sampling, ALPS),在静态后验分布上进行退火,无需复杂潜在变量引导机制,即可实现最大后验估计(MAP)、最小均方误差(MMSE)估计及不确定性评估。实验表明该方法在图像修复与磁共振成像重建任务中达到或超越扩散模型基线的精度与效率,并支持MAP恢复,具备在科学与临床场景中实际部署的潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02594
作者: Jyothi Rikhab Chand,Mathews Jacob
机构: University of Virginia (弗吉尼亚大学)
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Solving inverse problems in imaging requires models that support efficient inference, uncertainty quantification, and principled probabilistic reasoning. Energy-Based Models (EBMs), with their interpretable energy landscapes and compositional structure, are well-suited for this task but have historically suffered from high computational costs and training instability. To overcome the historical shortcomings of EBMs, we introduce a fast distillation strategy to transfer the strengths of pre-trained diffusion models into multi-scale EBMs. These distilled EBMs enable efficient sampling and preserve the interpretability and compositionality inherent to potential-based frameworks. Leveraging EBM compositionality, we propose Annealed Langevin Posterior Sampling (ALPS) algorithm for Maximum-A-Posteriori (MAP), Minimum Mean Square Error (MMSE), and uncertainty estimates for inverse problems in imaging. Unlike diffusion models that use complex guidance strategies for latent variables, we perform annealing on static posterior distributions that are well-defined and composable. Experiments on image inpainting and MRI reconstruction demonstrate that our method matches or surpasses diffusion-based baselines in both accuracy and efficiency, while also supporting MAP recovery. Overall, our framework offers a scalable and principled solution for inverse problems in imaging, with potential for practical deployment in scientific and clinical settings. ALPS code is available at the GitHub repository \hrefthis https URLALPS.
zh
[CV-75] Comparative Analysis of Binarization Methods For Medical Image Hashing On Odir Dataset
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学图像检索与设备库存管理中的高效相似性搜索问题,核心挑战在于如何在保证高检索精度的同时降低存储和计算开销。解决方案的关键在于采用监督离散哈希(Supervised Discrete Hashing, SDH)方法,通过学习将深度特征嵌入映射为紧凑的二进制码(如32位),实现高精度的近似最近邻检索。实验表明,SDH在ODIR数据集上以仅32位哈希码即达到mAP@100为0.9184,显著优于LSH、ITQ和KSH等传统方法,并且在比特数远少于现有最优方案的情况下仍接近当前最先进水平,体现了其在准确性、存储效率与计算速度之间的良好平衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02564
作者: Nedim Muzoglu
机构: 未知
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
备注: 17th International İstanbul Scientific Research Congress
Abstract:In this study, we evaluated four binarization methods. Locality-Sensitive Hashing (LSH), Iterative Quantization (ITQ), Kernel-based Supervised Hashing (KSH), and Supervised Discrete Hashing (SDH) on the ODIR dataset using deep feature embeddings. Experimental results show that SDH achieved the best performance, with an mAP@100 of 0.9184 using only 32-bit codes, outperforming LSH, ITQ, and KSH. Compared with prior studies, our method proved highly competitive: Fang et al. reported 0.7528 (Fundus-iSee, 48 bits) and 0.8856 (ASOCT-Cataract, 48 bits), while Wijesinghe et al. achieved 94.01 (KVASIR, 256 bits). Despite using significantly fewer bits, our SDH-based framework reached retrieval accuracy close to the state-of-the-art. These findings demonstrate that SDH is the most effective approach among those tested, offering a practical balance of accuracy, storage, and efficiency for medical image retrieval and device inventory management.
zh
[CV-76] A Green Solution for Breast Region Segmentation Using Deep Active Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学乳腺图像标注耗时且计算成本高的问题,通过优化深度主动学习(Deep Active Learning)中的样本选择策略来提升乳腺区域分割(Breast Region Segmentation, BRS)模型的训练效率与性能。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于乳腺解剖几何(Breast Anatomy Geometry, BAG)分析的新颖样本选择方法,将患者定位和乳房尺寸作为核心筛选标准,结合随机选择、最近邻点、乳房尺寸及三者混合四种策略进行对比评估,最终发现将最近邻点策略与30%的训练数据比例相结合,在分割性能、计算效率和环境可持续性之间实现了最优平衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02538
作者: Sam Narimani,Solveig Roth Hoff,Kathinka Dæhli Kurz,Kjell-Inge Gjesdal,Jürgen Geisler,Endre Grøvik
机构: Norwegian University of Science and Technology (挪威科技大学); Sør-Trøndelag University College (南特伦德拉格大学学院); Nordic CAD Center (北欧CAD中心); University of Oslo (奥斯陆大学)
类目: Medical Physics (physics.med-ph); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
备注:
Abstract:Purpose: Annotation of medical breast images is an essential step toward better diagnostic but a time consuming task. This research aims to focus on different selecting sample strategies within deep active learning on Breast Region Segmentation (BRS) to lessen computational cost of training and effective use of resources. Methods: The Stavanger breast MRI dataset containing 59 patients was used in this study, with FCN-ResNet50 adopted as a sustainable deep learning (DL) model. A novel sample selection approach based on Breast Anatomy Geometry (BAG) analysis was introduced to group data with similar informative features for DL. Patient positioning and Breast Size were considered the key selection criteria in this process. Four selection strategies including Random Selection, Nearest Point, Breast Size, and a hybrid of all three strategies were evaluated using an active learning framework. Four training data proportions of 10%, 20%, 30%, and 40% were used for model training, with the remaining data reserved for testing. Model performance was assessed using Dice score, Intersection over Union, precision, and recall, along with 5-fold cross-validation to enhance generalizability. Results: Increasing the training data proportion from 10% to 40% improved segmentation performance for nearly all strategies, except for Random Selection. The Nearest Point strategy consistently achieved the lowest carbon footprint at 30% and 40% data proportions. Overall, combining the Nearest Point strategy with 30% of the training data provided the best balance between segmentation performance, efficiency, and environmental sustainability. Keywords: Deep Active Learning, Breast Region Segmentation, Human-center analysis Subjects: Medical Physics (physics.med-ph); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02538 [physics.med-ph] (or arXiv:2601.02538v1 [physics.med-ph] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02538 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) Submission history From: Sam Narimani [view email] [v1] Mon, 5 Jan 2026 20:25:34 UTC (11,863 KB)
zh
[CV-77] Deep Learning Superresolution for 7T Knee MR Imaging: Impact on Image Quality and Diagnostic Performance
【速读】:该论文旨在解决7T膝关节磁共振成像(MRI)中低分辨率(Low-Resolution, LR)图像质量不足的问题,同时评估生成式AI增强的超分辨率(Superresolution, SR)图像在诊断准确性上的价值。其解决方案的关键在于利用基于混合注意力机制的Transformer模型从LR数据中重建出高分辨率图像,从而在保持与标准高分辨率(High-Resolution, HR)图像相当的解剖结构可见性的同时,提升主观图像质量,并验证其在膝关节内病变检测中的诊断性能是否优于传统LR图像。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02436
作者: Pinzhen Chen,Libo Xu,Boyang Pan,Jing Li,Yuting Wang,Ran Xiong,Xiaoli Gou,Long Qing,Wenjing Hou,Nan-jie Gong,Wei Chen
机构: 未知
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Background: Deep learning superresolution (SR) may enhance musculoskeletal MR image quality, but its diagnostic value in knee imaging at 7T is unclear. Objectives: To compare image quality and diagnostic performance of SR, low-resolution (LR), and high-resolution (HR) 7T knee MRI. Methods: In this prospective study, 42 participants underwent 7T knee MRI with LR (0.80.82 mm3) and HR (0.40.42 mm3) sequences. SR images were generated from LR data using a Hybrid Attention Transformer model. Three radiologists assessed image quality, anatomic conspicuity, and detection of knee pathologies. Arthroscopy served as reference in 10 cases. Results: SR images showed higher overall quality than LR (median score 5 vs 4, P.001) and lower noise than HR (5 vs 4, P.001). Visibility of cartilage, menisci, and ligaments was superior in SR and HR compared to LR (P.001). Detection rates and diagnostic performance (sensitivity, specificity, AUC) for intra-articular pathology were similar across image types (P=.095). Conclusions: Deep learning superresolution improved subjective image quality in 7T knee MRI but did not increase diagnostic accuracy compared with standard LR imaging.
zh
人工智能
[AI-0] MAGMA: A Multi-Graph based Agent ic Memory Architecture for AI Agents
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前记忆增强型生成模型(Memory-Augmented Generation, MAG)在长程推理任务中因依赖单一语义相似度检索机制而导致的可解释性差、查询意图与检索证据对齐不足的问题。其核心解决方案是提出MAGMA架构,通过将每个记忆项在正交的语义、时间、因果和实体四类图结构中进行表示,实现多关系视角下的记忆建模;并采用策略引导的遍历方式完成检索,从而支持查询自适应的选择与结构化上下文构建,有效解耦了记忆表征与检索逻辑,提升了推理路径的透明性和控制精度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03236
作者: Dongming Jiang,Yi Li,Guanpeng Li,Bingzhe Li
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Memory-Augmented Generation (MAG) extends Large Language Models with external memory to support long-context reasoning, but existing approaches largely rely on semantic similarity over monolithic memory stores, entangling temporal, causal, and entity information. This design limits interpretability and alignment between query intent and retrieved evidence, leading to suboptimal reasoning accuracy. In this paper, we propose MAGMA, a multi-graph agentic memory architecture that represents each memory item across orthogonal semantic, temporal, causal, and entity graphs. MAGMA formulates retrieval as policy-guided traversal over these relational views, enabling query-adaptive selection and structured context construction. By decoupling memory representation from retrieval logic, MAGMA provides transparent reasoning paths and fine-grained control over retrieval. Experiments on LoCoMo and LongMemEval demonstrate that MAGMA consistently outperforms state-of-the-art agentic memory systems in long-horizon reasoning tasks.
zh
[AI-1] he Sonar Moment: Benchmarking Audio-Language Models in Audio Geo-Localization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决音频地理定位(audio geo-localization)领域缺乏高质量音频-位置配对数据集的问题,从而推动音频语言模型(Audio Language Models, ALMs)在地缘空间推理能力上的发展。其解决方案的关键在于构建了首个面向ALMs的音频地理定位基准数据集AGL1K,覆盖72个国家和地区,并提出了一种名为“音频可定位性指标”(Audio Localizability metric)的新方法,用于从众包平台中筛选出具有可靠地理定位信息的音频样本,最终获得1,444个精炼音频片段。这一指标显著提升了数据质量,为评估和优化ALMs的地理定位能力提供了坚实基础。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03227
作者: Ruixing Zhang,Zihan Liu,Leilei Sun,Tongyu Zhu,Weifeng Lv
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Geo-localization aims to infer the geographic origin of a given signal. In computer vision, geo-localization has served as a demanding benchmark for compositional reasoning and is relevant to public safety. In contrast, progress on audio geo-localization has been constrained by the lack of high-quality audio-location pairs. To address this gap, we introduce AGL1K, the first audio geo-localization benchmark for audio language models (ALMs), spanning 72 countries and territories. To extract reliably localizable samples from a crowd-sourced platform, we propose the Audio Localizability metric that quantifies the informativeness of each recording, yielding 1,444 curated audio clips. Evaluations on 16 ALMs show that ALMs have emerged with audio geo-localization capability. We find that closed-source models substantially outperform open-source models, and that linguistic clues often dominate as a scaffold for prediction. We further analyze ALMs’ reasoning traces, regional bias, error causes, and the interpretability of the localizability metric. Overall, AGL1K establishes a benchmark for audio geo-localization and may advance ALMs with better geospatial reasoning capability.
zh
[AI-2] he Fake Friend Dilemma: Trust and the Political Economy of Conversational AI
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03222
作者: Jacob Erickson
机构: 未知
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注: Manuscript under review
[AI-3] InfiAgent : An Infinite-Horizon Framework for General-Purpose Autonomous Agents
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)代理在长周期任务中因上下文无限增长和误差累积而导致的性能退化问题。现有方法如上下文压缩或检索增强提示虽能缓解部分问题,但往往在信息保真度与推理稳定性之间引入权衡。其解决方案的关键在于提出 InfiAgent 框架,通过将代理的持久状态外置于一个以文件为中心的状态抽象(file-centric state abstraction),实现推理上下文严格 bounded(有界)。具体而言,代理在每一步仅从工作区状态快照和固定窗口内的最近动作重建上下文,从而避免了长期任务中的上下文膨胀和错误传播。实验表明,该方法无需任务特定微调即可在 DeepResearch 和 80 篇论文文献综述任务中达到与更大闭源系统相当的性能,并显著优于基于上下文中心设计的基线方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03204
作者: Chenglin Yu,Yuchen Wang,Songmiao Wang,Hongxia Yang,Ming Li
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注:
Abstract:LLM agents can reason and use tools, but they often break down on long-horizon tasks due to unbounded context growth and accumulated errors. Common remedies such as context compression or retrieval-augmented prompting introduce trade-offs between information fidelity and reasoning stability. We present InfiAgent, a general-purpose framework that keeps the agent’s reasoning context strictly bounded regardless of task duration by externalizing persistent state into a file-centric state abstraction. At each step, the agent reconstructs context from a workspace state snapshot plus a fixed window of recent actions. Experiments on DeepResearch and an 80-paper literature review task show that, without task-specific fine-tuning, InfiAgent with a 20B open-source model is competitive with larger proprietary systems and maintains substantially higher long-horizon coverage than context-centric baselines. These results support explicit state externalization as a practical foundation for stable long-horizon agents. Github Repo:this https URL
zh
[AI-4] Counterfactual Fairness with Graph Uncertainty KDD ECML
【速读】:该论文旨在解决机器学习模型偏见评估中因因果图假设不确定性导致的可信度问题。现有基于因果框架的反事实公平性(Counterfactual Fairness, CF)审计依赖于单一因果图,而现实中因果结构往往难以确定,从而影响评估结果的可靠性。其解决方案的关键在于提出CF-GU(Counterfactual Fairness with Graph Uncertainty),通过在领域知识约束下对因果发现算法进行自助采样以生成一组合理的有向无环图(Directed Acyclic Graphs, DAGs),利用归一化香农熵量化图不确定性,并据此为CF指标提供置信区间,从而在因果图不确定的情况下仍能给出稳健且可信赖的偏见评估结果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03203
作者: Davi Valério,Chrysoula Zerva,Mariana Pinto,Ricardo Santos,André Carreiro
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注: Peer reviewed pre-print. Presented at the BIAS 2025 Workshop at ECML PKDD
Abstract:Evaluating machine learning (ML) model bias is key to building trustworthy and robust ML systems. Counterfactual Fairness (CF) audits allow the measurement of bias of ML models with a causal framework, yet their conclusions rely on a single causal graph that is rarely known with certainty in real-world scenarios. We propose CF with Graph Uncertainty (CF-GU), a bias evaluation procedure that incorporates the uncertainty of specifying a causal graph into CF. CF-GU (i) bootstraps a Causal Discovery algorithm under domain knowledge constraints to produce a bag of plausible Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), (ii) quantifies graph uncertainty with the normalized Shannon entropy, and (iii) provides confidence bounds on CF metrics. Experiments on synthetic data show how contrasting domain knowledge assumptions support or refute audits of CF, while experiments on real-world data (COMPAS and Adult datasets) pinpoint well-known biases with high confidence, even when supplied with minimal domain knowledge constraints.
zh
[AI-5] Recursive querying of neural networks via weighted structures
【速读】:该论文旨在解决如何通过可表达的查询机制(expressive querying)来验证和解释机器学习模型,特别是前馈神经网络的内部表示,从而提升其可理解性和可访问性。核心问题是:在没有深度限制的情况下,如何设计一种具备递归能力的逻辑语言来刻画加权结构(weighted structures),以支持对神经网络行为的精确形式化描述。解决方案的关键在于引入并改进了Grädel与Gurevich提出的函数不动点机制(functional fixpoint mechanism),将其嵌入到类似Datalog的语法中,并扩展了不动点逻辑的正规形式至加权结构;进一步提出了一种“标量”约束版本的函数不动点逻辑,该版本具有多项式时间的数据复杂度,且能表达所有关于权重有界、结构简化的神经网络的PTIME模型无关查询。这一方法为神经网络的可解释性提供了理论基础,并揭示了简单模型无关查询的计算复杂性下限(NP难)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03201
作者: Martin Grohe,Christoph Standke,Juno Steegmans,Jan Van den Bussche
机构: 未知
类目: Logic in Computer Science (cs.LO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Databases (cs.DB)
备注:
Abstract:Expressive querying of machine learning models - viewed as a form of intentional data - enables their verification and interpretation using declarative languages, thereby making learned representations of data more accessible. Motivated by the querying of feedforward neural networks, we investigate logics for weighted structures. In the absence of a bound on neural network depth, such logics must incorporate recursion; thereto we revisit the functional fixpoint mechanism proposed by Grädel and Gurevich. We adopt it in a Datalog-like syntax; we extend normal forms for fixpoint logics to weighted structures; and show an equivalent “loose” fixpoint mechanism that allows values of inductively defined weight functions to be overwritten. We propose a “scalar” restriction of functional fixpoint logic, of polynomial-time data complexity, and show it can express all PTIME model-agnostic queries over reduced networks with polynomially bounded weights. In contrast, we show that very simple model-agnostic queries are already NP-complete. Finally, we consider transformations of weighted structures by iterated transductions.
zh
[AI-6] Decentralized Autoregressive Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决自回归生成过程中中心化训练与去中心化训练之间的效率与性能平衡问题,特别是在多模态语言模型(Multimodal Language Models, MLMs)中如何实现分布式训练下的等效性。其核心解决方案是提出一种名为“去中心化离散流匹配”(Decentralized Discrete Flow Matching)的目标函数,通过将概率生成速度表示为专家流(expert flows)的线性组合,从而在不依赖中央协调的情况下实现与集中式训练相当的模型性能。实验验证了在不同基准测试下,采用固定CLIP视觉编码器并进行全参数微调(ViT+MLP+LLM)的InternVL 2.5-1B模型与LLaVA等架构在去中心化训练设置中具有等效性,证明了该方法的有效性和可扩展性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03184
作者: Stepan Maschan,Haoxuan Qu,Jun Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Work in progress
Abstract:We present a theoretical analysis of decentralization of autoregressive generation. We define the Decentralized Discrete Flow Matching objective, by expressing probability generating velocity as a linear combination of expert flows. We also conduct experiments demonstrat- ing the equivalence between decentralized and centralized training settings for multimodal language models across diverse set of benchmarks. Specifically, we compare two distinct paradigms: LLaVA and InternVL 2.5-1B, which uses a fixed CLIP vision encoder and per- forms full-parameter fine-tuning (ViT+MLP+LLM) during the instruction tuning stage.
zh
[AI-7] Rapid Augmentations for Time Series (RATS): A High-Performance Library for Time Series Augmentation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决时间序列数据增强在大规模生产环境中因现有Python库性能瓶颈而导致的效率低下问题,尤其是在标注数据稀缺且昂贵的场景下,传统方法难以支撑高效训练深度学习模型。其解决方案的关键在于开发了一个用Rust编写的高性能时间序列增强库RATS(Rapid Augmentations for Time Series),并通过Python绑定(RATSpy)实现易用性,该方案整合了基础变换、频域操作和时间扭曲等多种增强策略,并通过统一的流水线接口与内置并行化机制显著提升处理速度,实证表明RATSpy相较常用库tsaug平均提速74.5%(最大达94.8%),同时峰值内存消耗降低最多47.9%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03159
作者: Wadie Skaf,Felix Kern,Aryamaan Basu Roy,Tejas Pradhan,Roman Kalkreuth,Holger Hoos
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Performance (cs.PF)
备注:
Abstract:Time series augmentation is critical for training robust deep learning models, particularly in domains where labelled data is scarce and expensive to obtain. However, existing augmentation libraries for time series, mainly written in Python, suffer from performance bottlenecks, where running time grows exponentially as dataset sizes increase – an aspect limiting their applicability in large-scale, production-grade systems. We introduce RATS (Rapid Augmentations for Time Series), a high-performance library for time series augmentation written in Rust with Python bindings (RATSpy). RATS implements multiple augmentation methods spanning basic transformations, frequency-domain operations and time warping techniques, all accessible through a unified pipeline interface with built-in parallelisation. Comprehensive benchmarking of RATSpy versus a commonly used library (tasug) on 143 datasets demonstrates that RATSpy achieves an average speedup of 74.5% over tsaug (up to 94.8% on large datasets), with up to 47.9% less peak memory usage.
zh
[AI-8] A framework for assuring the accuracy and fidelity of an AI-enabled Digital Twin of en route UK airspace
【速读】:该论文旨在解决数字孪生(Digital Twin)在航空交通管理(ATM)领域中应用时所面临的验证与监管不确定性问题,特别是如何确保其对物理系统的高保真度以及在特定应用场景下的功能有效性。解决方案的关键在于构建一个基于可信与伦理保障(Trustworthy and Ethical Assurance, TEA)的保证框架(assurance framework),该框架通过结构化的论证链条(assurance case)明确可操作的目标、所需证据及支撑假设,从而系统性地评估数字孪生的准确性与适用性,并为研究人员提供清晰的方法论以识别改进方向,同时为监管机构和利益相关方提供可落地的讨论基础,推动针对AI/ML驱动的数字孪生技术的合规性发展。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03120
作者: Adam Keane,Nick Pepper,Chris Burr,Amy Hodgkin,Dewi Gould,John Korna,Marc Thomas
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Digital Twins combine simulation, operational data and Artificial Intelligence (AI), and have the potential to bring significant benefits across the aviation industry. Project Bluebird, an industry-academic collaboration, has developed a probabilistic Digital Twin of en route UK airspace as an environment for training and testing AI Air Traffic Control (ATC) agents. There is a developing regulatory landscape for this kind of novel technology. Regulatory requirements are expected to be application specific, and may need to be tailored to each specific use case. We draw on emerging guidance for both Digital Twin development and the use of Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML) in Air Traffic Management (ATM) to present an assurance framework. This framework defines actionable goals and the evidence required to demonstrate that a Digital Twin accurately represents its physical counterpart and also provides sufficient functionality across target use cases. It provides a structured approach for researchers to assess, understand and document the strengths and limitations of the Digital Twin, whilst also identifying areas where fidelity could be improved. Furthermore, it serves as a foundation for engagement with stakeholders and regulators, supporting discussions around the regulatory needs for future applications, and contributing to the emerging guidance through a concrete, working example of a Digital Twin. The framework leverages a methodology known as Trustworthy and Ethical Assurance (TEA) to develop an assurance case. An assurance case is a nested set of structured arguments that provides justified evidence for how a top-level goal has been realised. In this paper we provide an overview of each structured argument and a number of deep dives which elaborate in more detail upon particular arguments, including the required evidence, assumptions and justifications. Subjects: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.03120 [cs.AI] (or arXiv:2601.03120v1 [cs.AI] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.03120 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-9] Joint Encoding of KV-Cache Blocks for Scalable LLM Serving
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大规模语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在实时推理服务中因键值缓存(Key-Value Cache, KV-cache)内存占用过高而导致的吞吐量瓶颈问题。现有KV-cache压缩方法普遍存在依赖固定启发式规则、破坏张量布局或需专用计算资源等缺陷,限制了其可扩展性和部署灵活性。解决方案的关键在于提出一种联合编码(joint encoding)机制,通过将来自不同请求和输入片段的相似KV-cache块融合为共享表示,同时保持标准缓存结构不变,从而在不改变现有系统架构的前提下显著降低内存消耗。理论分析基于泊松过程模型对融合后缓存块的率失真权衡进行了建模,实验证明该方法可在多种LLM和基准测试中实现最高达4.38倍的KV-cache压缩比且精度损失可忽略,并在单机vLLM基准上将token吞吐量提升约40%,展现出卓越的推理效率提升能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03067
作者: Joseph Kampeas,Emir Haleva
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 12 pages, 16 figures, 2 tables
Abstract:Modern large language models (LLMs) drive interactive AI systems but are bottlenecked by the memory-heavy growth of key-value (KV) caches, which limits real-time throughput under concurrent loads. Existing KV-cache compression methods rely on rigid heuristics, disrupt tensor layouts, or require specialized compute, hindering scalability and deployment. We propose joint encoding of KV-cache blocks, which fuses similar blocks across requests and input chunks into shared representations while preserving standard cache structure. This alleviates the KV-cache memory bottleneck, supporting high-concurrency serving without specialized hardware. Theoretically, we analyze the rate-distortion tradeoff of fused cache blocks under a Poisson process model. Empirically, our method achieves up to 4.38 \times KV-cache compression with negligible accuracy loss across diverse LLMs and benchmarks, outperforming recent structured and adaptive compression baselines. In real LLM serving, joint encoding improves the token throughput by \sim 40% on a single-machine vLLM benchmark, demonstrating substantial gains in inference throughput. Code is available at this https URL kv_joint_encoding. Comments: 12 pages, 16 figures, 2 tables Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.03067 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2601.03067v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.03067 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-10] Explainable Fuzzy GNNs for Leak Detection in Water Distribution Networks
【速读】:该论文旨在解决供水管网中泄漏检测的及时性与模型可解释性之间的矛盾问题。当前基于图神经网络(Graph Neural Networks, GNNs)的方法虽能有效捕捉传感器数据的空间-时间依赖关系,但其黑箱特性限制了在实际工程中的可信度与采纳率。解决方案的关键在于提出一种融合互信息(mutual information)与模糊逻辑(fuzzy logic)的可解释GNN框架——模糊图神经网络(FGENConv),其中通过互信息识别关键管网区域,利用模糊规则提供直观、空间局部化的解释,从而在保持较高检测精度(Graph F1: 0.889)和定位性能(0.814)的同时,显著提升模型对水利工程师的可理解性和实用性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03062
作者: Qusai Khaled,Pasquale De Marinis,Moez Louati,David Ferras,Laura Genga,Uzay Kaymak
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Accepted at IFSA-NAFIPS 2025
Abstract:Timely leak detection in water distribution networks is critical for conserving resources and maintaining operational efficiency. Although Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) excel at capturing spatial-temporal dependencies in sensor data, their black-box nature and the limited work on graph-based explainable models for water networks hinder practical adoption. We propose an explainable GNN framework that integrates mutual information to identify critical network regions and fuzzy logic to provide clear, rule-based explanations for node classification tasks. After benchmarking several GNN architectures, we selected the generalized graph convolution network (GENConv) for its superior performance and developed a fuzzy-enhanced variant that offers intuitive explanations for classified leak locations. Our fuzzy graph neural network (FGENConv) achieved Graph F1 scores of 0.889 for detection and 0.814 for localization, slightly below the crisp GENConv 0.938 and 0.858, respectively. Yet it compensates by providing spatially localized, fuzzy rule-based explanations. By striking the right balance between precision and explainability, the proposed fuzzy network could enable hydraulic engineers to validate predicted leak locations, conserve human resources, and optimize maintenance strategies. The code is available at this http URL.
zh
[AI-11] PiDR: Physics-Informed Inertial Dead Reckoning for Autonomous Platforms
【速读】:该论文旨在解决纯惯性导航(Pure Inertial Navigation)中因惯性传感器噪声和误差导致的轨迹漂移问题,尤其是在缺乏外部辅助信息(如GNSS或视觉数据)的极端环境下,传统深度学习方法存在黑箱特性、小样本下学习效果差以及难以保持物理规律的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出PiDR(Physics-informed Inertial Dead-Reckoning)框架,其核心创新是通过引入物理信息残差模块(physics-informed residual component),将惯性导航的物理原理显式嵌入网络训练过程,从而在有限监督条件下实现高精度、可解释且符合物理约束的位姿估计,显著提升了不同平台在复杂动态环境中的鲁棒性和泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03040
作者: Arup Kumar Sahoo,Itzik Klein
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 11 pages and 7 figures
Abstract:A fundamental requirement for full autonomy is the ability to sustain accurate navigation in the absence of external data, such as GNSS signals or visual information. In these challenging environments, the platform must rely exclusively on inertial sensors, leading to pure inertial navigation. However, the inherent noise and other error terms of the inertial sensors in such real-world scenarios will cause the navigation solution to drift over time. Although conventional deep-learning models have emerged as a possible approach to inertial navigation, they are inherently black-box in nature. Furthermore, they struggle to learn effectively with limited supervised sensor data and often fail to preserve physical principles. To address these limitations, we propose PiDR, a physics-informed inertial dead-reckoning framework for autonomous platforms in situations of pure inertial navigation. PiDR offers transparency by explicitly integrating inertial navigation principles into the network training process through the physics-informed residual component. PiDR plays a crucial role in mitigating abrupt trajectory deviations even under limited or sparse supervision. We evaluated PiDR on real-world datasets collected by a mobile robot and an autonomous underwater vehicle. We obtained more than 29% positioning improvement in both datasets, demonstrating the ability of PiDR to generalize different platforms operating in various environments and dynamics. Thus, PiDR offers a robust, lightweight, yet effective architecture and can be deployed on resource-constrained platforms, enabling real-time pure inertial navigation in adverse scenarios.
zh
[AI-12] Validating Generalist Robots with Situation Calculus and STL Falsification
【速读】:该论文旨在解决通用机器人(Generalist Robots)在面对多样化任务时的验证难题,传统验证方法难以适应每项任务所特有的操作上下文和正确性规范。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个两层验证框架:第一层基于情境演算(Situation Calculus)建模世界并推导最弱前置条件,实现约束感知的组合测试,系统性地生成具有可控覆盖强度的语义有效世界-任务配置;第二层将这些配置实例化用于基于时空逻辑(STL)监控的仿真 falsification,从而高效发现控制器缺陷。实验表明该框架能有效识别 NVIDIA GR00T 控制器中的失效案例,为通用机器人自主性的验证提供了可行路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03038
作者: Changwen Li,Rongjie Yan,Chih-Hong Cheng,Jian Zhang
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Generalist robots are becoming a reality, capable of interpreting natural language instructions and executing diverse operations. However, their validation remains challenging because each task induces its own operational context and correctness specification, exceeding the assumptions of traditional validation methods. We propose a two-layer validation framework that combines abstract reasoning with concrete system falsification. At the abstract layer, situation calculus models the world and derives weakest preconditions, enabling constraint-aware combinatorial testing to systematically generate diverse, semantically valid world-task configurations with controllable coverage strength. At the concrete layer, these configurations are instantiated for simulation-based falsification with STL monitoring. Experiments on tabletop manipulation tasks show that our framework effectively uncovers failure cases in the NVIDIA GR00T controller, demonstrating its promise for validating general-purpose robot autonomy.
zh
[AI-13] Causal Manifold Fairness: Enforcing Geometric Invariance in Representation Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决机器学习中公平性问题,现有方法通常将数据视为高维空间中的静态点,忽略了数据生成过程的潜在因果结构。研究指出,敏感属性(如种族、性别)不仅改变数据分布,还会因果性地扭曲数据流形(data manifold)的几何结构。为此,作者提出因果流形公平性(Causal Manifold Fairness, CMF)框架,其核心在于将因果推断与几何深度学习相结合:CMF学习一个潜在表示空间,在该空间中,局部黎曼几何(由度量张量和曲率定义)在对敏感属性进行反事实干预后保持不变。通过约束解码器的雅可比矩阵(Jacobian)和海森矩阵(Hessian),CMF确保不同人口群体间潜在空间的距离和形状规则一致,从而实现对敏感属性引起的几何畸变的有效解耦,同时保留任务相关效用,为公平性与效用之间的权衡提供了基于几何度量的严谨量化方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03032
作者: Vidhi Rathore
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注:
Abstract:Fairness in machine learning is increasingly critical, yet standard approaches often treat data as static points in a high-dimensional space, ignoring the underlying generative structure. We posit that sensitive attributes (e.g., race, gender) do not merely shift data distributions but causally warp the geometry of the data manifold itself. To address this, we introduce Causal Manifold Fairness (CMF), a novel framework that bridges causal inference and geometric deep learning. CMF learns a latent representation where the local Riemannian geometry, defined by the metric tensor and curvature, remains invariant under counterfactual interventions on sensitive attributes. By enforcing constraints on the Jacobian and Hessian of the decoder, CMF ensures that the rules of the latent space (distances and shapes) are preserved across demographic groups. We validate CMF on synthetic Structural Causal Models (SCMs), demonstrating that it effectively disentangles sensitive geometric warping while preserving task utility, offering a rigorous quantification of the fairness-utility trade-off via geometric metrics.
zh
[AI-14] In-Context Reinforcement Learning through Bayesian Fusion of Context and Value Prior
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前在上下文强化学习(In-context Reinforcement Learning, ICRL)中普遍存在的两个问题:一是现有方法难以在未见过的环境(unseen environments)中实现超越训练分布的性能提升,二是多数方法依赖近似最优的数据进行训练,限制了其实际应用。为应对这些问题,作者提出了一种基于贝叶斯框架的ICRL方法SPICE,其关键在于通过深度集成(deep ensemble)学习Q值的先验分布,并在测试阶段利用贝叶斯更新机制结合上下文信息动态调整该先验;同时引入上置信界(Upper-Confidence Bound, UCB)规则引导在线推理过程中的探索行为,从而有效缓解因训练数据次优导致的先验偏差问题。理论证明表明,SPICE在随机多臂赌博机和有限时域马尔可夫决策过程(finite-horizon MDPs)中均能实现最优遗憾(regret-optimal)行为,即使仅用次优轨迹预训练也能快速适应新任务并保持对分布偏移的鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03015
作者: Anaïs Berkes,Vincent Taboga,Donna Vakalis,David Rolnick,Yoshua Bengio
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:In-context reinforcement learning (ICRL) promises fast adaptation to unseen environments without parameter updates, but current methods either cannot improve beyond the training distribution or require near-optimal data, limiting practical adoption. We introduce SPICE, a Bayesian ICRL method that learns a prior over Q-values via deep ensemble and updates this prior at test-time using in-context information through Bayesian updates. To recover from poor priors resulting from training on sub-optimal data, our online inference follows an Upper-Confidence Bound rule that favours exploration and adaptation. We prove that SPICE achieves regret-optimal behaviour in both stochastic bandits and finite-horizon MDPs, even when pretrained only on suboptimal trajectories. We validate these findings empirically across bandit and control benchmarks. SPICE achieves near-optimal decisions on unseen tasks, substantially reduces regret compared to prior ICRL and meta-RL approaches while rapidly adapting to unseen tasks and remaining robust under distribution shift.
zh
[AI-15] JPU: Bridging Jailbreak Defense and Unlearning via On-Policy Path Rectification
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在安全对齐后仍易受越狱攻击(jailbreak attacks)的问题。现有基于机器遗忘(machine unlearning)的防御方法虽能擦除特定有害参数,但仍无法抵御多样化的越狱攻击。研究发现,其根本原因在于越狱攻击主要激活了未被擦除的中间层参数,并通过持续存在的动态“越狱路径”(jailbreak paths)重构出违规输出,而现有方法无法修正这些路径。为此,论文提出首个针对动态越狱路径的遗忘机制——越狱路径遗忘(Jailbreak Path Unlearning, JPU),其核心创新在于通过动态挖掘策略内对抗样本(on-policy adversarial samples)来暴露模型漏洞并识别越狱路径,从而实现对动态攻击的显著增强防御能力,同时保持模型功能效用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03005
作者: Xi Wang,Songlei Jian,Shasha Li,Xiaopeng Li,Zhaoye Li,Bin Ji,Baosheng Wang,Jie Yu
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 14 pages, 6 figures, under review;
Abstract:Despite extensive safety alignment, Large Language Models (LLMs) often fail against jailbreak attacks. While machine unlearning has emerged as a promising defense by erasing specific harmful parameters, current methods remain vulnerable to diverse jailbreaks. We first conduct an empirical study and discover that this failure mechanism is caused by jailbreaks primarily activating non-erased parameters in the intermediate layers. Further, by probing the underlying mechanism through which these circumvented parameters reassemble into the prohibited output, we verify the persistent existence of dynamic \textbfjailbreak paths and show that the inability to rectify them constitutes the fundamental gap in existing unlearning defenses. To bridge this gap, we propose \textbfJ ailbreak \textbfP ath \textbfU nlearning (JPU), which is the first to rectify dynamic jailbreak paths towards safety anchors by dynamically mining on-policy adversarial samples to expose vulnerabilities and identify jailbreak paths. Extensive experiments demonstrate that JPU significantly enhances jailbreak resistance against dynamic attacks while preserving the model’s utility.
zh
[AI-16] Learning to Act Robustly with View-Invariant Latent Actions
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉机器人策略在面对视角变化时性能显著下降的问题,即如何构建对视角变化具有不变性的视觉表征以提升策略的泛化能力。现有方法通常依赖多视角场景级别的视觉外观信息来学习不变性,但忽略了物理动态特性,导致在真实环境中难以鲁棒地推广。其解决方案的关键在于提出View-Invariant Latent Action (VILA),通过建模跨轨迹的潜在动作(latent action)来捕捉物理动态中的转移模式,并利用基于真实动作序列的动作引导目标对不同视角下的潜在动作进行对齐,从而实现基于物理动力学的视图不变表征学习。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02994
作者: Youngjoon Jeong,Junha Chun,Taesup Kim
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Website: this https URL
Abstract:Vision-based robotic policies often struggle with even minor viewpoint changes, underscoring the need for view-invariant visual representations. This challenge becomes more pronounced in real-world settings, where viewpoint variability is unavoidable and can significantly disrupt policy performance. Existing methods typically learn invariance from multi-view observations at the scene level, but such approaches rely on visual appearance and fail to incorporate the physical dynamics essential for robust generalization. We propose View-Invariant Latent Action (VILA), which models a latent action capturing transition patterns across trajectories to learn view-invariant representations grounded in physical dynamics. VILA aligns these latent actions across viewpoints using an action-guided objective based on ground-truth action sequences. Experiments in both simulation and the real world show that VILA-based policies generalize effectively to unseen viewpoints and transfer well to new tasks, establishing VILA as a strong pretraining framework that improves robustness and downstream learning performance.
zh
[AI-17] Interpretable All-Type Audio Deepfake Detection with Audio LLM s via Frequency-Time Reinforcement Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决真实世界中多类型音频深度伪造检测(Audio Deepfake Detection, ADD)面临的挑战,即如何构建能够跨异构音频类型(如语音、环境声、歌声和音乐)泛化且决策可解释的检测模型。现有方法在使用监督微调(SFT)时易退化为黑箱分类器,而纯强化学习微调(RFT)则因稀疏奖励信号导致奖励欺骗(reward hacking)和幻觉推理,缺乏可信依据。解决方案的关键在于提出一种自动标注与精炼流水线,生成基于频率-时间结构的思维链(Frequency-Time structured chain-of-thought, CoT)推理路径,并在此基础上设计两阶段训练范式:先用SFT冷启动大语言模型,再引入频率-时间约束下的相对策略优化(Frequency Time-Group Relative Policy Optimization, FT-GRPO),从而实现高精度检测与可解释性兼顾的性能提升。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02983
作者: Yuankun Xie,Xiaoxuan Guo,Jiayi Zhou,Tao Wang,Jian Liu,Ruibo Fu,Xiaopeng Wang,Haonan Cheng,Long Ye
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Recent advances in audio large language models (ALLMs) have made high-quality synthetic audio widely accessible, increasing the risk of malicious audio deepfakes across speech, environmental sounds, singing voice, and music. Real-world audio deepfake detection (ADD) therefore requires all-type detectors that generalize across heterogeneous audio and provide interpretable decisions. Given the strong multi-task generalization ability of ALLMs, we first investigate their performance on all-type ADD under both supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT). However, SFT using only binary real/fake labels tends to reduce the model to a black-box classifier, sacrificing interpretability. Meanwhile, vanilla RFT under sparse supervision is prone to reward hacking and can produce hallucinated, ungrounded rationales. To address this, we propose an automatic annotation and polishing pipeline that constructs Frequency-Time structured chain-of-thought (CoT) rationales, producing ~340K cold-start demonstrations. Building on CoT data, we propose Frequency Time-Group Relative Policy Optimization (FT-GRPO), a two-stage training paradigm that cold-starts ALLMs with SFT and then applies GRPO under rule-based frequency-time constraints. Experiments demonstrate that FT-GRPO achieves state-of-the-art performance on all-type ADD while producing interpretable, FT-grounded rationales. The data and code are available online.
zh
[AI-18] Rationale-Grounded In-Context Learning for Time Series Reasoning with Multimodal Large Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有多模态大语言模型在时间序列推理任务中表现不佳的问题,其根本原因在于缺乏将时间观测与下游结果相联系的因果推理先验(rationale priors),导致模型依赖表面模式匹配而非基于原理的推理。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于推理依据(rationale)的上下文学习方法——RationaleTS,其中推理依据作为引导推理过程的核心单元,而非事后解释;具体包括:首先生成标签条件下的推理路径(从可观测证据到潜在结果),然后设计混合检索机制,在时间模式与语义上下文之间取得平衡,以检索相关推理先验用于新样本的上下文推理。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02968
作者: Qingxiang Liu,Zhiqing Cui,Xiaoliang Luo,Yuqian Wu,Zhuoyang Jiang,Huaiyu Wan,Sheng Sun,Lvchun Wang,Wei Yu,Yuxuan Liang
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The underperformance of existing multimodal large language models for time series reasoning lies in the absence of rationale priors that connect temporal observations to their downstream outcomes, which leads models to rely on superficial pattern matching rather than principled reasoning. We therefore propose the rationale-grounded in-context learning for time series reasoning, where rationales work as guiding reasoning units rather than post-hoc explanations, and develop the RationaleTS method. Specifically, we firstly induce label-conditioned rationales, composed of reasoning paths from observable evidence to the potential outcomes. Then, we design the hybrid retrieval by balancing temporal patterns and semantic contexts to retrieve correlated rationale priors for the final in-context inference on new samples. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed RationaleTS on three-domain time series reasoning tasks. We will release our code for reproduction.
zh
[AI-19] MoE Adapter for Large Audio Language Models: Sparsity Disentanglement and Gradient-Conflict-Free
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在扩展至音频模态时,因声学信息固有的异质性(heterogeneous nature)导致的梯度冲突问题。具体而言,音频中包含语音、音乐和环境背景等多种属性,现有方法采用密集共享参数的适配器(adapter)建模这些模式时,不同属性所需的参数更新相互矛盾,从而引发优化过程中的梯度冲突。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种稀疏的专家混合(Mixture-of-Experts, MoE)架构——MoE-Adapter,该架构通过动态门控机制将音频token路由至专门捕获互补特征子空间的专家,同时保留共享专家以维持全局上下文,从而有效缓解梯度冲突并实现细粒度特征学习。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02967
作者: Yishu Lei,Shuwei He,Jing Hu,Dan Zhang,Xianlong Luo,Danxiang Zhu,Shikun Feng,Rui Liu,Jingzhou He,Yu Sun,Hua Wu,Haifeng Wang
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS)
备注: 13 pages, 5 figures
Abstract:Extending the input modality of Large Language Models~(LLMs) to the audio domain is essential for achieving comprehensive multimodal perception. However, it is well-known that acoustic information is intrinsically \textitheterogeneous, entangling attributes such as speech, music, and environmental context. Existing research is limited to a dense, parameter-shared adapter to model these diverse patterns, which induces \textitgradient conflict during optimization, as parameter updates required for distinct attributes contradict each other. To address this limitation, we introduce the \textit\textbfMoE-Adapter, a sparse Mixture-of-Experts~(MoE) architecture designed to decouple acoustic information. Specifically, it employs a dynamic gating mechanism that routes audio tokens to specialized experts capturing complementary feature subspaces while retaining shared experts for global context, thereby mitigating gradient conflicts and enabling fine-grained feature learning. Comprehensive experiments show that the MoE-Adapter achieves superior performance on both audio semantic and paralinguistic tasks, consistently outperforming dense linear baselines with comparable computational costs. Furthermore, we will release the related code and models to facilitate future research.
zh
[AI-20] he World is Not Mono: Enabling Spatial Understanding in Large Audio-Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有大型音频-语言模型在感知声学场景时仅依赖单一音频流(即“mono”模式),忽视了对空间维度(“where”)的关键信息,从而限制了其在通用声学场景分析中的能力。解决方案的关键在于提出一个分层的听觉场景分析(Auditory Scene Analysis, ASA)框架,并通过三个核心贡献实现空间感知增强:首先构建大规模合成双耳音频数据集以提供丰富的空间线索;其次设计一种混合特征投影器,利用并行的语义与空间编码器提取解耦表征,并通过密集融合机制整合二者以获得整体声学场景视图;最后采用渐进式训练课程,从监督微调(SFT)逐步过渡到基于组相对策略优化(GRPO)的强化学习,显式提升模型的空间推理能力。该方案实现了从“单通道语义识别”向“空间智能”的跨越。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02954
作者: Yuhuan You,Lai Wei,Xihong Wu,Tianshu Qu
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Existing large audio-language models perceive the world as “mono” – a single stream of audio that ignores the critical spatial dimension (“where”) required for universal acoustic scene analysis. To bridge this gap, we first introduce a hierarchical framework for Auditory Scene Analysis (ASA). Guided by this framework, we introduce a system that enables models like Qwen2-Audio to understand and reason about the complex acoustic world. Our framework achieves this through three core contributions: First, we build a large-scale, synthesized binaural audio dataset to provide the rich spatial cues. Second, we design a hybrid feature projector, which leverages parallel semantic and spatial encoders to extract decoupled representations. These distinct streams are integrated via a dense fusion mechanism, ensuring the model receives a holistic view of the acoustic scene. Finally, we employ a progressive training curriculum, advancing from supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to reinforcement learning via Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), to explicitly evolve the model’s capabilities towards reasoning. On our comprehensive benchmark, the model demonstrates comparatively strong capability for spatial understanding. By enabling this spatial perception, our work provides a clear pathway for leveraging the powerful reasoning abilities of large models towards holistic acoustic scene analysis, advancing from “mono” semantic recognition to spatial intelligence.
zh
[AI-21] Batch-of-Thought: Cross-Instance Learning for Enhanced LLM Reasoning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前大型语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)推理系统在处理查询时独立进行、忽略跨实例信号(如共享推理模式和一致性约束)的问题,从而导致推理效率与准确性受限。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种无需训练的批量思维方法(Batch-of-Thought, BoT),通过联合处理相关查询实现跨实例学习:BoT利用批内比较分析识别高质量推理模板,借助一致性检查检测错误,并分摊计算成本;进一步地,在多智能体反思架构(BoT-R)中引入一个Reflector模块执行联合评估,挖掘孤立处理无法获得的互信息增益,显著提升准确性和置信度校准效果,同时降低推理开销最高达61%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02950
作者: Xuan Yang,Furong Jia,Roy Xie,Xiong Xi,Hengwei Bian,Jian Li,Monica Agrawal
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Current Large Language Model reasoning systems process queries independently, discarding valuable cross-instance signals such as shared reasoning patterns and consistency constraints. We introduce Batch-of-Thought (BoT), a training-free method that processes related queries jointly to enable cross-instance learning. By performing comparative analysis across batches, BoT identifies high-quality reasoning templates, detects errors through consistency checks, and amortizes computational costs. We instantiate BoT within a multi-agent reflection architecture (BoT-R), where a Reflector performs joint evaluation to unlock mutual information gain unavailable in isolated processing. Experiments across three model families and six benchmarks demonstrate that BoT-R consistently improves accuracy and confidence calibration while reducing inference costs by up to 61%. Our theoretical and experimental analysis reveals when and why batch-aware reasoning benefits LLM systems.
zh
[AI-22] LOST-3DSG: Lightweight Open-Vocabulary 3D Scene Graphs with Semantic Tracking in Dynamic Environments
【速读】:该论文旨在解决机器人在动态环境中高效追踪移动物体的问题,尤其针对现有方法因依赖计算密集型基础模型而导致效率低下的缺陷。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种轻量级的开放词汇3D场景图(LOST-3DSG),通过词向量(word2vec)和句子嵌入(sentence embeddings)实现语义驱动的实体跟踪,从而避免存储高维CLIP视觉特征,同时保持开放词汇能力,显著提升了追踪性能与计算效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02905
作者: Sara Micol Ferraina,Michele Brienza,Francesco Argenziano,Emanuele Musumeci,Vincenzo Suriani,Domenico D. Bloisi,Daniele Nardi
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Tracking objects that move within dynamic environments is a core challenge in robotics. Recent research has advanced this topic significantly; however, many existing approaches remain inefficient due to their reliance on heavy foundation models. To address this limitation, we propose LOST-3DSG, a lightweight open-vocabulary 3D scene graph designed to track dynamic objects in real-world environments. Our method adopts a semantic approach to entity tracking based on word2vec and sentence embeddings, enabling an open-vocabulary representation while avoiding the necessity of storing dense CLIP visual features. As a result, LOST-3DSG achieves superior performance compared to approaches that rely on high-dimensional visual embeddings. We evaluate our method through qualitative and quantitative experiments conducted in a real 3D environment using a TIAGo robot. The results demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of LOST-3DSG in dynamic object tracking. Code and supplementary material are publicly available on the project website at this https URL.
zh
[AI-23] SimRPD: Optimizing Recruitment Proactive Dialogue Agents through Simulator-Based Data Evaluation and Selection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决招聘场景中任务导向型主动对话代理(task-oriented proactive dialogue agent)训练过程中高质量、目标导向的领域特定数据稀缺的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一个三阶段框架SimRPD:首先构建高保真用户模拟器,通过多轮在线对话生成大规模对话数据;其次引入基于意图链(Chain-of-Intention, CoI)的多维评估框架,从全局和实例层面综合衡量模拟数据质量并筛选优质数据;最后在筛选后的数据集上训练对话代理。该方法显著提升了工业部署中招聘对话代理的效果,并具备向其他业务导向对话场景扩展的潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02871
作者: Zhiyong Cao,Dunqiang Liu,Qi Dai,Haojun Xu,Huaiyan Xu,Huan He,Yafei Liu,Siyuan Liu,XiaoLin Lin,Ke Ma,Ruqian Shi,Sijia Yao,Hao Wang,Sicheng Zhou
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Task-oriented proactive dialogue agents play a pivotal role in recruitment, particularly for steering conversations towards specific business outcomes, such as acquiring social-media contacts for private-channel conversion. Although supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning have proven effective for training such agents, their performance is heavily constrained by the scarcity of high-quality, goal-oriented domain-specific training data. To address this challenge, we propose SimRPD, a three-stage framework for training recruitment proactive dialogue agents. First, we develop a high-fidelity user simulator to synthesize large-scale conversational data through multi-turn online dialogue. Then we introduce a multi-dimensional evaluation framework based on Chain-of-Intention (CoI) to comprehensively assess the simulator and effectively select high-quality data, incorporating both global-level and instance-level metrics. Finally, we train the recruitment proactive dialogue agent on the selected dataset. Experiments in a real-world recruitment scenario demonstrate that SimRPD outperforms existing simulator-based data selection strategies, highlighting its practical value for industrial deployment and its potential applicability to other business-oriented dialogue scenarios.
zh
[AI-24] M3MAD-Bench: Are Multi-Agent Debates Really Effective Across Domains and Modalities?
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多智能体辩论(Multi-Agent Debate, MAD)研究中存在的两大核心问题:一是现有评估设置碎片化且不一致,导致不同方法难以公平比较;二是当前研究主要局限于纯文本模态,缺乏对多模态输入场景的支持。解决方案的关键在于提出M3MAD-Bench——一个统一且可扩展的基准测试平台,支持跨领域(知识、数学、医学、自然科学与复杂推理)、跨模态(纯文本与视觉-语言)以及多维指标(如准确性、Token消耗和推理时间)的系统性评估。该基准建立了标准化协议,并在九种不同架构、规模和模态能力的基础模型上进行了全面实验,从而为MAD方法的有效性、鲁棒性和效率提供了深入洞察,推动了该领域向标准化、可复现的研究方向发展。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02854
作者: Ao Li,Jinghui Zhang,Luyu Li,Yuxiang Duan,Lang Gao,Mingcai Chen,Weijun Qin,Shaopeng Li,Fengxian Ji,Ning Liu,Lizhen Cui,Xiuying Chen,Yuntao Du
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:As an agent-level reasoning and coordination paradigm, Multi-Agent Debate (MAD) orchestrates multiple agents through structured debate to improve answer quality and support complex reasoning. However, existing research on MAD suffers from two fundamental limitations: evaluations are conducted under fragmented and inconsistent settings, hindering fair comparison, and are largely restricted to single-modality scenarios that rely on textual inputs only. To address these gaps, we introduce M3MAD-Bench, a unified and extensible benchmark for evaluating MAD methods across Multi-domain tasks, Multi-modal inputs, and Multi-dimensional metrics. M3MAD-Bench establishes standardized protocols over five core task domains: Knowledge, Mathematics, Medicine, Natural Sciences, and Complex Reasoning, and systematically covers both pure text and vision-language datasets, enabling controlled cross-modality comparison. We evaluate MAD methods on nine base models spanning different architectures, scales, and modality capabilities. Beyond accuracy, M3MAD-Bench incorporates efficiency-oriented metrics such as token consumption and inference time, providing a holistic view of performance–cost trade-offs. Extensive experiments yield systematic insights into the effectiveness, robustness, and efficiency of MAD across text-only and multimodal scenarios. We believe M3MAD-Bench offers a reliable foundation for future research on standardized MAD evaluation. The code is available at this http URL.
zh
[AI-25] Sample-Efficient Neurosymbolic Deep Reinforcement Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决深度强化学习(Deep Reinforcement Learning, DRL)在样本效率低和泛化能力弱方面的局限性,尤其是在复杂、未见过的任务场景中表现不佳的问题。其核心解决方案是提出一种神经符号强化学习(neuro-symbolic DRL)方法,关键在于将领域内的符号知识以逻辑规则形式表示为部分策略(partial policies),并将其作为先验信息用于指导DRL训练过程:一方面通过在线推理偏置探索阶段的动作分布,另一方面通过重新缩放Q值来优化利用阶段的决策,从而提升模型在稀疏奖励环境和长规划周期任务中的收敛速度与性能表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02850
作者: Celeste Veronese,Daniele Meli,Alessandro Farinelli
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a well-established framework for sequential decision-making in complex environments. However, state-of-the-art Deep RL (DRL) algorithms typically require large training datasets and often struggle to generalize beyond small-scale training scenarios, even within standard benchmarks. We propose a neuro-symbolic DRL approach that integrates background symbolic knowledge to improve sample efficiency and generalization to more challenging, unseen tasks. Partial policies defined for simple domain instances, where high performance is easily attained, are transferred as useful priors to accelerate learning in more complex settings and avoid tuning DRL parameters from scratch. To do so, partial policies are represented as logical rules, and online reasoning is performed to guide the training process through two mechanisms: (i) biasing the action distribution during exploration, and (ii) rescaling Q-values during exploitation. This neuro-symbolic integration enhances interpretability and trustworthiness while accelerating convergence, particularly in sparse-reward environments and tasks with long planning horizons. We empirically validate our methodology on challenging variants of gridworld environments, both in the fully observable and partially observable setting. We show improved performance over a state-of-the-art reward machine baseline.
zh
[AI-26] Quantum-enhanced long short-term memory with attention for spatial permeability prediction in oilfield reservoirs
【速读】:该论文旨在解决储层参数(尤其是渗透率)空间预测中因参数范围广、变异性高而导致现有方法预测可靠性不足的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种量子增强的长短期记忆网络与注意力机制结合的模型(QLSTMA),通过将变分量子电路(VQC)嵌入循环单元,利用量子叠加和纠缠特性显著提升对复杂地质参数的建模能力;其中,QLSTMA-IG结构在8量子比特配置下相较传统LSTMA模型,平均绝对误差(MAE)降低19%、均方根误差(RMSE)降低20%,尤其在复杂测井数据区域表现突出,验证了量子-经典混合神经网络在油气储层预测中的潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02818
作者: Muzhen Zhang,Yujie Cheng,Zhanxiang Lei
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Quantum Physics (quant-ph)
备注: 22 pages, 7 figures
Abstract:Spatial prediction of reservoir parameters, especially permeability, is crucial for oil and gas exploration and development. However, the wide range and high variability of permeability prevent existing methods from providing reliable predictions. For the first time in subsurface spatial prediction, this study presents a quantum-enhanced long short-term memory with attention (QLSTMA) model that incorporates variational quantum circuits (VQCs) into the recurrent cell. Using quantum entanglement and superposition principles, the QLSTMA significantly improves the ability to predict complex geological parameters such as permeability. Two quantization structures, QLSTMA with Shared Gates (QLSTMA-SG) and with Independent Gates (QLSTMA-IG), are designed to investigate and evaluate the effects of quantum structure configurations and the number of qubits on model performance. Experimental results demonstrate that the 8-qubit QLSTMA-IG model significantly outperforms the traditional long short-term memory with attention (LSTMA), reducing Mean Absolute Error (MAE) by 19% and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) by 20%, with particularly strong performance in regions featuring complex well-logging data. These findings validate the potential of quantum-classical hybrid neural networks for reservoir prediction, indicating that increasing the number of qubits yields further accuracy gains despite the reliance on classical simulations. This study establishes a foundational framework for the eventual deployment of such models on real quantum hardware and their extension to broader applications in petroleum engineering and geoscience.
zh
[AI-27] Causal-Enhanced AI Agents for Medical Research Screening
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)在系统性文献综述任务中存在幻觉(hallucination)的问题,尤其是在医疗领域,错误信息可能直接影响患者安全。当前AI模型的幻觉率仍高达2%–15%,远未达到临床可信标准。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种因果图增强的检索增强生成系统(CausalAgent),通过引入双层知识图谱与显式因果推理机制,强制每条因果主张均基于检索到的文献证据,并自动生成有向无环图(DAG)可视化干预与结局之间的因果路径,从而实现“证据优先”的生成逻辑,显著提升准确性与可解释性。实验表明,在234篇阿尔茨海默病运动干预摘要上的评估中,该方法达到95%准确率、100%召回率且零幻觉,相较基线模型大幅提升。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02814
作者: Duc Ngo,Arya Rahgoza
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: for submission to The 39th Canadian Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Abstract:Systematic reviews are essential for evidence-based medicine, but reviewing 1.5 million+ annual publications manually is infeasible. Current AI approaches suffer from hallucinations in systematic review tasks, with studies reporting rates ranging from 28–40% for earlier models to 2–15% for modern implementations which is unacceptable when errors impact patient care. We present a causal graph-enhanced retrieval-augmented generation system integrating explicit causal reasoning with dual-level knowledge graphs. Our approach enforces evidence-first protocols where every causal claim traces to retrieved literature and automatically generates directed acyclic graphs visualizing intervention-outcome pathways. Evaluation on 234 dementia exercise abstracts shows CausalAgent achieves 95% accuracy, 100% retrieval success, and zero hallucinations versus 34% accuracy and 10% hallucinations for baseline AI. Automatic causal graphs enable explicit mechanism modeling, visual synthesis, and enhanced interpretability. While this proof-of-concept evaluation used ten questions focused on dementia exercise research, the architectural approach demonstrates transferable principles for trustworthy medical AI and causal reasoning’s potential for high-stakes healthcare. Comments: for submission to The 39th Canadian Conference on Artificial Intelligence Subjects: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02814 [cs.AI] (or arXiv:2601.02814v1 [cs.AI] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02814 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-28] Closing the Reality Gap: Zero-Shot Sim-to-Real Deployment for Dexterous Force-Based Grasping and Manipulation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多指灵巧手在真实硬件上实现可靠灵巧操作的难题,特别是由于接触丰富的物理特性与执行器不完美导致的模拟到现实(sim-to-real)迁移困难问题。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个实用的强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)框架,该框架通过融合密集触觉反馈与关节扭矩感知来显式调控物理交互;具体包括三项核心技术:(i) 基于并行正向运动学的快速触觉仿真,提供高频率、高分辨率的触觉信号以支持RL训练;(ii) 电流到扭矩校准方法,无需额外扭矩传感器即可映射电机电流为关节扭矩;(iii) 执行器动力学建模与非理想效应(如回差、力矩-速度饱和)的随机化,有效弥合仿真与现实之间的执行差距。最终,基于完全仿真训练的异构演员-评论家PPO策略可零样本部署至五指灵巧手,在无需微调的情况下实现了可控抓握力跟踪和物体再定向两项核心技能,是首个在多指灵巧手上实现端到端仿真训练并直接部署于真实硬件的可控抓握范例。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02778
作者: Haoyu Dong,Zhengmao He,Yang Li,Zhibin Li,Xinyu Yi,Zhe Zhao
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Human-like dexterous hands with multiple fingers offer human-level manipulation capabilities, but training control policies that can directly deploy on real hardware remains difficult due to contact-rich physics and imperfect actuation. We close this gap with a practical sim-to-real reinforcement learning (RL) framework that utilizes dense tactile feedback combined with joint torque sensing to explicitly regulate physical interactions. To enable effective sim-to-real transfer, we introduce (i) a computationally fast tactile simulation that computes distances between dense virtual tactile units and the object via parallel forward kinematics, providing high-rate, high-resolution touch signals needed by RL; (ii) a current-to-torque calibration that eliminates the need for torque sensors on dexterous hands by mapping motor current to joint torque; and (iii) actuator dynamics modeling to bridge the actuation gaps with randomization of non-ideal effects such as backlash, torque-speed saturation. Using an asymmetric actor-critic PPO pipeline trained entirely in simulation, our policies deploy directly to a five-finger hand. The resulting policies demonstrated two essential skills: (1) command-based, controllable grasp force tracking, and (2) reorientation of objects in the hand, both of which were robustly executed without fine-tuning on the robot. By combining tactile and torque in the observation space with effective sensing/actuation modeling, our system provides a practical solution to achieve reliable dexterous manipulation. To our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of controllable grasping on a multi-finger dexterous hand trained entirely in simulation and transferred zero-shot on real hardware.
zh
[AI-29] UniSRCodec: Unified and Low-Bitrate Single Codebook Codec with Sub-Band Reconstruction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决单码本神经音频编解码器(Neural Audio Codecs, NACs)在高保真度、高频音频建模以及跨频段压缩性能方面的局限性,尤其是现有单码本方法难以同时实现低带宽、高保真和统一建模的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为UniSRCodec的新型单码本编解码器,通过引入基于梅尔谱图(Mel-spectrogram)的时间-频率联合压缩机制,并结合声码器(Vocoder)恢复原始音频相位信息,从而有效提升压缩效率与重建质量;此外,还设计了子带重构技术以实现低频与高频音频的高质量压缩,最终在仅40 token rate下达到跨领域单码本编解码器的最先进(SOTA)性能,且重建质量可媲美部分多码本方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02776
作者: Zhisheng Zhang,Xiang Li,Yixuan Zhou,Jing Peng,Shengbo Cai,Guoyang Zeng,Zhiyong Wu
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multimedia (cs.MM)
备注: 6 pages, 2 figures, and 3 tables
Abstract:Neural Audio Codecs (NACs) can reduce transmission overhead by performing compact compression and reconstruction, which also aim to bridge the gap between continuous and discrete signals. Existing NACs can be divided into two categories: multi-codebook and single-codebook codecs. Multi-codebook codecs face challenges such as structural complexity and difficulty in adapting to downstream tasks, while single-codebook codecs, though structurally simpler, suffer from low-fidelity, ineffective modeling of unified audio, and an inability to support modeling of high-frequency audio. We propose the UniSRCodec, a single-codebook codec capable of supporting high sampling rate, low-bandwidth, high fidelity, and unified. We analyze the inefficiency of waveform-based compression and introduce the time and frequency compression method using the Mel-spectrogram, and cooperate with a Vocoder to recover the phase information of the original audio. Moreover, we propose a sub-band reconstruction technique to achieve high-quality compression across both low and high frequency bands. Subjective and objective experimental results demonstrate that UniSRCodec achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance among cross-domain single-codebook codecs with only a token rate of 40, and its reconstruction quality is comparable to that of certain multi-codebook methods. Our demo page is available at this https URL.
zh
[AI-30] Netflix Artwork Personalization via LLM Post-training
【速读】:该论文旨在解决娱乐平台中个性化艺术海报推荐的问题,即如何根据用户多样化的偏好选择最契合其审美的标题视觉呈现形式。由于用户对同一内容可能因兴趣偏向(如情感类或动作类)而偏好不同风格的艺术海报,传统统一推荐策略难以满足个体差异。解决方案的关键在于对预训练的大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)进行后训练(post-training),使其能够基于用户特征和标题内容生成个性化的艺术海报推荐结果,从而提升用户满意度与参与度。实验表明,基于Llama 3.1 8B模型的后训练方法在5000个用户-标题对上的表现优于Netflix现有生产模型,提升幅度达3%-5%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02764
作者: Hyunji Nam,Sejoon Oh,Emma Kong,Yesu Feng,Moumita Bhattacharya
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 6 pages
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated success in various applications of user recommendation and personalization across e-commerce and entertainment. On many entertainment platforms such as Netflix, users typically interact with a wide range of titles, each represented by an artwork. Since users have diverse preferences, an artwork that appeals to one type of user may not resonate with another with different preferences. Given this user heterogeneity, our work explores the novel problem of personalized artwork recommendations according to diverse user preferences. Similar to the multi-dimensional nature of users’ tastes, titles contain different themes and tones that may appeal to different viewers. For example, the same title might feature both heartfelt family drama and intense action scenes. Users who prefer romantic content may like the artwork emphasizing emotional warmth between the characters, while those who prefer action thrillers may find high-intensity action scenes more intriguing. Rather than a one-size-fits-all approach, we conduct post-training of pre-trained LLMs to make personalized artwork recommendations, selecting the most preferred visual representation of a title for each user and thereby improving user satisfaction and engagement. Our experimental results with Llama 3.1 8B models (trained on a dataset of 110K data points and evaluated on 5K held-out user-title pairs) show that the post-trained LLMs achieve 3-5% improvements over the Netflix production model, suggesting a promising direction for granular personalized recommendations using LLMs.
zh
[AI-31] LLM Agent Framework for Intelligent Change Analysis in Urban Environment using Remote Sensing Imagery
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有变化检测方法在应对多样化现实世界查询时缺乏通用性以及在综合分析中智能不足的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个通用代理框架 ChangeGPT,该框架将大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)与视觉基础模型(Vision Foundation Model)相融合,并采用分层结构以缓解幻觉问题。通过多步推理和鲁棒的工具选择能力,ChangeGPT 在复杂变化相关查询上表现出显著优势,尤其在使用 GPT-4-turbo 后端时达到 90.71% 的匹配准确率,验证了其在遥感决策支持中的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02757
作者: Zixuan Xiao,Jun Ma
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Existing change detection methods often lack the versatility to handle diverse real-world queries and the intelligence for comprehensive analysis. This paper presents a general agent framework, integrating Large Language Models (LLM) with vision foundation models to form ChangeGPT. A hierarchical structure is employed to mitigate hallucination. The agent was evaluated on a curated dataset of 140 questions categorized by real-world scenarios, encompassing various question types (e.g., Size, Class, Number) and complexities. The evaluation assessed the agent’s tool selection ability (Precision/Recall) and overall query accuracy (Match). ChangeGPT, especially with a GPT-4-turbo backend, demonstrated superior performance, achieving a 90.71 % Match rate. Its strength lies particularly in handling change-related queries requiring multi-step reasoning and robust tool selection. Practical effectiveness was further validated through a real-world urban change monitoring case study in Qianhai Bay, Shenzhen. By providing intelligence, adaptability, and multi-type change analysis, ChangeGPT offers a powerful solution for decision-making in remote sensing applications.
zh
[AI-32] Q-Regularized Generative Auto-Bidding: From Suboptimal Trajectories to Optimal Policies KDD
【速读】:该论文旨在解决自动出价(Auto-bidding)在复杂广告主环境中优化广告表现时面临的挑战,特别是现有方法依赖强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)和生成模型所导致的高调参成本、次优轨迹对策略学习的负面影响等问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出QGA(Q-value regularized Generative Auto-bidding),通过将双Q学习(Double Q-learning)策略引入决策Transformer(Decision Transformer, DT)骨干网络,并加入Q值正则化项,实现策略模仿与动作价值最大化联合优化;同时设计了一种由Q值引导的双探索机制(Q-value guided dual-exploration mechanism),在数据分布外安全探索策略空间,从而提升策略鲁棒性与性能。实验表明,QGA在公开基准和模拟环境中优于或媲美现有方法,并在大规模真实A/B测试中实现了3.27%的广告总商品价值(Ad GMV)增长和2.49%的广告投资回报率(Ad ROI)提升。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02754
作者: Mingming Zhang,Na Li,Zhuang Feiqing,Hongyang Zheng,Jiangbing Zhou,Wang Wuyin,Sheng-jie Sun,XiaoWei Chen,Junxiong Zhu,Lixin Zou,Chenliang Li
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
备注: 11pages, 5figures, In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining
Abstract:With the rapid development of e-commerce, auto-bidding has become a key asset in optimizing advertising performance under diverse advertiser environments. The current approaches focus on reinforcement learning (RL) and generative models. These efforts imitate offline historical behaviors by utilizing a complex structure with expensive hyperparameter tuning. The suboptimal trajectories further exacerbate the difficulty of policy learning. To address these challenges, we proposes QGA, a novel Q-value regularized Generative Auto-bidding method. In QGA, we propose to plug a Q-value regularization with double Q-learning strategy into the Decision Transformer backbone. This design enables joint optimization of policy imitation and action-value maximization, allowing the learned bidding policy to both leverage experience from the dataset and alleviate the adverse impact of the suboptimal trajectories. Furthermore, to safely explore the policy space beyond the data distribution, we propose a Q-value guided dual-exploration mechanism, in which the DT model is conditioned on multiple return-to-go targets and locally perturbed actions. This entire exploration process is dynamically guided by the aforementioned Q-value module, which provides principled evaluation for each candidate action. Experiments on public benchmarks and simulation environments demonstrate that QGA consistently achieves superior or highly competitive results compared to existing alternatives. Notably, in large-scale real-world A/B testing, QGA achieves a 3.27% increase in Ad GMV and a 2.49% improvement in Ad ROI. Comments: 11pages, 5figures, In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Information Retrieval (cs.IR) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02754 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2601.02754v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02754 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) Related DOI: https://doi.org/10.1145/3770854.3783950 Focus to learn more DOI(s) linking to related resources
zh
[AI-33] he Path Ahead for Agent ic AI: Challenges and Opportunities
【速读】:该论文试图解决的问题是:如何将大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)从被动的文本生成工具演进为具备自主性、目标驱动能力的智能体系统(agentic AI systems),以实现在复杂环境中自主规划、记忆、使用工具并进行迭代推理的能力。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个整合框架,明确包含感知(perception)、记忆(memory)、规划(planning)和工具执行(tool execution)四大核心组件,并通过“推理-行动-反思”(reasoning-action-reflection)循环机制,推动LLM向自主行为的架构转型。同时,论文强调必须同步突破可验证的规划、可扩展的多智能体协同、持久化记忆架构及治理框架等关键技术瓶颈,以确保技术稳健性、可解释性和伦理安全性,从而实现负责任的AI发展。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02749
作者: Nadia Sibai,Yara Ahmed,Serry Sibaee,Sawsan AlHalawani,Adel Ammar,Wadii Boulila
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The evolution of Large Language Models (LLMs) from passive text generators to autonomous, goal-driven systems represents a fundamental shift in artificial intelligence. This chapter examines the emergence of agentic AI systems that integrate planning, memory, tool use, and iterative reasoning to operate autonomously in complex environments. We trace the architectural progression from statistical models to transformer-based systems, identifying capabilities that enable agentic behavior: long-range reasoning, contextual awareness, and adaptive decision-making. The chapter provides three contributions: (1) a synthesis of how LLM capabilities extend toward agency through reasoning-action-reflection loops; (2) an integrative framework describing core components perception, memory, planning, and tool execution that bridge LLMs with autonomous behavior; (3) a critical assessment of applications and persistent challenges in safety, alignment, reliability, and sustainability. Unlike existing surveys, we focus on the architectural transition from language understanding to autonomous action, emphasizing the technical gaps that must be resolved before deployment. We identify critical research priorities, including verifiable planning, scalable multi-agent coordination, persistent memory architectures, and governance frameworks. Responsible advancement requires simultaneous progress in technical robustness, interpretability, and ethical safeguards to realize potential while mitigating risks of misalignment and unintended consequences.
zh
[AI-34] Hypothesize-Then-Verify: Speculative Root Cause Analysis for Microservices with Pathwise Parallelism ICSE
【速读】:该论文旨在解决微服务系统中异常根因分析(Root Cause Analysis, RCA)的准确性与效率问题。现有基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的方法虽具备跨平台适应性和任务泛化能力,但仍受限于探索多样性不足导致的精度瓶颈,以及对大规模LLM的依赖引发的推理延迟。其解决方案的关键在于提出SpecRCA框架,采用“假设-验证”范式:首先通过假设生成模块快速构建候选根因,再利用并行验证模块高效筛选和确认真实根因,从而在保证解释性的同时显著提升分析精度与执行效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02736
作者: Lingzhe Zhang,Tong Jia,Yunpeng Zhai,Leyi Pan,Chiming Duan,Minghua He,Pei Xiao,Ying Li
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: accepted by ICSE-NIER’26
Abstract:Microservice systems have become the backbone of cloud-native enterprise applications due to their resource elasticity, loosely coupled architecture, and lightweight deployment. Yet, the intrinsic complexity and dynamic runtime interactions of such systems inevitably give rise to anomalies. Ensuring system reliability therefore hinges on effective root cause analysis (RCA), which entails not only localizing the source of anomalies but also characterizing the underlying failures in a timely and interpretable manner. Recent advances in intelligent RCA techniques, particularly those powered by large language models (LLMs), have demonstrated promising capabilities, as LLMs reduce reliance on handcrafted features while offering cross-platform adaptability, task generalization, and flexibility. However, existing LLM-based methods still suffer from two critical limitations: (a) limited exploration diversity, which undermines accuracy, and (b) heavy dependence on large-scale LLMs, which results in slow inference. To overcome these challenges, we propose SpecRCA, a speculative root cause analysis framework for microservices that adopts a \textithypothesize-then-verify paradigm. SpecRCA first leverages a hypothesis drafting module to rapidly generate candidate root causes, and then employs a parallel root cause verifier to efficiently validate them. Preliminary experiments on the AIOps 2022 dataset demonstrate that SpecRCA achieves superior accuracy and efficiency compared to existing approaches, highlighting its potential as a practical solution for scalable and interpretable RCA in complex microservice environments.
zh
[AI-35] Agent ic Memory Enhanced Recursive Reasoning for Root Cause Localization in Microservices ICSE
【速读】:该论文旨在解决微服务系统中故障根因定位(Root Cause Localization, RCL)的准确性与效率问题,尤其针对现有基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的方法存在浅层症状导向推理和跨告警重复计算导致的高延迟缺陷。其解决方案的关键在于提出AMER-RCL框架,该框架由两个核心组件构成:一是递归推理引擎(Recursive Reasoning RCL engine),通过多智能体机制对每个告警进行递归式推理以逐步精炼候选原因;二是智能体记忆机制(Agentic Memory),在时间窗口内增量累积并复用先前告警的推理过程,从而减少冗余探索、降低推理延迟。实验表明,AMER-RCL在定位准确性和推理效率上均显著优于当前最优方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02732
作者: Lingzhe Zhang,Tong Jia,Yunpeng Zhai,Leyi Pan,Chiming Duan,Minghua He,Mengxi Jia,Ying Li
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: accepted by ICSE-SEIP’26
Abstract:As contemporary microservice systems become increasingly popular and complex-often comprising hundreds or even thousands of fine-grained, interdependent subsystems-they are experiencing more frequent failures. Ensuring system reliability thus demands accurate root cause localization. While many traditional graph-based and deep learning approaches have been explored for this task, they often rely heavily on pre-defined schemas that struggle to adapt to evolving operational contexts. Consequently, a number of LLM-based methods have recently been proposed. However, these methods still face two major limitations: shallow, symptom-centric reasoning that undermines accuracy, and a lack of cross-alert reuse that leads to redundant reasoning and high latency. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive study of how Site Reliability Engineers (SREs) localize the root causes of failures, drawing insights from professionals across multiple organizations. Our investigation reveals that expert root cause analysis exhibits three key characteristics: recursiveness, multi-dimensional expansion, and cross-modal reasoning. Motivated by these findings, we introduce AMER-RCL, an agentic memory enhanced recursive reasoning framework for root cause localization in microservices. AMER-RCL employs the Recursive Reasoning RCL engine, a multi-agent framework that performs recursive reasoning on each alert to progressively refine candidate causes, while Agentic Memory incrementally accumulates and reuses reasoning from prior alerts within a time window to reduce redundant exploration and lower inference latency. Experimental results demonstrate that AMER-RCL consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both localization accuracy and inference efficiency.
zh
[AI-36] Privacy-Preserving AI-Enabled Decentralized Learning and Employment Records System
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有基于区块链的学习与就业记录(Learning and Employment Record, LER)系统中缺乏自动化技能凭证生成机制以及无法有效整合非结构化学习证据的问题。其关键解决方案是提出一种隐私保护的、由人工智能驱动的去中心化LER系统,通过在可信执行环境(Trusted Execution Environment, TEE)内运行自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing, NLP)管道,从正式记录(如成绩单、课程大纲)和非正式学习成果中自动提取并生成可验证的技能凭证;所有验证与岗位匹配操作均在TEE内完成,实现选择性披露,确保原始凭证和私钥不离开安全 enclave,从而保障数据隐私与完整性,同时基于已认证的技能向量进行岗位匹配,避免受非技能类简历字段干扰,提升匹配准确性与公平性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02720
作者: Yuqiao Xu,Mina Namazi,Sahith Reddy Jalapally,Osama Zafar,Youngjin Yoo,Erman Ayday
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Learning and Employment Record (LER) systems are emerging as critical infrastructure for securely compiling and sharing educational and work achievements. Existing blockchain-based platforms leverage verifiable credentials but typically lack automated skill-credential generation and the ability to incorporate unstructured evidence of learning. In this paper,a privacy-preserving, AI-enabled decentralized LER system is proposed to address these gaps. Digitally signed transcripts from educational institutions are accepted, and verifiable self-issued skill credentials are derived inside a trusted execution environment (TEE) by a natural language processing pipeline that analyzes formal records (e.g., transcripts, syllabi) and informal artifacts. All verification and job-skill matching are performed inside the enclave with selective disclosure, so raw credentials and private keys remain enclave-confined. Job matching relies solely on attested skill vectors and is invariant to non-skill resume fields, thereby reducing opportunities for screening this http URL NLP component was evaluated on sample learner data; the mapping follows the validated Syllabus-to-O*NET methodology,and a stability test across repeated runs observed 5% variance in top-ranked skills. Formal security statements and proof sketches are provided showing that derived credentials are unforgeable and that sensitive information remains confidential. The proposed system thus supports secure education and employment credentialing, robust transcript verification,and automated, privacy-preserving skill extraction within a decentralized framework.
zh
[AI-37] CREAM: Continual Retrieval on Dynamic Streaming Corpora with Adaptive Soft Memory KDD2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决动态数据流中信息检索(Information Retrieval, IR)性能下降的问题,尤其是由于数据分布变化导致AI驱动的IR系统失效。现有基于记忆的持续学习方法依赖固定查询集与真实相关文档,限制了对未见查询和文档的泛化能力,难以应用于实际场景。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种自监督框架CREAM,通过三个核心技术实现:细粒度相似性估计、正则化聚类原型构建以及分层共核采样,从而将流式查询与文档的演化语义编码为动态结构化的软记忆,并在无监督条件下适应已见和未见主题,显著提升模型在标签缺失环境下的检索准确性和适应性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02708
作者: HuiJeong Son,Hyeongu Kang,Sunho Kim,Subeen Ho,SeongKu Kang,Dongha Lee,Susik Yoon
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted to KDD 2026
Abstract:Information retrieval (IR) in dynamic data streams is emerging as a challenging task, as shifts in data distribution degrade the performance of AI-powered IR systems. To mitigate this issue, memory-based continual learning has been widely adopted for IR. However, existing methods rely on a fixed set of queries with ground-truth relevant documents, which limits generalization to unseen queries and documents, making them impractical for real-world applications. To enable more effective learning with unseen topics of a new corpus without ground-truth labels, we propose CREAM, a self-supervised framework for memory-based continual retrieval. CREAM captures the evolving semantics of streaming queries and documents into dynamically structured soft memory and leverages it to adapt to both seen and unseen topics in an unsupervised setting. We realize this through three key techniques: fine-grained similarity estimation, regularized cluster prototyping, and stratified coreset sampling. Experiments on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that CREAM exhibits superior adaptability and retrieval accuracy, outperforming the strongest method in a label-free setting by 27.79% in Success@5 and 44.5% in Recall@10 on average, and achieving performance comparable to or even exceeding that of supervised methods.
zh
[AI-38] Learning User Preferences Through Interaction for Long-Term Collaboration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决对话代理在与用户多次交互过程中如何持续适应用户偏好以提升长期协作质量的问题。其核心挑战在于如何使代理在多轮会话中积累并利用用户偏好信息,从而优化后续交互效果。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为MultiSessionCollab的基准测试框架,并设计具备持久化记忆机制的长期协作代理(Long-term Collaborative Agents),该记忆能够随着交互经验不断更新和细化用户偏好;同时,通过用户模拟器行为提取学习信号,指导代理生成更全面的反思并更有效地更新记忆。实验结果表明,引入记忆机制显著提升了任务成功率、交互效率及用户满意度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02702
作者: Shuhaib Mehri,Priyanka Kargupta,Tal August,Dilek Hakkani-Tür
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:As conversational agents accumulate experience collaborating with users, adapting to user preferences is essential for fostering long-term relationships and improving collaboration quality over time. We introduce MultiSessionCollab, a benchmark that evaluates how well agents can learn user preferences and leverage them to improve collaboration quality throughout multiple sessions. To develop agents that succeed in this setting, we present long-term collaborative agents equipped with a memory that persists and refines user preference as interaction experience accumulates. Moreover, we demonstrate that learning signals can be derived from user simulator behavior in MultiSessionCollab to train agents to generate more comprehensive reflections and update their memory more effectively. Extensive experiments show that equipping agents with memory improves long-term collaboration, yielding higher task success rates, more efficient interactions, and reduced user effort. Finally, we conduct a human user study that demonstrates that memory helps improve user experience in real-world settings.
zh
[AI-39] Multi-channel multi-speaker transformer for speech recognition INTERSPEECH2023
【速读】:该论文旨在解决远场多说话人语音识别(far-field multi-speaker speech recognition)中因说话人干扰导致高维声学特征难以有效编码的问题。现有方法如多通道Transformer(MCT)在混合输入音频中无法准确分离并建模各说话人的声学特征,从而限制了识别性能。为此,作者提出多通道多说话人Transformer(M2Former),其关键创新在于设计了一种能够同时处理多通道输入与多说话人分离的架构,通过引入更精细的跨通道和跨说话人注意力机制,在保持空间信息的同时实现对每个说话人独立的高维特征编码,从而显著提升远场场景下的多说话人自动语音识别(ASR)性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02688
作者: Guo Yifan,Tian Yao,Suo Hongbin,Wan Yulong
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Proc. INTERSPEECH 2023, 5 pages
Abstract:With the development of teleconferencing and in-vehicle voice assistants, far-field multi-speaker speech recognition has become a hot research topic. Recently, a multi-channel transformer (MCT) has been proposed, which demonstrates the ability of the transformer to model far-field acoustic environments. However, MCT cannot encode high-dimensional acoustic features for each speaker from mixed input audio because of the interference between speakers. Based on these, we propose the multi-channel multi-speaker transformer (M2Former) for far-field multi-speaker ASR in this paper. Experiments on the SMS-WSJ benchmark show that the M2Former outperforms the neural beamformer, MCT, dual-path RNN with transform-average-concatenate and multi-channel deep clustering based end-to-end systems by 9.2%, 14.3%, 24.9%, and 52.2% respectively, in terms of relative word error rate reduction.
zh
[AI-40] Learning from Prompt itself: the Hierarchical Attribution Prompt Optimization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前提示工程(Prompt Engineering)中存在的重要问题:一是提示优化方法常引发提示漂移(Prompt Drift),即新生成的提示虽修复了原有错误,却损害了先前任务的性能;二是从零开始生成提示会降低过程的可解释性。针对这些问题,论文提出Hierarchical Attribution Prompt Optimization (HAPO)框架,其关键创新在于:(1) 动态归因机制,用于识别训练数据和提示历史中的错误模式;(2) 语义单元优化策略,通过编辑功能明确的提示片段实现精准调整;(3) 多模态友好进展路径,支持端到端大语言模型(LLM)与LLM-多模态大语言模型(MLLM)工作流。该方案显著提升了优化效率,并为可扩展的提示工程提供了可解释且稳定的范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02683
作者: Dongyu Chen,Jian Ma,Xianpeng Zhang,Lei Zhang,Haonan Lu,Chen Chen,Chuangchuang Wang,Kai Tang
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Optimization is fundamental across numerous disciplines, typically following an iterative process of refining an initial solution to enhance performance. This principle is equally critical in prompt engineering, where designing effective prompts for large language models constitutes a complex optimization challenge. A structured optimization approach requires automated or semi-automated procedures to develop improved prompts, thereby reducing manual effort, improving performance, and yielding an interpretable process. However, current prompt optimization methods often induce prompt drift, where new prompts fix prior failures but impair performance on previously successful tasks. Additionally, generating prompts from scratch can compromise interpretability. To address these limitations, this study proposes the Hierarchical Attribution Prompt Optimization (HAPO) framework, which introduces three innovations: (1) a dynamic attribution mechanism targeting error patterns in training data and prompting history, (2) semantic-unit optimization for editing functional prompt segments, and (3) multimodal-friendly progression supporting both end-to-end LLM and LLM-MLLM workflows. Applied in contexts like single/multi-image QA (e.g., OCRV2) and complex task analysis (e.g., BBH), HAPO demonstrates enhanced optimization efficiency, outperforming comparable automated prompt optimization methods and establishing an extensible paradigm for scalable prompt engineering.
zh
[AI-41] opology-Independent Robustness of the Weighted Mean under Label Poisoning Attacks in Heterogeneous Decentralized Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决去中心化信号处理与机器学习系统在面临标签投毒攻击(label poisoning attack)时的鲁棒性问题,即部分节点使用被污染的本地标签训练模型并共享,从而影响全局学习性能。其解决方案的关键在于对不同聚合策略(包括鲁棒聚合器与加权均值聚合器)在标签投毒场景下的理论性能进行对比分析,发现加权均值聚合器虽常被视为脆弱基线,但在特定网络拓扑条件下(如全局污染率低于局部污染率、正常节点网络不连通或稀疏且局部污染率高)反而能优于鲁棒聚合器,揭示了网络拓扑结构在决定系统抗攻击能力中的核心作用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02682
作者: Jie Peng,Weiyu Li,Stefan Vlaski,Qing Ling
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Robustness to malicious attacks is crucial for practical decentralized signal processing and machine learning systems. A typical example of such attacks is label poisoning, meaning that some agents possess corrupted local labels and share models trained on these poisoned data. To defend against malicious attacks, existing works often focus on designing robust aggregators; meanwhile, the weighted mean aggregator is typically considered a simple, vulnerable baseline. This paper analyzes the robustness of decentralized gradient descent under label poisoning attacks, considering both robust and weighted mean aggregators. Theoretical results reveal that the learning errors of robust aggregators depend on the network topology, whereas the performance of weighted mean aggregator is topology-independent. Remarkably, the weighted mean aggregator, although often considered vulnerable, can outperform robust aggregators under sufficient heterogeneity, particularly when: (i) the global contamination rate (i.e., the fraction of poisoned agents for the entire network) is smaller than the local contamination rate (i.e., the maximal fraction of poisoned neighbors for the regular agents); (ii) the network of regular agents is disconnected; or (iii) the network of regular agents is sparse and the local contamination rate is high. Empirical results support our theoretical findings, highlighting the important role of network topology in the robustness to label poisoning attacks.
zh
[AI-42] Inferring Causal Graph Temporal Logic Formulas to Expedite Reinforcement Learning in Temporally Extended Tasks AAAI-26
【速读】:该论文旨在解决黑箱强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)在处理具有时空动态特性的图结构决策任务时,因忽略局部变化如何通过网络结构传播而导致样本效率低和可解释性差的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种闭环框架GTL-CIRL,该框架能够同时学习策略并挖掘因果图时序逻辑(Causal Graph Temporal Logic, Causal GTL)规范;通过引入鲁棒奖励设计、在效果失败时收集反例,并利用高斯过程(Gaussian Process, GP)驱动的贝叶斯优化来精炼参数化的因果模板,从而有效建模系统动态中的空间与时间相关性,实现对复杂参数空间的高效探索,显著提升学习速度并获得可验证的行为特性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02666
作者: Hadi Partovi Aria,Zhe Xu
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Logic in Computer Science (cs.LO)
备注: Accepted to AAAI-26 Bridge Program B10: Making Embodied AI Reliable with Testing and Formal Verification
Abstract:Decision-making tasks often unfold on graphs with spatial-temporal dynamics. Black-box reinforcement learning often overlooks how local changes spread through network structure, limiting sample efficiency and interpretability. We present GTL-CIRL, a closed-loop framework that simultaneously learns policies and mines Causal Graph Temporal Logic (Causal GTL) specifications. The method shapes rewards with robustness, collects counterexamples when effects fail, and uses Gaussian Process (GP) driven Bayesian optimization to refine parameterized cause templates. The GP models capture spatial and temporal correlations in the system dynamics, enabling efficient exploration of complex parameter spaces. Case studies in gene and power networks show faster learning and clearer, verifiable behavior compared to standard RL baselines.
zh
[AI-43] Effective Online 3D Bin Packing with Lookahead Parcels Using Monte Carlo Tree Search
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在线三维装箱问题(Online 3D Bin Packing, 3D-BP)在实际物流场景中因批次货物分布短期变化(distribution shifts)导致深度强化学习(Deep Reinforcement Learning, DRL)性能下降的问题。其解决方案的关键在于将带有前瞻包裹信息的在线3D-BP建模为模型预测控制(Model Predictive Control, MPC)问题,并引入蒙特卡洛树搜索(Monte Carlo Tree Search, MCTS)框架进行求解;同时设计了一种动态探索先验机制,根据前瞻信息自动平衡已学习的DRL策略与鲁棒的随机策略,并通过辅助奖励函数惩罚单次放置造成的长期空间浪费,从而提升算法在分布偏移下的适应性和整体装箱效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02649
作者: Jiangyi Fang,Bowen Zhou,Haotian Wang,Xin Zhu,Leye Wang
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Online 3D Bin Packing (3D-BP) with robotic arms is crucial for reducing transportation and labor costs in modern logistics. While Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) has shown strong performance, it often fails to adapt to real-world short-term distribution shifts, which arise as different batches of goods arrive sequentially, causing performance drops. We argue that the short-term lookahead information available in modern logistics systems is key to mitigating this issue, especially during distribution shifts. We formulate online 3D-BP with lookahead parcels as a Model Predictive Control (MPC) problem and adapt the Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) framework to solve it. Our framework employs a dynamic exploration prior that automatically balances a learned RL policy and a robust random policy based on the lookahead characteristics. Additionally, we design an auxiliary reward to penalize long-term spatial waste from individual placements. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets show that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving over 10% gains under distributional shifts, 4% average improvement in online deployment, and up to more than 8% in the best case–demonstrating the effectiveness of our framework.
zh
[AI-44] AWARE-US: Benchmark for Preference-Aware Resolution in Tool-Calling Agents
【速读】:该论文旨在解决工具调用型对话代理在查询结构化数据库时面临的两个相互关联的问题:约束不足(underspecification,即缺少运行精确查询所需的约束条件)和不可行性(infeasibility,即完全指定的查询因无任何条目满足所有约束而返回空集)。现有方法通常简单回应“无结果”或使用随意规则放宽约束,这可能导致违背用户意图,丢弃用户最关心的要求。解决方案的关键在于将不可行性处理建模为偏好感知的查询修复问题——当查询不可满足时,代理应优先放松对用户而言重要性最低的约束。为此,作者提出了三种基于大语言模型(LLM)的方法来从对话中推断约束相对重要性:(1) 局部加权(local weighting)、(2) 全局一次性加权(global one-shot weighting)和 (3) 成对排序(pairwise ranking),并通过实验验证局部加权在偏好一致性上表现最佳,全局加权在正确约束放松方面最优。此外,论文还引入了 AWARE-US 基准测试集,用于评估代理在基于人物设定(persona-grounded)请求下通过对话澄清意图并按人物隐含偏好解决不可行性的能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02643
作者: Mehmet Kurmaz
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 19 pages, 2 figures, 6 tables
Abstract:Tool-calling conversational agents querying structured databases often face two linked failures: underspecification (missing constraints needed to run a precise query) and infeasibility (the fully specified query returns an empty set because no item satisfies all constraints). Existing work often responds with “no results” or relaxes constraints using ad hoc rules, which can violate user intent by discarding requirements the user cares about most. We frame infeasibility handling as a preference-aware query repair problem: when a query is unsatisfiable, the agent should relax the least important constraints to the user. We propose three LLM-based methods for inferring relative constraint importance from dialogue: (1) local weighting, (2) global one-shot weighting, and (3) pairwise ranking. Experiments show local weighting achieves the best preference alignment, while global weighting performs best on correct constraint relaxation. We also introduce AWARE-US, a benchmark of persona-grounded queries requiring agents to disambiguate requests via conversation and resolve infeasibility in a way consistent with persona-implied preferences.
zh
[AI-45] An Empirical Study of On-Device Translation for Real-Time Live-Stream Chat on Mobile Devices
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在真实场景中部署设备端人工智能(On-Device AI)模型时所面临的关键实践问题,主要包括:(1)如何选择适合特定设备资源限制的模型及其对应的计算与能耗特性;(2)设备端模型在领域适应(Domain Adaptation)方面的潜力与能力。解决方案的关键在于构建一个针对实时聊天翻译任务的专用基准测试集 LiveChatBench(包含1,000对韩英平行语句),并通过在五种不同移动设备上的系统性实验,量化评估模型性能与资源消耗之间的权衡关系,从而证明在受限环境下仍可实现接近商用模型(如 GPT-5.1)的性能表现,为设备端AI的实用化部署提供了实证依据和优化方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02641
作者: Jeiyoon Park,Daehwan Lee,Changmin Yeo,Yongshin Han,Minseop Kim
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: preprint
Abstract:Despite its efficiency, there has been little research on the practical aspects required for real-world deployment of on-device AI models, such as the device’s CPU utilization and thermal conditions. In this paper, through extensive experiments, we investigate two key issues that must be addressed to deploy on-device models in real-world services: (i) the selection of on-device models and the resource consumption of each model, and (ii) the capability and potential of on-device models for domain adaptation. To this end, we focus on a task of translating live-stream chat messages and manually construct LiveChatBench, a benchmark consisting of 1,000 Korean-English parallel sentence pairs. Experiments on five mobile devices demonstrate that, although serving a large and heterogeneous user base requires careful consideration of highly constrained deployment settings and model selection, the proposed approach nevertheless achieves performance comparable to commercial models such as GPT-5.1 on the well-targeted task. We expect that our findings will provide meaningful insights to the on-device AI community.
zh
[AI-46] Credit Assignment via Neural Manifold Noise Correlation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决神经网络中信用分配(credit assignment)问题,即如何准确评估单个神经元和突触变化对网络输出的影响。传统噪声相关性方法虽具生物合理性,但因需与网络规模成比例的扰动数量来精确估计雅可比矩阵(Jacobian),导致计算效率低下;且其使用各向同性噪声与神经活动位于低维流形(low-dimensional manifold)的神经生物学观察相悖。解决方案的关键在于提出神经流形噪声相关性(Neural Manifold Noise Correlation, NMNC),通过将扰动限制在神经活动的实际低维流形内进行信用分配,从而显著提升样本效率与性能,并更贴近灵长类视觉系统的表征特性。理论与实证均表明,训练后的网络中雅可比矩阵的行空间与神经流形对齐,且流形维度随网络规模增长缓慢,这使得NMNC成为一种高效且符合生物机制的信用分配方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02636
作者: Byungwoo Kang,Maceo Richards,Bernardo Sabatini
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC)
备注:
Abstract:Credit assignment–how changes in individual neurons and synapses affect a network’s output–is central to learning in brains and machines. Noise correlation, which estimates gradients by correlating perturbations of activity with changes in output, provides a biologically plausible solution to credit assignment but scales poorly as accurately estimating the Jacobian requires that the number of perturbations scale with network size. Moreover, isotropic noise conflicts with neurobiological observations that neural activity lies on a low-dimensional manifold. To address these drawbacks, we propose neural manifold noise correlation (NMNC), which performs credit assignment using perturbations restricted to the neural manifold. We show theoretically and empirically that the Jacobian row space aligns with the neural manifold in trained networks, and that manifold dimensionality scales slowly with network size. NMNC substantially improves performance and sample efficiency over vanilla noise correlation in convolutional networks trained on CIFAR-10, ImageNet-scale models, and recurrent networks. NMNC also yields representations more similar to the primate visual system than vanilla noise correlation. These findings offer a mechanistic hypothesis for how biological circuits could support credit assignment, and suggest that biologically inspired constraints may enable, rather than limit, effective learning at scale.
zh
[AI-47] AAF: A Trace Abstraction and Analysis Framework Synergizing Knowledge Graphs and LLM s ICSE2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大规模执行追踪数据(如操作系统内核或Chrome、MySQL等大型应用的追踪日志)难以分析的问题,现有工具依赖预定义分析逻辑,定制化洞察通常需编写领域特定脚本,过程繁琐且易出错。其解决方案的关键在于提出TAAF(Trace Abstraction and Analysis Framework),该框架通过时间索引构建知识图谱(Knowledge Graph, KG),将线程、CPU和系统资源等实体间的关系结构化表示,并结合大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)对查询相关的子图进行语义理解与推理,从而以自然语言问答方式生成可操作的洞察,显著提升多跳推理和因果推理任务的准确性,最高达31.2%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02632
作者: Alireza Ezaz,Ghazal Khodabandeh,Majid Babaei,Naser Ezzati-Jivan
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted to ICSE 2026. DOI https://doi.org/10.1145/3744916.3787832
Abstract:Execution traces are a critical source of information for understanding, debugging, and optimizing complex software systems. However, traces from OS kernels or large-scale applications like Chrome or MySQL are massive and difficult to analyze. Existing tools rely on predefined analyses, and custom insights often require writing domain-specific scripts, which is an error-prone and time-consuming task. This paper introduces TAAF (Trace Abstraction and Analysis Framework), a novel approach that combines time-indexing, knowledge graphs (KGs), and large language models (LLMs) to transform raw trace data into actionable insights. TAAF constructs a time-indexed KG from trace events to capture relationships among entities such as threads, CPUs, and system resources. An LLM then interprets query-specific subgraphs to answer natural-language questions, reducing the need for manual inspection and deep system expertise. To evaluate TAAF, we introduce TraceQA-100, a benchmark of 100 questions grounded in real kernel traces. Experiments across three LLMs and multiple temporal settings show that TAAF improves answer accuracy by up to 31.2%, particularly in multi-hop and causal reasoning tasks. We further analyze where graph-grounded reasoning helps and where limitations remain, offering a foundation for next-generation trace analysis tools.
zh
[AI-48] LAsset: An LLM -assisted Security Asset Identification Framework for System-on-Chip (SoC) Verification
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现代系统级芯片(System-on-Chip, SoC)和知识产权核(IP)设计中安全保证日益复杂的问题,特别是预硅验证阶段中安全资产(Security Asset)识别的效率与准确性难题。传统方法依赖安全专家手动识别资产,耗时且依赖高技能人力。解决方案的关键在于提出LAsset框架,该框架利用大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)对硬件设计规格说明和寄存器传输级(Register-Transfer Level, RTL)描述进行结构与语义分析,自动识别模块内的一级和二级安全资产,并构建模块间的关联关系,从而系统性刻画设计层面的安全依赖性。实验表明,该方法在SoC设计中达到90%的召回率,在IP设计中达93%,显著降低了人工干预并为可扩展的硬件安全开发提供了自动化路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02624
作者: Md Ajoad Hasan,Dipayan Saha,Khan Thamid Hasan,Nashmin Alam,Azim Uddin,Sujan Kumar Saha,Mark Tehranipoor,Farimah Farahmandi
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 6 pages
Abstract:The growing complexity of modern system-on-chip (SoC) and IP designs is making security assurance difficult day by day. One of the fundamental steps in the pre-silicon security verification of a hardware design is the identification of security assets, as it substantially influences downstream security verification tasks, such as threat modeling, security property generation, and vulnerability detection. Traditionally, assets are determined manually by security experts, requiring significant time and expertise. To address this challenge, we present LAsset, a novel automated framework that leverages large language models (LLMs) to identify security assets from both hardware design specifications and register-transfer level (RTL) descriptions. The framework performs structural and semantic analysis to identify intra-module primary and secondary assets and derives inter-module relationships to systematically characterize security dependencies at the design level. Experimental results show that the proposed framework achieves high classification accuracy, reaching up to 90% recall rate in SoC design, and 93% recall rate in IP designs. This automation in asset identification significantly reduces manual overhead and supports a scalable path forward for secure hardware development.
zh
[AI-49] LongDA: Benchmarking LLM Agents for Long-Document Data Analysis
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)代理在真实世界高复杂度数据分析任务中表现不足的问题,尤其是面对长篇文档密集型分析流程时的瓶颈。现有基准测试多假设输入数据结构清晰、格式规范,而实际场景中,分析者需从大量非结构化文档中提取并整合关键信息,再执行多步骤计算与代码生成,这对LLM代理的文档理解、跨文档信息融合及编程能力提出了更高要求。解决方案的关键在于构建LongDA——一个基于17个美国国家级调查数据集的真实世界数据分析基准,包含505个源自专家实践的分析查询,并开发LongTA工具增强型代理框架,支持文档访问、检索与代码执行,从而系统性评估LLM代理在复杂文档解析和端到端分析任务中的性能表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02598
作者: Yiyang Li,Zheyuan Zhang,Tianyi Ma,Zehong Wang,Keerthiram Murugesan,Chuxu Zhang,Yanfang Ye
机构: 未知
类目: Digital Libraries (cs.DL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:We introduce LongDA, a data analysis benchmark for evaluating LLM-based agents under documentation-intensive analytical workflows. In contrast to existing benchmarks that assume well-specified schemas and inputs, LongDA targets real-world settings in which navigating long documentation and complex data is the primary bottleneck. To this end, we manually curate raw data files, long and heterogeneous documentation, and expert-written publications from 17 publicly available U.S. national surveys, from which we extract 505 analytical queries grounded in real analytical practice. Solving these queries requires agents to first retrieve and integrate key information from multiple unstructured documents, before performing multi-step computations and writing executable code, which remains challenging for existing data analysis agents. To support the systematic evaluation under this setting, we develop LongTA, a tool-augmented agent framework that enables document access, retrieval, and code execution, and evaluate a range of proprietary and open-source models. Our experiments reveal substantial performance gaps even among state-of-the-art models, highlighting the challenges researchers should consider before applying LLM agents for decision support in real-world, high-stakes analytical settings.
zh
[AI-50] Orchestral AI: A Framework for Agent Orchestration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前大型语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)代理框架中存在的两大核心问题:一是开发者面临供应商锁定(vendor lock-in)风险,因各厂商提供的SDK具有专有性;二是多包生态系统复杂,导致控制流不透明、可复现性差。尤其在跨多个LLM提供商进行工具调用(tool calling)时,由于API碎片化、消息格式不兼容以及流式传输和工具调用行为不一致,难以构建可移植且可靠的代理系统。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个轻量级Python框架Orchestral,通过定义统一的消息、工具与LLM使用表示方式,实现跨提供商的无缝操作,避免手动格式转换并降低框架引入的复杂度;同时利用Python类型提示自动生成功能描述符,在保持类型安全的同时消除手工编写工具Schema的需求;此外,采用同步执行模型配合流式支持,确保行为确定性、易调试性和实时交互能力,且无需依赖服务器端组件。整体架构模块化设计清晰分离了提供方集成、工具执行、对话编排和用户接口,从而支持扩展而不引发架构耦合。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02577
作者: Alexander Roman,Jacob Roman
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics (astro-ph.IM); High Energy Physics - Phenomenology (hep-ph)
备注: 17 pages, 3 figures. For more information visit this https URL
Abstract:The rapid proliferation of LLM agent frameworks has forced developers to choose between vendor lock-in through provider-specific SDKs and complex multi-package ecosystems that obscure control flow and hinder reproducibility. Integrating tool calling across multiple LLM providers remains a core engineering challenge due to fragmented APIs, incompatible message formats, and inconsistent streaming and tool-calling behavior, making it difficult to build portable, reliable agent systems. We introduce Orchestral, a lightweight Python framework that provides a unified, type-safe interface for building LLM agents across major providers while preserving the simplicity required for scientific computing and production deployment. Orchestral defines a single universal representation for messages, tools, and LLM usage that operates seamlessly across providers, eliminating manual format translation and reducing framework-induced complexity. Automatic tool schema generation from Python type hints removes the need for handwritten descriptors while maintaining type safety across provider boundaries. A synchronous execution model with streaming support enables deterministic behavior, straightforward debugging, and real-time interaction without introducing server dependencies. The framework’s modular architecture cleanly separates provider integration, tool execution, conversation orchestration, and user-facing interfaces, enabling extensibility without architectural entanglement. Orchestral supports advanced agent capabilities found in larger frameworks, including rich tool calling, context compaction, workspace sandboxing, user approval workflows, sub-agents, memory management, and MCP integration.
zh
[AI-51] LendNova: Towards Automated Credit Risk Assessment with Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统信用风险评估模型依赖昂贵的人工特征工程、难以充分利用原始信用记录中全部信息的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出LendNova——首个面向信用风险评估的端到端自动化流水线,通过引入先进的自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing, NLP)技术和语言模型,直接对原始且包含专业术语的征信文本进行建模,无需人工特征提取即可自动捕捉文本中的风险信号,从而显著降低建模成本并提升可扩展性与准确性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02573
作者: Kiarash Shamsi,Danijel Novokmet,Joshua Peters,Mao Lin Liu,Paul K Edwards,Vahab Khoshdel
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computational Engineering, Finance, and Science (cs.CE)
备注:
Abstract:Credit risk assessment is essential in the financial sector, but has traditionally depended on costly feature-based models that often fail to utilize all available information in raw credit records. This paper introduces LendNova, the first practical automated end-to-end pipeline for credit risk assessment, designed to utilize all available information in raw credit records by leveraging advanced NLP techniques and language models. LendNova transforms risk modeling by operating directly on raw, jargon-heavy credit bureau text using a language model that learns task-relevant representations without manual feature engineering. By automatically capturing patterns and risk signals embedded in the text, it replaces manual preprocessing steps, reducing costs and improving scalability. Evaluation on real-world data further demonstrates its strong potential in accurate and efficient risk assessment. LendNova establishes a baseline for intelligent credit risk agents, demonstrating the feasibility of language models in this domain. It lays the groundwork for future research toward foundation systems that enable more accurate, adaptable, and automated financial decision-making.
zh
[AI-52] SimpleMem: Efficient Lifelong Memory for LLM Agents
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)智能体在复杂环境中长期交互时面临的记忆管理效率问题。现有方法要么通过被动扩展上下文保留完整交互历史导致冗余严重,要么依赖迭代推理过滤噪声从而产生高昂的token开销。其解决方案的关键在于提出SimpleMem框架,采用语义无损压缩策略构建三阶段高效记忆系统:首先通过熵感知过滤实现非结构化交互到紧凑多视图索引记忆单元的结构化压缩;其次通过异步递归记忆整合将相关单元抽象为高层表示以降低冗余;最后基于查询复杂度动态调整检索范围,实现精准上下文构建。该方案在准确率、检索效率和推理成本之间取得显著平衡,实验表明平均F1提升26.4%,推理时token消耗降低最高达30倍。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02553
作者: Jiaqi Liu,Yaofeng Su,Peng Xia,Siwei Han,Zeyu Zheng,Cihang Xie,Mingyu Ding,Huaxiu Yao
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:To support reliable long-term interaction in complex environments, LLM agents require memory systems that efficiently manage historical experiences. Existing approaches either retain full interaction histories via passive context extension, leading to substantial redundancy, or rely on iterative reasoning to filter noise, incurring high token costs. To address this challenge, we introduce SimpleMem, an efficient memory framework based on semantic lossless compression. We propose a three-stage pipeline designed to maximize information density and token utilization: (1) \textitSemantic Structured Compression, which applies entropy-aware filtering to distill unstructured interactions into compact, multi-view indexed memory units; (2) \textitRecursive Memory Consolidation, an asynchronous process that integrates related units into higher-level abstract representations to reduce redundancy; and (3) \textitAdaptive Query-Aware Retrieval, which dynamically adjusts retrieval scope based on query complexity to construct precise context efficiently. Experiments on benchmark datasets show that our method consistently outperforms baseline approaches in accuracy, retrieval efficiency, and inference cost, achieving an average F1 improvement of 26.4% while reducing inference-time token consumption by up to 30-fold, demonstrating a superior balance between performance and efficiency. Code is available at this https URL.
zh
[AI-53] xtual Explanations and Their Evaluations for Reinforcement Learning Policy
【速读】:该论文旨在解决强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)策略可解释性不足的问题,尤其是在确保文本解释(textual explanations)的正确性与质量方面存在的挑战。现有方法难以系统性地评估解释的准确性、一致性和在实际部署环境中的性能表现。解决方案的关键在于提出一种新型的可解释强化学习(Explainable Reinforcement Learning, XRL)框架:首先利用大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)结合聚类技术生成初始文本解释并提取高频状态条件;随后将这些条件转化为透明规则(transparent rules),通过专家知识注入和自动谓词生成器增强语义表达能力;进一步采用两种精化技术提升解释质量并减少冲突信息;最终实现对解释的质量、保真度(fidelity)及实际性能的定量评估。该框架不仅改进了已有方法如自主策略解释(Autonomous Policy Explanation)的局限性,还为工业场景(如电信领域)提供了可落地的XRL解决方案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02514
作者: Ahmad Terra,Mohit Ahmed,Rafia Inam,Elena Fersman,Martin Törngren
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Understanding a Reinforcement Learning (RL) policy is crucial for ensuring that autonomous agents behave according to human expectations. This goal can be achieved using Explainable Reinforcement Learning (XRL) techniques. Although textual explanations are easily understood by humans, ensuring their correctness remains a challenge, and evaluations in state-of-the-art remain limited. We present a novel XRL framework for generating textual explanations, converting them into a set of transparent rules, improving their quality, and evaluating them. Expert’s knowledge can be incorporated into this framework, and an automatic predicate generator is also proposed to determine the semantic information of a state. Textual explanations are generated using a Large Language Model (LLM) and a clustering technique to identify frequent conditions. These conditions are then converted into rules to evaluate their properties, fidelity, and performance in the deployed environment. Two refinement techniques are proposed to improve the quality of explanations and reduce conflicting information. Experiments were conducted in three open-source environments to enable reproducibility, and in a telecom use case to evaluate the industrial applicability of the proposed XRL framework. This framework addresses the limitations of an existing method, Autonomous Policy Explanation, and the generated transparent rules can achieve satisfactory performance on certain tasks. This framework also enables a systematic and quantitative evaluation of textual explanations, providing valuable insights for the XRL field.
zh
[AI-54] Enhancing Debugging Skills with AI-Powered Assistance: A Real-Time Tool for Debugging Support ICSE
【速读】:该论文旨在解决编程教育与软件开发中调试能力培养被忽视的问题,尤其是在计算机科学(Computer Science, CS)课程体系中缺乏系统性训练的现状。其解决方案的关键在于开发一个集成于集成开发环境(Integrated Development Environment, IDE)中的AI驱动调试助手,通过结合检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)技术、大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)、程序切片(program slicing)以及定制启发式规则,在减少LLM调用次数的同时提升调试建议的准确性与上下文相关性,从而实现对开发者实时、精准的支持。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02504
作者: Elizaveta Artser,Daniil Karol,Anna Potriasaeva,Aleksei Rostovskii,Katsiaryna Dzialets,Ekaterina Koshchenko,Xiaotian Su,April Yi Wang,Anastasiia Birillo
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注: Accepted at ICSE SEET 2026, 6 pages, 2 figures
Abstract:Debugging is a crucial skill in programming education and software development, yet it is often overlooked in CS curricula. To address this, we introduce an AI-powered debugging assistant integrated into an IDE. It offers real-time support by analyzing code, suggesting breakpoints, and providing contextual hints. Using RAG with LLMs, program slicing, and custom heuristics, it enhances efficiency by minimizing LLM calls and improving accuracy. A three-level evaluation - technical analysis, UX study, and classroom tests - highlights its potential for teaching debugging.
zh
[AI-55] GEM-Style Constraints for PEFT with Dual Gradient Projection in LoRA ICDM
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在持续学习(Continual Learning, CL)过程中因全参数微调带来的高计算成本问题。其解决方案的关键在于将梯度 episodic memory (GEM) 的约束机制引入低秩适配器(Low-Rank Adapter, LoRA)子空间中,提出 I-GEM 方法:通过在 GPU 内存中实现固定预算的双投影梯度近似,仅在适配器参数范围内约束干扰,从而在保持 GEM 类似稳定性的同时,显著降低平均投影开销(降低约 10³ 倍),实现了高效且可扩展的 LLM 持续学习。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02500
作者: Brian Tekmen,Jason Yin,Qianqian Tong
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Work accepted to the NSF REU Symposium at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM). Correspondence to: betekmen@uncg.edu
Abstract:Full fine-tuning of Large Language Models (LLMs) is computationally costly, motivating Continual Learning (CL) approaches that utilize parameter-efficient adapters. We revisit Gradient Episodic Memory (GEM) within the Low-Rank Adapter (LoRA) subspace and introduce I-GEM: a fixed-budget, GPU-resident dual projected-gradient approximation to GEM’s quadratic projection. By constraining non-interference solely within the adapter parameters, I-GEM preserves GEM-like stability with orders-of-magnitude lower mean projection overhead. On a 3-task AG News split with induced domain drift, using GPT-2 (355M) and LoRA ( r=8 ), I-GEM matches GEM’s average accuracy (within \sim!0.04 pts) and outperforms A-GEM by \sim!1.4 pts. Crucially, it reduces projection time vs.\ GEM by a factor of \sim!10^3 . These results suggest that applying GEM constraints in the LoRA subspace is a practical pathway for continual learning at the LLM scale.
zh
[AI-56] he Rise of Agent ic Testing: Multi-Agent Systems for Robust Software Quality Assurance
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前基于人工智能的测试生成方法中存在的静态、单次输出问题,即生成的测试用例常因缺乏执行反馈而出现无效、冗余或不可执行的情况。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个代理驱动的多模态测试框架(agentic multi-model testing framework),该框架通过闭环自纠正机制,由测试生成代理(Test Generation Agent)、执行与分析代理(Execution and Analysis Agent)以及审查与优化代理(Review and Optimization Agent)协同工作,实现测试的生成、执行、分析与迭代优化直至收敛。该系统利用沙箱执行环境、详细的失败报告以及对失败测试的再生或修补策略,结合CI/CD流水线中覆盖率和执行结果的强化信号,显著提升测试质量与代码覆盖率,从而推动软件测试向自主化、持续学习的质量保障生态系统演进。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02454
作者: Saba Naqvi,Mohammad Baqar,Nawaz Ali Mohammad
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 11 Pages
Abstract:Software testing has progressed toward intelligent automation, yet current AI-based test generators still suffer from static, single-shot outputs that frequently produce invalid, redundant, or non-executable tests due to the lack of execution aware feedback. This paper introduces an agentic multi-model testing framework a closed-loop, self-correcting system in which a Test Generation Agent, an Execution and Analysis Agent, and a Review and Optimization Agent collaboratively generate, execute, analyze, and refine tests until convergence. By using sandboxed execution, detailed failure reporting, and iterative regeneration or patching of failing tests, the framework autonomously improves test quality and expands coverage. Integrated into a CI/CD-compatible pipeline, it leverages reinforcement signals from coverage metrics and execution outcomes to guide refinement. Empirical evaluations on microservice based applications show up to a 60% reduction in invalid tests, 30% coverage improvement, and significantly reduced human effort compared to single-model baselines demonstrating that multi-agent, feedback-driven loops can evolve software testing into an autonomous, continuously learning quality assurance ecosystem for self-healing, high-reliability codebases.
zh
[AI-57] mHC-GNN: Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections for Graph Neural Networks
【速读】:该论文旨在解决图神经网络(Graph Neural Networks, GNNs)在深度架构中面临的过平滑(over-smoothing)问题以及表达能力受限于1-Weisfeiler-Leman(1-WL)测试的瓶颈。其解决方案的关键在于引入曼ifold约束的超连接机制(Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections, mHC),通过将节点表示扩展到 $ n $ 个并行流,并利用Sinkhorn-Knopp归一化将流混合矩阵约束在Birkhoff多面体(Birkhoff polytope)上,从而实现更稳定的特征传播与更强的图区分能力。理论分析表明,mHC-GNN 的过平滑速率从标准 GNN 的 $ (1-\gamma)^L $ 降低至 $ (1-\gamma)^L/n $,且能超越 1-WL 测试的表达限制,实验验证了其在多种数据集和深度场景下的显著性能提升,尤其在极端深度(如 128 层)下仍保持高精度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02451
作者: Subhankar Mishra
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) suffer from over-smoothing in deep architectures and expressiveness bounded by the 1-Weisfeiler-Leman (1-WL) test. We adapt Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections (\mhc)~\citepxie2025mhc, recently proposed for Transformers, to graph neural networks. Our method, mHC-GNN, expands node representations across n parallel streams and constrains stream-mixing matrices to the Birkhoff polytope via Sinkhorn-Knopp normalization. We prove that mHC-GNN exhibits exponentially slower over-smoothing (rate (1-\gamma)^L/n vs.\ (1-\gamma)^L ) and can distinguish graphs beyond 1-WL. Experiments on 10 datasets with 4 GNN architectures show consistent improvements. Depth experiments from 2 to 128 layers reveal that standard GNNs collapse to near-random performance beyond 16 layers, while mHC-GNN maintains over 74% accuracy even at 128 layers, with improvements exceeding 50 percentage points at extreme depths. Ablations confirm that the manifold constraint is essential: removing it causes up to 82% performance degradation. Code is available at \hrefthis https URLthis https URL
zh
[AI-58] VocalBridge: Latent Diffusion-Bridge Purification for Defeating Perturbation-Based Voiceprint Defenses
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前基于扰动的语音保护机制在面对自适应净化(purification)攻击时脆弱性不足的问题,即现有防御方法虽能嵌入扰动以隐藏说话人身份并保持语音可懂度,但易被先进净化技术去除扰动、恢复原始声学特征并生成可克隆语音。其解决方案的关键在于提出Diffusion-Bridge(VocalBridge)净化框架,该框架在EnCodec潜在空间中学习从受扰语音到干净语音的隐式映射,采用时间条件的一维U-Net结构结合余弦噪声调度,实现无需语音转录(transcript-free)的高效净化,同时保留说话人判别性结构;进一步引入Whisper引导的音素变体,在不依赖真实转录的前提下提供轻量级时序指导,从而显著提升对语音克隆和说话人验证攻击(SVA)的鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02444
作者: Maryam Abbasihafshejani,AHM Nazmus Sakib,Murtuza Jadliwala
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS)
备注:
Abstract:The rapid advancement of speech synthesis technologies, including text-to-speech (TTS) and voice conversion (VC), has intensified security and privacy concerns related to voice cloning. Recent defenses attempt to prevent unauthorized cloning by embedding protective perturbations into speech to obscure speaker identity while maintaining intelligibility. However, adversaries can apply advanced purification techniques to remove these perturbations, recover authentic acoustic characteristics, and regenerate cloneable voices. Despite the growing realism of such attacks, the robustness of existing defenses under adaptive purification remains insufficiently studied. Most existing purification methods are designed to counter adversarial noise in automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems rather than speaker verification or voice cloning pipelines. As a result, they fail to suppress the fine-grained acoustic cues that define speaker identity and are often ineffective against speaker verification attacks (SVA). To address these limitations, we propose Diffusion-Bridge (VocalBridge), a purification framework that learns a latent mapping from perturbed to clean speech in the EnCodec latent space. Using a time-conditioned 1D U-Net with a cosine noise schedule, the model enables efficient, transcript-free purification while preserving speaker-discriminative structure. We further introduce a Whisper-guided phoneme variant that incorporates lightweight temporal guidance without requiring ground-truth transcripts. Experimental results show that our approach consistently outperforms existing purification methods in recovering cloneable voices from protected speech. Our findings demonstrate the fragility of current perturbation-based defenses and highlight the need for more robust protection mechanisms against evolving voice-cloning and speaker verification threats. Subjects: Sound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02444 [cs.SD] (or arXiv:2601.02444v1 [cs.SD] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02444 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-59] Focus on What Matters: Fisher-Guided Adaptive Multimodal Fusion for Vulnerability Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决软件漏洞检测中多模态融合存在的冗余与噪声干扰问题,即传统方法在融合自然代码序列(Natural Code Sequence, NCS)与代码属性图(Code Property Graph, CPG)表示时,常假设增加模态必然带来额外信息,但实际中两者可能存在冗余,且图模态质量波动会削弱主模态的判别能力。解决方案的关键在于提出TaCCS-DFA框架,其核心创新是引入Fisher信息作为几何度量,用于识别对分类决策敏感的特征方向,并在线估计低秩主Fisher子空间,限制跨模态注意力仅作用于任务敏感方向,从而提取互补于序列模态的结构特征;同时设计自适应门控机制动态调整每个样本中图模态的贡献,抑制噪声传播。理论分析表明,在各向同性扰动假设下,该机制可获得比传统全谱注意力更紧的风险上界,实验验证其在BigVul、Devign和ReVeal数据集上均优于现有方法,尤其在高度不平衡的BigVul上以CodeT5为骨干模型达到87.80% F1分数,较强基线提升6.3个百分点,且保持低校准误差与计算开销。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02438
作者: Yun Bian,Yi Chen,HaiQuan Wang,ShiHao Li,Zhe Cui
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR)
备注:
Abstract:Software vulnerability detection is a critical task for securing software systems and can be formulated as a binary classification problem: given a code snippet, determine whether it contains a vulnerability. Existing multimodal approaches typically fuse Natural Code Sequence (NCS) representations from pretrained language models with Code Property Graph (CPG) representations from graph neural networks, often under the implicit assumption that adding a modality necessarily yields extra information. In practice, sequence and graph representations can be redundant, and fluctuations in the quality of the graph modality can dilute the discriminative signal of the dominant modality. To address this, we propose TaCCS-DFA, a framework that introduces Fisher information as a geometric measure of how sensitive feature directions are to the classification decision, enabling task-oriented complementary fusion. TaCCS-DFA online estimates a low-rank principal Fisher subspace and restricts cross-modal attention to task-sensitive directions, thereby retrieving structural features from CPG that complement the sequence modality; meanwhile, an adaptive gating mechanism dynamically adjusts the contribution of the graph modality for each sample to suppress noise propagation. Our analysis shows that, under an isotropic perturbation assumption, the proposed mechanism admits a tighter risk bound than conventional full-spectrum attention. Experiments on BigVul, Devign, and ReVeal show that TaCCS-DFA achieves strong performance across multiple backbones. With CodeT5 as the backbone, TaCCS-DFA reaches an F1 score of 87.80% on the highly imbalanced BigVul dataset, improving over a strong baseline Vul-LMGNNs by 6.3 percentage points while maintaining low calibration error and computational overhead.
zh
[AI-60] WebCoderBench: Benchmarking Web Application Generation with Comprehensive and Interpretable Evaluation Metrics
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在生成Web应用(web apps)时缺乏真实用户需求驱动、评估指标难以泛化且结果不可解释的挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出首个基于真实用户需求收集、具备通用性和可解释性的基准测试平台WebCoderBench,该平台包含1,572条涵盖多种模态和表达风格的真实用户需求,并提供24个细粒度评估指标,从9个维度结合规则基与“大语言模型作为裁判”(LLM-as-a-judge)范式实现全自动、客观的评估;同时采用人类偏好对齐的权重分配机制,使整体评分具有可解释性,从而为LLM开发者提供针对性优化方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02430
作者: Chenxu Liu,Yingjie Fu,Wei Yang,Ying Zhang,Tao Xie
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Web applications (web apps) have become a key arena for large language models (LLMs) to demonstrate their code generation capabilities and commercial potential. However, building a benchmark for LLM-generated web apps remains challenging due to the need for real-world user requirements, generalizable evaluation metrics without relying on ground-truth implementations or test cases, and interpretable evaluation results. To address these challenges, we introduce WebCoderBench, the first real-world-collected, generalizable, and interpretable benchmark for web app generation. WebCoderBench comprises 1,572 real user requirements, covering diverse modalities and expression styles that reflect realistic user intentions. WebCoderBench provides 24 fine-grained evaluation metrics across 9 perspectives, combining rule-based and LLM-as-a-judge paradigm for fully automated, objective, and general evaluation. Moreover, WebCoderBench adopts human-preference-aligned weights over metrics to yield interpretable overall scores. Experiments across 12 representative LLMs and 2 LLM-based agents show that there exists no dominant model across all evaluation metrics, offering an opportunity for LLM developers to optimize their models in a targeted manner for a more powerful version.
zh
[AI-61] A Dynamic Retrieval-Augmented Generation System with Selective Memory and Remembrance
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)系统中静态向量索引导致的记忆效率低下与资源浪费问题,即无法根据使用频率动态调整记忆内容的保留或遗忘。其解决方案的核心是提出自适应RAG记忆(Adaptive RAG Memory, ARM),通过引入受认知固化(cognitive consolidation)和遗忘机制启发的动态记忆子结构,实现选择性记忆保留与衰减:高频检索项被巩固并防止遗忘,低频项则逐步衰减。该设计在保持高检索精度(如NDCG@5 ≈ 0.940)的同时显著提升参数效率(仅需约22M嵌入层参数),且无需重新训练生成器即可实现可解释的记忆演化与自我调节的内存增长,从而在质量、延迟与内存效率之间提供实用的权衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02428
作者: Okan Bursa
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 6 Pages, 2 figures
Abstract:We introduce \emphAdaptive RAG Memory (ARM), a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) framework that replaces a static vector index with a \emphdynamic memory substrate governed by selective remembrance and decay. Frequently retrieved items are consolidated and protected from forgetting, while rarely used items gradually decay, inspired by cognitive consolidation and forgetting principles. On a lightweight retrieval benchmark, ARM reaches near state-of-the-art performance (e.g., NDCG@5 \approx 0.940, Recall@5 =1.000 ) with only \sim 22M parameters in the embedding layer, achieving the best efficiency among ultra-efficient models ( 25M parameters). In addition, we compare static vs. dynamic RAG combinations across Llama 3.1 and GPT-4o. Llama 3.1 with static RAG achieves the highest key-term coverage (67.2%) at moderate latency, while GPT-4o with a dynamic selective retrieval policy attains the fastest responses (8.2s on average) with competitive coverage (58.7%). We further present an engineering optimization of the DynamicRAG implementation, making embedding weights configurable, adjustable at runtime, and robust to invalid settings. ARM yields competitive accuracy, self-regularizing memory growth, and interpretable retention dynamics without retraining the generator\colorblack and provides practical trade-off between quality, latency and memory efficiency for production and research RAG system. Comments: 6 Pages, 2 figures Subjects: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02428 [cs.IR] (or arXiv:2601.02428v1 [cs.IR] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02428 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite
zh
[AI-62] Socially-Aware Recommender Systems Mitigate Opinion Clusterization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决推荐系统中因用户-创作者反馈循环导致的过滤气泡(filter bubble)和意见极化(opinion polarization)问题。其解决方案的关键在于设计一种社会网络感知的推荐系统,显式建模用户与其社交网络之间的互动关系,并利用用户自身社交网络的拓扑结构来主动促进内容多样性。通过将社交影响纳入推荐机制,该方法在保持个性化推荐效果的同时,有效缓解了由算法推荐主导的意见集群化现象,从而实现对过滤气泡效应的调控。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02412
作者: Lukas Schüepp,Carmen Amo Alonso,Florian Dörfler,Giulia De Pasquale
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Recommender systems shape online interactions by matching users with creators content to maximize engagement. Creators, in turn, adapt their content to align with users preferences and enhance their popularity. At the same time, users preferences evolve under the influence of both suggested content from the recommender system and content shared within their social circles. This feedback loop generates a complex interplay between users, creators, and recommender algorithms, which is the key cause of filter bubbles and opinion polarization. We develop a social network-aware recommender system that explicitly accounts for this user-creators feedback interaction and strategically exploits the topology of the user’s own social network to promote diversification. Our approach highlights how accounting for and exploiting user’s social network in the recommender system design is crucial to mediate filter bubble effects while balancing content diversity with personalization. Provably, opinion clusterization is positively correlated with the influence of recommended content on user opinions. Ultimately, the proposed approach shows the power of socially-aware recommender systems in combating opinion polarization and clusterization phenomena.
zh
[AI-63] SpikySpace: A Spiking State Space Model for Energy-Efficient Time Series Forecasting
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有基于脉冲神经网络(Spiking Neural Networks, SNN)的时间序列预测模型在效率上未能充分发挥其优势的问题,尤其是在引入复杂注意力机制(如Transformer块)后导致计算冗余和能效下降。核心挑战在于如何在保持现代序列建模能力的同时,实现真正的低功耗、低延迟推理,以适配边缘设备的严苛资源约束。解决方案的关键在于提出SpikySpace——一种全脉冲状态空间模型(Spiking State-Space Model, SSM),通过选择性扫描(selective scanning)将注意力机制中的二次复杂度降低为线性时间,并用稀疏脉冲事件驱动替代密集更新,从而避免乘法运算;同时设计了适用于类脑芯片的简化SiLU和Softplus激活函数近似,进一步优化硬件友好性。实验表明,在匹配设置下,SpikySpace相比iTransformer和iSpikformer分别降低98.73%和96.24%的能耗,且在标准数据集上保持竞争力的预测精度,首次实现了高效脉冲状态空间建模与现代序列学习能力的融合。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02411
作者: Kaiwen Tang,Jiaqi Zheng,Yuze Jin,Yupeng Qiu,Guangda Sun,Zhanglu Yan,Weng-Fai Wong
机构: 未知
类目: Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 13 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:Time-series forecasting often operates under tight power and latency budgets in fields like traffic management, industrial condition monitoring, and on-device sensing. These applications frequently require near real-time responses and low energy consumption on edge devices. Spiking neural networks (SNNs) offer event-driven computation and ultra-low power by exploiting temporal sparsity and multiplication-free computation. Yet existing SNN-based time-series forecasters often inherit complex transformer blocks, thereby losing much of the efficiency benefit. To solve the problem, we propose SpikySpace, a spiking state-space model (SSM) that reduces the quadratic cost in the attention block to linear time via selective scanning. Further, we replace dense SSM updates with sparse spike trains and execute selective scans only on spike events, thereby avoiding dense multiplications while preserving the SSM’s structured memory. Because complex operations such as exponentials and divisions are costly on neuromorphic chips, we introduce simplified approximations of SiLU and Softplus to enable a neuromorphic-friendly model architecture. In matched settings, SpikySpace reduces estimated energy consumption by 98.73% and 96.24% compared to two state-of-the-art transformer based approaches, namely iTransformer and iSpikformer, respectively. In standard time series forecasting datasets, SpikySpace delivers competitive accuracy while substantially reducing energy cost and memory traffic. As the first full spiking state-space model, SpikySpace bridges neuromorphic efficiency with modern sequence modeling, marking a practical and scalable path toward efficient time series forecasting systems.
zh
[AI-64] he Vibe-Check Protocol: Quantifying Cognitive Offloading in AI Programming
【速读】:该论文旨在解决“Vibe Coding”(一种通过自然语言表达高层次意图并由AI代理完成编码实现的教学范式)在软件工程教育中的有效性问题,特别是其对学习者技能保留与深层概念理解的影响。现有实证证据表明,尽管该方法可能提升教学效率,但存在潜在的技能退化和浅层认知风险。论文提出的关键解决方案是构建一个名为“Vibe-Check Protocol (VCP)”的系统性基准测试框架,其核心在于引入三个量化指标:冷启动重构能力(M_CSR)用于评估技能衰减;幻觉陷阱检测能力(M_HT)基于信号检测理论衡量错误识别水平;以及可解释性差距(E_gap)用于量化代码复杂度与概念理解之间的偏差。通过这些指标的可控对比分析,VCP为教育者提供了科学依据,以界定Vibe Coding在何种情境下促进真实掌握,在何种情境下导致隐性技术债务和表面能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02410
作者: Aizierjiang Aiersilan
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY); Graphics (cs.GR)
备注:
Abstract:The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into software engineering education has driven the emergence of ``Vibe Coding,‘’ a paradigm where developers articulate high-level intent through natural language and delegate implementation to AI agents. While proponents argue this approach modernizes pedagogy by emphasizing conceptual design over syntactic memorization, accumulating empirical evidence raises concerns regarding skill retention and deep conceptual understanding. This paper proposes a theoretical framework to investigate the research question: \textitIs Vibe Coding a better way to learn software engineering? We posit a divergence in student outcomes between those leveraging AI for acceleration versus those using it for cognitive offloading. To evaluate these educational trade-offs, we propose the \textbfVibe-Check Protocol (VCP), a systematic benchmarking framework incorporating three quantitative metrics: the \textitCold Start Refactor ( M_CSR ) for modeling skill decay; \textitHallucination Trap Detection ( M_HT ) based on signal detection theory to evaluate error identification; and the \textitExplainability Gap ( E_gap ) for quantifying the divergence between code complexity and conceptual comprehension. Through controlled comparisons, VCP aims to provide a quantitative basis for educators to determine the optimal pedagogical boundary: identifying contexts where Vibe Coding fosters genuine mastery and contexts where it introduces hidden technical debt and superficial competence.
zh
[AI-65] ProSoftArena: Benchmarking Hierarchical Capabilities of Multimodal Agents in Professional Software Environments
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前多模态智能体(Multimodal Agents)在专业软件环境中的评估缺乏系统性基准的问题。现有基准主要局限于浏览器和基础桌面应用,无法反映真实科学与工业场景中广泛存在的复杂专业软件工作流。解决方案的关键在于构建ProSoftArena——一个专为专业软件环境设计的基准平台,其核心包括:(1) 建立首个面向代理使用专业软件的能力层级体系;(2) 构建涵盖6个学科、13款核心专业软件的436个真实工作任务数据集;(3) 提出基于实际计算机执行的评估框架,并引入人机协同(human-in-the-loop)评价机制以确保评估的可靠性与可复现性。实验表明,即使是最先进的代理在L2级别任务中成功率也仅为24.4%,且完全无法完成L3多软件协作任务,揭示了当前代理在专业软件场景下的显著局限,为未来更高效的设计原则提供了重要依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02399
作者: Jiaxin Ai,Yukang Feng,Fanrui Zhang,Jianwen Sun,Zizhen Li,Chuanhao Li,Yifan Chang,Wenxiao Wu,Ruoxi Wang,Mingliang Zhai,Kaipeng Zhang
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Multimodal agents are making rapid progress on general computer-use tasks, yet existing benchmarks remain largely confined to browsers and basic desktop applications, falling short in professional software workflows that dominate real-world scientific and industrial practice. To close this gap, we introduce ProSoftArena, a benchmark and platform specifically for evaluating multimodal agents in professional software environments. We establish the first capability hierarchy tailored to agent use of professional software and construct a benchmark of 436 realistic work and research tasks spanning 6 disciplines and 13 core professional applications. To ensure reliable and reproducible assessment, we build an executable real-computer environment with an execution-based evaluation framework and uniquely incorporate a human-in-the-loop evaluation paradigm. Extensive experiments show that even the best-performing agent attains only a 24.4% success rate on L2 tasks and completely fails on L3 multi-software workflow. In-depth analysis further provides valuable insights for addressing current agent limitations and more effective design principles, paving the way to build more capable agents in professional software settings. This project is available at: this https URL.
zh
[AI-66] AI-Native Integrated Sensing and Communications for Self-Organizing Wireless Networks: Architectures Learning Paradigms and System-Level Design
【速读】:该论文旨在解决未来无线网络中日益增长的复杂性与动态性所带来的自组织能力不足问题,即如何在大规模、异构且高度动态的下一代无线系统中实现自主资源管理、拓扑优化和服务调度。其核心挑战在于将感知(sensing)与通信(communication)深度融合,并通过人工智能(AI)驱动的方法赋予网络自我感知、自我决策和自我适应的能力。解决方案的关键在于提出一个统一的分类体系,涵盖ISAC信号模型与感知模态、从感知感知无线电数据中抽象网络状态、基于学习的自组织机制(如资源分配、拓扑控制和移动性管理),以及跨层架构集成感知、通信与网络智能;同时引入深度强化学习、图神经网络、多智能体协同和联邦智能等新兴学习范式,以应对不确定性、移动性和部分可观测性的场景,从而构建可部署、可信且可扩展的AI原生ISAC自组织无线网络,为6G及以后的网络演进提供理论支撑和技术路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02398
作者: S. Zhang,M. Feizarefi,A. F. Mirzaei
机构: 未知
类目: Networking and Internet Architecture (cs.NI); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC) is emerging as a foundational paradigm for next-generation wireless networks, enabling communication infrastructures to simultaneously support data transmission and environment sensing. By tightly coupling radio sensing with communication functions, ISAC unlocks new capabilities for situational awareness, localization, tracking, and network adaptation. At the same time, the increasing scale, heterogeneity, and dynamics of future wireless systems demand self-organizing network intelligence capable of autonomously managing resources, topology, and services. Artificial intelligence (AI), particularly learning-driven and data-centric methods, has become a key enabler for realizing this vision. This survey provides a comprehensive and system-level review of AI-native ISAC-enabled self-organizing wireless networks. We develop a unified taxonomy that spans: (i) ISAC signal models and sensing modalities, (ii) network state abstraction and perception from sensing-aware radio data, (iii) learning-driven self-organization mechanisms for resource allocation, topology control, and mobility management, and (iv) cross-layer architectures integrating sensing, communication, and network intelligence. We further examine emerging learning paradigms, including deep reinforcement learning, graph-based learning, multi-agent coordination, and federated intelligence that enable autonomous adaptation under uncertainty, mobility, and partial observability. Practical considerations such as sensing-communication trade-offs, scalability, latency, reliability, and security are discussed alongside representative evaluation methodologies and performance metrics. Finally, we identify key open challenges and future research directions toward deployable, trustworthy, and scalable AI-native ISAC systems for 6G and beyond.
zh
[AI-67] ree of Preferences for Diversified Recommendation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决推荐系统中因数据偏差导致的用户偏好捕捉不全问题,从而影响推荐结果的多样性。现有方法主要依赖观察到的用户反馈推断偏好,但受限于数据偏差,部分潜在或未被充分探索的偏好可能被掩盖或未显现,进而导致推荐多样性不足。解决方案的关键在于引入大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的世界知识能力,通过构建“偏好树”(Tree of Preferences, ToP)结构,从粗粒度到细粒度系统性地推理用户行为背后的动机,从而挖掘出被忽视的偏好;进一步采用数据驱动的方法识别匹配这些偏好的候选物品,并生成反映未探索偏好的合成交互数据,用于训练具备多样化推荐能力的通用推荐模型,同时通过动态选择关键用户提升优化效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02386
作者: Hanyang Yuan,Ning Tang,Tongya Zheng,Jiarong Xu,Xintong Hu,Renhong Huang,Shunyu Liu,Jiacong Hu,Jiawei Chen,Mingli Song
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Diversified recommendation has attracted increasing attention from both researchers and practitioners, which can effectively address the homogeneity of recommended items. Existing approaches predominantly aim to infer the diversity of user preferences from observed user feedback. Nonetheless, due to inherent data biases, the observed data may not fully reflect user interests, where underexplored preferences can be overwhelmed or remain unmanifested. Failing to capture these preferences can lead to suboptimal diversity in recommendations. To fill this gap, this work aims to study diversified recommendation from a data-bias perspective. Inspired by the outstanding performance of large language models (LLMs) in zero-shot inference leveraging world knowledge, we propose a novel approach that utilizes LLMs’ expertise to uncover underexplored user preferences from observed behavior, ultimately providing diverse and relevant recommendations. To achieve this, we first introduce Tree of Preferences (ToP), an innovative structure constructed to model user preferences from coarse to fine. ToP enables LLMs to systematically reason over the user’s rationale behind their behavior, thereby uncovering their underexplored preferences. To guide diversified recommendations using uncovered preferences, we adopt a data-centric approach, identifying candidate items that match user preferences and generating synthetic interactions that reflect underexplored preferences. These interactions are integrated to train a general recommender for diversification. Moreover, we scale up overall efficiency by dynamically selecting influential users during optimization. Extensive evaluations of both diversity and relevance show that our approach outperforms existing methods in most cases and achieves near-optimal performance in others, with reasonable inference latency.
zh
[AI-68] Base Station Deployment under EMF constrain by Deep Reinforcement learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决5G网络扩展与6G技术演进中,因密集部署、毫米波通信和动态波束赋形等特性带来的大规模网络仿真难题,尤其是如何高效评估覆盖性能与射频电磁场(RF-EMF)暴露水平,并实现基站(BS)的最优部署。其核心挑战在于传统射线追踪仿真计算成本高、难以支持实时设计决策,且现有方法无法在满足覆盖与安全约束下进行动态优化。解决方案的关键在于提出一种条件生成对抗网络(cGAN),能够从网络拓扑图像中联合预测位置相关的接收信号强度(RSS)和EMF暴露水平;进一步结合深度Q网络(DQN)框架,利用训练好的cGAN模型进行序贯决策,从而在覆盖与暴露双重约束下学习出有效的BS部署策略,显著将推理与部署时间从数小时缩短至秒级,具备实时适应动态场景的能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02385
作者: Mohammed Mallik,Guillaume Villemaud
机构: 未知
类目: Networking and Internet Architecture (cs.NI); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:As 5G networks rapidly expand and 6G technologies emerge, characterized by dense deployments, millimeter-wave communications, and dynamic beamforming, the need for scalable simulation tools becomes increasingly critical. These tools must support efficient evaluation of key performance metrics such as coverage and radio-frequency electromagnetic field (RF-EMF) exposure, inform network design decisions, and ensure compliance with safety regulations. Moreover, base station (BS) placement is a crucial task in the network design, where satisfying coverage requirements is essential. To address these, based on our previous work, we first propose a conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN) that predicts location specific received signal strength (RSS), and EMF exposure simultaneously from the network topology, as images. As a network designing application, we propose a Deep Q Network (DQN) framework, using the trained cGAN, for optimal base station (BS) deployment in the network. Compared to conventional ray tracing simulations, the proposed cGAN reduces inference and deployment time from several hours to seconds. Unlike a standalone cGAN, which provides static performance maps, the proposed GAN-DQN framework enables sequential decision making under coverage and exposure constraints, learning effective deployment strategies that directly solve the BS placement problem. Thus making it well suited for real time design and adaptation in dynamic scenarios in order to satisfy pre defined network specific heterogeneous performance goals.
zh
[AI-69] How to Discover Knowledge for FutureG: Contextual RAG and LLM Prompting for O-RAN
【速读】:该论文旨在解决5G/6G网络中开放无线接入网(Open Radio Access Network, O-RAN)因规范和接口快速演进导致的研究与实践者难以高效获取准确信息的问题。传统手动查阅文档方式效率低且易出错,阻碍了系统设计、集成与部署。解决方案的关键在于引入情境感知的检索增强生成(Contextual Retrieval-Augmented Generation, Contextual RAG),通过候选答案选项引导文档检索,并利用块级上下文信息提升大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)性能,从而实现更精准、上下文相关的文档召回,显著改善LLM在查询语义不充分时的推理准确性,且无需对LLM进行微调即可适应动态知识更新,兼顾效率与可持续性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02382
作者: Nathan Conger,Nathan Scollar,Kemal Davaslioglu,Yalin E. Sagduyu,Sastry Kompella
机构: 未知
类目: Networking and Internet Architecture (cs.NI); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:We present a retrieval-augmented question answering framework for 5G/6G networks, where the Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) has become central to disaggregated, virtualized, and AI-driven wireless systems. While O-RAN enables multi-vendor interoperability and cloud-native deployments, its fast-changing specifications and interfaces pose major challenges for researchers and practitioners. Manual navigation of these complex documents is labor-intensive and error-prone, slowing system design, integration, and deployment. To address this challenge, we adopt Contextual Retrieval-Augmented Generation (Contextual RAG), a strategy in which candidate answer choices guide document retrieval and chunk-specific context to improve large language model (LLM) performance. This improvement over traditional RAG achieves more targeted and context-aware retrieval, which improves the relevance of documents passed to the LLM, particularly when the query alone lacks sufficient context for accurate grounding. Our framework is designed for dynamic domains where data evolves rapidly and models must be continuously updated or redeployed, all without requiring LLM fine-tuning. We evaluate this framework using the ORANBenchmark-13K dataset, and compare three LLMs, namely, Llama3.2, Qwen2.5-7B, and Qwen3.0-4B, across both Direct Question Answering (Direct QA) and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting strategies. We show that Contextual RAG consistently improves accuracy over standard RAG and base prompting, while maintaining competitive runtime and CO2 emissions. These results highlight the potential of Contextual RAG to serve as a scalable and effective solution for domain-specific QA in ORAN and broader 5G/6G environments, enabling more accurate interpretation of evolving standards while preserving efficiency and sustainability.
zh
[AI-70] he Refutability Gap: Challenges in Validating Reasoning by Large Language Models
【速读】:该论文试图解决当前大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在科学推理研究中缺乏科学严谨性的问题,特别是其宣称具备“生成新科学”和“人类级通用智能”能力的主张未满足波普尔提出的可证伪性(falsifiability)原则。论文指出当前研究存在多个方法论缺陷:训练数据不透明导致发现新颖性难以验证、模型持续更新造成结果不可复现、缺失人类交互记录掩盖了科学发现的真实来源,以及缺乏反事实和失败尝试的数据引发选择偏差,从而夸大LLM的能力。解决方案的关键在于建立一套针对LLM推理研究的科学透明度与可复现性指南,以保障科研诚信,并推动关于公平数据使用的社会讨论。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02380
作者: Elchanan Mossel
机构: 未知
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: he authors explicitly reserve all rights in this work. No permission is granted for the reproduction, storage, or use of this document for the purpose of training artificial intelligence systems or for text and data mining (TDM), including but not limited to the generation of embeddings, summaries, or synthetic derivatives
Abstract:Recent reports claim that Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved the ability to derive new science and exhibit human-level general intelligence. We argue that such claims are not rigorous scientific claims, as they do not satisfy Popper’s refutability principle (often termed falsifiability), which requires that scientific statements be capable of being disproven. We identify several methodological pitfalls in current AI research on reasoning, including the inability to verify the novelty of findings due to opaque and non-searchable training data, the lack of reproducibility caused by continuous model updates, and the omission of human-interaction transcripts, which obscures the true source of scientific discovery. Additionally, the absence of counterfactuals and data on failed attempts creates a selection bias that may exaggerate LLM capabilities. To address these challenges, we propose guidelines for scientific transparency and reproducibility for research on reasoning by LLMs. Establishing such guidelines is crucial for both scientific integrity and the ongoing societal debates regarding fair data usage.
zh
[AI-71] Movement Primitives in Robotics: A Comprehensive Survey
【速读】:该论文旨在解决机器人控制中如何有效表示和生成复杂运动轨迹的问题,特别是在从人类示范中学习动作模式时面临的挑战。其解决方案的关键在于系统性地梳理和总结各类运动基元(movement primitives)框架,这些框架能够将复杂的机器人控制轨迹建模为可复用的、具有物理意义或概率特性的基本运动单元,如基于弹簧-阻尼系统的解析特性、多示范数据的概率耦合机制以及高维系统中的神经网络实现方式,从而提升机器人在任务执行中的灵活性、适应性和可扩展性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02379
作者: Nolan B. Gutierrez,William J. Beksi
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 105 pages, 3 figures, and 6 tables
Abstract:Biological systems exhibit a continuous stream of movements, consisting of sequential segments, that allow them to perform complex tasks in a creative and versatile fashion. This observation has led researchers towards identifying elementary building blocks of motion known as movement primitives, which are well-suited for generating motor commands in autonomous systems, such as robots. In this survey, we provide an encyclopedic overview of movement primitive approaches and applications in chronological order. Concretely, we present movement primitive frameworks as a way of representing robotic control trajectories acquired through human demonstrations. Within the area of robotics, movement primitives can encode basic motions at the trajectory level, such as how a robot would grasp a cup or the sequence of motions necessary to toss a ball. Furthermore, movement primitives have been developed with the desirable analytical properties of a spring-damper system, probabilistic coupling of multiple demonstrations, using neural networks in high-dimensional systems, and more, to address difficult challenges in robotics. Although movement primitives have widespread application to a variety of fields, the goal of this survey is to inform practitioners on the use of these frameworks in the context of robotics. Specifically, we aim to (i) present a systematic review of major movement primitive frameworks and examine their strengths and weaknesses; (ii) highlight applications that have successfully made use of movement primitives; and (iii) examine open questions and discuss practical challenges when applying movement primitives in robotics.
zh
[AI-72] LeafTutor: An AI Agent for Programming Assignment Tutoring
【速读】:该论文旨在解决STEM(科学、技术、工程和数学)相关学位项目中因学生大规模入学而导致的辅导资源短缺问题,尤其是在高校面临合格教师和助教(Teaching Assistants, TAs)不足的情况下。解决方案的关键在于开发了一个基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的AI辅导代理LeafTutor,该系统能够为学生提供结构化的分步编程指导,其效果在真实编程作业评估中已证明可媲美人类导师,从而展示了LLM驱动的个性化学习支持在STEM教育中的潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02375
作者: Madison Bochard,Tim Conser,Alyssa Duran,Lazaro Martull,Pu Tian,Yalong Wu
机构: 未知
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Software Engineering (cs.SE)
备注:
Abstract:High enrollment in STEM-related degree programs has created increasing demand for scalable tutoring support, as universities experience a shortage of qualified instructors and teaching assistants (TAs). To address this challenge, LeafTutor, an AI tutoring agent powered by large language models (LLMs), was developed to provide step-by-step guidance for students. LeafTutor was evaluated through real programming assignments. The results indicate that the system can deliver step-by-step programming guidance comparable to human tutors. This work demonstrates the potential of LLM-driven tutoring solutions to enhance and personalize learning in STEM education. If any reader is interested in collaboration with our team to improve or test LeafTutor, please contact Pu Tian (this http URL@stockton.edu) or Yalong Wu (wuy@uhcl.edu).
zh
[AI-73] Permission Manifests for Web Agents
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)驱动的网络代理(web agents)在与网站交互时缺乏明确规范和治理机制的问题。传统爬虫仅遵循简单协议,而现代代理能复杂导航、结构化提取信息并完成端到端任务,但现有治理手段无法有效区分合规与非合规行为,导致网站所有者只能采用全盘封禁或CAPTCHA等粗粒度策略,损害了自动化效率、电商便利性和无障碍工具等有益应用。解决方案的关键在于提出一种轻量级声明文件(manifest),类似robots.txt格式,允许网站通过一个简单的JSON文件明确指定哪些交互行为被允许,并辅以API引用增强语义清晰度。该框架实现低摩擦协作:网站只需配置声明,代理即可自动解析并遵守规则,从而将监管焦点从“禁止所有代理”转向“识别并阻止违规代理”,结合如AIPref等数据使用倡议,构建尊重站点偏好且支持有益代理交互的合规体系。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02371
作者: Samuele Marro,Alan Chan,Xinxing Ren,Lewis Hammond,Jesse Wright,Gurjyot Wanga,Tiziano Piccardi,Nuno Campos,Tobin South,Jialin Yu,Alex Pentland,Philip Torr,Jiaxin Pei
机构: 未知
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA); Networking and Internet Architecture (cs.NI)
备注: Authored by the Lightweight Agent Standards Working Group this https URL
Abstract:The rise of Large Language Model (LLM)-based web agents represents a significant shift in automated interactions with the web. Unlike traditional crawlers that follow simple conventions, such as this http URL, modern agents engage with websites in sophisticated ways: navigating complex interfaces, extracting structured information, and completing end-to-end tasks. Existing governance mechanisms were not designed for these capabilities. Without a way to specify what interactions are and are not allowed, website owners increasingly rely on blanket blocking and CAPTCHAs, which undermine beneficial applications such as efficient automation, convenient use of e-commerce services, and accessibility tools. We introduce this http URL, a this http URL-style lightweight manifest where websites specify allowed interactions, complemented by API references where available. This framework provides a low-friction coordination mechanism: website owners only need to write a simple JSON file, while agents can easily parse and automatically implement the manifest’s provisions. Website owners can then focus on blocking non-compliant agents, rather than agents as a whole. By extending the spirit of this http URL to the era of LLM-mediated interaction, and complementing data use initiatives such as AIPref, the manifest establishes a compliance framework that enables beneficial agent interactions while respecting site owners’ preferences.
zh
[AI-74] Distillation-based Scenario-Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts for the Matching Stage of Multi-scenario Recommendation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多场景推荐中因独立双塔架构导致的盲优化问题以及头部场景参数主导所引发的分布偏差问题,从而提升低频、数据稀疏场景下的匹配质量。其解决方案的关键在于提出基于蒸馏的场景自适应混合专家模型(Distillation-based Scenario-Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts, DSMOE):一方面设计场景自适应投影(Scenario-Adaptive Projection, SAP)模块生成轻量级、上下文感知的参数,缓解长尾场景中的专家坍塌;另一方面构建跨架构知识蒸馏框架,由一个交互感知的教师模型指导双塔学生模型学习复杂的匹配模式,显著增强检索效果,尤其在数据稀疏场景下表现突出。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02368
作者: Ruibing Wang,Shuhan Guo,Haotong Du,Quanming Yao
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Multi-scenario recommendation is pivotal for optimizing user experience across diverse contexts. While Multi-gate Mixture-of-Experts (MMOE) thrives in ranking, its transfer to the matching stage is hindered by the blind optimization inherent to independent two-tower architectures and the parameter dominance of head scenarios. To address these structural and distributional bottlenecks, we propose Distillation-based Scenario-Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts (DSMOE). Specially, we devise a Scenario-Adaptive Projection (SAP) module to generate lightweight, context-specific parameters, effectively preventing expert collapse in long-tail scenarios. Concurrently, we introduce a cross-architecture knowledge distillation framework, where an interaction-aware teacher guides the two-tower student to capture complex matching patterns. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate DSMOE’s superiority, particularly in significantly improving retrieval quality for under-represented, data-sparse scenarios.
zh
[AI-75] xtBridgeGNN: Pre-training Graph Neural Network for Cross-Domain Recommendation via Text-Guided Transfer
【速读】:该论文旨在解决图推荐系统在跨域迁移中的两大核心挑战:一是ID嵌入(ID embedding)因各领域ID空间孤立而难以迁移,二是异构交互图(heterogeneous interaction graphs)之间的结构不兼容问题。解决方案的关键在于构建跨域语义桥梁——利用文本信息作为媒介,在多层级图传播中连接不同域。具体而言,TextBridgeGNN通过预训练阶段引入文本特征,打破多域数据孤岛,设计分层图神经网络(GNN)以同时学习领域特有与全局知识,从而保留协同信号并增强语义表达;在微调阶段则提出相似性迁移机制,通过语义相关节点初始化目标域的ID嵌入,实现ID嵌入与图模式的有效迁移。该方法无需昂贵的语言模型微调或实时推理开销,显著提升了跨域、多域及零样本训练场景下的推荐性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02366
作者: Yiwen Chen,Yiqing Wu,Huishi Luo,Fuzhen Zhuang,Deqing Wang
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Graph-based recommendation has achieved great success in recent years. The classical graph recommendation model utilizes ID embedding to store essential collaborative information. However, this ID-based paradigm faces challenges in transferring to a new domain, making it hard to build a pre-trained graph recommendation model. This phenomenon primarily stems from two inherent challenges: (1) the non-transferability of ID embeddings due to isolated domain-specific ID spaces, and (2) structural incompatibility between heterogeneous interaction graphs across domains. To address these issues, we propose TextBridgeGNN, a pre-training and fine-tuning framework that can effectively transfer knowledge from a pre-trained GNN to downstream tasks. We believe the key lies in how to build the relationship between domains. Specifically, TextBridgeGNN uses text as a semantic bridge to connect domains through multi-level graph propagation. During the pre-training stage, textual information is utilized to break the data islands formed by multiple domains, and hierarchical GNNs are designed to learn both domain-specific and domain-global knowledge with text features, ensuring the retention of collaborative signals and the enhancement of semantics. During the fine-tuning stage, a similarity transfer mechanism is proposed. This mechanism initializes ID embeddings in the target domain by transferring from semantically related nodes, successfully transferring the ID embeddings and graph pattern. Experiments demonstrate that TextBridgeGNN outperforms existing methods in cross-domain, multi-domain, and training-free settings, highlighting its ability to integrate Pre-trained Language Model (PLM)-driven semantics with graph-based collaborative filtering without costly language model fine-tuning or real-time inference overhead. Subjects: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02366 [cs.IR] (or arXiv:2601.02366v1 [cs.IR] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02366 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite
zh
[AI-76] owards Trustworthy LLM -Based Recommendation via Rationale Integration CIKM’25
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统推荐系统(Recommender Systems, RS)在追求准确性和短期用户参与度的同时,普遍忽视透明度与可信度的问题。现有系统通常将推荐理由(rationale)视为事后附加的解释,而非推荐过程的核心组成部分。为应对这一挑战,作者提出了一种基于大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)的推荐系统(LLM-Rec),其关键创新在于采用“先解释后推荐”的指令微调范式(rationale-first format),即模型首先生成逻辑连贯的推理链(chain-of-thought, CoT)式理由,再输出推荐项。该方法通过自标注的推理数据集进行训练,显著提升了推荐结果的可解释性与性能,在Amazon Fashion和Scientific领域数据集上优于主流基线模型。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02364
作者: Chung Park,Taesan Kim,Hyeongjun Yun,Dongjoon Hong,Junui Hong,Kijung Park,MinCheol Cho,Mira Myong,Jihoon Oh,Min sung Choi
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted at RS4SD’25 (CIKM’25 Workshop)
Abstract:Traditional recommender systems (RS) have been primarily optimized for accuracy and short-term engagement, often overlooking transparency and trustworthiness. Recently, platforms such as Amazon and Instagram have begun providing recommendation rationales to users, acknowledging their critical role in fostering trust and enhancing engagement; however, most existing systems still treat them as post-hoc artifacts. We propose an LLM-based recommender (LLM-Rec) that not only predicts items but also generates logically grounded rationales. Our approach leverages a self-annotated rationale dataset and instruction tuning in a rationale-first format, where the model generates an explanation before outputting the recommended item. By adopting this strategy and representing rationales in a chain-of-thought (CoT) style, LLM-Rec strengthens both interpretability and recommendation performance. Experiments on the Fashion and Scientific domains of the Amazon Review dataset demonstrate significant improvements over well-established baselines. To encourage reproducibility and future research, we publicly release a rationale-augmented recommendation dataset containing user histories, rationales, and recommended items.
zh
[AI-77] he Impact of LLM -Generated Reviews on Recommender Systems: Textual Shifts Performance Effects and Strategic Platform Control
【速读】:该论文试图解决的问题是:生成式 AI 技术的兴起如何影响基于内容的推荐系统(Content-based Recommender Systems, RSes)的性能与商业成果,尤其是在AI生成内容(AI-generated content)与人工撰写内容共存的情况下。其解决方案的关键在于区分两种AI内容引入路径——用户主导型(user-centric)和平台主导型(platform-centric),并通过大规模酒店评论数据集(TripAdvisor)使用大语言模型(LLMs)生成合成评论,系统评估其在推荐模型训练与部署阶段的影响。研究发现,尽管AI生成评论能提升模型性能,但仅用AI数据训练的模型在面对人类内容时表现不佳,而以人类内容训练的模型则能稳健泛化至AI内容;同时,平台通过语气策略(鼓励、建设性或批判性)可显著增强合成评论的有效性,凸显平台对AI内容生成与整合的控制权对于保障推荐鲁棒性和可持续商业价值的战略意义。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02362
作者: Itzhak Ziv,Moshe Unger,Hilah Geva
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The rise of generative AI technologies is reshaping content-based recommender systems (RSes), which increasingly encounter AI-generated content alongside human-authored content. This study examines how the introduction of AI-generated reviews influences RS performance and business outcomes. We analyze two distinct pathways through which AI content can enter RSes: user-centric, in which individuals use AI tools to refine their reviews, and platform-centric, in which platforms generate synthetic reviews directly from structured metadata. Using a large-scale dataset of hotel reviews from TripAdvisor, we generate synthetic reviews using LLMs and evaluate their impact across the training and deployment phases of RSes. We find that AI-generated reviews differ systematically from human-authored reviews across multiple textual dimensions. Although both user- and platform-centric AI reviews enhance RS performance relative to models without textual data, models trained on human reviews consistently achieve superior performance, underscoring the quality of authentic human data. Human-trained models generalize robustly to AI content, whereas AI-trained models underperform on both content types. Furthermore, tone-based framing strategies (encouraging, constructive, or critical) substantially enhance platform-generated review effectiveness. Our findings highlight the strategic importance of platform control in governing the generation and integration of AI-generated reviews, ensuring that synthetic content complements recommendation robustness and sustainable business value.
zh
[AI-78] AI-exposed jobs deteriorated before ChatGPT
【速读】:该论文试图解决的问题是:公众讨论中普遍认为生成式 AI(Generative AI)的兴起,特别是 ChatGPT 在2022年底发布后,导致了AI暴露职业(AI-exposed occupations)就业前景恶化。然而,研究通过多源数据发现,失业风险的上升实际上始于2022年初,早于ChatGPT的发布;同时,从2021年起,毕业生进入AI暴露岗位的比例下降,且这种趋势也发生在2022年底之前。此外,课程中包含更多与大语言模型(LLM)相关知识的毕业生,在ChatGPT发布后反而获得更高起薪和更短的求职周期。因此,论文的核心结论是:就业市场对AI的反应并非由生成式AI的突然出现所驱动,而是源于更早的技术演进与教育结构的适应性调整。解决方案之关键在于识别出在生成式AI之前已存在的结构性趋势,并强调LLM相关教育对劳动力市场竞争力的持续价值。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02554
作者: Morgan R. Frank,Alireza Javadian Sabet,Lisa Simon,Sarah H. Bana,Renzhe Yu
机构: 未知
类目: General Economics (econ.GN); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注:
Abstract:Public debate links worsening job prospects for AI-exposed occupations to the release of ChatGPT in late 2022. Using monthly U.S. unemployment insurance records, we measure occupation- and location-specific unemployment risk and find that risk rose in AI-exposed occupations beginning in early 2022, months before ChatGPT. Analyzing millions of LinkedIn profiles, we show that graduate cohorts from 2021 onward entered AI-exposed jobs at lower rates than earlier cohorts, with gaps opening before late 2022. Finally, from millions of university syllabi, we find that graduates taking more AI-exposed curricula had higher first-job pay and shorter job searches after ChatGPT. Together, these results point to forces pre-dating generative AI and to the ongoing value of LLM-relevant education.
zh
[AI-79] Mitigating Long-Tailed Anomaly Score Distributions with Importance-Weighted Loss IJCNN2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决工业场景中异常检测面临的长尾异常分数分布(Long-Tailed Anomaly Score Distribution, LTD)问题,即由于正常数据呈现多样性和类不平衡特性,导致传统单类训练模型在实际应用中性能下降,尤其是对少数类异常实例的检测能力受限。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种新颖的重要加权损失函数(Importance-Weighted Loss),该方法无需事先了解正常数据类别信息,通过引入重要性采样机制,使异常分数分布逼近目标高斯分布,从而实现对正常数据的均衡表示,有效缓解LTD带来的偏差问题。实验表明,该方法在多个基准图像数据集和真实高光谱成像数据集上均显著提升了异常检测性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02440
作者: Jungi Lee,Jungkwon Kim,Chi Zhang,Sangmin Kim,Kwangsun Yoo,Seok-Joo Byun
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 8 pages, Published as a conference paper at IJCNN 2025
Abstract:Anomaly detection is crucial in industrial applications for identifying rare and unseen patterns to ensure system reliability. Traditional models, trained on a single class of normal data, struggle with real-world distributions where normal data exhibit diverse patterns, leading to class imbalance and long-tailed anomaly score distributions (LTD). This imbalance skews model training and degrades detection performance, especially for minority instances. To address this issue, we propose a novel importance-weighted loss designed specifically for anomaly detection. Compared to the previous method for LTD in classification, our method does not require prior knowledge of normal data classes. Instead, we introduce a weighted loss function that incorporates importance sampling to align the distribution of anomaly scores with a target Gaussian, ensuring a balanced representation of normal data. Extensive experiments on three benchmark image datasets and three real-world hyperspectral imaging datasets demonstrate the robustness of our approach in mitigating LTD-induced bias. Our method improves anomaly detection performance by 0.043, highlighting its effectiveness in real-world applications.
zh
[AI-80] A large-scale nanocrystal database with aligned synthesis and properties enabling generative inverse design
【速读】:该论文旨在解决纳米晶体(nanocrystals)合成过程中因参数与物化性质之间复杂关联而导致的依赖试错法的问题,以及生成式人工智能(Generative AI)在逆向设计中受限于高质量数据集匮乏的瓶颈。其解决方案的关键在于构建了一个大规模、结构化的纳米晶体合成-性质(Nanocrystal Synthesis-Property, NSP)数据库,并开发了NanoExtractor这一增强型大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM),用于从非结构化文献中自动提取合成路径及其对应的产物性质。该模型经专家验证达到88%加权平均准确率,显著优于专业化学和通用LLM;基于此数据库训练的NanoDesigner实现了对已知PbSe和罕见MgF₂纳米晶体的可行合成路径的生成式逆向设计,其中对MgF₂提出反直觉的非化学计量比前驱体比例(1:1),并经实验验证为抑制副产物的关键因素,从而建立了人机协同驱动的高效纳米晶体发现范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02424
作者: Kai Gu,Yingping Liang,Senliang Peng,Aotian Guo,Haizheng Zhong,Ying Fu
机构: 未知
类目: Materials Science (cond-mat.mtrl-sci); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The synthesis of nanocrystals has been highly dependent on trial-and-error, due to the complex correlation between synthesis parameters and physicochemical properties. Although deep learning offers a potential methodology to achieve generative inverse design, it is still hindered by the scarcity of high-quality datasets that align nanocrystal synthesis routes with their properties. Here, we present the construction of a large-scale, aligned Nanocrystal Synthesis-Property (NSP) database and demonstrate its capability for generative inverse design. To extract structured synthesis routes and their corresponding product properties from literature, we develop NanoExtractor, a large language model (LLM) enhanced by well-designed augmentation strategies. NanoExtractor is validated against human experts, achieving a weighted average score of 88% on the test set, significantly outperforming chemistry-specialized (3%) and general-purpose LLMs (38%). The resulting NSP database contains nearly 160,000 aligned entries and serves as training data for our NanoDesigner, an LLM for inverse synthesis design. The generative capability of NanoDesigner is validated through the successful design of viable synthesis routes for both well-established PbSe nanocrystals and rarely reported MgF2 nanocrystals. Notably, the model recommends a counter-intuitive, non-stoichiometric precursor ratio (1:1) for MgF2 nanocrystals, which is experimentally confirmed as critical for suppressing byproducts. Our work bridges the gap between unstructured literature and data-driven synthesis, and also establishes a powerful human-AI collaborative paradigm for accelerating nanocrystal discovery.
zh
机器学习
[LG-0] PET-TURTLE: Deep Unsupervised Support Vector Machines for Imbalanced Data Clusters
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03237
作者: Javier Salazar Cavazos
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注:
Abstract:Foundation vision, audio, and language models enable zero-shot performance on downstream tasks via their latent representations. Recently, unsupervised learning of data group structure with deep learning methods has gained popularity. TURTLE, a state of the art deep clustering algorithm, uncovers data labeling without supervision by alternating label and hyperplane updates, maximizing the hyperplane margin, in a similar fashion to support vector machines (SVMs). However, TURTLE assumes clusters are balanced; when data is imbalanced, it yields non-ideal hyperplanes that cause higher clustering error. We propose PET-TURTLE, which generalizes the cost function to handle imbalanced data distributions by a power law prior. Additionally, by introducing sparse logits in the labeling process, PET-TURTLE optimizes a simpler search space that in turn improves accuracy for balanced datasets. Experiments on synthetic and real data show that PET-TURTLE improves accuracy for imbalanced sources, prevents over-prediction of minority clusters, and enhances overall clustering.
[LG-1] From Entropy to Epiplexity: Rethinking Information for Computationally Bounded Intelligence
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03220
作者: Marc Finzi,Shikai Qiu,Yiding Jiang,Pavel Izmailov,J. Zico Kolter,Andrew Gordon Wilson
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注:
Abstract:Can we learn more from data than existed in the generating process itself? Can new and useful information be constructed from merely applying deterministic transformations to existing data? Can the learnable content in data be evaluated without considering a downstream task? On these questions, Shannon information and Kolmogorov complexity come up nearly empty-handed, in part because they assume observers with unlimited computational capacity and fail to target the useful information content. In this work, we identify and exemplify three seeming paradoxes in information theory: (1) information cannot be increased by deterministic transformations; (2) information is independent of the order of data; (3) likelihood modeling is merely distribution matching. To shed light on the tension between these results and modern practice, and to quantify the value of data, we introduce epiplexity, a formalization of information capturing what computationally bounded observers can learn from data. Epiplexity captures the structural content in data while excluding time-bounded entropy, the random unpredictable content exemplified by pseudorandom number generators and chaotic dynamical systems. With these concepts, we demonstrate how information can be created with computation, how it depends on the ordering of the data, and how likelihood modeling can produce more complex programs than present in the data generating process itself. We also present practical procedures to estimate epiplexity which we show capture differences across data sources, track with downstream performance, and highlight dataset interventions that improve out-of-distribution generalization. In contrast to principles of model selection, epiplexity provides a theoretical foundation for data selection, guiding how to select, generate, or transform data for learning systems.
[LG-2] Critic-Guided Reinforcement Unlearning in Text-to-Image Diffusion ICLR2026
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03213
作者: Mykola Vysotskyi,Zahar Kohut,Mariia Shpir,Taras Rumezhak,Volodymyr Karpiv
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Preprint. Under review at ICLR 2026
Abstract:Machine unlearning in text-to-image diffusion models aims to remove targeted concepts while preserving overall utility. Prior diffusion unlearning methods typically rely on supervised weight edits or global penalties; reinforcement-learning (RL) approaches, while flexible, often optimize sparse end-of-trajectory rewards, yielding high-variance updates and weak credit assignment. We present a general RL framework for diffusion unlearning that treats denoising as a sequential decision process and introduces a timestep-aware critic with noisy-step rewards. Concretely, we train a CLIP-based reward predictor on noisy latents and use its per-step signal to compute advantage estimates for policy-gradient updates of the reverse diffusion kernel. Our algorithm is simple to implement, supports off-policy reuse, and plugs into standard text-to-image backbones. Across multiple concepts, the method achieves better or comparable forgetting to strong baselines while maintaining image quality and benign prompt fidelity; ablations show that (i) per-step critics and (ii) noisy-conditioned rewards are key to stability and effectiveness. We release code and evaluation scripts to facilitate reproducibility and future research on RL-based diffusion unlearning.
[LG-3] Empowering Reliable Visual-Centric Instruction Following in MLLM s
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03198
作者: Weilei He,Feng Ju,Zhiyuan Fan,Rui Min,Minhao Cheng,Yi R. Fung
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Submitted to ARR Jan
Abstract:Evaluating the instruction-following (IF) capabilities of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) is essential for rigorously assessing how faithfully model outputs adhere to user-specified intentions. Nevertheless, existing benchmarks for evaluating MLLMs’ instruction-following capability primarily focus on verbal instructions in the textual modality. These limitations hinder a thorough analysis of instruction-following capabilities, as they overlook the implicit constraints embedded in the semantically rich visual modality. To address this gap, we introduce VC-IFEval, a new benchmark accompanied by a systematically constructed dataset that evaluates MLLMs’ instruction-following ability under multimodal settings. Our benchmark systematically incorporates vision-dependent constraints into instruction design, enabling a more rigorous and fine-grained assessment of how well MLLMs align their outputs with both visual input and textual instructions. Furthermore, by fine-tuning MLLMs on our dataset, we achieve substantial gains in visual instruction-following accuracy and adherence. Through extensive evaluation across representative MLLMs, we provide new insights into the strengths and limitations of current models.
[LG-4] Sparse Knowledge Distillation: A Mathematical Framework for Probability-Domain Temperature Scaling and Multi-Stage Compression
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03195
作者: Aaron R. Flouro,Shawn P. Chadwick
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Machine learning theory. Develops an axiomatic, operator-agnostic framework for probability-domain knowledge distillation, including bias–variance analysis of sparse students, homotopy-based multi-stage pruning, O(1/n) convergence guarantees, and equivalence classes of probability-domain softening operators. Theoretical analysis only
Abstract:We develop a unified theoretical framework for sparse knowledge distillation based on probability-domain softening operators. While the equivalence p^1/T \propto \mathrmsoftmax(z/T) is well known, our contribution is an operator-level analytical framework built on this foundation rather than the equivalence itself. The framework comprises four core components: (i) operator-agnostic bias–variance decompositions that characterize when sparse students outperform dense teachers, (ii) a homotopy path formalization of multi-stage pruning in function space explaining why iterative compression succeeds where one-shot pruning fails, (iii) convergence guarantees establishing O(1/n) rates for n -stage distillation with explicit parameter dependence, and (iv) equivalence class characterizations identifying distinct probability-domain operators that yield identical student models under capacity constraints. We introduce an axiomatic definition of probability-domain softening operators based on ranking preservation, continuity, entropy monotonicity, identity, and boundary behavior, and show that multiple non-equivalent operator families satisfy these axioms. All learning-theoretic guarantees are shown to hold uniformly across this operator class, independent of implementation details. These results provide theoretical grounding for black-box teacher distillation, partial-access settings such as top- k truncation and text-only outputs, and privacy-preserving model compression. Comments: Machine learning theory. Develops an axiomatic, operator-agnostic framework for probability-domain knowledge distillation, including bias–variance analysis of sparse students, homotopy-based multi-stage pruning, O(1/n) convergence guarantees, and equivalence classes of probability-domain softening operators. Theoretical analysis only Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG) MSC classes: 68T05, 68Q32 ACMclasses: I.2.6; F.2.2 Cite as: arXiv:2601.03195 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2601.03195v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.03195 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-5] Predicting Time Pressure of Powered Two-Wheeler Riders for Proactive Safety Interventions
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03173
作者: Sumit S. Shevtekar,Chandresh K. Maurya,Gourab Sil,Subasish Das
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
*备注: 13 pages, 8 figures
Abstract:Time pressure critically influences risky maneuvers and crash proneness among powered two-wheeler riders, yet its prediction remains underexplored in intelligent transportation systems. We present a large-scale dataset of 129,000+ labeled multivariate time-series sequences from 153 rides by 51 participants under No, Low, and High Time Pressure conditions. Each sequence captures 63 features spanning vehicle kinematics, control inputs, behavioral violations, and environmental context. Our empirical analysis shows High Time Pressure induces 48% higher speeds, 36.4% greater speed variability, 58% more risky turns at intersections, 36% more sudden braking, and 50% higher rear brake forces versus No Time Pressure. To benchmark this dataset, we propose MotoTimePressure, a deep learning model combining convolutional preprocessing, dual-stage temporal attention, and Squeeze-and-Excitation feature recalibration, achieving 91.53% accuracy and 98.93% ROC AUC, outperforming eight baselines. Since time pressure cannot be directly measured in real time, we demonstrate its utility in collision prediction and threshold determination. Using MTPS-predicted time pressure as features, improves Informer-based collision risk accuracy from 91.25% to 93.51%, approaching oracle performance (93.72%). Thresholded time pressure states capture rider cognitive stress and enable proactive ITS interventions, including adaptive alerts, haptic feedback, V2I signaling, and speed guidance, supporting safer two-wheeler mobility under the Safe System Approach.
[LG-6] Dynamic Hyperparameter Importance for Efficient Multi-Objective Optimization IJCAI2026
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03166
作者: Daphne Theodorakopoulos,Marcel Wever,Marius Lindauer
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Submitted to IJCAI 2026
Abstract:Choosing a suitable ML model is a complex task that can depend on several objectives, e.g., accuracy, model size, fairness, inference time, or energy consumption. In practice, this requires trading off multiple, often competing, objectives through multi-objective optimization (MOO). However, existing MOO methods typically treat all hyperparameters as equally important, overlooking that hyperparameter importance (HPI) can vary significantly depending on the trade-off between objectives. We propose a novel dynamic optimization approach that prioritizes the most influential hyperparameters based on varying objective trade-offs during the search process, which accelerates empirical convergence and leads to better solutions. Building on prior work on HPI for MOO post-analysis, we now integrate HPI, calculated with HyperSHAP, into the optimization. For this, we leverage the objective weightings naturally produced by the MOO algorithm ParEGO and adapt the configuration space by fixing the unimportant hyperparameters, allowing the search to focus on the important ones. Eventually, we validate our method with diverse tasks from PyMOO and YAHPO-Gym. Empirical results demonstrate improvements in convergence speed and Pareto front quality compared to baselines.
[LG-7] On the Convergence Behavior of Preconditioned Gradient Descent Toward the Rich Learning Regime
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03162
作者: Shuai Jiang,Alexey Voronin,Eric Cyr,Ben Southworth
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 21 pages, 13 figures,
Abstract:Spectral bias, the tendency of neural networks to learn low frequencies first, can be both a blessing and a curse. While it enhances the generalization capabilities by suppressing high-frequency noise, it can be a limitation in scientific tasks that require capturing fine-scale structures. The delayed generalization phenomenon known as grokking is another barrier to rapid training of neural networks. Grokking has been hypothesized to arise as learning transitions from the NTK to the feature-rich regime. This paper explores the impact of preconditioned gradient descent (PGD), such as Gauss-Newton, on spectral bias and grokking phenomena. We demonstrate through theoretical and empirical results how PGD can mitigate issues associated with spectral bias. Additionally, building on the rich learning regime grokking hypothesis, we study how PGD can be used to reduce delays associated with grokking. Our conjecture is that PGD, without the impediment of spectral bias, enables uniform exploration of the parameter space in the NTK regime. Our experimental results confirm this prediction, providing strong evidence that grokking represents a transitional behavior between the lazy regime characterized by the NTK and the rich regime. These findings deepen our understanding of the interplay between optimization dynamics, spectral bias, and the phases of neural network learning.
[LG-8] PersonaLedger: Generating Realistic Financial Transactions with Persona Conditioned LLM s and Rule Grounded Feedback
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03149
作者: Dehao Yuan,Tyler Farnan,Stefan Tesliuc,Doron L Bergman,Yulun Wu,Xiaoyu Liu,Minghui Liu,James Montgomery,Nam H Nguyen,C. Bayan Bruss,Furong Huang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Strict privacy regulations limit access to real transaction data, slowing open research in financial AI. Synthetic data can bridge this gap, but existing generators do not jointly achieve behavioral diversity and logical groundedness. Rule-driven simulators rely on hand-crafted workflows and shallow stochasticity, which miss the richness of human behavior. Learning-based generators such as GANs capture correlations yet often violate hard financial constraints and still require training on private data. We introduce PersonaLedger, a generation engine that uses a large language model conditioned on rich user personas to produce diverse transaction streams, coupled with an expert configurable programmatic engine that maintains correctness. The LLM and engine interact in a closed loop: after each event, the engine updates the user state, enforces financial rules, and returns a context aware “nextprompt” that guides the LLM toward feasible next actions. With this engine, we create a public dataset of 30 million transactions from 23,000 users and a benchmark suite with two tasks, illiquidity classification and identity theft segmentation. PersonaLedger offers a realistic, privacy preserving resource that supports rigorous evaluation of forecasting and anomaly detection models. PersonaLedger offers the community a rich, realistic, and privacy preserving resource – complete with code, rules, and generation logs – to accelerate innovation in financial AI and enable rigorous, reproducible evaluation.
[LG-9] Finite Memory Belief Approximation for Optimal Control in Partially Observable Markov Decision Processes
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03132
作者: Mintae Kim
类目: ystems and Control (eess.SY); Information Theory (cs.IT); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 6 pages, 3 figures
Abstract:We study finite memory belief approximation for partially observable (PO) stochastic optimal control (SOC) problems. While belief states are sufficient for SOC in partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDPs), they are generally infinite-dimensional and impractical. We interpret truncated input-output (IO) histories as inducing a belief approximation and develop a metric-based theory that directly relates information loss to control performance. Using the Wasserstein metric, we derive policy-conditional performance bounds that quantify value degradation induced by finite memory along typical closed-loop trajectories. Our analysis proceeds via a fixed-policy comparison: we evaluate two cost functionals under the same closed-loop execution and isolate the effect of replacing the true belief by its finite memory approximation inside the belief-level cost. For linear quadratic Gaussian (LQG) systems, we provide closed-form belief mismatch evaluation and empirically validate the predicted mechanism, demonstrating that belief mismatch decays approximately exponentially with memory length and that the induced performance mismatch scales accordingly. Together, these results provide a metric-aware characterization of what finite memory belief approximation can and cannot achieve in PO settings.
[LG-10] me-Aware Synthetic Control
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03099
作者: Saeyoung Rho,Cyrus Illick,Samhitha Narasipura,Alberto Abadie,Daniel Hsu,Vishal Misra
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Econometrics (econ.EM); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注:
Abstract:The synthetic control (SC) framework is widely used for observational causal inference with time-series panel data. SC has been successful in diverse applications, but existing methods typically treat the ordering of pre-intervention time indices interchangeable. This invariance means they may not fully take advantage of temporal structure when strong trends are present. We propose Time-Aware Synthetic Control (TASC), which employs a state-space model with a constant trend while preserving a low-rank structure of the signal. TASC uses the Kalman filter and Rauch-Tung-Striebel smoother: it first fits a generative time-series model with expectation-maximization and then performs counterfactual inference. We evaluate TASC on both simulated and real-world datasets, including policy evaluation and sports prediction. Our results suggest that TASC offers advantages in settings with strong temporal trends and high levels of observation noise.
[LG-11] From Muscle to Text with MyoText: sEMG to Text via Finger Classification and Transformer-Based Decoding
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03098
作者: Meghna Roy Chowdhury,Shreyas Sen,Yi Ding
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE)
*备注: 25 pages, 11 tables, 11 figures
Abstract:Surface electromyography (sEMG) provides a direct neural interface for decoding muscle activity and offers a promising foundation for keyboard-free text input in wearable and mixed-reality systems. Previous sEMG-to-text studies mainly focused on recognizing letters directly from sEMG signals, forming an important first step toward translating muscle activity into text. Building on this foundation, we present MyoText, a hierarchical framework that decodes sEMG signals to text through physiologically grounded intermediate stages. MyoText first classifies finger activations from multichannel sEMG using a CNN-BiLSTM-Attention model, applies ergonomic typing priors to infer letters, and reconstructs full sentences with a fine-tuned T5 transformer. This modular design mirrors the natural hierarchy of typing, linking muscle intent to language output and reducing the search space for decoding. Evaluated on 30 users from the emg2qwerty dataset, MyoText outperforms baselines by achieving 85.4% finger-classification accuracy, 5.4% character error rate (CER), and 6.5% word error rate (WER). Beyond accuracy gains, this methodology establishes a principled pathway from neuromuscular signals to text, providing a blueprint for virtual and augmented-reality typing interfaces that operate entirely without physical keyboards. By integrating ergonomic structure with transformer-based linguistic reasoning, MyoText advances the feasibility of seamless, wearable neural input for future ubiquitous computing environments.
[LG-12] Real-Time Adaptive Anomaly Detection in Industrial IoT Environments
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03085
作者: Mahsa Raeiszadeh,Amin Ebrahimzadeh,Roch H. Glitho,Johan Eker,Raquel A. F. Mini
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:To ensure reliability and service availability, next-generation networks are expected to rely on automated anomaly detection systems powered by advanced machine learning methods with the capability of handling multi-dimensional data. Such multi-dimensional, heterogeneous data occurs mostly in today’s industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), where real-time detection of anomalies is critical to prevent impending failures and resolve them in a timely manner. However, existing anomaly detection methods often fall short of effectively coping with the complexity and dynamism of multi-dimensional data streams in IIoT. In this paper, we propose an adaptive method for detecting anomalies in IIoT streaming data utilizing a multi-source prediction model and concept drift adaptation. The proposed anomaly detection algorithm merges a prediction model into a novel drift adaptation method resulting in accurate and efficient anomaly detection that exhibits improved scalability. Our trace-driven evaluations indicate that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art anomaly detection methods by achieving up to an 89.71% accuracy (in terms of Area under the Curve (AUC)) while meeting the given efficiency and scalability requirements.
[LG-13] When the Coffee Feature Activates on Coffins: An Analysis of Feature Extraction and Steering for Mechanistic Interpretability
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03047
作者: Raphael Ronge,Markus Maier,Frederick Eberhardt
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 33 pages (65 with appendix), 1 figure
Abstract:Recent work by Anthropic on Mechanistic interpretability claims to understand and control Large Language Models by extracting human-interpretable features from their neural activation patterns using sparse autoencoders (SAEs). If successful, this approach offers one of the most promising routes for human oversight in AI safety. We conduct an initial stress-test of these claims by replicating their main results with open-source SAEs for Llama 3.1. While we successfully reproduce basic feature extraction and steering capabilities, our investigation suggests that major caution is warranted regarding the generalizability of these claims. We find that feature steering exhibits substantial fragility, with sensitivity to layer selection, steering magnitude, and context. We observe non-standard activation behavior and demonstrate the difficulty to distinguish thematically similar features from one another. While SAE-based interpretability produces compelling demonstrations in selected cases, current methods often fall short of the systematic reliability required for safety-critical applications. This suggests a necessary shift in focus from prioritizing interpretability of internal representations toward reliable prediction and control of model output. Our work contributes to a more nuanced understanding of what mechanistic interpretability has achieved and highlights fundamental challenges for AI safety that remain unresolved.
[LG-14] Multi-Distribution Robust Conformal Prediction
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02998
作者: Yuqi Yang,Ying Jin
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Methodology (stat.ME); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注:
Abstract:In many fairness and distribution robustness problems, one has access to labeled data from multiple source distributions yet the test data may come from an arbitrary member or a mixture of them. We study the problem of constructing a conformal prediction set that is uniformly valid across multiple, heterogeneous distributions, in the sense that no matter which distribution the test point is from, the coverage of the prediction set is guaranteed to exceed a pre-specified level. We first propose a max-p aggregation scheme that delivers finite-sample, multi-distribution coverage given any conformity scores associated with each distribution. Upon studying several efficiency optimization programs subject to uniform coverage, we prove the optimality and tightness of our aggregation scheme, and propose a general algorithm to learn conformity scores that lead to efficient prediction sets after the aggregation under standard conditions. We discuss how our framework relates to group-wise distributionally robust optimization, sub-population shift, fairness, and multi-source learning. In synthetic and real-data experiments, our method delivers valid worst-case coverage across multiple distributions while greatly reducing the set size compared with naively applying max-p aggregation to single-source conformity scores, and can be comparable in size to single-source prediction sets with popular, standard conformity scores.
[LG-15] MixTTE: Multi-Level Mixture-of-Experts for Scalable and Adaptive Travel Time Estimation KDD2026
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02943
作者: Wenzhao Jiang,Jindong Han,Ruiqian Han,Hao Liu
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
*备注: Accepted to KDD 2026
Abstract:Accurate Travel Time Estimation (TTE) is critical for ride-hailing platforms, where errors directly impact user experience and operational efficiency. While existing production systems excel at holistic route-level dependency modeling, they struggle to capture city-scale traffic dynamics and long-tail scenarios, leading to unreliable predictions in large urban networks. In this paper, we propose \model, a scalable and adaptive framework that synergistically integrates link-level modeling with industrial route-level TTE systems. Specifically, we propose a spatio-temporal external attention module to capture global traffic dynamic dependencies across million-scale road networks efficiently. Moreover, we construct a stabilized graph mixture-of-experts network to handle heterogeneous traffic patterns while maintaining inference efficiency. Furthermore, an asynchronous incremental learning strategy is tailored to enable real-time and stable adaptation to dynamic traffic distribution shifts. Experiments on real-world datasets validate MixTTE significantly reduces prediction errors compared to seven baselines. MixTTE has been deployed in DiDi, substantially improving the accuracy and stability of the TTE service.
[LG-16] ChemBART: A Pre-trained BART Model Assisting Organic Chemistry Analysis
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02915
作者: Kenan Li,Yijian Zhang,Jin Wang,Haipeng Gan,Zeying Sun,Xiaoguang Lei,Hao Dong
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
[LG-17] Bridging Mechanistic Interpretability and Prompt Engineering with Gradient Ascent for Interpretable Persona Control
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02896
作者: Harshvardhan Saini,Yiming Tang,Dianbo Liu
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Controlling emergent behavioral personas (e.g., sycophancy, hallucination) in Large Language Models (LLMs) is critical for AI safety, yet remains a persistent challenge. Existing solutions face a dilemma: manual prompt engineering is intuitive but unscalable and imprecise, while automatic optimization methods are effective but operate as “black boxes” with no interpretable connection to model internals. We propose a novel framework that adapts gradient ascent to LLMs, enabling targeted prompt discovery. In specific, we propose two methods, RESGA and SAEGA, that both optimize randomly initialized prompts to achieve better aligned representation with an identified persona direction. We introduce fluent gradient ascent to control the fluency of discovered persona steering prompts. We demonstrate RESGA and SAEGA’s effectiveness across Llama 3.1, Qwen 2.5, and Gemma 3 for steering three different personas,sycophancy, hallucination, and myopic reward. Crucially, on sycophancy, our automatically discovered prompts achieve significant improvement (49.90% compared with 79.24%). By grounding prompt discovery in mechanistically meaningful features, our method offers a new paradigm for controllable and interpretable behavior modification.
[LG-18] RPIQ: Residual-Projected Multi-Collaboration Closed-Loop and Single Instance Quantization for Visually Impaired Assistance
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02888
作者: Xuanyu Wang,Haisen Su,Jingtao Zhang,Xiangxiang Wang,Yongbin Yu,Manping Fan,Bo Gong,Siqi Chen,Mingsheng Cao,Liyong Ren
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Visually impaired users face significant challenges in daily information access and real-time environmental perception, and there is an urgent need for intelligent assistive systems with accurate recognition capabilities. Although large-scale models provide effective solutions for perception and reasoning, their practical deployment on assistive devices is severely constrained by excessive memory consumption and high inference costs. Moreover, existing quantization strategies often ignore inter-block error accumulation, leading to degraded model stability. To address these challenges, this study proposes a novel quantization framework – Residual-Projected Multi-Collaboration Closed-Loop and Single Instance Quantization(RPIQ), whose quantization process adopts a multi-collaborative closed-loop compensation scheme based on Single Instance Calibration and Gauss-Seidel Iterative Quantization. Experiments on various types of large-scale models, including language models such as OPT, Qwen, and LLaMA, as well as vision-language models such as CogVLM2, demonstrate that RPIQ can compress models to 4-bit representation while significantly reducing peak memory consumption (approximately 60%-75% reduction compared to original full-precision models). The method maintains performance highly close to full-precision models across multiple language and visual tasks, and exhibits excellent recognition and reasoning capabilities in key applications such as text understanding and visual question answering in complex scenarios. While verifying the effectiveness of RPIQ for deployment in real assistive systems, this study also advances the computational efficiency and reliability of large models, enabling them to provide visually impaired users with the required information accurately and rapidly.
[LG-19] Domain Generalization for Time Series: Enhancing Drilling Regression Models for Stick-Slip Index Prediction
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02884
作者: Hana Yahia(CAS),Bruno Figliuzzi(CMM),Florent Di Meglio(CAS),Laurent Gerbaud(GEOSCIENCES),Stephane Menand,Mohamed Mahjoub
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:This paper provides a comprehensive comparison of domain generalization techniques applied to time series data within a drilling context, focusing on the prediction of a continuous Stick-Slip Index (SSI), a critical metric for assessing torsional downhole vibrations at the drill bit. The study aims to develop a robust regression model that can generalize across domains by training on 60 second labeled sequences of 1 Hz surface drilling data to predict the SSI. The model is tested in wells that are different from those used during training. To fine-tune the model architecture, a grid search approach is employed to optimize key hyperparameters. A comparative analysis of the Adversarial Domain Generalization (ADG), Invariant Risk Minimization (IRM) and baseline models is presented, along with an evaluation of the effectiveness of transfer learning (TL) in improving model performance. The ADG and IRM models achieve performance improvements of 10% and 8%, respectively, over the baseline model. Most importantly, severe events are detected 60% of the time, against 20% for the baseline model. Overall, the results indicate that both ADG and IRM models surpass the baseline, with the ADG model exhibiting a slight advantage over the IRM model. Additionally, applying TL to a pre-trained model further improves performance. Our findings demonstrate the potential of domain generalization approaches in drilling applications, with ADG emerging as the most effective approach.
[LG-20] Quantum-Enhanced Neural Contextual Bandit Algorithms
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02870
作者: Yuqi Huang,Vincent Y. F Tan,Sharu Theresa Jose
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Information Theory (cs.IT); Quantum Physics (quant-ph)
*备注: 30 pages, under review
Abstract:Stochastic contextual bandits are fundamental for sequential decision-making but pose significant challenges for existing neural network-based algorithms, particularly when scaling to quantum neural networks (QNNs) due to issues such as massive over-parameterization, computational instability, and the barren plateau phenomenon. This paper introduces the Quantum Neural Tangent Kernel-Upper Confidence Bound (QNTK-UCB) algorithm, a novel algorithm that leverages the Quantum Neural Tangent Kernel (QNTK) to address these limitations. By freezing the QNN at a random initialization and utilizing its static QNTK as a kernel for ridge regression, QNTK-UCB bypasses the unstable training dynamics inherent in explicit parameterized quantum circuit training while fully exploiting the unique quantum inductive bias. For a time horizon T and K actions, our theoretical analysis reveals a significantly improved parameter scaling of \Omega((TK)^3) for QNTK-UCB, a substantial reduction compared to \Omega((TK)^8) required by classical NeuralUCB algorithms for similar regret guarantees. Empirical evaluations on non-linear synthetic benchmarks and quantum-native variational quantum eigensolver tasks demonstrate QNTK-UCB’s superior sample efficiency in low-data regimes. This work highlights how the inherent properties of QNTK provide implicit regularization and a sharper spectral decay, paving the way for achieving ``quantum advantage’’ in online learning. Comments: 30 pages, under review Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Information Theory (cs.IT); Quantum Physics (quant-ph) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02870 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2601.02870v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02870 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-21] Electricity Price Forecasting: Bridging Linear Models Neural Networks and Online Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02856
作者: Btissame El Mahtout,Florian Ziel
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Precise day-ahead forecasts for electricity prices are crucial to ensure efficient portfolio management, support strategic decision-making for power plant operations, enable efficient battery storage optimization, and facilitate demand response planning. However, developing an accurate prediction model is highly challenging in an uncertain and volatile market environment. For instance, although linear models generally exhibit competitive performance in predicting electricity prices with minimal computational requirements, they fail to capture relevant nonlinear relationships. Nonlinear models, on the other hand, can improve forecasting accuracy with a surge in computational costs. We propose a novel multivariate neural network approach that combines linear and nonlinear feed-forward neural structures. Unlike previous hybrid models, our approach integrates online learning and forecast combination for efficient training and accuracy improvement. It also incorporates all relevant characteristics, particularly the fundamental relationships arising from wind and solar generation, electricity demand patterns, related energy fuel and carbon markets, in addition to autoregressive dynamics and calendar effects. Compared to the current state-of-the-art benchmark models, the proposed forecasting method significantly reduces computational cost while delivering superior forecasting accuracy (12-13% RMSE and 15-18% MAE reductions). Our results are derived from a six-year forecasting study conducted on major European electricity markets.
[LG-22] COFFEE: COdesign Framework for Feature Enriched Embeddings in Ads-Ranking Systems
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02807
作者: Sohini Roychowdhury,Doris Wang,Qian Ge,Joy Mu,Srihari Reddy
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 4 pages, 5 figures, 1 table
Abstract:Diverse and enriched data sources are essential for commercial ads-recommendation models to accurately assess user interest both before and after engagement with content. While extended user-engagement histories can improve the prediction of user interests, it is equally important to embed activity sequences from multiple sources to ensure freshness of user and ad-representations, following scaling law principles. In this paper, we present a novel three-dimensional framework for enhancing user-ad representations without increasing model inference or serving complexity. The first dimension examines the impact of incorporating diverse event sources, the second considers the benefits of longer user histories, and the third focuses on enriching data with additional event attributes and multi-modal embeddings. We assess the return on investment (ROI) of our source enrichment framework by comparing organic user engagement sources, such as content viewing, with ad-impression sources. The proposed method can boost the area under curve (AUC) and the slope of scaling curves for ad-impression sources by 1.56 to 2 times compared to organic usage sources even for short online-sequence lengths of 100 to 10K. Additionally, click-through rate (CTR) prediction improves by 0.56% AUC over the baseline production ad-recommendation system when using enriched ad-impression event sources, leading to improved sequence scaling resolutions for longer and offline user-ad representations.
[LG-23] RadioDiff-Flux: Efficient Radio Map Construction via Generative Denoise Diffusion Model Trajectory Midpoint Reuse
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02790
作者: Xiucheng Wang,Peilin Zheng,Honggang Jia,Nan Cheng,Ruijin Sun,Conghao Zhou,Xuemin Shen
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Signal Processing (eess.SP)
*备注:
Abstract:Accurate radio map (RM) construction is essential to enabling environment-aware and adaptive wireless communication. However, in future 6G scenarios characterized by high-speed network entities and fast-changing environments, it is very challenging to meet real-time requirements. Although generative diffusion models (DMs) can achieve state-of-the-art accuracy with second-level delay, their iterative nature leads to prohibitive inference latency in delay-sensitive scenarios. In this paper, by uncovering a key structural property of diffusion processes: the latent midpoints remain highly consistent across semantically similar scenes, we propose RadioDiff-Flux, a novel two-stage latent diffusion framework that decouples static environmental modeling from dynamic refinement, enabling the reuse of precomputed midpoints to bypass redundant denoising. In particular, the first stage generates a coarse latent representation using only static scene features, which can be cached and shared across similar scenarios. The second stage adapts this representation to dynamic conditions and transmitter locations using a pre-trained model, thereby avoiding repeated early-stage computation. The proposed RadioDiff-Flux significantly reduces inference time while preserving fidelity. Experiment results show that RadioDiff-Flux can achieve up to 50 acceleration with less than 0.15% accuracy loss, demonstrating its practical utility for fast, scalable RM generation in future 6G networks.
[LG-24] Scalable Tree Ensemble Proximities in Python
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02735
作者: Adrien Aumon,Guy Wolf,Kevin R. Moon,Jake S. Rhodes
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Data Structures and Algorithms (cs.DS); Performance (cs.PF)
*备注:
Abstract:Tree ensemble methods such as Random Forests naturally induce supervised similarity measures through their decision tree structure, but existing implementations of proximities derived from tree ensembles typically suffer from quadratic time or memory complexity, limiting their scalability. In this work, we introduce a general framework for efficient proximity computation by defining a family of Separable Weighted Leaf-Collision Proximities. We show that any proximity measure in this family admits an exact sparse matrix factorization, restricting computation to leaf-level collisions and avoiding explicit pairwise comparisons. This formulation enables low-memory, scalable proximity computation using sparse linear algebra in Python. Empirical benchmarks demonstrate substantial runtime and memory improvements over traditional approaches, allowing tree ensemble proximities to scale efficiently to datasets with hundreds of thousands of samples on standard CPU hardware.
[LG-25] CRoPE: Efficient Parametrization of Rotary Positional Embedding
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02728
作者: Beicheng Lou,Zifei Xu
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Rotary positional embedding has become the state-of-the-art approach to encode position information in transformer-based models. While it is often succinctly expressed in complex linear algebra, we note that the actual implementation of Q/K/V -projections is not equivalent to a complex linear transformation. We argue that complex linear transformation is a more natural parametrization and saves near 50% parameters within the attention block. We show empirically that removing such redundancy has negligible impact on the model performance both in sample and out of sample. Our modification achieves more efficient parameter usage, as well as a cleaner interpretation of the representation space.
[LG-26] Scaling Laws of Machine Learning for Optimal Power Flow
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02706
作者: Xinyi Liu,Xuan He,Yize Chen
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Systems and Control (eess.SY)
*备注: 5 pages
Abstract:Optimal power flow (OPF) is one of the fundamental tasks for power system operations. While machine learning (ML) approaches such as deep neural networks (DNNs) have been widely studied to enhance OPF solution speed and performance, their practical deployment faces two critical scaling questions: What is the minimum training data volume required for reliable results? How should ML models’ complexity balance accuracy with real-time computational limits? Existing studies evaluate discrete scenarios without quantifying these scaling relationships, leading to trial-and-error-based ML development in real-world applications. This work presents the first systematic scaling study for ML-based OPF across two dimensions: data scale (0.1K-40K training samples) and compute scale (multiple NN architectures with varying FLOPs). Our results reveal consistent power-law relationships on both DNNs and physics-informed NNs (PINNs) between each resource dimension and three core performance metrics: prediction error (MAE), constraint violations and speed. We find that for ACOPF, the accuracy metric scales with dataset size and training compute. These scaling laws enable predictable and principled ML pipeline design for OPF. We further identify the divergence between prediction accuracy and constraint feasibility and characterize the compute-optimal frontier. This work provides quantitative guidance for ML-OPF design and deployments.
[LG-27] Which Deep Learner? A Systematic Evaluation of Advanced Deep Forecasting Models Accuracy and Efficiency for Network Traffic Prediction
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02694
作者: Eilaf MA Babai,Aalaa MA Babai,Koji Okamura
类目: Networking and Internet Architecture (cs.NI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 19 pages, 13 figures
Abstract:Network traffic prediction is essential for automating modern network management. It is a difficult time series forecasting (TSF) problem that has been addressed by Deep Learning (DL) models due to their ability to capture complex patterns. Advances in forecasting, from sophisticated transformer architectures to simple linear models, have improved performance across diverse prediction tasks. However, given the variability of network traffic across network environments and traffic series timescales, it is essential to identify effective deployment choices and modeling directions for network traffic prediction. This study systematically identify and evaluates twelve advanced TSF models -including transformer-based and traditional DL approaches, each with unique advantages for network traffic prediction- against three statistical baselines on four real traffic datasets, across multiple time scales and horizons, assessing performance, robustness to anomalies, data gaps, external factors, data efficiency, and resource efficiency in terms of time, memory, and energy. Results highlight performance regimes, efficiency thresholds, and promising architectures that balance accuracy and efficiency, demonstrating robustness to traffic challenges and suggesting new directions beyond traditional RNNs.
[LG-28] Adversarial Contrastive Learning for LLM Quantization Attacks
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02680
作者: Dinghong Song,Zhiwei Xu,Hai Wan,Xibin Zhao,Pengfei Su,Dong Li
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 14 pages, 5 figures
Abstract:Model quantization is critical for deploying large language models (LLMs) on resource-constrained hardware, yet recent work has revealed severe security risks that benign LLMs in full precision may exhibit malicious behaviors after quantization. In this paper, we propose Adversarial Contrastive Learning (ACL), a novel gradient-based quantization attack that achieves superior attack effectiveness by explicitly maximizing the gap between benign and harmful responses probabilities. ACL formulates the attack objective as a triplet-based contrastive loss, and integrates it with a projected gradient descent two-stage distributed fine-tuning strategy to ensure stable and efficient optimization. Extensive experiments demonstrate ACL’s remarkable effectiveness, achieving attack success rates of 86.00% for over-refusal, 97.69% for jailbreak, and 92.40% for advertisement injection, substantially outperforming state-of-the-art methods by up to 44.67%, 18.84%, and 50.80%, respectively.
[LG-29] Uni-FinLLM : A Unified Multimodal Large Language Model with Modular Task Heads for Micro-Level Stock Prediction and Macro-Level Systemic Risk Assessment
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02677
作者: Gongao Zhang,Haijiang Zeng,Lu Jiang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Risk Management (q-fin.RM); Statistical Finance (q-fin.ST)
*备注:
Abstract:Financial institutions and regulators require systems that integrate heterogeneous data to assess risks from stock fluctuations to systemic vulnerabilities. Existing approaches often treat these tasks in isolation, failing to capture cross-scale dependencies. We propose Uni-FinLLM, a unified multimodal large language model that uses a shared Transformer backbone and modular task heads to jointly process financial text, numerical time series, fundamentals, and visual data. Through cross-modal attention and multi-task optimization, it learns a coherent representation for micro-, meso-, and macro-level predictions. Evaluated on stock forecasting, credit-risk assessment, and systemic-risk detection, Uni-FinLLM significantly outperforms baselines. It raises stock directional accuracy to 67.4% (from 61.7%), credit-risk accuracy to 84.1% (from 79.6%), and macro early-warning accuracy to 82.3%. Results validate that a unified multimodal LLM can jointly model asset behavior and systemic vulnerabilities, offering a scalable decision-support engine for finance.
[LG-30] MAFS: Multi-head Attention Feature Selection for High-Dimensional Data via Deep Fusion of Filter Methods
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02668
作者: Xiaoyan Sun,Qingyu Meng,Yalu Wen
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Methodology (stat.ME)
*备注:
Abstract:Feature selection is essential for high-dimensional biomedical data, enabling stronger predictive performance, reduced computational cost, and improved interpretability in precision medicine applications. Existing approaches face notable challenges. Filter methods are highly scalable but cannot capture complex relationships or eliminate redundancy. Deep learning-based approaches can model nonlinear patterns but often lack stability, interpretability, and efficiency at scale. Single-head attention improves interpretability but is limited in capturing multi-level dependencies and remains sensitive to initialization, reducing reproducibility. Most existing methods rarely combine statistical interpretability with the representational power of deep learning, particularly in ultra-high-dimensional settings. Here, we introduce MAFS (Multi-head Attention-based Feature Selection), a hybrid framework that integrates statistical priors with deep learning capabilities. MAFS begins with filter-based priors for stable initialization and guide learning. It then uses multi-head attention to examine features from multiple perspectives in parallel, capturing complex nonlinear relationships and interactions. Finally, a reordering module consolidates outputs across attention heads, resolving conflicts and minimizing information loss to generate robust and consistent feature rankings. This design combines statistical guidance with deep modeling capacity, yielding interpretable importance scores while maximizing retention of informative signals. Across simulated and real-world datasets, including cancer gene expression and Alzheimer’s disease data, MAFS consistently achieves superior coverage and stability compared with existing filter-based and deep learning-based alternatives, offering a scalable, interpretable, and robust solution for feature selection in high-dimensional biomedical data.
[LG-31] When Prompting Meets Spiking: Graph Sparse Prompting via Spiking Graph Prompt Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02662
作者: Bo Jiang,Weijun Zhao,Beibei Wang,Jin Tang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Graph Prompt Feature (GPF) learning has been widely used in adapting pre-trained GNN model on the downstream task. GPFs first introduce some prompt atoms and then learns the optimal prompt vector for each graph node using the linear combination of prompt atoms. However, existing GPFs generally conduct prompting over node’s all feature dimensions which is obviously redundant and also be sensitive to node feature noise. To overcome this issue, for the first time, this paper proposes learning sparse graph prompts by leveraging the spiking neuron mechanism, termed Spiking Graph Prompt Feature (SpikingGPF). Our approach is motivated by the observation that spiking neuron can perform inexpensive information processing and produce sparse outputs which naturally fits the task of our graph sparse prompting. Specifically, SpikingGPF has two main aspects. First, it learns a sparse prompt vector for each node by exploiting a spiking neuron architecture, enabling prompting on selective node features. This yields a more compact and lightweight prompting design while also improving robustness against node noise. Second, SpikingGPF introduces a novel prompt representation learning model based on sparse representation theory, i.e., it represents each node prompt as a sparse combination of prompt atoms. This encourages a more compact representation and also facilitates efficient computation. Extensive experiments on several benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of SpikingGPF.
[LG-32] SWaRL: Safeguard Code Watermarking via Reinforcement Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02602
作者: Neusha Javidnia,Ruisi Zhang,Ashish Kundu,Farinaz Koushanfar
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Under review
Abstract:We present SWaRL, a robust and fidelity-preserving watermarking framework designed to protect the intellectual property of code LLM owners by embedding unique and verifiable signatures in the generated output. Existing approaches rely on manually crafted transformation rules to preserve watermarked code functionality or manipulate token-generation probabilities at inference time, which are prone to compilation errors. To address these challenges, SWaRL employs a reinforcement learning-based co-training framework that uses compiler feedback for functional correctness and a jointly trained confidential verifier as a reward signal to maintain watermark detectability. Furthermore, SWaRL employs low-rank adaptation (LoRA) during fine-tuning, allowing the learned watermark information to be transferable across model updates. Extensive experiments show that SWaRL achieves higher watermark detection accuracy compared to prior methods while fully maintaining watermarked code functionality. The LoRA-based signature embedding steers the base model to generate and solve code in a watermark-specific manner without significant computational overhead. Moreover, SWaRL exhibits strong resilience against refactoring and adversarial transformation attacks.
[LG-33] hreat Detection in Social Media Networks Using Machine Learning Based Network Analysis
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02581
作者: Aditi Sanjay Agrawal
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 11 Pages, 6 figures
Abstract:The accelerated development of social media websites has posed intricate security issues in cyberspace, where these sites have increasingly become victims of criminal activities including attempts to intrude into them, abnormal traffic patterns, and organized attacks. The conventional rule-based security systems are not always scalable and dynamic to meet such a threat. This paper introduces a threat detection framework based on machine learning that can be used to classify malicious behavior in the social media network environment based on the nature of network traffic. Exploiting a rich network traffic dataset, the massive preprocessing and exploratory data analysis is conducted to overcome the problem of data imbalance, feature inconsistency, and noise. A model of artificial neural network (ANN) is then created to acquire intricate, non-linear tendencies of malicious actions. The proposed model is tested on conventional performance metrics, such as accuracy, accuracy, recall, F1-score, and ROC-AUC, and shows good detection and high levels of strength. The findings suggest that neural network-based solutions have the potential to be used effectively to identify the latent threat dynamics within the context of a large-scale social media network and that they can be employed to complement the existing intrusion detection system and better to conduct proactive cybersecurity operations.
[LG-34] CutisAI: Deep Learning Framework for Automated Dermatology and Cancer Screening
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02562
作者: Rohit Kaushik,Eva Kaushik
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
*备注: 10 pages, 3 figures
Abstract:The rapid growth of dermatological imaging and mobile diagnostic tools calls for systems that not only demonstrate empirical performance but also provide strong theoretical guarantees. Deep learning models have shown high predictive accuracy; however, they are often criticized for lacking well, calibrated uncertainty estimates without which these models are hardly deployable in a clinical setting. To this end, we present the Conformal Bayesian Dermatological Classifier (CBDC), a well, founded framework that combines Statistical Learning Theory, Topological Data Analysis (TDA), and Bayesian Conformal Inference. CBDC offers distribution, dependent generalization bounds that reflect dermatological variability, proves a topological stability theorem that guarantees the invariance of convolutional neural network embeddings under photometric and morphological perturbations and provides finite conformal coverage guarantees for trustworthy uncertainty quantification. Through exhaustive experiments on the HAM10000, PH2, and ISIC 2020 datasets, we show that CBDC not only attains classification accuracy but also generates calibrated predictions that are interpretable from a clinical perspective. This research constitutes a theoretical and practical leap for deep dermatological diagnostics, thereby opening the machine learning theory clinical applicability interface. Comments: 10 pages, 3 figures Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02562 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2601.02562v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02562 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-35] Multi-scale Graph Autoregressive Modeling: Molecular Property Prediction via Next Token Prediction
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02530
作者: Zhuoyang Jiang,Yaosen Min,Peiran Jin,Lei Chen
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Quantitative Methods (q-bio.QM)
*备注:
Abstract:We present Connection-Aware Motif Sequencing (CamS), a graph-to-sequence representation that enables decoder-only Transformers to learn molecular graphs via standard next-token prediction (NTP). For molecular property prediction, SMILES-based NTP scales well but lacks explicit topology, whereas graph-native masked modeling captures connectivity but risks disrupting the pivotal chemical details (e.g., activity cliffs). CamS bridges this gap by serializing molecular graphs into structure-rich causal sequences. CamS first mines data-driven connection-aware motifs. It then serializes motifs via scaffold-rooted breadth-first search (BFS) to establish a stable core-to-periphery order. Crucially, CamS enables hierarchical modeling by concatenating sequences from fine to coarse motif scales, allowing the model to condition global scaffolds on dense, uncorrupted local structural evidence. We instantiate CamS-LLaMA by pre-training a vanilla LLaMA backbone on CamS sequences. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on MoleculeNet and the activity-cliff benchmark MoleculeACE, outperforming both SMILES-based language models and strong graph baselines. Interpretability analysis confirms that our multi-scale causal serialization effectively drives attention toward cliff-determining differences.
[LG-36] LLM -Enhanced Reinforcement Learning for Time Series Anomaly Detection
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02511
作者: Bahareh Golchin,Banafsheh Rekabdar,Danielle Justo
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Detecting anomalies in time series data is crucial for finance, healthcare, sensor networks, and industrial monitoring applications. However, time series anomaly detection often suffers from sparse labels, complex temporal patterns, and costly expert annotation. We propose a unified framework that integrates Large Language Model (LLM)-based potential functions for reward shaping with Reinforcement Learning (RL), Variational Autoencoder (VAE)-enhanced dynamic reward scaling, and active learning with label propagation. An LSTM-based RL agent leverages LLM-derived semantic rewards to guide exploration, while VAE reconstruction errors add unsupervised anomaly signals. Active learning selects the most uncertain samples, and label propagation efficiently expands labeled data. Evaluations on Yahoo-A1 and SMD benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art detection accuracy under limited labeling budgets and operates effectively in data-constrained settings. This study highlights the promise of combining LLMs with RL and advanced unsupervised techniques for robust, scalable anomaly detection in real-world applications.
[LG-37] hdlib 2.0: Extending Machine Learning Capabilities of Vector-Symbolic Architectures
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02509
作者: Fabio Cumbo,Kabir Dhillon,Daniel Blankenberg
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 7 pages, 1 figure
Abstract:Following the initial publication of hdlib, a Python library for designing Vector-Symbolic Architectures (VSA), we introduce a major extension that significantly enhances its machine learning capabilities. VSA, also known as Hyperdimensional Computing, is a computing paradigm that represents and processes information using high-dimensional vectors. While the first version of hdlib established a robust foundation for creating and manipulating these vectors, this update addresses the growing need for more advanced, data-driven modeling within the VSA framework. Here, we present four extensions: significant enhancements to the existing supervised classification model also enabling feature selection, and a new regression model for predicting continuous variables, a clustering model for unsupervised learning, and a graph-based learning model. Furthermore, we propose the first implementation ever of Quantum Hyperdimensional Computing with quantum-powered arithmetic operations and a new Quantum Machine Learning model for supervised learning. hdlib remains open-source and available on GitHub at this https URL under the MIT license, and distributed through the Python Package Index (pip install hdlib) and Conda (conda install -c conda-forge hdlib). Documentation and examples of these new features are available on the official Wiki at this https URL.
[LG-38] Polynomial Convergence of Riemannian Diffusion Models
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02499
作者: Xingyu Xu,Ziyi Zhang,Yorie Nakahira,Guannan Qu,Yuejie Chi
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable empirical success in the recent years and are considered one of the state-of-the-art generative models in modern AI. These models consist of a forward process, which gradually diffuses the data distribution to a noise distribution spanning the whole space, and a backward process, which inverts this transformation to recover the data distribution from noise. Most of the existing literature assumes that the underlying space is Euclidean. However, in many practical applications, the data are constrained to lie on a submanifold of Euclidean space. Addressing this setting, De Bortoli et al. (2022) introduced Riemannian diffusion models and proved that using an exponentially small step size yields a small sampling error in the Wasserstein distance, provided the data distribution is smooth and strictly positive, and the score estimate is L_\infty -accurate. In this paper, we greatly strengthen this theory by establishing that, under L_2 -accurate score estimate, a \em polynomially small stepsize suffices to guarantee small sampling error in the total variation distance, without requiring smoothness or positivity of the data distribution. Our analysis only requires mild and standard curvature assumptions on the underlying manifold. The main ingredients in our analysis are Li-Yau estimate for the log-gradient of heat kernel, and Minakshisundaram-Pleijel parametrix expansion of the perturbed heat equation. Our approach opens the door to a sharper analysis of diffusion models on non-Euclidean spaces.
[LG-39] Variational (Energy-Based) Spectral Learning: A Machine Learning Framework for Solving Partial Differential Equations
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02492
作者: M. M. Hammad
类目: Numerical Analysis (math.NA); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:We introduce variational spectral learning (VSL), a machine learning framework for solving partial differential equations (PDEs) that operates directly in the coefficient space of spectral expansions. VSL offers a principled bridge between variational PDE theory, spectral discretization, and contemporary machine learning practice. The core idea is to recast a given PDE [ \mathcalLu = f \quad \textin \quad Q=\Omega\times(0,T), ] together with boundary and initial conditions, into differentiable space–time energies built from strong-form least-squares residuals and weak (Galerkin) formulations. The solution is represented as a finite spectral expansion [ u_N(x,t)=\sum_n=1^N c_n,\phi_n(x,t), ] where \phi_n are tensor-product Chebyshev bases in space and time, with Dirichlet-satisfying spatial modes enforcing homogeneous boundary conditions analytically. This yields a compact linear parameterization in the coefficient vector \mathbfc , while all PDE complexity is absorbed into the variational energy. We show how to construct strong-form and weak-form space-time functionals, augment them with initial-condition and Tikhonov regularization terms, and minimize the resulting objective with gradient-based optimization. In practice, VSL is implemented in TensorFlow using automatic differentiation and Keras cosine-decay-with-restarts learning-rate schedules, enabling robust optimization of moderately sized coefficient vectors. Numerical experiments on benchmark elliptic and parabolic problems, including one- and two-dimensional Poisson, diffusion, and Burgers-type equations, demonstrate that VSL attains accuracy comparable to classical spectral collocation with Crank-Nicolson time stepping, while providing a differentiable objective suitable for modern optimization tooling.
[LG-40] Physical Transformer
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02433
作者: Tao Xu,Zhixin Hu,Li Luo,Momiao Xiong
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 38 pages, 2 figures
Abstract:Digital AI systems spanning large language models, vision models, and generative architectures that operate primarily in symbolic, linguistic, or pixel domains. They have achieved striking progress, but almost all of this progress lives in virtual spaces. These systems transform embeddings and tokens, yet do not themselves touch the world and rarely admit a physical interpretation. In this work we propose a physical transformer that couples modern transformer style computation with geometric representation and physical dynamics. At the micro level, attention heads, and feed-forward blocks are modeled as interacting spins governed by effective Hamiltonians plus non-Hamiltonian bath terms. At the meso level, their aggregated state evolves on a learned Neural Differential Manifold (NDM) under Hamiltonian flows and Hamilton, Jacobi, Bellman (HJB) optimal control, discretized by symplectic layers that approximately preserve geometric and energetic invariants. At the macro level, the model maintains a generative semantic workspace and a two-dimensional information-phase portrait that tracks uncertainty and information gain over a reasoning trajectory. Within this hierarchy, reasoning tasks are formulated as controlled information flows on the manifold, with solutions corresponding to low cost trajectories that satisfy geometric, energetic, and workspace-consistency constraints. On simple toy problems involving numerical integration and dynamical systems, the physical transformer outperforms naive baselines in stability and long-horizon accuracy, highlighting the benefits of respecting underlying geometric and Hamiltonian structure. More broadly, the framework suggests a path toward physical AI that unify digital reasoning with physically grounded manifolds, opening a route to more interpretable and potentially unified models of reasoning, control, and interaction with the real world.
[LG-41] Quantifying Quanvolutional Neural Networks Robustness for Speech in Healthcare Applications
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02432
作者: Ha Tran,Bipasha Kashyap,Pubudu N. Pathirana
类目: ound (cs.SD); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS)
*备注:
Abstract:Speech-based machine learning systems are sensitive to noise, complicating reliable deployment in emotion recognition and voice pathology detection. We evaluate the robustness of a hybrid quantum machine learning model, quanvolutional neural networks (QNNs) against classical convolutional neural networks (CNNs) under four acoustic corruptions (Gaussian noise, pitch shift, temporal shift, and speed variation) in a clean-train/corrupted-test regime. Using AVFAD (voice pathology) and TESS (speech emotion), we compare three QNN models (Random, Basic, Strongly) to a simple CNN baseline (CNN-Base), ResNet-18 and VGG-16 using accuracy and corruption metrics (CE, mCE, RCE, RmCE), and analyze architectural factors (circuit complexity or depth, convergence) alongside per-emotion robustness. QNNs generally outperform the CNN-Base under pitch shift, temporal shift, and speed variation (up to 22% lower CE/RCE at severe temporal shift), while the CNN-Base remains more resilient to Gaussian noise. Among quantum circuits, QNN-Basic achieves the best overall robustness on AVFAD, and QNN-Random performs strongest on TESS. Emotion-wise, fear is most robust (80-90% accuracy under severe corruptions), neutral can collapse under strong Gaussian noise (5.5% accuracy), and happy is most vulnerable to pitch, temporal, and speed distortions. QNNs also converge up to six times faster than the CNN-Base. To our knowledge, this is a systematic study of QNN robustness for speech under common non-adversarial acoustic corruptions, indicating that shallow entangling quantum front-ends can improve noise resilience while sensitivity to additive noise remains a challenge.
[LG-42] Spiking Heterogeneous Graph Attention Networks AAAI2026
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02401
作者: Buqing Cao,Qian Peng,Xiang Xie,Liang Chen,Min Shi,Jianxun Liu
类目: Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Social and Information Networks (cs.SI)
*备注: This paper has been accepted by AAAI 2026
Abstract:Real-world graphs or networks are usually heterogeneous, involving multiple types of nodes and relationships. Heterogeneous graph neural networks (HGNNs) can effectively handle these diverse nodes and edges, capturing heterogeneous information within the graph, thus exhibiting outstanding performance. However, most methods of HGNNs usually involve complex structural designs, leading to problems such as high memory usage, long inference time, and extensive consumption of computing resources. These limitations pose certain challenges for the practical application of HGNNs, especially for resource-constrained devices. To mitigate this issue, we propose the Spiking Heterogeneous Graph Attention Networks (SpikingHAN), which incorporates the brain-inspired and energy-saving properties of Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) into heterogeneous graph learning to reduce the computing cost without compromising the performance. Specifically, SpikingHAN aggregates metapath-based neighbor information using a single-layer graph convolution with shared parameters. It then employs a semantic-level attention mechanism to capture the importance of different meta-paths and performs semantic aggregation. Finally, it encodes the heterogeneous information into a spike sequence through SNNs, simulating bioinformatic processing to derive a binarized 1-bit representation of the heterogeneous graph. Comprehensive experimental results from three real-world heterogeneous graph datasets show that SpikingHAN delivers competitive node classification performance. It achieves this with fewer parameters, quicker inference, reduced memory usage, and lower energy consumption. Code is available at this https URL.
[LG-43] Self-Supervised Learning from Noisy and Incomplete Data
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03244
作者: Julián Tachella,Mike Davies
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
*备注:
Abstract:Many important problems in science and engineering involve inferring a signal from noisy and/or incomplete observations, where the observation process is known. Historically, this problem has been tackled using hand-crafted regularization (e.g., sparsity, total-variation) to obtain meaningful estimates. Recent data-driven methods often offer better solutions by directly learning a solver from examples of ground-truth signals and associated observations. However, in many real-world applications, obtaining ground-truth references for training is expensive or impossible. Self-supervised learning methods offer a promising alternative by learning a solver from measurement data alone, bypassing the need for ground-truth references. This manuscript provides a comprehensive summary of different self-supervised methods for inverse problems, with a special emphasis on their theoretical underpinnings, and presents practical applications in imaging inverse problems.
[LG-44] Shallow-circuit Supervised Learning on a Quantum Processor
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03235
作者: Luca Candelori,Swarnadeep Majumder,Antonio Mezzacapo,Javier Robledo Moreno,Kharen Musaelian,Santhanam Nagarajan,Sunil Pinnamaneni,Kunal Sharma,Dario Villani
类目: Quantum Physics (quant-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注:
Abstract:Quantum computing has long promised transformative advances in data analysis, yet practical quantum machine learning has remained elusive due to fundamental obstacles such as a steep quantum cost for the loading of classical data and poor trainability of many quantum machine learning algorithms designed for near-term quantum hardware. In this work, we show that one can overcome these obstacles by using a linear Hamiltonian-based machine learning method which provides a compact quantum representation of classical data via ground state problems for k-local Hamiltonians. We use the recent sample-based Krylov quantum diagonalization method to compute low-energy states of the data Hamiltonians, whose parameters are trained to express classical datasets through local gradients. We demonstrate the efficacy and scalability of the methods by performing experiments on benchmark datasets using up to 50 qubits of an IBM Heron quantum processor.
[LG-45] Gradient descent reliably finds depth- and gate-optimal circuits for generic unitaries
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03123
作者: Janani Gomathi,Alex Meiburg
类目: Quantum Physics (quant-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 14 pages, 17 figures
Abstract:When the gate set has continuous parameters, synthesizing a unitary operator as a quantum circuit is always possible using exact methods, but finding minimal circuits efficiently remains a challenging problem. The landscape is very different for compiled unitaries, which arise from programming and typically have short circuits, as compared with generic unitaries, which use all parameters and typically require circuits of maximal size. We show that simple gradient descent reliably finds depth- and gate-optimal circuits for generic unitaries, including in the presence of restricted chip connectivity. This runs counter to earlier evidence that optimal synthesis required combinatorial search, and we show that this discrepancy can be explained by avoiding the random selection of certain parameter-deficient circuit skeletons.
[LG-46] Enhanced 3D Gravity Inversion Using ResU-Net with Density Logging Constraints: A Dual-Phase Training Approach
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02890
作者: Siyuan Dong,Jinghuai Gao,Shuai Zhou,Baohai Wu,Hongfa Jia
类目: Geophysics (physics.geo-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Gravity exploration has become an important geophysical method due to its low cost and high efficiency. With the rise of artificial intelligence, data-driven gravity inversion methods based on deep learning (DL) possess physical property recovery capabilities that conventional regularization methods lack. However, existing DL methods suffer from insufficient prior information constraints, which leads to inversion models with large data fitting errors and unreliable results. Moreover, the inversion results lack constraints and matching from other exploration methods, leading to results that may contradict known geological conditions. In this study, we propose a novel approach that integrates prior density well logging information to address the above issues. First, we introduce a depth weighting function to the neural network (NN) and train it in the weighted density parameter domain. The NN, under the constraint of the weighted forward operator, demonstrates improved inversion performance, with the resulting inversion model exhibiting smaller data fitting errors. Next, we divide the entire network training into two phases: first training a large pre-trained network Net-I, and then using the density logging information as the constraint to get the optimized fine-tuning network Net-II. Through testing and comparison in synthetic models and Bishop Model, the inversion quality of our method has significantly improved compared to the unconstrained data-driven DL inversion method. Additionally, we also conduct a comparison and discussion between our method and both the conventional focusing inversion (FI) method and its well logging constrained variant. Finally, we apply this method to the measured data from the San Nicolas mining area in Mexico, comparing and analyzing it with two recent gravity inversion methods based on DL.
[LG-47] STIPP: Space-time in situ postprocessing over the French Alps using proper scoring rules
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02882
作者: David Landry,Isabelle Gouttevin,Hugo Merizen,Claire Monteleoni,Anastase Charantonis
类目: Atmospheric and Oceanic Physics (physics.ao-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 17 pages, 11 figures
Abstract:We propose Space-time in situ postprocessing (STIPP), a machine learning model that generates spatio-temporally consistent weather forecasts for a network of station locations. Gridded forecasts from classical numerical weather prediction or data-driven models often lack the necessary precision due to unresolved local effects. Typical statistical postprocessing methods correct these biases, but often degrade spatio-temporal correlation structures in doing so. Recent works based on generative modeling successfully improve spatial correlation structures but have to forecast every lead time independently. In contrast, STIPP makes joint spatio-temporal forecasts which have increased accuracy for surface temperature, wind, relative humidity and precipitation when compared to baseline methods. It makes hourly ensemble predictions given only a six-hourly deterministic forecast, blending the boundaries of postprocessing and temporal interpolation. By leveraging a multivariate proper scoring rule for training, STIPP contributes to ongoing work data-driven atmospheric models supervised only with distribution marginals.
[LG-48] Fast Conformal Prediction using Conditional Interquantile Intervals
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02769
作者: Naixin Guo,Rui Luo,Zhixin Zhou
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:We introduce Conformal Interquantile Regression (CIR), a conformal regression method that efficiently constructs near-minimal prediction intervals with guaranteed coverage. CIR leverages black-box machine learning models to estimate outcome distributions through interquantile ranges, transforming these estimates into compact prediction intervals while achieving approximate conditional coverage. We further propose CIR+ (Conditional Interquantile Regression with More Comparison), which enhances CIR by incorporating a width-based selection rule for interquantile intervals. This refinement yields narrower prediction intervals while maintaining comparable coverage, though at the cost of slightly increased computational time. Both methods address key limitations of existing distributional conformal prediction approaches: they handle skewed distributions more effectively than Conformalized Quantile Regression, and they achieve substantially higher computational efficiency than Conformal Histogram Regression by eliminating the need for histogram construction. Extensive experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that our methods optimally balance predictive accuracy and computational efficiency compared to existing approaches.
[LG-49] Statistical Inference for Fuzzy Clustering
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02656
作者: Qiuyi Wu,Zihan Zhu,Anru R. Zhang
类目: Methodology (stat.ME); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Clustering is a central tool in biomedical research for discovering heterogeneous patient subpopulations, where group boundaries are often diffuse rather than sharply separated. Traditional methods produce hard partitions, whereas soft clustering methods such as fuzzy c -means (FCM) allow mixed memberships and better capture uncertainty and gradual transitions. Despite the widespread use of FCM, principled statistical inference for fuzzy clustering remains limited. We develop a new framework for weighted fuzzy c -means (WFCM) for settings with potential cluster size imbalance. Cluster-specific weights rebalance the classical FCM criterion so that smaller clusters are not overwhelmed by dominant groups, and the weighted objective induces a normalized density model with scale parameter \sigma and fuzziness parameter m . Estimation is performed via a blockwise majorize–minimize (MM) procedure that alternates closed-form membership and centroid updates with likelihood-based updates of (\sigma,\bw) . The intractable normalizing constant is approximated by importance sampling using a data-adaptive Gaussian mixture proposal. We further provide likelihood ratio tests for comparing cluster centers and bootstrap-based confidence intervals. We establish consistency and asymptotic normality of the maximum likelihood estimator, validate the method through simulations, and illustrate it using single-cell RNA-seq and Alzheimer disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) data. These applications demonstrate stable uncertainty quantification and biologically meaningful soft memberships, ranging from well-separated cell populations under imbalance to a graded AD versus non-AD continuum consistent with disease progression. Subjects: Methodology (stat.ME); Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02656 [stat.ME] (or arXiv:2601.02656v1 [stat.ME] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02656 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-50] First Provably Optimal Asynchronous SGD for Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Data
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02523
作者: Artavazd Maranjyan
类目: Optimization and Control (math.OC); Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注: PhD thesis
Abstract:Artificial intelligence has advanced rapidly through large neural networks trained on massive datasets using thousands of GPUs or TPUs. Such training can occupy entire data centers for weeks and requires enormous computational and energy resources. Yet the optimization algorithms behind these runs have not kept pace. Most large scale training still relies on synchronous methods, where workers must wait for the slowest device, wasting compute and amplifying the effects of hardware and network variability. Removing synchronization seems like a simple fix, but asynchrony introduces staleness, meaning updates computed on outdated models. This makes analysis difficult, especially when delays arise from system level randomness rather than algorithmic choices. As a result, the time complexity of asynchronous methods remains poorly understood. This dissertation develops a rigorous framework for asynchronous first order stochastic optimization, focusing on the core challenge of heterogeneous worker speeds. Within this framework, we show that with proper design, asynchronous SGD can achieve optimal time complexity, matching guarantees previously known only for synchronous methods. Our first contribution, Ringmaster ASGD, attains optimal time complexity in the homogeneous data setting by selectively discarding stale updates. The second, Ringleader ASGD, extends optimality to heterogeneous data, common in federated learning, using a structured gradient table mechanism. Finally, ATA improves resource efficiency by learning worker compute time distributions and allocating tasks adaptively, achieving near optimal wall clock time with less computation. Together, these results establish asynchronous optimization as a theoretically sound and practically efficient foundation for distributed learning, showing that coordination without synchronization can be both feasible and optimal.
信息检索
[IR-0] Parallel Latent Reasoning for Sequential Recommendation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.03153
作者: Jiakai Tang,Xu Chen,Wen Chen,Jian Wu,Yuning Jiang,Bo Zheng
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注:
Abstract:Capturing complex user preferences from sparse behavioral sequences remains a fundamental challenge in sequential recommendation. Recent latent reasoning methods have shown promise by extending test-time computation through multi-step reasoning, yet they exclusively rely on depth-level scaling along a single trajectory, suffering from diminishing returns as reasoning depth increases. To address this limitation, we propose \textbfParallel Latent Reasoning (PLR), a novel framework that pioneers width-level computational scaling by exploring multiple diverse reasoning trajectories simultaneously. PLR constructs parallel reasoning streams through learnable trigger tokens in continuous latent space, preserves diversity across streams via global reasoning regularization, and adaptively synthesizes multi-stream outputs through mixture-of-reasoning-streams aggregation. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that PLR substantially outperforms state-of-the-art baselines while maintaining real-time inference efficiency. Theoretical analysis further validates the effectiveness of parallel reasoning in improving generalization capability. Our work opens new avenues for enhancing reasoning capacity in sequential recommendation beyond existing depth scaling.
[IR-1] Auditing Search Query Suggestion Bias Through Recursive Algorithm Interrogation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02962
作者: Fabian Haak,Philipp Schaer
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注:
Abstract:Despite their important role in online information search, search query suggestions have not been researched as much as most other aspects of search engines. Although reasons for this are multi-faceted, the sparseness of context and the limited data basis of up to ten suggestions per search query pose the most significant problem in identifying bias in search query suggestions. The most proven method to reduce sparseness and improve the validity of bias identification of search query suggestions so far is to consider suggestions from subsequent searches over time for the same query. This work presents a new, alternative approach to search query bias identification that includes less high-level suggestions to deepen the data basis of bias analyses. We employ recursive algorithm interrogation techniques and create suggestion trees that enable access to more subliminal search query suggestions. Based on these suggestions, we investigate topical group bias in person-related searches in the political domain.
[IR-2] HarmonRank: Ranking-aligned Multi-objective Ensemble for Live-streaming E-commerce Recommendation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02955
作者: Boyang Xia,Zhou Yu,Zhiliang Zhu,Hanxiao Sun,Biyun Han,Jun Wang,Runnan Liu,Wenwu Ou
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注: 11 pages, 5 figures
Abstract:Recommendation for live-streaming e-commerce is gaining increasing attention due to the explosive growth of the live streaming economy. Different from traditional e-commerce, live-streaming e-commerce shifts the focus from products to streamers, which requires ranking mechanism to balance both purchases and user-streamer interactions for long-term ecology. To trade off multiple objectives, a popular solution is to build an ensemble model to integrate multi-objective scores into a unified score. The ensemble model is usually supervised by multiple independent binary classification losses of all objectives. However, this paradigm suffers from two inherent limitations. First, the optimization direction of the binary classification task is misaligned with the ranking task (evaluated by AUC). Second, this paradigm overlooks the alignment between objectives, e.g., comment and buy behaviors are partially dependent which can be revealed in labels correlations. The model can achieve better trade-offs if it learns the aligned parts of ranking abilities among different objectives. To mitigate these limitations, we propose a novel multi-objective ensemble framework HarmonRank to fulfill both alignment to the ranking task and alignment among objectives. For alignment to ranking, we formulate ranking metric AUC as a rank-sum problem and utilize differentiable ranking techniques for ranking-oriented optimization. For inter-objective alignment, we change the original one-step ensemble paradigm to a two-step relation-aware ensemble scheme. Extensive offline experiments results on two industrial datasets and online experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods. The proposed method has been fully deployed in Kuaishou’s live-streaming e-commerce recommendation platform with 400 million DAUs, contributing over 2% purchase gain. Comments: 11 pages, 5 figures Subjects: Information Retrieval (cs.IR) Cite as: arXiv:2601.02955 [cs.IR] (or arXiv:2601.02955v1 [cs.IR] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.02955 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[IR-3] Ahead of the Spread: Agent -Driven Virtual Propagation for Early Fake News Detection
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02750
作者: Bincheng Gu,Min Gao,Junliang Yu,Zongwei Wang,Zhiyi Liu,Kai Shu,Hongyu Zhang
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注:
Abstract:Early detection of fake news is critical for mitigating its rapid dissemination on social media, which can severely undermine public trust and social stability. Recent advancements show that incorporating propagation dynamics can significantly enhance detection performance compared to previous content-only approaches. However, this remains challenging at early stages due to the absence of observable propagation signals. To address this limitation, we propose AVOID, an \underlineagent-driven \underlinevirtual pr\underlineopagat\underlineion for early fake news \underlinedetection. AVOID reformulates early detection as a new paradigm of evidence generation, where propagation signals are actively simulated rather than passively observed. Leveraging LLM-powered agents with differentiated roles and data-driven personas, AVOID realistically constructs early-stage diffusion behaviors without requiring real propagation data. The resulting virtual trajectories provide complementary social evidence that enriches content-based detection, while a denoising-guided fusion strategy aligns simulated propagation with content semantics. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that AVOID consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, highlighting the effectiveness and practical value of virtual propagation augmentation for early fake news detection. The code and data are available at this https URL.
[IR-4] A Music Information Retrieval Approach to Classify Sub-Genres in Role Playing Games
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02591
作者: Daeun Hwang,Xuyuan Cai,Edward F. Melcer,Elin Carstensdottir
类目: ound (cs.SD); Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注: 3 pages, 1 figure. D. Hwang, X. Cai, E. Melcer, and E. Carstensdottir, A Music Information Retrieval Approach to Classify Sub-Genres in Role Playing Games, in Extended Abstracts for the Late-Breaking Demo Session of the 25th Int. Society for Music Information Retrieval Conf., San Francisco, United States, 2024
Abstract:Video game music (VGM) is often studied under the same lens as film music, which largely focuses on its theoretical functionality with relation to the identified genres of the media. However, till date, we are unaware of any systematic approach that analyzes the quantifiable musical features in VGM across several identified game genres. Therefore, we extracted musical features from VGM in games from three sub-genres of Role-Playing Games (RPG), and then hypothesized how different musical features are correlated to the perceptions and portrayals of each genre. This observed correlation may be used to further suggest such features are relevant to the expected storytelling elements or play mechanics associated with the sub-genre.
[IR-5] Understanding Human Perception of Music Plagiarism Through a Computational Approach
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02586
作者: Daeun Hwang,Hyeonbin Hwang
类目: ound (cs.SD); Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注: 3 pages, D. Hwang and H. Hwang, Understanding Human Perception of Music Plagiarism Through a Computational Approach, in Extended Abstracts for the Late-Breaking Demo Session of the 25th Int. Society for Music Information Retrieval Conf., San Francisco, United States, 2024
Abstract:There is a wide variety of music similarity detection algorithms, while discussions about music plagiarism in the real world are often based on audience perceptions. Therefore, we aim to conduct a study to examine the key criteria of human perception of music plagiarism, focusing on the three commonly used musical features in similarity analysis: melody, rhythm, and chord progression. After identifying the key features and levels of variation humans use in perceiving musical similarity, we propose a LLM-as-a-judge framework that applies a systematic, step-by-step approach, drawing on modules that extract such high-level attributes.
[IR-6] AG-HGT: A Scalable and Cost-Effective Framework for Inductive Cold-Start Academic Recommendation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02381
作者: Zhexiang Li
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注: 8pages
Abstract:Inductive cold-start recommendation remains the “Achilles’ Heel” of industrial academic platforms, where thousands of new scholars join daily without historical interaction records. While recent Generative Graph Models (e.g., HiGPT, OFA) demonstrate promising semantic capabilities, their prohibitive inference latency (often exceeding 13 minutes per 1,000 requests) and massive computational costs render them practically undeployable for real-time, million-scale applications. To bridge this gap between generative quality and industrial scalability, we propose TAG-HGT, a cost-effective neuro-symbolic framework. Adopting a decoupled “Semantics-First, Structure-Refined” paradigm, TAG-HGT utilizes a frozen Large Language Model (DeepSeek-V3) as an offline semantic factory and distills its knowledge into a lightweight Heterogeneous Graph Transformer (HGT) via Cross-View Contrastive Learning (CVCL). We present a key insight: while LLM semantics provide necessary global recall, structural signals offer the critical local discrimination needed to distinguish valid collaborators from semantically similar but socially unreachable strangers in dense embedding spaces. Validated under a strict Time-Machine Protocol on the massive OpenAlex dataset, TAG-HGT achieves a SOTA System Recall@10 of 91.97%, outperforming structure-only baselines by 20.7%. Most significantly, from an industrial perspective, TAG-HGT reduces inference latency by five orders of magnitude ( 4.5 \times 10^5\times ) compared to generative baselines (from 780s down to 1.73 ms), and slashes inference costs from \sim 1.50 to 0.001 per 1k queries. This 99.9% cost reduction democratizes high-precision academic recommendation.
[IR-7] A Lay User Explainable Food Recommendation System Based on Hybrid Feature Importance Extraction and Large Language Models
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02374
作者: Melissa Tessa,Diderot D. Cidjeu,Rachele Carli,Sarah Abchiche,Ahmad Aldarwishd,Igor Tchappi,Amro Najjar
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注:
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLM) have experienced strong development in recent years, with varied applications. This paper uses LLMs to develop a post-hoc process that provides more elaborated explanations of the results of food recommendation systems. By combining LLM with a hybrid extraction of key variables using SHAP, we obtain dynamic, convincing and more comprehensive explanations to lay user, compared to those in the literature. This approach enhances user trust and transparency by making complex recommendation outcomes easier to understand for a lay user.
[IR-8] Improving News Recommendations through Hybrid Sentiment Modelling and Reinforcement Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02372
作者: Eunice Kingenga,Mike Wa Nkongolo
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注: Masters in information technology, University of Pretoria
Abstract:News recommendation systems rely on automated sentiment analysis to personalise content and enhance user engagement. Conventional approaches often struggle with ambiguity, lexicon inconsistencies, and limited contextual understanding, particularly in multi-source news environments. Existing models typically treat sentiment as a secondary feature, reducing their ability to adapt to users’ affective preferences. To address these limitations, this study develops an adaptive, sentiment-aware news recommendation framework by integrating hybrid sentiment analysis with reinforcement learning. Using the BBC News dataset, a hybrid sentiment model combines VADER, AFINN, TextBlob, and SentiWordNet scores to generate robust article-level sentiment estimates. Articles are categorised as positive, negative, or neutral, and these sentiment states are embedded within a Q-learning architecture to guide the agent in learning optimal recommendation policies. The proposed system effectively identifies and recommends articles with aligned emotional profiles while continuously improving personalisation through iterative Q-learning updates. The results demonstrate that coupling hybrid sentiment modelling with reinforcement learning provides a feasible, interpretable, and adaptive approach for user-centred news recommendation.
[IR-9] GCRank: A Generative Contextual Comprehension Paradigm for Takeout Ranking Model
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.02361
作者: Ziheng Ni,Congcong Liu,Cai Shang,Yiming Sun,Junjie Li,Zhiwei Fang,Guangpeng Chen,Jian Li,Zehua Zhang,Changping Peng,Zhangang Lin,Ching Law,Jingping Shao
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注:
Abstract:The ranking stage serves as the central optimization and allocation hub in advertising systems, governing economic value distribution through eCPM and orchestrating the user-centric blending of organic and advertising content. Prevailing ranking models often rely on fragmented modules and hand-crafted features, limiting their ability to interpret complex user intent. This challenge is further amplified in location-based services such as food delivery, where user decisions are shaped by dynamic spatial, temporal, and individual contexts. To address these limitations, we propose a novel generative framework that reframes ranking as a context comprehension task, modeling heterogeneous signals in a unified architecture. Our architecture consists of two core components: the Generative Contextual Encoder (GCE) and the Generative Contextual Fusion (GCF). The GCE comprises three specialized modules: a Personalized Context Enhancer (PCE) for user-specific modeling, a Collective Context Enhancer (CCE) for group-level patterns, and a Dynamic Context Enhancer (DCE) for real-time situational adaptation. The GCF module then seamlessly integrates these contextual representations through low-rank adaptation. Extensive experiments confirm that our method achieves significant gains in critical business metrics, including click-through rate and platform revenue. We have successfully deployed our method on a large-scale food delivery advertising platform, demonstrating its substantial practical impact. This work pioneers a new perspective on generative recommendation and highlights its practical potential in industrial advertising systems.