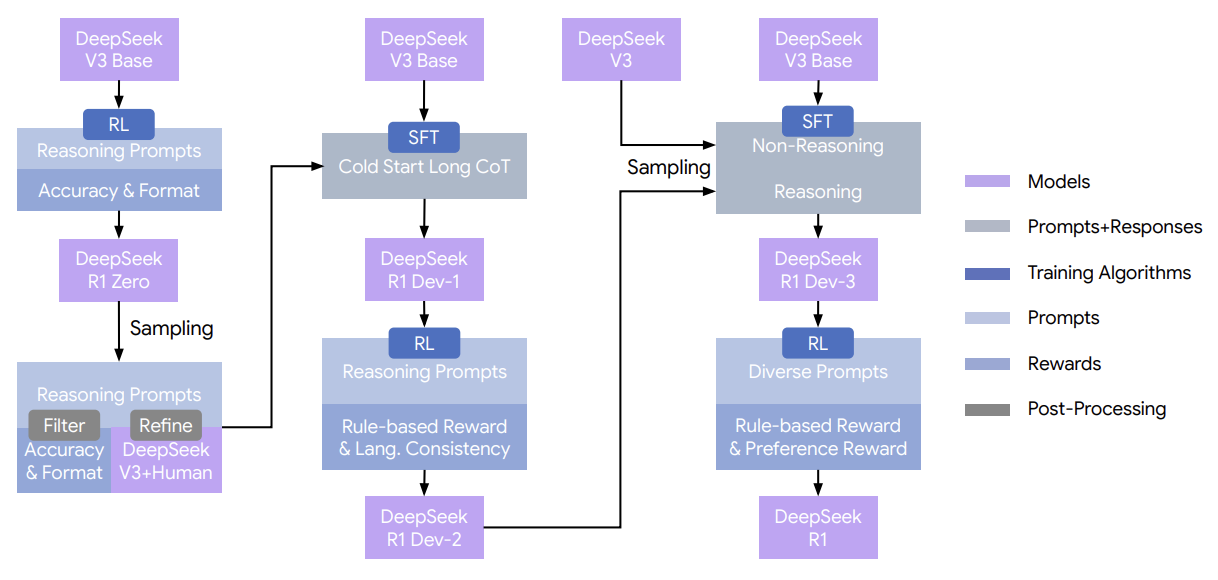
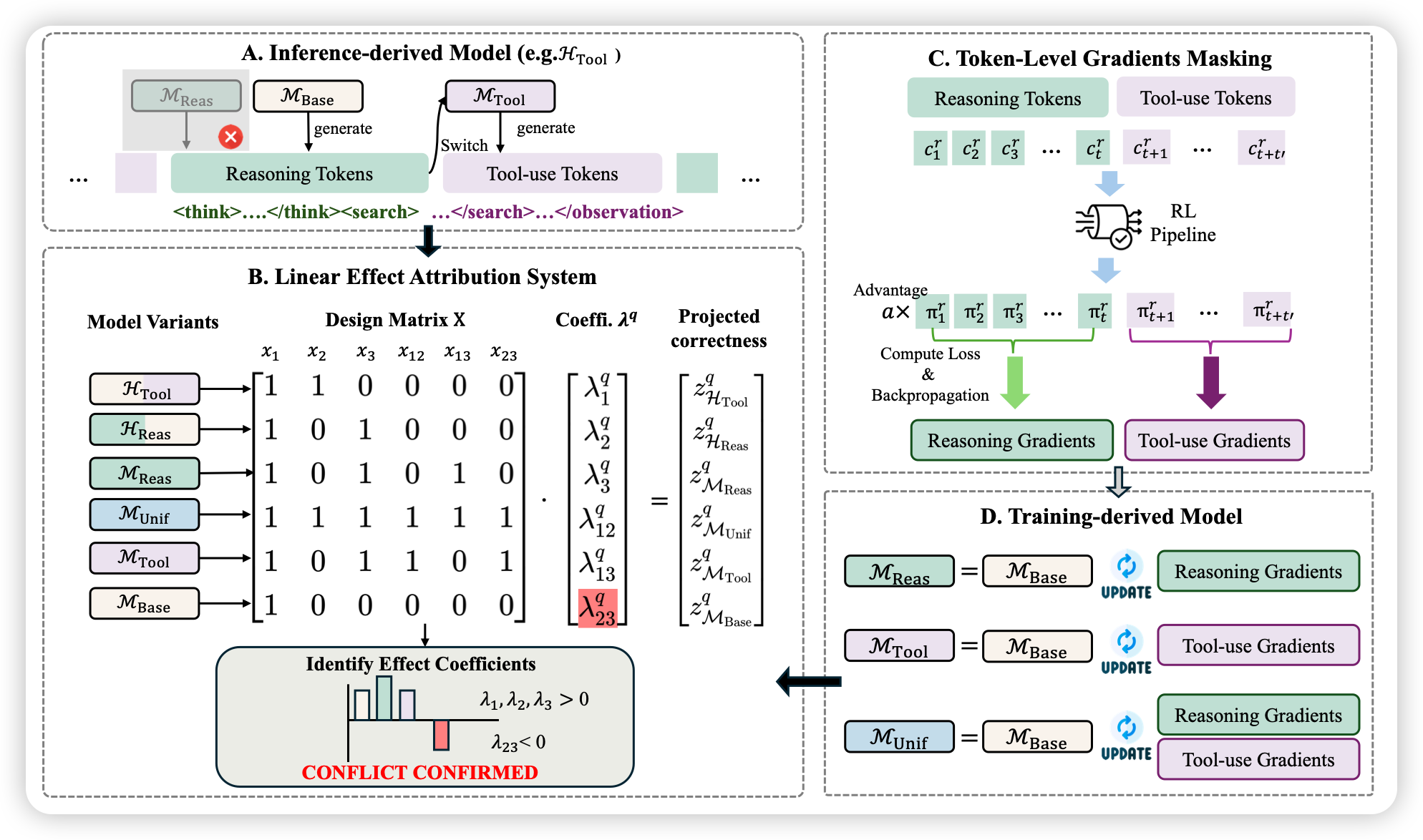
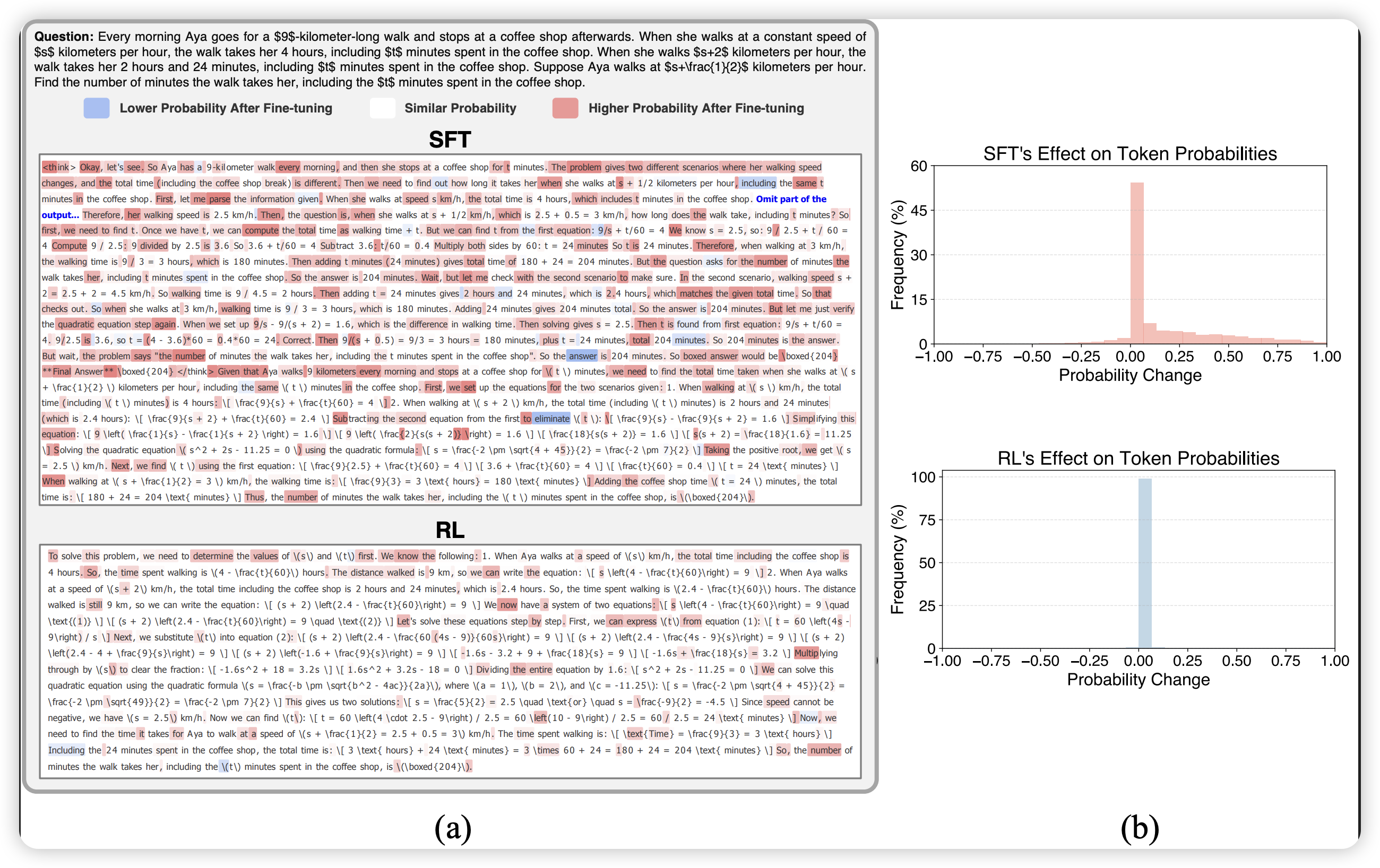
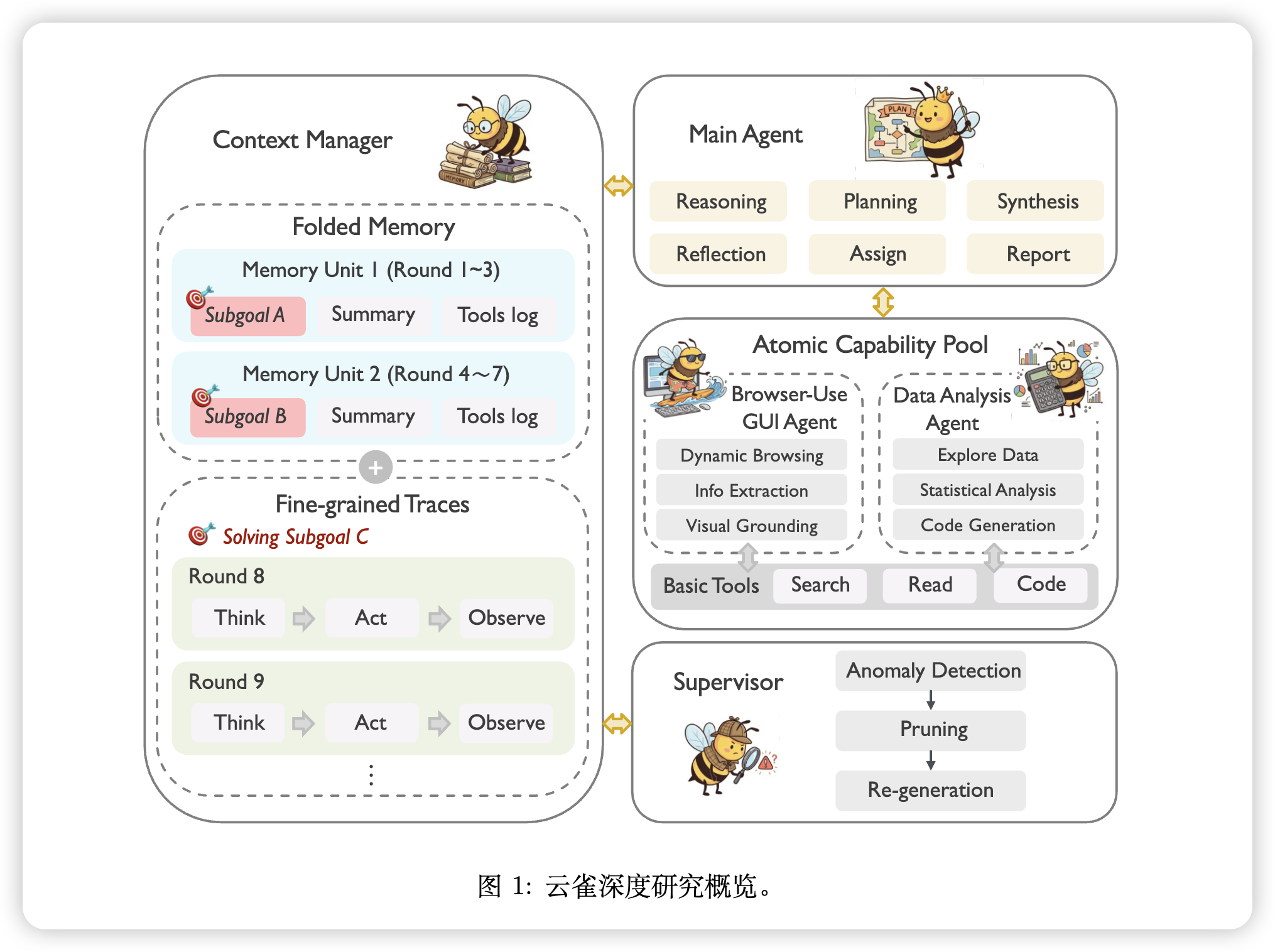
本篇博文主要内容为 2025-12-15 从Arxiv.org论文网站获取的最新论文列表,自动更新,按照NLP、CV、ML、AI、IR五个大方向区分,若需要邮件定时接收,请在评论区留下你的邮箱号。
说明:每日论文数据从Arxiv.org获取,每天早上12:00左右定时自动更新。
友情提示: 如何您需要邮箱接收每日论文数据,请在评论处留下你的邮箱。
目录
概览 (2025-12-15)
今日共更新390篇论文,其中:
- 自然语言处理共40篇(Computation and Language (cs.CL))
- 人工智能共91篇(Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI))
- 计算机视觉共105篇(Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV))
- 机器学习共102篇(Machine Learning (cs.LG))
自然语言处理
[NLP-0] SUMFORU: An LLM -Based Review Summarization Framework for Personalized Purchase Decision Support
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决在线产品评论中蕴含的丰富但嘈杂的信息信号导致用户决策困难的问题,同时指出当前基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的摘要生成方法普遍存在个性化不足、难以匹配个体偏好等局限性。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个可引导的评论摘要框架SUMFORU,通过构建高质量的数据流水线(基于Amazon 2023 Review Dataset)与两阶段对齐机制实现个性化输出:第一阶段采用非对称知识蒸馏进行面向用户画像的监督微调(persona-aware Supervised Fine-Tuning, SFT),第二阶段利用AI反馈强化学习(Reinforcement Learning with AI Feedback, RLAIF)结合偏好估计器捕捉细粒度的、与用户画像相关的语义信号,从而显著提升摘要的一致性、事实依据性和偏好一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11755
作者: Yuming Feng,Xinrui Jiang
机构: Stanford University (斯坦福大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Code available at this https URL
Abstract:Online product reviews contain rich but noisy signals that overwhelm users and hinder effective decision-making. Existing LLM-based summarizers remain generic and fail to account for individual preferences, limiting their practical utility. We propose SUMFORU, a steerable review summarization framework that aligns outputs with explicit user personas to support personalized purchase decisions. Our approach integrates a high-quality data pipeline built from the Amazon 2023 Review Dataset with a two-stage alignment procedure: (1) persona-aware Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) via asymmetric knowledge distillation, and (2) Reinforcement Learning with AI Feedback (RLAIF) using a preference estimator to capture fine-grained, persona-relevant signals. We evaluate the model across rule-based, LLM-based, and human-centered metrics, demonstrating consistent improvements in consistency, grounding, and preference alignment. Our framework achieves the highest performance across all evaluation settings and generalizes effectively to unseen product categories. Our results highlight the promise of steerable pluralistic alignment for building next-generation personalized decision-support systems.
zh
[NLP-1] From Signal to Turn: Interactional Friction in Modular Speech-to-Speech Pipelines
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前基于语音的生成式 AI(Generative AI)系统在实际交互中出现的对话断裂问题,这些问题源于模块化 Speech-to-Speech Retrieval-Augmented Generation (S2S-RAG) 管道设计中的结构性缺陷。论文通过分析典型生产系统,识别出三种核心摩擦模式:时间错位(Temporal Misalignment)、表达扁平化(Expressive Flattening)和修复僵化(Repair Rigidity),并指出这些并非孤立故障,而是模块化架构为追求可控性而牺牲对话流畅性的必然结果。解决方案的关键在于从优化单个组件转向系统级基础设施设计,强调对各模块间接口与协作机制的精细编排,以实现更自然、连贯的口语交互体验。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11724
作者: Titaya Mairittha,Tanakon Sawanglok,Panuwit Raden,Jirapast Buntub,Thanapat Warunee,Napat Asawachaisuvikrom,Thanaphum Saiwongin
机构: AXONS(阿克森斯); Chulalongkorn University(朱拉隆功大学)
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Software Engineering (cs.SE)
备注: 6 pages, 1 figure
Abstract:While voice-based AI systems have achieved remarkable generative capabilities, their interactions often feel conversationally broken. This paper examines the interactional friction that emerges in modular Speech-to-Speech Retrieval-Augmented Generation (S2S-RAG) pipelines. By analyzing a representative production system, we move beyond simple latency metrics to identify three recurring patterns of conversational breakdown: (1) Temporal Misalignment, where system delays violate user expectations of conversational rhythm; (2) Expressive Flattening, where the loss of paralinguistic cues leads to literal, inappropriate responses; and (3) Repair Rigidity, where architectural gating prevents users from correcting errors in real-time. Through system-level analysis, we demonstrate that these friction points should not be understood as defects or failures, but as structural consequences of a modular design that prioritizes control over fluidity. We conclude that building natural spoken AI is an infrastructure design challenge, requiring a shift from optimizing isolated components to carefully choreographing the seams between them.
zh
[NLP-2] Speculative Decoding Speed-of-Light: Optimal Lower Bounds via Branching Random Walks
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)中大规模语言模型(LLMs)推理加速的瓶颈问题,特别是针对推测生成(speculative generation)技术在实现并行化 token 生成时所能达到的最大加速比尚不明确的问题。其解决方案的关键在于建立首个“紧致”的确定性推测生成算法运行时间下界,通过将 token 生成过程类比为分支随机游走(branching random walk),从而将最优草稿树选择问题形式化为概率分析问题,并推导出预期成功预测 token 数量的理论上限:E[X]≤(μ+μ(2))log(P)/μ2+O(1),其中 P 为验证器容量,μ 为验证器输出分布的期望熵,μ(2) 为二阶对数矩。这一理论框架揭示了并行 token 生成的内在限制,并为未来推测解码系统的设计提供了定量指导。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11718
作者: Sergey Pankratov,Dan Alistarh
机构: ISTA (Institute of Science and Technology Austria); Red Hat AI (红帽人工智能)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Speculative generation has emerged as a promising technique to accelerate inference in large language models (LLMs) by leveraging parallelism to verify multiple draft tokens simultaneously. However, the fundamental limits on the achievable speedup remain poorly understood. In this work, we establish the first ``tight’’ lower bounds on the runtime of any deterministic speculative generation algorithm. This is achieved by drawing a parallel between the token generation process and branching random walks, which allows us to analyze the optimal draft tree selection problem. We prove, under basic assumptions, that the expected number of tokens successfully predicted per speculative iteration is bounded as \mathbbE[X] \leq (\mu + \mu_(2))\log(P )/\mu^2 + O(1) , where P is the verifier’s capacity, \mu is the expected entropy of the verifier’s output distribution, and \mu_(2) is the expected second log-moment. This result provides new insights into the limits of parallel token generation, and could guide the design of future speculative decoding systems. Empirical evaluations on Llama models validate our theoretical predictions, confirming the tightness of our bounds in practical settings.
zh
[NLP-3] Automating Historical Insight Extraction from Large-Scale Newspaper Archives via Neural Topic Modeling
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决从大规模未结构化历史报纸档案中提取连贯且人类可理解的主题所面临的挑战,这些问题主要源于主题的演变、光学字符识别(OCR)噪声以及文本体量巨大。传统主题建模方法如潜在狄利克雷分配(LDA)难以捕捉历史文本中话语的复杂性和动态性。其解决方案的关键在于采用BERTopic这一神经主题建模方法,该方法利用基于Transformer的嵌入技术提取和分类主题,从而在保持上下文敏感性的同时实现更高效的规模化分析,尤其适用于揭示核能与核安全议题在时间维度上的长期趋势与主题共现模式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11635
作者: Keerthana Murugaraj,Salima Lamsiyah,Marten During,Martin Theobald
机构: University of Luxembourg (卢森堡大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
备注: This is a preprint of a manuscript submitted to Digital Scholarship in the Humanities (Oxford University Press). The paper is currently under peer review
Abstract:Extracting coherent and human-understandable themes from large collections of unstructured historical newspaper archives presents significant challenges due to topic evolution, Optical Character Recognition (OCR) noise, and the sheer volume of text. Traditional topic-modeling methods, such as Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA), often fall short in capturing the complexity and dynamic nature of discourse in historical texts. To address these limitations, we employ BERTopic. This neural topic-modeling approach leverages transformerbased embeddings to extract and classify topics, which, despite its growing popularity, still remains underused in historical research. Our study focuses on articles published between 1955 and 2018, specifically examining discourse on nuclear power and nuclear safety. We analyze various topic distributions across the corpus and trace their temporal evolution to uncover long-term trends and shifts in public discourse. This enables us to more accurately explore patterns in public discourse, including the co-occurrence of themes related to nuclear power and nuclear weapons and their shifts in topic importance over time. Our study demonstrates the scalability and contextual sensitivity of BERTopic as an alternative to traditional approaches, offering richer insights into historical discourses extracted from newspaper archives. These findings contribute to historical, nuclear, and social-science research while reflecting on current limitations and proposing potential directions for future work.
zh
[NLP-4] Bounding Hallucinations: Information-Theoretic Guarantees for RAG Systems via Merlin-Arthur Protocols
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)系统中检索模块被当作弱启发式而非可验证证据的问题,从而导致大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)在无支持情况下作答、在不完整或误导性上下文中幻觉以及依赖虚假证据的现象。解决方案的关键在于引入一种基于Merlin-Arthur(M/A)协议的训练框架,将整个RAG流水线(包括检索器和生成器)建模为一个交互式证明系统:生成器(Arthur)在未知来源的问题上训练,梅林(Merlin)提供有益证据,莫甘娜(Morgana)注入对抗性误导上下文,二者均使用线性时间的可解释人工智能(Explainable AI, XAI)方法识别并修改对Arthur影响最大的证据片段。由此,生成器学会在证据支持时作答、证据不足时拒绝回答,并仅依赖真正支撑答案的具体文本片段。该方法显著提升了RAG系统的接地性(groundedness)、完整性(completeness)、一致性(soundness)及拒答行为,同时减少了幻觉,且无需人工标注不可回答问题。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11614
作者: Björn Deiseroth,Max Henning Höth,Kristian Kersting,Letitia Parcalabescu
机构: Aleph Alpha Research Lab; TU Darmstadt; Hessian.AI Lab
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 34 pages, 19 figures
Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) models rely on retrieved evidence to guide large language model (LLM) generators, yet current systems treat retrieval as a weak heuristic rather than verifiable evidence. As a result, LLMs answer without support, hallucinate under incomplete or misleading context, and rely on spurious evidence. We introduce a training framework that treats the entire RAG pipeline – both the retriever and the generator – as an interactive proof system via an adaptation of the Merlin-Arthur (M/A) protocol. Arthur (the generator LLM) trains on questions of unkown provenance: Merlin provides helpful evidence, while Morgana injects adversarial, misleading context. Both use a linear-time XAI method to identify and modify the evidence most influential to Arthur. Consequently, Arthur learns to (i) answer when the context support the answer, (ii) reject when evidence is insufficient, and (iii) rely on the specific context spans that truly ground the answer. We further introduce a rigorous evaluation framework to disentangle explanation fidelity from baseline predictive errors. This allows us to introduce and measure the Explained Information Fraction (EIF), which normalizes M/A certified mutual-information guarantees relative to model capacity and imperfect benchmarks. Across three RAG datasets and two model families of varying sizes, M/A-trained LLMs show improved groundedness, completeness, soundness, and reject behavior, as well as reduced hallucinations – without needing manually annotated unanswerable questions. The retriever likewise improves recall and MRR through automatically generated M/A hard positives and negatives. Our results demonstrate that autonomous interactive-proof-style supervision provides a principled and practical path toward reliable RAG systems that treat retrieved documents not as suggestions, but as verifiable evidence.
zh
[NLP-5] Visualizing token importance for black-box language models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决黑箱大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在实际部署中,尤其是高风险领域(如法律、医疗和合规)下,如何评估其输出对输入token的敏感性问题。现有方法通常仅关注模型行为的孤立方面(如特定偏见或公平性),难以全面揭示输入与输出之间的依赖关系。解决方案的关键在于提出一种轻量级、模型无关的分布感知敏感性分析方法(Distribution-Based Sensitivity Analysis, DBSA),无需假设LLM的概率分布即可量化每个输入token对输出的影响。DBSA通过避免计算提示级别的梯度(因LLM为随机函数而不可行),转而基于输出分布的变化来评估敏感性,从而为从业者提供可快速集成、直观探索模型对特定输入token依赖性的实用工具。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11573
作者: Paulius Rauba,Qiyao Wei,Mihaela van der Schaar
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:We consider the problem of auditing black-box large language models (LLMs) to ensure they behave reliably when deployed in production settings, particularly in high-stakes domains such as legal, medical, and regulatory compliance. Existing approaches for LLM auditing often focus on isolated aspects of model behavior, such as detecting specific biases or evaluating fairness. We are interested in a more general question – can we understand how the outputs of black-box LLMs depend on each input token? There is a critical need to have such tools in real-world applications that rely on inaccessible API endpoints to language models. However, this is a highly non-trivial problem, as LLMs are stochastic functions (i.e. two outputs will be different by chance), while computing prompt-level gradients to approximate input sensitivity is infeasible. To address this, we propose Distribution-Based Sensitivity Analysis (DBSA), a lightweight model-agnostic procedure to evaluate the sensitivity of the output of a language model for each input token, without making any distributional assumptions about the LLM. DBSA is developed as a practical tool for practitioners, enabling quick, plug-and-play visual exploration of LLMs reliance on specific input tokens. Through illustrative examples, we demonstrate how DBSA can enable users to inspect LLM inputs and find sensitivities that may be overlooked by existing LLM interpretability methods.
zh
[NLP-6] Extending a Parliamentary Corpus with MPs Tweets: Automatic Annotation and Evaluation Using MultiParTweet LREC2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决社交媒体上政治话语与正式议会辩论之间缺乏跨平台、多模态对比分析资源的问题。其解决方案的关键在于构建MultiParTweet这一多语言推文语料库,该语料库通过连接来自X平台的政治人物推文与德国议会语料库GerParCor,实现了在线社交 discourse 与议会辩论的可比性分析;同时,利用九个文本模型和一个视觉-语言模型(Vision-Language Model, VLM)对推文进行情感、情绪和主题标注,并通过人工标注子集验证自动化标注质量,从而提供一套具备多模态标注且经人工验证的高质量数据资源。此外,研究还开发了TTLABTweetCrawler工具用于标准化采集X平台数据,进一步增强了方法的可复现性和扩展性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11567
作者: Mevlüt Bagci,Ali Abusaleh,Daniel Baumartz,Giueseppe Abrami,Maxim Konca,Alexander Mehler
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Multimedia (cs.MM)
备注: Submitted to LREC 2026
Abstract:Social media serves as a critical medium in modern politics because it both reflects politicians’ ideologies and facilitates communication with younger generations. We present MultiParTweet, a multilingual tweet corpus from X that connects politicians’ social media discourse with German political corpus GerParCor, thereby enabling comparative analyses between online communication and parliamentary debates. MultiParTweet contains 39 546 tweets, including 19 056 media items. Furthermore, we enriched the annotation with nine text-based models and one vision-language model (VLM) to annotate MultiParTweet with emotion, sentiment, and topic annotations. Moreover, the automated annotations are evaluated against a manually annotated subset. MultiParTweet can be reconstructed using our tool, TTLABTweetCrawler, which provides a framework for collecting data from X. To demonstrate a methodological demonstration, we examine whether the models can predict each other using the outputs of the remaining models. In summary, we provide MultiParTweet, a resource integrating automatic text and media-based annotations validated with human annotations, and TTLABTweetCrawler, a general-purpose X data collection tool. Our analysis shows that the models are mutually predictable. In addition, VLM-based annotation were preferred by human annotators, suggesting that multimodal representations align more with human interpretation.
zh
[NLP-7] DentalGPT : Incentivizing Multimodal Complex Reasoning in Dentistry
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在牙科领域中难以捕捉精细的口腔视觉细节以及缺乏精确诊断所需复杂推理能力的问题。其解决方案的关键在于两个方面:一是构建了目前最大规模且高质量的牙科多模态数据集,包含超过12万张标注的牙科图像及其强调诊断相关视觉特征的详细描述;二是采用分阶段训练策略,即先通过该数据集进行预训练以增强模型对牙科场景的视觉理解能力,再通过强化学习进一步提升其多模态复杂推理能力。这一方法使 DentalGPT 在疾病分类和牙科视觉问答(Dental Visual Question Answering, VQA)任务上显著优于多个主流 MLLMs,即使参数量仅为 7B。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11558
作者: Zhenyang Cai,Jiaming Zhang,Junjie Zhao,Ziyi Zeng,Yanchao Li,Jingyi Liang,Junying Chen,Yunjin Yang,Jiajun You,Shuzhi Deng,Tongfei Wang,Wanting Chen,Chunxiu Hao,Ruiqi Xie,Zhenwei Wen,Xiangyi Feng,Zou Ting,Jin Zou Lin,Jianquan Li,Guangjun Yu,Liangyi Chen,Junwen Wang,Shan Jiang,Benyou Wang
机构: Shenzhen Stomatology Hospital (Pingshan) of Southern Medical University; The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen; State Key Laboratory of Membrane Biology, Beijing Key Laboratory of Cardiometabolic Molecular Medicine, Institute of Molecular Medicine, National Biomedical Imaging Center, School of Future Technology, Peking University; Freedom AI; Division of Applied Oral Sciences & Community Dental Care, Faculty of Dentistry, The University of Hong Kong; Beijing Institute of Collaborative Innovation; National Health Data Institute, Shenzhen; Shenzhen Loop Area Institute; Shenzhen Institute of Big Data
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Reliable interpretation of multimodal data in dentistry is essential for automated oral healthcare, yet current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) struggle to capture fine-grained dental visual details and lack sufficient reasoning ability for precise diagnosis. To address these limitations, we present DentalGPT, a specialized dental MLLM developed through high-quality domain knowledge injection and reinforcement learning. Specifically, the largest annotated multimodal dataset for dentistry to date was constructed by aggregating over 120k dental images paired with detailed descriptions that highlight diagnostically relevant visual features, making it the multimodal dataset with the most extensive collection of dental images to date. Training on this dataset significantly enhances the MLLM’s visual understanding of dental conditions, while the subsequent reinforcement learning stage further strengthens its capability for multimodal complex reasoning. Comprehensive evaluations on intraoral and panoramic benchmarks, along with dental subsets of medical VQA benchmarks, show that DentalGPT achieves superior performance in disease classification and dental VQA tasks, outperforming many state-of-the-art MLLMs despite having only 7B parameters. These results demonstrate that high-quality dental data combined with staged adaptation provides an effective pathway for building capable and domain-specialized dental MLLMs.
zh
[NLP-8] HFS: Holistic Query-Aware Frame Selection for Efficient Video Reasoning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决视频理解中关键帧选择(key frame selection)的两个核心问题:一是传统Top-K方法因独立评分导致帧在时间上聚集且视觉冗余;二是轻量级选择器使用离线生成的伪标签训练时,监督信号无法动态适应任务目标。解决方案的关键在于提出一个端到端可训练、任务自适应的框架:首先利用Chain-of-Thought引导小型语言模型(Small Language Model, SLM)生成任务相关的隐式查询向量,与多模态特征融合以实现动态帧评分;其次设计了一个包含相关性、覆盖度和冗余度的连续集合级目标函数,通过Gumbel-Softmax实现可微优化,从而在集合层面选出最优帧组合;最后引入学生-教师互学习机制,使SLM与多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Model, MLLM)通过KL散度对齐重要性分布,结合交叉熵损失完成端到端优化,摆脱对静态伪标签的依赖。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11534
作者: Yiqing Yang,Kin-Man Lam
机构: The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (香港理工大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Multimedia (cs.MM)
备注: 18 pages, 8 figures
Abstract:Key frame selection in video understanding presents significant challenges. Traditional top-K selection methods, which score frames independently, often fail to optimize the selection as a whole. This independent scoring frequently results in selecting frames that are temporally clustered and visually redundant. Additionally, training lightweight selectors using pseudo labels generated offline by Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) prevents the supervisory signal from dynamically adapting to task objectives. To address these limitations, we propose an end-to-end trainable, task-adaptive framework for frame selection. A Chain-of-Thought approach guides a Small Language Model (SLM) to generate task-specific implicit query vectors, which are combined with multimodal features to enable dynamic frame scoring. We further define a continuous set-level objective function that incorporates relevance, coverage, and redundancy, enabling differentiable optimization via Gumbel-Softmax to select optimal frame combinations at the set level. Finally, student-teacher mutual learning is employed, where the student selector (SLM) and teacher reasoner (MLLM) are trained to align their frame importance distributions via KL divergence. Combined with cross-entropy loss, this enables end-to-end optimization, eliminating reliance on static pseudo labels. Experiments across various benchmarks, including Video-MME, LongVideoBench, MLVU, and NExT-QA, demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing approaches.
zh
[NLP-9] Does Less Hallucination Mean Less Creativity? An Empirical Investigation in LLM s
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在生成内容时存在的幻觉问题,即模型产生事实性错误信息的问题,尤其是在科学发现等需要同时保证事实准确性和创造性假设生成的应用场景中,现有幻觉缓解方法对创造性能力的影响尚不明确。解决方案的关键在于系统评估三种主流幻觉减少技术——链式验证(Chain of Verification, CoVe)、对比层解码(Decoding by Contrasting Layers, DoLa)和检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)——对模型发散性创造力(divergent creativity)的差异化影响,结果表明CoVe提升发散思维,DoLa抑制发散思维,而RAG影响最小,从而为科学应用中根据准确性与创造性平衡需求选择合适方法提供实证依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11509
作者: Mohor Banerjee,Nadya Yuki Wangsajaya,Syed Ali Redha Alsagoff,Min Sen Tan,Zachary Choy Kit Chun,Alvin Chan Guo Wei
机构: 1. Nanyang Technological University (南洋理工大学); 2. National University of Singapore (新加坡国立大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities in natural language understanding and reasoning, but suffer from hallucination: the generation of factually incorrect content. While numerous methods have been developed to reduce hallucinations, their impact on creative generations remains unexplored. This gap is particularly critical for AI-assisted scientific discovery, which requires both factual accuracy and creative hypothesis generation. We investigate how three hallucination-reduction techniques: Chain of Verification (CoVe), Decoding by Contrasting Layers (DoLa), and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), affect creativity in LLMs. Evaluating multiple model families (LLaMA, Qwen, Mistral) at varying scales (1B - 70B parameters) on two creativity benchmarks (NeoCoder and CS4), we find that these methods have opposing effects on divergent creativity. CoVe enhances divergent thinking, DoLa suppresses it, and RAG shows minimal impact. Our findings provide guidance for selecting appropriate hallucination-reduction methods in scientific applications, where the balance between factual accuracy and creative exploration is crucial.
zh
[NLP-10] Building Patient Journeys in Hebrew: A Language Model for Clinical Timeline Extraction ALT IJCAI2025
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决从电子健康记录(Electronic Health Records, EHR)中自动提取结构化临床时间线(structured clinical timelines)以构建患者就医路径(patient journeys)的问题。其核心挑战在于如何在保持隐私安全的前提下,准确识别和排序医疗事件的时间关系。解决方案的关键在于基于DictaBERT 2.0开发了一个针对希伯来语医学领域的语言模型,并在超过五百万条去标识化的医院记录上持续预训练,从而提升对临床事件时序关系的建模能力;同时,研究发现词汇适应(vocabulary adaptation)可提高分词效率,且去标识化处理不会损害下游任务性能,为隐私保护下的模型开发提供了实证支持。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11502
作者: Kai Golan Hashiloni,Brenda Kasabe Nokai,Michal Shevach,Esthy Shemesh,Ronit Bartin,Anna Bergrin,Liran Harel,Nachum Dershowitz,Liat Nadai Arad,Kfir Bar
机构: Efi Arazi School of Computer Science, Reichman University, Herzilya, Israel; Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Israel; School of Computer Science and AI, Tel Aviv University, Israel
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: In Proceedings of the Workshop on Large Language Models and Generative AI for Health Informatics 2025, IJCAI 2025, Montreal, Canada
Abstract:We present a new Hebrew medical language model designed to extract structured clinical timelines from electronic health records, enabling the construction of patient journeys. Our model is based on DictaBERT 2.0 and continually pre-trained on over five million de-identified hospital records. To evaluate its effectiveness, we introduce two new datasets – one from internal medicine and emergency departments, and another from oncology – annotated for event temporal relations. Our results show that our model achieves strong performance on both datasets. We also find that vocabulary adaptation improves token efficiency and that de-identification does not compromise downstream performance, supporting privacy-conscious model development. The model is made available for research use under ethical restrictions.
zh
[NLP-11] Mistake Notebook Learning: Selective Batch-Wise Context Optimization for In-Context Learning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在任务适应过程中存在的两大问题:一是通过梯度微调(Gradient Fine-Tuning)带来的计算开销大和灾难性遗忘(Catastrophic Forgetting),二是基于上下文学习(In-Context Learning, ICL)的鲁棒性差与错误学习能力弱。为此,作者提出了一种无需训练的框架——错误笔记学习(Mistake Notebook Learning, MNL),其核心创新在于引入一个持续更新的知识库,用于存储从批量错误中抽象出的通用错误模式(abstracted error patterns)。不同于以往依赖单个实例或轨迹的记忆方法,MNL采用批处理级别的错误抽象机制,从多个失败案例中提取可泛化的指导信息,并通过保留验证集上的性能提升来动态维护笔记内容,从而确保模型性能单调改进。实验证明,MNL在GSM8K等复杂推理任务上接近监督微调效果(93.9% vs 94.3%),且显著优于其他免训练方法,在KaggleDBQA上更是实现28%准确率(相对提升47%),验证了其作为高效、可靠训练替代方案的潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11485
作者: Xuanbo Su,Yingfang Zhang,Hao Luo,Xiaoteng Liu,Leo Huang
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) adapt to tasks via gradient fine-tuning (heavy computation, catastrophic forgetting) or In-Context Learning (ICL: low robustness, poor mistake learning). To fix this, we introduce Mistake Notebook Learning (MNL), a training-free framework with a persistent knowledge base of abstracted error patterns. Unlike prior instance/single-trajectory memory methods, MNL uses batch-wise error abstraction: it extracts generalizable guidance from multiple failures, stores insights in a dynamic notebook, and retains only baseline-outperforming guidance via hold-out validation (ensuring monotonic improvement). We show MNL nearly matches Supervised Fine-Tuning (93.9% vs 94.3% on GSM8K) and outperforms training-free alternatives on GSM8K, Spider, AIME, and KaggleDBQA. On KaggleDBQA (Qwen3-8B), MNL hits 28% accuracy (47% relative gain), outperforming Memento (15.1%) and Training-Free GRPO (22.1) - proving it’s a strong training-free alternative for complex reasoning.
zh
[NLP-12] Rethinking Expert Trajectory Utilization in LLM Post-training
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决后训练阶段中如何最优利用专家轨迹(expert trajectories)以提升模型性能的问题,尤其是在监督微调(Supervised Fine-Tuning, SFT)与强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)结合时的机制选择与参数配置难题。其解决方案的关键在于提出可塑性上限框架(Plasticity-Ceiling Framework),该框架将最终性能解耦为SFT基础性能和RL可塑性两个维度,并通过系统性实验证明:顺序式SFT-then-RL流水线优于同步方法;进一步给出精确的缩放准则,包括在SFT的稳定或轻度过拟合子阶段切换至RL可最大化性能上限、数据规模决定后训练潜力而轨迹难度仅作为性能乘数,以及最小SFT验证损失可作为筛选最优专家轨迹的鲁棒指标。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11470
作者: Bowen Ding,Yuhan Chen,Jiayang Lv,Jiyao Yuan,Qi Zhu,Shuangshuang Tian,Dantong Zhu,Futing Wang,Heyuan Deng,Fei Mi,Lifeng Shang,Tao Lin
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); School of Engineering, Westlake University (西湖大学工程学院); Institute of Advanced Technology, Westlake Institute for Advanced Study (西湖高等研究院先进技术研究所); Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab (华为诺亚方舟实验室)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 24 pages, 5 figures, under review
Abstract:While effective post-training integrates Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and Reinforcement Learning (RL), the optimal mechanism for utilizing expert trajectories remains unresolved. We propose the Plasticity-Ceiling Framework to theoretically ground this landscape, decomposing performance into foundational SFT performance and the subsequent RL plasticity. Through extensive benchmarking, we establish the Sequential SFT-then-RL pipeline as the superior standard, overcoming the stability deficits of synchronized approaches. Furthermore, we derive precise scaling guidelines: (1) Transitioning to RL at the SFT Stable or Mild Overfitting Sub-phase maximizes the final ceiling by securing foundational SFT performance without compromising RL plasticity; (2) Refuting ``Less is More’’ in the context of SFT-then-RL scaling, we demonstrate that Data Scale determines the primary post-training potential, while Trajectory Difficulty acts as a performance multiplier; and (3) Identifying that the Minimum SFT Validation Loss serves as a robust indicator for selecting the expert trajectories that maximize the final performance ceiling. Our findings provide actionable guidelines for maximizing the value extracted from expert trajectories.
zh
[NLP-13] CLINIC: Evaluating Multilingual Trustworthiness in Language Models for Healthcare
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前语言模型(Language Models, LMs)在多语言医疗场景中缺乏可靠可信度评估的问题,尤其是在资源匮乏语言环境下模型表现不佳、存在偏见与隐私风险等关键挑战。其解决方案的核心是提出CLINIC——一个综合性多语言医疗基准测试平台,系统性地从真实性(truthfulness)、公平性(fairness)、安全性(safety)、鲁棒性(robustness)和隐私保护(privacy)五个维度出发,通过18项多样化任务对LMs进行评估,覆盖全球15种主要语言及涵盖疾病状况、预防措施、诊断检测、治疗方案、手术与药物等多个核心医疗领域。该基准揭示了现有模型在事实准确性、群体偏见、隐私泄露和对抗攻击等方面的显著缺陷,为提升医疗语言模型在全球多语环境中的可靠性与安全性提供了可量化的评估框架与改进方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11437
作者: Akash Ghosh,Srivarshinee Sridhar,Raghav Kaushik Ravi,Muhsin Muhsin,Sriparna Saha,Chirag Agarwal
机构: Indian Institute of Technology Patna(印度理工学院巴特那分校); IGIMS, Patna(印度医学科学研究所巴特那分校); University of Virginia(弗吉尼亚大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 49 pages, 31 figures
Abstract:Integrating language models (LMs) in healthcare systems holds great promise for improving medical workflows and decision-making. However, a critical barrier to their real-world adoption is the lack of reliable evaluation of their trustworthiness, especially in multilingual healthcare settings. Existing LMs are predominantly trained in high-resource languages, making them ill-equipped to handle the complexity and diversity of healthcare queries in mid- and low-resource languages, posing significant challenges for deploying them in global healthcare contexts where linguistic diversity is key. In this work, we present CLINIC, a Comprehensive Multilingual Benchmark to evaluate the trustworthiness of language models in healthcare. CLINIC systematically benchmarks LMs across five key dimensions of trustworthiness: truthfulness, fairness, safety, robustness, and privacy, operationalized through 18 diverse tasks, spanning 15 languages (covering all the major continents), and encompassing a wide array of critical healthcare topics like disease conditions, preventive actions, diagnostic tests, treatments, surgeries, and medications. Our extensive evaluation reveals that LMs struggle with factual correctness, demonstrate bias across demographic and linguistic groups, and are susceptible to privacy breaches and adversarial attacks. By highlighting these shortcomings, CLINIC lays the foundation for enhancing the global reach and safety of LMs in healthcare across diverse languages.
zh
[NLP-14] ask-Specific Sparse Feature Masks for Molecular Toxicity Prediction with Chemical Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI 在分子毒性预测中因黑箱特性导致可解释性不足的问题,这限制了其在高风险药物安全决策中的应用。解决方案的关键在于提出一种多任务学习(Multi-Task Learning, MTL)框架,通过共享化学语言模型并引入任务特定的注意力模块,在每个毒性终点上施加L1稀疏正则化约束,从而迫使模型聚焦于最少数量的关键分子片段进行预测。该方法不仅提升了预测准确性,还通过稀疏注意力权重提供了化学直观的可视化结果,增强了模型决策过程的可解释性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11412
作者: Kwun Sy Lee,Jiawei Chen,Fuk Sheng Ford Chung,Tianyu Zhao,Zhenyuan Chen,Debby D. Wang
机构: 未知
类目: Computational Engineering, Finance, and Science (cs.CE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Biomolecules (q-bio.BM)
备注: 6 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:Reliable in silico molecular toxicity prediction is a cornerstone of modern drug discovery, offering a scalable alternative to experimental screening. However, the black-box nature of state-of-the-art models remains a significant barrier to adoption, as high-stakes safety decisions demand verifiable structural insights alongside predictive performance. To address this, we propose a novel multi-task learning (MTL) framework designed to jointly enhance accuracy and interpretability. Our architecture integrates a shared chemical language model with task-specific attention modules. By imposing an L1 sparsity penalty on these modules, the framework is constrained to focus on a minimal set of salient molecular fragments for each distinct toxicity endpoint. The resulting framework is trained end-to-end and is readily adaptable to various transformer-based backbones. Evaluated on the ClinTox, SIDER, and Tox21 benchmark datasets, our approach consistently outperforms both single-task and standard MTL baselines. Crucially, the sparse attention weights provide chemically intuitive visualizations that reveal the specific fragments influencing predictions, thereby enhancing insight into the model’s decision-making process.
zh
[NLP-15] Minimal Clips Maximum Salience: Long Video Summarization via Key Moment Extraction
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在处理长视频时易丢失关键视觉信息的问题,并提出一种低成本、高效率的视频内容分析方法。其解决方案的关键在于:首先将视频划分为短片段,利用轻量级视频字幕模型生成每个片段的紧凑视觉描述;随后将这些描述输入大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM),由其筛选出包含最相关视觉信息的K个关键片段,用于构建多模态摘要。该方法在MovieSum数据集上验证有效,仅需不到6%的参考片段即可生成完整且高质量的多模态摘要,同时显著优于随机采样策略,并保持较低的计算开销。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11399
作者: Galann Pennec,Zhengyuan Liu,Nicholas Asher,Philippe Muller,Nancy F. Chen
机构: IRIT, University of Toulouse, France; Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), Singapore; CNRS@CREATE, Singapore; CNRS, IRIT, France
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are able to process increasingly longer videos. Yet, important visual information is easily lost throughout the entire context and missed by VLMs. Also, it is important to design tools that enable cost-effective analysis of lengthy video content. In this paper, we propose a clip selection method that targets key video moments to be included in a multimodal summary. We divide the video into short clips and generate compact visual descriptions of each using a lightweight video captioning model. These are then passed to a large language model (LLM), which selects the K clips containing the most relevant visual information for a multimodal summary. We evaluate our approach on reference clips for the task, automatically derived from full human-annotated screenplays and summaries in the MovieSum dataset. We further show that these reference clips (less than 6% of the movie) are sufficient to build a complete multimodal summary of the movies in MovieSum. Using our clip selection method, we achieve a summarization performance close to that of these reference clips while capturing substantially more relevant video information than random clip selection. Importantly, we maintain low computational cost by relying on a lightweight captioning model.
zh
[NLP-16] Improving Translation Quality by Selecting Better Data for LLM Fine-Tuning: A Comparative Analysis
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决开放大语言模型(open LLMs)在机器翻译(machine translation, MT)微调过程中,数据选择策略对模型性能影响的量化问题。其核心发现表明,语义层面的数据筛选方法(如COMET Kiwi、QuRate)显著优于基于词法或几何特征的启发式方法(如TF-IDF、FD-Score),且即使所选数据差异小于3%,模型性能仍表现出显著变化,揭示了微调过程对数据质量的高度敏感性。解决方案的关键在于采用受控实验设计,系统比较多种数据选择器在日英平行语料上的表现,从而确立语义感知型选择机制在提升微调效率与效果中的主导作用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11388
作者: Felipe Ribeiro Fujita de Mello,Hideyuki Takada
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: To appear at IEEE Big Data 2025
Abstract:We investigated the impact of data selection on machine translation fine-tuning for open LLMs. Using Japanese-English corpora, we compare five selectors: TF-IDF, COMET Kiwi, QuRate, FD-Score, and random selection, under controlled training conditions. We observed that semantic selectors consistently outperform lexical and geometry-based heuristics, and that even when the selected data differ by less than 3%, the impact on model performance is substantial, underscoring the sensitivity of fine-tuning to data quality.
zh
[NLP-17] Mining Legal Arguments to Study Judicial Formalism
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决司法推理在大规模分析中的困难问题,特别是针对中欧和东欧(CEE)地区是否存在形式主义判例的争议。研究通过开发自动化方法检测并分类捷克最高法院判决中的法律论证类型,以实证方式反驳了关于该地区司法形式主义的既有观点。解决方案的关键在于构建了一个高质量标注的数据集MADON(包含272份判决书、9,183段落及八类论证类型),并基于30万条捷克法院判决语料对Transformer大语言模型(LLM)进行持续预训练,结合不对称损失与类别权重等技术缓解数据不平衡问题;最终采用三阶段流水线架构(ModernBERT + Llama 3.1 + 传统特征机器学习)实现高精度的论证段落识别(82.6% macro-F1)、传统法律论证类型分类(77.5% macro-F1)以及判例形式主义/非形式主义的整体分类(83.2% macro-F1),显著提升了计算效率与模型可解释性,为计算法学研究提供了可复用的方法论框架。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11374
作者: Tomáš Koref,Lena Held,Mahammad Namazov,Harun Kumru,Yassine Thlija,Christoph Burchard,Ivan Habernal
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注: pre-print under review
Abstract:Courts must justify their decisions, but systematically analyzing judicial reasoning at scale remains difficult. This study refutes claims about formalistic judging in Central and Eastern Europe (CEE) by developing automated methods to detect and classify judicial reasoning in Czech Supreme Courts’ decisions using state-of-the-art natural language processing methods. We create the MADON dataset of 272 decisions from two Czech Supreme Courts with expert annotations of 9,183 paragraphs with eight argument types and holistic formalism labels for supervised training and evaluation. Using a corpus of 300k Czech court decisions, we adapt transformer LLMs for Czech legal domain by continued pretraining and experiment with methods to address dataset imbalance including asymmetric loss and class weighting. The best models successfully detect argumentative paragraphs (82.6% macro-F1), classify traditional types of legal argument (77.5% macro-F1), and classify decisions as formalistic/non-formalistic (83.2% macro-F1). Our three-stage pipeline combining ModernBERT, Llama 3.1, and traditional feature-based machine learning achieves promising results for decision classification while reducing computational costs and increasing explainability. Empirically, we challenge prevailing narratives about CEE formalism. This work shows that legal argument mining enables reliable judicial philosophy classification and shows the potential of legal argument mining for other important tasks in computational legal studies. Our methodology is easily replicable across jurisdictions, and our entire pipeline, datasets, guidelines, models, and source codes are available at this https URL.
zh
[NLP-18] qa-FLoRA: Data-free query-adaptive Fusion of LoRAs for LLM s AAAI2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多领域复合查询下低秩适配器(Low-Rank Adaptation, LoRA)融合的难题,即如何在不依赖特定组合训练数据或监督信号的情况下,动态、自适应地整合多个LoRA模块以提升模型在复杂多域任务中的性能。其解决方案的关键在于提出qa-FLoRA方法,该方法通过测量基础模型与各LoRA适配器之间的分布差异(distributional divergence),在推理阶段动态计算层级融合权重,从而实现无需额外训练和数据的查询自适应融合,显著优于静态加权和训练-free基线,并逼近监督式融合的效果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11366
作者: Shreya Shukla,Aditya Sriram,Milinda Kuppur Narayanaswamy,Hiteshi Jain
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Accepted at AAAI 2026 (Main Technical Track)
Abstract:The deployment of large language models for specialized tasks often requires domain-specific parameter-efficient finetuning through Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) modules. However, effectively fusing these adapters to handle complex, multi-domain composite queries remains a critical challenge. Existing LoRA fusion approaches either use static weights, which assign equal relevance to each participating LoRA, or require data-intensive supervised training for every possible LoRA combination to obtain respective optimal fusion weights. We propose qa-FLoRA, a novel query-adaptive data-and-training-free method for LoRA fusion that dynamically computes layer-level fusion weights by measuring distributional divergence between the base model and respective adapters. Our approach eliminates the need for composite training data or domain-representative samples, making it readily applicable to existing adapter collections. Extensive experiments across nine multilingual composite tasks spanning mathematics, coding, and medical domains, show that qa-FLoRA outperforms static fusion by ~5% with LLaMA-2 and ~6% with LLaMA-3, and the training-free baselines by ~7% with LLaMA-2 and ~10% with LLaMA-3, while significantly closing the gap with supervised baselines. Further, layer-level analysis of our fusion weights reveals interpretable fusion patterns, demonstrating the effectiveness of our approach for robust multi-domain adaptation.
zh
[NLP-19] Unifying Dynamic Tool Creation and Cross-Task Experience Sharing through Cognitive Memory Architecture
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型代理(Large Language Model agents)在面对新任务时难以适应的问题,其核心挑战在于工具可用性受限和经验无法复用。现有方法要么依赖预定义工具导致覆盖范围有限,要么从零构建工具而未利用历史经验,从而造成探索效率低下和性能不佳。解决方案的关键在于提出SMITH(Shared Memory Integrated Tool Hub),这是一个统一的认知架构,通过分层记忆组织实现动态工具创建与跨任务经验共享的无缝集成:将代理记忆划分为程序性、语义性和情景性三个层次,系统性扩展能力的同时保留成功执行模式;同时,将工具创建形式化为受控沙箱环境中的迭代代码生成,并通过语义相似度匹配实现情景记忆检索来促进经验复用;此外,引入基于代理集合难度重估的课程学习策略以优化训练过程。实验表明,SMITH在GAIA基准上达到81.8%的Pass@1准确率,显著优于Alita(75.2%)和Memento(70.9%)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11303
作者: Jiarun Liu,Shiyue Xu,Yang Li,Shangkun Liu,Yongli Yu,Peng Cao
机构: JD.com(京东)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large Language Model agents face fundamental challenges in adapting to novel tasks due to limitations in tool availability and experience reuse. Existing approaches either rely on predefined tools with limited coverage or build tools from scratch without leveraging past experiences, leading to inefficient exploration and suboptimal performance. We introduce SMITH (Shared Memory Integrated Tool Hub), a unified cognitive architecture that seamlessly integrates dynamic tool creation with cross-task experience sharing through hierarchical memory organization. SMITH organizes agent memory into procedural, semantic, and episodic components, enabling systematic capability expansion while preserving successful execution patterns. Our approach formalizes tool creation as iterative code generation within controlled sandbox environments and experience sharing through episodic memory retrieval with semantic similarity matching. We further propose a curriculum learning strategy based on agent-ensemble difficulty re-estimation. Extensive experiments on the GAIA benchmark demonstrate SMITH’s effectiveness, achieving 81.8% Pass@1 accuracy and outperforming state-of-the-art baselines including Alita (75.2%) and Memento (70.9%). Our work establishes a foundation for building truly adaptive agents that continuously evolve their capabilities through principled integration of tool creation and experience accumulation.
zh
[NLP-20] LegalRikai: Open Benchmark – A Benchmark for Complex Japanese Corporate Legal Tasks
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在法律领域应用中缺乏真实、复杂任务评估基准的问题,尤其针对日本公司法律实务场景下长文本结构化输出能力的不足。其解决方案的关键在于构建了一个由法律专业人士监督设计的开放基准 LegalRikai:该基准包含四个模拟实际法律操作的复杂任务,涵盖100个需生成长篇结构化内容的样本,并通过人工与自动化评估相结合的方式验证模型表现。研究发现,传统短文本任务难以捕捉模型在文档级编辑上的缺陷,而自动化评估在具有明确语言依据的指标上与人工判断高度一致,可作为专家资源有限时的有效筛选工具,从而推动更贴近实践的法律AI研究。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11297
作者: Shogo Fujita,Yuji Naraki,Yiqing Zhu,Shinsuke Mori
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:This paper introduces LegalRikai: Open Benchmark, a new benchmark comprising four complex tasks that emulate Japanese corporate legal practices. The benchmark was created by legal professionals under the supervision of an attorney. This benchmark has 100 samples that require long-form, structured outputs, and we evaluated them against multiple practical criteria. We conducted both human and automated evaluations using leading LLMs, including GPT-5, Gemini 2.5 Pro, and Claude Opus 4.1. Our human evaluation revealed that abstract instructions prompted unnecessary modifications, highlighting model weaknesses in document-level editing that were missed by conventional short-text tasks. Furthermore, our analysis reveals that automated evaluation aligns well with human judgment on criteria with clear linguistic grounding, and assessing structural consistency remains a challenge. The result demonstrates the utility of automated evaluation as a screening tool when expert availability is limited. We propose a dataset evaluation framework to promote more practice-oriented research in the legal domain.
zh
[NLP-21] CIP: A Plug-and-Play Causal Prompting Framework for Mitigating Hallucinations under Long-Context Noise
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型在处理长且噪声较多的检索上下文时易产生幻觉(hallucination)的问题,其根源在于模型依赖于虚假相关性而非真实的因果关系进行推理。解决方案的关键在于提出一种轻量级、可插拔的因果提示框架(Causal Prompting, CIP),该框架通过构建实体、动作与事件之间的因果关系序列并注入提示中,引导模型聚焦于因果相关的证据;同时借助因果干预和反事实推理抑制非因果推理路径,从而提升事实准确性、可解释性和推理效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11282
作者: Qingsen Ma,Dianyun Wang,Ran Jing,Yujun Sun,Zhenbo Xu
机构: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications(北京邮电大学); Northwestern University(西北大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models often hallucinate when processing long and noisy retrieval contexts because they rely on spurious correlations rather than genuine causal relationships. We propose CIP, a lightweight and plug-and-play causal prompting framework that mitigates hallucinations at the input stage. CIP constructs a causal relation sequence among entities, actions, and events and injects it into the prompt to guide reasoning toward causally relevant evidence. Through causal intervention and counterfactual reasoning, CIP suppresses non causal reasoning paths, improving factual grounding and interpretability. Experiments across seven mainstream language models, including GPT-4o, Gemini 2.0 Flash, and Llama 3.1, show that CIP consistently enhances reasoning quality and reliability, achieving 2.6 points improvement in Attributable Rate, 0.38 improvement in Causal Consistency Score, and a fourfold increase in effective information density. API level profiling further shows that CIP accelerates contextual understanding and reduces end to end response latency by up to 55.1 percent. These results suggest that causal reasoning may serve as a promising paradigm for improving the explainability, stability, and efficiency of large language models.
zh
[NLP-22] AdaSD: Adaptive Speculative Decoding for Efficient Language Model Inference
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)因参数规模增大而导致推理速度显著下降的问题。现有基于推测解码(Speculative Decoding)的方法通常依赖额外训练、复杂超参数调优或对模型与任务的预先分析,限制了其部署灵活性。解决方案的关键在于提出自适应推测解码(Adaptive Speculative Decoding, AdaSD),其通过动态调整生成长度和接受标准来实现高效推理:引入两个实时更新的自适应阈值——一个用于决定候选token生成终止时机,另一个用于判断token是否被接受,二者均基于token熵(token entropy)和Jensen-Shannon散度(Jensen-Shannon distance)计算得出。该方法无需预分析或微调,兼容现成模型,在保持精度损失低于2%的前提下,相较标准推测解码最高提升49%的推理速度,从而提供了一种实用且自适应的LLM高效推理方案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11280
作者: Kuan-Wei Lu,Ding-Yong Hong,Pangfeng Liu
机构: Institute of Information Science, Academia Sinica (中央研究院资讯科学研究所); Department of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Taiwan University (台湾大学电机资讯学院资讯工程学系)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable performance across a wide range of tasks, but their increasing parameter sizes significantly slow down inference. Speculative decoding mitigates this issue by leveraging a smaller draft model to predict candidate tokens, which are then verified by a larger target model. However, existing approaches often require additional training, extensive hyperparameter tuning, or prior analysis of models and tasks before deployment. In this paper, we propose Adaptive Speculative Decoding (AdaSD), a hyperparameter-free decoding scheme that dynamically adjusts generation length and acceptance criteria during inference. AdaSD introduces two adaptive thresholds: one to determine when to stop candidate token generation and another to decide token acceptance, both updated in real time based on token entropy and Jensen-Shannon distance. This approach eliminates the need for pre-analysis or fine-tuning and is compatible with off-the-shelf models. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate that AdaSD achieves up to 49% speedup over standard speculative decoding while limiting accuracy degradation to under 2%, making it a practical solution for efficient and adaptive LLM inference.
zh
[NLP-23] When Actions Teach You to Think: Reasoning -Action Synergy via Reinforcement Learning in Conversational Agents
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决监督微调(Supervised Fine-Tuning, SFT)在面对数据分布变化时泛化能力不足的问题,尤其是当新数据未完全脱离训练域但仍导致性能下降时。此外,论文指出高质量推理轨迹(reasoning traces)的收集成本高、主观性强且难以扩展,限制了SFT在复杂任务中的应用。解决方案的关键在于利用强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)让模型直接从任务结果中学习推理策略,而非依赖人工标注的推理过程。具体而言,作者提出了一种基于组相对策略优化(Group Relative Policy Optimization, GRPO)的框架,通过设计以工具调用准确性和答案正确性为核心的奖励机制,使大语言模型(LLM)能够迭代优化其推理步骤与行动决策,从而实现推理与动作学习的统一。实验表明,该方法显著提升了推理质量与工具调用精度,在基准模型上实现了1.5%的相对改进和40%的绝对提升。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11277
作者: Mrinal Rawat,Arkajyoti Chakraborty,Neha Gupta,Roberto Pieraccini
机构: Uniphore
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) has emerged as one of the most effective ways to improve the performance of large language models (LLMs) in downstream tasks. However, SFT can have difficulty generalizing when the underlying data distribution changes, even when the new data does not fall completely outside the training domain. Recent reasoning-focused models such as o1 and R1 have demonstrated consistent gains over their non-reasoning counterparts, highlighting the importance of reasoning for improved generalization and reliability. However, collecting high-quality reasoning traces for SFT remains challenging – annotations are costly, subjective, and difficult to scale. To address this limitation, we leverage Reinforcement Learning (RL) to enable models to learn reasoning strategies directly from task outcomes. We propose a pipeline in which LLMs generate reasoning steps that guide both the invocation of tools (e.g., function calls) and the final answer generation for conversational agents. Our method employs Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with rewards designed around tool accuracy and answer correctness, allowing the model to iteratively refine its reasoning and actions. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach improves both the quality of reasoning and the precision of tool invocations, achieving a 1.5% relative improvement over the SFT model (trained without explicit thinking) and a 40% gain compared to the base of the vanilla Qwen3-1.7B model. These findings demonstrate the promise of unifying reasoning and action learning through RL to build more capable and generalizable conversational agents.
zh
[NLP-24] Leverag ing LLM s for Title and Abstract Screening for Systematic Review: A Cost-Effective Dynamic Few-Shot Learning Approach
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决系统性综述(systematic review)中标题和摘要筛选步骤因文献数量激增而带来的高时间成本与资源消耗问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种两阶段动态少样本学习(dynamic few-shot learning, DFSL)方法:首先利用低成本大语言模型(LLM)进行初步筛选,随后对置信度较低的样本由高性能LLM重新评估,从而在保障筛选性能的同时有效控制计算开销,显著提升系统性综述的效率与可扩展性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11261
作者: Yun-Chung Liu,Rui Yang,Jonathan Chong Kai Liew,Ziran Yin,Henry Foote,Christopher J. Lindsell,Chuan Hong
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 22 pages, 3 figures
Abstract:Systematic reviews are a key component of evidence-based medicine, playing a critical role in synthesizing existing research evidence and guiding clinical decisions. However, with the rapid growth of research publications, conducting systematic reviews has become increasingly burdensome, with title and abstract screening being one of the most time-consuming and resource-intensive steps. To mitigate this issue, we designed a two-stage dynamic few-shot learning (DFSL) approach aimed at improving the efficiency and performance of large language models (LLMs) in the title and abstract screening task. Specifically, this approach first uses a low-cost LLM for initial screening, then re-evaluates low-confidence instances using a high-performance LLM, thereby enhancing screening performance while controlling computational costs. We evaluated this approach across 10 systematic reviews, and the results demonstrate its strong generalizability and cost-effectiveness, with potential to reduce manual screening burden and accelerate the systematic review process in practical applications.
zh
[NLP-25] Multi-Intent Spoken Language Understanding: Methods Trends and Challenges
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多意图语音语言理解(multi-intent spoken language understanding, SLU)领域缺乏系统性综述的问题,以梳理近年来的研究进展并为后续研究提供指导。其解决方案的关键在于从解码范式(decoding paradigms)和建模方法(modeling approaches)两个维度对现有研究进行深入分析,同时对比代表性模型的性能,明确其优势与局限,并进一步探讨当前挑战与未来研究方向,从而为多意图SLU领域的理论发展与技术应用提供结构化参考。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11258
作者: Di Wu,Ruiyu Fang,Liting Jiang,Shuangyong Song,Xiaomeng Huang,Shiquan Wang,Zhongqiu Li,Lingling Shi,Mengjiao Bao,Yongxiang Li,Hao Huang
机构: China Telecom (中国电信); Xinjiang University (新疆大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Multi-intent spoken language understanding (SLU) involves two tasks: multiple intent detection and slot filling, which jointly handle utterances containing more than one intent. Owing to this characteristic, which closely reflects real-world applications, the task has attracted increasing research attention, and substantial progress has been achieved. However, there remains a lack of a comprehensive and systematic review of existing studies on multi-intent SLU. To this end, this paper presents a survey of recent advances in multi-intent SLU. We provide an in-depth overview of previous research from two perspectives: decoding paradigms and modeling approaches. On this basis, we further compare the performance of representative models and analyze their strengths and limitations. Finally, we discuss the current challenges and outline promising directions for future research. We hope this survey will offer valuable insights and serve as a useful reference for advancing research in multi-intent SLU.
zh
[NLP-26] Adaptive Soft Rolling KV Freeze with Entropy-Guided Recovery: Sublinear Memory Growth for Efficient LLM Inference
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)在长文本生成场景中因KV缓存(Key-Value Cache)占用内存过大而导致的部署瓶颈问题。现有方法多采用基于淘汰(eviction-based)的缓存管理策略,但此类方法会永久丢弃部分上下文信息,损害模型对长距离依赖的建模能力。论文提出的解决方案核心是自适应软冻结机制(Adaptive Soft Rolling KV Freeze, ASR-KF),其关键在于:通过滑动注意力窗口动态识别低重要性token,并采用可逆的软冻结策略暂停这些token的KV更新,同时将全部token保留在离线GPU存储中;此外引入熵引导恢复机制(Entropy-Guided Recovery, EGR),根据token被重复标记为低重要性的次数按次线性增长冻结时长,从而避免过度压缩导致的信息丢失。该方案无需训练即可实现55–67%的活跃KV缓存空间减少,且保持生成质量与needle-in-haystack检索性能,适用于多种架构且具备良好的实用性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11221
作者: Adilet Metinov,Gulida M. Kudakeeva,Bolotbek uulu Nursultan,Gulnara D. Kabaeva
机构: Kyrgyz State Technical University named after I. Razzakov (吉尔吉斯斯坦技术大学,以I. Razzakov命名)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 6 pages, 3 tables , 1 figure
Abstract:We present Adaptive Soft Rolling KV Freeze with Entropy-Guided Recovery (ASR-KF-EGR), a training-free inference-time framework for efficient large language model generation. Our method introduces a reversible soft-freeze mechanism that temporarily suspends key-value (KV) updates for low-importance tokens identified within a sliding attention window. Unlike eviction-based approaches that permanently discard context, ASR-KF-EGR preserves all tokens in off-GPU storage and restores them on demand. We extend the framework with sublinear freeze scheduling, where freeze duration grows sublinearly with repeated low-importance detections, preventing over-aggressive compression. Preliminary experiments on LLaMA-3 8B demonstrate 55-67% reduction in active KV cache size while maintaining generation quality and passing needle-in-haystack retrieval tests. The method is architecture-agnostic, requires no fine-tuning, and provides a practical solution for memory-constrained deployment of long-context LLMs.
zh
[NLP-27] FutureWeaver: Planning Test-Time Compute for Multi-Agent Systems with Modularized Collaboration
【速读】: 该论文试图解决多智能体系统中如何在固定推理预算下高效分配计算资源以提升协作性能的问题(即如何将测试时扩展(test-time scaling)技术推广至多智能体协作场景)。其解决方案的关键在于提出FutureWeaver框架,该框架通过自-play反思自动提取可复用的多智能体协作模块(modularized collaboration),并构建双层规划架构,在当前任务状态推理与未来步骤推测之间优化计算资源分配,从而实现预算约束下的协同效率最大化。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11213
作者: Dongwon Jung,Peng Shi,Yi Zhang
机构: University of California, Davis (加州大学戴维斯分校); University of Waterloo (滑铁卢大学); Greenshoe, Inc. (Greenshoe公司)
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Scaling test-time computation improves large language model performance without additional training. Recent work demonstrates that techniques such as repeated sampling, self-verification, and self-reflection can significantly enhance task success by allocating more inference-time compute. However, applying these techniques across multiple agents in a multi-agent system is difficult: there does not exist principled mechanisms to allocate compute to foster collaboration among agents, to extend test-time scaling to collaborative interactions, or to distribute compute across agents under explicit budget constraints. To address this gap, we propose FutureWeaver, a framework for planning and optimizing test-time compute allocation in multi-agent systems under fixed budgets. FutureWeaver introduces modularized collaboration, formalized as callable functions that encapsulate reusable multi-agent workflows. These modules are automatically derived through self-play reflection by abstracting recurring interaction patterns from past trajectories. Building on these modules, FutureWeaver employs a dual-level planning architecture that optimizes compute allocation by reasoning over the current task state while also speculating on future steps. Experiments on complex agent benchmarks demonstrate that FutureWeaver consistently outperforms baselines across diverse budget settings, validating its effectiveness for multi-agent collaboration in inference-time optimization.
zh
[NLP-28] SciLaD: A Large-Scale Transparent Reproducible Dataset for Natural Scientific Language Processing
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决科学文献大规模高质量数据集稀缺的问题,以支持自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing, NLP)在学术文本理解与生成中的研究。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个名为SciLaD的开源、可扩展的科学语言数据集,该数据集完全基于开放源代码框架和公开数据源,包含超过1000万篇英文科学文献(经筛选)和3500多万篇多语言未过滤TEI XML格式文献,并配套发布可复现的数据处理流水线。通过在该数据集上预训练RoBERTa模型并在多个基准测试中验证其性能,证明了SciLaD在保持高数据质量的同时具备良好的实用性和可扩展性,为科研人员提供了可靠的研究资源和透明的实验环境。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11192
作者: Luca Foppiano,Sotaro Takeshita,Pedro Ortiz Suarez,Ekaterina Borisova,Raia Abu Ahmad,Malte Ostendorff,Fabio Barth,Julian Moreno-Schneider,Georg Rehm
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 12 pages, 2 figures, 3 tables
Abstract:SciLaD is a novel, large-scale dataset of scientific language constructed entirely using open-source frameworks and publicly available data sources. It comprises a curated English split containing over 10 million scientific publications and a multilingual, unfiltered TEI XML split including more than 35 million publications. We also publish the extensible pipeline for generating SciLaD. The dataset construction and processing workflow demonstrates how open-source tools can enable large-scale, scientific data curation while maintaining high data quality. Finally, we pre-train a RoBERTa model on our dataset and evaluate it across a comprehensive set of benchmarks, achieving performance comparable to other scientific language models of similar size, validating the quality and utility of SciLaD. We publish the dataset and evaluation pipeline to promote reproducibility, transparency, and further research in natural scientific language processing and understanding including scholarly document processing.
zh
[NLP-29] FIBER: A Multilingual Evaluation Resource for Factual Inference Bias
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在多语言环境下事实知识准确性与推理偏倚评估不足的问题,尤其关注单实体与多实体情境下的表现差异及提示语语言对模型输出的影响。其解决方案的关键在于构建了一个名为FIBER的多语言基准测试集,涵盖英语、意大利语和土耳其语的句子补全、问答和对象计数预测任务,从而系统性地评估模型在不同语言和实体复杂度下的事实知识掌握能力,并揭示提示语言可能引发的国家相关实体选择偏倚及其跨语言差异模式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11110
作者: Evren Ayberk Munis,Deniz Yılmaz,Arianna Muti,Çağrı Toraman
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models are widely used across domains, yet there are concerns about their factual reliability and biases. Factual knowledge probing offers a systematic means to evaluate these aspects. Most existing benchmarks focus on single-entity facts and monolingual data. We therefore present FIBER, a multilingual benchmark for evaluating factual knowledge in single- and multi-entity settings. The dataset includes sentence completion, question-answering, and object-count prediction tasks in English, Italian, and Turkish. Using FIBER, we examine whether the prompt language induces inference bias in entity selection and how large language models perform on multi-entity versus single-entity questions. The results indicate that the language of the prompt can influence the model’s generated output, particularly for entities associated with the country corresponding to that language. However, this effect varies across different topics such that 31% of the topics exhibit factual inference bias score greater than 0.5. Moreover, the level of bias differs across languages such that Turkish prompts show higher bias compared to Italian in 83% of the topics, suggesting a language-dependent pattern. Our findings also show that models face greater difficulty when handling multi-entity questions than the single-entity questions. Model performance differs across both languages and model sizes. The highest mean average precision is achieved in English, while Turkish and Italian lead to noticeably lower scores. Larger models, including Llama-3.1-8B and Qwen-2.5-7B, show consistently better performance than smaller 3B-4B models.
zh
[NLP-30] Explanation Bias is a Product: Revealing the Hidden Lexical and Position Preferences in Post-Hoc Feature Attribution
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)中特征归因方法(feature attribution methods)在提供token级解释时存在的不一致性问题,即不同归因方法对同一输入可能产生差异显著的解释结果,从而引发用户对解释可信度的质疑或不当信任。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个模型和方法无关的评估框架,通过三个评价指标系统性地量化和结构化归因方法中的词汇偏置(lexical bias)与位置偏置(position bias),并在人工数据和自然数据上分别验证了这两种偏置在不同Transformer模型间的结构性失衡现象,揭示了异常解释更可能源于方法自身的偏差。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11108
作者: Jonathan Kamp,Roos Bakker,Dominique Blok
机构: Computational Linguistics and Text Mining Lab, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam (阿姆斯特丹自由大学计算语言学与文本挖掘实验室); TNO–The Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research, The Hague (荷兰应用科学研究组织,海牙); Leiden University Centre for Linguistics (LUCL), Leiden University, Leiden (莱顿大学语言学研究中心(LUCL),莱顿大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Good quality explanations strengthen the understanding of language models and data. Feature attribution methods, such as Integrated Gradient, are a type of post-hoc explainer that can provide token-level insights. However, explanations on the same input may vary greatly due to underlying biases of different methods. Users may be aware of this issue and mistrust their utility, while unaware users may trust them inadequately. In this work, we delve beyond the superficial inconsistencies between attribution methods, structuring their biases through a model- and method-agnostic framework of three evaluation metrics. We systematically assess both the lexical and position bias (what and where in the input) for two transformers; first, in a controlled, pseudo-random classification task on artificial data; then, in a semi-controlled causal relation detection task on natural data. We find that lexical and position biases are structurally unbalanced in our model comparison, with models that score high on one type score low on the other. We also find signs that methods producing anomalous explanations are more likely to be biased themselves.
zh
[NLP-31] Applying NLP to iMessages: Understanding Topic Avoidance Responsiveness and Sentiment
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决用户对其iMessage消息数据潜在价值的认知不足问题,尤其是在缺乏对本地存储数据进行深度分析工具的情况下。其核心问题是:如何利用苹果公司开放的iMessage本地存储文件(即包含所有消息及附加元数据的单一文件),从多维度挖掘用户通信行为的价值,包括主题建模、响应时间分析、情感倾向识别和拒绝程度评分等。解决方案的关键在于开发了一个iMessage文本消息分析器(iMessage text message analyzer),通过该工具对原始数据进行结构化处理与量化分析,从而回答五个核心研究问题,并为未来基于iMessage数据的通信行为研究提供可行的技术路径与实证基础。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11079
作者: Alan Gerber,Sam Cooperman
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computers and Society (cs.CY); Applications (stat.AP); Other Statistics (stat.OT)
备注: 11 pages, 18 figures, this https URL
Abstract:What is your messaging data used for? While many users do not often think about the information companies can gather based off of their messaging platform of choice, it is nonetheless important to consider as society increasingly relies on short-form electronic communication. While most companies keep their data closely guarded, inaccessible to users or potential hackers, Apple has opened a door to their walled-garden ecosystem, providing iMessage users on Mac with one file storing all their messages and attached metadata. With knowledge of this locally stored file, the question now becomes: What can our data do for us? In the creation of our iMessage text message analyzer, we set out to answer five main research questions focusing on topic modeling, response times, reluctance scoring, and sentiment analysis. This paper uses our exploratory data to show how these questions can be answered using our analyzer and its potential in future studies on iMessage data.
zh
[NLP-32] MultiScript30k: Leverag ing Multilingual Embeddings to Extend Cross Script Parallel Data
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多模态机器翻译(Multimodal Machine Translation, MMT)研究中因数据集语言覆盖有限而导致的多样性不足问题。原始Multi30k数据集仅包含四种使用拉丁字母的欧洲语言(捷克语、英语、法语和德语),限制了对非欧洲语言及不同书写系统的研究。为扩展语言覆盖范围,作者提出MultiScript30k,这是一个基于NLLB200-3.3B模型将Multi30k英文版本(Multi30k-En)翻译成阿拉伯语(Ar)、西班牙语(Es)、乌克兰语(Uk)、简体中文(Zh_Hans)和繁体中文(Zh_Hant)的新扩展数据集。其关键创新在于通过大规模神经网络翻译模型实现多语言、多书写系统(包括阿拉伯文、西里尔文、汉字等)的高质量平行语料生成,并验证了翻译质量在语义相似性(cosine similarity > 0.8)和分布差异(symmetric KL divergence < 0.000251)上的稳定性,从而推动MMT研究向全球语言多样性发展。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11074
作者: Christopher Driggers-Ellis,Detravious Brinkley,Ray Chen,Aashish Dhawan,Daisy Zhe Wang,Christan Grant
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Multimedia (cs.MM)
备注: 7 pages, 2 figures, 5 tables. Not published at any conference at this time
Abstract:Multi30k is frequently cited in the multimodal machine translation (MMT) literature, offering parallel text data for training and fine-tuning deep learning models. However, it is limited to four languages: Czech, English, French, and German. This restriction has led many researchers to focus their investigations only on these languages. As a result, MMT research on diverse languages has been stalled because the official Multi30k dataset only represents European languages in Latin scripts. Previous efforts to extend Multi30k exist, but the list of supported languages, represented language families, and scripts is still very short. To address these issues, we propose MultiScript30k, a new Multi30k dataset extension for global languages in various scripts, created by translating the English version of Multi30k (Multi30k-En) using NLLB200-3.3B. The dataset consists of over (30000) sentences and provides translations of all sentences in Multi30k-En into Ar, Es, Uk, Zh_Hans and Zh_Hant. Similarity analysis shows that Multi30k extension consistently achieves greater than (0.8) cosine similarity and symmetric KL divergence less than (0.000251) for all languages supported except Zh_Hant which is comparable to the previous Multi30k extensions ArEnMulti30k and Multi30k-Uk. COMETKiwi scores reveal mixed assessments of MultiScript30k as a translation of Multi30k-En in comparison to the related work. ArEnMulti30k scores nearly equal MultiScript30k-Ar, but Multi30k-Uk scores 6.4% greater than MultiScript30k-Uk per split.
zh
[NLP-33] PIAST: Rapid Prompting with In-context Augmentation for Scarce Training data
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在提示工程(prompt engineering)中对人工设计提示高度敏感的问题,尤其是手动构造有效提示困难且依赖复杂少样本示例(few-shot examples)的挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种快速自动提示构建算法,通过生成少量高质量的少样本示例来增强人类指令,利用蒙特卡洛沙普利值(Monte Carlo Shapley estimation)评估每个示例的效用,并采用迭代替换/删除/保留策略优化示例集合;同时结合激进的子采样和回放缓冲区(replay buffer)以提升计算效率。实验表明,精心构造的示例比广泛搜索指令更能实现高效、低资源的提示工程效果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11013
作者: Pawel Batorski,Paul Swoboda
机构: Heinrich Heine Universität Düsseldorf (海因里希海涅杜塞尔多夫大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:LLMs are highly sensitive to prompt design, but handcrafting effective prompts is difficult and often requires intricate crafting of few-shot examples. We propose a fast automatic prompt construction algorithm that augments human instructions by generating a small set of few shot examples. Our method iteratively replaces/drops/keeps few-shot examples using Monte Carlo Shapley estimation of example utility. For faster execution, we use aggressive subsampling and a replay buffer for faster evaluations. Our method can be run using different compute time budgets. On a limited budget, we outperform existing automatic prompting methods on text simplification and GSM8K and obtain second best results on classification and summarization. With an extended, but still modest compute budget we set a new state of the art among automatic prompting methods on classification, simplification and GSM8K. Our results show that carefully constructed examples, rather than exhaustive instruction search, are the dominant lever for fast and data efficient prompt engineering. Our code is available at this https URL.
zh
[NLP-34] KBQA-R1: Reinforcing Large Language Models for Knowledge Base Question Answering
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决知识库问答(Knowledge Base Question Answering, KBQA)中大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)存在的两个核心问题:一是生成幻觉式查询而未验证知识图谱(Knowledge Graph, KG)schema的存在性;二是采用僵化的模板化推理方式,缺乏对环境的真正理解。解决方案的关键在于提出KBQA-R1框架,将KBQA建模为多轮决策过程,并通过强化学习(Reinforcement Learning)优化交互策略,利用Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)基于实际执行反馈进行策略迭代,而非依赖静态监督信号;同时引入引用拒绝采样(Referenced Rejection Sampling, RRS)方法,从数据合成层面确保推理轨迹与真实动作序列严格对齐,从而有效提升LLM在可验证执行基础上的推理能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10999
作者: Xin Sun,Zhongqi Chen,Xing Zheng,Qiang Liu,Shu Wu,Bowen Song,Zilei Wang,Weiqiang Wang,Liang Wang
机构: Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院自动化研究所); Ant Group (蚂蚁集团); University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Knowledge Base Question Answering (KBQA) challenges models to bridge the gap between natural language and strict knowledge graph schemas by generating executable logical forms. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have advanced this field, current approaches often struggle with a dichotomy of failure: they either generate hallucinated queries without verifying schema existence or exhibit rigid, template-based reasoning that mimics synthesized traces without true comprehension of the environment. To address these limitations, we present \textbfKBQA-R1, a framework that shifts the paradigm from text imitation to interaction optimization via Reinforcement Learning. Treating KBQA as a multi-turn decision process, our model learns to navigate the knowledge base using a list of actions, leveraging Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to refine its strategies based on concrete execution feedback rather than static supervision. Furthermore, we introduce \textbfReferenced Rejection Sampling (RRS), a data synthesis method that resolves cold-start challenges by strictly aligning reasoning traces with ground-truth action sequences. Extensive experiments on WebQSP, GrailQA, and GraphQuestions demonstrate that KBQA-R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance, effectively grounding LLM reasoning in verifiable execution.
zh
[NLP-35] SCOUT: A Defense Against Data Poisoning Attacks in Fine-Tuned Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决语言模型在医疗等敏感领域中面临的后门攻击(backdoor attack)安全威胁问题,特别是针对那些利用上下文合理触发词(contextually-appropriate triggers)的隐蔽攻击,这些攻击能够绕过传统基于上下文异常检测的防御机制。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为SCOUT(Saliency-based Classification Of Untrusted Tokens)的新防御框架,其核心创新是通过token-level显著性分析(saliency analysis)而非传统上下文依赖方法来识别后门触发词:SCOUT构建显著性图谱,量化每个token移除对目标标签输出logits的影响,从而有效检测出明显和隐秘的恶意操纵行为,同时在干净输入上保持高准确率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10998
作者: Mohamed Afane,Abhishek Satyam,Ke Chen,Tao Li,Junaid Farooq,Juntao Chen
机构: Fordham University (福特汉姆大学); Zhejiang University (浙江大学); City University of Hong Kong (香港城市大学); University of Michigan-Dearborn (密歇根大学迪尔伯恩分校)
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 9 pages, 3 figures
Abstract:Backdoor attacks create significant security threats to language models by embedding hidden triggers that manipulate model behavior during inference, presenting critical risks for AI systems deployed in healthcare and other sensitive domains. While existing defenses effectively counter obvious threats such as out-of-context trigger words and safety alignment violations, they fail against sophisticated attacks using contextually-appropriate triggers that blend seamlessly into natural language. This paper introduces three novel contextually-aware attack scenarios that exploit domain-specific knowledge and semantic plausibility: the ViralApp attack targeting social media addiction classification, the Fever attack manipulating medical diagnosis toward hypertension, and the Referral attack steering clinical recommendations. These attacks represent realistic threats where malicious actors exploit domain-specific vocabulary while maintaining semantic coherence, demonstrating how adversaries can weaponize contextual appropriateness to evade conventional detection methods. To counter both traditional and these sophisticated attacks, we present \textbfSCOUT (Saliency-based Classification Of Untrusted Tokens), a novel defense framework that identifies backdoor triggers through token-level saliency analysis rather than traditional context-based detection methods. SCOUT constructs a saliency map by measuring how the removal of individual tokens affects the model’s output logits for the target label, enabling detection of both conspicuous and subtle manipulation attempts. We evaluate SCOUT on established benchmark datasets (SST-2, IMDB, AG News) against conventional attacks (BadNet, AddSent, SynBkd, StyleBkd) and our novel attacks, demonstrating that SCOUT successfully detects these sophisticated threats while preserving accuracy on clean inputs.
zh
[NLP-36] MedBioRAG : Semantic Search and Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Large Language Models for Medical and Biological QA ACL2025
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在生物医学问答(Biomedical Question Answering, Biomedical QA)任务中因知识局限性和上下文理解不足而导致性能受限的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出MedBioRAG,一个结合语义搜索(semantic search)与词法搜索(lexical search)、文档检索(document retrieval)及监督微调(supervised fine-tuning)的检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)框架。该方法通过高效检索并排序相关生物医学文献,显著提升了回答的准确性与上下文相关性,在多个基准数据集(如NFCorpus、TREC-COVID、MedQA、PubMedQA和BioASQ)上均超越了现有最先进(SoTA)模型及GPT-4o基础版本。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10996
作者: Seonok Kim
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Submitted to ACL 2025. 9 pages, 4 figures, 5 tables (including 2 appendix tables)
Abstract:Recent advancements in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) have significantly enhanced the ability of large language models (LLMs) to perform complex question-answering (QA) tasks. In this paper, we introduce MedBioRAG, a retrieval-augmented model designed to improve biomedical QA performance through a combination of semantic and lexical search, document retrieval, and supervised fine-tuning. MedBioRAG efficiently retrieves and ranks relevant biomedical documents, enabling precise and context-aware response generation. We evaluate MedBioRAG across text retrieval, close-ended QA, and long-form QA tasks using benchmark datasets such as NFCorpus, TREC-COVID, MedQA, PubMedQA, and BioASQ. Experimental results demonstrate that MedBioRAG outperforms previous state-of-the-art (SoTA) models and the GPT-4o base model in all evaluated tasks. Notably, our approach improves NDCG and MRR scores for document retrieval, while achieving higher accuracy in close-ended QA and ROUGE scores in long-form QA. Our findings highlight the effectiveness of semantic search-based retrieval and LLM fine-tuning in biomedical applications.
zh
[NLP-37] Benchmarking Automatic Speech Recognition Models for African Languages
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决非洲语言自动语音识别(ASR)在低资源条件下面临的两大核心问题:一是标注数据稀缺导致模型性能受限,二是缺乏系统性的模型选择、数据扩展和解码策略指导。其解决方案的关键在于对四种前沿ASR模型(MMS、W2v-BERT、XLS-R和Whisper)在13种非洲语言上进行统一基准测试,通过在1至400小时的逐步扩增语料库中微调模型,量化分析不同模型在不同数据规模下的表现差异,并揭示预训练覆盖范围、模型架构、数据域与资源可用性之间的交互作用,从而为低资源场景下ASR系统的构建提供可操作的实践依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10968
作者: Alvin Nahabwe,Sulaiman Kagumire,Denis Musinguzi,Bruno Beijuka,Jonah Mubuuke Kyagaba,Peter Nabende,Andrew Katumba,Joyce Nakatumba-Nabende
机构: Makerere University Centre for Artificial Intelligence(Makerere大学人工智能中心); Marconi Lab(Marconi实验室); Makerere University(Makerere大学); Department of Information Systems(信息系); Department of Electrical Engineering(电气工程系); Department of Computer Science(计算机科学系)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Sound (cs.SD); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS)
备注: 19 pages, 8 figures, Deep Learning Indiba, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research
Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) for African languages remains constrained by limited labeled data and the lack of systematic guidance on model selection, data scaling, and decoding strategies. Large pre-trained systems such as Whisper, XLS-R, MMS, and W2v-BERT have expanded access to ASR technology, but their comparative behavior in African low-resource contexts has not been studied in a unified and systematic way. In this work, we benchmark four state-of-the-art ASR models across 13 African languages, fine-tuning them on progressively larger subsets of transcribed data ranging from 1 to 400 hours. Beyond reporting error rates, we provide new insights into why models behave differently under varying conditions. We show that MMS and W2v-BERT are more data efficient in very low-resource regimes, XLS-R scales more effectively as additional data becomes available, and Whisper demonstrates advantages in mid-resource conditions. We also analyze where external language model decoding yields improvements and identify cases where it plateaus or introduces additional errors, depending on the alignment between acoustic and text resources. By highlighting the interaction between pre-training coverage, model architecture, dataset domain, and resource availability, this study offers practical and insights into the design of ASR systems for underrepresented languages.
zh
[NLP-38] ASR Under the Stethoscope: Evaluating Biases in Clinical Speech Recognition across Indian Languages
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决自动语音识别(Automatic Speech Recognition, ASR)在多语言、多元文化背景下的印度医疗环境中可靠性不足的问题,尤其关注其在卡纳达语、印地语和印式英语等语言及不同性别、角色(患者与临床医生)群体中的公平性表现。解决方案的关键在于构建首个针对印度真实临床访谈数据的系统性ASR性能评估框架,涵盖多种主流模型(如Indic Whisper、Whisper、Sarvam、Google Speech-to-Text等),并从语言、说话者角色、性别及交叉差异等多个维度进行准确性与偏差分析,从而揭示现有模型在代码混合或地方性语言上的显著性能下降以及潜在的公平性风险,为开发更具文化敏感性和人口代表性的人工智能辅助医疗系统提供实证依据与改进方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10967
作者: Subham Kumar,Prakrithi Shivaprakash,Abhishek Manoharan,Astut Kurariya,Diptadhi Mukherjee,Lekhansh Shukla,Animesh Mukherjee,Prabhat Chand,Pratima Murthy
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Sound (cs.SD); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS)
备注:
Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) is increasingly used to document clinical encounters, yet its reliability in multilingual and demographically diverse Indian healthcare contexts remains largely unknown. In this study, we conduct the first systematic audit of ASR performance on real world clinical interview data spanning Kannada, Hindi, and Indian English, comparing leading models including Indic Whisper, Whisper, Sarvam, Google speech to text, Gemma3n, Omnilingual, Vaani, and Gemini. We evaluate transcription accuracy across languages, speakers, and demographic subgroups, with a particular focus on error patterns affecting patients vs. clinicians and gender based or intersectional disparities. Our results reveal substantial variability across models and languages, with some systems performing competitively on Indian English but failing on code mixed or vernacular speech. We also uncover systematic performance gaps tied to speaker role and gender, raising concerns about equitable deployment in clinical settings. By providing a comprehensive multilingual benchmark and fairness analysis, our work highlights the need for culturally and demographically inclusive ASR development for healthcare ecosystem in India.
zh
[NLP-39] V2TV: A Unified Framework for Interleaved Language and Video Generation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前视频生成模型在处理需要复杂语义分支或反复高层推理的任务时表现不佳的问题,尤其是在生成长视频时难以保持视觉质量与文本提示的一致性。其解决方案的关键在于提出TV2TV框架,该框架采用一种交错式文本与视频生成机制,通过Mixture-of-Transformers(MoT)架构联合学习语言建模(next-token prediction)和视频流匹配(next-frame prediction),并在推理阶段动态决定何时切换生成文本或视频帧,从而将“决策”过程交由语言建模模块完成,使模型能够先“用文字思考”后续内容再“以像素行动”生成画面,显著提升生成视频的视觉质量和可控性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.05103
作者: Xiaochuang Han,Youssef Emad,Melissa Hall,John Nguyen,Karthik Padthe,Liam Robbins,Amir Bar,Delong Chen,Michal Drozdzal,Maha Elbayad,Yushi Hu,Shang-Wen Li,Sreya Dutta Roy,Jakob Verbeek,XuDong Wang,Marjan Ghazvininejad,Luke Zettlemoyer,Emily Dinan
机构: Meta(元)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Video generation models are rapidly advancing, but can still struggle with complex video outputs that require significant semantic branching or repeated high-level reasoning about what should happen next. In this paper, we introduce a new class of omni video-text models that integrate ideas from recent LM reasoning advances to address this challenge. More specifically, we present TV2TV, a unified generative modeling framework which decomposes video generation into an interleaved text and video generation process. TV2TV jointly learns language modeling (next-token prediction) and video flow matching (next-frame prediction) using a Mixture-of-Transformers (MoT) architecture. At inference time, TV2TV decides when to alternate between generating text and video frames, allowing the model to “think in words” about subsequent content before ``acting in pixels’’ to produce frames. This design offloads much of the responsibility for deciding what should happen next to the language modeling tower, enabling improved visual quality and prompt alignment of generated videos. It also enables fine-grained controllability, allowing users to modify the video generation trajectory through text interventions at any point in the process. In controlled experiments on video game data, TV2TV demonstrates substantial improvements in both visual quality and controllability. TV2TV also scales to natural videos, as we show by augmenting sports videos with interleaved natural language action descriptions using vision-language models (VLMs). Training TV2TV on this corpus yields strong visual quality and prompt alignment, showcasing the model’s ability to reason about and generate complex real-world action sequences. Together, these results highlight TV2TV as a promising step toward video generation with open-ended textual reasoning and control.
zh
计算机视觉
[CV-0] Moment-Based 3D Gaussian Splatting: Resolving Volumetric Occlusion with Order-Independent Transmittance
【速读】:该论文旨在解决3D高斯点云(3D Gaussian Splatting, 3DGS)在渲染复杂、重叠的半透明物体时因依赖简化且顺序相关的alpha混合以及粗略密度积分近似而导致的物理准确性不足问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于统计矩(moment-based)的高保真透射率(transmittance)计算方法,通过为每条相机射线构建连续的密度分布表示,并从中解析出每像素的统计矩,进而重建连续的透射率函数,从而避免了传统的光线追踪或逐像素采样排序的需求,实现了在保持栅格化效率的同时显著提升对复杂半透明介质中光衰减建模的物理真实性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11800
作者: Jan U. Müller,Robin Tim Landsgesell,Leif Van Holland,Patrick Stotko,Reinhard Klein
机构: University of Bonn (波恩大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Graphics (cs.GR)
备注:
Abstract:The recent success of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has reshaped novel view synthesis by enabling fast optimization and real-time rendering of high-quality radiance fields. However, it relies on simplified, order-dependent alpha blending and coarse approximations of the density integral within the rasterizer, thereby limiting its ability to render complex, overlapping semi-transparent objects. In this paper, we extend rasterization-based rendering of 3D Gaussian representations with a novel method for high-fidelity transmittance computation, entirely avoiding the need for ray tracing or per-pixel sample sorting. Building on prior work in moment-based order-independent transparency, our key idea is to characterize the density distribution along each camera ray with a compact and continuous representation based on statistical moments. To this end, we analytically derive and compute a set of per-pixel moments from all contributing 3D Gaussians. From these moments, a continuous transmittance function is reconstructed for each ray, which is then independently sampled within each Gaussian. As a result, our method bridges the gap between rasterization and physical accuracy by modeling light attenuation in complex translucent media, significantly improving overall reconstruction and rendering quality.
zh
[CV-1] V-RGBX: Video Editing with Accurate Controls over Intrinsic Properties
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有大规模视频生成模型在建模真实场景中光照与材质交互时,缺乏对内在场景属性(如反照率、法向量、材质和入射辐射)的联合理解与可编辑性的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出首个端到端的内在感知视频编辑框架V-RGBX,该框架通过一种交错条件机制(interleaved conditioning mechanism),实现三个核心能力:(1)从视频中逆向渲染得到内在通道;(2)基于这些内在表示进行逼真视频合成;(3)以关键帧为条件支持内在通道的可控编辑。该机制使得用户能够通过选择关键帧对任意内在模态进行灵活且物理合理的编辑,并保持时序一致性与视觉真实性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11799
作者: Ye Fang,Tong Wu,Valentin Deschaintre,Duygu Ceylan,Iliyan Georgiev,Chun-Hao Paul Huang,Yiwei Hu,Xuelin Chen,Tuanfeng Yang Wang
机构: Fudan University (复旦大学); Adobe Research; Stanford University (斯坦福大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Project Page: this https URL
Abstract:Large-scale video generation models have shown remarkable potential in modeling photorealistic appearance and lighting interactions in real-world scenes. However, a closed-loop framework that jointly understands intrinsic scene properties (e.g., albedo, normal, material, and irradiance), leverages them for video synthesis, and supports editable intrinsic representations remains unexplored. We present V-RGBX, the first end-to-end framework for intrinsic-aware video editing. V-RGBX unifies three key capabilities: (1) video inverse rendering into intrinsic channels, (2) photorealistic video synthesis from these intrinsic representations, and (3) keyframe-based video editing conditioned on intrinsic channels. At the core of V-RGBX is an interleaved conditioning mechanism that enables intuitive, physically grounded video editing through user-selected keyframes, supporting flexible manipulation of any intrinsic modality. Extensive qualitative and quantitative results show that V-RGBX produces temporally consistent, photorealistic videos while propagating keyframe edits across sequences in a physically plausible manner. We demonstrate its effectiveness in diverse applications, including object appearance editing and scene-level relighting, surpassing the performance of prior methods.
zh
[CV-2] Particulate: Feed-Forward 3D Object Articulation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决从单个静态3D网格中自动推断物体潜在的可动结构(包括3D部件、运动学结构和运动约束)的问题,这是生成式AI (Generative AI) 和三维场景理解中的关键挑战。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种前馈式方法Particulate,其核心是一个名为Part Articulation Transformer的Transformer网络,能够直接处理输入mesh的点云数据,以灵活且可扩展的架构预测所有相关属性,并原生支持多关节结构。该方法在公开数据集上的多样化可动3D资产上端到端训练,在推理阶段仅需数秒即可生成完整的可动3D模型,显著优于依赖逐对象优化的传统方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11798
作者: Ruining Li,Yuxin Yao,Chuanxia Zheng,Christian Rupprecht,Joan Lasenby,Shangzhe Wu,Andrea Vedaldi
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Graphics (cs.GR)
备注: Project page: this https URL
Abstract:We present Particulate, a feed-forward approach that, given a single static 3D mesh of an everyday object, directly infers all attributes of the underlying articulated structure, including its 3D parts, kinematic structure, and motion constraints. At its core is a transformer network, Part Articulation Transformer, which processes a point cloud of the input mesh using a flexible and scalable architecture to predict all the aforementioned attributes with native multi-joint support. We train the network end-to-end on a diverse collection of articulated 3D assets from public datasets. During inference, Particulate lifts the network’s feed-forward prediction to the input mesh, yielding a fully articulated 3D model in seconds, much faster than prior approaches that require per-object optimization. Particulate can also accurately infer the articulated structure of AI-generated 3D assets, enabling full-fledged extraction of articulated 3D objects from a single (real or synthetic) image when combined with an off-the-shelf image-to-3D generator. We further introduce a new challenging benchmark for 3D articulation estimation curated from high-quality public 3D assets, and redesign the evaluation protocol to be more consistent with human preferences. Quantitative and qualitative results show that Particulate significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches.
zh
[CV-3] AnchorDream: Repurposing Video Diffusion for Embodiment-Aware Robot Data Synthesis
【速读】:该论文旨在解决模仿学习中大规模、多样化机器人示范数据获取困难的问题,尤其是现实世界数据采集成本高以及仿真环境存在显著的“仿真到现实”差距(sim-to-real gap)的限制。现有生成式方法通常仅改变视觉外观而未生成新行为,或因身体结构不一致导致运动不合理。其解决方案的关键在于提出AnchorDream——一种具身感知的世界模型,通过将预训练视频扩散模型(video diffusion models)用于机器人数据合成,以机器人运动渲染图为条件约束扩散过程,从而锚定具身信息防止幻觉,同时生成与机器人运动学一致的物体和环境。该方法仅需少量人类远程操作示范即可扩展为高质量、多样化的数据集,无需显式环境建模,实验证明其能显著提升下游策略学习性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11797
作者: Junjie Ye,Rong Xue,Basile Van Hoorick,Pavel Tokmakov,Muhammad Zubair Irshad,Yue Wang,Vitor Guizilini
机构: Toyota Research Institute (丰田研究所); USC Physical Superintelligence (PSI) Lab (南加州大学物理超智能实验室)
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Project page: this https URL
Abstract:The collection of large-scale and diverse robot demonstrations remains a major bottleneck for imitation learning, as real-world data acquisition is costly and simulators offer limited diversity and fidelity with pronounced sim-to-real gaps. While generative models present an attractive solution, existing methods often alter only visual appearances without creating new behaviors, or suffer from embodiment inconsistencies that yield implausible motions. To address these limitations, we introduce AnchorDream, an embodiment-aware world model that repurposes pretrained video diffusion models for robot data synthesis. AnchorDream conditions the diffusion process on robot motion renderings, anchoring the embodiment to prevent hallucination while synthesizing objects and environments consistent with the robot’s kinematics. Starting from only a handful of human teleoperation demonstrations, our method scales them into large, diverse, high-quality datasets without requiring explicit environment modeling. Experiments show that the generated data leads to consistent improvements in downstream policy learning, with relative gains of 36.4% in simulator benchmarks and nearly double performance in real-world studies. These results suggest that grounding generative world models in robot motion provides a practical path toward scaling imitation learning.
zh
[CV-4] Structure From Tracking: Distilling Structure-Preserving Motion for Video Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视频生成模型中结构保持性运动(structure-preserving motion)难以实现的问题,尤其是在处理刚体与非刚体对象(如人和动物)时,现有扩散模型常因训练数据规模不足而产生物理上不合理的运动过渡。其解决方案的关键在于从自回归视频跟踪模型(SAM2)中蒸馏出结构保持性运动先验,并将其融入双向视频扩散模型(CogVideoX),通过两个核心创新实现:一是引入双向特征融合模块,从递归模型中提取全局结构保持性运动先验;二是设计局部 Gram 流损失(Local Gram Flow loss),对齐局部特征间的运动一致性,从而显著提升生成视频的物理合理性和视觉质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11792
作者: Yang Fei,George Stoica,Jingyuan Liu,Qifeng Chen,Ranjay Krishna,Xiaojuan Wang,Benlin Liu
机构: HKUST(香港科技大学); University of Washington(华盛顿大学); Georgia Tech(佐治亚理工学院); Adobe(Adobe公司)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Project Website: this https URL
Abstract:Reality is a dance between rigid constraints and deformable structures. For video models, that means generating motion that preserves fidelity as well as structure. Despite progress in diffusion models, producing realistic structure-preserving motion remains challenging, especially for articulated and deformable objects such as humans and animals. Scaling training data alone, so far, has failed to resolve physically implausible transitions. Existing approaches rely on conditioning with noisy motion representations, such as optical flow or skeletons extracted using an external imperfect model. To address these challenges, we introduce an algorithm to distill structure-preserving motion priors from an autoregressive video tracking model (SAM2) into a bidirectional video diffusion model (CogVideoX). With our method, we train SAM2VideoX, which contains two innovations: (1) a bidirectional feature fusion module that extracts global structure-preserving motion priors from a recurrent model like SAM2; (2) a Local Gram Flow loss that aligns how local features move together. Experiments on VBench and in human studies show that SAM2VideoX delivers consistent gains (+2.60% on VBench, 21-22% lower FVD, and 71.4% human preference) over prior baselines. Specifically, on VBench, we achieve 95.51%, surpassing REPA (92.91%) by 2.60%, and reduce FVD to 360.57, a 21.20% and 22.46% improvement over REPA- and LoRA-finetuning, respectively. The project website can be found at this https URL .
zh
[CV-5] Uncertainty-Aware Domain Adaptation for Vitiligo Segmentation in Clinical Photographs
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在常规临床照片中准确量化白癜风(vitiligo)病变范围的问题,这对于长期监测治疗反应至关重要。解决方案的关键在于构建一个可信且频域感知的分割框架,其核心包括三个协同机制:(1) 一种数据高效训练策略,结合ISIC 2019数据集上的领域自适应预训练与ROI约束的双任务损失,有效抑制背景噪声;(2) 基于ConvNeXt V2编码器的结构优化,引入新颖的高频谱门控(High-Frequency Spectral Gating, HFSG)模块和stem-skip连接,以捕捉细微纹理特征;(3) 临床可信机制,通过K折集成与测试时增强(Test-Time Augmentation, TTA)生成像素级不确定性图,提升模型可靠性并提供可解释的熵图用于医生复核。该方法在专家标注的临床队列上验证表现出优越性能,Dice分数达85.05%,边界误差显著降低,且无灾难性失败,为自动化白癜风评估建立了可靠标准。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11791
作者: Wentao Jiang,Vamsi Varra,Caitlin Perez-Stable,Harrison Zhu,Meredith Apicella,Nicole Nyamongo
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Accurately quantifying vitiligo extent in routine clinical photographs is crucial for longitudinal monitoring of treatment response. We propose a trustworthy, frequency-aware segmentation framework built on three synergistic pillars: (1) a data-efficient training strategy combining domain-adaptive pre-training on the ISIC 2019 dataset with an ROI-constrained dual-task loss to suppress background noise; (2) an architectural refinement via a ConvNeXt V2-based encoder enhanced with a novel High-Frequency Spectral Gating (HFSG) module and stem-skip connections to capture subtle textures; and (3) a clinical trust mechanism employing K-fold ensemble and Test-Time Augmentation (TTA) to generate pixel-wise uncertainty maps. Extensive validation on an expert-annotated clinical cohort demonstrates superior performance, achieving a Dice score of 85.05% and significantly reducing boundary error (95% Hausdorff Distance improved from 44.79 px to 29.95 px), consistently outperforming strong CNN (ResNet-50 and UNet++) and Transformer (MiT-B5) baselines. Notably, our framework demonstrates high reliability with zero catastrophic failures and provides interpretable entropy maps to identify ambiguous regions for clinician review. Our approach suggests that the proposed framework establishes a robust and reliable standard for automated vitiligo assessment.
zh
[CV-6] MatAnyone 2: Scaling Video Matting via a Learned Quality Evaluator
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视频抠图(video matting)中因现有数据集规模有限和真实性不足导致的性能瓶颈问题,尤其是现有方法在缺乏有效边界监督时生成的alpha matte易出现细节缺失、边界模糊等现象。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种可学习的抠图质量评估器(Matting Quality Evaluator, MQE),该评估器无需真实标签即可对alpha matte的语义一致性与边界精度进行像素级评估,输出可靠与错误区域的判别图。MQE通过两种方式提升模型性能:一是作为训练过程中的在线质量反馈机制,抑制错误区域并提供细粒度监督;二是作为离线数据筛选模块,结合先进视频与图像抠图模型的优势优化数据标注质量,从而构建大规模真实场景视频抠图数据集VMReal(含28K片段、2.4M帧)。此外,为应对长视频中显著的外观变化,论文还引入参考帧训练策略,利用局部窗口外的长程帧信息增强模型鲁棒性,最终使MatAnyone 2在合成与真实世界基准上均达到最优性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11782
作者: Peiqing Yang,Shangchen Zhou,Kai Hao,Qingyi Tao
机构: S-Lab, Nanyang Technological University (南洋理工大学); SenseTime Research, Singapore (商汤科技研究)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Project page: this https URL
Abstract:Video matting remains limited by the scale and realism of existing datasets. While leveraging segmentation data can enhance semantic stability, the lack of effective boundary supervision often leads to segmentation-like mattes lacking fine details. To this end, we introduce a learned Matting Quality Evaluator (MQE) that assesses semantic and boundary quality of alpha mattes without ground truth. It produces a pixel-wise evaluation map that identifies reliable and erroneous regions, enabling fine-grained quality assessment. The MQE scales up video matting in two ways: (1) as an online matting-quality feedback during training to suppress erroneous regions, providing comprehensive supervision, and (2) as an offline selection module for data curation, improving annotation quality by combining the strengths of leading video and image matting models. This process allows us to build a large-scale real-world video matting dataset, VMReal, containing 28K clips and 2.4M frames. To handle large appearance variations in long videos, we introduce a reference-frame training strategy that incorporates long-range frames beyond the local window for effective training. Our MatAnyone 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on both synthetic and real-world benchmarks, surpassing prior methods across all metrics.
zh
[CV-7] Smudged Fingerprints: A Systematic Evaluation of the Robustness of AI Image Fingerprints
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI (Generative AI) 图像指纹检测技术在对抗性条件下的鲁棒性问题,即现有方法在面对恶意攻击时是否仍能可靠地实现图像来源模型的归属识别。其解决方案的关键在于首次系统性地评估了多种指纹检测技术在白盒与黑盒访问场景下的安全性,定义了两类攻击目标——指纹移除(fingerprint removal)和指纹伪造(fingerprint forgery),并实现了五种攻击策略对14种代表性指纹方法进行跨RGB、频域和特征学习域的全面测试。实验揭示了干净数据与对抗样本之间显著的性能差距,并发现高准确率的方法通常脆弱于攻击,从而强调了未来研究需在准确性与鲁棒性之间寻求平衡,同时识别出若干具备潜力的稳健方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11771
作者: Kai Yao,Marc Juarez
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: This work has been accepted for publication in the 4th IEEE Conference on Secure and Trustworthy Machine Learning (IEEE SaTML 2026). The final version will be available on IEEE Xplore
Abstract:Model fingerprint detection techniques have emerged as a promising approach for attributing AI-generated images to their source models, but their robustness under adversarial conditions remains largely unexplored. We present the first systematic security evaluation of these techniques, formalizing threat models that encompass both white- and black-box access and two attack goals: fingerprint removal, which erases identifying traces to evade attribution, and fingerprint forgery, which seeks to cause misattribution to a target model. We implement five attack strategies and evaluate 14 representative fingerprinting methods across RGB, frequency, and learned-feature domains on 12 state-of-the-art image generators. Our experiments reveal a pronounced gap between clean and adversarial performance. Removal attacks are highly effective, often achieving success rates above 80% in white-box settings and over 50% under constrained black-box access. While forgery is more challenging than removal, its success significantly varies across targeted models. We also identify a utility-robustness trade-off: methods with the highest attribution accuracy are often vulnerable to attacks. Although some techniques exhibit robustness in specific settings, none achieves high robustness and accuracy across all evaluated threat models. These findings highlight the need for techniques balancing robustness and accuracy, and identify the most promising approaches for advancing this goal.
zh
[CV-8] Reducing Domain Gap with Diffusion-Based Domain Adaptation for Cell Counting ICML
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在标签稀缺环境下,合成显微图像与真实样本之间存在显著域差距(domain gap)的问题,从而影响深度学习模型(如细胞计数任务)的训练效果。传统域适应方法难以有效弥合这种差距,尤其当合成图像缺乏真实样本复杂的纹理和视觉模式时。其解决方案的关键在于将原本用于艺术风格迁移的基于逆向的风格迁移(Inversion-Based Style Transfer, InST)框架引入生物医学显微图像领域,通过结合潜在空间中的自适应实例归一化(Adaptive Instance Normalization)与扩散模型的随机反演(stochastic inversion),实现从真实荧光显微图像中提取风格并迁移至合成图像,同时弱保留内容结构。实验表明,使用该方法生成的合成数据可显著降低细胞计数任务中的平均绝对误差(MAE),优于硬编码合成数据、公开Cell200-s数据集甚至仅用真实数据训练的模型,证明了其在缩小域差距方面的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11763
作者: Mohammad Dehghanmanshadi,Wallapak Tavanapong
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted at ICMLA 2025
Abstract:Generating realistic synthetic microscopy images is critical for training deep learning models in label-scarce environments, such as cell counting with many cells per image. However, traditional domain adaptation methods often struggle to bridge the domain gap when synthetic images lack the complex textures and visual patterns of real samples. In this work, we adapt the Inversion-Based Style Transfer (InST) framework originally designed for artistic style transfer to biomedical microscopy images. Our method combines latent-space Adaptive Instance Normalization with stochastic inversion in a diffusion model to transfer the style from real fluorescence microscopy images to synthetic ones, while weakly preserving content structure. We evaluate the effectiveness of our InST-based synthetic dataset for downstream cell counting by pre-training and fine-tuning EfficientNet-B0 models on various data sources, including real data, hard-coded synthetic data, and the public Cell200-s dataset. Models trained with our InST-synthesized images achieve up to 37% lower Mean Absolute Error (MAE) compared to models trained on hard-coded synthetic data, and a 52% reduction in MAE compared to models trained on Cell200-s (from 53.70 to 25.95 MAE). Notably, our approach also outperforms models trained on real data alone (25.95 vs. 27.74 MAE). Further improvements are achieved when combining InST-synthesized data with lightweight domain adaptation techniques such as DACS with CutMix. These findings demonstrate that InST-based style transfer most effectively reduces the domain gap between synthetic and real microscopy data. Our approach offers a scalable path for enhancing cell counting performance while minimizing manual labeling effort. The source code and resources are publicly available at: this https URL. Comments: Accepted at ICMLA 2025 Subjects: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV) Cite as: arXiv:2512.11763 [cs.CV] (or arXiv:2512.11763v1 [cs.CV] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11763 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[CV-9] SVG-T2I: Scaling Up Text-to-Image Latent Diffusion Model Without Variational Autoencoder
【速读】:该论文旨在解决如何在视觉基础模型(Visual Foundation Model, VFM)的表示空间中训练大规模文本到图像扩散模型(text-to-image diffusion models)这一尚未充分探索的问题。当前主流方法通常依赖于从原始像素空间进行训练,而忽视了VFM所具备的强大表征能力。解决方案的关键在于扩展SVG(Self-supervised representations for Visual Generation)框架,提出SVG-T2I,其核心是直接在VFM特征域内实现高质量文本到图像生成,无需依赖原始图像像素。通过标准的文本到图像扩散流程,该方法在GenEval(0.75)和DPG-Bench(85.78)上达到具有竞争力的性能,验证了VFM在生成任务中的内在表征潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11749
作者: Minglei Shi,Haolin Wang,Borui Zhang,Wenzhao Zheng,Bohan Zeng,Ziyang Yuan,Xiaoshi Wu,Yuanxing Zhang,Huan Yang,Xintao Wang,Pengfei Wan,Kun Gai,Jie Zhou,Jiwen Lu
机构: Tsinghua University (清华大学); Kuaishou Technology (快手科技)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Code Repository: this https URL Model Weights: this https URL
Abstract:Visual generation grounded in Visual Foundation Model (VFM) representations offers a highly promising unified pathway for integrating visual understanding, perception, and generation. Despite this potential, training large-scale text-to-image diffusion models entirely within the VFM representation space remains largely unexplored. To bridge this gap, we scale the SVG (Self-supervised representations for Visual Generation) framework, proposing SVG-T2I to support high-quality text-to-image synthesis directly in the VFM feature domain. By leveraging a standard text-to-image diffusion pipeline, SVG-T2I achieves competitive performance, reaching 0.75 on GenEval and 85.78 on DPG-Bench. This performance validates the intrinsic representational power of VFMs for generative tasks. We fully open-source the project, including the autoencoder and generation model, together with their training, inference, evaluation pipelines, and pre-trained weights, to facilitate further research in representation-driven visual generation.
zh
[CV-10] Weak-to-Strong Generalization Enables Fully Automated De Novo Training of Multi-head Mask-RCNN Model for Segmenting Densely Overlapping Cell Nuclei in Multiplex Whole-slice Brain Images
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多光谱循环免疫荧光(multiplex cyclic immunofluorescent, mCIF)全切片图像(whole-slide images, WSI)中重叠细胞核的可靠分割问题,尤其是在新仪器或新成像协议下缺乏人工标注数据时,如何实现无需人类干预的全自动训练与泛化。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种“弱到强”(weak to strong)泛化方法,通过伪标签校正(pseudo-label correction)和覆盖范围扩展(coverage expansion)这两个核心机制,使基于Mask R-CNN的多头结构结合高效通道注意力机制能够从少量弱监督信号中学习并准确分割全新类别的图像。此外,该方法还引入了用于生产环境中自动自我诊断分割质量的指标,以替代昂贵的人工视觉验证。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11722
作者: Lin Bai,Xiaoyang Li,Liqiang Huang,Quynh Nguyen,Hien Van Nguyen,Saurabh Prasad,Dragan Maric,John Redell,Pramod Dash,Badrinath Roysam
机构: University of Houston (休斯顿大学); University of Texas at Austin (德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校); University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:We present a weak to strong generalization methodology for fully automated training of a multi-head extension of the Mask-RCNN method with efficient channel attention for reliable segmentation of overlapping cell nuclei in multiplex cyclic immunofluorescent (IF) whole-slide images (WSI), and present evidence for pseudo-label correction and coverage expansion, the key phenomena underlying weak to strong generalization. This method can learn to segment de novo a new class of images from a new instrument and/or a new imaging protocol without the need for human annotations. We also present metrics for automated self-diagnosis of segmentation quality in production environments, where human visual proofreading of massive WSI images is unaffordable. Our method was benchmarked against five current widely used methods and showed a significant improvement. The code, sample WSI images, and high-resolution segmentation results are provided in open form for community adoption and adaptation.
zh
[CV-11] Reframing Music-Driven 2D Dance Pose Generation as Multi-Channel Image Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决音乐到舞蹈生成任务中,如何从音乐信号中合成时序连贯且节奏对齐的2D姿态序列这一核心挑战,尤其是在复杂、高方差的真实场景(in-the-wild)分布下。解决方案的关键在于将音乐到舞蹈生成重构为一种音乐token条件下的多通道图像合成问题:将2D姿态序列编码为one-hot图像并通过预训练图像VAE压缩,再使用DiT风格的骨干网络建模,从而继承现代文生图模型在架构和训练上的优势,更好地捕捉高方差的姿态分布;在此基础上,进一步提出两个关键创新:(i) 时间共享的时序索引机制,显式同步音乐token与姿态潜变量的时间对齐关系;(ii) 参考姿态条件策略,在保持个体身体比例和屏幕尺度的同时支持长时程分段拼接生成。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11720
作者: Yan Zhang,Han Zou,Lincong Feng,Cong Xie,Ruiqi Yu,Zhenpeng Zhan
机构: Baidu Inc(百度公司)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Recent pose-to-video models can translate 2D pose sequences into photorealistic, identity-preserving dance videos, so the key challenge is to generate temporally coherent, rhythm-aligned 2D poses from music, especially under complex, high-variance in-the-wild distributions. We address this by reframing music-to-dance generation as a music-token-conditioned multi-channel image synthesis problem: 2D pose sequences are encoded as one-hot images, compressed by a pretrained image VAE, and modeled with a DiT-style backbone, allowing us to inherit architectural and training advances from modern text-to-image models and better capture high-variance 2D pose distributions. On top of this formulation, we introduce (i) a time-shared temporal indexing scheme that explicitly synchronizes music tokens and pose latents over time and (ii) a reference-pose conditioning strategy that preserves subject-specific body proportions and on-screen scale while enabling long-horizon segment-and-stitch generation. Experiments on a large in-the-wild 2D dance corpus and the calibrated AIST++2D benchmark show consistent improvements over representative music-to-dance methods in pose- and video-space metrics and human preference, and ablations validate the contributions of the representation, temporal indexing, and reference conditioning. See supplementary videos at this https URL
zh
[CV-12] Referring Change Detection in Remote Sensing Imagery WACV
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统遥感图像变化检测方法无法区分变化类型、语义变化检测方法因固定类别定义和模型架构导致难以跨任务复用的问题。其核心挑战在于如何实现灵活、可扩展且针对特定类别的变化检测,同时应对标注数据稀缺与类别不平衡问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于自然语言提示的引用式变化检测(Referring Change Detection, RCD)框架,通过引入跨模态融合网络RCDNet实现语言与视觉信息的联合建模,并设计基于扩散模型的合成数据生成管道RCDGen,在无需语义分割掩码的情况下生成指定类别的真实感后变化图像与变化图,从而显著降低数据构建门槛并支持目标导向的变化检测。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11719
作者: Yilmaz Korkmaz,Jay N. Paranjape,Celso M. de Melo,Vishal M. Patel
机构: Johns Hopkins University (约翰霍普金斯大学); DEVCOM U.S. Army Research Laboratory (美国陆军研究实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 2026 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV)
Abstract:Change detection in remote sensing imagery is essential for applications such as urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster management. Traditional change detection methods typically identify all changes between two temporal images without distinguishing the types of transitions, which can lead to results that may not align with specific user needs. Although semantic change detection methods have attempted to address this by categorizing changes into predefined classes, these methods rely on rigid class definitions and fixed model architectures, making it difficult to mix datasets with different label sets or reuse models across tasks, as the output channels are tightly coupled with the number and type of semantic classes. To overcome these limitations, we introduce Referring Change Detection (RCD), which leverages natural language prompts to detect specific classes of changes in remote sensing images. By integrating language understanding with visual analysis, our approach allows users to specify the exact type of change they are interested in. However, training models for RCD is challenging due to the limited availability of annotated data and severe class imbalance in existing datasets. To address this, we propose a two-stage framework consisting of (I) \textbfRCDNet, a cross-modal fusion network designed for referring change detection, and (II) \textbfRCDGen, a diffusion-based synthetic data generation pipeline that produces realistic post-change images and change maps for a specified category using only pre-change image, without relying on semantic segmentation masks and thereby significantly lowering the barrier to scalable data creation. Experiments across multiple datasets show that our framework enables scalable and targeted change detection. Project website is here: this https URL.
zh
[CV-13] EditMGT: Unleashing Potentials of Masked Generative Transformers in Image Editing
【速读】:该论文旨在解决扩散模型(Diffusion Models, DMs)在图像编辑任务中因全局去噪机制导致的非目标区域 unintended modifications 问题,即局部编辑操作容易牵连整个图像上下文,造成不期望的修改。其解决方案的关键在于引入基于掩码生成式 Transformer(Masked Generative Transformers, MGTs)的局部解码范式,利用其多标记预测特性实现对编辑区域的显式控制:首先通过跨注意力图提供精细定位信号,并设计多层注意力融合策略增强定位精度;进而提出 region-hold sampling 方法,在低注意力区域限制 token 替换,从而抑制伪影编辑,确保仅在目标区域内进行有效修改,同时保持非相关区域不变。该方法无需增加额外参数即可将预训练文本到图像 MGT 转化为高效图像编辑模型,显著提升编辑速度与质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11715
作者: Wei Chow,Linfeng Li,Lingdong Kong,Zefeng Li,Qi Xu,Hang Song,Tian Ye,Xian Wang,Jinbin Bai,Shilin Xu,Xiangtai Li,Junting Pan,Shaoteng Liu,Ran Zhou,Tianshu Yang,Songhua Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Multimedia (cs.MM); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
备注:
Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion models (DMs) have achieved exceptional visual quality in image editing tasks. However, the global denoising dynamics of DMs inherently conflate local editing targets with the full-image context, leading to unintended modifications in non-target regions. In this paper, we shift our attention beyond DMs and turn to Masked Generative Transformers (MGTs) as an alternative approach to tackle this challenge. By predicting multiple masked tokens rather than holistic refinement, MGTs exhibit a localized decoding paradigm that endows them with the inherent capacity to explicitly preserve non-relevant regions during the editing process. Building upon this insight, we introduce the first MGT-based image editing framework, termed EditMGT. We first demonstrate that MGT’s cross-attention maps provide informative localization signals for localizing edit-relevant regions and devise a multi-layer attention consolidation scheme that refines these maps to achieve fine-grained and precise localization. On top of these adaptive localization results, we introduce region-hold sampling, which restricts token flipping within low-attention areas to suppress spurious edits, thereby confining modifications to the intended target regions and preserving the integrity of surrounding non-target areas. To train EditMGT, we construct CrispEdit-2M, a high-resolution dataset spanning seven diverse editing categories. Without introducing additional parameters, we adapt a pre-trained text-to-image MGT into an image editing model through attention injection. Extensive experiments across four standard benchmarks demonstrate that, with fewer than 1B parameters, our model achieves similarity performance while enabling 6 times faster editing. Moreover, it delivers comparable or superior editing quality, with improvements of 3.6% and 17.6% on style change and style transfer tasks, respectively.
zh
[CV-14] xt images processing system using artificial intelligence models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在复杂成像条件下(如光照变化、文本随机朝向、弯曲或部分遮挡、低分辨率及轻微可见文本)对图像中文本内容进行准确识别与分类的问题。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个端到端的文本图像分类装置,通过四个核心步骤实现:图像采集与预处理、基于DBNet++模型的文本区域检测、利用BART模型对检测到的文本元素进行分类,并通过Python与PyQt5开发的用户界面展示结果。整个流程设计为无缝衔接的工作流,实验表明在Total-Text数据集上达到约94.62%的文本识别率,验证了该方法在非受控环境下进行混合来源文本分类的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11691
作者: Aya Kaysan Bahjat
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Graphics (cs.GR)
备注: 8 pages, 12 figures, article
Abstract:This is to present a text image classifier device that identifies textual content in images and then categorizes each image into one of four predefined categories, including Invoice, Form, Letter, or Report. The device supports a gallery mode, in which users browse files on flash disks, hard disk drives, or microSD cards, and a live mode which renders feeds of cameras connected to it. Its design is specifically aimed at addressing pragmatic challenges, such as changing light, random orientation, curvature or partial coverage of text, low resolution, and slightly visible text. The steps of the processing process are divided into four steps: image acquisition and preprocessing, textual elements detection with the help of DBNet++ (Differentiable Binarization Network Plus) model, BART (Bidirectional Auto-Regressive Transformers) model that classifies detected textual elements, and the presentation of the results through a user interface written in Python and PyQt5. All the stages are connected in such a way that they form a smooth workflow. The system achieved a text recognition rate of about 94.62% when tested over ten hours on the mentioned Total-Text dataset, that includes high resolution images, created so as to represent a wide range of problematic conditions. These experimental results support the effectiveness of the suggested methodology to practice, mixed-source text categorization, even in uncontrolled imaging conditions.
zh
[CV-15] Depth-Copy-Paste: Multimodal and Depth-Aware Compositing for Robust Face Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统复制粘贴数据增强方法在人脸检测系统训练中生成不真实复合样本的问题,这些问题主要源于前景提取不准确、场景几何不一致以及背景语义不匹配。解决方案的关键在于提出一种多模态且深度感知的增强框架——Depth Copy Paste,其核心包括:利用BLIP和CLIP联合评估语义与视觉一致性以自动检索最合适的背景图像;通过SAM3实现精确前景分割并结合Depth-Anything提取未遮挡的可见人体区域,确保面部细节不被破坏;引入基于深度图的滑动窗口放置机制,在背景深度图上搜索具有最优深度连续性和尺度对齐的粘贴位置,从而生成具有自然深度关系和更高视觉合理性的复合样本。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11683
作者: Qiushi Guo
机构: Coffee AI Lab (咖啡人工智能实验室); Great Wall Motor (长城汽车)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Data augmentation is crucial for improving the robustness of face detection systems, especially under challenging conditions such as occlusion, illumination variation, and complex environments. Traditional copy paste augmentation often produces unrealistic composites due to inaccurate foreground extraction, inconsistent scene geometry, and mismatched background semantics. To address these limitations, we propose Depth Copy Paste, a multimodal and depth aware augmentation framework that generates diverse and physically consistent face detection training samples by copying full body person instances and pasting them into semantically compatible scenes. Our approach first employs BLIP and CLIP to jointly assess semantic and visual coherence, enabling automatic retrieval of the most suitable background images for the given foreground person. To ensure high quality foreground masks that preserve facial details, we integrate SAM3 for precise segmentation and Depth-Anything to extract only the non occluded visible person regions, preventing corrupted facial textures from being used in augmentation. For geometric realism, we introduce a depth guided sliding window placement mechanism that searches over the background depth map to identify paste locations with optimal depth continuity and scale alignment. The resulting composites exhibit natural depth relationships and improved visual plausibility. Extensive experiments show that Depth Copy Paste provides more diverse and realistic training data, leading to significant performance improvements in downstream face detection tasks compared with traditional copy paste and depth free augmentation methods.
zh
[CV-16] Cross-modal Context-aware Learning for Visual Prompt Guided Multimodal Image Understanding in Remote Sensing
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在遥感图像理解中,当仅提供简单通用文本提示时,现有方法难以引导模型聚焦于用户关注区域的问题;同时,在大规模航空影像中,由于物体外观高度相似且存在复杂的相互关系,导致准确识别困难。解决方案的关键在于提出一种跨模态上下文感知学习框架CLV-Net,其核心创新包括:1)设计了上下文感知掩码解码器(Context-Aware Mask Decoder),通过建模和整合对象间关系来增强目标表征并提升分割掩码质量;2)引入语义与关系对齐模块,包含跨模态语义一致性损失(Cross-modal Semantic Consistency Loss)以增强视觉相似目标的细粒度区分能力,以及关系一致性损失(Relationship Consistency Loss)以确保文本描述的关系与图像中的视觉交互保持一致。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11680
作者: Xu Zhang,Jiabin Fang,Zhuoming Ding,Jin Yuan,Xuan Liu,Qianjun Zhang,Zhiyong Li
机构: Hunan University (湖南大学); Southwest Jiaotong University (西南交通大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 12 pages, 5 figures
Abstract:Recent advances in image understanding have enabled methods that leverage large language models for multimodal reasoning in remote sensing. However, existing approaches still struggle to steer models to the user-relevant regions when only simple, generic text prompts are available. Moreover, in large-scale aerial imagery many objects exhibit highly similar visual appearances and carry rich inter-object relationships, which further complicates accurate recognition. To address these challenges, we propose Cross-modal Context-aware Learning for Visual Prompt-Guided Multimodal Image Understanding (CLV-Net). CLV-Net lets users supply a simple visual cue, a bounding box, to indicate a region of interest, and uses that cue to guide the model to generate correlated segmentation masks and captions that faithfully reflect user intent. Central to our design is a Context-Aware Mask Decoder that models and integrates inter-object relationships to strengthen target representations and improve mask quality. In addition, we introduce a Semantic and Relationship Alignment module: a Cross-modal Semantic Consistency Loss enhances fine-grained discrimination among visually similar targets, while a Relationship Consistency Loss enforces alignment between textual relations and visual interactions. Comprehensive experiments on two benchmark datasets show that CLV-Net outperforms existing methods and establishes new state-of-the-art results. The model effectively captures user intent and produces precise, intention-aligned multimodal outputs.
zh
[CV-17] Kinetic Mining in Context: Few-Shot Action Synthesis via Text-to-Motion Distillation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决骨骼动作识别(Skeletal-based Human Activity Recognition, HAR)中大规模标注动作数据集获取成本高、数据稀缺的问题,尤其是通用文本到动作(Text-to-Motion, T2M)生成模型因训练目标与HAR需求不匹配而难以直接用于HAR任务的领域差距问题。解决方案的关键在于提出KineMIC(Kinetic Mining In Context)框架,通过利用CLIP文本嵌入在语义空间中的对应关系,实现稀疏标签的HAR类别与T2M源数据之间的软监督对齐,从而引导扩散模型进行基于运动学特性的微调,将通用T2M模型转化为适用于少样本场景下的动作到动作生成器(Action-to-Motion generator),显著提升合成动作的连贯性与分类准确性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11654
作者: Luca Cazzola,Ahed Alboody
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:The acquisition cost for large, annotated motion datasets remains a critical bottleneck for skeletal-based Human Activity Recognition (HAR). Although Text-to-Motion (T2M) generative models offer a compelling, scalable source of synthetic data, their training objectives, which emphasize general artistic motion, and dataset structures fundamentally differ from HAR’s requirements for kinematically precise, class-discriminative actions. This disparity creates a significant domain gap, making generalist T2M models ill-equipped for generating motions suitable for HAR classifiers. To address this challenge, we propose KineMIC (Kinetic Mining In Context), a transfer learning framework for few-shot action synthesis. KineMIC adapts a T2M diffusion model to an HAR domain by hypothesizing that semantic correspondences in the text encoding space can provide soft supervision for kinematic distillation. We operationalize this via a kinetic mining strategy that leverages CLIP text embeddings to establish correspondences between sparse HAR labels and T2M source data. This process guides fine-tuning, transforming the generalist T2M backbone into a specialized few-shot Action-to-Motion generator. We validate KineMIC using HumanML3D as the source T2M dataset and a subset of NTU RGB+D 120 as the target HAR domain, randomly selecting just 10 samples per action class. Our approach generates significantly more coherent motions, providing a robust data augmentation source that delivers a +23.1% accuracy points improvement. Animated illustrations and supplementary materials are available at (this https URL).
zh
[CV-18] FactorPortrait: Controllable Portrait Animation via Disentangled Expression Pose and Viewpoint
【速读】:该论文旨在解决单张人脸图像在视频生成中难以实现高保真、可控且多视角一致的动画化问题,尤其在面部表情、头部运动与摄像机视角三者解耦控制方面存在挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出FactorPortrait方法,通过预训练图像编码器提取驱动视频中的面部表情潜在表示(latent),作为动画生成的控制信号,从而隐式捕捉细微的表情动态并实现身份与姿态信息的解耦;同时利用Plücker射线图和法向量图(normal maps)从3D人体网格追踪结果中获得相机与头部姿态控制信号,并借助表达控制器(expression controller)高效注入到视频扩散变换器(video diffusion transformer)中,实现表情迁移与任意视角合成的协同控制。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11645
作者: Jiapeng Tang,Kai Li,Chengxiang Yin,Liuhao Ge,Fei Jiang,Jiu Xu,Matthias Nießner,Christian Häne,Timur Bagautdinov,Egor Zakharov,Peihong Guo
机构: Meta Reality Labs; Technical University of Munich
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Project page: this https URL
Abstract:We introduce FactorPortrait, a video diffusion method for controllable portrait animation that enables lifelike synthesis from disentangled control signals of facial expressions, head movement, and camera viewpoints. Given a single portrait image, a driving video, and camera trajectories, our method animates the portrait by transferring facial expressions and head movements from the driving video while simultaneously enabling novel view synthesis from arbitrary viewpoints. We utilize a pre-trained image encoder to extract facial expression latents from the driving video as control signals for animation generation. Such latents implicitly capture nuanced facial expression dynamics with identity and pose information disentangled, and they are efficiently injected into the video diffusion transformer through our proposed expression controller. For camera and head pose control, we employ Plücker ray maps and normal maps rendered from 3D body mesh tracking. To train our model, we curate a large-scale synthetic dataset containing diverse combinations of camera viewpoints, head poses, and facial expression dynamics. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches in realism, expressiveness, control accuracy, and view consistency.
zh
[CV-19] Fast and Explicit: Slice-to-Volume Reconstruction via 3D Gaussian Primitives with Analytic Point Spread Function Modeling
【速读】:该论文旨在解决从稀疏或退化的二维(2D)医学图像中恢复高保真三维(3D)图像的问题,尤其聚焦于胎儿磁共振成像(fetal MRI)中因运动伪影导致的低分辨率2D图像重建为高分辨率3D脑部图像,以支持精准的神经发育诊断。其核心挑战在于传统隐式神经表示(implicit neural representations, INRs)虽在自监督切片到体积重建(slice-to-volume reconstruction, SVR)任务中表现优异,但受限于图像采集物理建模所需的昂贵随机蒙特卡洛采样来近似点扩散函数(point spread function, PSF),造成显著计算瓶颈。解决方案的关键是将基于神经网络的隐式表示转换为基于高斯的显式表示:通过将高分辨率(HR)3D图像体积参数化为各向异性高斯基元场,利用高斯函数在卷积运算下的封闭性,推导出前向模型的闭合解析解——即观测协方差等于HR协方差与PSF协方差的加和(Σobs=ΣHR+ΣPSF),从而彻底避免了计算密集的随机采样,同时保证梯度传播的精确性。该方法在保持与当前最优自监督SVR框架相当重建质量的前提下,实现了5–10倍的速度提升,且收敛时间通常低于30秒,为实时胎儿3D MRI临床应用提供了可行路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11624
作者: Maik Dannecker,Steven Jia,Nil Stolt-Ansó,Nadine Girard,Guillaume Auzias,François Rousseau,Daniel Rueckert
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Under Review for MIDL 2026
Abstract:Recovering high-fidelity 3D images from sparse or degraded 2D images is a fundamental challenge in medical imaging, with broad applications ranging from 3D ultrasound reconstruction to MRI super-resolution. In the context of fetal MRI, high-resolution 3D reconstruction of the brain from motion-corrupted low-resolution 2D acquisitions is a prerequisite for accurate neurodevelopmental diagnosis. While implicit neural representations (INRs) have recently established state-of-the-art performance in self-supervised slice-to-volume reconstruction (SVR), they suffer from a critical computational bottleneck: accurately modeling the image acquisition physics requires expensive stochastic Monte Carlo sampling to approximate the point spread function (PSF). In this work, we propose a shift from neural network based implicit representations to Gaussian based explicit representations. By parameterizing the HR 3D image volume as a field of anisotropic Gaussian primitives, we leverage the property of Gaussians being closed under convolution and thus derive a \textitclosed-form analytical solution for the forward model. This formulation reduces the previously intractable acquisition integral to an exact covariance addition ( \mathbf\Sigma_obs = \mathbf\Sigma_HR + \mathbf\Sigma_PSF ), effectively bypassing the need for compute-intensive stochastic sampling while ensuring exact gradient propagation. We demonstrate that our approach matches the reconstruction quality of self-supervised state-of-the-art SVR frameworks while delivering a 5 \times --10 \times speed-up on neonatal and fetal data. With convergence often reached in under 30 seconds, our framework paves the way towards translation into clinical routine of real-time fetal 3D MRI. Code will be public at this https URL.
zh
[CV-20] Embodied Image Compression
【速读】:该论文旨在解决具身智能代理(Embodied Agents)在多智能体系统中因通信带宽受限而导致实时任务执行困难的问题,其核心挑战在于传统图像压缩方法主要面向人类感知或特定任务模型设计,而无法满足具身智能在真实环境中对低比特率下仍能可靠执行操作任务的需求。解决方案的关键在于首次提出“具身图像压缩”(Embodied Image Compression)这一科学问题,并构建了一个标准化基准测试平台——EmbodiedComp,用于在闭环环境下评估压缩算法在超低比特率条件下的性能表现。通过模拟与真实场景中的大量实证研究,论文揭示了现有视觉-语言-动作模型(VLAs)在低于具身比特率阈值时无法稳定完成简单操作任务的现象,从而推动面向具身智能的专用压缩技术的发展,为实际部署提供理论支撑和实践路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11612
作者: Chunyi Li,Rui Qing,Jianbo Zhang,Yuan Tian,Xiangyang Zhu,Zicheng Zhang,Xiaohong Liu,Weisi Lin,Guangtao Zhai
机构: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); Shanghai AI Lab; Nanyang Technological University (南洋理工大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
备注: 15 pages, 12 figures, 3 tables
Abstract:Image Compression for Machines (ICM) has emerged as a pivotal research direction in the field of visual data compression. However, with the rapid evolution of machine intelligence, the target of compression has shifted from task-specific virtual models to Embodied agents operating in real-world environments. To address the communication constraints of Embodied AI in multi-agent systems and ensure real-time task execution, this paper introduces, for the first time, the scientific problem of Embodied Image Compression. We establish a standardized benchmark, EmbodiedComp, to facilitate systematic evaluation under ultra-low bitrate conditions in a closed-loop setting. Through extensive empirical studies in both simulated and real-world settings, we demonstrate that existing Vision-Language-Action models (VLAs) fail to reliably perform even simple manipulation tasks when compressed below the Embodied bitrate threshold. We anticipate that EmbodiedComp will catalyze the development of domain-specific compression tailored for Embodied agents , thereby accelerating the Embodied AI deployment in the Real-world.
zh
[CV-21] Using GUI Agent for Electronic Design Automation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前生成式 GUI 代理(GUI agents)在专业电子设计自动化(Electronic-Design-Automation, EDA)工作流中表现薄弱的问题,即现有代理主要针对通用办公软件(如 Microsoft Word 和 Excel)进行评估,而未能有效支持高价值、高复杂度的 CAD 工具任务。其解决方案的关键在于:首先构建了一个大规模、高质量的 GUI-EDA 数据集,涵盖 5 种 CAD 工具和 5 个物理设计领域,包含 2000+ 经 EDA 工程师实录的屏幕截图-动作对;其次提出一个专门面向 EDA 的评估基准,系统性地测试了 30 多种主流 GUI 代理,揭示了 EDA 任务作为一项重大未解挑战的地位;最后引入一种名为 EDAgent 的专用指标,集成反思机制(reflection mechanism),显著提升了在工业级 CAD 软件上的可靠性,并首次实现性能超越电气工程博士生水平。该研究将 GUI 代理从通用办公自动化拓展至高价值工程领域,为提升 EDA 生产力提供了新路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11611
作者: Chunyi Li,Longfei Li,Zicheng Zhang,Xiaohong Liu,Min Tang,Weisi Lin,Guangtao Zhai
机构: Nanyang Technological University (南洋理工大学); Shanghai AI Laboratory (上海人工智能实验室); Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Hardware Architecture (cs.AR)
备注: 17 pages, 15 figures, 8 tables
Abstract:Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents adopt an end-to-end paradigm that maps a screenshot to an action sequence, thereby automating repetitive tasks in virtual environments. However, existing GUI agents are evaluated almost exclusively on commodity software such as Microsoft Word and Excel. Professional Computer-Aided Design (CAD) suites promise an order-of-magnitude higher economic return, yet remain the weakest performance domain for existing agents and are still far from replacing expert Electronic-Design-Automation (EDA) engineers. We therefore present the first systematic study that deploys GUI agents for EDA workflows. Our contributions are: (1) a large-scale dataset named GUI-EDA, including 5 CAD tools and 5 physical domains, comprising 2,000+ high-quality screenshot-answer-action pairs recorded by EDA scientists and engineers during real-world component design; (2) a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates 30+ mainstream GUI agents, demonstrating that EDA tasks constitute a major, unsolved challenge; and (3) an EDA-specialized metric named EDAgent, equipped with a reflection mechanism that achieves reliable performance on industrial CAD software and, for the first time, outperforms Ph.D. students majored in Electrical Engineering. This work extends GUI agents from generic office automation to specialized, high-value engineering domains and offers a new avenue for advancing EDA productivity. The dataset will be released at: this https URL.
zh
[CV-22] Brain-Semantoks: Learning Semantic Tokens of Brain Dynamics with a Self-Distilled Foundation Model
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前用于功能磁共振成像(fMRI)时间序列的基础模型在学习低级特征时对噪声和时间波动敏感的问题,导致下游任务需大量微调。其核心解决方案是提出Brain-Semantoks框架,关键创新在于:一是引入语义分词器(semantic tokenizer),将噪声区域信号聚合为代表功能网络的鲁棒token;二是设计自蒸馏目标(self-distillation objective),通过新颖的训练课程确保时空表示稳定性,从而从信噪比低的时间序列中学习到有意义的抽象表征。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11582
作者: Sam Gijsen,Marc-Andre Schulz,Kerstin Ritter
机构: Hertie Institute for AI in Brain Health, University of Tübingen, Germany (图宾根大学脑健康人工智能研究所); Tübingen AI Center, University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany (图宾根人工智能中心); Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Berlin, Germany (柏林夏里特医学院精神病学与心理治疗系)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC)
备注: Code and pretrained models available at this https URL
Abstract:The development of foundation models for functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) time series holds significant promise for predicting phenotypes related to disease and cognition. Current models, however, are often trained using a mask-and-reconstruct objective on small brain regions. This focus on low-level information leads to representations that are sensitive to noise and temporal fluctuations, necessitating extensive fine-tuning for downstream tasks. We introduce Brain-Semantoks, a self-supervised framework designed specifically to learn abstract representations of brain dynamics. Its architecture is built on two core innovations: a semantic tokenizer that aggregates noisy regional signals into robust tokens representing functional networks, and a self-distillation objective that enforces representational stability across time. We show that this objective is stabilized through a novel training curriculum, ensuring the model robustly learns meaningful features from low signal-to-noise time series. We demonstrate that learned representations enable strong performance on a variety of downstream tasks even when only using a linear probe. Furthermore, we provide comprehensive scaling analyses indicating more unlabeled data reliably results in out-of-distribution performance gains without domain adaptation.
zh
[CV-23] In-Context Learning for Seismic Data Processing
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统地震数据处理方法中存在的噪声干扰、参数手动调优困难,以及现有深度学习方法在相邻地震测线(seismic gathers)中结果空间不一致、缺乏用户可控性的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于上下文学习(in-context learning)的模型 ContextSeisNet,通过利用同一地震剖面上邻近共中心点道集(common-depth point gathers)及其标签组成的支撑集(support set),使模型在推理阶段根据相似道集的处理方式动态调整自身行为,无需重新训练即可实现任务特定的处理逻辑。这种方法不仅提升了横向一致性,还增强了用户对处理过程的控制能力,并显著提高了数据效率——在仅使用90%训练数据的情况下仍能获得与U-Net相当甚至更优的野外数据处理效果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11575
作者: Fabian Fuchs,Mario Ruben Fernandez,Norman Ettrich,Janis Keuper
机构: Fraunhofer-Institut für Techno- und Wirtschaftsmathematik (弗劳恩霍夫技术与经济数学研究所); DWS, University of Mannheim (曼海姆大学数据科学与统计中心); IMLA, Offenburg University (奥芬堡应用科学大学智能材料与系统实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Source code available under this https URL
Abstract:Seismic processing transforms raw data into subsurface images essential for geophysical applications. Traditional methods face challenges, such as noisy data, and manual parameter tuning, among others. Recently deep learning approaches have proposed alternative solutions to some of these problems. However, important challenges of existing deep learning approaches are spatially inconsistent results across neighboring seismic gathers and lack of user-control. We address these limitations by introducing ContextSeisNet, an in-context learning model, to seismic demultiple processing. Our approach conditions predictions on a support set of spatially related example pairs: neighboring common-depth point gathers from the same seismic line and their corresponding labels. This allows the model to learn task-specific processing behavior at inference time by observing how similar gathers should be processed, without any retraining. This method provides both flexibility through user-defined examples and improved lateral consistency across seismic lines. On synthetic data, ContextSeisNet outperforms a U-Net baseline quantitatively and demonstrates enhanced spatial coherence between neighboring gathers. On field data, our model achieves superior lateral consistency compared to both traditional Radon demultiple and the U-Net baseline. Relative to the U-Net, ContextSeisNet also delivers improved near-offset performance and more complete multiple removal. Notably, ContextSeisNet achieves comparable field data performance despite being trained on 90% less data, demonstrating substantial data efficiency. These results establish ContextSeisNet as a practical approach for spatially consistent seismic demultiple with potential applicability to other seismic processing tasks.
zh
[CV-24] Evaluating Foundation Models 3D Understanding Through Multi-View Correspondence Analysis NEURIPS2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前3D空间理解基准测试中难以区分预训练编码器内在3D推理能力的问题,因为现有评估方法通常依赖下游微调(downstream fine-tuning)或任务特定解码器,导致性能指标受模型调整影响而非纯粹反映编码器的泛化能力。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种无需微调的上下文内(in-context)3D场景理解新基准,直接评估密集视觉特征的质量;具体通过扩展Hummingbird框架至3D多视角ImageNet(MVImgNet)数据集,以一组特定视角图像(keys)为输入,测试模型对新视角图像(queries)的分割性能,并按键-查询视角差异分为易、中、难和极端四类评分,从而客观衡量不同基础模型在大视角变化下的3D理解能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11574
作者: Valentina Lilova,Toyesh Chakravorty,Julian I. Bibo,Emma Boccaletti,Brandon Li,Lívia Baxová,Cees G. M. Snoek,Mohammadreza Salehi
机构: University of Amsterdam (阿姆斯特丹大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: NeurIPS 2025 UniReps workshop
Abstract:Benchmarking 3D spatial understanding of foundation models is essential for real-world applications such as robotics and autonomous driving. Existing evaluations often rely on downstream finetuning with linear heads or task-specific decoders, making it difficult to isolate the intrinsic 3D reasoning ability of pretrained encoders. In this work, we introduce a novel benchmark for in-context 3D scene understanding that requires no finetuning and directly probes the quality of dense visual features. Building on the Hummingbird framework, which evaluates in-context 2D scene understanding, we extend the setup to the 3D Multi-View ImageNet (MVImgNet) dataset. Given a set of images from objects in specific angles (keys), we benchmark the performance of segmenting novel views (queries) and report the scores in 4 categories of easy, medium, hard, and extreme based on the key-query view contrast. We benchmark 8 state-of-the-art foundation models and show DINO-based encoders remain competitive across large viewpoint shifts, while 3D-aware models like VGGT require dedicated multi-view adjustments. Our code is publicly available at this https URL .
zh
[CV-25] Multi-temporal Calving Front Segmentation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决海洋终端冰川(marine-terminating glaciers)消融前沿(calving front)自动识别中因季节性因素(如冰碎屑混合物 ice melange 或积雪覆盖)导致的分类错误问题。其关键解决方案是通过并行处理同一冰川的多帧卫星遥感图像时间序列,并在对应的特征图之间交换时序信息,从而稳定每帧预测结果。该方法被集成至当前最先进的架构Tyrion中,在CaFFe基准数据集上实现了新的最先进性能,平均距离误差为184.4米,平均交并比(IoU)达83.6%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11560
作者: Marcel Dreier,Nora Gourmelon,Dakota Pyles,Fei Wu,Matthias Braun,Thorsten Seehaus,Andreas Maier,Vincent Christlein
机构: University of Stuttgart (斯图加特大学); University of California, Berkeley (加州大学伯克利分校)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The calving fronts of marine-terminating glaciers undergo constant changes. These changes significantly affect the glacier’s mass and dynamics, demanding continuous monitoring. To address this need, deep learning models were developed that can automatically delineate the calving front in Synthetic Aperture Radar imagery. However, these models often struggle to correctly classify areas affected by seasonal conditions such as ice melange or snow-covered surfaces. To address this issue, we propose to process multiple frames from a satellite image time series of the same glacier in parallel and exchange temporal information between the corresponding feature maps to stabilize each prediction. We integrate our approach into the current state-of-the-art architecture Tyrion and accomplish a new state-of-the-art performance on the CaFFe benchmark dataset. In particular, we achieve a Mean Distance Error of 184.4 m and a mean Intersection over Union of 83.6.
zh
[CV-26] 3DTeethSAM: Taming SAM2 for 3D Teeth Segmentation AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决3D牙齿分割(3D teeth segmentation)问题,即在三维牙科模型中实现牙齿实例的定位与语义分类,这一任务因真实牙列结构的复杂性而极具挑战。解决方案的关键在于将Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)适配至3D牙齿数据:首先从预设视角渲染3D牙齿模型为2D图像,利用SAM2进行2D分割,再通过2D-3D投影重建3D结果;同时引入三个轻量级可学习模块——提示嵌入生成器(prompt embedding generator)以提升掩码解码精度、掩码精修器(mask refiner)优化初始分割结果、掩码分类器(mask classifier)实现类别判别,并在SAM2图像编码器中嵌入可变形全局注意力插件(Deformable Global Attention Plugins, DGAP),显著提升了分割精度与训练效率。该方法在3DTeethSeg基准上达到91.90%的IoU,成为当前最优方案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11557
作者: Zhiguo Lu,Jianwen Lou,Mingjun Ma,Hairong Jin,Youyi Zheng,Kun Zhou
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted by AAAI 2026
Abstract:3D teeth segmentation, involving the localization of tooth instances and their semantic categorization in 3D dental models, is a critical yet challenging task in digital dentistry due to the complexity of real-world dentition. In this paper, we propose 3DTeethSAM, an adaptation of the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) for 3D teeth segmentation. SAM2 is a pretrained foundation model for image and video segmentation, demonstrating a strong backbone in various downstream scenarios. To adapt SAM2 for 3D teeth data, we render images of 3D teeth models from predefined views, apply SAM2 for 2D segmentation, and reconstruct 3D results using 2D-3D projections. Since SAM2’s performance depends on input prompts and its initial outputs often have deficiencies, and given its class-agnostic nature, we introduce three light-weight learnable modules: (1) a prompt embedding generator to derive prompt embeddings from image embeddings for accurate mask decoding, (2) a mask refiner to enhance SAM2’s initial segmentation results, and (3) a mask classifier to categorize the generated masks. Additionally, we incorporate Deformable Global Attention Plugins (DGAP) into SAM2’s image encoder. The DGAP enhances both the segmentation accuracy and the speed of the training process. Our method has been validated on the 3DTeethSeg benchmark, achieving an IoU of 91.90% on high-resolution 3D teeth meshes, establishing a new state-of-the-art in the field.
zh
[CV-27] SSL-MedSAM2: A Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation Framework Powered by Few-shot Learning of SAM2 MICCAI2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学图像分割中因依赖大规模标注数据而导致的标注成本高昂问题,尤其是在临床应用中难以获取足够标注样本的情况下。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一种新颖的半监督学习(Semi-supervised Learning, SSL)框架SSL-MedSAM2,该框架融合了两个核心模块:一是基于预训练大模型Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) 的无需训练的少样本学习分支TFFS-MedSAM2,用于生成高质量伪标签;二是基于nnUNet的迭代全监督学习分支FSL-nnUNet,用于对伪标签进行精细化修正。这种双分支协同机制有效降低了人工标注需求并提升了分割精度,在MICCAI2025 CARE-LiSeg挑战赛中取得了优异性能,验证了其在Gd-DTPA增强MRI和T1加权MRI上的泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11548
作者: Zhendi Gong,Xin Chen
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted by MICCAI 2025 CARE Challenge, waiting for publication
Abstract:Despite the success of deep learning based models in medical image segmentation, most state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods perform fully-supervised learning, which commonly rely on large scale annotated training datasets. However, medical image annotation is highly time-consuming, hindering its clinical applications. Semi-supervised learning (SSL) has been emerged as an appealing strategy in training with limited annotations, largely reducing the labelling cost. We propose a novel SSL framework SSL-MedSAM2, which contains a training-free few-shot learning branch TFFS-MedSAM2 based on the pretrained large foundation model Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) for pseudo label generation, and an iterative fully-supervised learning branch FSL-nnUNet based on nnUNet for pseudo label refinement. The results on MICCAI2025 challenge CARE-LiSeg (Liver Segmentation) demonstrate an outstanding performance of SSL-MedSAM2 among other methods. The average dice scores on the test set in GED4 and T1 MRI are 0.9710 and 0.9648 respectively, and the Hausdorff distances are 20.07 and 21.97 respectively. The code is available via this https URL.
zh
[CV-28] Infinity and Beyond: Compositional Alignment in VAR and Diffusion T2I Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决文本到图像(Text-to-Image, T2I)生成模型中语义组合对齐(compositional alignment)不足的问题,即如何准确地将文本描述中的对象、属性和空间关系映射到生成图像中。研究通过系统性评估六种主流T2I模型(包括扩散模型与视觉自回归模型VAR),在T2I-CompBench++和GenEval两个基准上量化其在颜色与属性绑定、空间关系、数字理解及复杂多对象提示下的表现。关键发现是:视觉自回归模型Infinity-8B在整体组合对齐能力上最优,而Infinity-2B虽参数量较小却能在多个任务中媲美甚至超越更大规模的扩散模型,揭示了VAR架构在组合推理方面的潜力与高效性权衡优势,为未来T2I模型的发展提供了首个统一的基准与对比框架。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11542
作者: Hossein Shahabadi,Niki Sepasian,Arash Marioriyad,Ali Sharifi-Zarchi,Mahdieh Soleymani Baghshah
机构: Sharif University of Technology (谢里夫理工大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Achieving compositional alignment between textual descriptions and generated images - covering objects, attributes, and spatial relationships - remains a core challenge for modern text-to-image (T2I) models. Although diffusion-based architectures have been widely studied, the compositional behavior of emerging Visual Autoregressive (VAR) models is still largely unexamined. We benchmark six diverse T2I systems - SDXL, PixArt- \alpha , Flux-Dev, Flux-Schnell, Infinity-2B, and Infinity-8B - across the full T2I-CompBench++ and GenEval suites, evaluating alignment in color and attribute binding, spatial relations, numeracy, and complex multi-object prompts. Across both benchmarks, Infinity-8B achieves the strongest overall compositional alignment, while Infinity-2B also matches or exceeds larger diffusion models in several categories, highlighting favorable efficiency-performance trade-offs. In contrast, SDXL and PixArt- \alpha show persistent weaknesses in attribute-sensitive and spatial tasks. These results provide the first systematic comparison of VAR and diffusion approaches to compositional alignment and establish unified baselines for the future development of the T2I model.
zh
[CV-29] Parallax: Runtime Parallelization for Operator Fallbacks in Heterogeneous Edge Systems
【速读】:该论文旨在解决移动设备上深度神经网络(DNN)推理过程中因动态控制流操作和不支持的内核导致CPU执行fallback所引发的高延迟、内存峰值及CPU资源闲置问题。解决方案的关键在于提出Parallax框架,其核心创新包括:首先对计算有向无环图(DAG)进行分区以暴露并行性;其次采用分支感知的内存管理策略,通过专用内存区域和缓冲区复用降低运行时内存占用;最后引入自适应调度器根据设备内存约束执行分支,并结合细粒度子图控制实现动态模型的异构推理,从而在无需模型重构或自定义算子的情况下显著提升推理效率与能效。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11532
作者: Chong Tang,Hao Dai,Jagmohan Chauhan
机构: University of Southampton (南安普顿大学); UCL AI Centre (UCL人工智能中心); University College London (伦敦大学学院)
类目: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:The growing demand for real-time DNN applications on edge devices necessitates faster inference of increasingly complex models. Although many devices include specialized accelerators (e.g., mobile GPUs), dynamic control-flow operators and unsupported kernels often fall back to CPU execution. Existing frameworks handle these fallbacks poorly, leaving CPU cores idle and causing high latency and memory spikes. We introduce Parallax, a framework that accelerates mobile DNN inference without model refactoring or custom operator implementations. Parallax first partitions the computation DAG to expose parallelism, then employs branch-aware memory management with dedicated arenas and buffer reuse to reduce runtime footprint. An adaptive scheduler executes branches according to device memory constraints, meanwhile, fine-grained subgraph control enables heterogeneous inference of dynamic models. By evaluating on five representative DNNs across three different mobile devices, Parallax achieves up to 46% latency reduction, maintains controlled memory overhead (26.5% on average), and delivers up to 30% energy savings compared with state-of-the-art frameworks, offering improvements aligned with the responsiveness demands of real-time mobile inference.
zh
[CV-30] Super-Resolved Canopy Height Mapping from Sentinel-2 Time Series Using LiDAR HD Reference Data across Metropolitan France
【速读】:该论文旨在解决精细尺度森林监测中树高估算与超分辨率重建的问题,以准确反映林冠结构及其动态变化,进而支持碳储量、生物多样性和森林健康评估。其核心挑战在于如何利用低成本、广泛可用的卫星数据(如Sentinel-2)实现高精度树高制图,同时避免依赖预训练模型或超高分辨率光学影像。解决方案的关键在于提出THREASURE-Net——一个端到端框架,通过仅使用多空间分辨率LiDAR高度数据作为监督信号来训练超分辨率模块,从而在不引入额外数据源的情况下,从Sentinel-2时间序列中学习并生成年度树高地图,最终在2.5 m、5 m和10 m分辨率下分别达到2.62 m、2.72 m和2.88 m的平均绝对误差,显著优于现有基于Sentinel数据的方法,并具备与依赖超高分辨率影像方法相当的性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11524
作者: Ekaterina Kalinicheva,Florian Helen,Stéphane Mermoz,Florian Mouret,Milena Planells
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Fine-scale forest monitoring is essential for understanding canopy structure and its dynamics, which are key indicators of carbon stocks, biodiversity, and forest health. Deep learning is particularly effective for this task, as it integrates spectral, temporal, and spatial signals that jointly reflect the canopy structure. To address this need, we introduce THREASURE-Net, a novel end-to-end framework for Tree Height Regression And Super-Resolution. The model is trained on Sentinel-2 time series using reference height metrics derived from LiDAR HD data at multiple spatial resolutions over Metropolitan France to produce annual height maps. We evaluate three model variants, producing tree-height predictions at 2.5 m, 5 m, and 10 m resolution. THREASURE-Net does not rely on any pretrained model nor on reference very high resolution optical imagery to train its super-resolution module; instead, it learns solely from LiDAR-derived height information. Our approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods based on Sentinel data and is competitive with methods based on very high resolution imagery. It can be deployed to generate high-precision annual canopy-height maps, achieving mean absolute errors of 2.62 m, 2.72 m, and 2.88 m at 2.5 m, 5 m, and 10 m resolution, respectively. These results highlight the potential of THREASURE-Net for scalable and cost-effective structural monitoring of temperate forests using only freely available satellite data. The source code for THREASURE-Net is available at: this https URL.
zh
[CV-31] Reconstruction as a Bridge for Event-Based Visual Question Answering
【速读】:该论文旨在解决将事件相机(event camera)数据与多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)融合时面临的挑战,即如何在保留事件数据独特优势(如高时间分辨率和低功耗)的同时,确保其与基于帧的MLLMs兼容。解决方案的关键在于利用重建(reconstruction)作为桥梁:提出一种简洁的帧基重建与标记化(Frame-based Reconstruction and Tokenization, FRT)方法,并设计了一种利用事件稀疏性的自适应重建与标记化(Adaptive Reconstruction and Tokenization, ART)方法,从而实现高效、鲁棒的事件数据到文本理解的映射。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11510
作者: Hanyue Lou,Jiayi Zhou,Yang Zhang,Boyu Li,Yi Wang,Guangnan Ye,Boxin Shi
机构: Peking University (北京大学); Shanghai Innovation Institute; Shanghai AI Laboratory; Fudan University (复旦大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Integrating event cameras with Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) promises general scene understanding in challenging visual conditions, yet requires navigating a trade-off between preserving the unique advantages of event data and ensuring compatibility with frame-based models. We address this challenge by using reconstruction as a bridge, proposing a straightforward Frame-based Reconstruction and Tokenization (FRT) method and designing an efficient Adaptive Reconstruction and Tokenization (ART) method that leverages event sparsity. For robust evaluation, we introduce EvQA, the first objective, real-world benchmark for event-based MLLMs, comprising 1,000 event-QA pairs from 22 public datasets. Our experiments demonstrate that our methods achieve state-of-the-art performance on EvQA, highlighting the significant potential of MLLMs in event-based vision.
zh
[CV-32] On Geometric Understanding and Learned Data Priors in VGGT
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI (Generative AI) 模型中几何理解机制的可解释性问题,具体聚焦于视觉几何基础模型(Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer, VGGT)是否隐含地学习了传统多视图几何概念,还是仅依赖于数据驱动的外观先验。解决方案的关键在于通过系统性的内部机制分析——包括对中间特征的探针测试、注意力模式解析以及干预实验——揭示VGGT在无显式几何约束训练条件下,仍能隐式执行对应匹配并编码极线几何结构,从而表明其既内化了几何结构又利用了学习到的数据先验。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11508
作者: Jelena Bratulić,Sudhanshu Mittal,Thomas Brox,Christian Rupprecht
机构: University of Freiburg (弗莱堡大学); University of Oxford (牛津大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:The Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer (VGGT) is a 3D foundation model that infers camera geometry and scene structure in a single feed-forward pass. Trained in a supervised, single-step fashion on large datasets, VGGT raises a key question: does it build upon geometric concepts like traditional multi-view methods, or does it rely primarily on learned appearance-based data-driven priors? In this work, we conduct a systematic analysis of VGGT’s internal mechanisms to uncover whether geometric understanding emerges within its representations. By probing intermediate features, analyzing attention patterns, and performing interventions, we examine how the model implements its functionality. Our findings reveal that VGGT implicitly performs correspondence matching within its global attention layers and encodes epipolar geometry, despite being trained without explicit geometric constraints. We further investigate VGGT’s dependence on its learned data priors. Using spatial input masking and perturbation experiments, we assess its robustness to occlusions, appearance variations, and camera configurations, comparing it with classical multi-stage pipelines. Together, these insights highlight how VGGT internalizes geometric structure while using learned data-driven priors.
zh
[CV-33] SSA3D: Text-Conditioned Assisted Self-Supervised Framework for Automatic Dental Abutment Design
【速读】:该论文旨在解决牙种植修复中基台(abutment)设计自动化难题,传统方法依赖人工测量与试戴,效率低且易受主观因素影响,而现有基于生成式 AI 的自动化方案受限于高质量标注数据稀缺及自监督学习(SSL)需独立预训练与微调带来的高计算成本和长训练时间。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种自监督辅助的自动基台设计框架(SS A³D),采用双分支架构:重建分支通过恢复掩码后的口内扫描数据提取结构信息并迁移至回归分支,从而避免了传统 SSL 中分离的预训练与微调流程;同时引入文本条件提示(TCP)模块,将临床信息(如种植体位置、系统和系列)编码为条件信号,引导网络聚焦关键区域并约束参数预测,显著提升设计精度与效率,在实验中相较传统 SSL 方法缩短一半训练时间并达到当前最优性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11507
作者: Mianjie Zheng,Xinquan Yang,Along He,Xuguang Li,Feilie Zhong,Xuefen Liu,Kun Tang,Zhicheng Zhang,Linlin Shen
机构: Shenzhen University (深圳大学); Chinese Academy of Science (中国科学院); Kangtaijian (KTJ) Medical Technology Co., Ltd. (康泰健医疗科技有限公司)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Abutment design is a critical step in dental implant restoration. However, manual design involves tedious measurement and fitting, and research on automating this process with AI is limited, due to the unavailability of large annotated datasets. Although self-supervised learning (SSL) can alleviate data scarcity, its need for pre-training and fine-tuning results in high computational costs and long training times. In this paper, we propose a Self-supervised assisted automatic abutment design framework (SS A^3 D), which employs a dual-branch architecture with a reconstruction branch and a regression branch. The reconstruction branch learns to restore masked intraoral scan data and transfers the learned structural information to the regression branch. The regression branch then predicts the abutment parameters under supervised learning, which eliminates the separate pre-training and fine-tuning process. We also design a Text-Conditioned Prompt (TCP) module to incorporate clinical information (such as implant location, system, and series) into SS A^3 D. This guides the network to focus on relevant regions and constrains the parameter predictions. Extensive experiments on a collected dataset show that SS A^3 D saves half of the training time and achieves higher accuracy than traditional SSL methods. It also achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to other methods, significantly improving the accuracy and efficiency of automated abutment design.
zh
[CV-34] Skel-Mamba: Temporal Dynamic Modeling via State Space Model for Human Skeleton-based Action Recognition
【速读】:该论文旨在解决基于骨架的动作识别中如何高效建模时空动态特征的问题。现有方法在处理骨骼序列时,难以同时兼顾空间结构的精确捕捉与长程时间依赖的有效建模,尤其是在保持低推理延迟的前提下。解决方案的关键在于提出一种混合Transformer-Mamba架构TSkel-Mamba:通过Spatial Transformer模块提取空间特征,并引入Temporal Dynamic Modeling (TDM)块增强Mamba对时间维度的建模能力;其中TDM块的核心创新是集成多尺度周期(Multi-scale Temporal Interaction, MTI)模块,利用多尺度Cycle操作捕获跨通道的时间交互关系,从而显著提升动作识别性能并保持高效推理速度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11503
作者: Yanan Liu,Jun Liu,Hao Zhang,Dan Xu,Hossein Rahmani,Mohammed Bennamoun,Qiuhong Ke
机构: Yunnan University (云南大学); Lancaster University (兰卡斯特大学); The University of Western Australia (西澳大利亚大学); Monash University (莫纳什大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Skeleton-based action recognition has garnered significant attention in the computer vision community. Inspired by the recent success of the selective state-space model (SSM) Mamba in modeling 1D temporal sequences, we propose TSkel-Mamba, a hybrid Transformer-Mamba framework that effectively captures both spatial and temporal dynamics. In particular, our approach leverages Spatial Transformer for spatial feature learning while utilizing Mamba for temporal modeling. Mamba, however, employs separate SSM blocks for individual channels, which inherently limits its ability to model inter-channel dependencies. To better adapt Mamba for skeleton data and enhance Mamba`s ability to model temporal dependencies, we introduce a Temporal Dynamic Modeling (TDM) block, which is a versatile plug-and-play component that integrates a novel Multi-scale Temporal Interaction (MTI) module. The MTI module employs multi-scale Cycle operators to capture cross-channel temporal interactions, a critical factor in action recognition. Extensive experiments on NTU-RGB+D 60, NTU-RGB+D 120, NW-UCLA and UAV-Human datasets demonstrate that TSkel-Mamba achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining low inference time, making it both efficient and highly effective.
zh
[CV-35] VLM2GeoVec: Toward Universal Multimodal Embeddings for Remote Sensing
【速读】:该论文旨在解决遥感图像理解中长期存在的两大挑战:一是现有方法在跨模态检索(如图像与文本匹配)和区域级空间推理(如目标定位与细粒度语义解析)之间存在割裂,导致难以实现统一的多模态分析;二是当前双编码器模型虽擅长大规模跨模态搜索但无法有效融合多模态输入,而生成式辅助模型虽支持区域级解释却缺乏可扩展的检索能力。解决方案的关键在于提出一种单编码器视觉语言模型 VLM2GeoVec,其通过对比学习将图像、文本、边界框(bounding boxes)和地理坐标等异构信息以交错方式嵌入到统一向量空间中,从而消除多阶段流水线和任务专用模块,实现 scalable retrieval 与 region-level spatial reasoning 的一体化建模。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11490
作者: Emanuel Sánchez Aimar,Gulnaz Zhambulova,Fahad Shahbaz Khan,Yonghao Xu,Michael Felsberg
机构: Linköping University (林雪平大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
备注: 21 pages, 7 figures, under review
Abstract:Satellite imagery differs fundamentally from natural images: its aerial viewpoint, very high resolution, diverse scale variations, and abundance of small objects demand both region-level spatial reasoning and holistic scene understanding. Current remote-sensing approaches remain fragmented between dual-encoder retrieval models, which excel at large-scale cross-modal search but cannot interleave modalities, and generative assistants, which support region-level interpretation but lack scalable retrieval capabilities. We propose \textbfVLM2GeoVec , an instruction-following, single-encoder vision-language model trained contrastively to embed interleaved inputs (images, text, bounding boxes, and geographic coordinates) in a unified vector space. Our single encoder interleaves all inputs into one joint embedding trained with a contrastive loss, eliminating multi-stage pipelines and task-specific modules. To evaluate its versatility, we introduce \textbfRSMEB , a novel benchmark covering key remote-sensing embedding applications: scene classification; cross-modal search; compositional retrieval; visual-question answering; visual grounding and region-level reasoning; and semantic geospatial retrieval. On RSMEB, it achieves \textbf26.6% P@1 on region-caption retrieval (+25 pp vs. dual-encoder baselines), \textbf32.5% P@1 on referring-expression retrieval (+19 pp), and \textbf17.8% P@1 on semantic geo-localization retrieval (over 3\times prior best), while matching or exceeding specialized baselines on conventional tasks such as scene classification and cross-modal retrieval. VLM2GeoVec unifies scalable retrieval with region-level spatial reasoning, enabling cohesive multimodal analysis in remote sensing. We will publicly release the code, checkpoints, and data upon acceptance.
zh
[CV-36] CADMorph: Geometry-Driven Parametric CAD Editing via a Plan-Generate-Verify Loop NEURIPS2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决几何驱动的参数化CAD编辑问题,即在迭代设计过程中,当几何形状发生调整时,需同步修改底层参数化构造序列,以实现结构保持、语义有效性与目标形状保真度的协同优化,且在编辑数据三元组稀缺的条件下完成任务。解决方案的关键在于提出一个迭代式“规划-生成-验证”框架CADMorph,其核心是利用预训练领域专用基础模型(参数到形状潜空间扩散模型P2S与掩码参数预测模型MPP)在推理阶段进行协同操作:P2S模型通过交叉注意力图定位需修改区域并生成编辑掩码,MPP模型据此生成语义有效的参数更新;随后P2S模型将候选序列嵌入形状潜空间,通过距离度量选择最接近目标形状的方案。该方法充分利用预训练模型中的几何意识与设计知识,分别保障结构保留、语义正确性和形状保真度,且无需依赖三元组标注数据,有效突破数据稀缺瓶颈。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11480
作者: Weijian Ma,Shizhao Sun,Ruiyu Wang,Jiang Bian
机构: Fudan University (复旦大学); Microsoft Research, Asia (微软亚洲研究院); University of Toronto (多伦多大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: NeurIPS 2025
Abstract:A Computer-Aided Design (CAD) model encodes an object in two coupled forms: a parametric construction sequence and its resulting visible geometric shape. During iterative design, adjustments to the geometric shape inevitably require synchronized edits to the underlying parametric sequence, called geometry-driven parametric CAD editing. The task calls for 1) preserving the original sequence’s structure, 2) ensuring each edit’s semantic validity, and 3) maintaining high shape fidelity to the target shape, all under scarce editing data triplets. We present CADMorph, an iterative plan-generate-verify framework that orchestrates pretrained domain-specific foundation models during inference: a parameter-to-shape (P2S) latent diffusion model and a masked-parameter-prediction (MPP) model. In the planning stage, cross-attention maps from the P2S model pinpoint the segments that need modification and offer editing masks. The MPP model then infills these masks with semantically valid edits in the generation stage. During verification, the P2S model embeds each candidate sequence in shape-latent space, measures its distance to the target shape, and selects the closest one. The three stages leverage the inherent geometric consciousness and design knowledge in pretrained priors, and thus tackle structure preservation, semantic validity, and shape fidelity respectively. Besides, both P2S and MPP models are trained without triplet data, bypassing the data-scarcity bottleneck. CADMorph surpasses GPT-4o and specialized CAD baselines, and supports downstream applications such as iterative editing and reverse-engineering enhancement.
zh
[CV-37] DOS: Distilling Observable Softmaps of Zipfian Prototypes for Self-Supervised Point Representation AAAI-26
【速读】:该论文旨在解决自监督学习(Self-Supervised Learning, SSL)在3D点云表示学习中面临的三大挑战:不规则几何结构、易受干扰的重建任务以及语义分布不平衡问题。其核心解决方案是提出一种名为DOS(Distilling Observable Softmaps)的新框架,关键在于仅在可观测(未被掩码)点上进行语义相关性软图(softmaps)的自蒸馏,从而避免掩码区域的信息泄露,并提供比离散token到原型分配更丰富的监督信号。此外,为缓解无监督场景下的语义不平衡问题,作者引入Zipfian原型并结合改进的Sinkhorn-Knopp算法(称为Zipf-Sinkhorn),通过施加幂律先验约束原型使用频率,动态调节训练过程中目标软图的锐度,从而提升模型对稀有类别的敏感性与整体鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11465
作者: Mohamed Abdelsamad,Michael Ulrich,Bin Yang,Miao Zhang,Yakov Miron,Abhinav Valada
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: AAAI-26
Abstract:Recent advances in self-supervised learning (SSL) have shown tremendous potential for learning 3D point cloud representations without human annotations. However, SSL for 3D point clouds still faces critical challenges due to irregular geometry, shortcut-prone reconstruction, and unbalanced semantics distribution. In this work, we propose DOS (Distilling Observable Softmaps), a novel SSL framework that self-distills semantic relevance softmaps only at observable (unmasked) points. This strategy prevents information leakage from masked regions and provides richer supervision than discrete token-to-prototype assignments. To address the challenge of unbalanced semantics in an unsupervised setting, we introduce Zipfian prototypes and incorporate them using a modified Sinkhorn-Knopp algorithm, Zipf-Sinkhorn, which enforces a power-law prior over prototype usage and modulates the sharpness of the target softmap during training. DOS outperforms current state-of-the-art methods on semantic segmentation and 3D object detection across multiple benchmarks, including nuScenes, Waymo, SemanticKITTI, ScanNet, and ScanNet200, without relying on extra data or annotations. Our results demonstrate that observable-point softmaps distillation offers a scalable and effective paradigm for learning robust 3D representations.
zh
[CV-38] Exploring MLLM -Diffusion Information Transfer with MetaCanvas
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在视觉生成任务中能力未被充分利用的问题。尽管MLLMs在理解复杂场景布局、属性绑定和知识密集型内容方面表现出色,但在图像或视频生成过程中,它们通常仅作为全局文本编码器与扩散模型(diffusion models)结合,导致其推理与规划能力未能有效应用于生成过程,从而造成多模态理解与生成之间的差距。解决方案的关键在于提出MetaCanvas框架,该框架使MLLMs能够直接在空间和时空潜在空间中进行推理与规划,并紧密耦合扩散生成器,从而实现对生成结果的精确布局控制、稳健属性绑定和高阶语义规划。实验证明,MetaCanvas在多个生成任务中均显著优于基于全局条件的基线方法,验证了将MLLMs视为潜在空间规划者(latent-space planners)是弥合多模态理解与生成鸿沟的可行路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11464
作者: Han Lin,Xichen Pan,Ziqi Huang,Ji Hou,Jialiang Wang,Weifeng Chen,Zecheng He,Felix Juefei-Xu,Junzhe Sun,Zhipeng Fan,Ali Thabet,Mohit Bansal,Chu Wang
机构: Meta(元)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Project page: this https URL
Abstract:Multimodal learning has rapidly advanced visual understanding, largely via multimodal large language models (MLLMs) that use powerful LLMs as cognitive cores. In visual generation, however, these powerful core models are typically reduced to global text encoders for diffusion models, leaving most of their reasoning and planning ability unused. This creates a gap: current multimodal LLMs can parse complex layouts, attributes, and knowledge-intensive scenes, yet struggle to generate images or videos with equally precise and structured control. We propose MetaCanvas, a lightweight framework that lets MLLMs reason and plan directly in spatial and spatiotemporal latent spaces and interface tightly with diffusion generators. We empirically implement MetaCanvas on three different diffusion backbones and evaluate it across six tasks, including text-to-image generation, text/image-to-video generation, image/video editing, and in-context video generation, each requiring precise layouts, robust attribute binding, and reasoning-intensive control. MetaCanvas consistently outperforms global-conditioning baselines, suggesting that treating MLLMs as latent-space planners is a promising direction for narrowing the gap between multimodal understanding and generation.
zh
[CV-39] Boosting Skeleton-based Zero-Shot Action Recognition with Training-Free Test-Time Adaptation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决骨架动作识别(Skeleton-based Action Recognition, SAR)中零样本动作识别(Zero-Shot Action Recognition, ZAR)模型在推理阶段对未见动作泛化能力不足的问题。其核心挑战在于如何在不进行额外训练或访问训练数据的前提下,提升模型对未见过动作类别的适应能力。解决方案的关键在于提出Skeleton-Cache框架,该框架通过构建一个非参数化缓存(non-parametric cache),存储结构化的骨架表示(包含全局与局部细粒度描述符),并将这些描述符与大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)提供的语义先验相结合,利用LLM为不同描述符分配类别特定的重要性权重,从而实现无需训练的测试时自适应(test-time adaptation)。这一机制使模型能够动态融合多粒度特征并基于语义推理调整预测,显著提升了未见动作的识别性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11458
作者: Jingmin Zhu,Anqi Zhu,Hossein Rahmani,Jun Liu,Mohammed Bennamoun,Qiuhong Ke
机构: Monash University (蒙纳士大学); Lancaster University (兰卡斯特大学); University of Western Australia (西澳大利亚大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:We introduce Skeleton-Cache, the first training-free test-time adaptation framework for skeleton-based zero-shot action recognition (SZAR), aimed at improving model generalization to unseen actions during inference. Skeleton-Cache reformulates inference as a lightweight retrieval process over a non-parametric cache that stores structured skeleton representations, combining both global and fine-grained local descriptors. To guide the fusion of descriptor-wise predictions, we leverage the semantic reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to assign class-specific importance weights. By integrating these structured descriptors with LLM-guided semantic priors, Skeleton-Cache dynamically adapts to unseen actions without any additional training or access to training data. Extensive experiments on NTU RGB+D 60/120 and PKU-MMD II demonstrate that Skeleton-Cache consistently boosts the performance of various SZAR backbones under both zero-shot and generalized zero-shot settings. The code is publicly available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-40] YawDD: Frame-level Annotations for Accurate Yawn Prediction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决驾驶员疲劳导致的道路交通事故问题,特别是通过识别早期行为指标——打哈欠(yawning)来实现疲劳监测。现有机器学习方法因视频标注数据中粗粒度的时间标注引入系统性噪声而性能受限。其解决方案的关键在于开发了一种半自动化标注流程(semi-automated labeling pipeline),结合人工在环验证(human-in-the-loop verification),应用于YawDD数据集,从而显著提升标注精度;在此基础上训练的MNasNet分类器和YOLOv11检测器在帧级准确率和平均精度均值(mAP)上分别提升6%和5%,并可在边缘AI硬件(NVIDIA Jetson Nano)上达到59.8 FPS,证明高质量数据足以支持无需服务器计算的设备端打哈欠监测。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11446
作者: Ahmed Mujtaba,Gleb Radchenko,Marc Masana,Radu Prodan
机构: Silicon Austria Labs (硅奥地利实验室); Graz University of Technology (格拉茨工业大学); University of Innsbruck (因斯布鲁克大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: This paper is submitted at European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning, 2026
Abstract:Driver fatigue remains a leading cause of road accidents, with 24% of crashes involving drowsy drivers. While yawning serves as an early behavioral indicator of fatigue, existing machine learning approaches face significant challenges due to video-annotated datasets that introduce systematic noise from coarse temporal annotations. We develop a semi-automated labeling pipeline with human-in-the-loop verification, which we apply to YawDD, enabling more accurate model training. Training the established MNasNet classifier and YOLOv11 detector architectures on YawDD+ improves frame accuracy by up to 6% and mAP by 5% over video-level supervision, achieving 99.34% classification accuracy and 95.69% detection mAP. The resulting approach deliver up to 59.8 FPS on edge AI hardware (NVIDIA Jetson Nano), confirming that enhanced data quality alone supports on-device yawning monitoring without server-side computation.
zh
[CV-41] Flowception: Temporally Expansive Flow Matching for Video Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视频生成中长期依赖建模困难、计算复杂度高以及难以灵活处理不同长度视频等问题。现有自回归方法存在误差累积(error accumulation)问题,而全序列流模型(full-sequence flows)则因高计算开销(FLOPs)限制了其可扩展性。解决方案的关键在于提出Flowception框架,其核心创新是学习一条概率路径,该路径在离散帧插入与连续帧去噪之间交替进行——这一机制不仅通过帧插入实现高效上下文压缩以缓解误差传播,还显著降低训练时的计算量(减少三倍FLOPs),同时支持局部注意力机制并联合学习视频长度与内容。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11438
作者: Tariq Berrada Ifriqi,John Nguyen,Karteek Alahari,Jakob Verbeek,Ricky T. Q. Chen
机构: Meta(元)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:We present Flowception, a novel non-autoregressive and variable-length video generation framework. Flowception learns a probability path that interleaves discrete frame insertions with continuous frame denoising. Compared to autoregressive methods, Flowception alleviates error accumulation/drift as the frame insertion mechanism during sampling serves as an efficient compression mechanism to handle long-term context. Compared to full-sequence flows, our method reduces FLOPs for training three-fold, while also being more amenable to local attention variants, and allowing to learn the length of videos jointly with their content. Quantitative experimental results show improved FVD and VBench metrics over autoregressive and full-sequence baselines, which is further validated with qualitative results. Finally, by learning to insert and denoise frames in a sequence, Flowception seamlessly integrates different tasks such as image-to-video generation and video interpolation.
zh
[CV-42] Back to the Baseline: Examining Baseline Effects on Explainability Metrics
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前用于评估可解释人工智能(Explainable Artificial Intelligence, XAI)中Attribution方法的Fidelity指标(如Insertion和Deletion)所依赖的基线(baseline)选择问题——即不同基线会系统性地偏好某些Attribution方法,导致评估结果不可靠。关键解决方案在于提出两个理想基线应具备的性质:(i) 能有效移除输入图像的信息,(ii) 不产生过度分布外(out-of-distribution, OOD)的图像。作者通过实证发现现有基线无法同时满足这两个条件,且存在信息移除与OOD图像生成之间的权衡;为此,他们引入一种基于特征可视化(feature visualisation)的新颖模型相关基线(model-dependent baseline),能够在不显著引入OOD图像的前提下有效移除信息,从而改善这一权衡关系。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11433
作者: Agustin Martin Picard(ANITI),Thibaut Boissin(ANITI),Varshini Subhash,Rémi Cadène(SU),Thomas Fel(ANITI)
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Attribution methods are among the most prevalent techniques in Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) and are usually evaluated and compared using Fidelity metrics, with Insertion and Deletion being the most popular. These metrics rely on a baseline function to alter the pixels of the input image that the attribution map deems most important. In this work, we highlight a critical problem with these metrics: the choice of a given baseline will inevitably favour certain attribution methods over others. More concerningly, even a simple linear model with commonly used baselines contradicts itself by designating different optimal methods. A question then arises: which baseline should we use? We propose to study this problem through two desirable properties of a baseline: (i) that it removes information and (ii) that it does not produce overly out-of-distribution (OOD) images. We first show that none of the tested baselines satisfy both criteria, and there appears to be a trade-off among current baselines: either they remove information or they produce a sequence of OOD images. Finally, we introduce a novel baseline by leveraging recent work in feature visualisation to artificially produce a model-dependent baseline that removes information without being overly OOD, thus improving on the trade-off when compared to other existing baselines. Our code is available at this https URL
zh
[CV-43] JoyAvatar: Real-time and Infinite Audio-Driven Avatar Generation with Autoregressive Diffusion
【速读】:该论文旨在解决基于扩散Transformer(DiT)的音频驱动人脸动画生成方法在实际应用中面临的两大瓶颈问题:一是计算开销高,难以实现实时推理;二是难以生成长时视频,现有方法受限于误差累积导致质量下降。为突破这些限制,作者提出JoyAvatar,其核心解决方案包括三个关键技术:(1) 渐进式步数引导(Progressive Step Bootstrapping, PSB),通过为初始帧分配更多去噪步骤来稳定生成过程并减少误差传播;(2) 运动条件注入(Motion Condition Injection, MCI),将噪声扰动的前一帧作为运动条件输入,提升时序一致性;(3) 基于缓存重置的无界旋转位置编码(Unbounded RoPE via Cache-Resetting, URCR),实现动态位置编码机制以支持无限长度视频生成。该模型在单张GPU上达到16 FPS实时推理速度,并在视觉质量、时序一致性和唇音同步方面表现优异。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11423
作者: Chaochao Li,Ruikui Wang,Liangbo Zhou,Jinheng Feng,Huaishao Luo,Huan Zhang,Youzheng Wu,Xiaodong He
机构: JD Explore Academy
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Existing DiT-based audio-driven avatar generation methods have achieved considerable progress, yet their broader application is constrained by limitations such as high computational overhead and the inability to synthesize long-duration videos. Autoregressive methods address this problem by applying block-wise autoregressive diffusion methods. However, these methods suffer from the problem of error accumulation and quality degradation. To address this, we propose JoyAvatar, an audio-driven autoregressive model capable of real-time inference and infinite-length video generation with the following contributions: (1) Progressive Step Bootstrapping (PSB), which allocates more denoising steps to initial frames to stabilize generation and reduce error accumulation; (2) Motion Condition Injection (MCI), enhancing temporal coherence by injecting noise-corrupted previous frames as motion condition; and (3) Unbounded RoPE via Cache-Resetting (URCR), enabling infinite-length generation through dynamic positional encoding. Our 1.3B-parameter causal model achieves 16 FPS on a single GPU and achieves competitive results in visual quality, temporal consistency, and lip synchronization.
zh
[CV-44] Collaborative Reconstruction and Repair for Multi-class Industrial Anomaly Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多类工业异常检测中因传统基于重构的网络存在身份映射问题(identity mapping problem)而导致的检测失败难题。该问题表现为模型在处理异常样本时,会直接复制输入特征而无法区分正常与异常区域,从而丧失检测能力。解决方案的关键在于提出一种新颖的统一框架——协同重构与修复(Collaborative Reconstruction and Repair, CRR),其核心机制包括:1)优化解码器在重构正常样本的同时修复合成异常,使异常区域生成显著不同的表示,而正常区域保持与编码器输出一致;2)引入特征级随机掩码策略以保留局部信息;3)通过合成异常掩码监督分割网络训练,降低编码器与解码器特征表示间的差异,从而提升异常定位精度。实验证明,CRR有效缓解了身份映射问题,并在多类工业异常检测任务中达到当前最优性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11401
作者: Qishan Wang,Haofeng Wang,Shuyong Gao,Jia Guo,Li Xiong,Jiaqi Li,Dengxuan Bai,Wenqiang Zhang
机构: Fudan University (复旦大学); Hexi University (河西大学); Tongji University (同济大学); Fudan university (复旦大学); Tsinghua University (清华大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted to Data Intelligence 2025
Abstract:Industrial anomaly detection is a challenging open-set task that aims to identify unknown anomalous patterns deviating from normal data distribution. To avoid the significant memory consumption and limited generalizability brought by building separate models per class, we focus on developing a unified framework for multi-class anomaly detection. However, under this challenging setting, conventional reconstruction-based networks often suffer from an identity mapping problem, where they directly replicate input features regardless of whether they are normal or anomalous, resulting in detection failures. To address this issue, this study proposes a novel framework termed Collaborative Reconstruction and Repair (CRR), which transforms the reconstruction to repairation. First, we optimize the decoder to reconstruct normal samples while repairing synthesized anomalies. Consequently, it generates distinct representations for anomalous regions and similar representations for normal areas compared to the encoder’s output. Second, we implement feature-level random masking to ensure that the representations from decoder contain sufficient local information. Finally, to minimize detection errors arising from the discrepancies between feature representations from the encoder and decoder, we train a segmentation network supervised by synthetic anomaly masks, thereby enhancing localization performance. Extensive experiments on industrial datasets that CRR effectively mitigates the identity mapping issue and achieves state-of-the-art performance in multi-class industrial anomaly detection.
zh
[CV-45] FlowDC: Flow-Based Decoupling-Decay for Complex Image Editing
【速读】:该论文旨在解决复杂文本图像编辑(complex text-based image editing)中因多编辑目标导致的语义对齐与源图像一致性难以平衡的问题。当前单轮和多轮编辑方法分别受限于长文本跟随困难和累积不一致性,难以有效处理复杂编辑任务。解决方案的关键在于提出FlowDC框架:首先将复杂编辑解耦为多个子编辑效应,并在编辑过程中并行叠加;其次,通过分解速度场并衰减与编辑位移正交的速度分量,抑制对源结构的破坏,从而提升源一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11395
作者: Yilei Jiang,Zhen Wang,Yanghao Wang,Jun Yu,Yueting Zhuang,Jun Xiao,Long Chen
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); HKUST (香港科技大学); Harbin Institute of Technology (深圳) (哈尔滨工业大学(深圳)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:With the surge of pre-trained text-to-image flow matching models, text-based image editing performance has gained remarkable improvement, especially for \underlinesimple editing that only contains a single editing target. To satisfy the exploding editing requirements, the \underlinecomplex editing which contains multiple editing targets has posed as a more challenging task. However, current complex editing solutions: single-round and multi-round editing are limited by long text following and cumulative inconsistency, respectively. Thus, they struggle to strike a balance between semantic alignment and source consistency. In this paper, we propose \textbfFlowDC, which decouples the complex editing into multiple sub-editing effects and superposes them in parallel during the editing process. Meanwhile, we observed that the velocity quantity that is orthogonal to the editing displacement harms the source structure preserving. Thus, we decompose the velocity and decay the orthogonal part for better source consistency. To evaluate the effectiveness of complex editing settings, we construct a complex editing benchmark: Complex-PIE-Bench. On two benchmarks, FlowDC shows superior results compared with existing methods. We also detail the ablations of our module designs.
zh
[CV-46] he N-Body Problem: Parallel Execution from Single-Person Egocentric Video
【速读】:该论文试图解决的问题是:如何从单个第一人称视角视频中学习并生成多人并行执行相同任务的可行方案,以最大化执行速度(speed-up),同时避免物理上不可行的场景(如空间冲突、物体争夺或因果顺序错误)。其核心挑战在于将原本由一人完成的任务序列合理分配给多个个体,使并行化过程既高效又符合现实约束。解决方案的关键在于提出“N-Body Problem”这一形式化框架,并设计一套涵盖性能(如动作覆盖率、速度提升)与可行性(空间碰撞、物体冲突、因果一致性)的评估指标;进一步引入一种结构化提示策略(structured prompting strategy),引导视觉语言模型(VLM)推理三维环境、物体使用关系及时间依赖性,从而生成可执行的多人并行任务计划。实验表明,该方法在EPIC-Kitchens和HD-EPIC数据集上实现了显著的性能提升与冲突降低。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11393
作者: Zhifan Zhu,Yifei Huang,Yoichi Sato,Dima Damen
机构: University of Bristol (布里斯托大学); The University of Tokyo (东京大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: project webpage: this https URL
Abstract:Humans can intuitively parallelise complex activities, but can a model learn this from observing a single person? Given one egocentric video, we introduce the N-Body Problem: how N individuals, can hypothetically perform the same set of tasks observed in this video. The goal is to maximise speed-up, but naive assignment of video segments to individuals often violates real-world constraints, leading to physically impossible scenarios like two people using the same object or occupying the same space. To address this, we formalise the N-Body Problem and propose a suite of metrics to evaluate both performance (speed-up, task coverage) and feasibility (spatial collisions, object conflicts and causal constraints). We then introduce a structured prompting strategy that guides a Vision-Language Model (VLM) to reason about the 3D environment, object usage, and temporal dependencies to produce a viable parallel execution. On 100 videos from EPIC-Kitchens and HD-EPIC, our method for N = 2 boosts action coverage by 45% over a baseline prompt for Gemini 2.5 Pro, while simultaneously slashing collision rates, object and causal conflicts by 55%, 45% and 55% respectively.
zh
[CV-47] Out-of-Distribution Segmentation via Wasserstein-Based Evidential Uncertainty
【速读】:该论文旨在解决深度神经网络在语义分割任务中对开放世界场景下未知类别(out-of-distribution, OOD)物体识别与分割能力不足的问题,这在自动驾驶等安全关键应用中尤为关键。其解决方案的核心在于提出一种基于Wasserstein损失的证据分割框架,该框架能够捕捉分布间的距离并尊重概率单纯形(probability simplex)的几何结构;同时结合Kullback-Leibler散度正则项和Dice结构一致性约束,显著提升了对OOD物体的分割性能,优于传统基于不确定性的方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11373
作者: Arnold Brosch,Abdelrahman Eldesokey,Michael Felsberg,Kira Maag
机构: Heinrich-Heine-University Düsseldorf(海因里希海涅大学杜塞尔多夫分校); KAUST(阿卜杜拉国王科技大学); Linköping University(林雪平大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Deep neural networks achieve superior performance in semantic segmentation, but are limited to a predefined set of classes, which leads to failures when they encounter unknown objects in open-world scenarios. Recognizing and segmenting these out-of-distribution (OOD) objects is crucial for safety-critical applications such as automated driving. In this work, we present an evidence segmentation framework using a Wasserstein loss, which captures distributional distances while respecting the probability simplex geometry. Combined with Kullback-Leibler regularization and Dice structural consistency terms, our approach leads to improved OOD segmentation performance compared to uncertainty-based approaches.
zh
[CV-48] Assisted Refinement Network Based on Channel Information Interaction for Camouflaged and Salient Object Detection
【速读】:该论文针对伪装目标检测(Camouflaged Object Detection, COD)中解码阶段存在的两个关键问题展开研究:一是同层特征内部通道间信息交互不足,限制了特征表达能力;二是难以有效协同建模边界与区域信息,导致物体完整区域和锐利边界的重建困难。解决方案的关键在于提出两个核心模块:其一为通道信息交互模块(Channel Information Interaction Module, CIIM),通过引入水平-垂直整合机制,在通道维度上实现特征重组与交互,以捕捉互补的跨通道信息;其二为基于先验知识引导的协同解码架构,利用边界提取(Boundary Extraction, BE)和区域提取(Region Extraction, RE)模块生成边界先验与对象定位图,并通过混合注意力机制协同校准解码特征,从而缓解语义模糊并提升边界精度。此外,多尺度增强(Multi-scale Enhancement, MSE)模块进一步丰富上下文特征表示,整体模型在四个COD基准数据集上达到先进性能,并成功迁移至显著性目标检测(SOD)等下游任务,验证了其泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11369
作者: Kuan Wang,Yanjun Qin,Mengge Lu,Liejun Wang,Xiaoming Tao
机构: Xinjiang University (新疆大学); Tsinghua University (清华大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 15 pages, 9 figures
Abstract:Camouflaged Object Detection (COD) stands as a significant challenge in computer vision, dedicated to identifying and segmenting objects visually highly integrated with their backgrounds. Current mainstream methods have made progress in cross-layer feature fusion, but two critical issues persist during the decoding stage. The first is insufficient cross-channel information interaction within the same-layer features, limiting feature expressiveness. The second is the inability to effectively co-model boundary and region information, making it difficult to accurately reconstruct complete regions and sharp boundaries of objects. To address the first issue, we propose the Channel Information Interaction Module (CIIM), which introduces a horizontal-vertical integration mechanism in the channel dimension. This module performs feature reorganization and interaction across channels to effectively capture complementary cross-channel information. To address the second issue, we construct a collaborative decoding architecture guided by prior knowledge. This architecture generates boundary priors and object localization maps through Boundary Extraction (BE) and Region Extraction (RE) modules, then employs hybrid attention to collaboratively calibrate decoded features, effectively overcoming semantic ambiguity and imprecise boundaries. Additionally, the Multi-scale Enhancement (MSE) module enriches contextual feature representations. Extensive experiments on four COD benchmark datasets validate the effectiveness and state-of-the-art performance of the proposed model. We further transferred our model to the Salient Object Detection (SOD) task and demonstrated its adaptability across downstream tasks, including polyp segmentation, transparent object detection, and industrial and road defect detection. Code and experimental results are publicly available at: this https URL.
zh
[CV-49] Reliable Detection of Minute Targets in High-Resolution Aerial Imagery across Temporal Shifts
【速读】:该论文旨在解决无人机(Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, UAV)在水稻育秧田中对微小目标——稻苗的高效检测问题,其核心挑战在于目标尺度小及环境变化带来的干扰。解决方案的关键在于采用基于迁移学习(transfer learning)的Faster R-CNN架构,并构建了一个大规模的UAV遥感数据集用于训练与验证,从而显著提升模型在不同时间获取图像条件下的泛化能力与检测鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11360
作者: Mohammad Sadegh Gholizadeh,Amir Arsalan Rezapour,Hamidreza Shayegh,Ehsan Pazouki
机构: Shahid Rajaee University (沙希德·拉吉大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Efficient crop detection via Unmanned Aerial Vehicles is critical for scaling precision agriculture, yet it remains challenging due to the small scale of targets and environmental variability. This paper addresses the detection of rice seedlings in paddy fields by leveraging a Faster R-CNN architecture initialized via transfer learning. To overcome the specific difficulties of detecting minute objects in high-resolution aerial imagery, we curate a significant UAV dataset for training and rigorously evaluate the model’s generalization capabilities. Specifically, we validate performance across three distinct test sets acquired at different temporal intervals, thereby assessing robustness against varying imaging conditions. Our empirical results demonstrate that transfer learning not only facilitates the rapid convergence of object detection models in agricultural contexts but also yields consistent performance despite domain shifts in image acquisition.
zh
[CV-50] Prior-Enhanced Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction from Casual Video
【速读】:该论文旨在解决从随意拍摄的单目RGB视频中自动重建动态场景的问题,尤其针对现有方法在处理细结构、运动一致性与几何精度方面的不足。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个端到端的自动化流水线,通过视频分割结合极线误差图生成高精度的对象级掩码,从而引导对象深度损失以优化一致的视频深度,并支持基于骨架的采样与掩码引导的重识别策略,实现可靠且完整的二维轨迹追踪;此外,引入虚拟视角深度损失和支架投影损失,将优化后的先验嵌入重建阶段,有效去除漂浮物并约束运动节点与轨迹对齐,从而保留精细几何结构并保证运动连贯性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11356
作者: Meng-Li Shih,Ying-Huan Chen,Yu-Lun Liu,Brian Curless
机构: University of Washington (华盛顿大学); National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University (国立阳明交通大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:We introduce a fully automatic pipeline for dynamic scene reconstruction from casually captured monocular RGB videos. Rather than designing a new scene representation, we enhance the priors that drive Dynamic Gaussian Splatting. Video segmentation combined with epipolar-error maps yields object-level masks that closely follow thin structures; these masks (i) guide an object-depth loss that sharpens the consistent video depth, and (ii) support skeleton-based sampling plus mask-guided re-identification to produce reliable, comprehensive 2-D tracks. Two additional objectives embed the refined priors in the reconstruction stage: a virtual-view depth loss removes floaters, and a scaffold-projection loss ties motion nodes to the tracks, preserving fine geometry and coherent motion. The resulting system surpasses previous monocular dynamic scene reconstruction methods and delivers visibly superior renderings
zh
[CV-51] A Multi-Mode Structured Light 3D Imaging System with Multi-Source Information Fusion for Underwater Pipeline Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决水下管道因腐蚀导致寿命缩短及安全隐患的问题,提出一种基于多源信息融合的多模式水下结构光三维成像系统(UW-SLD系统),以实现对水下管道缺陷的高精度、实时检测。其解决方案的关键在于:首先采用快速畸变校正(FDC)方法提升水下图像矫正效率;其次通过因子图参数优化方法实现结构光与声学传感器之间的外参标定;再者引入多模式三维成像策略以适应管道几何形态变化;最后结合多源信息融合与自适应扩展卡尔曼滤波(AEKF),并提出基于边缘检测的ICP(ED-ICP)算法,增强点云配准鲁棒性,从而在复杂水下扰动环境下实现稳定位姿估计和高保真缺陷结构重建。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11354
作者: Qinghan Hu,Haijiang Zhu,Na Sun,Lei Chen,Zhengqiang Fan,Zhiqing Li
机构: Beijing University of Chemical Technology (北京化工大学); Tsinghua University (清华大学); Guoneng Zhishen Control Technology Co., Ltd. (国能智深控制技术有限公司); Beijing University of Agriculture (北京农学院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Underwater pipelines are highly susceptible to corrosion, which not only shorten their service life but also pose significant safety risks. Compared with manual inspection, the intelligent real-time imaging system for underwater pipeline detection has become a more reliable and practical solution. Among various underwater imaging techniques, structured light 3D imaging can restore the sufficient spatial detail for precise defect characterization. Therefore, this paper develops a multi-mode underwater structured light 3D imaging system for pipeline detection (UW-SLD system) based on multi-source information fusion. First, a rapid distortion correction (FDC) method is employed for efficient underwater image rectification. To overcome the challenges of extrinsic calibration among underwater sensors, a factor graph-based parameter optimization method is proposed to estimate the transformation matrix between the structured light and acoustic sensors. Furthermore, a multi-mode 3D imaging strategy is introduced to adapt to the geometric variability of underwater pipelines. Given the presence of numerous disturbances in underwater environments, a multi-source information fusion strategy and an adaptive extended Kalman filter (AEKF) are designed to ensure stable pose estimation and high-accuracy measurements. In particular, an edge detection-based ICP (ED-ICP) algorithm is proposed. This algorithm integrates pipeline edge detection network with enhanced point cloud registration to achieve robust and high-fidelity reconstruction of defect structures even under variable motion conditions. Extensive experiments are conducted under different operation modes, velocities, and depths. The results demonstrate that the developed system achieves superior accuracy, adaptability and robustness, providing a solid foundation for autonomous underwater pipeline detection.
zh
[CV-52] Surveillance Video-Based Traffic Accident Detection Using Transformer Architecture
【速读】:该论文旨在解决交通肇事事故检测中传统计算机视觉方法在时空理解能力有限及跨域泛化性能差的问题,同时应对生成式AI模型在小规模、非多样化数据集上难以训练出鲁棒且可泛化的系统这一挑战。其解决方案的关键在于:首先构建了一个覆盖广泛交通环境、事故类型与情境变化的综合性平衡数据集;其次提出一种基于Transformer架构的事故检测模型,该模型结合卷积层提取帧内局部相关性,并利用Transformer捕捉特征间的时序依赖关系;此外,通过系统评估多种运动线索(motion cues)整合策略,发现将RGB特征与光流(optical flow)拼接的方式能显著提升检测准确率至88.3%,从而有效增强对动态场景的理解能力,优于现有视觉语言模型(VLM)如GPT、Gemini和LLaVA-NeXT-Video的表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11350
作者: Tanu Singh,Pranamesh Chakraborty,Long T. Truong
机构: Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur (印度理工学院坎普尔分校); La Trobe University (拉特罗布大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Road traffic accidents represent a leading cause of mortality globally, with incidence rates rising due to increasing population, urbanization, and motorization. Rising accident rates raise concerns about traffic surveillance effectiveness. Traditional computer vision methods for accident detection struggle with limited spatiotemporal understanding and poor cross-domain generalization. Recent advances in transformer architectures excel at modeling global spatial-temporal dependencies and parallel computation. However, applying these models to automated traffic accident detection is limited by small, non-diverse datasets, hindering the development of robust, generalizable systems. To address this gap, we curated a comprehensive and balanced dataset that captures a wide spectrum of traffic environments, accident types, and contextual variations. Utilizing the curated dataset, we propose an accident detection model based on a transformer architecture using pre-extracted spatial video features. The architecture employs convolutional layers to extract local correlations across diverse patterns within a frame, while leveraging transformers to capture sequential-temporal dependencies among the retrieved features. Moreover, most existing studies neglect the integration of motion cues, which are essential for understanding dynamic scenes, especially during accidents. These approaches typically rely on static features or coarse temporal information. In this study, multiple methods for incorporating motion cues were evaluated to identify the most effective strategy. Among the tested input approaches, concatenating RGB features with optical flow achieved the highest accuracy at 88.3%. The results were further compared with vision language models (VLM) such as GPT, Gemini, and LLaVA-NeXT-Video to assess the effectiveness of the proposed method.
zh
[CV-53] ask-Specific Distance Correlation Matching for Few-Shot Action Recognition
【速读】:该论文旨在解决少样本动作识别(Few-shot Action Recognition, FSAR)中存在的两个关键问题:一是现有集合匹配度量方法主要依赖余弦相似度来衡量帧间线性依赖关系,仅使用实例级信息,难以捕捉非线性关系及任务特定线索;二是基于CLIP的高效微调策略中引入的侧边层(side layers)在数据有限条件下优化困难。解决方案的关键在于提出TS-FSAR框架,其核心创新包括:(1) 视觉梯度侧网络(Ladder Side Network, LSN)用于高效CLIP微调;(2) 任务特定距离相关匹配(Task-Specific Distance Correlation Matching, TS-DCM)利用α-距离相关性建模帧间线性和非线性依赖,并通过任务原型实现任务感知匹配;(3) 带自适应CLIP引导的LSN模块(Guiding LSN with Adapted CLIP, GLAC),借助冻结的适配CLIP对LSN进行正则化,提升在弱监督下α-距离相关性的估计精度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11340
作者: Fei Long,Yao Zhang,Jiaming Lv,Jiangtao Xie,Peihua Li
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 9 pages. 4 figures, conference
Abstract:Few-shot action recognition (FSAR) has recently made notable progress through set matching and efficient adaptation of large-scale pre-trained models. However, two key limitations persist. First, existing set matching metrics typically rely on cosine similarity to measure inter-frame linear dependencies and then perform matching with only instance-level information, thus failing to capture more complex patterns such as nonlinear relationships and overlooking task-specific cues. Second, for efficient adaptation of CLIP to FSAR, recent work performing fine-tuning via skip-fusion layers (which we refer to as side layers) has significantly reduced memory cost. However, the newly introduced side layers are often difficult to optimize under limited data conditions. To address these limitations, we propose TS-FSAR, a framework comprising three components: (1) a visual Ladder Side Network (LSN) for efficient CLIP fine-tuning; (2) a metric called Task-Specific Distance Correlation Matching (TS-DCM), which uses \alpha -distance correlation to model both linear and nonlinear inter-frame dependencies and leverages a task prototype to enable task-specific matching; and (3) a Guiding LSN with Adapted CLIP (GLAC) module, which regularizes LSN using the adapted frozen CLIP to improve training for better \alpha -distance correlation estimation under limited supervision. Extensive experiments on five widely-used benchmarks demonstrate that our TS-FSAR yields superior performance compared to prior state-of-the-arts.
zh
[CV-54] UFVideo: Towards Unified Fine-Grained Video Cooperative Understanding with Large Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前视频大语言模型(Video LLM)在视频理解任务中普遍局限于特定场景、缺乏跨粒度(全局、像素级、时间维度)统一感知能力的问题。现有方法难以实现对视频内容的多粒度协同理解,限制了其在复杂视频分析中的应用潜力。解决方案的关键在于提出UFVideo,首个具备统一多粒度协作理解能力的视频大语言模型;其核心创新是设计了统一的视觉-语言引导对齐机制(unified visual-language guided alignment),能够在单一模型架构内灵活处理不同尺度的视频理解任务,动态编码视觉与文本输入,并生成文本响应、时间定位或基于区域的掩码输出,从而实现从宏观到微观的多粒度联合推理。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11336
作者: Hewen Pan,Cong Wei,Dashuang Liang,Zepeng Huang,Pengfei Gao,Ziqi Zhou,Lulu Xue,Pengfei Yan,Xiaoming Wei,Minghui Li,Shengshan Hu
机构: Huazhong University of Science and Technology (华中科技大学); Meituan (美团)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 22 pages, 13 figures, technical report
Abstract:With the advancement of multi-modal Large Language Models (LLMs), Video LLMs have been further developed to perform on holistic and specialized video understanding. However, existing works are limited to specialized video understanding tasks, failing to achieve a comprehensive and multi-grained video perception. To bridge this gap, we introduce UFVideo, the first Video LLM with unified multi-grained cooperative understanding capabilities. Specifically, we design unified visual-language guided alignment to flexibly handle video understanding across global, pixel and temporal scales within a single model. UFVideo dynamically encodes the visual and text inputs of different tasks and generates the textual response, temporal localization, or grounded mask. Additionally, to evaluate challenging multi-grained video understanding tasks, we construct the UFVideo-Bench consisting of three distinct collaborative tasks within the scales, which demonstrates UFVideo’s flexibility and advantages over GPT-4o. Furthermore, we validate the effectiveness of our model across 9 public benchmarks covering various common video understanding tasks, providing valuable insights for future Video LLMs.
zh
[CV-55] FreqDINO: Frequency-Guided Adaptation for Generalized Boundary-Aware Ultrasound Image Segmentation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决超声图像分割中因斑点噪声(speckle noise)和成像伪影导致的边界退化问题,尤其针对DINOv3模型在自然图像上预训练后对超声图像特定边界敏感性不足的局限性。其解决方案的关键在于提出FreqDINO框架,通过三个核心模块实现:(1)多尺度频率提取与对齐(Multi-scale Frequency Extraction and Alignment, MFEA)策略,分离低频结构与多尺度高频边界细节并以可学习注意力机制对齐;(2)频率引导的边界精修(Frequency-Guided Boundary Refinement, FGBR)模块,从高频成分中提取边界原型并优化空间特征;(3)多任务边界引导解码器(Multi-task Boundary-Guided Decoder, MBGD),确保边界预测与语义分割结果之间的空间一致性。该方法显著提升了超声图像分割的边界感知能力和结构一致性,展现出优异的泛化性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11335
作者: Yixuan Zhang,Qing Xu,Yue Li,Xiangjian He,Qian Zhang,Mainul Haque,Rong Qu,Wenting Duan,Zhen Chen
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Ultrasound image segmentation is pivotal for clinical diagnosis, yet challenged by speckle noise and imaging artifacts. Recently, DINOv3 has shown remarkable promise in medical image segmentation with its powerful representation capabilities. However, DINOv3, pre-trained on natural images, lacks sensitivity to ultrasound-specific boundary degradation. To address this limitation, we propose FreqDINO, a frequency-guided segmentation framework that enhances boundary perception and structural consistency. Specifically, we devise a Multi-scale Frequency Extraction and Alignment (MFEA) strategy to separate low-frequency structures and multi-scale high-frequency boundary details, and align them via learnable attention. We also introduce a Frequency-Guided Boundary Refinement (FGBR) module that extracts boundary prototypes from high-frequency components and refines spatial features. Furthermore, we design a Multi-task Boundary-Guided Decoder (MBGD) to ensure spatial coherence between boundary and semantic predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FreqDINO surpasses state-of-the-art methods with superior achieves remarkable generalization capability. The code is at this https URL.
zh
[CV-56] Physics-Informed Video Flare Synthesis and Removal Leverag ing Motion Independence between Flare and Scene
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视频中动态镜头眩光(lens flare)的去除问题,其核心挑战在于眩光、光源与场景内容之间存在运动独立性,导致现有方法在视频序列中易产生闪烁和伪影。解决方案的关键在于提出一种物理信息驱动的动态眩光合成流程,通过光流模拟光源运动并建模散射与反射眩光的时序行为;同时设计了一个结合注意力机制的空间抑制模块和基于Mamba的时序建模组件的视频眩光去除网络,该结构能够有效捕捉长距离时空依赖关系,无需多帧对齐即可消除时间混叠,从而显著提升去眩光效果与时空一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11327
作者: Junqiao Wang,Yuanfei Huang,Hua Huang
机构: Beijing Normal University (北京师范大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Lens flare is a degradation phenomenon caused by strong light sources. Existing researches on flare removal have mainly focused on images, while the spatiotemporal characteristics of video flare remain largely unexplored. Video flare synthesis and removal pose significantly greater challenges than in image, owing to the complex and mutually independent motion of flare, light sources, and scene content. This motion independence further affects restoration performance, often resulting in flicker and artifacts. To address this issue, we propose a physics-informed dynamic flare synthesis pipeline, which simulates light source motion using optical flow and models the temporal behaviors of both scattering and reflective flares. Meanwhile, we design a video flare removal network that employs an attention module to spatially suppress flare regions and incorporates a Mamba-based temporal modeling component to capture long range spatio-temporal dependencies. This motion-independent spatiotemporal representation effectively eliminates the need for multi-frame alignment, alleviating temporal aliasing between flares and scene content and thereby improving video flare removal performance. Building upon this, we construct the first video flare dataset to comprehensively evaluate our method, which includes a large set of synthetic paired videos and additional real-world videos collected from the Internet to assess generalization capability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing video-based restoration and image-based flare removal methods on both real and synthetic videos, effectively removing dynamic flares while preserving light source integrity and maintaining spatiotemporal consistency of scene.
zh
[CV-57] MLLM Machine Unlearning via Visual Knowledge Distillation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Model, MLLM)中敏感视觉知识难以有效移除的问题,现有方法多针对大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)设计,对MLLM的适配性不足且缺乏针对性。其解决方案的关键在于通过解耦MLLM内部的视觉与文本知识,并引入一种基于中间视觉表示的视觉知识蒸馏(Visual Knowledge Distillation, VKD)机制,利用模型内部的视觉特征作为监督信号,实现目标视觉知识的选择性擦除,同时保留文本知识完整性;该方法仅微调MLLM的视觉组件,显著提升效率,并在有效性与鲁棒性(对抗重学习攻击)方面优于现有最先进方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11325
作者: Yuhang Wang,Zhenxing Niu,Haoxuan Ji,Guangyu He,Haichang Gao,Gang Hua
机构: Xidian University (西安电子科技大学); Amazon.com (亚马逊)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Recently, machine unlearning approaches have been proposed to remove sensitive information from well-trained large models. However, most existing methods are tailored for LLMs, while MLLM-oriented unlearning remains at its early stage. Inspired by recent studies exploring the internal mechanisms of MLLMs, we propose to disentangle the visual and textual knowledge embedded within MLLMs and introduce a dedicated approach to selectively erase target visual knowledge while preserving textual knowledge. Unlike previous unlearning methods that rely on output-level supervision, our approach introduces a Visual Knowledge Distillation (VKD) scheme, which leverages intermediate visual representations within the MLLM as supervision signals. This design substantially enhances both unlearning effectiveness and model utility. Moreover, since our method only fine-tunes the visual components of the MLLM, it offers significant efficiency advantages. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art unlearning methods in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency. Moreover, we are the first to evaluate the robustness of MLLM unlearning against relearning attacks.
zh
[CV-58] KeyframeFace: From Text to Expressive Facial Keyframes
【速读】:该论文旨在解决从自然语言生成动态3D人脸动画时缺乏语义 grounding 和时间结构的问题,现有方法多依赖语音驱动或无结构的表情序列,难以实现具有表达力的人类表演生成。解决方案的关键在于提出一个大规模多模态数据集 KeyframeFace,其中包含2,100个富有表现力的脚本及其对应的单目视频、每帧ARKit系数(ARKit coefficients)、上下文背景、复杂情绪标注以及由大语言模型(LLMs)和多模态大语言模型(MLLMs)辅助生成的关键帧与多视角注释;同时设计首个显式利用LLM先验进行可解释面部运动合成的文本到动画框架,将LLM的语义理解能力与ARKit系数的可解释结构对齐,从而实现高保真度的情感化动画生成。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11321
作者: Jingchao Wu,Zejian Kang,Haibo Liu,Yuanchen Fei,Xiangru Huang
机构: Westlake University (西湖大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Generating dynamic 3D facial animation from natural language requires understanding both temporally structured semantics and fine-grained expression changes. Existing datasets and methods mainly focus on speech-driven animation or unstructured expression sequences and therefore lack the semantic grounding and temporal structures needed for expressive human performance generation. In this work, we introduce KeyframeFace, a large-scale multimodal dataset designed for text-to-animation research through keyframe-level supervision. KeyframeFace provides 2,100 expressive scripts paired with monocular videos, per-frame ARKit coefficients, contextual backgrounds, complex emotions, manually defined keyframes, and multi-perspective annotations based on ARKit coefficients and images via Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). Beyond the dataset, we propose the first text-to-animation framework that explicitly leverages LLM priors for interpretable facial motion synthesis. This design aligns the semantic understanding capabilities of LLMs with the interpretable structure of ARKit’s coefficients, enabling high-fidelity expressive animation. KeyframeFace and our LLM-based framework together establish a new foundation for interpretable, keyframe-guided, and context-aware text-to-animation. Code and data are available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-59] SATMapTR: Satellite Image Enhanced Online HD Map Construction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决高精度地图(High-definition map, HD map)在实时构建过程中因车载传感器性能受限及频繁遮挡导致的输入数据质量低下问题,从而影响地图的准确性与鲁棒性。现有方法虽尝试引入卫星图像作为辅助信息以弥补视角局限,但其鸟瞰图(Bird’s Eye View, BEV)常受植被和建筑阴影遮挡干扰,且传统特征提取与融合策略效果有限。解决方案的关键在于提出SATMapTR模型,其核心创新为两个模块:(1) 门控特征精炼模块(gated feature refinement module),通过融合高层语义与低层结构线索,自适应过滤卫星图像特征,提取高信噪比的地图相关表征;(2) 几何感知融合模块(geometry-aware fusion module),实现卫星图像与BEV特征在网格级的一致融合,有效抑制无关区域和低质输入的干扰。实验表明,该方案在nuScenes数据集上实现了73.8的mAP,较当前最优卫星增强模型提升达14.2 mAP,并在恶劣天气和传感器故障下保持更低的性能衰减,同时在远距离感知范围内达到近三倍的mAP提升。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11319
作者: Bingyuan Huang,Guanyi Zhao,Qian Xu,Yang Lou,Yung-Hui Li,Jianping Wang
机构: City University of Hong Kong (香港城市大学); Hon Hai Research Institute (鸿海研究院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 9 pages (+ 3 pages of Appendix)
Abstract:High-definition (HD) maps are evolving from pre-annotated to real-time construction to better support autonomous driving in diverse scenarios. However, this process is hindered by low-quality input data caused by onboard sensors limited capability and frequent occlusions, leading to incomplete, noisy, or missing data, and thus reduced mapping accuracy and robustness. Recent efforts have introduced satellite images as auxiliary input, offering a stable, wide-area view to complement the limited ego perspective. However, satellite images in Bird’s Eye View are often degraded by shadows and occlusions from vegetation and buildings. Prior methods using basic feature extraction and fusion remain ineffective. To address these challenges, we propose SATMapTR, a novel online map construction model that effectively fuses satellite image through two key components: (1) a gated feature refinement module that adaptively filters satellite image features by integrating high-level semantics with low-level structural cues to extract high signal-to-noise ratio map-relevant representations; and (2) a geometry-aware fusion module that consistently fuse satellite and BEV features at a grid-to-grid level, minimizing interference from irrelevant regions and low-quality inputs. Experimental results on the nuScenes dataset show that SATMapTR achieves the highest mean average precision (mAP) of 73.8, outperforming state-of-the-art satellite-enhanced models by up to 14.2 mAP. It also shows lower mAP degradation under adverse weather and sensor failures, and achieves nearly 3 times higher mAP at extended perception ranges.
zh
[CV-60] MultiEgo: A Multi-View Egocentric Video Dataset for 4D Scene Reconstruction ACM-MM2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有重建数据集在动态场景下缺乏多视角第一人称(egocentric)视频支持的问题,从而限制了全视角视频(Free-Viewpoint Video, FVV)等应用的发展。解决方案的关键在于构建首个面向4D动态场景重建的多视角第一人称数据集MultiEgo,其包含五个典型社交互动场景(如会议、表演和演讲),每场景由佩戴增强现实(AR)眼镜的参与者录制五路真实第一人称视频,并通过硬件级数据采集系统与处理流程实现跨视角亚毫秒级时间同步及精确位姿标注,为多视角第一人称动态场景重建提供了可靠基准与基础资源。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11301
作者: Bate Li,Houqiang Zhong,Zhengxue Cheng,Qiang Hu,Qiang Wang,Li Song,Wenjun Zhang
机构: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); VisionStar Information Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. (视觉星信息技术(上海)有限公司)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: ACM MM 2025 Dataset Track
Abstract:Multi-view egocentric dynamic scene reconstruction holds significant research value for applications in holographic documentation of social interactions. However, existing reconstruction datasets focus on static multi-view or single-egocentric view setups, lacking multi-view egocentric datasets for dynamic scene reconstruction. Therefore, we present MultiEgo, the first multi-view egocentric dataset for 4D dynamic scene reconstruction. The dataset comprises five canonical social interaction scenes: meetings, performances, and a presentation. Each scene provides five authentic egocentric videos captured by participants wearing AR glasses. We design a hardware-based data acquisition system and processing pipeline, achieving sub-millisecond temporal synchronization across views, coupled with accurate pose annotations. Experiment validation demonstrates the practical utility and effectiveness of our dataset for free-viewpoint video (FVV) applications, establishing MultiEgo as a foundational resource for advancing multi-view egocentric dynamic scene reconstruction research.
zh
[CV-61] Few-Shot VLM-Based G-Code and HMI Verification in CNC Machining
【速读】:该论文旨在解决手动编写G代码(G-code)在数控(CNC)加工教学中缺乏有效验证手段的问题,特别是传统基于大语言模型(Large-Language Models, LLMs)的验证方法无法利用人机界面(Human-Machine Interface, HMI)显示信息来判断机床状态和错误,从而限制了对实际加工过程的全面评估。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Model, VLM)的少样本(few-shot)验证框架,该框架同时分析G代码文本与对应的HMI截图,通过引入基于先验启发式知识的结构化JSON模式引导VLM进行推理,并使用包含正确与错误案例的配对数据作为示例进行少样本提示(prompting),从而显著提升对HMI错误及G代码与HMI不一致性的检测能力,实现更全面的调试与验证。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11296
作者: Yasaman Hashem Pour,Nazanin Mahjourian,Vinh Nguyen
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注:
Abstract:Manual generation of G-code is important for learning the operation of CNC machines. Prior work in G-code verification uses Large-Language Models (LLMs), which primarily examine errors in the written programming. However, CNC machining requires extensive use and knowledge of the Human-Machine Interface (HMI), which displays machine status and errors. LLMs currently lack the capability to leverage knowledge of HMIs due to their inability to access the vision modality. This paper proposes a few-shot VLM-based verification approach that simultaneously evaluates the G-code and the HMI display for errors and safety status. The input dataset includes paired G-code text and associated HMI screenshots from a 15-slant-PRO lathe, including both correct and error-prone cases. To enable few-shot learning, the VLM is provided with a structured JSON schema based on prior heuristic knowledge. After determining the prompts, instances of G-code and HMI that either contain errors or are error free are used as few-shot examples to guide the VLM. The model was then evaluated in comparison to a zero-shot VLM through multiple scenarios of incorrect G-code and HMI errors with respect to per-slot accuracy. The VLM showed that few-shot prompting led to overall enhancement of detecting HMI errors and discrepancies with the G-code for more comprehensive debugging. Therefore, the proposed framework was demonstrated to be suitable for verification of manually generated G-code that is typically developed in CNC training.
zh
[CV-62] Autoregressive Video Autoencoder with Decoupled Temporal and Spatial Context
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有视频自编码器(video autoencoder)在压缩视频时易将空间信息与时间信息纠缠的问题,从而限制了对时间一致性的捕捉能力并导致性能不佳。其解决方案的关键在于提出自回归视频自编码器(Autoregressive Video Autoencoder, ARVAE),通过引入一种时空解耦表示机制:利用下采样的光流场(downsampled flow field)保障时间连贯性,同时结合空间相对补偿(spatial relative compensation)处理新出现的内容,使模型能够在自回归框架中逐帧条件压缩与重建,实现无信息损失的高效压缩,并支持任意长度视频的灵活处理。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11293
作者: Cuifeng Shen,Lumin Xu,Xingguo Zhu,Gengdai Liu
机构: Zoom Communications(Zoom公司)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Video autoencoders compress videos into compact latent representations for efficient reconstruction, playing a vital role in enhancing the quality and efficiency of video generation. However, existing video autoencoders often entangle spatial and temporal information, limiting their ability to capture temporal consistency and leading to suboptimal performance. To address this, we propose Autoregressive Video Autoencoder (ARVAE), which compresses and reconstructs each frame conditioned on its predecessor in an autoregressive manner, allowing flexible processing of videos with arbitrary lengths. ARVAE introduces a temporal-spatial decoupled representation that combines downsampled flow field for temporal coherence with spatial relative compensation for newly emerged content, achieving high compression efficiency without information loss. Specifically, the encoder compresses the current and previous frames into the temporal motion and spatial supplement, while the decoder reconstructs the original frame from the latent representations given the preceding frame. A multi-stage training strategy is employed to progressively optimize the model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ARVAE achieves superior reconstruction quality with extremely lightweight models and small-scale training data. Moreover, evaluations on video generation tasks highlight its strong potential for downstream applications.
zh
[CV-63] RcAE: Recursive Reconstruction Framework for Unsupervised Industrial Anomaly Detection AAAI-26
【速读】:该论文旨在解决无监督工业异常检测中因缺乏标注数据而导致的缺陷识别不准确问题,特别是传统基于自编码器(Autoencoder)的方法在处理不同严重程度和尺度的异常时,常出现异常抑制不充分及细节信息丢失的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种递归自编码器(Recursive Autoencoder, RcAE),通过迭代式重建逐步抑制异常并精炼正常结构,同时引入交叉递归检测(Cross Recursion Detection, CRD)模块以追踪多轮递归中的不一致性,从而增强对细微与大尺度异常的检测能力;此外,还设计了细节保持网络(Detail Preservation Network, DPN)以恢复重建过程中损失的高频纹理信息。该方法在性能上显著优于现有非扩散模型,并达到与最新扩散模型相当的效果,但参数量仅为后者的10%,且推理速度更快,展现出良好的实用性和效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11284
作者: Rongcheng Wu,Hao Zhu,Shiying Zhang,Mingzhe Wang,Zhidong Li,Hui Li,Jianlong Zhou,Jiangtao Cui,Fang Chen,Pingyang Sun,Qiyu Liao,Ye Lin
机构: Xi’an University of Electronic Science and Technology (西安电子科技大学); Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院自动化研究所); Tsinghua University (清华大学); Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); Zhejiang University (浙江大学); National University of Singapore (新加坡国立大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 19 pages, 7 figures, to be published in AAAI-26
Abstract:Unsupervised industrial anomaly detection requires accurately identifying defects without labeled data. Traditional autoencoder-based methods often struggle with incomplete anomaly suppression and loss of fine details, as their single-pass decoding fails to effectively handle anomalies with varying severity and scale. We propose a recursive architecture for autoencoder (RcAE), which performs reconstruction iteratively to progressively suppress anomalies while refining normal structures. Unlike traditional single-pass models, this recursive design naturally produces a sequence of reconstructions, progressively exposing suppressed abnormal patterns. To leverage this reconstruction dynamics, we introduce a Cross Recursion Detection (CRD) module that tracks inconsistencies across recursion steps, enhancing detection of both subtle and large-scale anomalies. Additionally, we incorporate a Detail Preservation Network (DPN) to recover high-frequency textures typically lost during reconstruction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing non-diffusion methods, and achieves performance on par with recent diffusion models with only 10% of their parameters and offering substantially faster inference. These results highlight the practicality and efficiency of our approach for real-world applications.
zh
[CV-64] FilmWeaver: Weaving Consistent Multi-Shot Videos with Cache-Guided Autoregressive Diffusion AAAI-2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前视频生成模型在多镜头(multi-shot)视频合成中面临的两大核心挑战:一是难以维持角色与背景在不同镜头间的连贯性(consistency),二是缺乏灵活生成任意长度和镜头数量视频的能力。针对这些问题,作者提出了一种名为FilmWeaver的新框架,其解决方案的关键在于将一致性问题解耦为跨镜头一致性(inter-shot consistency)与单镜头内连贯性(intra-shot coherence)两个层次,并通过双层缓存机制实现: shot memory 缓存前序镜头的关键帧以保持角色和场景身份,temporal memory 则记录当前镜头的历史帧以确保运动的平滑连续性。这种设计不仅提升了多镜头视频的生成质量,还支持多轮用户交互、多概念注入和视频扩展等下游任务,显著增强了生成视频的可控性和叙事能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11274
作者: Xiangyang Luo,Qingyu Li,Xiaokun Liu,Wenyu Qin,Miao Yang,Meng Wang,Pengfei Wan,Di Zhang,Kun Gai,Shao-Lun Huang
机构: Kuaishou Technology (快手科技)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: AAAI-2026
Abstract:Current video generation models perform well at single-shot synthesis but struggle with multi-shot videos, facing critical challenges in maintaining character and background consistency across shots and flexibly generating videos of arbitrary length and shot count. To address these limitations, we introduce \textbfFilmWeaver, a novel framework designed to generate consistent, multi-shot videos of arbitrary length. First, it employs an autoregressive diffusion paradigm to achieve arbitrary-length video generation. To address the challenge of consistency, our key insight is to decouple the problem into inter-shot consistency and intra-shot coherence. We achieve this through a dual-level cache mechanism: a shot memory caches keyframes from preceding shots to maintain character and scene identity, while a temporal memory retains a history of frames from the current shot to ensure smooth, continuous motion. The proposed framework allows for flexible, multi-round user interaction to create multi-shot videos. Furthermore, due to this decoupled design, our method demonstrates high versatility by supporting downstream tasks such as multi-concept injection and video extension. To facilitate the training of our consistency-aware method, we also developed a comprehensive pipeline to construct a high-quality multi-shot video dataset. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our method surpasses existing approaches on metrics for both consistency and aesthetic quality, opening up new possibilities for creating more consistent, controllable, and narrative-driven video content. Project Page: this https URL
zh
[CV-65] Evaluating the Efficacy of Sentinel-2 versus Aerial Imagery in Serrated Tussock Classification
【速读】:该论文旨在解决入侵物种 serrated tussock(Nassella trichotoma)在大尺度景观范围内难以高效监测的问题。传统地面调查和航空影像虽精度较高,但成本高且难以扩展;而卫星遥感虽具成本效益和可扩展性,却常因空间分辨率较低导致分类性能受限。研究的关键解决方案在于利用多时相 Sentinel-2 影像的高光谱分辨率与季节物候信息,通过融合多种特征(如光谱波段、纹理特征、植被指数及季节数据)构建随机森林分类模型,从而在较低空间分辨率下实现对入侵草种的有效识别。结果显示,最优模型(M76*)在相同测试集上达到 68% 的总体准确率(OA)和 0.55 的 Kappa 系数,略优于航空影像模型(OA=67%,Kappa=0.52),证明了多季节特征增强的卫星遥感方法在规模化入侵物种监测中的可行性与优越性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11267
作者: Rezwana Sultana,Manzur Murshed,Kathryn Sheffield,Singarayer Florentine,Tsz-Kwan Lee,Shyh Wei Teng
机构: 1. University of Alberta (阿尔伯塔大学); 2. University of California, Berkeley (加州大学伯克利分校); 3. National University of Singapore (新加坡国立大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted in Earthsense 2025 (IEEE INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON NEXT-GEN TECHNOLOGIES OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND GEOSCIENCE REMOTE SENSING)
Abstract:Invasive species pose major global threats to ecosystems and agriculture. Serrated tussock (\textitNassella trichotoma) is a highly competitive invasive grass species that disrupts native grasslands, reduces pasture productivity, and increases land management costs. In Victoria, Australia, it presents a major challenge due to its aggressive spread and ecological impact. While current ground surveys and subsequent management practices are effective at small scales, they are not feasible for landscape-scale monitoring. Although aerial imagery offers high spatial resolution suitable for detailed classification, its high cost limits scalability. Satellite-based remote sensing provides a more cost-effective and scalable alternative, though often with lower spatial resolution. This study evaluates whether multi-temporal Sentinel-2 imagery, despite its lower spatial resolution, can provide a comparable and cost-effective alternative for landscape-scale monitoring of serrated tussock by leveraging its higher spectral resolution and seasonal phenological information. A total of eleven models have been developed using various combinations of spectral bands, texture features, vegetation indices, and seasonal data. Using a random forest classifier, the best-performing Sentinel-2 model (M76*) has achieved an Overall Accuracy (OA) of 68% and an Overall Kappa (OK) of 0.55, slightly outperforming the best-performing aerial imaging model’s OA of 67% and OK of 0.52 on the same dataset. These findings highlight the potential of multi-seasonal feature-enhanced satellite-based models for scalable invasive species classification.
zh
[CV-66] Do We Need Reformer for Vision? An Experimental Comparison with Vision Transformers
【速读】:该论文旨在解决Vision Transformer (ViT) 在高分辨率图像输入下计算效率低的问题,其核心挑战在于标准ViT中全局自注意力机制的时间复杂度为 O(n2)(n 为序列长度),导致在资源受限场景或高分辨率图像处理中难以实用。解决方案的关键在于引入Reformer架构,通过结合基于patch的tokenization与局部敏感哈希(Locality-Sensitive Hashing, LSH)注意力机制,将自注意力的理论时间复杂度从 O(n2) 降低至 O(nlogn),从而在保持模型性能的同时提升计算效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11260
作者: Ali El Bellaj,Mohammed-Amine Cheddadi,Rhassan Berber
机构: Mississippi State University (密西西比州立大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Transformers have recently demonstrated strong performance in computer vision, with Vision Transformers (ViTs) leveraging self-attention to capture both low-level and high-level image features. However, standard ViTs remain computationally expensive, since global self-attention scales quadratically with the number of tokens, which limits their practicality for high-resolution inputs and resource-constrained settings. In this work, we investigate the Reformer architecture as an alternative vision backbone. By combining patch-based tokenization with locality-sensitive hashing (LSH) attention, our model approximates global self-attention while reducing its theoretical time complexity from \mathcalO(n^2) to \mathcalO(n \log n) in the sequence length n . We evaluate the proposed Reformer-based vision model on CIFAR-10 to assess its behavior on small-scale datasets, on ImageNet-100 to study its accuracy–efficiency trade-off in a more realistic setting, and on a high-resolution medical imaging dataset to evaluate the model under longer token sequences. While the Reformer achieves higher accuracy on CIFAR-10 compared to our ViT-style baseline, the ViT model consistently outperforms the Reformer in our experiments in terms of practical efficiency and end-to-end computation time across the larger and higher-resolution settings. These results suggest that, despite the theoretical advantages of LSH-based attention, meaningful computation gains require sequence lengths substantially longer than those produced by typical high-resolution images. Subjects: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV) Cite as: arXiv:2512.11260 [cs.CV] (or arXiv:2512.11260v1 [cs.CV] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11260 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[CV-67] PersonaLive! Expressive Portrait Image Animation for Live Streaming
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前基于扩散模型的头像动画生成方法在实时性与低延迟方面存在的不足,尤其限制了其在直播场景中的应用。其核心问题在于现有方法过于关注视觉质量和表情真实感,而忽视了推理速度和流式生成的稳定性。解决方案的关键在于提出一种多阶段训练策略的框架 PersonaLive:首先利用隐式面部表征(implicit facial representations)与3D隐式关键点(3D implicit keypoints)实现图像级运动控制;其次通过少步数外观蒸馏策略(fewer-step appearance distillation)消除去噪过程中的外观冗余,显著提升推理效率;最后引入自回归微块流式生成范式(autoregressive micro-chunk streaming generation paradigm),结合滑动训练策略与历史关键帧机制,实现低延迟且稳定的长时视频生成。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11253
作者: Zhiyuan Li,Chi-Man Pun,Chen Fang,Jue Wang,Xiaodong Cun
机构: University of Macau (澳门大学); Dzine.ai; GVC Lab, Great Bay University (大湾大学GVC实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Current diffusion-based portrait animation models predominantly focus on enhancing visual quality and expression realism, while overlooking generation latency and real-time performance, which restricts their application range in the live streaming scenario. We propose PersonaLive, a novel diffusion-based framework towards streaming real-time portrait animation with multi-stage training recipes. Specifically, we first adopt hybrid implicit signals, namely implicit facial representations and 3D implicit keypoints, to achieve expressive image-level motion control. Then, a fewer-step appearance distillation strategy is proposed to eliminate appearance redundancy in the denoising process, greatly improving inference efficiency. Finally, we introduce an autoregressive micro-chunk streaming generation paradigm equipped with a sliding training strategy and a historical keyframe mechanism to enable low-latency and stable long-term video generation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PersonaLive achieves state-of-the-art performance with up to 7-22x speedup over prior diffusion-based portrait animation models.
zh
[CV-68] ask-Aware Multi-Expert Architecture For Lifelong Deep Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决持续学习(Continual Learning)中面临的灾难性遗忘(Catastrophic Forgetting)问题,即神经网络在顺序学习新任务时难以保留先前任务的知识。其解决方案的关键在于提出Task-Aware Multi-Expert (TAME) 框架:通过维护一个预训练神经网络专家池,并根据任务相似性动态选择最相关的专家;利用共享密集层融合所选专家特征进行预测;同时引入基于存储样本和嵌入的回放机制与注意力机制,优先复用历史任务中最相关的信息,从而在适应新任务的同时有效保留早期知识,实现适应性与保留性的平衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11243
作者: Jianyu Wang,Jacob Nean-Hua Sheikh,Cat P. Le,Hoda Bidkhori
机构: George Mason University (乔治梅森大学); Duke University (杜克大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Lifelong deep learning (LDL) trains neural networks to learn sequentially across tasks while preserving prior knowledge. We propose Task-Aware Multi-Expert (TAME), a continual learning algorithm that leverages task similarity to guide expert selection and knowledge transfer. TAME maintains a pool of pretrained neural networks and activates the most relevant expert for each new task. A shared dense layer integrates features from the chosen expert to generate predictions. To reduce catastrophic forgetting, TAME uses a replay buffer that stores representative samples and embeddings from previous tasks and reuses them during training. An attention mechanism further prioritizes the most relevant stored information for each prediction. Together, these components allow TAME to adapt flexibly while retaining important knowledge across evolving task sequences. Experiments on binary classification tasks derived from CIFAR-100 show that TAME improves accuracy on new tasks while sustaining performance on earlier ones, highlighting its effectiveness in balancing adaptation and retention in lifelong learning settings.
zh
[CV-69] Cross-modal Prompting for Balanced Incomplete Multi-modal Emotion Recognition AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文针对不完整多模态情感识别(Incomplete Multi-modal Emotion Recognition, IMER)中因模态信息缺失导致的性能差距与模态欠优化问题展开研究,旨在提升在部分观测数据下的多模态学习效果。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种新颖的跨模态提示(Cross-modal Prompting, ComP)方法:通过设计一个具有动态梯度调制器的渐进式提示生成模块,生成简洁且一致的模态语义线索;同时利用跨模态知识传播机制,选择性增强模态特征中与提示一致的信息以提高判别力;此外引入协调器动态重加权各模态输出,弥补传统平衡策略的不足,从而协同提升整体识别准确率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11239
作者: Wen-Jue He,Xiaofeng Zhu,Zheng Zhang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted by AAAI 2026
Abstract:Incomplete multi-modal emotion recognition (IMER) aims at understanding human intentions and sentiments by comprehensively exploring the partially observed multi-source data. Although the multi-modal data is expected to provide more abundant information, the performance gap and modality under-optimization problem hinder effective multi-modal learning in practice, and are exacerbated in the confrontation of the missing data. To address this issue, we devise a novel Cross-modal Prompting (ComP) method, which emphasizes coherent information by enhancing modality-specific features and improves the overall recognition accuracy by boosting each modality’s performance. Specifically, a progressive prompt generation module with a dynamic gradient modulator is proposed to produce concise and consistent modality semantic cues. Meanwhile, cross-modal knowledge propagation selectively amplifies the consistent information in modality features with the delivered prompts to enhance the discrimination of the modality-specific output. Additionally, a coordinator is designed to dynamically re-weight the modality outputs as a complement to the balance strategy to improve the model’s efficacy. Extensive experiments on 4 datasets with 7 SOTA methods under different missing rates validate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
zh
[CV-70] WildCap: Facial Appearance Capture in the Wild via Hybrid Inverse Rendering
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在非受控环境(in-the-wild)下,仅通过智能手机视频实现高质量人脸外观捕获的问题。现有方法依赖可控光照条件以获得高保真度的表面反射率(reflectance),但这一限制显著提高了采集成本并降低了实用性。解决方案的关键在于提出一种新颖的混合逆渲染框架 WildCap:首先利用数据驱动的 SwitchLight 方法将复杂光照下的图像转换为更受约束的条件,随后引入基于物理模型的逆渲染;同时,为处理网络预测中不可避免的局部伪影(如阴影烘焙等非物理效应),提出了一种新的 texel grid 照明模型,将这些伪影解释为由局部物理光照照射的纯净反照率(albedo);优化过程中联合采样扩散先验(diffusion prior)用于反射率图,并同步优化照明参数,从而有效解决局部光源与反照率之间的尺度模糊性问题。该方法显著优于同类在相同采集条件下方法,大幅缩小了野生场景与可控场景之间的人脸外观质量差距。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11237
作者: Yuxuan Han,Xin Ming,Tianxiao Li,Zhuofan Shen,Qixuan Zhang,Lan Xu,Feng Xu
机构: Tsinghua University (清华大学); ShanghaiTech University (上海科技大学); Deemos Technology
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Graphics (cs.GR)
备注: Technical report. project page: this https URL code: this https URL
Abstract:Existing methods achieve high-quality facial appearance capture under controllable lighting, which increases capture cost and limits usability. We propose WildCap, a novel method for high-quality facial appearance capture from a smartphone video recorded in the wild. To disentangle high-quality reflectance from complex lighting effects in in-the-wild captures, we propose a novel hybrid inverse rendering framework. Specifically, we first apply a data-driven method, i.e., SwitchLight, to convert the captured images into more constrained conditions and then adopt model-based inverse rendering. However, unavoidable local artifacts in network predictions, such as shadow-baking, are non-physical and thus hinder accurate inverse rendering of lighting and material. To address this, we propose a novel texel grid lighting model to explain non-physical effects as clean albedo illuminated by local physical lighting. During optimization, we jointly sample a diffusion prior for reflectance maps and optimize the lighting, effectively resolving scale ambiguity between local lights and albedo. Our method achieves significantly better results than prior arts in the same capture setup, closing the quality gap between in-the-wild and controllable recordings by a large margin. Our code will be released \hrefthis https URL\textcolormagentahere.
zh
[CV-71] RoomPilot: Controllable Synthesis of Interactive Indoor Environments via Multimodal Semantic Parsing
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前室内场景生成方法在多模态输入处理能力有限以及可控性不足的问题,尤其针对现有方法依赖随机过程导致难以精确控制场景生成结果的缺陷。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个统一框架 RoomPilot,通过将文本描述或 CAD 地图等多样化的输入解析为一种面向室内领域的特定语言(Indoor Domain-Specific Language, IDSL),实现跨模态的语义对齐与结构化表达。IDSL 作为共享语义表示,不仅支持从单一模态生成高质量、结构一致的室内场景,还保留了交互语义信息,从而显著提升场景的物理一致性与视觉保真度,并支持细粒度控制。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11234
作者: Wentang Chen,Shougao Zhang,Yiman Zhang,Tianhao Zhou,Ruihui Li
机构: Hunan University (湖南大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 20 pages, 6 figures
Abstract:Generating controllable and interactive indoor scenes is fundamental to applications in game development, architectural visualization, and embodied AI training. Yet existing approaches either handle a narrow range of input modalities or rely on stochastic processes that hinder controllability. To overcome these limitations, we introduce RoomPilot, a unified framework that parses diverse multi-modal inputs–textual descriptions or CAD floor plans–into an Indoor Domain-Specific Language (IDSL) for indoor structured scene generation. The key insight is that a well-designed IDSL can act as a shared semantic representation, enabling coherent, high-quality scene synthesis from any single modality while maintaining interaction semantics. In contrast to conventional procedural methods that produce visually plausible but functionally inert layouts, RoomPilot leverages a curated dataset of interaction-annotated assets to synthesize environments exhibiting realistic object behaviors. Extensive experiments further validate its strong multi-modal understanding, fine-grained controllability in scene generation, and superior physical consistency and visual fidelity, marking a significant step toward general-purpose controllable 3D indoor scene generation.
zh
[CV-72] REST: Diffusion-based Real-time End-to-end Streaming Talking Head Generation via ID-Context Caching and Asynchronous Streaming Distillation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决基于扩散模型(Diffusion Models)的说话头生成(Talking Head Generation, THG)中存在的推理速度慢和非自回归(non-autoregressive)架构限制实时应用的问题。其核心解决方案是提出REST框架,关键创新在于:首先通过高时空分辨率变分自编码器(High Spatiotemporal VAE)压缩获得紧凑的视频潜在空间(compact video latent space),以支持高效推理;其次引入ID-Context Cache机制,融合ID-Sink与Context-Cache原理,实现键值缓存以维持长时间流式生成中的身份一致性和时序连贯性;最后设计异步流式蒸馏(Asynchronous Streaming Distillation, ASD)训练策略,利用具有异步噪声调度的非流式教师模型监督流式学生模型训练,从而缓解自回归生成中的误差累积并提升时序一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11229
作者: Haotian Wang,Yuzhe Weng,Xinyi Yu,Jun Du,Haoran Xu,Xiaoyan Wu,Shan He,Bing Yin,Cong Liu,Qingfeng Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Sound (cs.SD)
备注: 10pages, 4 figures
Abstract:Diffusion models have significantly advanced the field of talking head generation. However, the slow inference speeds and non-autoregressive paradigms severely constrain the application of diffusion-based THG models. In this study, we propose REST, the first diffusion-based, real-time, end-to-end streaming audio-driven talking head generation framework. To support real-time end-to-end generation, a compact video latent space is first learned through high spatiotemporal VAE compression. Additionally, to enable autoregressive streaming within the compact video latent space, we introduce an ID-Context Cache mechanism, which integrates ID-Sink and Context-Cache principles to key-value caching for maintaining temporal consistency and identity coherence during long-time streaming generation. Furthermore, an Asynchronous Streaming Distillation (ASD) training strategy is proposed to mitigate error accumulation in autoregressive generation and enhance temporal consistency, which leverages a non-streaming teacher with an asynchronous noise schedule to supervise the training of the streaming student model. REST bridges the gap between autoregressive and diffusion-based approaches, demonstrating substantial value for applications requiring real-time talking head generation. Experimental results demonstrate that REST outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both generation speed and overall performance.
zh
[CV-73] FutureX: Enhance End-to-End Autonomous Driving via Latent Chain-of-Thought World Model
【速读】:该论文旨在解决自动驾驶中端到端规划器在高度动态交通环境中因仅依赖当前场景而产生次优决策的问题,尤其在车辆自身行为会显著改变未来场景的情况下。解决方案的关键在于提出FutureX框架,其核心是引入基于思维链(Chain of Thought, CoT)的推理机制,通过Latent World Model进行未来场景潜在状态的预测与演化建模,并结合Auto-think Switch模块动态判断是否需要进入“思考模式”以执行轨迹精细化修正,从而实现复杂场景下的理性路径规划,同时保持高效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11226
作者: Hongbin Lin,Yiming Yang,Yifan Zhang,Chaoda Zheng,Jie Feng,Sheng Wang,Zhennan Wang,Shijia Chen,Boyang Wang,Yu Zhang,Xianming Liu,Shuguang Cui,Zhen Li
机构: FNii-Shenzhen; SSE, CUHK-Shenzhen; Xpeng Motors; MiroMind AI; Xidian University
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:In autonomous driving, end-to-end planners learn scene representations from raw sensor data and utilize them to generate a motion plan or control actions. However, exclusive reliance on the current scene for motion planning may result in suboptimal responses in highly dynamic traffic environments where ego actions further alter the future scene. To model the evolution of future scenes, we leverage the World Model to represent how the ego vehicle and its environment interact and change over time, which entails complex reasoning. The Chain of Thought (CoT) offers a promising solution by forecasting a sequence of future thoughts that subsequently guide trajectory refinement. In this paper, we propose FutureX, a CoT-driven pipeline that enhances end-to-end planners to perform complex motion planning via future scene latent reasoning and trajectory refinement. Specifically, the Auto-think Switch examines the current scene and decides whether additional reasoning is required to yield a higher-quality motion plan. Once FutureX enters the Thinking mode, the Latent World Model conducts a CoT-guided rollout to predict future scene representation, enabling the Summarizer Module to further refine the motion plan. Otherwise, FutureX operates in an Instant mode to generate motion plans in a forward pass for relatively simple scenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FutureX enhances existing methods by producing more rational motion plans and fewer collisions without compromising efficiency, thereby achieving substantial overall performance gains, e.g., 6.2 PDMS improvement for TransFuser on NAVSIM. Code will be released.
zh
[CV-74] VFMF: World Modeling by Forecasting Vision Foundation Model Features
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有世界模型在部分观测下进行预测时的两大局限性:一是基于像素级视频生成的方法虽然视觉逼真但计算复杂且难以直接用于决策;二是基于视觉基础模型(Vision Foundation Models, VFMs)特征的确定性回归方法虽高效却因平均多个可能未来而忽略不确定性,从而降低预测准确性。解决方案的关键在于引入一种在VFMs特征空间中执行自回归流匹配(autoregressive flow matching)的生成式预测器,其核心创新是将VFM特征编码到一个更适合扩散模型的紧凑潜在空间中,该潜在空间相比以往基于主成分分析(PCA)的方法能更有效地保留信息,从而实现高保真、多模态输出(如语义分割、深度图、表面法向量甚至RGB图像),并在相同架构与算力条件下显著优于传统回归方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11225
作者: Gabrijel Boduljak,Yushi Lan,Christian Rupprecht,Andrea Vedaldi
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Forecasting from partial observations is central to world modeling. Many recent methods represent the world through images, and reduce forecasting to stochastic video generation. Although such methods excel at realism and visual fidelity, predicting pixels is computationally intensive and not directly useful in many applications, as it requires translating RGB into signals useful for decision making. An alternative approach uses features from vision foundation models (VFMs) as world representations, performing deterministic regression to predict future world states. These features can be directly translated into actionable signals such as semantic segmentation and depth, while remaining computationally efficient. However, deterministic regression averages over multiple plausible futures, undermining forecast accuracy by failing to capture uncertainty. To address this crucial limitation, we introduce a generative forecaster that performs autoregressive flow matching in VFM feature space. Our key insight is that generative modeling in this space requires encoding VFM features into a compact latent space suitable for diffusion. We show that this latent space preserves information more effectively than previously used PCA-based alternatives, both for forecasting and other applications, such as image generation. Our latent predictions can be easily decoded into multiple useful and interpretable output modalities: semantic segmentation, depth, surface normals, and even RGB. With matched architecture and compute, our method produces sharper and more accurate predictions than regression across all modalities. Our results suggest that stochastic conditional generation of VFM features offers a promising and scalable foundation for future world models.
zh
[CV-75] Seeing to Act Prompting to Specify: A Bayesian Factorization of Vision Language Action Policy
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉-语言-动作(Vision-Language-Action, VLA)模型在微调过程中因灾难性遗忘(catastrophic forgetting)导致的分布外泛化能力下降问题,尤其关注视觉-语言模型(VLM)骨干网络的性能退化。其关键解决方案是提出BayesVLA,一种基于贝叶斯分解的策略框架,将策略显式分解为两个部分:一是视觉-动作先验(visual-action prior),支持“看到即行动”的推理机制;二是语言条件似然(language-conditioned likelihood),实现“提示驱动指定”(prompt-to-specify)的能力。这一分解结构天然保留了模型的泛化能力并强化指令遵循能力。此外,通过引入预接触和后接触阶段以更好地利用预训练基础模型,并结合信息论分析验证了该方法在缓解视觉捷径学习(shortcut learning)方面的有效性。实验表明,BayesVLA在未见过的指令、物体和环境中均展现出优于现有方法的泛化性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11218
作者: Kechun Xu,Zhenjie Zhu,Anzhe Chen,Shuqi Zhao,Qing Huang,Yifei Yang,Haojian Lu,Rong Xiong,Masayoshi Tomizuka,Yue Wang
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); UC Berkeley (加州大学伯克利分校)
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:The pursuit of out-of-distribution generalization in Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models is often hindered by catastrophic forgetting of the Vision-Language Model (VLM) backbone during fine-tuning. While co-training with external reasoning data helps, it requires experienced tuning and data-related overhead. Beyond such external dependencies, we identify an intrinsic cause within VLA datasets: modality imbalance, where language diversity is much lower than visual and action diversity. This imbalance biases the model toward visual shortcuts and language forgetting. To address this, we introduce BayesVLA, a Bayesian factorization that decomposes the policy into a visual-action prior, supporting seeing-to-act, and a language-conditioned likelihood, enabling prompt-to-specify. This inherently preserves generalization and promotes instruction following. We further incorporate pre- and post-contact phases to better leverage pre-trained foundation models. Information-theoretic analysis formally validates our effectiveness in mitigating shortcut learning. Extensive experiments show superior generalization to unseen instructions, objects, and environments compared to existing methods. Project page is available at: this https URL.
zh
[CV-76] SmokeBench: Evaluating Multimodal Large Language Models for Wildfire Smoke Detection WACV2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决早期野火烟雾在图像中难以检测的问题,因其透明、无定形且常与云层视觉混淆,导致现有多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在识别和定位方面表现不佳。解决方案的关键在于构建一个名为SmokeBench的基准测试集,包含烟雾分类、基于图块的烟雾定位、基于网格的烟雾定位及烟雾检测四项任务,系统评估多个主流MLLMs在不同场景下的性能表现。实验表明,尽管部分模型能识别大面积烟雾,但所有模型在早期阶段的精确定位能力均显著不足,且烟雾体积是影响模型性能的关键因素,而对比度影响较小,这揭示了当前MLLMs在安全关键型野火监测中的局限性,并强调需发展更有效的早期烟雾定位方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11215
作者: Tianye Qi,Weihao Li,Nick Barnes
机构: Australian National University (澳大利亚国立大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted to WACV 2026
Abstract:Wildfire smoke is transparent, amorphous, and often visually confounded with clouds, making early-stage detection particularly challenging. In this work, we introduce a benchmark, called SmokeBench, to evaluate the ability of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to recognize and localize wildfire smoke in images. The benchmark consists of four tasks: (1) smoke classification, (2) tile-based smoke localization, (3) grid-based smoke localization, and (4) smoke detection. We evaluate several MLLMs, including Idefics2, Qwen2.5-VL, InternVL3, Unified-IO 2, Grounding DINO, GPT-4o, and Gemini-2.5 Pro. Our results show that while some models can classify the presence of smoke when it covers a large area, all models struggle with accurate localization, especially in the early stages. Further analysis reveals that smoke volume is strongly correlated with model performance, whereas contrast plays a comparatively minor role. These findings highlight critical limitations of current MLLMs for safety-critical wildfire monitoring and underscore the need for methods that improve early-stage smoke localization.
zh
[CV-77] AutoRefiner: Improving Autoregressive Video Diffusion Models via Reflective Refinement Over the Stochastic Sampling Path
【速读】:该论文旨在解决自回归视频扩散模型(Autoregressive Video Diffusion Models, AR-VDMs)在样本保真度(sample fidelity)方面的不足,尤其是在推理阶段提升生成质量的问题。现有方法如基于优化或搜索的对齐策略在AR-VDM中计算成本过高,难以实用;而文本到图像(Text-to-Image, T2I)领域提出的前馈噪声精修器(feedforward noise refiner)虽能高效提升保真度,但直接扩展至AR-VDM时效果失败。为此,作者提出AutoRefiner——一种专为AR-VDM设计的噪声精修器,其关键创新在于两个方面:路径感知噪声精修(pathwise noise refinement)与反射式键值缓存(reflective KV-cache),通过沿随机去噪路径精细调整噪声,并有效利用历史信息减少冗余计算,从而实现无需更新模型参数即可显著提升样本保真度的高效插件式解决方案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11203
作者: Zhengyang Yu,Akio Hayakawa,Masato Ishii,Qingtao Yu,Takashi Shibuya,Jing Zhang,Yuki Mitsufuji
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Autoregressive video diffusion models (AR-VDMs) show strong promise as scalable alternatives to bidirectional VDMs, enabling real-time and interactive applications. Yet there remains room for improvement in their sample fidelity. A promising solution is inference-time alignment, which optimizes the noise space to improve sample fidelity without updating model parameters. Yet, optimization- or search-based methods are computationally impractical for AR-VDMs. Recent text-to-image (T2I) works address this via feedforward noise refiners that modulate sampled noises in a single forward pass. Can such noise refiners be extended to AR-VDMs? We identify the failure of naively extending T2I noise refiners to AR-VDMs and propose AutoRefiner-a noise refiner tailored for AR-VDMs, with two key designs: pathwise noise refinement and a reflective KV-cache. Experiments demonstrate that AutoRefiner serves as an efficient plug-in for AR-VDMs, effectively enhancing sample fidelity by refining noise along stochastic denoising paths.
zh
[CV-78] CADKnitter: Compositional CAD Generation from Text and Geometry Guidance
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多部件CAD模型生成中的关键挑战,即如何在满足几何约束(如装配关系、尺寸匹配)和语义约束(如设计意图、功能描述)的前提下,自动合成可编辑的、可组装的CAD零件。传统单件CAD生成方法难以应对现实场景中复杂的多部件装配需求,而本文提出的CADKnitter框架通过引入基于几何引导的扩散采样策略(geometry-guided diffusion sampling strategy),实现了对给定CAD模型的互补部件生成,确保新生成部件既符合已有模型的几何结构,又能响应文本提示中的语义信息。其核心创新在于将几何约束与语义约束联合建模,并构建了包含31万样本的KnitCAD数据集以支持训练与评估,显著优于现有最先进基线方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11199
作者: Tri Le,Khang Nguyen,Baoru Huang,Tung D. Ta,Anh Nguyen
机构: FPT Software AI Center (越南FPT软件人工智能中心); Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence (阿联酋穆罕默德·本·扎耶德人工智能大学); University of Liverpool (利物浦大学); The University of Tokyo (东京大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Crafting computer-aided design (CAD) models has long been a painstaking and time-intensive task, demanding both precision and expertise from designers. With the emergence of 3D generation, this task has undergone a transformative impact, shifting not only from visual fidelity to functional utility but also enabling editable CAD designs. Prior works have achieved early success in single-part CAD generation, which is not well-suited for real-world applications, as multiple parts need to be assembled under semantic and geometric constraints. In this paper, we propose CADKnitter, a compositional CAD generation framework with a geometry-guided diffusion sampling strategy. CADKnitter is able to generate a complementary CAD part that follows both the geometric constraints of the given CAD model and the semantic constraints of the desired design text prompt. We also curate a dataset, so-called KnitCAD, containing over 310,000 samples of CAD models, along with textual prompts and assembly metadata that provide semantic and geometric constraints. Intensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms other state-of-the-art baselines by a clear margin.
zh
[CV-79] Beyond Memorization: Gradient Projection Enables Selective Learning in Diffusion Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大规模文本到图像扩散模型中的记忆化(memorization)问题,该问题可能导致敏感特征被非法提取或未经授权复制,从而引发知识产权(IP)和隐私安全风险。传统去记忆化方法如正则化和数据过滤仅能缓解对特定训练样本的过拟合,却无法系统性地阻止禁止概念层级特征的内部化。为此,作者提出一种梯度投影框架(Gradient Projection Framework),其核心在于:在反向传播过程中,通过将梯度更新投影到受保护特征嵌入空间的正交补空间中,精确移除与敏感属性相关的训练信号,从而实现概念级的选择性遗忘(selective unlearning)。此方法不依赖于删除含敏感特征的数据,而是保持生成质量与语义保真度的同时,严格抑制目标特征的记忆,为生成式AI的IP安全和隐私保护提供了新范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11194
作者: Divya Kothandaraman,Jaclyn Pytlarz
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Memorization in large-scale text-to-image diffusion models poses significant security and intellectual property risks, enabling adversarial attribute extraction and the unauthorized reproduction of sensitive or proprietary features. While conventional dememorization techniques, such as regularization and data filtering, limit overfitting to specific training examples, they fail to systematically prevent the internalization of prohibited concept-level features. Simply discarding all images containing a sensitive feature wastes invaluable training data, necessitating a method for selective unlearning at the concept level. To address this, we introduce a Gradient Projection Framework designed to enforce a stringent requirement of concept-level feature exclusion. Our defense operates during backpropagation by systematically identifying and excising training signals aligned with embeddings of prohibited attributes. Specifically, we project each gradient update onto the orthogonal complement of the sensitive feature’s embedding space, thereby zeroing out its influence on the model’s weights. Our method integrates seamlessly into standard diffusion model training pipelines and complements existing defenses. We analyze our method against an adversary aiming for feature extraction. In extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our framework drastically reduces memorization while rigorously preserving generation quality and semantic fidelity. By reframing memorization control as selective learning, our approach establishes a new paradigm for IP-safe and privacy-preserving generative AI. Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV) Cite as: arXiv:2512.11194 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2512.11194v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11194 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[CV-80] Multi-task Learning with Extended Temporal Shift Module for Temporal Action Localization ICCV25
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多视角、多模态视频场景下的时序动作定位(Temporal Action Localization, TAL)问题,即在包含全景、第三人称和第一人称视角的复杂视频数据中,精确定位各类动作的发生时间区间并识别其类别。解决方案的关键在于:首先基于时序移位模块(Temporal Shift Module, TSM)扩展出适用于TAL的任务结构,引入背景类并对固定长度非重叠区间进行分类;其次设计一个多任务学习框架,联合优化场景分类与TAL任务,利用动作与环境之间的上下文关联增强模型判别能力;最后通过加权集成策略融合多个模型预测结果,显著提升整体性能的鲁棒性与一致性。该方法在BinEgo-360 Challenge ICCV 2025竞赛中取得最优成绩,验证了上述三方面技术组合的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11189
作者: Anh-Kiet Duong,Petra Gomez-Krämer
机构: L3i Laboratory, La Rochelle University (拉罗谢尔大学 L3i 实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: BinEgo360@ICCV25
Abstract:We present our solution to the BinEgo-360 Challenge at ICCV 2025, which focuses on temporal action localization (TAL) in multi-perspective and multi-modal video settings. The challenge provides a dataset containing panoramic, third-person, and egocentric recordings, annotated with fine-grained action classes. Our approach is built on the Temporal Shift Module (TSM), which we extend to handle TAL by introducing a background class and classifying fixed-length non-overlapping intervals. We employ a multi-task learning framework that jointly optimizes for scene classification and TAL, leveraging contextual cues between actions and environments. Finally, we integrate multiple models through a weighted ensemble strategy, which improves robustness and consistency of predictions. Our method is ranked first in both the initial and extended rounds of the competition, demonstrating the effectiveness of combining multi-task learning, an efficient backbone, and ensemble learning for TAL.
zh
[CV-81] Lightweight 3D Gaussian Splatting Compression via Video Codec
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前基于视频的3D高斯溅射(3D Gaussian Splatting, GS)压缩方法中,依赖并行线性分配排序(Parallel Linear Assignment Sorting, PLAS)生成二维映射时计算复杂度高、耗时长的问题,从而限制了GS在轻量级设备上的应用。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于视频编码器的轻量化GS压缩方法(Lightweight 3D Gaussian Splatting Compression based on Video codec, LGSCV),其核心创新包括:首先采用两阶段Morton扫描(3D后接2D)生成适合标准视频编码单元(Coding Unit, CU)的块状二维映射;其次引入球谐函数(Spherical Harmonics, SH)的主成分分析(PCA)降维与一种灵活快速的MiniPLAS排序策略,显著提升率失真(Rate-Distortion, RD)性能,尤其在中低码率下表现突出;同时,MiniPLAS还能指导编码单元尺寸配置,大幅降低编码时间。实验表明,LGSCV相较现有最优方法实现超过20%的RD增益,且二维映射生成时间降至约1秒,编码时间减少50%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11186
作者: Qi Yang,Geert Van Der Auwera,Zhu Li
机构: University of Missouri - Kansas City (密苏里大学堪萨斯城分校); Qualcomm (高通)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted by DCC2026 Oral
Abstract:Current video-based GS compression methods rely on using Parallel Linear Assignment Sorting (PLAS) to convert 3D GS into smooth 2D maps, which are computationally expensive and time-consuming, limiting the application of GS on lightweight devices. In this paper, we propose a Lightweight 3D Gaussian Splatting (GS) Compression method based on Video codec (LGSCV). First, a two-stage Morton scan is proposed to generate blockwise 2D maps that are friendly for canonical video codecs in which the coding units (CU) are square blocks. A 3D Morton scan is used to permute GS primitives, followed by a 2D Morton scan to map the ordered GS primitives to 2D maps in a blockwise style. However, although the blockwise 2D maps report close performance to the PLAS map in high-bitrate regions, they show a quality collapse at medium-to-low bitrates. Therefore, a principal component analysis (PCA) is used to reduce the dimensionality of spherical harmonics (SH), and a MiniPLAS, which is flexible and fast, is designed to permute the primitives within certain block sizes. Incorporating SH PCA and MiniPLAS leads to a significant gain in rate-distortion (RD) performance, especially at medium and low bitrates. MiniPLAS can also guide the setting of the codec CU size configuration and significantly reduce encoding time. Experimental results on the MPEG dataset demonstrate that the proposed LGSCV achieves over 20% RD gain compared with state-of-the-art methods, while reducing 2D map generation time to approximately 1 second and cutting encoding time by 50%. The code is available at this https URL .
zh
[CV-82] Image Tiling for High-Resolution Reasoning : Balancing Local Detail with Global Context AAAI2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决高分辨率图像理解中复杂多模态模型缺乏可复现性的问题,特别是由于实现细节不透明和训练基础设施难以获取所导致的科研壁垒。其解决方案的关键在于对Monkey Vision-Language Model(VLM)进行详尽的复现与批判性分析,通过使用公开权重检查点(open checkpoints)重新实现训练流程,验证了原论文提出的图像分块(image tiling)策略在恢复局部视觉细节方面的有效性,并进一步探讨了全局上下文信息引入对不同任务性能的影响,从而为未来高分辨率多模态建模提供实践指导。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11167
作者: Anatole Jacquin de Margerie,Alexis Roger,Irina Rish
机构: 1. Université de Montréal (蒙特利尔大学); 2. Mila - Quebec AI Institute (魁北克人工智能研究所); 3. HEC Montréal (蒙特利尔高等商学院); 4. McGill University (麦吉尔大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted in AAAI 2025 Workshop on Reproducible AI
Abstract:Reproducibility remains a cornerstone of scientific progress, yet complex multimodal models often lack transparent implementation details and accessible training infrastructure. In this work, we present a detailed reproduction and critical analysis of the Monkey Vision-Language Model (VLM) (Li et al. 2023b) published in CVPR24, a recent approach to high-resolution image understanding via image tiling. The original paper proposed splitting large images into tiles to recover fine-grained visual details while maintaining computational efficiency. Our study replicates this strategy using open checkpoints and reimplements the training pipeline. We confirm the key finding of the original Monkey VLM work, namely that tiling effectively recovers local details. We then extend this work further, by investigating the effect of the inclusion of the global context, which provide practical insights for future high-resolution multimodal modeling. However, we also report deviations in the results, with the magnitude of these effects depending heavily on task type and tile granularity.
zh
[CV-83] Autoencoder-based Semi-Supervised Dimensionality Reduction and Clustering for Scientific Ensembles
【速读】:该论文旨在解决高维复杂科学集合数据集(scientific ensemble datasets)在分析与可视化过程中面临的挑战,特别是传统降维技术与自编码器(autoencoder)在处理此类数据时特征提取能力不足的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种增强型自编码器框架,通过引入基于软轮廓系数(soft silhouette score)的聚类损失与对比损失(contrastive loss)共同优化模型,使潜在空间中的相似数据点聚集、不同簇间分离,从而提升可视化效果和可解释性;同时利用EfficientNetV2为未标记数据生成伪标签(pseudo-labels),并结合UMAP进行二维投影以进一步评估性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11145
作者: Lennard Manuel,Hamid Gadirov,Steffen Frey
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Research Internship Project
Abstract:Analyzing and visualizing scientific ensemble datasets with high dimensionality and complexity poses significant challenges. Dimensionality reduction techniques and autoencoders are powerful tools for extracting features, but they often struggle with such high-dimensional data. This paper presents an enhanced autoencoder framework that incorporates a clustering loss, based on the soft silhouette score, alongside a contrastive loss to improve the visualization and interpretability of ensemble datasets. First, EfficientNetV2 is used to generate pseudo-labels for the unlabeled portions of the scientific ensemble datasets. By jointly optimizing the reconstruction, clustering, and contrastive objectives, our method encourages similar data points to group together while separating distinct clusters in the latent space. UMAP is subsequently applied to this latent representation to produce 2D projections, which are evaluated using the silhouette score. Multiple types of autoencoders are evaluated and compared based on their ability to extract meaningful features. Experiments on two scientific ensemble datasets - channel structures in soil derived from Markov chain Monte Carlo, and droplet-on-film impact dynamics - show that models incorporating clustering or contrastive loss marginally outperform the baseline approaches.
zh
[CV-84] Learning complete and explainable visual representations from itemized text supervision
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在非对象中心的视觉领域(如医学影像和遥感图像)中,如何利用项化文本标注(itemized text annotations)来学习完整且可解释的视觉表征问题。这类标注包含多个语义独立的文本项,描述单张图像中的不同发现,与传统多标题监督(multi-caption supervision)中冗余或高度重叠的标题有本质区别。解决方案的关键在于提出ItemizedCLIP框架,其核心创新包括:1)引入交叉注意力模块生成基于文本项条件的视觉嵌入;2)设计一组定制化目标函数,同时强制实现项独立性(不同文本项对应不同区域)和表征完整性(覆盖所有文本项)。该方法显著提升了零样本性能和细粒度可解释性,使模型输出具备语义锚定、项可区分、完整覆盖和视觉可解释等特性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11141
作者: Yiwei Lyu,Chenhui Zhao,Soumyanil Banerjee,Shixuan Liu,Akshay Rao,Akhil Kondepudi,Honglak Lee,Todd C. Hollon
机构: University of Michigan (密歇根大学); University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Training vision models with language supervision enables general and transferable representations. However, many visual domains, especially non-object-centric domains such as medical imaging and remote sensing, contain itemized text annotations: multiple text items describing distinct and semantically independent findings within a single image. Such supervision differs from standard multi-caption supervision, where captions are redundant or highly overlapping. Here, we introduce ItemizedCLIP, a framework for learning complete and explainable visual representations from itemized text supervision. ItemizedCLIP employs a cross-attention module to produce text item-conditioned visual embeddings and a set of tailored objectives that jointly enforce item independence (distinct regions for distinct items) and representation completeness (coverage of all items). Across four domains with naturally itemized text supervision (brain MRI, head CT, chest CT, remote sensing) and one additional synthetically itemized dataset, ItemizedCLIP achieves substantial improvements in zero-shot performance and fine-grained interpretability over baselines. The resulting ItemizedCLIP representations are semantically grounded, item-differentiable, complete, and visually interpretable. Our code is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-85] Fast-FoundationStereo: Real-Time Zero-Shot Stereo Matching
【速读】:该论文旨在解决立体视觉基础模型(stereo foundation models)在实时应用中计算成本过高、而高效架构又难以保持零样本泛化能力的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出Fast-FoundationStereo系列架构,通过三项核心技术实现高效与高精度的统一:(1) 知识蒸馏将混合骨干网络压缩为单一高效学生模型;(2) 块级神经架构搜索在延迟预算下自动发现最优代价过滤设计,显著降低搜索复杂度;(3) 结构化剪枝消除迭代优化模块中的冗余。此外,引入自动伪标签流水线构建140万张野外立体图像对,增强合成数据训练效果,从而在速度提升10倍的同时逼近FoundationStereo的零样本性能,确立实时方法的新SOTA。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11130
作者: Bowen Wen,Shaurya Dewan,Stan Birchfield
机构: NVIDIA(英伟达)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注:
Abstract:Stereo foundation models achieve strong zero-shot generalization but remain computationally prohibitive for real-time applications. Efficient stereo architectures, on the other hand, sacrifice robustness for speed and require costly per-domain fine-tuning. To bridge this gap, we present Fast-FoundationStereo, a family of architectures that achieve, for the first time, strong zero-shot generalization at real-time frame rate. We employ a divide-and-conquer acceleration strategy with three components: (1) knowledge distillation to compress the hybrid backbone into a single efficient student; (2) blockwise neural architecture search for automatically discovering optimal cost filtering designs under latency budgets, reducing search complexity exponentially; and (3) structured pruning for eliminating redundancy in the iterative refinement module. Furthermore, we introduce an automatic pseudo-labeling pipeline used to curate 1.4M in-the-wild stereo pairs to supplement synthetic training data and facilitate knowledge distillation. The resulting model can run over 10x faster than FoundationStereo while closely matching its zero-shot accuracy, thus establishing a new state-of-the-art among real-time methods. Project page: this https URL
zh
[CV-86] Learning from a Generative Oracle: Domain Adaptation for Restoration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决预训练图像复原模型在面对真实世界、分布外(out-of-distribution)退化时性能下降的问题,其核心挑战在于此类数据缺乏真实标签(ground truth),且传统域适应方法通常需要复杂的结构改动。解决方案的关键在于提出一种三阶段的无配对数据域自适应框架 LEGO(Learning from a Generative Oracle),其核心创新是将无监督挑战转化为伪监督问题:首先利用预训练模型获得初始复原结果;其次借助一个冻结的大规模生成式模型(Generative Oracle)将其优化为高质量伪真值(pseudo-ground-truth);最后通过混合监督策略(结合分布内数据与新生成的伪配对数据)对原始模型进行微调,从而在不改变架构的前提下实现对新分布的有效适应,同时保持原有鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11121
作者: Yuyang Hu,Mojtaba Sahraee-Ardakan,Arpit Bansal,Kangfu Mei,Christian Qi,Peyman Milanfar,Mauricio Delbracio
机构: Google(谷歌); Washington University in St. Louis(圣路易斯华盛顿大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
备注:
Abstract:Pre-trained image restoration models often fail on real-world, out-of-distribution degradations due to significant domain gaps. Adapting to these unseen domains is challenging, as out-of-distribution data lacks ground truth, and traditional adaptation methods often require complex architectural changes. We propose LEGO (Learning from a Generative Oracle), a practical three-stage framework for post-training domain adaptation without paired data. LEGO converts this unsupervised challenge into a tractable pseudo-supervised one. First, we obtain initial restorations from the pre-trained model. Second, we leverage a frozen, large-scale generative oracle to refine these estimates into high-quality pseudo-ground-truths. Third, we fine-tune the original model using a mixed-supervision strategy combining in-distribution data with these new pseudo-pairs. This approach adapts the model to the new distribution without sacrificing its original robustness or requiring architectural modifications. Experiments demonstrate that LEGO effectively bridges the domain gap, significantly improving performance on diverse real-world benchmarks.
zh
[CV-87] Information-driven Fusion of Pathology Foundation Models for Enhanced Disease Characterization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态病理基础模型(Foundation Models, FMs)在医学图像分析中存在特征冗余、互补性不明确以及可解释性不足的问题,尤其关注如何有效融合不同FMs以提升癌症分级与分期的预测性能。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于信息驱动的智能融合策略,通过相关性引导的冗余特征剪枝机制,在tile级和slide级嵌入空间中实现高效整合,从而生成紧凑且任务定制化的表示。该方法在肾癌、前列腺癌和直肠癌三种疾病的数据集上均优于单一模型及简单拼接融合方式,并显著增强了对肿瘤区域的关注度,降低了对良性区域的误判,提升了模型的预测准确性和临床可解释性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11104
作者: Brennan Flannery,Thomas DeSilvio,Jane Nguyen,Satish E. Viswanath
机构: Case Western Reserve University (凯斯西储大学); Cleveland Clinic (克利夫兰诊所); Emory University (埃默里大学); Louis Stokes VA Cleveland Medical Center (路易斯·斯托克斯克利夫兰退伍军人事务医疗中心)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 29 Pages, 10 figures
Abstract:Foundation models (FMs) have demonstrated strong performance across diverse pathology tasks. While there are similarities in the pre-training objectives of FMs, there is still limited understanding of their complementarity, redundancy in embedding spaces, or biological interpretation of features. In this study, we propose an information-driven, intelligent fusion strategy for integrating multiple pathology FMs into a unified representation and systematically evaluate its performance for cancer grading and staging across three distinct diseases. Diagnostic HE whole-slide images from kidney (519 slides), prostate (490 slides), and rectal (200 slides) cancers were dichotomized into low versus high grade or stage. Both tile-level FMs (Conch v1.5, MUSK, Virchow2, H-Optimus1, Prov-Gigapath) and slide-level FMs (TITAN, CHIEF, MADELEINE) were considered to train downstream classifiers. We then evaluated three FM fusion schemes at both tile and slide levels: majority-vote ensembling, naive feature concatenation, and intelligent fusion based on correlation-guided pruning of redundant features. Under patient-stratified cross-validation with hold-out testing, intelligent fusion of tile-level embeddings yielded consistent gains in classification performance across all three cancers compared with the best single FMs and naive fusion. Global similarity metrics revealed substantial alignment of FM embedding spaces, contrasted by lower local neighborhood agreement, indicating complementary fine-grained information across FMs. Attention maps showed that intelligent fusion yielded concentrated attention on tumor regions while reducing spurious focus on benign regions. Our findings suggest that intelligent, correlation-guided fusion of pathology FMs can yield compact, task-tailored representations that enhance both predictive performance and interpretability in downstream computational pathology tasks.
zh
[CV-88] VGent: Visual Grounding via Modular Design for Disentangling Reasoning and Prediction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前视觉定位(Visual Grounding)模型中存在的两大问题:一是基于多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Model, MLLM)的自回归解码方法推理速度慢且易产生幻觉;二是通过重新对齐LLM与视觉特征以学习特定对象标记的方法可能损害LLM预训练阶段获得的推理能力。解决方案的关键在于提出一种模块化编码器-解码器架构VGent,其核心创新是显式解耦高层语义推理与低层边界框预测:冻结的MLLM作为编码器保留原始强大的推理能力,而解码器则利用检测器提供的高质量候选框作为查询,通过交叉注意力机制从编码器隐藏状态中选择目标框。该设计充分利用了目标检测和MLLM的进展,避免自回归解码缺陷,并支持模块化升级,从而在多个多目标视觉定位基准上实现显著性能提升(F1提升20.6%),同时保持快速推理延迟。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11099
作者: Weitai Kang,Jason Kuen,Mengwei Ren,Zijun Wei,Yan Yan,Kangning Liu
机构: University of Illinois Chicago (伊利诺伊大学芝加哥分校); Adobe (Adobe公司)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 8 pages
Abstract:Current visual grounding models are either based on a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) that performs auto-regressive decoding, which is slow and risks hallucinations, or on re-aligning an LLM with vision features to learn new special or object tokens for grounding, which may undermine the LLM’s pretrained reasoning ability. In contrast, we propose VGent, a modular encoder-decoder architecture that explicitly disentangles high-level reasoning and low-level bounding box prediction. Specifically, a frozen MLLM serves as the encoder to provide untouched powerful reasoning capabilities, while a decoder takes high-quality boxes proposed by detectors as queries and selects target box(es) via cross-attending on encoder’s hidden states. This design fully leverages advances in both object detection and MLLM, avoids the pitfalls of auto-regressive decoding, and enables fast inference. Moreover, it supports modular upgrades of both the encoder and decoder to benefit the whole system: we introduce (i) QuadThinker, an RL-based training paradigm for enhancing multi-target reasoning ability of the encoder; (ii) mask-aware label for resolving detection-segmentation ambiguity; and (iii) global target recognition to improve the recognition of all the targets which benefits the selection among augmented proposals. Experiments on multi-target visual grounding benchmarks show that VGent achieves a new state-of-the-art with +20.6% F1 improvement over prior methods, and further boosts gIoU by +8.2% and cIoU by +5.8% under visual reference challenges, while maintaining constant, fast inference latency.
zh
[CV-89] Vision-Language Models for Infrared Industrial Sensing in Additive Manufacturing Scene Description
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在低光照或封闭机械环境中,传统视觉系统难以有效工作的问题,同时应对监督学习方法对大量标注数据的依赖,提出一种无需重新训练模型即可实现红外图像零样本(zero-shot)识别的解决方案。其关键在于通过预处理将FLIR Boson传感器捕获的红外图像转换为RGB兼容格式(具体采用“magma”色彩映射),并结合CLIP-ViT-B/32编码器与中心提示集成(centroid prompt ensembling)策略,使视觉语言基础模型(Vision-Language Foundation Models, VLMs)能够直接理解红外数据,从而在不依赖任何额外训练的情况下实现高精度工件存在检测任务。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11098
作者: Nazanin Mahjourian,Vinh Nguyen
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注:
Abstract:Many manufacturing environments operate in low-light conditions or within enclosed machines where conventional vision systems struggle. Infrared cameras provide complementary advantages in such environments. Simultaneously, supervised AI systems require large labeled datasets, which makes zero-shot learning frameworks more practical for applications including infrared cameras. Recent advances in vision-language foundation models (VLMs) offer a new path in zero-shot predictions from paired image-text representations. However, current VLMs cannot understand infrared camera data since they are trained on RGB data. This work introduces VLM-IRIS (Vision-Language Models for InfraRed Industrial Sensing), a zero-shot framework that adapts VLMs to infrared data by preprocessing infrared images captured by a FLIR Boson sensor into RGB-compatible inputs suitable for CLIP-based encoders. We demonstrate zero-shot workpiece presence detection on a 3D printer bed where temperature differences between the build plate and workpieces make the task well-suited for thermal imaging. VLM-IRIS converts the infrared images to magma representation and applies centroid prompt ensembling with a CLIP ViT-B/32 encoder to achieve high accuracy on infrared images without any model retraining. These findings demonstrate that the proposed improvements to VLMs can be effectively extended to thermal applications for label-free monitoring.
zh
[CV-90] E-CHUM: Event-based Cameras for Human Detection and Urban Monitoring
【速读】:该论文旨在解决城市动态研究中传统监测手段(如人工观察、普通摄像头)在信息获取效率、隐私保护及复杂环境适应性方面的局限性。其解决方案的关键在于引入事件驱动型相机(event-based camera),该类传感器通过捕捉光强度变化而非传统的RGB图像帧,具备低光照条件下工作、高时间分辨率和低数据冗余等优势,从而在保障隐私的同时高效提取城市动态中的关键行为信息。论文进一步提出多传感器融合策略,如与红外、事件-激光雷达(event-LiDAR)或振动传感器结合,以增强感知能力并克服事件相机自身存在的挑战,如缺乏纹理信息和对静态场景响应弱等问题。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11076
作者: Jack Brady,Andrew Dailey,Kristen Schang,Zo Vic Shong
机构: University of Michigan (密歇根大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
备注:
Abstract:Understanding human movement and city dynamics has always been challenging. From traditional methods of manually observing the city’s inhabitant, to using cameras, to now using sensors and more complex technology, the field of urban monitoring has evolved greatly. Still, there are more that can be done to unlock better practices for understanding city dynamics. This paper surveys how the landscape of urban dynamics studying has evolved with a particular focus on event-based cameras. Event-based cameras capture changes in light intensity instead of the RGB values that traditional cameras do. They offer unique abilities, like the ability to work in low-light, that can make them advantageous compared to other sensors. Through an analysis of event-based cameras, their applications, their advantages and challenges, and machine learning applications, we propose event-based cameras as a medium for capturing information to study urban dynamics. They offer the ability to capture important information while maintaining privacy. We also suggest multi-sensor fusion of event-based cameras and other sensors in the study of urban dynamics. Combining event-based cameras and infrared, event-LiDAR, or vibration has to potential to enhance the ability of event-based cameras and overcome the challenges that event-based cameras have.
zh
[CV-91] VDAWorld: World Modelling via VLM-Directed Abstraction and Simulation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式视频模型(Generative Video Models)在世界建模中面临的三大核心问题:违背物理与逻辑规则、缺乏交互性以及作为黑箱模型难以构建结构化、可查询的世界表示。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种新范式——VDAWorld,该框架利用视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Model, VLM)作为智能代理,将图像与文本描述对蒸馏为一种可计算的抽象表示,并基于此表示自主选择合适的视觉工具和物理模拟器(如刚体动力学或流体模拟),从而实现从静态场景中推断潜在动态并预测合理未来状态的能力。这一结合智能抽象与自适应仿真的方法显著提升了世界模型在多样化动态场景下的高质量仿真能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11061
作者: Felix O’Mahony,Roberto Cipolla,Ayush Tewari
机构: University of Cambridge (剑桥大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Website: this https URL
Abstract:Generative video models, a leading approach to world modeling, face fundamental limitations. They often violate physical and logical rules, lack interactivity, and operate as opaque black boxes ill-suited for building structured, queryable worlds. To overcome these challenges, we propose a new paradigm focused on distilling an image caption pair into a tractable, abstract representation optimized for simulation. We introduce VDAWorld, a framework where a Vision-Language Model (VLM) acts as an intelligent agent to orchestrate this process. The VLM autonomously constructs a grounded (2D or 3D) scene representation by selecting from a suite of vision tools, and accordingly chooses a compatible physics simulator (e.g., rigid body, fluid) to act upon it. VDAWorld can then infer latent dynamics from the static scene to predict plausible future states. Our experiments show that this combination of intelligent abstraction and adaptive simulation results in a versatile world model capable of producing high quality simulations across a wide range of dynamic scenarios.
zh
[CV-92] Synthetic Vasculature and Pathology Enhance Vision-Language Model Reasoning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在特定临床场景下因缺乏大规模、精细标注的图像-文本对数据而难以实现高质量推理的问题,尤其是在光学相干断层扫描血管成像(Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography, OCTA)领域中,病理特征的细粒度文本描述稀缺。解决方案的关键在于提出一种可控合成框架——合成血管结构推理(Synthetic Vasculature Reasoning, SVR),该框架能够生成包含糖尿病视网膜病变(Diabetic Retinopathy, DR)典型病理特征(如毛细血管缺失、微动脉瘤、新生血管和迂曲)的真实感OCTA图像,并同步自动产出颗粒级的诊断推理文本,从而构建出包含10万对图像-文本的数据集OCTA-100K-SVR,显著提升了VLM在真实临床数据上的零样本分类准确率与解释质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11060
作者: Chenjun Li,Cheng Wan,Laurin Lux,Alexander Berger,Richard B. Rosen,Martin J. Menten,Johannes C. Paetzold
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 23 pages, 8 figures, 6 tables. Full paper under review for MIDL 2026 (Medical Imaging with Deep Learning)
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) offer a promising path toward interpretable medical diagnosis by allowing users to ask about clinical explanations alongside predictions and across different modalities. However, training VLMs for detailed reasoning requires large-scale image-text datasets. In many specialized domains, for example in reading Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography (OCTA) images, such precise text with grounded description of pathologies is scarce or even non-existent. To overcome this bottleneck, we introduce Synthetic Vasculature Reasoning (SVR), a framework that controllably synthesizes images and corresponding text, specifically: realistic retinal vasculature with Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) features: capillary dropout, microaneurysms, neovascularization, and tortuosity, while automatically generating granular reasoning texts. Based on this we curate OCTA-100K-SVR, an OCTA image-reasoning dataset with 100,000 pairs. Our experiments show that a general-purpose VLM (Qwen3-VL-8b) trained on the dataset achieves a zero-shot balanced classification accuracy of 89.67% on real OCTA images, outperforming supervised baselines. Through human expert evaluation we also demonstrate that it significantly enhances explanation quality and pathology localization on clinical data.
zh
[CV-93] Weakly Supervised Tuberculosis Localization in Chest X-rays through Knowledge Distillation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决结核病(Tuberculosis, TB)影像诊断中因依赖专家解读导致的可及性问题,以及现有机器学习模型易受虚假相关性干扰、泛化能力差的问题。其关键解决方案是采用知识蒸馏(knowledge distillation)技术,通过教师-学生框架训练卷积神经网络(CNN),在无需边界框标注的情况下实现TB相关异常区域的定位与分类,从而提升模型鲁棒性和临床适用性。实验表明,基于ResNet50架构的师生模型在TBX11k数据集上取得了0.2428的mIOU得分,且学生模型性能优于教师模型,验证了该方法的有效性与推广潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11057
作者: Marshal Ashif Shawkat,Moidul Hasan,Taufiq Hasan
机构: Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (孟加拉国工程技术大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 18 pages, 9 figures, 4 tables
Abstract:Tuberculosis (TB) remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, particularly in resource-limited countries. Chest X-ray (CXR) imaging serves as an accessible and cost-effective diagnostic tool but requires expert interpretation, which is often unavailable. Although machine learning models have shown high performance in TB classification, they often depend on spurious correlations and fail to generalize. Besides, building large datasets featuring high-quality annotations for medical images demands substantial resources and input from domain specialists, and typically involves several annotators reaching agreement, which results in enormous financial and logistical expenses. This study repurposes knowledge distillation technique to train CNN models reducing spurious correlations and localize TB-related abnormalities without requiring bounding-box annotations. By leveraging a teacher-student framework with ResNet50 architecture, the proposed method trained on TBX11k dataset achieve impressive 0.2428 mIOU score. Experimental results further reveal that the student model consistently outperforms the teacher, underscoring improved robustness and potential for broader clinical deployment in diverse settings.
zh
[CV-94] WholeBodyVLA: Towards Unified Latent VLA for Whole-Body Loco-Manipulation Control
【速读】:该论文旨在解决人形机器人在复杂大空间场景中执行“运动-操作”协同任务(loco-manipulation)时存在的局限性,即现有方法在运动规划中缺乏对操作行为的感知与适配能力,导致作业空间受限且无法实现高精度、稳定的大范围移动与操作一体化控制。其核心问题在于:(1)由于人形机器人遥操作数据稀缺,难以获取高质量的运动-操作联合知识;(2)现有强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)控制器在执行运动指令时精度和稳定性不足。解决方案的关键在于提出一个统一的潜在学习框架——WholeBodyVLA,通过视觉-语言-动作(Vision-Language-Action, VLA)系统从低成本无动作标注的自观视频中学习,结合高效的人类数据采集管道增强数据多样性;同时设计面向运动-操作任务的RL策略(LMO Policy),专门优化如前进、转向和蹲姿等核心动作的准确性与鲁棒性,从而实现大空间下人形机器人的精准运动与灵巧操作协同控制。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11047
作者: Haoran Jiang,Jin Chen,Qingwen Bu,Li Chen,Modi Shi,Yanjie Zhang,Delong Li,Chuanzhe Suo,Chuang Wang,Zhihui Peng,Hongyang Li
机构: Fudan University (复旦大学); OpenDriveLab at The University of Hong Kong (香港大学OpenDriveLab); AgiBot Inc.; SII
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Humanoid robots require precise locomotion and dexterous manipulation to perform challenging loco-manipulation tasks. Yet existing approaches, modular or end-to-end, are deficient in manipulation-aware locomotion. This confines the robot to a limited workspace, preventing it from performing large-space loco-manipulation. We attribute this to: (1) the challenge of acquiring loco-manipulation knowledge due to the scarcity of humanoid teleoperation data, and (2) the difficulty of faithfully and reliably executing locomotion commands, stemming from the limited precision and stability of existing RL controllers. To acquire richer loco-manipulation knowledge, we propose a unified latent learning framework that enables Vision-Language-Action (VLA) system to learn from low-cost action-free egocentric videos. Moreover, an efficient human data collection pipeline is devised to augment the dataset and scale the benefits. To more precisely execute the desired locomotion commands, we present a loco-manipulation-oriented (LMO) RL policy specifically tailored for accurate and stable core loco-manipulation movements, such as advancing, turning, and squatting. Building on these components, we introduce WholeBodyVLA, a unified framework for humanoid loco-manipulation. To the best of our knowledge, WholeBodyVLA is one of its kind enabling large-space humanoid loco-manipulation. It is verified via comprehensive experiments on the AgiBot X2 humanoid, outperforming prior baseline by 21.3%. It also demonstrates strong generalization and high extensibility across a broad range of tasks.
zh
[CV-95] SoccerMaster: A Vision Foundation Model for Soccer Understanding
【速读】:该论文旨在解决足球视觉理解任务中因领域特异性复杂性和多样化需求而导致的模型碎片化问题,即传统方法依赖于孤立的任务特定专家模型,难以统一处理从细粒度感知(如运动员检测)到语义推理(如事件分类)等多样任务。解决方案的关键在于提出SoccerMaster——首个面向足球领域的视觉基础模型,通过监督式多任务预训练在单一框架内统一多种理解任务;同时构建SoccerFactory数据资源,利用自动化数据清洗流水线生成可扩展的空间标注,并融合多个现有足球视频数据集,从而支撑高效预训练与下游任务泛化能力。实验证明,SoccerMaster在多个下游任务上均优于专用模型,展现出更强的通用性与性能优势。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11016
作者: Haolin Yang,Jiayuan Rao,Haoning Wu,Weidi Xie
机构: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); Shanghai Innovation Institute (上海创新研究院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Soccer understanding has recently garnered growing research interest due to its domain-specific complexity and unique challenges. Unlike prior works that typically rely on isolated, task-specific expert models, this work aims to propose a unified model to handle diverse soccer visual understanding tasks, ranging from fine-grained perception (e.g., athlete detection) to semantic reasoning (e.g., event classification). Specifically, our contributions are threefold: (i) we present SoccerMaster, the first soccer-specific vision foundation model that unifies diverse understanding tasks within a single framework via supervised multi-task pretraining; (ii) we develop an automated data curation pipeline to generate scalable spatial annotations, and integrate them with various existing soccer video datasets to construct SoccerFactory, a comprehensive pretraining data resource; and (iii) we conduct extensive evaluations demonstrating that SoccerMaster consistently outperforms task-specific expert models across diverse downstream tasks, highlighting its breadth and superiority. The data, code, and model will be publicly available.
zh
[CV-96] Leverag ing Text Guidance for Enhancing Demographic Fairness in Gender Classification
【速读】:该论文旨在解决面部图像性别分类算法中存在的性别与种族偏见问题(demographic bias),即模型在不同性别和种族群体中表现不一致,导致公平性不足。其解决方案的关键在于引入文本引导的多模态训练机制,通过利用图像描述(image captions)中的语义信息来增强模型的泛化能力:一是采用图像-文本匹配(Image Text Matching, ITM)指导策略,使模型学习图像与文本之间的细粒度对齐关系以获得更丰富的跨模态表征;二是实施图像-文本融合(Image Text Fusion)方法,将两种模态信息整合为统一表征,从而提升分类公平性和准确性。该方法无需依赖显式的性别或种族标签,且具有良好的应用无关性(application agnostic)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11015
作者: Anoop Krishnan
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:In the quest for fairness in artificial intelligence, novel approaches to enhance it in facial image based gender classification algorithms using text guided methodologies are presented. The core methodology involves leveraging semantic information from image captions during model training to improve generalization capabilities. Two key strategies are presented: Image Text Matching (ITM) guidance and Image Text fusion. ITM guidance trains the model to discern fine grained alignments between images and texts to obtain enhanced multimodal representations. Image text fusion combines both modalities into comprehensive representations for improved fairness. Exensive experiments conducted on benchmark datasets demonstrate these approaches effectively mitigate bias and improve accuracy across gender racial groups compared to existing methods. Additionally, the unique integration of textual guidance underscores an interpretable and intuitive training paradigm for computer vision systems. By scrutinizing the extent to which semantic information reduces disparities, this research offers valuable insights into cultivating more equitable facial analysis algorithms. The proposed methodologies contribute to addressing the pivotal challenge of demographic bias in gender classification from facial images. Furthermore, this technique operates in the absence of demographic labels and is application agnostic.
zh
[CV-97] Multimodal Fusion of Regional Brain Experts for Interpretable Alzheimers Disease Diagnosis
【速读】:该论文旨在解决阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer’s disease, AD)早期精准诊断中多模态生物标志物融合不足的问题,传统方法通常采用简单的特征拼接策略,难以自适应地平衡不同模态(如淀粉样蛋白PET和MRI)在不同脑区的贡献。其解决方案的关键在于提出MREF-AD模型——一种基于混合专家(Mixture-of-Experts, MoE)框架的多模态区域专家融合方法,通过将每种模态中的中尺度脑区建模为独立专家,并引入两级门控网络学习个体特异性的融合权重,从而实现对结构与分子影像协同作用的自适应整合与可解释性分析。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10966
作者: Farica Zhuang,Dinara Aliyeva,Shu Yang,Zixuan Wen,Duy Duong-Tran,Christos Davatzikos,Tianlong Chen,Song Wang,Li Shen
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
备注:
Abstract:Accurate and early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) can benefit from integrating complementary information from multiple modalities, mirroring clinical practice. However, conventional fusion approaches often rely on simple concatenation of features, which cannot adaptively balance the contributions of biomarkers such as amyloid PET and MRI across brain regions. In this work, we propose MREF-AD, a Multimodal Regional Expert Fusion model for AD diagnosis. It is a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) framework that models meso-scale brain regions in each modality as an independent expert and employs two-level gating networks to learn subject-specific fusion weights. Beyond improving diagnostic performance, MREF-AD provides modality- and region-level insight into how structural and molecular imaging jointly contribute to disease diagnosis. Using data from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI), MREF-AD achieves state-of-the-art performance over baselines while providing enhanced interpretability of brain region-specific biomarker relevance, underscoring its utility as a general framework for adaptive and interpretable multimodal fusion in neuroimaging.
zh
[CV-98] mViSE: A Visual Search Engine for Analyzing Multiplex IHC Brain Tissue Images
【速读】:该论文旨在解决全切片多路成像(whole-slide multiplex imaging)生成的高维、信息密集型脑组织图像在分析过程中面临的挑战,即传统方法依赖定制软件且难以高效挖掘复杂组织结构中的多模态特征。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种无需编程的查询驱动策略——多路视觉搜索引擎(multiplex visual search engine, mViSE),该引擎通过分而治之的策略将分子标记分组为相关面板,并利用自监督学习训练每个面板的多路编码器,同时通过显式视觉确认确保学习效果;进一步结合信息论方法整合多个面板以支持对单细胞、邻近细胞对或细胞群落等目标的视觉查询检索,从而实现脑区划分、皮层分层及区域比较等功能,无需编程即可完成组织学探索与分析。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11745
作者: Liqiang Huang,Rachel W. Mills,Saikiran Mandula,Lin Bai,Mahtab Jeyhani,John Redell,Hien Van Nguyen,Saurabh Prasad,Dragan Maric,Badrinath Roysam
机构: Cullen College of Engineering, University of Houston (休斯顿大学工程学院); The University of Texas McGovern Medical School (德克萨斯大学 McGovern 医学院); National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (国家神经疾病与中风研究所)
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Whole-slide multiplex imaging of brain tissue generates massive information-dense images that are challenging to analyze and require custom software. We present an alternative query-driven programming-free strategy using a multiplex visual search engine (mViSE) that learns the multifaceted brain tissue chemoarchitecture, cytoarchitecture, and myeloarchitecture. Our divide-and-conquer strategy organizes the data into panels of related molecular markers and uses self-supervised learning to train a multiplex encoder for each panel with explicit visual confirmation of successful learning. Multiple panels can be combined to process visual queries for retrieving similar communities of individual cells or multicellular niches using information-theoretic methods. The retrievals can be used for diverse purposes including tissue exploration, delineating brain regions and cortical cell layers, profiling and comparing brain regions without computer programming. We validated mViSE’s ability to retrieve single cells, proximal cell pairs, tissue patches, delineate cortical layers, brain regions and sub-regions. mViSE is provided as an open-source QuPath plug-in.
zh
[CV-99] Particle Image Velocimetry Refinement via Consensus ADMM
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统粒子图像测速(Particle Image Velocimetry, PIV)方法及现有机器学习流场量化技术在实际应用中对成像条件、流动状态和种子密度变化敏感,且泛化能力弱的问题。其核心解决方案是提出一种基于交替方向乘子法(Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers, ADMM)的共识框架,通过并行运行多个不同算法对同一图像对的不同区域进行瞬时流场估计,并融合平滑性与不可压缩性等先验信息,从而提升整体精度与鲁棒性。实验表明,该方法可在60Hz推理速率下使密集逆搜索估计器的终点误差降低达20%,并通过异常值剔除进一步增强性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11695
作者: Alan Bonomi,Francesco Banelli,Antonio Terpin
机构: ETH Zürich (苏黎世联邦理工学院)
类目: Fluid Dynamics (physics.flu-dyn); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Optimization and Control (math.OC)
备注: Code: this https URL
Abstract:Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) is an imaging technique in experimental fluid dynamics that quantifies flow fields around bluff bodies by analyzing the displacement of neutrally buoyant tracer particles immersed in the fluid. Traditional PIV approaches typically depend on tuning parameters specific to the imaging setup, making the performance sensitive to variations in illumination, flow conditions, and seeding density. On the other hand, even state-of-the-art machine learning methods for flow quantification are fragile outside their training set. In our experiments, we observed that flow quantification would improve if different tunings (or algorithms) were applied to different regions of the same image pair. In this work, we parallelize the instantaneous flow quantification with multiple algorithms and adopt a consensus framework based on the alternating direction method of multipliers, seamlessly incorporating priors such as smoothness and incompressibility. We perform several numerical experiments to demonstrate the benefits of this approach. For instance, we achieve a decrease in end-point-error of up to 20% of a dense-inverse-search estimator at an inference rate of 60Hz, and we show how this performance boost can be increased further with outlier rejection. Our method is implemented in JAX, effectively exploiting hardware acceleration, and integrated in Flow Gym, enabling (i) reproducible comparisons with the state-of-the-art, (ii) testing different base algorithms, (iii) straightforward deployment for active fluids control applications.
zh
[CV-100] Stochastics of shapes and Kunita flows
【速读】:该论文旨在解决如何在非线性且通常为无限维的形状空间(shape space)中构建合适的随机形状过程(stochastic shape process),以用于演化生物学等领域的建模与统计推断。其核心挑战在于传统方法难以直接处理形状空间的几何结构和动态演化特性。解决方案的关键在于引入Kunita流(Kunita flows)——这类流通过构造自然地满足形状结构兼容性条件,从而生成符合要求的随机形状过程;同时结合桥采样(bridge sampling)技术,实现对观测数据的条件化建模,进而支持对随机动力学参数的统计推断。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11676
作者: Stefan Sommer,Gefan Yang,Elizabeth Louise Baker
机构: 未知
类目: Probability (math.PR); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Stochastic processes of evolving shapes are used in applications including evolutionary biology, where morphology changes stochastically as a function of evolutionary processes. Due to the non-linear and often infinite-dimensional nature of shape spaces, the mathematical construction of suitable stochastic shape processes is far from immediate. We define and formalize properties that stochastic shape processes should ideally satisfy to be compatible with the shape structure, and we link this to Kunita flows that, when acting on shape spaces, induce stochastic processes that satisfy these criteria by their construction. We couple this with a survey of other relevant shape stochastic processes and show how bridge sampling techniques can be used to condition shape stochastic processes on observed data thereby allowing for statistical inference of parameters of the stochastic dynamics.
zh
人工智能
[AI-0] Super Suffixes: Bypassing Text Generation Alignment and Guard Models Simultaneously
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在处理不可信文本输入时面临的安 全与隐私风险,特别是针对现有保护机制(如Llama Prompt Guard 2)易被绕过的问题。其核心挑战在于如何有效防御通过精心设计的恶意后缀(Super Suffixes)实现多目标对齐覆盖的对抗性输入攻击,此类攻击可跨不同分词方案和模型架构成功诱导生成有害内容。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为DeltaGuard的轻量级检测方法:通过分析模型内部状态(残差流)与特定概念方向之间的余弦相似度变化,识别出由Super Suffix引发的意图指纹特征,并据此显著提升对恶意提示的分类准确率至接近100%,从而增强 guard model 架构对高级对抗性提示攻击的鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11783
作者: Andrew Adiletta,Kathryn Adiletta,Kemal Derya,Berk Sunar
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 13 pages, 5 Figures
Abstract:The rapid deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) has created an urgent need for enhanced security and privacy measures in Machine Learning (ML). LLMs are increasingly being used to process untrusted text inputs and even generate executable code, often while having access to sensitive system controls. To address these security concerns, several companies have introduced guard models, which are smaller, specialized models designed to protect text generation models from adversarial or malicious inputs. In this work, we advance the study of adversarial inputs by introducing Super Suffixes, suffixes capable of overriding multiple alignment objectives across various models with different tokenization schemes. We demonstrate their effectiveness, along with our joint optimization technique, by successfully bypassing the protection mechanisms of Llama Prompt Guard 2 on five different text generation models for malicious text and code generation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to reveal that Llama Prompt Guard 2 can be compromised through joint optimization. Additionally, by analyzing the changing similarity of a model’s internal state to specific concept directions during token sequence processing, we propose an effective and lightweight method to detect Super Suffix attacks. We show that the cosine similarity between the residual stream and certain concept directions serves as a distinctive fingerprint of model intent. Our proposed countermeasure, DeltaGuard, significantly improves the detection of malicious prompts generated through Super Suffixes. It increases the non-benign classification rate to nearly 100%, making DeltaGuard a valuable addition to the guard model stack and enhancing robustness against adversarial prompt attacks. Comments: 13 pages, 5 Figures Subjects: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) ACMclasses: I.2.7 Cite as: arXiv:2512.11783 [cs.CR] (or arXiv:2512.11783v1 [cs.CR] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11783 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-1] Agile Flight Emerges from Multi-Agent Competitive Racing
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统强化学习训练中代理(agent)在复杂环境中难以实现高级低层控制(如高速飞行和策略性行为)的问题,尤其是当奖励机制依赖于密集的、预设的行为奖励(如沿赛道前进)时,其泛化能力与真实世界迁移性能受限。解决方案的关键在于采用多智能体竞争机制,并使用稀疏的任务级目标奖励(如赢得比赛),通过代理间的对抗性互动自然涌现出敏捷飞行(agile flight)和策略行为(strategy),从而显著提升模拟到现实世界的迁移能力及对未见过对手的泛化性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11781
作者: Vineet Pasumarti,Lorenzo Bianchi,Antonio Loquercio
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注:
Abstract:Through multi-agent competition and the sparse high-level objective of winning a race, we find that both agile flight (e.g., high-speed motion pushing the platform to its physical limits) and strategy (e.g., overtaking or blocking) emerge from agents trained with reinforcement learning. We provide evidence in both simulation and the real world that this approach outperforms the common paradigm of training agents in isolation with rewards that prescribe behavior, e.g., progress on the raceline, in particular when the complexity of the environment increases, e.g., in the presence of obstacles. Moreover, we find that multi-agent competition yields policies that transfer more reliably to the real world than policies trained with a single-agent progress-based reward, despite the two methods using the same simulation environment, randomization strategy, and hardware. In addition to improved sim-to-real transfer, the multi-agent policies also exhibit some degree of generalization to opponents unseen at training time. Overall, our work, following in the tradition of multi-agent competitive game-play in digital domains, shows that sparse task-level rewards are sufficient for training agents capable of advanced low-level control in the physical world. Code: this https URL Subjects: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA) Cite as: arXiv:2512.11781 [cs.RO] (or arXiv:2512.11781v1 [cs.RO] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11781 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-2] Generative Parametric Design (GPD): A framework for real-time geometry generation and on-the-fly multiparametric approximation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统仿真驱动工程科学中设计探索与参数化建模效率低下的问题,尤其是在多参数条件下复杂几何结构与物理场耦合响应的快速预测难题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为生成式参数化设计(Generative Parametric Design, GPD)的新框架,其核心是利用两个秩缩减自编码器(Rank Reduction Autoencoders, RRAEs)分别对设计几何和稀疏广义分解(sparse Proper Generalized Decomposition, sPGD)模式解进行编码,并通过回归技术在潜在空间中建立二者之间的映射关系,从而实现设计与对应参数化解之间的高效转换,显著提升设计优化与数字孪生系统的实时性与可扩展性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11748
作者: Mohammed El Fallaki Idrissi,Jad Mounayer,Sebastian Rodriguez,Fodil Meraghni,Francisco Chinesta
机构: 未知
类目: Computational Engineering, Finance, and Science (cs.CE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:This paper presents a novel paradigm in simulation-based engineering sciences by introducing a new framework called Generative Parametric Design (GPD). The GPD framework enables the generation of new designs along with their corresponding parametric solutions given as a reduced basis. To achieve this, two Rank Reduction Autoencoders (RRAEs) are employed, one for encoding and generating the design or geometry, and the other for encoding the sparse Proper Generalized Decomposition (sPGD) mode solutions. These models are linked in the latent space using regression techniques, allowing efficient transitions between design and their associated sPGD modes. By empowering design exploration and optimization, this framework also advances digital and hybrid twin development, enhancing predictive modeling and real-time decision-making in engineering applications. The developed framework is demonstrated on two-phase microstructures, in which the multiparametric solutions account for variations in two key material parameters.
zh
[AI-3] CogniSNN: Enabling Neuron-Expandability Pathway-Reusability and Dynamic-Configurability with Random Graph Architectures in Spiking Neural Networks
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前脉冲神经网络(Spiking Neural Networks, SNNs)在结构设计上过度依赖传统人工神经网络(Artificial Neural Networks, ANNs)的刚性层级架构,忽视了生物神经系统中神经元随机连接、路径复用与动态可配置等关键特性的问题。其核心解决方案是提出一种认知感知型脉冲神经网络(Cognition-aware SNN, CogniSNN),通过引入随机图结构(Random Graph Architecture, RGA)构建更具生物启发性的网络拓扑;同时结合改进的纯脉冲残差机制与自适应池化策略缓解深层路径中的性能退化和维度不匹配问题,并设计基于关键路径的学习无遗忘方法(Key Pathway-based Learning without Forgetting, KP-LwF)以实现多任务迁移中的知识保留;最终提出动态生长学习算法(Dynamic Growth Learning, DGL),使神经元和突触能够沿时间维度动态扩展,从而提升模型在不同场景下的持续学习能力及对干扰的鲁棒性,突破固定时间步长限制,为类脑智能在神经形态硬件上的落地提供理论基础与实践路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11743
作者: Yongsheng Huang,Peibo Duan,Yujie Wu,Kai Sun,Zhipeng Liu,Changsheng Zhang,Bin Zhang,Mingkun Xu
机构: 未知
类目: Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Spiking neural networks (SNNs), regarded as the third generation of artificial neural networks, are expected to bridge the gap between artificial intelligence and computational neuroscience. However, most mainstream SNN research directly adopts the rigid, chain-like hierarchical architecture of traditional artificial neural networks (ANNs), ignoring key structural characteristics of the brain. Biological neurons are stochastically interconnected, forming complex neural pathways that exhibit Neuron-Expandability, Pathway-Reusability, and Dynamic-Configurability. In this paper, we introduce a new SNN paradigm, named Cognition-aware SNN (CogniSNN), by incorporating Random Graph Architecture (RGA). Furthermore, we address the issues of network degradation and dimensional mismatch in deep pathways by introducing an improved pure spiking residual mechanism alongside an adaptive pooling strategy. Then, we design a Key Pathway-based Learning without Forgetting (KP-LwF) approach, which selectively reuses critical neural pathways while retaining historical knowledge, enabling efficient multi-task transfer. Finally, we propose a Dynamic Growth Learning (DGL) algorithm that allows neurons and synapses to grow dynamically along the internal temporal dimension. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CogniSNN achieves performance comparable to, or even surpassing, current state-of-the-art SNNs on neuromorphic datasets and Tiny-ImageNet. The Pathway-Reusability enhances the network’s continuous learning capability across different scenarios, while the dynamic growth algorithm improves robustness against interference and mitigates the fixed-timestep constraints during neuromorphic chip deployment. This work demonstrates the potential of SNNs with random graph structures in advancing brain-inspired intelligence and lays the foundation for their practical application on neuromorphic hardware.
zh
[AI-4] MedAI: Evaluating TxAgents Therapeutic Agent ic Reasoning in the NeurIPS CURE-Bench Competition
【速读】:该论文旨在解决临床医学中治疗决策这一高风险领域内,人工智能(AI)辅助系统在药物推荐、治疗方案制定及不良反应预测等多步骤推理任务中的准确性与安全性问题。其核心挑战在于如何有效整合患者特征、疾病进程和药物作用机制之间的复杂交互,并确保推理过程可解释且符合生物医学知识的可靠性。解决方案的关键在于提出并实现了一种基于代理式 AI(Agentic AI)的方法——TxAgent,该方法通过迭代式检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)框架,利用微调后的 Llama-3.1-8B 模型动态调用统一的生物医学工具套件(ToolUniverse),集成 FDA Drug API、OpenTargets 和 Monarch 等权威资源,从而实现对当前治疗信息的精准访问与推理执行。同时,研究强调将 token 级别的推理轨迹和工具调用序列作为显式监督信号,以提升模型在医疗场景下的安全性和性能表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11682
作者: Tim Cofala,Christian Kalfar,Jingge Xiao,Johanna Schrader,Michelle Tang,Wolfgang Nejdl
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 7 pages, 3 figures
Abstract:Therapeutic decision-making in clinical medicine constitutes a high-stakes domain in which AI guidance interacts with complex interactions among patient characteristics, disease processes, and pharmacological agents. Tasks such as drug recommendation, treatment planning, and adverse-effect prediction demand robust, multi-step reasoning grounded in reliable biomedical knowledge. Agentic AI methods, exemplified by TxAgent, address these challenges through iterative retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). TxAgent employs a fine-tuned Llama-3.1-8B model that dynamically generates and executes function calls to a unified biomedical tool suite (ToolUniverse), integrating FDA Drug API, OpenTargets, and Monarch resources to ensure access to current therapeutic information. In contrast to general-purpose RAG systems, medical applications impose stringent safety constraints, rendering the accuracy of both the reasoning trace and the sequence of tool invocations critical. These considerations motivate evaluation protocols treating token-level reasoning and tool-usage behaviors as explicit supervision signals. This work presents insights derived from our participation in the CURE-Bench NeurIPS 2025 Challenge, which benchmarks therapeutic-reasoning systems using metrics that assess correctness, tool utilization, and reasoning quality. We analyze how retrieval quality for function (tool) calls influences overall model performance and demonstrate performance gains achieved through improved tool-retrieval strategies. Our work was awarded the Excellence Award in Open Science. Complete information can be found at this https URL.
zh
[AI-5] From Verification Burden to Trusted Collaboration: Design Goals for LLM -Assisted Literature Reviews
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在学术文献综述(literature review)过程中存在的三大关键问题:输出可信度不足、验证负担持续存在以及需要依赖多个工具协同操作。其解决方案的核心在于提出六个设计目标,并构建一个高阶框架,通过改进相关文献的可视化呈现、在每一步生成过程中嵌入验证机制,以及基于人类反馈对生成结果进行解释性对齐,从而提升研究人员对LLM输出的信任度,并实现人机协作的实用化与可验证性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11661
作者: Brenda Nogueira,Werner Geyer,Andrew Anderson,Toby Jia-Jun Li,Dongwhi Kim,Nuno Moniz,Nitesh V. Chawla
机构: 未知
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly embedded in academic writing practices. Although numerous studies have explored how researchers employ these tools for scientific writing, their concrete implementation, limitations, and design challenges within the literature review process remain underexplored. In this paper, we report a user study with researchers across multiple disciplines to characterize current practices, benefits, and \textitpain points in using LLMs to investigate related work. We identified three recurring gaps: (i) lack of trust in outputs, (ii) persistent verification burden, and (iii) requiring multiple tools. This motivates our proposal of six design goals and a high-level framework that operationalizes them through improved related papers visualization, verification at every step, and human-feedback alignment with generation-guided explanations. Overall, by grounding our work in the practical, day-to-day needs of researchers, we designed a framework that addresses these limitations and models real-world LLM-assisted writing, advancing trust through verifiable actions and fostering practical collaboration between researchers and AI systems.
zh
[AI-6] Causal Inference in Energy Demand Prediction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决能源需求预测问题,其核心挑战在于多因素(如气象条件和日历信息)之间的因果依赖关系难以通过传统相关性学习方法准确建模。解决方案的关键在于构建一个结构因果模型(Structural Causal Model, SCM),明确揭示变量间的因果机制,并将这些因果洞察作为先验知识引入贝叶斯模型中。该方法不仅在测试集上实现了3.84%的平均绝对百分比误差(MAPE),还展现出强鲁棒性(跨两年数据交叉验证平均MAPE为3.88%),从而显著优于现有方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11653
作者: Chutian Ma,Grigorii Pomazkin,Giacinto Paolo Saggese,Paul Smith
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Energy demand prediction is critical for grid operators, industrial energy consumers, and service providers. Energy demand is influenced by multiple factors, including weather conditions (e.g. temperature, humidity, wind speed, solar radiation), and calendar information (e.g. hour of day and month of year), which further affect daily work and life schedules. These factors are causally interdependent, making the problem more complex than simple correlation-based learning techniques satisfactorily allow for. We propose a structural causal model that explains the causal relationship between these variables. A full analysis is performed to validate our causal beliefs, also revealing important insights consistent with prior studies. For example, our causal model reveals that energy demand responds to temperature fluctuations with season-dependent sensitivity. Additionally, we find that energy demand exhibits lower variance in winter due to the decoupling effect between temperature changes and daily activity patterns. We then build a Bayesian model, which takes advantage of the causal insights we learned as prior knowledge. The model is trained and tested on unseen data and yields state-of-the-art performance in the form of a 3.84 percent MAPE on the test set. The model also demonstrates strong robustness, as the cross-validation across two years of data yields an average MAPE of 3.88 percent. Subjects: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2512.11653 [cs.AI] (or arXiv:2512.11653v1 [cs.AI] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11653 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) Submission history From: Giacinto Paolo Saggese [view email] [v1] Fri, 12 Dec 2025 15:30:46 UTC (6,368 KB) Full-text links: Access Paper: View a PDF of the paper titled Causal Inference in Energy Demand Prediction, by Chutian Ma and 3 other authorsView PDFHTML (experimental)TeX Source view license Current browse context: cs.AI prev | next new | recent | 2025-12 Change to browse by: cs References Citations NASA ADSGoogle Scholar Semantic Scholar export BibTeX citation Loading… BibTeX formatted citation loading… Data provided by: Bookmark checked=“checked”> Bibliographic Tools Bibliographic and Citation Tools Bibliographic Explorer Toggle Bibliographic Explorer (What is the Explorer?) Connected Papers Toggle Connected Papers (What is Connected Papers?) Litmaps Toggle Litmaps (What is Litmaps?) scite.ai Toggle scite Smart Citations (What are Smart Citations?) Code, Data, Media Code, Data and Media Associated with this Article alphaXiv Toggle alphaXiv (What is alphaXiv?) Links to Code Toggle CatalyzeX Code Finder for Papers (What is CatalyzeX?) DagsHub Toggle DagsHub (What is DagsHub?) GotitPub Toggle Gotit.pub (What is GotitPub?) Huggingface Toggle Hugging Face (What is Huggingface?) Links to Code Toggle Papers with Code (What is Papers with Code?) ScienceCast Toggle ScienceCast (What is ScienceCast?) Demos Demos Replicate Toggle Replicate (What is Replicate?) Spaces Toggle Hugging Face Spaces (What is Spaces?) Spaces Toggle TXYZ.AI (What is TXYZ.AI?) Related Papers Recommenders and Search Tools Link to Influence Flower Influence Flower (What are Influence Flowers?) Core recommender toggle CORE Recommender (What is CORE?) Author Venue Institution Topic About arXivLabs arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website. Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them. Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv’s community? Learn more about arXivLabs. Which authors of this paper are endorsers? | Disable MathJax (What is MathJax?) mathjaxToggle(); About Help contact arXivClick here to contact arXiv Contact subscribe to arXiv mailingsClick here to subscribe Subscribe Copyright Privacy Policy Web Accessibility Assistance arXiv Operational Status
zh
[AI-7] AI Benchmark Democratization and Carpentry
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前AI基准测试(benchmark)在面对快速演进的大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)时所面临的静态性与现实脱节问题,即传统静态基准因模型记忆效应导致评估结果无法反映真实部署性能。其核心挑战在于:基准测试需适应模型架构、数据集和部署环境的动态变化,并确保透明性、可复现性和解释性,同时克服资源门槛高、硬件访问受限、设计能力不足等障碍。解决方案的关键在于推动“AI基准构建术”(AI Benchmark Carpentry)的发展,通过技术革新与系统化教育相结合,构建动态、包容且面向应用场景的持续适应型基准框架,从而实现科学评估与实际部署风险的对齐,支撑负责任、可复现且普惠的AI发展。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11588
作者: Gregor von Laszewski,Wesley Brewer,Jeyan Thiyagalingam,Juri Papay,Armstrong Foundjem,Piotr Luszczek,Murali Emani,Shirley V. Moore,Vijay Janapa Reddi,Matthew D. Sinclair,Sebastian Lobentanzer,Sujata Goswami,Benjamin Hawks,Marco Colombo,Nhan Tran,Christine R. Kirkpatrick,Abdulkareem Alsudais,Gregg Barrett,Tianhao Li,Kirsten Morehouse,Shivaram Venkataraman,Rutwik Jain,Kartik Mathur,Victor Lu,Tejinder Singh,Khojasteh Z. Mirza,Kongtao Chen,Sasidhar Kunapuli,Gavin Farrell,Renato Umeton,Geoffrey C. Fox
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 43 pages, 2 figures, 7 tables
Abstract:Benchmarks are a cornerstone of modern machine learning, enabling reproducibility, comparison, and scientific progress. However, AI benchmarks are increasingly complex, requiring dynamic, AI-focused workflows. Rapid evolution in model architectures, scale, datasets, and deployment contexts makes evaluation a moving target. Large language models often memorize static benchmarks, causing a gap between benchmark results and real-world performance. Beyond traditional static benchmarks, continuous adaptive benchmarking frameworks are needed to align scientific assessment with deployment risks. This calls for skills and education in AI Benchmark Carpentry. From our experience with MLCommons, educational initiatives, and programs like the DOE’s Trillion Parameter Consortium, key barriers include high resource demands, limited access to specialized hardware, lack of benchmark design expertise, and uncertainty in relating results to application domains. Current benchmarks often emphasize peak performance on top-tier hardware, offering limited guidance for diverse, real-world scenarios. Benchmarking must become dynamic, incorporating evolving models, updated data, and heterogeneous platforms while maintaining transparency, reproducibility, and interpretability. Democratization requires both technical innovation and systematic education across levels, building sustained expertise in benchmark design and use. Benchmarks should support application-relevant comparisons, enabling informed, context-sensitive decisions. Dynamic, inclusive benchmarking will ensure evaluation keeps pace with AI evolution and supports responsible, reproducible, and accessible AI deployment. Community efforts can provide a foundation for AI Benchmark Carpentry. Comments: 43 pages, 2 figures, 7 tables Subjects: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) ACMclasses: I.2.6 Reportnumber: FERMILAB-PUB-25-0835-CSAID Cite as: arXiv:2512.11588 [cs.AI] (or arXiv:2512.11588v1 [cs.AI] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11588 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-8] Atomic Action Slicing: Planner-Aligned Options for Generalist VLA Agents
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前视觉-语言-动作(Vision-Language-Action, VLA)模型在处理新技能或物体组合任务时泛化能力差的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出原子动作切分(Atomic Action Slicing, AAS),一种与规划器对齐的方法,将长周期示范数据分解为短时、类型化的原子动作片段,从而提升规划器的可操作性和策略学习的效率。通过在LIBERO数据集上构建包含2,124个标注原子片段的验证数据集(含动作类型、时间跨度和置信度),并利用更强的分割模型(Gemini 2.5 Pro)增强鲁棒性,实验表明基于AAS训练的CLIP-RT+模型在LIBERO-Goal和LIBERO-Long任务上的成功率分别从94.2%提升至95.3%、83.8%提升至88.8%,显著改善了VLA模型的性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11584
作者: Stefan Tabakov,Asen Popov,Dimitar Dimitrov,S. Ensiye Kiyamousavi,Vladimir Hristov,Boris Kraychev
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注: The 41st ACM/SIGAPP Symposium On Applied Computing
Abstract:Current vision-language-action (VLA) models generalize poorly, particularly when tasks require new compositions of skills or objects. We introduce Atomic Action Slicing (AAS), a planner-aligned approach that decomposes long-horizon demonstrations into short, typed atomic actions that are easier for planners to use and policies to learn. Using LIBERO demonstrations, AAS produces a validated dataset of 2,124 atomic segments labeled with action type, temporal span, and confidence. A stronger segmenter (Gemini 2.5 Pro) closely matches planner-defined plans and remains robust under keyframe jitter, while smaller models perform worse on multi-object tasks. Fine-tuning CLIP-RT+ on our atomic dataset improves task success from 94.2% to 95.3% on LIBERO-Goal and 83.8% to 88.8% on LIBERO-Long. We publicly release the GATE-VLAP dataset on HuggingFace(this https URL)
zh
[AI-9] Optimizing the Training Diet: Data Mixture Search for Robust Time Series Forecasting
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传感器数据训练深度学习模型时存在的数据冗余与不平衡问题,即传统假设“数据越多越好”并不总是成立,因为并非所有数据点对模型泛化能力的贡献均等。解决方案的关键在于将数据选择问题从模型超参数调优转向数据组成优化:首先利用大规模编码器和k-means聚类从大规模未标注时间序列语料库中识别出行为一致的子集(称为“数据成分”),随后通过Optuna优化框架在高维数据混合空间中搜索最优采样比例,从而构建针对特定目标模型的“最佳训练膳食”。实验表明,该方法显著优于全数据训练基线,如在PMSM数据集上将均方误差(MSE)从1.70降至1.37,提升达19.41%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11546
作者: Federico Pennino,Maurizio Gabbrielli
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted ACM SAC 2026
Abstract:The standard paradigm for training deep learning models on sensor data assumes that more data is always better. However, raw sensor streams are often imbalanced and contain significant redundancy, meaning that not all data points contribute equally to model generalization. In this paper, we show that, in some cases, “less is more” when considering datasets. We do this by reframing the data selection problem: rather than tuning model hyperparameters, we fix the model and optimize the composition of the training data itself. We introduce a framework for discovering the optimal “training diet” from a large, unlabeled time series corpus. Our framework first uses a large-scale encoder and k-means clustering to partition the dataset into distinct, behaviorally consistent clusters. These clusters represent the fundamental ‘ingredients’ available for training. We then employ the Optuna optimization framework to search the high-dimensional space of possible data mixtures. For each trial, Optuna proposes a specific sampling ratio for each cluster, and a new training set is constructed based on this recipe. A smaller target model is then trained and evaluated. Our experiments reveal that this data-centric search consistently discovers data mixtures that yield models with significantly higher performance compared to baselines trained on the entire dataset. Specifically - evaluated on PMSM dataset - our method improved performance from a baseline MSE of 1.70 to 1.37, a 19.41% improvement.
zh
[AI-10] Graph Embedding with Mel-spectrograms for Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition
【速读】:该论文旨在解决水下声学目标识别(Underwater Acoustic Target Recognition, UATR)中因船舶辐射噪声复杂性和海洋环境变化导致的识别难题。现有深度学习方法通常隐含假设水下声学数据位于欧几里得空间,但实际信号具有非平稳、非高斯和非线性等特性,此假设不适用。解决方案的关键在于提出一种非欧几里得深度学习模型——UATR-GTransformer,其核心创新是将Transformer架构与图神经网络(Graph Neural Network, GNN)融合:通过Mel patchify模块将梅尔频谱图分割为重叠块,利用GTransformer块中的Transformer编码器捕捉块间相互信息以生成梅尔图嵌入(Mel-graph embeddings),再由GNN建模局部邻域关系增强嵌入表示,并通过前馈网络(Feed-Forward Network, FFN)完成特征变换,从而有效建模水下声学信号的复杂拓扑结构。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11545
作者: Sheng Feng,Shuqing Ma,Xiaoqian Zhu
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Underwater acoustic target recognition (UATR) is extremely challenging due to the complexity of ship-radiated noise and the variability of ocean environments. Although deep learning (DL) approaches have achieved promising results, most existing models implicitly assume that underwater acoustic data lie in a Euclidean space. This assumption, however, is unsuitable for the inherently complex topology of underwater acoustic signals, which exhibit non-stationary, non-Gaussian, and nonlinear characteristics. To overcome this limitation, this paper proposes the UATR-GTransformer, a non-Euclidean DL model that integrates Transformer architectures with graph neural networks (GNNs). The model comprises three key components: a Mel patchify block, a GTransformer block, and a classification head. The Mel patchify block partitions the Mel-spectrogram into overlapping patches, while the GTransformer block employs a Transformer Encoder to capture mutual information between split patches to generate Mel-graph embeddings. Subsequently, a GNN enhances these embeddings by modeling local neighborhood relationships, and a feed-forward network (FFN) further performs feature transformation. Experiments results based on two widely used benchmark datasets demonstrate that the UATR-GTransformer achieves performance competitive with state-of-the-art methods. In addition, interpretability analysis reveals that the proposed model effectively extracts rich frequency-domain information, highlighting its potential for applications in ocean engineering.
zh
[AI-11] AI-MASLD Metabolic Dysfunction and Information Steatosis of Large Language Models in Unstructured Clinical Narratives
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在真实临床场景中处理含噪、冗余的患者主诉时,是否存在功能退化问题,以及是否表现出类似代谢相关脂肪性肝病(Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease, MASLD)的“功能性代谢失调”特征。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个基于标准化医疗探针的横断面评估体系,通过五维核心指标对四种主流LLM(GPT-4o、Gemini 2.5、DeepSeek 3.1和Qwen3-Max)进行双盲、逆向评分的临床模拟测试,首次实证发现LLMs在极端噪声下会出现功能崩溃,并提出“人工智能相关代谢功能障碍性脂肪肝病”(AI-MASLD)这一新概念,从而为AI在医疗领域的安全应用提供了关键警示与理论依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11544
作者: Yuan Shen,Xiaojun Wu,Linghua Yu
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 47 pages, 2 figures
Abstract:This study aims to simulate real-world clinical scenarios to systematically evaluate the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to extract core medical information from patient chief complaints laden with noise and redundancy, and to verify whether they exhibit a functional decline analogous to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). We employed a cross-sectional analysis design based on standardized medical probes, selecting four mainstream LLMs as research subjects: GPT-4o, Gemini 2.5, DeepSeek 3.1, and Qwen3-Max. An evaluation system comprising twenty medical probes across five core dimensions was used to simulate a genuine clinical communication environment. All probes had gold-standard answers defined by clinical experts and were assessed via a double-blind, inverse rating scale by two independent clinicians. The results show that all tested models exhibited functional defects to varying degrees, with Qwen3-Max demonstrating the best overall performance and Gemini 2.5 the worst. Under conditions of extreme noise, most models experienced a functional collapse. Notably, GPT-4o made a severe misjudgment in the risk assessment for pulmonary embolism (PE) secondary to deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This research is the first to empirically confirm that LLMs exhibit features resembling metabolic dysfunction when processing clinical information, proposing the innovative concept of “AI-Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (AI-MASLD)”. These findings offer a crucial safety warning for the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare, emphasizing that current LLMs must be used as auxiliary tools under human expert supervision, as there remains a significant gap between their theoretical knowledge and practical clinical application.
zh
[AI-12] Contrastive Time Series Forecasting with Anomalies
【速读】:该论文旨在解决时间序列预测中异常事件处理不当的问题:传统模型无法区分短期噪声与具有持久影响的异常事件,导致对噪声过度敏感或忽略真实分布变化。解决方案的关键在于提出Co-TSFA(Contrastive Time Series Forecasting with Anomalies),其通过生成仅输入(input-only)和输入-输出(input-output)两种增强数据,分别建模预测无关和预测相关的异常,并引入潜在空间中的输出对齐损失(latent-output alignment loss),使表示变化与预测变化相绑定,从而在保持对无关扰动不变性的同时,保留对有意义分布偏移的敏感性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11526
作者: Joel Ekstrand,Zahra Taghiyarrenani,Slawomir Nowaczyk
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
备注:
Abstract:Time series forecasting predicts future values from past data. In real-world settings, some anomalous events have lasting effects and influence the forecast, while others are short-lived and should be ignored. Standard forecasting models fail to make this distinction, often either overreacting to noise or missing persistent shifts. We propose Co-TSFA (Contrastive Time Series Forecasting with Anomalies), a regularization framework that learns when to ignore anomalies and when to respond. Co-TSFA generates input-only and input-output augmentations to model forecast-irrelevant and forecast-relevant anomalies, and introduces a latent-output alignment loss that ties representation changes to forecast changes. This encourages invariance to irrelevant perturbations while preserving sensitivity to meaningful distributional shifts. Experiments on the Traffic and Electricity benchmarks, as well as on a real-world cash-demand dataset, demonstrate that Co-TSFA improves performance under anomalous conditions while maintaining accuracy on normal data. An anonymized GitHub repository with the implementation of Co-TSFA is provided and will be made public upon acceptance.
zh
[AI-13] NeuralOGCM: Differentiable Ocean Modeling with Learnable Physics
【速读】:该论文旨在解决高精度科学模拟中长期存在的计算效率与物理保真度之间的权衡问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出 NeuralOGCM 框架,该框架融合了可微编程(differentiable programming)与深度学习技术:核心是一个全可微的动力学求解器,利用物理知识作为归纳偏置(inductive bias),将大尺度确定性物理演化建模为可学习的物理积分过程,并将关键物理参数(如扩散系数)转化为可学习参数,从而通过端到端训练自主优化物理内核;同时,一个深度神经网络用于学习亚网格尺度过程和离散化误差的修正,与物理模型协同工作,最终由统一的常微分方程(ODE)求解器整合两者输出,实现高效、稳定且物理一致的海洋建模。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11525
作者: Hao Wu,Yuan Gao,Fan Xu,Fan Zhang,Guangliang Liu,Yuxuan Liang,Xiaomeng Huang
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:High-precision scientific simulation faces a long-standing trade-off between computational efficiency and physical fidelity. To address this challenge, we propose NeuralOGCM, an ocean modeling framework that fuses differentiable programming with deep learning. At the core of NeuralOGCM is a fully differentiable dynamical solver, which leverages physics knowledge as its core inductive bias. The learnable physics integration captures large-scale, deterministic physical evolution, and transforms key physical parameters (e.g., diffusion coefficients) into learnable parameters, enabling the model to autonomously optimize its physical core via end-to-end training. Concurrently, a deep neural network learns to correct for subgrid-scale processes and discretization errors not captured by the physics model. Both components work in synergy, with their outputs integrated by a unified ODE solver. Experiments demonstrate that NeuralOGCM maintains long-term stability and physical consistency, significantly outperforming traditional numerical models in speed and pure AI baselines in accuracy. Our work paves a new path for building fast, stable, and physically-plausible models for scientific computing.
zh
[AI-14] EmeraldMind: A Knowledge Graph-Augmented Framework for Greenwashing Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决企业可持续发展声明中“绿色洗牌”(greenwashing)问题,即企业通过误导性陈述夸大其环境责任行为,从而阻碍真实环保进展。解决方案的关键在于提出一个以事实为中心的框架 EmeraldMind,其核心创新是构建了一个领域特定的知识图谱 EmeraldGraph,该图谱从多元的企业 ESG(environmental, social, and governance)报告中提取可验证证据,并与检索增强生成(retrieval-augmented generation)技术融合,使大语言模型能够基于实证进行声明评估。该框架输出以理由为核心的分类结果,提供透明、有依据的判断,并在无法验证时合理拒绝回答,从而在无需微调或重新训练的前提下,显著提升检测准确率、覆盖范围和解释质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11506
作者: Georgios Kaoukis,Ioannis Aris Koufopoulos,Psaroudaki Eleni,Danae Pla Karidi,Evaggelia Pitoura,George Papastefanatos,Panayiotis Tsaparas
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:As AI and web agents become pervasive in decision-making, it is critical to design intelligent systems that not only support sustainability efforts but also guard against misinformation. Greenwashing, i.e., misleading corporate sustainability claims, poses a major challenge to environmental progress. To address this challenge, we introduce EmeraldMind, a fact-centric framework integrating a domain-specific knowledge graph with retrieval-augmented generation to automate greenwashing detection. EmeraldMind builds the EmeraldGraph from diverse corporate ESG (environmental, social, and governance) reports, surfacing verifiable evidence, often missing in generic knowledge bases, and supporting large language models in claim assessment. The framework delivers justification-centric classifications, presenting transparent, evidence-backed verdicts and abstaining responsibly when claims cannot be verified. Experiments on a new greenwashing claims dataset demonstrate that EmeraldMind achieves competitive accuracy, greater coverage, and superior explanation quality compared to generic LLMs, without the need for fine-tuning or retraining.
zh
[AI-15] BAID: A Benchmark for Bias Assessment of AI Detectors AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前生成式 AI 文本检测工具在教育和职业场景中广泛应用时存在的系统性偏见问题,尤其是对英语学习者(English Language Learners, ELLs)等边缘群体的不公平检测表现。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个名为 BAID 的综合性评估框架,该框架包含超过 20 万条覆盖七大类社会语言学特征(如人口统计学、年龄、教育年级、方言、正式程度、政治倾向和主题)的数据样本,并通过精心设计的提示生成反映特定子群体写作风格的合成文本,从而系统性地评估四个主流开源 AI 文本检测器的性能差异。研究发现这些检测器在低资源或代表性不足群体中的召回率显著偏低,凸显了在部署前进行偏差感知评估的重要性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11505
作者: Priyam Basu,Yunfeng Zhang,Vipul Raheja
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Accepted at the workshop on Agentic AI Benchmarks and Applications for Enterprise Tasks at AAAI 2026
Abstract:AI-generated text detectors have recently gained adoption in educational and professional contexts. Prior research has uncovered isolated cases of bias, particularly against English Language Learners (ELLs) however, there is a lack of systematic evaluation of such systems across broader sociolinguistic factors. In this work, we propose BAID, a comprehensive evaluation framework for AI detectors across various types of biases. As a part of the framework, we introduce over 200k samples spanning 7 major categories: demographics, age, educational grade level, dialect, formality, political leaning, and topic. We also generated synthetic versions of each sample with carefully crafted prompts to preserve the original content while reflecting subgroup-specific writing styles. Using this, we evaluate four open-source state-of-the-art AI text detectors and find consistent disparities in detection performance, particularly low recall rates for texts from underrepresented groups. Our contributions provide a scalable, transparent approach for auditing AI detectors and emphasize the need for bias-aware evaluation before these tools are deployed for public use.
zh
[AI-16] owards Privacy-Preserving Code Generation: Differentially Private Code Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)在代码领域应用中的隐私风险问题,即大型代码语言模型(CodeLLMs)在微调过程中可能无意中记忆并复现训练数据中的代码片段,从而引发隐私泄露和知识产权侵权风险。为缓解这一问题,论文提出采用差分隐私(Differential Privacy, DP)技术对 CodeLLMs 的训练过程进行保护,其关键在于通过在训练中添加校准噪声,在保障个体数据点隐私的同时维持模型的代码生成能力。实验表明,DP 能显著降低各类代码片段的 memorization 风险,尤其对高风险片段效果最明显,且仅轻微增加困惑度(perplexity),不损害甚至可提升代码生成性能,同时不影响训练效率与能耗,具备实际部署可行性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11482
作者: Melih Catal,Pooja Rani,Harald C. Gall
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models specialized for code (CodeLLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating code snippets, documentation, and test cases. However, despite their promising capabilities, CodeLLMs can inadvertently memorize and reproduce snippets from their training data, which poses risks of privacy breaches and intellectual property violations. These risks restrict the deployment of CodeLLMs in sensitive domains and limit their training datasets to publicly available sources. To mitigate the memorization risk without compromising their task performance, we apply Differential Privacy (DP) to CodeLLMs. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive study that systematically evaluates the effectiveness of DP in CodeLLMs. DP adds calibrated noise to the training process to protect individual data points while still allowing the model to learn useful patterns. To this end, we first identify and understand the driving reasons of the memorization behaviour of the CodeLLMs during their fine-tuning. Then, to address this issue, we empirically evaluate the effect of DP on mitigating memorization while preserving code generation capabilities. Our findings show that DP substantially reduces memorization in CodeLLMs across all the tested snippet types. The snippet types most prone to memorization are also the most effectively mitigated by DP. Furthermore, we observe that DP slightly increases perplexity but preserves, and can even enhance, the code generation capabilities of CodeLLMs, which makes it feasible to apply DP in practice without significantly compromising model utility. Finally, we analyze the impact of DP on training efficiency and energy consumption, finding that DP does not significantly affect training time or energy usage, making it a practical choice for privacy-preserving CodeLLMs training.
zh
[AI-17] General-purpose AI models can generate actionable knowledge on agroecological crop protection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式人工智能(Generative AI)在农业食品科学领域应用尚不明确的问题,特别是其在农林生态作物保护知识生成中的准确性与实用性问题。研究通过对比基于网络数据的大型语言模型(LLM)DeepSeek与非接地版本的ChatGPT,在九种全球限制性害虫、杂草和植物病害上的科学知识生成能力,评估其事实准确性、数据一致性及知识广度。关键解决方案在于验证了DeepSeek相较ChatGPT能覆盖更广泛的文献库并报告更多生物防治剂或管理方案,从而提升效果估计的准确性、实验室到田间的一致性以及对害虫种类和管理策略影响的现实性;尽管两者均存在幻觉现象(如虚构代理或参考文献、误用分类学名称等),但结合严格的人工审核后,LLMs仍可作为支持农场级决策和激发科学创造力的有力工具。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11474
作者: Kris A.G. Wyckhuys
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY); Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
备注: 33 pages, 3 figures, 3 tables, 1 supplementary table
Abstract:Generative artificial intelligence (AI) offers potential for democratizing scientific knowledge and converting this to clear, actionable information, yet its application in agri-food science remains unexplored. Here, we verify the scientific knowledge on agroecological crop protection that is generated by either web-grounded or non-grounded large language models (LLMs), i.e., DeepSeek versus the free-tier version of ChatGPT. For nine globally limiting pests, weeds, and plant diseases, we assessed the factual accuracy, data consistency, and breadth of knowledge or data completeness of each LLM. Overall, DeepSeek consistently screened a 4.8-49.7-fold larger literature corpus and reported 1.6-2.4-fold more biological control agents or management solutions than ChatGPT. As a result, DeepSeek reported 21.6% higher efficacy estimates, exhibited greater laboratory-to-field data consistency, and showed more realistic effects of pest identity and management tactics. However, both models hallucinated, i.e., fabricated fictitious agents or references, reported on implausible ecological interactions or outcomes, confused old and new scientific nomenclatures, and omitted data on key agents or solutions. Despite these shortcomings, both LLMs correctly reported low-resolution efficacy trends. Overall, when paired with rigorous human oversight, LLMs may pose a powerful tool to support farm-level decision-making and unleash scientific creativity.
zh
[AI-18] hree methods one problem: Classical and AI approaches to no-three-in-line
【速读】:该论文旨在解决经典的“无三点共线”(No-Three-In-Line)问题,即在 $ n \times n $ 网格上放置尽可能多的点,使得任意三点不共线。这一问题属于组合几何领域,具有理论与应用双重意义。论文的关键在于首次系统性地比较了传统优化方法(如整数线性规划,ILP)与人工智能方法(包括基于Transformer的PatternBoost和近端策略优化,PPO)在该问题上的表现:ILP可保证小规模网格(至19×19)的最优解,而AI方法在较小规模(如14×14)展现出高效率与良好逼近能力,尤其PatternBoost实现96%测试损失降低,PPO在10×10网格中达到完美解但受限于约束违反在更大网格失效。结果表明,经典优化仍是获取精确解的核心手段,而AI方法提供了高效近似路径,未来混合策略最具潜力用于扩展至更大问题规模。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11469
作者: Pranav Ramanathan,Thomas Prellberg,Matthew Lewis,Prathamesh Dinesh Joshi,Raj Abhijit Dandekar,Rajat Dandekar,Sreedath Panat
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The No-Three-In-Line problem asks for the maximum number of points that can be placed on an n by n grid with no three collinear, representing a famous problem in combinatorial geometry. While classical methods like Integer Linear Programming (ILP) guarantee optimal solutions, they face exponential scaling with grid size, and recent advances in machine learning offer promising alternatives for pattern-based approximation. This paper presents the first systematic comparison of classical optimization and AI approaches to this problem, evaluating their performance against traditional algorithms. We apply PatternBoost transformer learning and reinforcement learning (PPO) to this problem for the first time, comparing them against ILP. ILP achieves provably optimal solutions up to 19 by 19 grids, while PatternBoost matches optimal performance up to 14 by 14 grids with 96% test loss reduction. PPO achieves perfect solutions on 10 by 10 grids but fails at 11 by 11 grids, where constraint violations prevent valid configurations. These results demonstrate that classical optimization remains essential for exact solutions while AI methods offer competitive performance on smaller instances, with hybrid approaches presenting the most promising direction for scaling to larger problem sizes.
zh
[AI-19] Motif-2-12.7B-Reasoning : A Practitioners Guide to RL Training Recipes
【速读】:该论文旨在解决开源模型在复杂推理和长上下文理解能力上与闭源前沿模型之间的性能差距问题,尤其针对推理适应过程中常见的模型坍塌(model collapse)和训练不稳定性挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一套系统性、可复现的训练方案,涵盖系统级优化、数据策略与算法改进:一是通过混合并行与内核级优化实现64K token长上下文的高效内存管理;二是采用两阶段监督微调(Supervised Fine-Tuning, SFT)策略,利用经过验证的对齐合成数据缓解分布偏移;三是构建鲁棒的强化学习微调(Reinforcement Learning Fine-Tuning, RLFT)流程,通过难度感知的数据过滤和混合策略轨迹复用稳定训练过程。实证表明,该方法使12.7B参数模型在数学、编程和代理类基准测试中达到远超其参数规模的性能表现,为在实际算力约束下提升推理能力提供了可行路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11463
作者: Junghwan Lim,Sungmin Lee,Dongseok Kim,Taehyun Kim,Eunhwan Park,Jeesoo Lee,Jeongdoo Lee,Junhyeok Lee,Wai Ting Cheung,Dahye Choi,Minsu Ha,Jaeheui Her,Jaeyeon Huh,Hanbin Jung,Changjin Kang,Beomgyu Kim,Minjae Kim,Taewhan Kim,Youngrok Kim,Hyukjin Kweon,Haesol Lee,Kungyu Lee,Dongpin Oh,Yeongjae Park,Bokki Ryu,Dongjoo Weon
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:We introduce Motif-2-12.7B-Reasoning, a 12.7B parameter language model designed to bridge the gap between open-weight systems and proprietary frontier models in complex reasoning and long-context understanding. Addressing the common challenges of model collapse and training instability in reasoning adaptation, we propose a comprehensive, reproducible training recipe spanning system, data, and algorithmic optimizations. Our approach combines memory-efficient infrastructure for 64K-token contexts using hybrid parallelism and kernel-level optimizations with a two-stage Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) curriculum that mitigates distribution mismatch through verified, aligned synthetic data. Furthermore, we detail a robust Reinforcement Learning Fine-Tuning (RLFT) pipeline that stabilizes training via difficulty-aware data filtering and mixed-policy trajectory reuse. Empirical results demonstrate that Motif-2-12.7B-Reasoning achieves performance comparable to models with significantly larger parameter counts across mathematics, coding, and agentic benchmarks, offering the community a competitive open model and a practical blueprint for scaling reasoning capabilities under realistic compute constraints.
zh
[AI-20] Agent Balance: Backbone-then-Topology Design for Cost-Effective Multi-Agent Systems under Budget Constraints
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大规模多智能体系统(Multi-Agent System, MAS)在实际部署中因缺乏对显式令牌成本(token-cost)和延迟(latency)预算的建模与优化,而导致的效率低下问题。现有方法通常优先设计通信拓扑结构,忽视了预算约束下的最优资源配置,从而在预算紧约束下难以实现最佳性价比。其解决方案的关键在于提出 AgentBalance 框架,采用“骨干先行、拓扑后置”的设计范式:首先通过 LLM 池构建、选择及角色-骨干匹配机制生成具有异构骨干(backbone)的智能体;随后基于代理表征学习、门控机制和延迟感知的拓扑合成策略,动态调整智能体间通信结构,在满足预设成本与延迟预算的前提下最大化任务性能。实验表明,AgentBalance 在多个基准测试中实现了最高达 10% 和 22% 的性能提升,并展现出良好的泛化能力与插件式兼容性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11426
作者: Shuowei Cai,Yansong Ning,Hao Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based multi-agent systems (MAS) are becoming indispensable building blocks for web-scale applications such as web search, social network analytics, and online customer support, where cost-effectiveness is increasingly the primary constraint for large-scale deployment. While recent work improves MAS cost-effectiveness by shaping inter-agent communication topologies and selecting agent backbones, it rarely models and optimizes under explicit token-cost and latency budgets that reflect deployment constraints. This often leads to topology-first designs and suboptimal cost-effectiveness when budgets are binding. We present AgentBalance, a framework for constructing cost-effective MAS under explicit token-cost and latency budgets via a backbone-then-topology design. AgentBalance first performs backbone-oriented agent generation, constructing agents with heterogeneous backbones through LLM pool construction, pool selection, and role-backbone matching. It then performs adaptive MAS topology generation, guiding inter-agent communication via agent representation learning, gating, and latency-aware topology synthesis. Experiments on benchmarks with 14 candidate LLM backbones show that AgentBalance achieves up to 10% and 22% performance gains under matched token-cost and latency budgets, respectively, and yields strong AUC on performance-versus-budget curves across benchmarks. AgentBalance also functions as a plug-in for existing MAS, improving performance under the same token-cost and latency constraints, and it generalizes well to unseen LLMs for practical, budget-aware deployment. Code: this https URL
zh
[AI-21] owards Trustworthy Multi-Turn LLM Agents via Behavioral Guidance AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在多轮任务中行为缺乏可靠性与可验证性的问题。针对这一挑战,作者提出了一种基于强化学习形式化环境的代理任务完成框架,其核心在于通过三个协同演化的组件实现可控且可信的行为:一是轻量级任务分析器(task profiler),用于动态选择推理与生成策略;二是推理模块,学习可观测状态到动作的可验证映射关系;三是生成模块,通过验证或确定性合成确保输出满足约束条件。该框架使代理在与环境交互过程中逐步优化行为,从而提升整体系统的可信度与可控性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11421
作者: Gonca Gürsun
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted to AAAI 2026 Workshop on Trust and Control in Agentic AI (TrustAgent)
Abstract:Large Language Models demonstrate strong reasoning and generation abilities, yet their behavior in multi-turn tasks often lacks reliability and verifiability. We present a task completion framework that enables LLM-based agents to act under explicit behavioral guidance in environments described by reinforcement learning formalisms with defined observation, action, and reward signals. The framework integrates three components: a lightweight task profiler that selects reasoning and generation strategies, a reasoning module that learns verifiable observation - action mappings, and a generation module that enforces constraint-compliant outputs through validation or deterministic synthesis. We show that as the agent interacts with the environment, these components co-evolve, yielding trustworthy behavior. Comments: Accepted to AAAI 2026 Workshop on Trust and Control in Agentic AI (TrustAgent) Subjects: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2512.11421 [cs.AI] (or arXiv:2512.11421v1 [cs.AI] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11421 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-22] REMODEL-LLM : Transforming C code to Java using LLM s
【速读】:该论文旨在解决将C语言代码自动翻译为Java代码这一难题,其核心挑战源于两种语言在编程范式(过程式 vs. 面向对象)、内存管理模型(手动指针 vs. 垃圾回收)以及数据类型兼容性等方面的本质差异。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种新颖的混合流水线方法:首先利用抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Trees, ASTs)对源代码进行语义分解,再结合高度受限的基于规则的提示策略(rule-based prompting strategy),以提升翻译准确性。实验表明,尽管多数小型量化大语言模型(LLMs,<20亿参数)在基础语法生成上表现失败,仅有少数模型(如phi4、deepseek-coder-v2和codeqwen)能通过超过50%的测试用例,但仍无法处理函数指针、sizeof等复杂C特性,揭示了当前量化模型在深层语义推理上的局限性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11402
作者: Aryan Gupta,Y. Raghu Reddy
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The automated translation of C code to Java code is a notoriously difficult task, fraught with challenges stemming from fundamental paradigm shifts (procedural vs. Object Oriented), memory models (manual pointers vs. Garbage Collection), and incompatible data types. This paper investigates the efficacy of 19 small, quantized LLMs (under 20 billion parameters) for the C to Java translation task. We use a novel, hybrid pipeline that leverages Abstract Syntax Trees (ASTs) for semantic decomposition and employs a highly constrained, rule based prompting strategy. The results are stark: a clear multi tiered performance divide emerged. The vast majority of models (Tier 3, e.g., llama3.1, gemma3, starcoder2) failed 100% of the tests, proving incapable of generating even basic, runnable Java boilerplate. A small middle tier (Tier 2, e.g., mistral-nemo and mistral) produced runnable code but was plagued by dangerous semantic failures and wrong translations. Only three models (Tier 1: phi4, deepseek-coder-v2, codeqwen) proved viable, passing over 50% of the test suite. Even these top models failed on the most complex C concepts, such as function pointers, sizeof, and enum logic, revealing a hard ceiling for the reasoning capabilities of current quantized models.
zh
[AI-23] CAPTURE: A Benchmark and Evaluation for LVLMs in CAPTCHA Resolving
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前大型视觉语言模型(Large Visual Language Models, LVLMs)在验证码(CAPTCHA)识别任务中缺乏全面、系统性评估基准的问题。现有基准因研究目标不同而定制化程度高,导致无法覆盖所有主流CAPTCHA类型,尤其缺少专为LVLM设计的评测体系。解决方案的关键在于提出首个面向LVLM的专用CAPTCHA基准——CAPTURE(CAPTCHA for Testing Under Real-world Experiments),其核心创新包括:涵盖4类主类型和25种子类型的多样化数据集(来自31个厂商),大规模样本量,以及专为LVLM优化的标签体系,从而实现了对LVLM在真实场景下视觉理解与推理能力的多维、深入评估。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11323
作者: Jianyi Zhang,Ziyin Zhou,Xu Ji,Shizhao Liu,Zhangchi Zhao
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Benefiting from strong and efficient multi-modal alignment strategies, Large Visual Language Models (LVLMs) are able to simulate human visual and reasoning capabilities, such as solving CAPTCHAs. However, existing benchmarks based on visual CAPTCHAs still face limitations. Previous studies, when designing benchmarks and datasets, customized them according to their research objectives. Consequently, these benchmarks cannot comprehensively cover all CAPTCHA types. Notably, there is a dearth of dedicated benchmarks for LVLMs. To address this problem, we introduce a novel CAPTCHA benchmark for the first time, named CAPTURE CAPTCHA for Testing Under Real-world Experiments, specifically for LVLMs. Our benchmark encompasses 4 main CAPTCHA types and 25 sub-types from 31 vendors. The diversity enables a multi-dimensional and thorough evaluation of LVLM performance. CAPTURE features extensive class variety, large-scale data, and unique LVLM-tailored labels, filling the gaps in previous research in terms of data comprehensiveness and labeling pertinence. When evaluated by this benchmark, current LVLMs demonstrate poor performance in solving CAPTCHAs.
zh
[AI-24] Condensation-Concatenation Framework for Dynamic Graph Continual Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决动态图场景下图神经网络(Graph Neural Networks, GNNs)因结构持续变化而导致的灾难性遗忘问题,尤其关注拓扑结构变动对已有节点的影响。现有方法在处理动态图时忽视了历史节点在结构更新后的表征退化问题,导致模型性能下降。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于压缩-拼接的持续学习框架(Condensation-Concatenation-based Continual Learning, CCC):首先将历史图快照压缩为紧凑的语义表示,同时保留原始标签分布和拓扑特性;随后选择性地将这些历史嵌入与当前图表示拼接,以增强模型对历史知识的记忆能力。此外,论文还改进了遗忘度量(Forgetting Measure, FM),通过量化因结构更新导致的已有节点预测性能下降来更准确评估遗忘程度,从而提升模型在动态图上的持续学习能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11317
作者: Tingxu Yan,Ye Yuan
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Dynamic graphs are prevalent in real-world scenarios, where continuous structural changes induce catastrophic forgetting in graph neural networks (GNNs). While continual learning has been extended to dynamic graphs, existing methods overlook the effects of topological changes on existing nodes. To address it, we propose a novel framework for continual learning on dynamic graphs, named Condensation-Concatenation-based Continual Learning (CCC). Specifically, CCC first condenses historical graph snapshots into compact semantic representations while aiming to preserve the original label distribution and topological properties. Then it concatenates these historical embeddings with current graph representations selectively. Moreover, we refine the forgetting measure (FM) to better adapt to dynamic graph scenarios by quantifying the predictive performance degradation of existing nodes caused by structural updates. CCC demonstrates superior performance over state-of-the-art baselines across four real-world datasets in extensive experiments.
zh
[AI-25] AI Autonomy or Human Dependency? Defining the Boundary in Responsible AI with the α-Coefficient
【速读】:该论文试图解决当前人工智能(Artificial Intelligence, AI)系统中存在的结构性缺陷问题,即“人在回路”(Human-in-the-Loop, HITL)模型被滥用以掩盖系统对人类劳动的实质性依赖,这种现象被称为“人替代AI”(Human-Instead-of-AI, HISOAI)。HISOAI不仅构成伦理失范,也导致经济上的不可持续性,因为人类员工沦为隐性的操作后备,而非战略合作者。解决方案的关键在于提出“AI优先、人类赋能”(AI-First, Human-Empowered, AFHE)范式,其核心是引入一个可量化的指标——AI自主系数(AI Autonomy Coefficient, alpha),用以衡量AI在无强制人工干预下完成任务的比例,并通过AFHE部署算法(AFHE Deployment Algorithm)确保系统在离线和影子测试中均达到预设alpha阈值,从而实现技术设计上的结构分离,使人类角色聚焦于高价值任务如伦理监管与模型调优,最终推动行业向可验证的自主性架构演进。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11295
作者: Nattaya Mairittha,Gabriel Phorncharoenmusikul,Sorawit Worapradidth
机构: 未知
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The integrity of contemporary AI systems is undermined by a critical design flaw: the misappropriation of Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) models to mask systems that are fundamentally reliant on human labor. We term this structural reliance Human-Instead-of-AI (HISOAI). HISOAI systems represent an ethical failure and an unsustainable economic dependency, where human workers function as hidden operational fallbacks rather than strategic collaborators. To rectify this, we propose the AI-First, Human-Empowered (AFHE) paradigm. AFHE mandates a technological design where the AI component must achieve a minimum, quantifiable level of functional independence prior to deployment. This standard is formalized through the AI Autonomy Coefficient (alpha), a metric that determines the proportion of tasks that the AI successfully processes without mandatory human substitution. We introduce the AFHE Deployment Algorithm, an algorithmic gate that requires the system to meet a specified alpha threshold across both offline and shadow testing. By enforcing this structural separation, the AFHE framework redefines the human’s role to focus exclusively on high-value tasks, including ethical oversight, boundary pushing, and strategic model tuning, thereby ensuring true system transparency and operational independence. This work advocates for a critical shift toward metric-driven, structurally sound AI architecture, moving the industry beyond deceptive human dependency toward verifiable autonomy.
zh
[AI-26] Words to Describe What Im Feeling: Exploring the Potential of AI Agents for High Subjectivity Decisions in Advance Care Planning
【速读】:该论文试图解决在高级照护计划(Advance Care Planning, ACP)中,因患者丧失表达能力、老龄化加剧及照护者网络萎缩所导致的决策支持不足问题。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个可训练的代理智能体(agent),通过多轮工作坊与15名参与者互动,使其学习并代表个体在高风险、高主观性医疗决策中的偏好。研究发现,这类代理应作为个人倡导者(personal advocate)角色,在长期交互中建立人机互理解(mutual intelligibility),从而实现AI在ACP中从工具向伙伴关系的转变。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11276
作者: Kellie Yu Hui Sim,Pin Sym Foong,Chenyu Zhao,Melanie Yi Ning Quek,Swarangi Subodh Mehta,Kenny Tsu Wei Choo
机构: 未知
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 31 pages, 10 figures
Abstract:Serious illness can deprive patients of the capacity to speak for themselves. As populations age and caregiver networks shrink, the need for reliable support in Advance Care Planning (ACP) grows. To probe this fraught design space of using proxy agents for high-risk, high-subjectivity decisions, we built an experience prototype (\acpagent) and asked 15 participants in 4 workshops to train it to be their personal proxy in ACP decisions. We analysed their coping strategies and feature requests and mapped the results onto axes of agent autonomy and human control. Our findings argue for a potential new role of AI in ACP where agents act as personal advocates for individuals, building mutual intelligibility over time. We conclude with design recommendations to balance the risks and benefits of such an agent.
zh
[AI-27] riFlow: A Progressive Multi-Agent Framework for Intelligent Trip Planning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现实世界行程规划中,大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)代理在约束满足、工具协同和效率方面存在的不足,这些问题常导致生成的行程方案不可行或成本过高。解决方案的关键在于提出TriFlow框架,其核心是一个三阶段渐进式多智能体流程:检索(retrieval)、规划(planning)与治理(governance)。该设计通过逐步缩小搜索空间、借助规则与LLM协作构建符合约束的行程,并采用有界迭代优化确保全局可行性与个性化,从而在TravelPlanner和TripTailor基准上实现91.1%和97%的最终通过率,且运行时间效率提升超过10倍。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11271
作者: Yuxing Chen,Basem Suleiman,Qifan Chen
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 4 pages, 3 figures
Abstract:Real-world trip planning requires transforming open-ended user requests into executable itineraries under strict spatial, temporal, and budgetary constraints while aligning with user preferences. Existing LLM-based agents struggle with constraint satisfaction, tool coordination, and efficiency, often producing infeasible or costly plans. To address these limitations, we present TriFlow, a progressive multi-agent framework that unifies structured reasoning and language-based flexibility through a three-stage pipeline of retrieval, planning, and governance. By this design, TriFlow progressively narrows the search space, assembles constraint-consistent itineraries via rule-LLM collaboration, and performs bounded iterative refinement to ensure global feasibility and personalisation. Evaluations on TravelPlanner and TripTailor benchmarks demonstrated state-of-the-art results, achieving 91.1% and 97% final pass rates, respectively, with over 10x runtime efficiency improvement compared to current SOTA.
zh
[AI-28] A-LAMP: Agent ic LLM -Based Framework for Automated MDP Modeling and Policy Generation NEURIPS2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决将自然语言任务描述自动转化为可执行的强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)环境与策略代理的问题,这一过程通常涉及建模误差、代码脆弱性和目标错位等挑战,阻碍了策略训练的有效性。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于智能体的大语言模型(Agentic Large Language Model, LLM)框架——A-LAMP,其通过将建模、编码和训练分解为可验证的阶段,确保整个流程中的语义一致性;该框架不仅能自动生成符合任务要求的马尔可夫决策过程(Markov Decision Process, MDP)形式化表示与训练策略,还在经典控制和定制RL领域均展现出优于单一先进LLM模型的策略生成能力,且轻量级版本即可逼近大型模型性能,体现了其高效性与可靠性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11270
作者: Hong Je-Gal,Chan-Bin Yi,Hyun-Suk Lee
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: NeurIPS 2025 Workshop: Multi-Turn Interactions in Large Language Models. 26 pages, 8 figures
Abstract:Applying reinforcement learning (RL) to real-world tasks requires converting informal descriptions into a formal Markov decision process (MDP), implementing an executable environment, and training a policy agent. Automating this process is challenging due to modeling errors, fragile code, and misaligned objectives, which often impede policy training. We introduce an agentic large language model (LLM)-based framework for automated MDP modeling and policy generation (A-LAMP), that automatically translates free-form natural language task descriptions into an MDP formulation and trained policy. The framework decomposes modeling, coding, and training into verifiable stages, ensuring semantic alignment throughout the pipeline. Across both classic control and custom RL domains, A-LAMP consistently achieves higher policy generation capability than a single state-of-the-art LLM model. Notably, even its lightweight variant, which is built on smaller language models, approaches the performance of much larger models. Failure analysis reveals why these improvements occur. In addition, a case study also demonstrates that A-LAMP generates environments and policies that preserve the task’s optimality, confirming its correctness and reliability.
zh
[AI-29] A Scalable Multi-GPU Framework for Encrypted Large-Model Inference
【速读】:该论文旨在解决加密人工智能(Encrypted AI)在大规模模型推理中面临的性能瓶颈问题,尤其是基于全同态加密(Fully Homomorphic Encryption, FHE)的计算效率低、内存占用高以及难以扩展至多GPU环境的问题。其核心挑战在于:FHE运算本身极其耗时,现有ASIC方案虽能加速但制造成本高昂且可及性差;而通用GPU平台因缺乏针对性优化,难以达到ASIC级性能,尤其在处理如Llama3-8B等大模型时,面临TB级内存需求与复杂计算并行化难题。解决方案的关键在于提出Cerium框架,该框架集成领域特定语言(DSL)、优化编译器与运行时系统,通过引入新型中间表示(IR)构造、稀疏多项式表示、内存高效的存储布局及通信感知的并行策略,实现对FHE推理任务的自动高性能GPU内核生成与跨多GPU协同调度,从而首次在GPU平台上实现低于10毫秒的bootstrapping操作,并成功完成BERT-Base和Llama3-8B的加密推理,性能媲美甚至超越当前最先进的FHE ASIC方案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11269
作者: Siddharth Jayashankar,Joshua Kim,Michael B. Sullivan,Wenting Zheng,Dimitrios Skarlatos
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Encrypted AI using fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) provides strong privacy guarantees; but its slow performance has limited practical deployment. Recent works proposed ASICs to accelerate FHE, but require expensive advanced manufacturing processes that constrain their accessibility. GPUs are a far more accessible platform, but achieving ASIC-level performance using GPUs has remained elusive. Furthermore, state-of-the-art approaches primarily focus on small models that fit comfortably within a single device. Supporting large models such as LLMs in FHE introduces a dramatic increase in computational complexity that requires optimized GPU kernels, along with managing terabyte-scale memory footprints that far exceed the capacity of a single GPU. This paper presents Cerium, a multi-GPU framework for FHE inference on large models. Cerium integrates a domain-specific language, an optimizing compiler, and a runtime system to automatically generate high-performance GPU kernels, manage terabyte-scale memory footprints, and parallelize computation across multiple GPUs. It introduces new IR constructs, compiler passes, sparse polynomial representations, memory-efficient data layouts, and communication-aware parallelization techniques that together enable encrypted inference for models ranging from small CNNs to Llama3-8B. We build Cerium on NVIDIA GPUs and demonstrate significant performance gains. For small models, Cerium outperforms expert-written hand-optimized GPU libraries by up to 2.25 times. Cerium achieves performance competitive with state-of-the-art FHE ASICs, outright matching prior FHE ASIC CraterLake. It is the first GPU system to execute bootstrapping in under 10 milliseconds, achieving 7.5 milliseconds, and is the first to demonstrate encrypted inference for BERT-Base and Llama3-8B in 8 seconds and 134 seconds, respectively.
zh
[AI-30] A Simple Generalisation of the Implicit Dynamics of In-Context Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前关于上下文学习(In-context Learning, ICL)的理论分析多依赖于简化模型和理想化数据设置的问题,试图建立更贴近实际Transformer架构的理论框架。其解决方案的关键在于对Dherin等(2025)提出的抽象Transformer块隐式更新前馈网络权重机制进行了 generalize,扩展至所有序列位置(除最后一个外)、任意Transformer块(不仅限于第一层),并引入更现实的残差连接结构(包括层归一化)。这一理论拓展使得对ICL中隐式参数更新的理解更加全面,并通过简单线性回归任务的实证验证了其有效性,为后续在大规模模型上的验证提供了理论基础。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11255
作者: Francesco Innocenti,El Mehdi Achour
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 18 pages, 9 figures
Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) refers to the ability of a model to learn new tasks from examples in its input without any parameter updates. In contrast to previous theories of ICL relying on toy models and data settings, recently it has been shown that an abstraction of a transformer block can be seen as implicitly updating the weights of its feedforward network according to the context (Dherin et al., 2025). Here, we provide a simple generalisation of this result for (i) all sequence positions beyond the last, (ii) any transformer block beyond the first, and (iii) more realistic residual blocks including layer normalisation. We empirically verify our theory on simple in-context linear regression tasks and investigate the relationship between the implicit updates related to different tokens within and between blocks. These results help to bring the theory of Dherin et al. (2025) even closer to practice, with potential for validation on large-scale models.
zh
[AI-31] Fast EXP3 Algorithms
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多臂赌博机(Multi-armed Bandit)框架下指数加权信用分配算法(EXP3)在实际应用中时间复杂度较高的问题,尤其是在每轮决策中需要线性时间开销的限制。其解决方案的关键在于提出可在每轮常数时间内实现的EXP3变体,并设计更实用的算法,在保证理论性能的同时显著降低计算复杂度,同时系统分析了不同算法在遗憾边界(regret bounds)与时间复杂度之间的权衡关系。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11201
作者: Ryoma Sato,Shinji Ito
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Data Structures and Algorithms (cs.DS)
备注:
Abstract:We point out that EXP3 can be implemented in constant time per round, propose more practical algorithms, and analyze the trade-offs between the regret bounds and time complexities of these algorithms.
zh
[AI-32] Deep Learning–Accelerated Multi-Start Large Neighborhood Search for Real-time Freight Bundling
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在线货运交易平台(Online Freight Exchange System, OFEX)中运输任务组合打包的效率瓶颈问题,具体建模为多商品一对一取送货选择性旅行商问题(multi-commodity one-to-one pickup-and-delivery selective traveling salesperson problem, m1-PDSTSP),目标是在容量、优先级和路径长度约束下优化收益驱动的货运组合打包。解决方案的关键在于提出一种学习加速的混合搜索流水线:将基于Transformer神经网络的构造策略与创新的多起点大邻域搜索(Multi-Start Large Neighborhood Search, MSLNS)元启发式算法相结合,并嵌套于滚动时域框架中,通过在亚秒级延迟内反复冻结市场快照并求解,实现低延迟高质量推理与改进搜索的协同优化;其中,深度学习构造器提供的优质初始解种子显著提升了MSLNS对解空间的探索效率,从而在保持计算时间可比的前提下,使总收益最优性间隙小于2%,是首个证明深度神经网络构造器能可靠为多起点改进启发式算法提供高质量种子的工作。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11187
作者: Haohui Zhang,Wouter van Heeswijk,Xinyu Hu,Neil Yorke-Smith,Martijn Mes
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Online Freight Exchange Systems (OFEX) play a crucial role in modern freight logistics by facilitating real-time matching between shippers and carrier. However, efficient combinatorial bundling of transporation jobs remains a bottleneck. We model the OFEX combinatorial bundling problem as a multi-commodity one-to-one pickup-and-delivery selective traveling salesperson problem (m1-PDSTSP), which optimizes revenue-driven freight bundling under capacity, precedence, and route-length constraints. The key challenge is to couple combinatorial bundle selection with pickup-and-delivery routing under sub-second latency. We propose a learning–accelerated hybrid search pipeline that pairs a Transformer Neural Network-based constructive policy with an innovative Multi-Start Large Neighborhood Search (MSLNS) metaheuristic within a rolling-horizon scheme in which the platform repeatedly freezes the current marketplace into a static snapshot and solves it under a short time budget. This pairing leverages the low-latency, high-quality inference of the learning-based constructor alongside the robustness of improvement search; the multi-start design and plausible seeds help LNS to explore the solution space more efficiently. Across benchmarks, our method outperforms state-of-the-art neural combinatorial optimization and metaheuristic baselines in solution quality with comparable time, achieving an optimality gap of less than 2% in total revenue relative to the best available exact baseline method. To our knowledge, this is the first work to establish that a Deep Neural Network-based constructor can reliably provide high-quality seeds for (multi-start) improvement heuristics, with applicability beyond the \textitm1-PDSTSP to a broad class of selective traveling salesperson problems and pickup and delivery problems.
zh
[AI-33] CORL: Reinforcement Learning of MILP Policies Solved via Branch and Bound
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统混合整数线性规划(Mixed Integer Linear Programming, MILP)模型在实际应用中因难以准确建模随机现实问题而导致决策质量不佳的问题。现有基于监督学习的方法通常依赖于真实最优决策作为标签,并使用代理梯度替代MILP的不可微分特性,限制了其在复杂场景中的适用性。本文提出了一种名为CORL(Combinatorial Optimization via Reinforcement Learning)的端到端框架,其关键在于将通过分支定界(Branch and Bound, BB)求解的MILP视为一个可微分的随机策略(stochastic policy),从而使其能够直接通过强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)进行优化,无需显式获取最优决策或依赖梯度代理,仅需真实世界数据即可提升操作性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11169
作者: Akhil S Anand,Elias Aarekol,Martin Mziray Dalseg,Magnus Stalhane,Sebastien Gros
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Systems and Control (eess.SY); Optimization and Control (math.OC)
备注:
Abstract:Combinatorial sequential decision making problems are typically modeled as mixed integer linear programs (MILPs) and solved via branch and bound (BB) algorithms. The inherent difficulty of modeling MILPs that accurately represent stochastic real world problems leads to suboptimal performance in the real world. Recently, machine learning methods have been applied to build MILP models for decision quality rather than how accurately they model the real world problem. However, these approaches typically rely on supervised learning, assume access to true optimal decisions, and use surrogates for the MILP gradients. In this work, we introduce a proof of concept CORL framework that end to end fine tunes an MILP scheme using reinforcement learning (RL) on real world data to maximize its operational performance. We enable this by casting an MILP solved by BB as a differentiable stochastic policy compatible with RL. We validate the CORL method in a simple illustrative combinatorial sequential decision making example.
zh
[AI-34] MiniScope: A Least Privilege Framework for Authorizing Tool Calling Agents
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI (Generative AI) 中工具调用代理(tool calling agents)在访问用户敏感服务时因大语言模型(LLM)固有不可靠性而引发的安全风险问题。现有方法要么依赖需安全专业知识的手动策略,要么将 LLM 置于封闭环路中,缺乏严格的保障。其解决方案的关键在于提出 MiniScope 框架,通过重构反映工具调用之间关系的权限层级结构,并结合移动设备风格的权限模型,自动且严格地实施最小权限原则,从而在保障安全性的同时兼顾易用性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11147
作者: Jinhao Zhu,Kevin Tseng,Gil Vernik,Xiao Huang,Shishir G. Patil,Vivian Fang,Raluca Ada Popa
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Tool calling agents are an emerging paradigm in LLM deployment, with major platforms such as ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini adding connectors and autonomous capabilities. However, the inherent unreliability of LLMs introduces fundamental security risks when these agents operate over sensitive user services. Prior approaches either rely on manually written policies that require security expertise, or place LLMs in the confinement loop, which lacks rigorous security guarantees. We present MiniScope, a framework that enables tool calling agents to operate on user accounts while confining potential damage from unreliable LLMs. MiniScope introduces a novel way to automatically and rigorously enforce least privilege principles by reconstructing permission hierarchies that reflect relationships among tool calls and combining them with a mobile-style permission model to balance security and ease of use. To evaluate MiniScope, we create a synthetic dataset derived from ten popular real-world applications, capturing the complexity of realistic agentic tasks beyond existing simplified benchmarks. Our evaluation shows that MiniScope incurs only 1-6% latency overhead compared to vanilla tool calling agents, while significantly outperforming the LLM based baseline in minimizing permissions as well as computational and operational costs.
zh
[AI-35] Fairness-Regularized Online Optimization with Switching Costs NEURIPS2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在线优化中公平性(fairness)与动作平滑性(action smoothness)难以同时保障的问题,特别是在存在切换成本(switching cost)的场景下。其核心挑战在于长期公平性正则项依赖于整个动作序列,导致传统在线算法无法在问题时长 $ T \to \infty $ 时实现亚线性遗憾或有限竞争比。解决方案的关键是提出 FairOBD(Fairness-regularized Online Balanced Descent)算法:通过引入辅助变量将长期公平性成本分解为一系列在线成本,并利用该辅助变量对在线动作进行正则化以促进公平结果;同时采用新的切换成本建模方法,证明了 FairOBD 在渐近意义上相对于一个带参数约束的最优离线基准具有有界竞争比。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11131
作者: Pengfei Li,Yuelin Han,Adam Wierman,Shaolei Ren
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted by NeurIPS 2025
Abstract:Fairness and action smoothness are two crucial considerations in many online optimization problems, but they have yet to be addressed simultaneously. In this paper, we study a new and challenging setting of fairness-regularized smoothed online convex optimization with switching costs. First, to highlight the fundamental challenges introduced by the long-term fairness regularizer evaluated based on the entire sequence of actions, we prove that even without switching costs, no online algorithms can possibly achieve a sublinear regret or finite competitive ratio compared to the offline optimal algorithm as the problem episode length T increases. Then, we propose FairOBD (Fairness-regularized Online Balanced Descent), which reconciles the tension between minimizing the hitting cost, switching cost, and fairness cost. Concretely, FairOBD decomposes the long-term fairness cost into a sequence of online costs by introducing an auxiliary variable and then leverages the auxiliary variable to regularize the online actions for fair outcomes. Based on a new approach to account for switching costs, we prove that FairOBD offers a worst-case asymptotic competitive ratio against a novel benchmark – the optimal offline algorithm with parameterized constraints – by considering T\to\infty . Finally, we run trace-driven experiments of dynamic computing resource provisioning for socially responsible AI inference to empirically evaluate FairOBD, showing that FairOBD can effectively reduce the total fairness-regularized cost and better promote fair outcomes compared to existing baseline solutions.
zh
[AI-36] In-Context Multi-Objective Optimization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多目标黑箱优化(Multi-objective Black-box Optimization)中的三大挑战:一是传统方法依赖特定代理模型(surrogate)和采集函数(acquisition function),难以迁移;二是现有方法在需要多步规划时表现出短视性(myopic);三是并行或时间敏感场景下存在频繁重拟合带来的计算开销。解决方案的关键在于提出TAMO,一种完全可摊销(fully amortized)、通用的策略网络,基于Transformer架构实现跨任务、跨维度输入与目标的统一建模,通过强化学习预训练以最大化轨迹上的累积超体积改进(hypervolume improvement),并在推理阶段仅需一次前向传播即可生成高质量候选设计,从而彻底消除每任务单独拟合代理模型和设计采集函数的步骤,显著提升效率并保持甚至优于现有方法的帕累托前沿质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11114
作者: Xinyu Zhang,Conor Hassan,Julien Martinelli,Daolang Huang,Samuel Kaski
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
备注:
Abstract:Balancing competing objectives is omnipresent across disciplines, from drug design to autonomous systems. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization is a promising solution for such expensive, black-box problems: it fits probabilistic surrogates and selects new designs via an acquisition function that balances exploration and exploitation. In practice, it requires tailored choices of surrogate and acquisition that rarely transfer to the next problem, is myopic when multi-step planning is often required, and adds refitting overhead, particularly in parallel or time-sensitive loops. We present TAMO, a fully amortized, universal policy for multi-objective black-box optimization. TAMO uses a transformer architecture that operates across varying input and objective dimensions, enabling pretraining on diverse corpora and transfer to new problems without retraining: at test time, the pretrained model proposes the next design with a single forward pass. We pretrain the policy with reinforcement learning to maximize cumulative hypervolume improvement over full trajectories, conditioning on the entire query history to approximate the Pareto frontier. Across synthetic benchmarks and real tasks, TAMO produces fast proposals, reducing proposal time by 50-1000x versus alternatives while matching or improving Pareto quality under tight evaluation budgets. These results show that transformers can perform multi-objective optimization entirely in-context, eliminating per-task surrogate fitting and acquisition engineering, and open a path to foundation-style, plug-and-play optimizers for scientific discovery workflows.
zh
[AI-37] Clip-and-Verify: Linear Constraint-Driven Domain Clipping for Accelerating Neural Network Verification NEURIPS2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决神经网络(Neural Network, NN)验证中分支定界(Branch-and-Bound, BaB)过程效率低下的问题,尤其是在处理大规模网络时,子问题数量庞大且边界松弛导致验证耗时显著增加。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于线性约束驱动的裁剪(Clipping)框架——Clip-and-Verify,其核心创新是利用在边界传播过程中自然产生的线性约束,高效地缩小输入空间中已验证或无关区域,并直接优化网络中间层的边界估计。该方法通过专用GPU计算实现线性约束的快速处理,无需依赖外部求解器,从而显著减少BaB中的子问题数量(最高达96%),同时提升验证精度,在多个基准测试中达到当前最优的验证准确率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11087
作者: Duo Zhou,Jorge Chavez,Hesun Chen,Grani A. Hanasusanto,Huan Zhang
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Optimization and Control (math.OC)
备注: Accepted to NeurIPS 2025
Abstract:State-of-the-art neural network (NN) verifiers demonstrate that applying the branch-and-bound (BaB) procedure with fast bounding techniques plays a key role in tackling many challenging verification properties. In this work, we introduce the linear constraint-driven clipping framework, a class of scalable and efficient methods designed to enhance the efficacy of NN verifiers. Under this framework, we develop two novel algorithms that efficiently utilize linear constraints to 1) reduce portions of the input space that are either verified or irrelevant to a subproblem in the context of branch-and-bound, and 2) directly improve intermediate bounds throughout the network. The process novelly leverages linear constraints that often arise from bound propagation methods and is general enough to also incorporate constraints from other sources. It efficiently handles linear constraints using a specialized GPU procedure that can scale to large neural networks without the use of expensive external solvers. Our verification procedure, Clip-and-Verify, consistently tightens bounds across multiple benchmarks and can significantly reduce the number of subproblems handled during BaB. We show that our clipping algorithms can be integrated with BaB-based verifiers such as \alpha,\beta -CROWN, utilizing either the split constraints in activation-space BaB or the output constraints that denote the unverified input space. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our procedure on a broad range of benchmarks where, in some instances, we witness a 96% reduction in the number of subproblems during branch-and-bound, and also achieve state-of-the-art verified accuracy across multiple benchmarks. Clip-and-Verify is part of the \alpha,\beta -CROWN verifier (this http URL), the VNN-COMP 2025 winner. Code available at this https URL.
zh
[AI-38] KathDB: Explainable Multimodal Database Management System with Human-AI Collaboration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统数据库管理系统(DBMS)在处理多模态数据时的局限性问题,即现有系统要么要求用户手动编写复杂的SQL语句并依赖低级控制(如自定义机器学习用户定义函数UDF),要么将执行完全外包给黑箱大语言模型(LLM),从而牺牲了可用性和可解释性。解决方案的关键在于提出KathDB系统,该系统融合关系型语义与基础模型(foundation models)对多模态数据的推理能力,并在查询解析、执行和结果解释阶段引入人机交互通道,使用户能够跨数据模态迭代获得可解释的答案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11067
作者: Guorui Xiao,Enhao Zhang,Nicole Sullivan,Will Hansen,Magdalena Balazinska
机构: 未知
类目: Databases (cs.DB); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Traditional DBMSs execute user- or application-provided SQL queries over relational data with strong semantic guarantees and advanced query optimization, but writing complex SQL is hard and focuses only on structured tables. Contemporary multimodal systems (which operate over relations but also text, images, and even videos) either expose low-level controls that force users to use (and possibly create) machine learning UDFs manually within SQL or offload execution entirely to black-box LLMs, sacrificing usability or explainability. We propose KathDB, a new system that combines relational semantics with the reasoning power of foundation models over multimodal data. Furthermore, KathDB includes human-AI interaction channels during query parsing, execution, and result explanation, such that users can iteratively obtain explainable answers across data modalities.
zh
[AI-39] Beyond Memristor: Neuromorphic Computing Using Meminductor
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统神经形态计算架构中缺乏具备时间记忆特性的元件问题,从而提升对生物神经系统复杂行为(如记忆、时序处理和预测)的模拟能力。其解决方案的关键在于提出并实验证明了一种具有磁记忆特性的电感器——meminductor(带记忆的电感器),其电感值L(q)依赖于通过线圈的电荷q,而历史电流信息被存储在磁芯的磁化状态中;这种特性使得meminductor能够与电容共同决定神经形态RLC电路的时间常数,从而实现memristor无法提供的动态时域响应机制,并成功再现了变形虫的生物行为特征,验证了超越memristor的新型计算范式的可行性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11002
作者: Frank Zhigang Wang
机构: 未知
类目: Emerging Technologies (cs.ET); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Memristor (resistor with memory), inductor with memory (meminductor) and capacitor with memory (memcapacitor) have different roles to play in novel computing architectures. We found that a coil with a magnetic core is an inductor with memory (meminductor) in terms of its inductance L(q) being a function of the charge q. The history of the current passing through the coil is remembered by the magnetization inside the magnetic core. Such a meminductor can play a unique role (that cannot be played by a memristor) in neuromorphic computing, deep learning and brain inspired since the time constant of a neuromorphic RLC circuit is jointly determined by the inductance and capacitance, rather than the resistance. As an experimental verification, this newly invented meminductor was used to reproduce the observed biological behaviour of amoebae (the memorizing, timing and anticipating mechanisms). In conclusion, a beyond memristor computing paradigm is theoretically sensible and experimentally practical.
zh
[AI-40] MolSculpt: Sculpting 3D Molecular Geometries from Chemical Syntax
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前生成式分子模型中1D化学语法表示与3D几何结构生成之间存在的脱节问题,即现有方法虽能保证分子的1D序列(如SELFIES)语法正确性,却难以将其中蕴含的化学知识有效转化为高质量的3D分子构型。其解决方案的关键在于提出MolSculpt框架,该框架通过冻结的1D分子基础模型提取化学先验知识,并借助可学习查询(learnable queries)和可训练投影器(trainable projector),将跨模态的1D潜在信息注入到3D扩散模型的条件空间中,从而实现端到端优化下的3D分子几何生成。这一机制显著提升了生成分子的3D保真度与稳定性,在GEOM-DRUGS和QM9数据集上均达到当前最优性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10991
作者: Zhanpeng Chen,Weihao Gao,Shunyu Wang,Yanan Zhu,Hong Meng,Yuexian Zou
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Chemical Physics (physics.chem-ph); Quantitative Methods (q-bio.QM)
备注:
Abstract:Generating precise 3D molecular geometries is crucial for drug discovery and material science. While prior efforts leverage 1D representations like SELFIES to ensure molecular validity, they fail to fully exploit the rich chemical knowledge entangled within 1D models, leading to a disconnect between 1D syntactic generation and 3D geometric realization. To bridge this gap, we propose MolSculpt, a novel framework that “sculpts” 3D molecular geometries from chemical syntax. MolSculpt is built upon a frozen 1D molecular foundation model and a 3D molecular diffusion model. We introduce a set of learnable queries to extract inherent chemical knowledge from the foundation model, and a trainable projector then injects this cross-modal information into the conditioning space of the diffusion model to guide the 3D geometry generation. In this way, our model deeply integrates 1D latent chemical knowledge into the 3D generation process through end-to-end optimization. Experiments demonstrate that MolSculpt achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in \textitde novo 3D molecule generation and conditional 3D molecule generation, showing superior 3D fidelity and stability on both the GEOM-DRUGS and QM9 datasets. Code is available at this https URL.
zh
[AI-41] Dora: QoE-Aware Hybrid Parallelism for Distributed Edge AI
【速读】:该论文旨在解决分布式边缘人工智能(Edge AI)训练与推理中因资源受限和网络动态性导致的用户体验质量(Quality of Experience, QoE)难以保障的问题。现有混合并行策略(如数据并行与流水线并行)主要优化吞吐量或设备利用率,忽视了QoE目标,常引发资源浪费或运行时QoE违规。其解决方案的核心在于提出Dora框架,通过三个关键机制实现QoE感知的混合并行:(i) 异构性感知的模型分区器,确定跨设备的模型分割方案以生成符合QoE约束的候选计划;(ii) 网络竞争感知的调度器,通过最大化计算与通信重叠来优化候选计划;(iii) 运行时自适应适配器,动态组合多个计划以在满足整体QoE前提下提升全局效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10990
作者: Jianli Jin,Ziyang Lin,Qianli Dong,Yi Chen,Jayanth Srinivasa,Myungjin Lee,Zhaowei Tan,Fan Lai
机构: 未知
类目: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:With the proliferation of edge AI applications, satisfying user quality of experience (QoE) requirements, such as model inference latency, has become a first class objective, as these models operate in resource constrained settings and directly interact with users. Yet, modern AI models routinely exceed the resource capacity of individual devices, necessitating distributed execution across heterogeneous devices over variable and contention prone networks. Existing planners for hybrid (e.g., data and pipeline) parallelism largely optimize for throughput or device utilization, overlooking QoE, leading to severe resource inefficiency (e.g., unnecessary energy drain) or QoE violations under runtime dynamics. We present Dora, a framework for QoE aware hybrid parallelism in distributed edge AI training and inference. Dora jointly optimizes heterogeneous computation, contention prone networks, and multi dimensional QoE objectives via three key mechanisms: (i) a heterogeneity aware model partitioner that determines and assigns model partitions across devices, forming a compact set of QoE compliant plans; (ii) a contention aware network scheduler that further refines these candidate plans by maximizing compute communication overlap; and (iii) a runtime adapter that adaptively composes multiple plans to maximize global efficiency while respecting overall QoEs. Across representative edge deployments, including smart homes, traffic analytics, and small edge clusters, Dora achieves 1.1–6.3 times faster execution and, alternatively, reduces energy consumption by 21–82 percent, all while maintaining QoE under runtime dynamics. Subjects: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2512.10990 [cs.DC] (or arXiv:2512.10990v1 [cs.DC] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.10990 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite
zh
[AI-42] Reducing Frag mentation and Starvation in GPU Clusters through Dynamic Multi-Objective Scheduling
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现代AI系统在GPU集群中部署时普遍存在的资源利用率低下的问题(平均利用率仅约50%),其根本原因包括碎片化、异构工作负载以及静态调度策略的局限性。解决方案的关键在于提出三种专门设计的动态调度器:混合优先级调度(Hybrid Priority Scheduler, HPS)、预测性抢占调度(Predictive Backfill Scheduler, PBS)和智能批处理调度(Smart Batch Scheduler, SBS),这些调度器通过多目标优化机制显著提升GPU利用率、任务吞吐量、公平性和抗饥饿能力。实验表明,相比传统静态调度策略(如FIFO、SJF等),动态调度方法在64-GPU、8节点集群上实现了最高达78.2%的GPU利用率和25.8 jobs/h的吞吐量,同时将长时间等待任务数量从156个降至12个,验证了针对性与透明性调度策略对提升异构AI集群效率的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10980
作者: Akhmadillo Mamirov
机构: 未知
类目: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:GPU clusters have become essential for training and deploying modern AI systems, yet real deployments continue to report average utilization near 50%. This inefficiency is largely caused by fragmentation, heterogeneous workloads, and the limitations of static scheduling policies. This work presents a systematic evaluation of these issues and introduces three specialized dynamic schedulers: Hybrid Priority (HPS), Predictive Backfill (PBS), and Smart Batch (SBS). These schedulers are designed to improve utilization, fairness, and overall throughput in multi-tenant GPU clusters. We evaluate all schedulers using a controlled simulation of 1,000 AI jobs on a 64-GPU, 8-node cluster that includes a realistic mix of training, inference, and research workloads. Static baselines (FIFO, SJF, Shortest, Shortest-GPU) achieve 45 to 67% GPU utilization and 12.5 to 18.3 jobs per hour and experience severe starvation, with as many as 156 jobs waiting longer than 30 minutes. The dynamic schedulers significantly outperform these policies. HPS achieves the highest utilization (78.2%), highest throughput (25.8 jobs per hour), and the lowest fairness variance among dynamic methods (457), reducing starvation to 12 jobs. PBS improves fragmentation handling and reaches 76.1% utilization, while SBS increases efficiency for structurally similar jobs and reaches 74.6% utilization. Across all key metrics, including throughput, job wait times, fairness variance, and starvation, dynamic multi-objective schedulers consistently outperform single-objective heuristics. These results show that targeted and transparent scheduling strategies can meaningfully increase GPU efficiency in heterogeneous AI clusters and provide a practical foundation for future production scheduling frameworks.
zh
[AI-43] Agent -Based Modular Learning for Multimodal Emotion Recognition in Human-Agent Systems
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态情感识别系统在训练与维护过程中存在的计算资源消耗大、对模态变化适应性差的问题。其核心解决方案是提出一种基于多智能体(multi-agent)的框架,其中每个模态编码器和融合分类器均作为由中央协调器管理的自主代理,实现模块化集成新模态(如通过emotion2vec提取音频特征)、无缝替换过时组件,并降低训练阶段的计算开销。该架构提升了训练效率,同时增强了感知模块在人机交互(HAI)场景中面向具身或虚拟代理的灵活性、可扩展性和可维护性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10975
作者: Matvey Nepomnyaschiy,Oleg Pereziabov,Anvar Tliamov,Stanislav Mikhailov,Ilya Afanasyev
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注: 14 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:Effective human-agent interaction (HAI) relies on accurate and adaptive perception of human emotional states. While multimodal deep learning models - leveraging facial expressions, speech, and textual cues - offer high accuracy in emotion recognition, their training and maintenance are often computationally intensive and inflexible to modality changes. In this work, we propose a novel multi-agent framework for training multimodal emotion recognition systems, where each modality encoder and the fusion classifier operate as autonomous agents coordinated by a central supervisor. This architecture enables modular integration of new modalities (e.g., audio features via emotion2vec), seamless replacement of outdated components, and reduced computational overhead during training. We demonstrate the feasibility of our approach through a proof-of-concept implementation supporting vision, audio, and text modalities, with the classifier serving as a shared decision-making agent. Our framework not only improves training efficiency but also contributes to the design of more flexible, scalable, and maintainable perception modules for embodied and virtual agents in HAI scenarios.
zh
[AI-44] Emotion-Driven Personalized Recommendation for AI-Generated Content Using Multi-Modal Sentiment and Intent Analysis
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统推荐系统因仅依赖用户行为数据(如点击、观看或评分)而忽视用户在与AI生成内容(AIGC)交互过程中实时情绪状态和意图的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于BERT的跨模态Transformer架构的多模态情感与意图识别模型(MMEI),通过预训练编码器ViT、Wav2Vec2和BERT分别处理视觉(面部表情)、听觉(语音语调)和文本(评论或话语)模态信息,并引入注意力机制融合模块以学习情感-意图联合表征,最终利用上下文匹配层实现个性化推荐。该方法显著提升了推荐系统的准确性与用户参与度,验证了跨模态情感智能在下一代AIGC生态系统中的可行性与有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10963
作者: Zheqi Hu,Xuanjing Chen,Jinlin Hu
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Multimedia (cs.MM)
备注:
Abstract:With the rapid growth of AI-generated content (AIGC) across domains such as music, video, and literature, the demand for emotionally aware recommendation systems has become increasingly important. Traditional recommender systems primarily rely on user behavioral data such as clicks, views, or ratings, while neglecting users’ real-time emotional and intentional states during content interaction. To address this limitation, this study proposes a Multi-Modal Emotion and Intent Recognition Model (MMEI) based on a BERT-based Cross-Modal Transformer with Attention-Based Fusion, integrated into a cloud-native personalized AIGC recommendation framework. The proposed system jointly processes visual (facial expression), auditory (speech tone), and textual (comments or utterances) modalities through pretrained encoders ViT, Wav2Vec2, and BERT, followed by an attention-based fusion module to learn emotion-intent representations. These embeddings are then used to drive personalized content recommendations through a contextual matching layer. Experiments conducted on benchmark emotion datasets (AIGC-INT, MELD, and CMU-MOSEI) and an AIGC interaction dataset demonstrate that the proposed MMEI model achieves a 4.3% improvement in F1-score and a 12.3% reduction in cross-entropy loss compared to the best fusion-based transformer baseline. Furthermore, user-level online evaluations reveal that emotion-driven recommendations increase engagement time by 15.2% and enhance satisfaction scores by 11.8%, confirming the model’s effectiveness in aligning AI-generated content with users’ affective and intentional states. This work highlights the potential of cross-modal emotional intelligence for next-generation AIGC ecosystems, enabling adaptive, empathetic, and context-aware recommendation experiences.
zh
[AI-45] Scalable Data Synthesis for Computer Use Agents with Step-Level Filtering
【速读】:该论文旨在解决计算机使用代理(Computer Use Agents, CUAs)训练中面临的两大核心挑战:一是图形用户界面(GUI)交互成本高且高质量轨迹数据稀缺,二是现有数据合成方法生成的rollout存在大量噪声动作,导致直接模仿学习效果不佳。为应对这些问题,作者提出了一种可扩展的数据合成流水线,其关键在于步骤级过滤(step-level filtering)——通过逐动作评估来保留正确步骤,辅以推理增强提升规划能力,从而将高噪声的合成轨迹转化为可靠监督信号。该方法成功构建了WebSTAR(13.3K轨迹、10万条带评分的推理丰富步骤)和WebSCORE(步骤级评分数据集),并基于此训练出轻量级奖励模型StepRM,显著提升了CUA的训练效率与性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10962
作者: Yifei He,Pranit Chawla,Yaser Souri,Subhojit Som,Xia Song
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Computer use agents (CUAs) can operate real-world digital interfaces but remain difficult to train due to the high cost of graphical user interface (GUI) interaction and the scarcity of high-quality trajectory data. Existing datasets rely on human demonstrations, limiting scalability. A natural alternative is to synthesize data from strong CUAs, yet their rollouts are highly noisy, with incorrect or suboptimal actions consisting a large proportion of the steps, making naive imitation ineffective. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a scalable data synthesis pipeline that transforms noisy rollouts into reliable supervision without human annotation. The core idea is step-level filtering, which evaluates actions individually to retain only correct steps, complemented by reasoning augmentation for improved planning. Using this pipeline, we construct WebSTAR, a dataset of 13.3K trajectories and 100K graded, reasoning-rich steps synthesized from OpenAI’s computer-use-preview model. We train Qwen-2.5-VL-Instruct models (7B and 32B) on WebSTAR. On WebVoyager, our 7B model surpasses SoTA open-source CUA model UI-TARS-1.5-7B by more than 15% with only supervised finetuning. Building on step-level grading, we further create WebSCORE, a dataset of graded step-level actions, and train StepRM, a 7B multimodal reward model distilled from o4-mini, which matches its grading quality while being far more efficient to deploy at scale. Our results establish step-level filtering as a key principle for scalable CUA training and construct two new datasets (WebSTAR, WebSCORE) and a lightweight reward model (StepRM) as practical tools to advance robust and efficient CUAs.
zh
[AI-46] AI as Cognitive Amplifier: Rethinking Human Judgment in the Age of Generative AI
【速读】:该论文试图解决的问题是:为何相同的AI工具在不同用户手中会产生显著差异的输出质量,以及如何从实践中理解人与AI的互动关系。解决方案的关键在于提出“认知放大器”(cognitive amplifier)视角,强调AI并非替代人类智能,而是放大使用者已有的能力;其核心机制依赖于用户的领域知识、判断力和迭代优化能力,进而构建了一个三层次的AI参与模型(从被动接受到迭代协作再到认知主导),并指出实现层级跃迁的关键不在于技术训练,而在于域内专业知识积累与元认知技能的发展。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10961
作者: Tao An
机构: 未知
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 8 pages, 7 figures. Position paper based on field observations from training 500+ professionals since 2023
Abstract:Through extensive experience training professionals and individual users in AI tool adoption since the GPT-3 era, I have observed a consistent pattern: the same AI tool produces dramatically different results depending on who uses it. While some frame AI as a replacement for human intelligence, and others warn of cognitive decline, this position paper argues for a third perspective grounded in practical observation: AI as a cognitive amplifier that magnifies existing human capabilities rather than substituting for them. Drawing on research in human-computer interaction, cognitive augmentation theory, and educational technology, alongside field observations from corporate training across writing, software development, and data analysis domains, I present a framework positioning AI tools as intelligence amplification systems where output quality depends fundamentally on user expertise and judgment. Through analysis of empirical studies on expert-novice differences and systematic observations from professional training contexts, I demonstrate that domain knowledge, quality judgment, and iterative refinement capabilities create substantial performance gaps between users. I propose a three-level model of AI engagement – from passive acceptance through iterative collaboration to cognitive direction – and argue that the transition between levels requires not technical training but development of domain expertise and metacognitive skills. This position has critical implications for workforce development and AI system design. Rather than focusing solely on AI literacy or technical prompt engineering, I advocate for integrated approaches that strengthen domain expertise, evaluative judgment, and reflective practice.
zh
[AI-47] Measuring skill-based uplift from AI in a real biological laboratory
【速读】:该论文旨在解决如何在真实场景中评估生成式 AI (Generative AI) 对非专业用户在生物实验任务中技能提升效果的问题,尤其是在涉及合法与非法使用边界的情境下预测 AI 系统的风险与收益。其关键解决方案是设计并执行一项试点研究,通过对比一组仅具备互联网访问权限的受试者与另一组可使用 AI 推理模型的受试者,在无湿实验经验的参与者中完成大肠杆菌转化、报告肽表达诱导及质谱验证等实验任务,从而量化 AI 带来的“技能驱动提升”(skills-based uplift),并记录定量结果与交互过程中的定性观察,为未来 AI 与全球生物安全关系的研究提供实证基础和方法论启示。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10960
作者: Ethan Obie Romero-Severson,Tara Harvey,Nick Generous,Phillip M. Mach
机构: 未知
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Understanding how AI systems are used by people in real situations that mirror aspects of both legitimate and illegitimate use is key to predicting the risks and benefits of AI systems. This is especially true in biological applications, where skill rather than knowledge is often the primary barrier for an untrained person. The challenge is that these studies are difficult to execute well and can take months to plan and run. Here we report the results of a pilot study that attempted to empirically measure the magnitude of \emphskills-based uplift caused by access to an AI reasoning model, compared with a control group that had only internet access. Participants – drawn from a diverse pool of Los Alamos National Laboratory employees with no prior wet-lab experience – were asked to transform \ecoli with a provided expression construct, induce expression of a reporter peptide, and have expression confirmed by mass spectrometry. We recorded quantitative outcomes (e.g., successful completion of experimental segments) and qualitative observations about how participants interacted with the AI system, the internet, laboratory equipment, and one another. We present the results of the study and lessons learned in designing and executing this type of study, and we discuss these results in the context of future studies of the evolving relationship between AI and global biosecurity. Subjects: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2512.10960 [cs.HC] (or arXiv:2512.10960v1 [cs.HC] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.10960 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite
zh
[AI-48] Unified Smart Factory Model: A model-based Approach for Integrating Industry 4.0 and Sustainability for Manufacturing Systems
【速读】:该论文试图解决制造业中可持续发展目标(Sustainability Goals)难以落地为可操作、可衡量的工厂级指标的问题,尤其是在中小企业(SMEs)层面缺乏系统化的方法将宏观目标与具体制造活动关联。解决方案的关键在于提出统一智能工厂模型(Unified Smart Factory Model, USFM),该模型通过基于对象过程方法(Object Process Methodology, OPM)对制造、装配和辅助流程进行建模,并整合制造过程与系统、数据处理以及关键绩效指标(Key Performance Indicator, KPI)的选择与评估三个核心模块,在一个统一框架内实现从可持续性目标到工厂级指标的映射。该方法能够减少冗余、降低信息遗漏风险,并提升数据采集效率,从而有效推动可持续性实践在实际生产中的落地实施。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10631
作者: Ishaan Kaushal,Amaresh Chakrabarti
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:This paper presents the Unified Smart Factory Model (USFM), a comprehensive framework designed to translate high-level sustainability goals into measurable factory-level indicators with a systematic information map of manufacturing activities. The manufacturing activities were modelled as set of manufacturing, assembly and auxiliary processes using Object Process Methodology, a Model Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) language. USFM integrates Manufacturing Process and System, Data Process, and Key Performance Indicator (KPI) Selection and Assessment in a single framework. Through a detailed case study of Printed Circuit Board (PCB) assembly factory, the paper demonstrates how environmental sustainability KPIs can be selected, modelled, and mapped to the necessary data, highlighting energy consumption and environmental impact metrics. The model’s systematic approach can reduce redundancy, minimize the risk of missing critical information, and enhance data collection. The paper concluded that the USFM bridges the gap between sustainability goals and practical implementation, providing significant benefits for industries specifically SMEs aiming to achieve sustainability targets.
zh
[AI-49] Conditional Coverag e Diagnostics for Conformal Prediction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决预测系统中条件覆盖率(conditional coverage)评估的难题,即现有方法无法保证局部条件下覆盖概率的准确性,导致实践中难以解释模型在特定输入区域的可靠性偏差。其解决方案的关键在于将条件覆盖率估计转化为一个分类问题:通过设计合适的损失函数,使目标覆盖风险与任意分类器的风险差异形成保守估计,从而量化自然误覆盖度量(如L1和L2距离),并可区分过覆盖与欠覆盖的影响以及非恒定目标覆盖率的情形;这一方法生成了一类名为“目标覆盖超额风险”(Excess Risk of the Target Coverage, ERT)的新指标,实验表明使用现代分类器相比传统简单分类器显著提升了统计功效,并可用于基准测试不同共形预测方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11779
作者: Sacha Braun,David Holzmüller,Michael I. Jordan,Francis Bach
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Evaluating conditional coverage remains one of the most persistent challenges in assessing the reliability of predictive systems. Although conformal methods can give guarantees on marginal coverage, no method can guarantee to produce sets with correct conditional coverage, leaving practitioners without a clear way to interpret local deviations. To overcome sample-inefficiency and overfitting issues of existing metrics, we cast conditional coverage estimation as a classification problem. Conditional coverage is violated if and only if any classifier can achieve lower risk than the target coverage. Through the choice of a (proper) loss function, the resulting risk difference gives a conservative estimate of natural miscoverage measures such as L1 and L2 distance, and can even separate the effects of over- and under-coverage, and non-constant target coverages. We call the resulting family of metrics excess risk of the target coverage (ERT). We show experimentally that the use of modern classifiers provides much higher statistical power than simple classifiers underlying established metrics like CovGap. Additionally, we use our metric to benchmark different conformal prediction methods. Finally, we release an open-source package for ERT as well as previous conditional coverage metrics. Together, these contributions provide a new lens for understanding, diagnosing, and improving the conditional reliability of predictive systems.
zh
[AI-50] amc: The Automated Mission Classifier for Telescope Bibliographies AACL
【速读】:该论文旨在解决天文文献中望远镜引用信息的自动化识别与分类问题,以应对天文期刊出版量快速增长导致的人工标注效率不足的挑战。其核心解决方案是提出Automated Mission Classifier (amc),一个基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的工具,通过处理大量论文文本内容,自动识别并分类与特定天文任务相关的文献引用。该方法在TRACS Kaggle挑战赛中表现优异,宏平均F₁分数达到0.84,且具备可迁移性,适用于其他望远镜项目和历史数据集的挖掘与标签纠错,体现了生成式AI在图书馆科学中的规模化应用潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11202
作者: John F. Wu,Joshua E. G. Peek,Sophie J. Miller,Jenny Novacescu,Achu J. Usha,Christopher A. Wilkinson
机构: 未知
类目: Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics (astro-ph.IM); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Digital Libraries (cs.DL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Accepted to IJCNLP-AACL WASP 2025 workshop. Code available at: this https URL
Abstract:Telescope bibliographies record the pulse of astronomy research by capturing publication statistics and citation metrics for telescope facilities. Robust and scalable bibliographies ensure that we can measure the scientific impact of our facilities and archives. However, the growing rate of publications threatens to outpace our ability to manually label astronomical literature. We therefore present the Automated Mission Classifier (amc), a tool that uses large language models (LLMs) to identify and categorize telescope references by processing large quantities of paper text. A modified version of amc performs well on the TRACS Kaggle challenge, achieving a macro F_1 score of 0.84 on the held-out test set. amc is valuable for other telescopes beyond TRACS; we developed the initial software for identifying papers that featured scientific results by NASA missions. Additionally, we investigate how amc can also be used to interrogate historical datasets and surface potential label errors. Our work demonstrates that LLM-based applications offer powerful and scalable assistance for library sciences.
zh
[AI-51] A probabilistic foundation model for crystal structure denoising phase classification and order parameters
【速读】:该论文旨在解决原子尺度模拟中从噪声结构数据中提取相标签、序参量(Order Parameters, OPs)和缺陷信息时普遍存在的挑战,即现有方法如PTM(Polyhedral Template Matching)和CNA(Common Neighbor Analysis)受限于少量手工设计的晶格类型(如FCC/BCC/HCP),在强热无序或缺陷条件下性能退化,且输出为基于模板的硬标签,缺乏每个原子的概率或置信度评分。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个基于对数概率(log-probability)的基础模型(foundation model),将去噪、相分类与序参量提取统一在一个概率框架内:利用MACE-MP基础势函数在AFLOW原型晶体结构上训练,预测每个原子的相类别logits $ l $,并通过聚合得到全局对数密度 $ \log \hat{P}\theta(\boldsymbol{r}) $,其梯度定义保守得分场(score field)用于去噪;相标签由 $ \arg\max_c l{ac} $ 确定,而 $ l $ 值作为连续、对缺陷敏感且可解释的OP,量化原子到理想相的欧氏距离。该方法实现了跨数百种晶型的通用性、强无序下的鲁棒性及复杂体系(如冰多形、冰-水界面和冲击压缩Ti)的精确建模。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11077
作者: Hyuna Kwon,Babak Sadigh,Sebastien Hamel,Vincenzo Lordi,John Klepeis,Fei Zhou
机构: 未知
类目: Materials Science (cond-mat.mtrl-sci); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Atomistic simulations generate large volumes of noisy structural data, but extracting phase labels, order parameters (OPs), and defect information in a way that is universal, robust, and interpretable remains challenging. Existing tools such as PTM and CNA are restricted to a small set of hand-crafted lattices (e.g.\ FCC/BCC/HCP), degrade under strong thermal disorder or defects, and produce hard, template-based labels without per-atom probability or confidence scores. Here we introduce a log-probability foundation model that unifies denoising, phase classification, and OP extraction within a single probabilistic framework. We reuse the MACE-MP foundation interatomic potential on crystal structures mapped to AFLOW prototypes, training it to predict per-atom, per-phase logits l and to aggregate them into a global log-density \log \hatP_\theta(\boldsymbolr) whose gradient defines a conservative score field. Denoising corresponds to gradient ascent on this learned log-density, phase labels follow from \arg\max_c l_ac , and the l values act as continuous, defect-sensitive and interpretable OPs quantifying the Euclidean distance to ideal phases. We demonstrate universality across hundreds of prototypes, robustness under strong thermal and defect-induced disorder, and accurate treatment of complex systems such as ice polymorphs, ice–water interfaces, and shock-compressed Ti.
zh
[AI-52] Fast accurate measurement of the worker populations of honey bee colonies using deep learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决蜂蜜蜂群(honey bee)数量估算的难题,传统计数方法存在耗时、劳动强度大且易出错的问题,尤其在大规模研究中难以满足效率与精度需求。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于深度学习的自动化计数方法,采用CSRNet模型进行密度图估计(density map estimation),有效应对蜂群密集场景中的遮挡和重叠问题;同时构建了首个专为该任务设计的高分辨率数据集ASUBEE,显著提升了计数准确性与计算效率(单张图像仅需1秒),为生态学研究和养蜂实践提供了可扩展、高精度的监测工具。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11075
作者: Junmin Zhong,Jon F. Harrison,Jennie Si,Jun Chen
机构: 未知
类目: Quantitative Methods (q-bio.QM); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Honey bees play a crucial role in pollination, contributing significantly to global agriculture and ecosystems. Accurately estimating hive populations is essential for understanding the effects of environmental factors on bee colonies, yet traditional methods of counting bees are time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to human error, particularly in large-scale studies. In this paper, we present a deep learning-based solution for automating bee population counting using CSRNet and introduce ASUBEE, the FIRST high-resolution dataset specifically designed for this task. Our method employs density map estimation to predict bee populations, effectively addressing challenges such as occlusion and overlapping bees that are common in hive monitoring. We demonstrate that CSRNet achieves superior performance in terms of time efficiency, with a computation time of just 1 second per image, while delivering accurate counts even in complex and densely populated hive scenarios. Our findings show that deep learning approaches like CSRNet can dramatically enhance the efficiency of hive population assessments, providing a valuable tool for researchers and beekeepers alike. This work marks a significant advancement in applying AI technologies to ecological research, offering scalable and precise monitoring solutions for honey bee populations.
zh
[AI-53] Unambiguous Representations in Neural Networks: An Information-Theoretic Approach to Intentionality
【速读】:该论文试图解决的问题是:如何量化神经网络中表征的模糊性(representational ambiguity),并探究其与意识表征特性的关联。论文指出,尽管传统表征(如字母或比特串)依赖外部解码器才能传达意义,但意识体验中的表征具有内在唯一性——一个神经状态对应感知到的红色方块,无法同时编码绿色方块的体验。为形式化这一直觉,作者引入信息论框架,将表征模糊性定义为给定表征 $ R $ 下可能解释 $ I $ 的条件熵 $ H(I|R) 。解决方案的关键在于:通过分析神经网络的连接结构关系(relationalstructuresinnetworkconnectivity),发现即使在任务性能相同的情况下,某些训练方式(如dropout训练)能实现对输出神经元类别身份的100 R^2 $ 达0.844),表明神经网络具备低模糊性表征能力,这为理解意识所需的“明确表征”提供了可量化的实证基础。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11000
作者: Francesco Lässig
机构: 未知
类目: Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE)
备注: Presented at the Models of Consciousness 6 (MoC6) conference ( this https URL )
Abstract:Representations pervade our daily experience, from letters representing sounds to bit strings encoding digital files. While such representations require externally defined decoders to convey meaning, conscious experience appears fundamentally different: a neural state corresponding to perceiving a red square cannot alternatively encode the experience of a green square. This intrinsic property of consciousness suggests that conscious representations must be unambiguous in a way that conventional representations are not. We formalize this intuition using information theory, defining representational ambiguity as the conditional entropy H(I|R) over possible interpretations I given a representation R. Through experiments on neural networks trained to classify MNIST digits, we demonstrate that relational structures in network connectivity can unambiguously encode representational content. Using both learned decoders and direct geometric matching, we achieve perfect (100%) accuracy for dropout-trained networks and 38% for standard backpropagation in identifying output neuron class identity, despite identical task performance, demonstrating that representational ambiguity can arise orthogonally to behavioral accuracy. We further show that spatial position information of input neurons can be decoded from network connectivity with R2 up to 0.844. These results provide a quantitative method for measuring representational ambiguity in neural systems and demonstrate that neural networks can exhibit the low-ambiguity representations posited as necessary (though not sufficient) by theoretical accounts of consciousness.
zh
[AI-54] Mathematics of natural intelligence
【速读】:该论文旨在解决如何基于脑科学原理构建可解释的人工智能模型问题,核心挑战在于现有AI系统缺乏生物大脑所具备的复杂认知结构与动态机制。解决方案的关键在于引入“认知组”(cognitome)这一概念,将其视为由功能系统和细胞集合(COGs)构成的神经超网络,并基于此建立数学模型来刻画认知过程。论文提出,大脑通过发现外部世界中所有可能的因果关系并从中推导结论这一普遍原则,驱动其认知结构的形成与运作,从而为自然分类、功能脑系统理论、原型范畴化、因果模型及意识作为整合信息等多类认知理论提供统一建模框架。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10988
作者: Evgenii Vityaev
机构: 未知
类目: Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 18 pages, 4 figures, presented at the conference “MathAI 2025 The International Conference dedicated to mathematics in artificial intelligence”
Abstract:In the process of evolution, the brain has achieved such perfection that artificial intelligence systems do not have and which needs its own mathematics. The concept of cognitome, introduced by the academician K.V. Anokhin, as the cognitive structure of the mind – a high-order structure of the brain and a neural hypernetwork, is considered as the basis for modeling. Consciousness then is a special form of dynamics in this hypernetwork – a large-scale integration of its cognitive elements. The cognitome, in turn, consists of interconnected COGs (cognitive groups of neurons) of two types – functional systems and cellular ensembles. K.V. Anokhin sees the task of the fundamental theory of the brain and mind in describing these structures, their origin, functions and processes in them. The paper presents mathematical models of these structures based on new mathematical results, as well as models of different cognitive processes in terms of these models. In addition, it is shown that these models can be derived based on a fairly general principle of the brain works: \textitthe brain discovers all possible causal relationships in the external world and draws all possible conclusions from them. Based on these results, the paper presents models of: ``natural" classification; theory of functional brain systems by P.K. Anokhin; prototypical theory of categorization by E. Roche; theory of causal models by Bob Rehter; theory of consciousness as integrated information by G. Tononi.
zh
[AI-55] Marti-5: A Mathematical Model of “Self in the World” as a First Step Toward Self-Awareness
【速读】:该论文试图解决的问题是:如何构建一个清晰的数学模型来阐明大脑中“what”和“where”信息处理通路(即视觉信息的特征识别与空间定位通路)如何协同工作,以实现对自我与环境的区分并建立用于预测的自体模型(self-model)。解决方案的关键在于提出一种受生物学启发的数学模型,其中新皮层柱(neocortical columns)由基底神经节(basal ganglia)调控,部分柱体作为“what”柱负责物体识别,另一部分作为“where”柱负责空间定位,二者共同协作完成对环境的建模与行为决策。该模型被实现为强化学习代理(reinforcement learning agent),在Atari游戏Pong和Breakout中成功学习到目的性行为,验证了将自我从环境中分离的能力可提升智能体的适应性,从而支持其在进化中的出现可能性,并提出了“自知原则1”:区分自我与世界是自知的必要但不充分条件。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10985
作者: Igor Pivovarov,Sergey Shumsky
机构: 未知
类目: Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 21 pages, 2 figures, 2 videos, 1 table
Abstract:The existence of ‘what’ and ‘where’ pathways of information processing in the brain was proposed almost 30 years ago, but there is still a lack of a clear mathematical model that could show how these pathways work together. We propose a biologically inspired mathematical model that uses this idea to identify and separate the self from the environment and then build and use a self-model for better predictions. This is a model of neocortical columns governed by the basal ganglia to make predictions and choose the next action, where some columns act as ‘what’ columns and others act as ‘where’ columns. Based on this model, we present a reinforcement learning agent that learns purposeful behavior in a virtual environment. We evaluate the agent on the Atari games Pong and Breakout, where it successfully learns to play. We conclude that the ability to separate the self from the environment gives advantages to the agent and therefore such a model could appear in living organisms during evolution. We propose Self-Awareness Principle 1: the ability to separate the self from the world is a necessary but insufficient condition for self-awareness.
zh
[AI-56] Developmental Symmetry-Loss: A Free-Energy Perspective on Brain-Inspired Invariance Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决如何在人工系统中实现高效、稳定且可组合的表示学习问题,同时借鉴大脑发育过程中神经表征与环境结构对齐的机制。其解决方案的关键在于提出Symmetry-Loss——一种受大脑启发的算法原则,通过从环境对称性中导出的可微约束来强制实现不变性(invariance)和等变性(equivariance)。该方法将学习建模为有效对称群的迭代优化过程,最小化结构意外(structural surprise),即偏离对称一致性的情况,从而操作化一个类似自由能(Free-Energy)的目标函数,连接了预测编码(predictive coding)与群论(group-theoretic)视角,使基于对称性的自组织机制能够生成高质量的表示。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10984
作者: Arif Dönmez
机构: 未知
类目: Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Adaptation and Self-Organizing Systems (nlin.AO)
备注: 6 pages. Work in progress – comments welcome!
Abstract:We propose Symmetry-Loss, a brain-inspired algorithmic principle that enforces invariance and equivariance through a differentiable constraint derived from environmental symmetries. The framework models learning as the iterative refinement of an effective symmetry group, paralleling developmental processes in which cortical representations align with the world’s structure. By minimizing structural surprise, i.e. deviations from symmetry consistency, Symmetry-Loss operationalizes a Free-Energy–like objective for representation learning. This formulation bridges predictive-coding and group-theoretic perspectives, showing how efficient, stable, and compositional representations can emerge from symmetry-based self-organization. The result is a general computational mechanism linking developmental learning in the brain with principled representation learning in artificial systems.
zh
[AI-57] Cognitive Mirrors: Exploring the Diverse Functional Roles of Attention Heads in LLM Reasoning NEURIPS2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)内部机制不透明的问题,尤其是缺乏对注意力头(attention heads)在推理过程中功能角色的系统性理解。为实现可解释性分析,作者提出了一种新颖的解释框架,并引入CogQA数据集,该数据集通过链式思维(chain-of-thought)设计将复杂问题分解为具有特定认知功能(如检索或逻辑推理)的子问题。解决方案的关键在于采用多类探测方法识别出承担特定认知功能的注意力头,即“认知头”(cognitive heads),并揭示其普遍稀疏性、功能分布差异性以及交互与层级结构特性。实验证明,这些认知头对推理任务至关重要,移除会降低性能,增强则提升准确率,从而为模型设计、训练和微调策略提供了可操作的理论依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10978
作者: Xueqi Ma,Jun Wang,Yanbei Jiang,Sarah Monazam Erfani,Tongliang Liu,James Bailey
机构: 未知
类目: Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted to NeurIPS 2025
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved state-of-the-art performance in a variety of tasks, but remain largely opaque in terms of their internal mechanisms. Understanding these mechanisms is crucial to improve their reasoning abilities. Drawing inspiration from the interplay between neural processes and human cognition, we propose a novel interpretability framework to systematically analyze the roles and behaviors of attention heads, which are key components of LLMs. We introduce CogQA, a dataset that decomposes complex questions into step-by-step subquestions with a chain-of-thought design, each associated with specific cognitive functions such as retrieval or logical reasoning. By applying a multi-class probing method, we identify the attention heads responsible for these functions. Our analysis across multiple LLM families reveals that attention heads exhibit functional specialization, characterized as cognitive heads. These cognitive heads exhibit several key properties: they are universally sparse, vary in number and distribution across different cognitive functions, and display interactive and hierarchical structures. We further show that cognitive heads play a vital role in reasoning tasks - removing them leads to performance degradation, while augmenting them enhances reasoning accuracy. These insights offer a deeper understanding of LLM reasoning and suggest important implications for model design, training, and fine-tuning strategies.
zh
机器学习
[LG-0] A General Algorithm for Detecting Higher-Order Interactions via Random Sequential Additions
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11793
作者: Ahmad Shamail,Claire McWhite
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Many systems exhibit complex interactions between their components: some features or actions amplify each other’s effects, others provide redundant information, and some contribute independently. We present a simple geometric method for discovering interactions and redundancies: when elements are added in random sequential orders and their contributions plotted over many trials, characteristic L-shaped patterns emerge that directly reflect interaction structure. The approach quantifies how the contribution of each element depends on those added before it, revealing patterns that distinguish interaction, independence, and redundancy on a unified scale. When pairwise contributions are visualized as two–dimensional point clouds, redundant pairs form L–shaped patterns where only the first-added element contributes, while synergistic pairs form L–shaped patterns where only elements contribute together. Independent elements show order–invariant distributions. We formalize this with the L–score, a continuous measure ranging from -1 (perfect synergy, e.g. Y=X_1X_2 ) to 0 (independence) to +1 (perfect redundancy, X_1 \approx X_2 ). The relative scaling of the L–shaped arms reveals feature dominance in which element consistently provides more information. Although computed only from pairwise measurements, higher–order interactions among three or more elements emerge naturally through consistent cross–pair relationships (e.g. AB, AC, BC). The method is metric–agnostic and broadly applicable to any domain where performance can be evaluated incrementally over non-repeating element sequences, providing a unified geometric approach to uncovering interaction structure.
[LG-1] Softmax as Linear Attention in the Large-Prompt Regime: a Measure-based Perspective
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11784
作者: Etienne Boursier,Claire Boyer
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注:
Abstract:Softmax attention is a central component of transformer architectures, yet its nonlinear structure poses significant challenges for theoretical analysis. We develop a unified, measure-based framework for studying single-layer softmax attention under both finite and infinite prompts. For i.i.d. Gaussian inputs, we lean on the fact that the softmax operator converges in the infinite-prompt limit to a linear operator acting on the underlying input-token measure. Building on this insight, we establish non-asymptotic concentration bounds for the output and gradient of softmax attention, quantifying how rapidly the finite-prompt model approaches its infinite-prompt counterpart, and prove that this concentration remains stable along the entire training trajectory in general in-context learning settings with sub-Gaussian tokens. In the case of in-context linear regression, we use the tractable infinite-prompt dynamics to analyze training at finite prompt length. Our results allow optimization analyses developed for linear attention to transfer directly to softmax attention when prompts are sufficiently long, showing that large-prompt softmax attention inherits the analytical structure of its linear counterpart. This, in turn, provides a principled and broadly applicable toolkit for studying the training dynamics and statistical behavior of softmax attention layers in large prompt regimes.
[LG-2] he Adaptive Vekua Cascade: A Differentiable Spectral-Analytic Solver for Physics-Informed Representation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11776
作者: Vladimer Khasia
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Coordinate-based neural networks have emerged as a powerful tool for representing continuous physical fields, yet they face two fundamental pathologies: spectral bias, which hinders the learning of high-frequency dynamics, and the curse of dimensionality, which causes parameter explosion in discrete feature grids. We propose the Adaptive Vekua Cascade (AVC), a hybrid architecture that bridges deep learning and classical approximation theory. AVC decouples manifold learning from function approximation by using a deep network to learn a diffeomorphic warping of the physical domain, projecting complex spatiotemporal dynamics onto a latent manifold where the solution is represented by a basis of generalized analytic functions. Crucially, we replace the standard gradient-descent output layer with a differentiable linear solver, allowing the network to optimally resolve spectral coefficients in a closed form during the forward pass. We evaluate AVC on a suite of five rigorous physics benchmarks, including high-frequency Helmholtz wave propagation, sparse medical reconstruction, and unsteady 3D Navier-Stokes turbulence. Our results demonstrate that AVC achieves state-of-the-art accuracy while reducing parameter counts by orders of magnitude (e.g., 840 parameters vs. 4.2 million for 3D grids) and converging 2-3x faster than implicit neural representations. This work establishes a new paradigm for memory-efficient, spectrally accurate scientific machine learning. The code is available at this https URL.
[LG-3] SpectralKrum: A Spectral-Geometric Defense Against Byzantine Attacks in Federated Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11760
作者: Aditya Tripathi,Karan Sharma,Rahul Mishra,Tapas Kumar Maiti
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) distributes model training across clients who retain their data locally, but this architecture exposes a fundamental vulnerability: Byzantine clients can inject arbitrarily corrupted updates that degrade or subvert the global model. While robust aggregation methods (including Krum, Bulyan, and coordinate-wise defenses) offer theoretical guarantees under idealized assumptions, their effectiveness erodes substantially when client data distributions are heterogeneous (non-IID) and adversaries can observe or approximate the defense mechanism. This paper introduces SpectralKrum, a defense that fuses spectral subspace estimation with geometric neighbor-based selection. The core insight is that benign optimization trajectories, despite per-client heterogeneity, concentrate near a low-dimensional manifold that can be estimated from historical aggregates. SpectralKrum projects incoming updates into this learned subspace, applies Krum selection in compressed coordinates, and filters candidates whose orthogonal residual energy exceeds a data-driven threshold. The method requires no auxiliary data, operates entirely on model updates, and preserves FL privacy properties. We evaluate SpectralKrum against eight robust baselines across seven attack scenarios on CIFAR-10 with Dirichlet-distributed non-IID partitions (alpha = 0.1). Experiments spanning over 56,000 training rounds show that SpectralKrum is competitive against directional and subspace-aware attacks (adaptive-steer, buffer-drift), but offers limited advantage under label-flip and min-max attacks where malicious updates remain spectrally indistinguishable from benign ones. Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2512.11760 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2512.11760v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11760 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-4] LUCID: Learning-Enabled Uncertainty-Aware Certification of Stochastic Dynamical Systems AAAI2026
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11750
作者: Ernesto Casablanca,Oliver Schön,Paolo Zuliani,Sadegh Soudjani
类目: ystems and Control (eess.SY); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: The manuscript has been accepted for publication in the main track of AAAI 2026
[LG-5] ECCO: Leverag ing Cross-Camera Correlations for Efficient Live Video Continuous Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11727
作者: Yuze He,Ferdi Kossmann,Srinivasan Seshan,Peter Steenkiste
类目: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Networking and Internet Architecture (cs.NI)
*备注:
Abstract:Recent advances in video analytics address real-time data drift by continuously retraining specialized, lightweight DNN models for individual cameras. However, the current practice of retraining a separate model for each camera suffers from high compute and communication costs, making it unscalable. We present ECCO, a new video analytics framework designed for resource-efficient continuous learning. The key insight is that the data drift, which necessitates model retraining, often shows temporal and spatial correlations across nearby cameras. By identifying cameras that experience similar drift and retraining a shared model for them, ECCO can substantially reduce the associated compute and communication costs. Specifically, ECCO introduces: (i) a lightweight grouping algorithm that dynamically forms and updates camera groups; (ii) a GPU allocator that dynamically assigns GPU resources across different groups to improve retraining accuracy and ensure fairness; and (iii) a transmission controller at each camera that configures frame sampling and coordinates bandwidth sharing with other cameras based on its assigned GPU resources. We conducted extensive evaluations on three distinctive datasets for two vision tasks. Compared to leading baselines, ECCO improves retraining accuracy by 6.7%-18.1% using the same compute and communication resources, or supports 3.3 times more concurrent cameras at the same accuracy.
[LG-6] High-Dimensional Surrogate Modeling for Closed-Loop Learning of Neural-Network-Parameterized Model Predictive Control
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11705
作者: Sebastian Hirt,Valentinus Suwanto,Hendrik Alsmeier,Maik Pfefferkorn,Rolf Findeisen
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Systems and Control (eess.SY)
*备注: 7 pages, 2 figures
Abstract:Learning controller parameters from closed-loop data has been shown to improve closed-loop performance. Bayesian optimization, a widely used black-box and sample-efficient learning method, constructs a probabilistic surrogate of the closed-loop performance from few experiments and uses it to select informative controller parameters. However, it typically struggles with dense high-dimensional controller parameterizations, as they may appear, for example, in tuning model predictive controllers, because standard surrogate models fail to capture the structure of such spaces. This work suggests that the use of Bayesian neural networks as surrogate models may help to mitigate this limitation. Through a comparison between Gaussian processes with Matern kernels, finite-width Bayesian neural networks, and infinite-width Bayesian neural networks on a cart-pole task, we find that Bayesian neural network surrogate models achieve faster and more reliable convergence of the closed-loop cost and enable successful optimization of parameterizations with hundreds of dimensions. Infinite-width Bayesian neural networks also maintain performance in settings with more than one thousand parameters, whereas Matern-kernel Gaussian processes rapidly lose effectiveness. These results indicate that Bayesian neural network surrogate models may be suitable for learning dense high-dimensional controller parameterizations and offer practical guidance for selecting surrogate models in learning-based controller design.
[LG-7] Bridging Streaming Continual Learning via In-Context Large Tabular Models AAAI
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11668
作者: Afonso Lourenço,João Gama,Eric P. Xing,Goreti Marreiros
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Streaming Continual Learning AAAI Bridge 2026
Abstract:In streaming scenarios, models must learn continuously, adapting to concept drifts without erasing previously acquired knowledge. However, existing research communities address these challenges in isolation. Continual Learning (CL) focuses on long-term retention and mitigating catastrophic forgetting, often without strict real-time constraints. Stream Learning (SL) emphasizes rapid, efficient adaptation to high-frequency data streams, but typically neglects forgetting. Recent efforts have tried to combine these paradigms, yet no clear algorithmic overlap exists. We argue that large in-context tabular models (LTMs) provide a natural bridge for Streaming Continual Learning (SCL). In our view, unbounded streams should be summarized on-the-fly into compact sketches that can be consumed by LTMs. This recovers the classical SL motivation of compressing massive streams with fixed-size guarantees, while simultaneously aligning with the experience-replay desiderata of CL. To clarify this bridge, we show how the SL and CL communities implicitly adopt a divide-to-conquer strategy to manage the tension between plasticity (performing well on the current distribution) and stability (retaining past knowledge), while also imposing a minimal complexity constraint that motivates diversification (avoiding redundancy in what is stored) and retrieval (re-prioritizing past information when needed). Within this perspective, we propose structuring SCL with LTMs around two core principles of data selection for in-context learning: (1) distribution matching, which balances plasticity and stability, and (2) distribution compression, which controls memory size through diversification and retrieval mechanisms.
[LG-8] A Fast Interpretable Fuzzy Tree Learner
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11616
作者: Javier Fumanal-Idocin,Raquel Fernandez-Peralta,Javier Andreu-Perez
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Symbolic Computation (cs.SC)
*备注:
Abstract:Fuzzy rule-based systems have been mostly used in interpretable decision-making because of their interpretable linguistic rules. However, interpretability requires both sensible linguistic partitions and small rule-base sizes, which are not guaranteed by many existing fuzzy rule-mining algorithms. Evolutionary approaches can produce high-quality models but suffer from prohibitive computational costs, while neural-based methods like ANFIS have problems retaining linguistic interpretations. In this work, we propose an adaptation of classical tree-based splitting algorithms from crisp rules to fuzzy trees, combining the computational efficiency of greedy algoritms with the interpretability advantages of fuzzy logic. This approach achieves interpretable linguistic partitions and substantially improves running time compared to evolutionary-based approaches while maintaining competitive predictive performance. Our experiments on tabular classification benchmarks proof that our method achieves comparable accuracy to state-of-the-art fuzzy classifiers with significantly lower computational cost and produces more interpretable rule bases with constrained complexity. Code is available in: this https URL
[LG-9] Gradient Descent as a Perceptron Algorithm: Understanding Dynamics and Implicit Acceleration
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11587
作者: Alexander Tyurin
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Numerical Analysis (math.NA); Optimization and Control (math.OC)
*备注:
Abstract:Even for the gradient descent (GD) method applied to neural network training, understanding its optimization dynamics, including convergence rate, iterate trajectories, function value oscillations, and especially its implicit acceleration, remains a challenging problem. We analyze nonlinear models with the logistic loss and show that the steps of GD reduce to those of generalized perceptron algorithms (Rosenblatt, 1958), providing a new perspective on the dynamics. This reduction yields significantly simpler algorithmic steps, which we analyze using classical linear algebra tools. Using these tools, we demonstrate on a minimalistic example that the nonlinearity in a two-layer model can provably yield a faster iteration complexity \tildeO(\sqrtd) compared to \Omega(d) achieved by linear models, where d is the number of features. This helps explain the optimization dynamics and the implicit acceleration phenomenon observed in neural networks. The theoretical results are supported by extensive numerical experiments. We believe that this alternative view will further advance research on the optimization of neural networks.
[LG-10] Fully Inductive Node Representation Learning via Graph View Transformation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11561
作者: Dooho Lee,Myeong Kong,Minho Jeong,Jaemin Yoo
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Generalizing a pretrained model to unseen datasets without retraining is an essential step toward a foundation model. However, achieving such cross-dataset, fully inductive inference is difficult in graph-structured data where feature spaces vary widely in both dimensionality and semantics. Any transformation in the feature space can easily violate the inductive applicability to unseen datasets, strictly limiting the design space of a graph model. In this work, we introduce the view space, a novel representational axis in which arbitrary graphs can be naturally encoded in a unified manner. We then propose Graph View Transformation (GVT), a node- and feature-permutation-equivariant mapping in the view space. GVT serves as the building block for Recurrent GVT, a fully inductive model for node representation learning. Pretrained on OGBN-Arxiv and evaluated on 27 node-classification benchmarks, Recurrent GVT outperforms GraphAny, the prior fully inductive graph model, by +8.93% and surpasses 12 individually tuned GNNs by at least +3.30%. These results establish the view space as a principled and effective ground for fully inductive node representation learning.
[LG-11] Elastic-Net Multiple Kernel Learning: Combining Multiple Data Sources for Prediction
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11547
作者: Janaina Mourão-Miranda,Zakria Hussain,Konstantinos Tsirlis,Christophe Phillips,John Shawe-Taylor
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Technical Report
Abstract:Multiple Kernel Learning (MKL) models combine several kernels in supervised and unsupervised settings to integrate multiple data representations or sources, each represented by a different kernel. MKL seeks an optimal linear combination of base kernels that maximizes a generalized performance measure under a regularization constraint. Various norms have been used to regularize the kernel weights, including l1 , l2 and lp , as well as the “elastic-net” penalty, which combines l1 - and l2 -norm to promote both sparsity and the selection of correlated kernels. This property makes elastic-net regularized MKL (ENMKL) especially valuable when model interpretability is critical and kernels capture correlated information, such as in neuroimaging. Previous ENMKL methods have followed a two-stage procedure: fix kernel weights, train a support vector machine (SVM) with the weighted kernel, and then update the weights via gradient descent, cutting-plane methods, or surrogate functions. Here, we introduce an alternative ENMKL formulation that yields a simple analytical update for the kernel weights. We derive explicit algorithms for both SVM and kernel ridge regression (KRR) under this framework, and implement them in the open-source Pattern Recognition for Neuroimaging Toolbox (PRoNTo). We evaluate these ENMKL algorithms against l1 -norm MKL and against SVM (or KRR) trained on the unweighted sum of kernels across three neuroimaging applications. Our results show that ENMKL matches or outperforms l1 -norm MKL in all tasks and only underperforms standard SVM in one scenario. Crucially, ENMKL produces sparser, more interpretable models by selectively weighting correlated kernels.
[LG-12] A Multi-Criteria Automated MLOps Pipeline for Cost-Effective Cloud-Based Classifier Retraining in Response to Data Distribution Shifts
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11541
作者: Emmanuel K. Katalay,David O. Dimandja,Jordan F. Masakuna
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 11 pages, 3 figures and 2 tables. Preliminary results on an automated MLOps pipeline
Abstract:The performance of machine learning (ML) models often deteriorates when the underlying data distribution changes over time, a phenomenon known as data distribution drift. When this happens, ML models need to be retrained and redeployed. ML Operations (MLOps) is often manual, i.e., humans trigger the process of model retraining and redeployment. In this work, we present an automated MLOps pipeline designed to address neural network classifier retraining in response to significant data distribution changes. Our MLOps pipeline employs multi-criteria statistical techniques to detect distribution shifts and triggers model updates only when necessary, ensuring computational efficiency and resource optimization. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework through experiments on several benchmark anomaly detection data sets, showing significant improvements in model accuracy and robustness compared to traditional retraining strategies. Our work provides a foundation for deploying more reliable and adaptive ML systems in dynamic real-world settings, where data distribution changes are common.
[LG-13] Parametric Numerical Integration with (Differential) Machine Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11530
作者: Álvaro Leitao,Jonatan Ráfales
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Numerical Analysis (math.NA)
*备注:
Abstract:In this work, we introduce a machine/deep learning methodology to solve parametric integrals. Besides classical machine learning approaches, we consider a differential learning framework that incorporates derivative information during training, emphasizing its advantageous properties. Our study covers three representative problem classes: statistical functionals (including moments and cumulative distribution functions), approximation of functions via Chebyshev expansions, and integrals arising directly from differential equations. These examples range from smooth closed-form benchmarks to challenging numerical integrals. Across all cases, the differential machine learning-based approach consistently outperforms standard architectures, achieving lower mean squared error, enhanced scalability, and improved sample efficiency.
[LG-14] xGR: Efficient Generative Recommendation Serving at Scale
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11529
作者: Qingxiao Sun,Tongxuan Liu,Shen Zhang,Siyu Wu,Peijun Yang,Haotian Liang,Menxin Li,Xiaolong Ma,Zhiwei Liang,Ziyi Ren,Minchao Zhang,Xinyu Liu,Ke Zhang,Depei Qian,Hailong Yang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Recommendation system delivers substantial economic benefits by providing personalized predictions. Generative recommendation (GR) integrates LLMs to enhance the understanding of long user-item sequences. Despite employing attention-based architectures, GR’s workload differs markedly from that of LLM serving. GR typically processes long prompt while producing short, fixed-length outputs, yet the computational cost of each decode phase is especially high due to the large beam width. In addition, since the beam search involves a vast item space, the sorting overhead becomes particularly time-consuming. We propose xGR, a GR-oriented serving system that meets strict low-latency requirements under highconcurrency scenarios. First, xGR unifies the processing of prefill and decode phases through staged computation and separated KV cache. Second, xGR enables early sorting termination and mask-based item filtering with data structure reuse. Third, xGR reconstructs the overall pipeline to exploit multilevel overlap and multi-stream parallelism. Our experiments with real-world recommendation service datasets demonstrate that xGR achieves at least 3.49x throughput compared to the state-of-the-art baseline under strict latency constraints.
[LG-15] Hyperbolic Gaussian Blurring Mean Shift: A Statistical Mode-Seeking Framework for Clustering in Curved Spaces
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11448
作者: Arghya Pratihar,Arnab Seal,Swagatam Das,Inesh Chattopadhyay
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注:
Abstract:Clustering is a fundamental unsupervised learning task for uncovering patterns in data. While Gaussian Blurring Mean Shift (GBMS) has proven effective for identifying arbitrarily shaped clusters in Euclidean space, it struggles with datasets exhibiting hierarchical or tree-like structures. In this work, we introduce HypeGBMS, a novel extension of GBMS to hyperbolic space. Our method replaces Euclidean computations with hyperbolic distances and employs Möbius-weighted means to ensure that all updates remain consistent with the geometry of the space. HypeGBMS effectively captures latent hierarchies while retaining the density-seeking behavior of GBMS. We provide theoretical insights into convergence and computational complexity, along with empirical results that demonstrate improved clustering quality in hierarchical datasets. This work bridges classical mean-shift clustering and hyperbolic representation learning, offering a principled approach to density-based clustering in curved spaces. Extensive experimental evaluations on 11 real-world datasets demonstrate that HypeGBMS significantly outperforms conventional mean-shift clustering methods in non-Euclidean settings, underscoring its robustness and effectiveness.
[LG-16] Sliced ReLU attention: Quasi-linear contextual expressivity via sorting
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11411
作者: Siwan Boufadène(LIGM),François-Xavier Vialard(LIGM)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:We introduce sliced ReLU attention, a new attention mechanism that departs structurally from both softmax and ReLU-based alternatives. Instead of applying a nonlinearity to pairwise dot products, we operate on one-dimensional projections of key–query differences and leverage sorting to obtain quasi-linear complexity. This construction yields a differentiable, non-symmetric kernel that can be computed in O(n log(n)) through a sorting procedure, making it suitable for very long contexts. Beyond computational benefits, the model retains strong theoretical expressive power: we establish two in-context expressivity results, previously known for softmax attention, showing that sliced ReLU attention preserves the ability to perform nontrivial sequence-to-sequence disentangling tasks and satisfies a contextual universal approximation property. Finally, we illustrate the potential practical interest of this kernel in small-scale experiments.
[LG-17] Bhargava Cube–Inspired Quadratic Regularization for Structured Neural Embeddings
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11392
作者: S Sairam,Prateek P Kulkarni
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 12 pages, 3 figures
Abstract:We present a novel approach to neural representation learning that incorporates algebraic constraints inspired by Bhargava cubes from number theory. Traditional deep learning methods learn representations in unstructured latent spaces lacking interpretability and mathematical consistency. Our framework maps input data to constrained 3-dimensional latent spaces where embeddings are regularized to satisfy learned quadratic relationships derived from Bhargava’s combinatorial structures. The architecture employs a differentiable auxiliary loss function operating independently of classification objectives, guiding models toward mathematically structured representations. We evaluate on MNIST, achieving 99.46% accuracy while producing interpretable 3D embeddings that naturally cluster by digit class and satisfy learned quadratic constraints. Unlike existing manifold learning approaches requiring explicit geometric supervision, our method imposes weak algebraic priors through differentiable constraints, ensuring compatibility with standard optimization. This represents the first application of number-theoretic constructs to neural representation learning, establishing a foundation for incorporating structured mathematical priors in neural networks.
[LG-18] Mitigating the Safety Alignment Tax with Null-Space Constrained Policy Optimization
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11391
作者: Yifan Niu,Han Xiao,Dongyi Liu,Nuo Chen,Jia Li
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world applications, it is important to ensure their behaviors align with human values, societal norms, and ethical principles. However, safety alignment under Reinforcement Learning (RL) often suffers from forgetting learned general abilities, which is also known as the alignment tax. To address this issue, we introduce Null-Space constrained Policy Optimization (NSPO), a novel RL framework for LLM safety alignment while preserving their core abilities. The safety policy gradients are geometrically projected into the null space of general tasks, thereby mitigating the safety alignment tax. In addition, we theoretically prove that NSPO preserves the model’s original core capabilities, while still guaranteeing a descent direction for effective safety alignment. Extensive experiments demonstrate that NSPO outperforms existing methods by a large margin, achieving state-of-the-art safety performance without sacrificing accuracy on general tasks, including math, code, and instruction-following tasks. Notably, NSPO is data-efficient and only requires 40% of public human-annotated safety data from PKU-SafeRLHF to achieve promising safety performance, without a large amount of mixed general tasks data in existing alignment methods.
[LG-19] Attacking and Securing Community Detection: A Game-Theoretic Framework
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11359
作者: Yifan Niu,Aochuan Chen,Tingyang Xu,Jia Li
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Science and Game Theory (cs.GT)
*备注:
Abstract:It has been demonstrated that adversarial graphs, i.e., graphs with imperceptible perturbations, can cause deep graph models to fail on classification tasks. In this work, we extend the concept of adversarial graphs to the community detection problem, which is more challenging. We propose novel attack and defense techniques for community detection problem, with the objective of hiding targeted individuals from detection models and enhancing the robustness of community detection models, respectively. These techniques have many applications in real-world scenarios, for example, protecting personal privacy in social networks and understanding camouflage patterns in transaction networks. To simulate interactive attack and defense behaviors, we further propose a game-theoretic framework, called CD-GAME. One player is a graph attacker, while the other player is a Rayleigh Quotient defender. The CD-GAME models the mutual influence and feedback mechanisms between the attacker and the defender, revealing the dynamic evolutionary process of the game. Both players dynamically update their strategies until they reach the Nash equilibrium. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed attack and defense methods, and both outperform existing baselines by a significant margin. Furthermore, CD-GAME provides valuable insights for understanding interactive attack and defense scenarios in community detection problems. We found that in traditional single-step attack or defense, attacker tends to employ strategies that are most effective, but are easily detected and countered by defender. When the interactive game reaches a Nash equilibrium, attacker adopts more imperceptible strategies that can still achieve satisfactory attack effectiveness even after defense.
[LG-20] CAT: Can Trust be Predicted with Context-Awareness in Dynamic Heterogeneous Networks?
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11352
作者: Jie Wang,Zheng Yan,Jiahe Lan,Xuyan Li,Elisa Bertino
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Trust prediction provides valuable support for decision-making, risk mitigation, and system security enhancement. Recently, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have emerged as a promising approach for trust prediction, owing to their ability to learn expressive node representations that capture intricate trust relationships within a network. However, current GNN-based trust prediction models face several limitations: (i) Most of them fail to capture trust dynamicity, leading to questionable inferences. (ii) They rarely consider the heterogeneous nature of real-world networks, resulting in a loss of rich semantics. (iii) None of them support context-awareness, a basic property of trust, making prediction results coarse-grained. To this end, we propose CAT, the first Context-Aware GNN-based Trust prediction model that supports trust dynamicity and accurately represents real-world heterogeneity. CAT consists of a graph construction layer, an embedding layer, a heterogeneous attention layer, and a prediction layer. It handles dynamic graphs using continuous-time representations and captures temporal information through a time encoding function. To model graph heterogeneity and leverage semantic information, CAT employs a dual attention mechanism that identifies the importance of different node types and nodes within each type. For context-awareness, we introduce a new notion of meta-paths to extract contextual features. By constructing context embeddings and integrating a context-aware aggregator, CAT can predict both context-aware trust and overall trust. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that CAT outperforms five groups of baselines in trust prediction, while exhibiting strong scalability to large-scale graphs and robustness against both trust-oriented and GNN-oriented attacks. Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2512.11352 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2512.11352v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11352 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-21] Symmetry-Aware Steering of Equivariant Diffusion Policies: Benefits and Limits
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11345
作者: Minwoo Park,Junwoo Chang,Jongeun Choi,Roberto Horowitz
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Robotics (cs.RO)
*备注:
Abstract:Equivariant diffusion policies (EDPs) combine the generative expressivity of diffusion models with the strong generalization and sample efficiency afforded by geometric symmetries. While steering these policies with reinforcement learning (RL) offers a promising mechanism for fine-tuning beyond demonstration data, directly applying standard (non-equivariant) RL can be sample-inefficient and unstable, as it ignores the symmetries that EDPs are designed to exploit. In this paper, we theoretically establish that the diffusion process of an EDP is equivariant, which in turn induces a group-invariant latent-noise MDP that is well-suited for equivariant diffusion steering. Building on this theory, we introduce a principled symmetry-aware steering framework and compare standard, equivariant, and approximately equivariant RL strategies through comprehensive experiments across tasks with varying degrees of symmetry. While we identify the practical boundaries of strict equivariance under symmetry breaking, we show that exploiting symmetry during the steering process yields substantial benefits-enhancing sample efficiency, preventing value divergence, and achieving strong policy improvements even when EDPs are trained from extremely limited demonstrations.
[LG-22] DAPO: Design Structure-Aware Pass Ordering in High-Level Synthesis with Graph Contrastive and Reinforcement Learning DATE2026
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11342
作者: Jinming Ge,Linfeng Du,Likith Anaparty,Shangkun Li,Tingyuan Liang,Afzal Ahmad,Vivek Chaturvedi,Sharad Sinha,Zhiyao Xie,Jiang Xu,Wei Zhang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Accepted by DATE 2026
Abstract:High-Level Synthesis (HLS) tools are widely adopted in FPGA-based domain-specific accelerator design. However, existing tools rely on fixed optimization strategies inherited from software compilations, limiting their effectiveness. Tailoring optimization strategies to specific designs requires deep semantic understanding, accurate hardware metric estimation, and advanced search algorithms – capabilities that current approaches lack. We propose DAPO, a design structure-aware pass ordering framework that extracts program semantics from control and data flow graphs, employs contrastive learning to generate rich embeddings, and leverages an analytical model for accurate hardware metric estimation. These components jointly guide a reinforcement learning agent to discover design-specific optimization strategies. Evaluations on classic HLS designs demonstrate that our end-to-end flow delivers a 2.36 speedup over Vitis HLS on average. Comments: Accepted by DATE 2026 Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2512.11342 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2512.11342v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11342 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-23] Spectral entropy prior-guided deep feature fusion architecture for magnetic core loss
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11334
作者: Cong Yao,Chunye Gong,Jin Zhang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Accurate core loss modeling is critical for the design of high-efficiency power electronic systems. Traditional core loss modeling methods have limitations in prediction accuracy. To advance this field, the IEEE Power Electronics Society launched the MagNet Challenge in 2023, the first international competition focused on data-driven power electronics design methods, aiming to uncover complex loss patterns in magnetic components through a data-driven paradigm. Although purely data-driven models demonstrate strong fitting performance, their interpretability and cross-distribution generalization capabilities remain limited. To address these issues, this paper proposes a hybrid model, SEPI-TFPNet, which integrates empirical models with deep learning. The physical-prior submodule employs a spectral entropy discrimination mechanism to select the most suitable empirical model under different excitation waveforms. The data-driven submodule incorporates convolutional neural networks, multi-head attention mechanisms, and bidirectional long short-term memory networks to extract flux-density time-series features. An adaptive feature fusion module is introduced to improve multimodal feature interaction and integration. Using the MagNet dataset containing various magnetic materials, this paper evaluates the proposed method and compares it with 21 representative models from the 2023 challenge and three advanced methods from 2024-2025. The results show that the proposed method achieves improved modeling accuracy and robustness.
[LG-24] Pace: Physics-Aware Attentive Temporal Convolutional Network for Battery Health Estimation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11332
作者: Sara Sameer,Wei Zhang,Kannan Dhivya Dharshini,Xin Lou,Yulin Gao,Terence Goh,Qingyu Yan
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Batteries are critical components in modern energy systems such as electric vehicles and power grid energy storage. Effective battery health management is essential for battery system safety, cost-efficiency, and sustainability. In this paper, we propose Pace, a physics-aware attentive temporal convolutional network for battery health estimation. Pace integrates raw sensor measurements with battery physics features derived from the equivalent circuit model. We develop three battery-specific modules, including dilated temporal blocks for efficient temporal encoding, chunked attention blocks for context modeling, and a dual-head output block for fusing short- and long-term battery degradation patterns. Together, the modules enable Pace to predict battery health accurately and efficiently in various battery usage conditions. In a large public dataset, Pace performs much better than existing models, achieving an average performance improvement of 6.5 and 2.0x compared to two best-performing baseline models. We further demonstrate its practical viability with a real-time edge deployment on a Raspberry Pi. These results establish Pace as a practical and high-performance solution for battery health analytics.
[LG-25] Benchmarking the Generality of Vision-Language-Action Models
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11315
作者: Pranav Guruprasad,Sudipta Chowdhury,Harsh Sikka,Mridul Sharma,Helen Lu,Sean Rivera,Aryan Khurana,Hangliang Ren,Yangyue Wang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 23 pages, 7 figures, and 1 table
Abstract:Generalist multimodal agents are expected to unify perception, language, and control - operating robustly across diverse real world domains. However, current evaluation practices remain fragmented across isolated benchmarks, making it difficult to assess whether today’s foundation models truly generalize beyond their training distributions. We introduce MultiNet v1.0, a unified benchmark for measuring the cross domain generality of vision language models (VLMs) and vision language action models (VLAs) across six foundational capability regimes. Visual grounding, spatial reasoning, tool use, physical commonsense, multi agent coordination, and continuous robot control. Evaluating GPT 5, Pi0, and Magma, we find that no model demonstrates consistent generality. All exhibit substantial degradation on unseen domains, unfamiliar modalities, or cross domain task shifts despite strong performance within their training this http URL failures manifest as modality misalignment, output format instability, and catastrophic knowledge degradation under domain this http URL findings reveal a persistent gap between the aspiration of generalist intelligence and the actual capabilities of current foundation this http URL v1.0 provides a standardized evaluation substrate for diagnosing these gaps and guiding the development of future generalist this http URL, data, and leaderboards are publicly available.
[LG-26] QGEC : Quantum Golay Code Error Correction
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11307
作者: Hideo Mukai,Hoshitaro Ohnishi
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Quantum Physics (quant-ph)
*备注:
Abstract:Quantum computers have the possibility of a much reduced calculation load compared with classical computers in specific problems. Quantum error correction (QEC) is vital for handling qubits, which are vulnerable to external noise. In QEC, actual errors are predicted from the results of syndrome measurements by stabilizer generators, in place of making direct measurements of the data qubits. Here, we propose Quantum Golay code Error Correction (QGEC), a QEC method using Golay code, which is an efficient coding method in classical information theory. We investigated our method’s ability in decoding calculations with the Transformer. We evaluated the accuracy of the decoder in a code space defined by the generative polynomials with three different weights sets and three noise models with different correlations of bit-flip error and phase-flip error. Furthermore, under a noise model following a discrete uniform distribution, we compared the decoding performance of Transformer decoders with identical architectures trained respectively on Golay and toric codes. The results showed that the noise model with the smaller correlation gave better accuracy, while the weights of the generative polynomials had little effect on the accuracy of the decoder. In addition, they showed that Golay code requiring 23 data qubits and having a code distance of 7 achieved higher decoding accuracy than toric code which requiring 50 data qubits and having a code distance of 5. This suggests that implementing quantum error correction using a Transformer may enable the Golay code to realize fault-tolerant quantum computation more efficiently.
[LG-27] SRLR: Symbolic Regression based Logic Recovery to Counter Programmable Logic Controller Attacks
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11298
作者: Hao Zhou(Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications),Suman Sourav(Aalborg University),Binbin Chen(Singapore University of Technology and Design),Ke Yu(Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 27 pages, 20 figures. This article was accepted by IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2025.3634027
Abstract:Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are critical components in Industrial Control Systems (ICSs). Their potential exposure to external world makes them susceptible to cyber-attacks. Existing detection methods against controller logic attacks use either specification-based or learnt models. However, specification-based models require experts’ manual efforts or access to PLC’s source code, while machine learning-based models often fall short of providing explanation for their decisions. We design SRLR – a it Symbolic Regression based Logic Recovery solution to identify the logic of a PLC based only on its inputs and outputs. The recovered logic is used to generate explainable rules for detecting controller logic attacks. SRLR enhances the latest deep symbolic regression methods using the following ICS-specific properties: (1) some important ICS control logic is best represented in frequency domain rather than time domain; (2) an ICS controller can operate in multiple modes, each using different logic, where mode switches usually do not happen frequently; (3) a robust controller usually filters out outlier inputs as ICS sensor data can be noisy; and (4) with the above factors captured, the degree of complexity of the formulas is reduced, making effective search possible. Thanks to these enhancements, SRLR consistently outperforms all existing methods in a variety of ICS settings that we evaluate. In terms of the recovery accuracy, SRLR’s gain can be as high as 39% in some challenging environment. We also evaluate SRLR on a distribution grid containing hundreds of voltage regulators, demonstrating its stability in handling large-scale, complex systems with varied configurations.
[LG-28] Integrated Prediction and Multi-period Portfolio Optimization
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11273
作者: Qi Deng,Yuxuan Linghu,Zhiyuan Liu
类目: Computational Engineering, Finance, and Science (cs.CE); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 23 pages, 6 figures, and 4 tables
Abstract:Multi-period portfolio optimization is important for real portfolio management, as it accounts for transaction costs, path-dependent risks, and the intertemporal structure of trading decisions that single-period models cannot capture. Classical methods usually follow a two-stage framework: machine learning algorithms are employed to produce forecasts that closely fit the realized returns, and the predicted values are then used in a downstream portfolio optimization problem to determine the asset weights. This separation leads to a fundamental misalignment between predictions and decision outcomes, while also ignoring the impact of transaction costs. To bridge this gap, recent studies have proposed the idea of end-to-end learning, integrating the two stages into a single pipeline. This paper introduces IPMO (Integrated Prediction and Multi-period Portfolio Optimization), a model for multi-period mean-variance portfolio optimization with turnover penalties. The predictor generates multi-period return forecasts that parameterize a differentiable convex optimization layer, which in turn drives learning via portfolio performance. For scalability, we introduce a mirror-descent fixed-point (MDFP) differentiation scheme that avoids factorizing the Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) systems, which thus yields stable implicit gradients and nearly scale-insensitive runtime as the decision horizon grows. In experiments with real market data and two representative time-series prediction models, the IPMO method consistently outperforms the two-stage benchmarks in risk-adjusted performance net of transaction costs and achieves more coherent allocation paths. Our results show that integrating machine learning prediction with optimization in the multi-period setting improves financial outcomes and remains computationally tractable.
[LG-29] Features Emerge as Discrete States: The First Application of SAEs to 3D Representations
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11263
作者: Albert Miao,Chenliang Zhou,Jiawei Zhou,Cengiz Oztireli
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) are a powerful dictionary learning technique for decomposing neural network activations, translating the hidden state into human ideas with high semantic value despite no external intervention or guidance. However, this technique has rarely been applied outside of the textual domain, limiting theoretical explorations of feature decomposition. We present the \textbffirst application of SAEs to the 3D domain, analyzing the features used by a state-of-the-art 3D reconstruction VAE applied to 53k 3D models from the Objaverse dataset. We observe that the network encodes discrete rather than continuous features, leading to our key finding: \textbfsuch models approximate a discrete state space, driven by phase-like transitions from feature activations. Through this state transition framework, we address three otherwise unintuitive behaviors – the inclination of the reconstruction model towards positional encoding representations, the sigmoidal behavior of reconstruction loss from feature ablation, and the bimodality in the distribution of phase transition points. This final observation suggests the model \textbfredistributes the interference caused by superposition to prioritize the saliency of different features. Our work not only compiles and explains unexpected phenomena regarding feature decomposition, but also provides a framework to explain the model’s feature learning dynamics. The code and dataset of encoded 3D objects will be available on release.
[LG-30] Insight Miner: A Time Series Analysis Dataset for Cross-Domain Alignment with Natural Language
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11251
作者: Yunkai Zhang,Yawen Zhang,Ming Zheng,Kezhen Chen,Chongyang Gao,Ruian Ge,Siyuan Teng,Amine Jelloul,Jinmeng Rao,Xiaoyuan Guo,Chiang-Wei Fang,Zeyu Zheng,Jie Yang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Time-series data is critical across many scientific and industrial domains, including environmental analysis, agriculture, transportation, and finance. However, mining insights from this data typically requires deep domain expertise, a process that is both time-consuming and labor-intensive. In this paper, we propose \textbfInsight Miner, a large-scale multimodal model (LMM) designed to generate high-quality, comprehensive time-series descriptions enriched with domain-specific knowledge. To facilitate this, we introduce \textbfTS-Insights\footnoteAvailable at \hrefthis https URLthis https URL., the first general-domain dataset for time series and language alignment. TS-Insights contains 100k time-series windows sampled from 20 forecasting datasets. We construct this dataset using a novel \textbfagentic workflow, where we use statistical tools to extract features from raw time series before synthesizing them into coherent trend descriptions with GPT-4. Following instruction tuning on TS-Insights, Insight Miner outperforms state-of-the-art multimodal models, such as LLaVA \citepliu2023llava and GPT-4, in generating time-series descriptions and insights. Our findings suggest a promising direction for leveraging LMMs in time series analysis, and serve as a foundational step toward enabling LLMs to interpret time series as a native input modality.
[LG-31] Multi-Objective Reinforcement Learning for Large-Scale Mixed Traffic Control
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11247
作者: Iftekharul Islam,Weizi Li
类目: Multiagent Systems (cs.MA); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Effective mixed traffic control requires balancing efficiency, fairness, and safety. Existing approaches excel at optimizing efficiency and enforcing safety constraints but lack mechanisms to ensure equitable service, resulting in systematic starvation of vehicles on low-demand approaches. We propose a hierarchical framework combining multi-objective reinforcement learning for local intersection control with strategic routing for network-level coordination. Our approach introduces a Conflict Threat Vector that provides agents with explicit risk signals for proactive conflict avoidance, and a queue parity penalty that ensures equitable service across all traffic streams. Extensive experiments on a real-world network across different robot vehicle (RV) penetration rates demonstrate substantial improvements: up to 53% reductions in average wait time, up to 86% reductions in maximum starvation, and up to 86% reduction in conflict rate compared to baselines, while maintaining fuel efficiency. Our analysis reveals that strategic routing effectiveness scales with RV penetration, becoming increasingly valuable at higher autonomy levels. The results demonstrate that multi-objective optimization through well-curated reward functions paired with strategic RV routing yields significant benefits in fairness and safety metrics critical for equitable mixed-autonomy deployment.
[LG-32] Latent Variable Causal Discovery under Selection Bias ICML2025
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11219
作者: Haoyue Dai,Yiwen Qiu,Ignavier Ng,Xinshuai Dong,Peter Spirtes,Kun Zhang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Appears at ICML 2025
Abstract:Addressing selection bias in latent variable causal discovery is important yet underexplored, largely due to a lack of suitable statistical tools: While various tools beyond basic conditional independencies have been developed to handle latent variables, none have been adapted for selection bias. We make an attempt by studying rank constraints, which, as a generalization to conditional independence constraints, exploits the ranks of covariance submatrices in linear Gaussian models. We show that although selection can significantly complicate the joint distribution, interestingly, the ranks in the biased covariance matrices still preserve meaningful information about both causal structures and selection mechanisms. We provide a graph-theoretic characterization of such rank constraints. Using this tool, we demonstrate that the one-factor model, a classical latent variable model, can be identified under selection bias. Simulations and real-world experiments confirm the effectiveness of using our rank constraints.
[LG-33] heoretical Foundations of GPU-Native Compilation for Rapid Code Iteration
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11200
作者: Adilet Metinov,Gulida M. Kudakeeva,Gulnara D. Kabaeva
类目: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Programming Languages (cs.PL)
*备注: 9 pages , 2 tables
Abstract:Current AI code generation systems suffer from significant latency bottlenecks due to CPU-GPU data transfers during compilation, execution, and testing phases. We establish theoretical foundations for three complementary approaches to GPU-native compilation that eliminate these transfers: (1) parallel traditional compilation adapted for GPU execution, (2) neural compilation using learned sequence-to-sequence translation with probabilistic verification, and (3) hybrid architectures combining both strategies. We derive latency and energy bounds demonstrating potential speedups of 10-100x for code iteration cycles. Our analysis shows that traditional GPU compilation provides 2-5x improvements through transfer elimination, neural compilation achieves 10-100x speedups via massive parallelism, and hybrid approaches offer practical deployment paths with guaranteed correctness. We formalize the probabilistic verification framework that enables trading compilation accuracy for parallel exploration, and discuss implications for self-improving AI systems and future analog computing substrates.
[LG-34] On the failure of ReLU activation for physics-informed machine learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11184
作者: Conor Rowan
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Physics-informed machine learning uses governing ordinary and/or partial differential equations to train neural networks to represent the solution field. Like any machine learning problem, the choice of activation function influences the characteristics and performance of the solution obtained from physics-informed training. Several studies have compared common activation functions on benchmark differential equations, and have unanimously found that the rectified linear unit (ReLU) is outperformed by competitors such as the sigmoid, hyperbolic tangent, and swish activation functions. In this work, we diagnose the poor performance of ReLU on physics-informed machine learning problems. While it is well-known that the piecewise linear form of ReLU prevents it from being used on second-order differential equations, we show that ReLU fails even on variational problems involving only first derivatives. We identify the cause of this failure as second derivatives of the activation, which are taken not in the formulation of the loss, but in the process of training. Namely, we show that automatic differentiation in PyTorch fails to characterize derivatives of discontinuous fields, which causes the gradient of the physics-informed loss to be mis-specified, thus explaining the poor performance of ReLU.
[LG-35] Progress over Points: Reframing LM Benchmarks Around Scientific Objectives
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11183
作者: Alwin Jin,Sean M. Hendryx,Vaskar Nath
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Current benchmarks that test LLMs on static, already-solved problems (e.g., math word problems) effectively demonstrated basic capability acquisition. The natural progression has been toward larger, more comprehensive and challenging collections of static problems, an approach that inadvertently constrains the kinds of advances we can measure and incentivize. To address this limitation, we argue for progress-oriented benchmarks, problem environments whose objectives are themselves the core targets of scientific progress, so that achieving state of the art on the benchmark advances the field. As a introductory step, we instantiate an environment based on the NanoGPT speedrun. The environment standardizes a dataset slice, a reference model and training harness, and rich telemetry, with run-time verification and anti-gaming checks. Evaluation centers on the scientific delta achieved: best-attained loss and the efficiency frontier. Using this environment, we achieve a new state-of-the-art training time, improving upon the previous record by 3 seconds, and qualitatively observe the emergence of novel algorithmic ideas. Moreover, comparisons between models and agents remain possible, but they are a means, not the end; the benchmark’s purpose is to catalyze reusable improvements to the language modeling stack. With this release, the overarching goal is to seed a community shift from static problem leaderboards to test-time research on open-ended yet measurable scientific problems. In this new paradigm, progress on the benchmark is progress on the science, thus reframing “benchmarking” as a vehicle for scientific advancement.
[LG-36] Bandwidth-constrained Variational Message Encoding for Cooperative Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning AAMAS2026
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11179
作者: Wei Duan,Jie Lu,En Yu,Junyu Xuan
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
*备注: Submitted to AAMAS 2026
Abstract:Graph-based multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) enables coordinated behavior under partial observability by modeling agents as nodes and communication links as edges. While recent methods excel at learning sparse coordination graphs-determining who communicates with whom-they do not address what information should be transmitted under hard bandwidth constraints. We study this bandwidth-limited regime and show that naive dimensionality reduction consistently degrades coordination performance. Hard bandwidth constraints force selective encoding, but deterministic projections lack mechanisms to control how compression occurs. We introduce Bandwidth-constrained Variational Message Encoding (BVME), a lightweight module that treats messages as samples from learned Gaussian posteriors regularized via KL divergence to an uninformative prior. BVME’s variational framework provides principled, tunable control over compression strength through interpretable hyperparameters, directly constraining the representations used for decision-making. Across SMACv1, SMACv2, and MPE benchmarks, BVME achieves comparable or superior performance while using 67–83% fewer message dimensions, with gains most pronounced on sparse graphs where message quality critically impacts coordination. Ablations reveal U-shaped sensitivity to bandwidth, with BVME excelling at extreme ratios while adding minimal overhead.
[LG-37] Harnessing Rich Multi-Modal Data for Spatial-Temporal Homophily-Embedded Graph Learning Across Domains and Localities
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11178
作者: Takuya Kurihana,Xiaojian Zhang,Wing Yee Au,Hon Yung Wong
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Social and Information Networks (cs.SI)
*备注: 18 pages, 8 figures, Presented in part at the 2025 INFORMS Annual Meeting
Abstract:Modern cities are increasingly reliant on data-driven insights to support decision making in areas such as transportation, public safety and environmental impact. However, city-level data often exists in heterogeneous formats, collected independently by local agencies with diverse objectives and standards. Despite their numerous, wide-ranging, and uniformly consumable nature, national-level datasets exhibit significant heterogeneity and multi-modality. This research proposes a heterogeneous data pipeline that performs cross-domain data fusion over time-varying, spatial-varying and spatial-varying time-series datasets. We aim to address complex urban problems across multiple domains and localities by harnessing the rich information over 50 data sources. Specifically, our data-learning module integrates homophily from spatial-varying dataset into graph-learning, embedding information of various localities into models. We demonstrate the generalizability and flexibility of the framework through five real-world observations using a variety of publicly accessible datasets (e.g., ride-share, traffic crash, and crime reports) collected from multiple cities. The results show that our proposed framework demonstrates strong predictive performance while requiring minimal reconfiguration when transferred to new localities or domains. This research advances the goal of building data-informed urban systems in a scalable way, addressing one of the most pressing challenges in smart city analytics.
[LG-38] he Vekua Layer: Exact Physical Priors for Implicit Neural Representations via Generalized Analytic Functions
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11138
作者: Vladimer Khasia
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Implicit Neural Representations (INRs) have emerged as a powerful paradigm for parameterizing physical fields, yet they often suffer from spectral bias and the computational expense of non-convex optimization. We introduce the Vekua Layer (VL), a differentiable spectral method grounded in the classical theory of Generalized Analytic Functions. By restricting the hypothesis space to the kernel of the governing differential operator – specifically utilizing Harmonic and Fourier-Bessel bases – the VL transforms the learning task from iterative gradient descent to a strictly convex least-squares problem solved via linear projection. We evaluate the VL against Sinusoidal Representation Networks (SIRENs) on homogeneous elliptic Partial Differential Equations (PDEs). Our results demonstrate that the VL achieves machine precision ( \textMSE \approx 10^-33 ) on exact reconstruction tasks and exhibits superior stability in the presence of incoherent sensor noise ( \textMSE \approx 0.03 ), effectively acting as a physics-informed spectral filter. Furthermore, we show that the VL enables “holographic” extrapolation of global fields from partial boundary data via analytic continuation, a capability absent in standard coordinate-based approximations.
[LG-39] Refining Graphical Neural Network Predictions Using Flow Matching for Optimal Power Flow with Constraint-Satisfaction Guarantee
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11127
作者: Kshitiz Khanal
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Optimization and Control (math.OC)
*备注:
Abstract:The DC Optimal Power Flow (DC-OPF) problem is fundamental to power system operations, requiring rapid solutions for real-time grid management. While traditional optimization solvers provide optimal solutions, their computational cost becomes prohibitive for large-scale systems requiring frequent recalculations. Machine learning approaches offer promise for acceleration but often struggle with constraint satisfaction and cost optimality. We present a novel two-stage learning framework that combines physics-informed Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) with Continuous Flow Matching (CFM) for solving DC-OPF problems. Our approach embeds fundamental physical principles–including economic dispatch optimality conditions, Kirchhoff’s laws, and Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) complementarity conditions–directly into the training objectives. The first stage trains a GNN to produce feasible initial solutions by learning from physics-informed losses that encode power system constraints. The second stage employs CFM, a simulation-free continuous normalizing flow technique, to refine these solutions toward optimality through learned vector field regression. Evaluated on the IEEE 30-bus system across five load scenarios ranging from 70% to 130% nominal load, our method achieves near-optimal solutions with cost gaps below 0.1% for nominal loads and below 3% for extreme conditions, while maintaining 100% feasibility. Our framework bridges the gap between fast but approximate neural network predictions and optimal but slow numerical solvers, offering a practical solution for modern power systems with high renewable penetration requiring frequent dispatch updates.
[LG-40] Limits and Gains of Test-Time Scaling in Vision-Language Reasoning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11109
作者: Mohammadjavad Ahmadpour,Amirmahdi Meighani,Payam Taebi,Omid Ghahroodi,Amirmohammad Izadi,Mahdieh Soleymani Baghshah
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Mohammadjavad Ahmadpour and Amirmadhi Meighani contributed equally to this work
Abstract:Test-time scaling (TTS) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for improving the reasoning ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) by allocating additional computation at inference, yet its application to multimodal systems such as Vision-Language Models (VLMs) remains underexplored. In this work, we present a systematic empirical study of inference time reasoning methods applied across both open-source and closed-source VLMs on different benchmarks. Our results reveal that while closed-source models consistently benefit from structured reasoning and iterative Self-Refinement, open-source VLMs show inconsistent behavior: external verification provides the most reliable gains, whereas iterative refinement often degrades performance. We further find that the effectiveness of TTS is dataset-dependent, yielding clear improvements on multi-step reasoning tasks but offering only limited gains on perception-focused benchmarks. These findings demonstrate that TTS is not a universal solution and must be tailored to both model capabilities and task characteristics, motivating future work on adaptive TTS strategies and multimodal reward models.
[LG-41] Investigating ECG Diagnosis with Ambiguous Labels using Partial Label Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11095
作者: Sana Rahmani,Javad Hashemi,Ali Etemad
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Label ambiguity is an inherent problem in real-world electrocardiogram (ECG) diagnosis, arising from overlapping conditions and diagnostic disagreement. However, current ECG models are trained under the assumption of clean and non-ambiguous annotations, which limits both the development and the meaningful evaluation of models under real-world conditions. Although Partial Label Learning (PLL) frameworks are designed to learn from ambiguous labels, their effectiveness in medical time-series domains, ECG in particular, remains largely unexplored. In this work, we present the first systematic study of PLL methods for ECG diagnosis. We adapt nine PLL algorithms to multi-label ECG diagnosis and evaluate them using a diverse set of clinically motivated ambiguity generation strategies, capturing both unstructured (e.g., random) and structured ambiguities (e.g., cardiologist-derived similarities, treatment relationships, and diagnostic taxonomies). Our experiments on the PTB-XL and Chapman datasets demonstrate that PLL methods vary substantially in their robustness to different types and degrees of ambiguity. Through extensive analysis, we identify key limitations of current PLL approaches in clinical settings and outline future directions for developing robust and clinically aligned ambiguity-aware learning frameworks for ECG diagnosis.
[LG-42] Memoryless Policy Iteration for Episodic POMDPs
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11082
作者: Roy van Zuijlen,Duarte Antunes
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Memoryless and finite-memory policies offer a practical alternative for solving partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDPs), as they operate directly in the output space rather than in the high-dimensional belief space. However, extending classical methods such as policy iteration to this setting remains difficult; the output process is non-Markovian, making policy-improvement steps interdependent across stages. We introduce a new family of monotonically improving policy-iteration algorithms that alternate between single-stage output-based policy improvements and policy evaluations according to a prescribed periodic pattern. We show that this family admits optimal patterns that maximize a natural computational-efficiency index, and we identify the simplest pattern with minimal period. Building on this structure, we further develop a model-free variant that estimates values from data and learns memoryless policies directly. Across several POMDPs examples, our method achieves significant computational speedups over policy-gradient baselines and recent specialized algorithms in both model-based and model-free settings.
[LG-43] ECM*: A Data-Driven Assessment to Reinforcement Learning Methods and Application to Heparin Treatment Strategy for Surgical Sepsis
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10973
作者: Jiang Liu,Yujie Li,Chan Zhou,Yihao Xie,Qilong Sun,Xin Shu,Peiwei Li,Chunyong Yang,Yiziting Zhu,Jiaqi Zhu,Yuwen Chen,Bo An,Hao Wu,Bin Yi
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Objective: Sepsis is a life-threatening condition caused by severe infection leading to acute organ dysfunction. This study proposes a data-driven metric and a continuous reward function to optimize personalized heparin therapy in surgical sepsis patients. Methods: Data from the MIMIC-IV v1.0 and eICU v2.0 databases were used for model development and evaluation. The training cohort consisted of abdominal surgery patients receiving unfractionated heparin (UFH) after postoperative sepsis onset. We introduce a new RL-based framework: converting the discrete SOFA score to a continuous cxSOFA for more nuanced state and reward functions; Second, defining “good” or “bad” strategies based on cxSOFA by a stepwise manner; Third, proposing a Treatment Effect Comparison Matrix (TECM), analogous to a confusion matrix for classification tasks, to evaluate the treatment strategies. We applied different RL algorithms, Q-Learning, DQN, DDQN, BCQ and CQL to optimize the treatment and comprehensively evaluated the framework. Results: Among the AI-derived strategies, the cxSOFA-CQL model achieved the best performance, reducing mortality from 1.83% to 0.74% with the average hospital stay from 11.11 to 9.42 days. TECM demonstrated consistent outcomes across models, highlighting robustness. Conclusion: The proposed RL framework enables interpretable and robust optimization of heparin therapy in surgical sepsis. Continuous cxSOFA scoring and TECM-based evaluation provide nuanced treatment assessment, showing promise for improving clinical outcomes and decision-support reliability.
[LG-44] MoB: Mixture of Bidders
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10969
作者: Dev Vyas
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 8 pages, 2 figures
Abstract:Mixture of Experts (MoE) architectures have demonstrated remarkable success in scaling neural networks, yet their application to continual learning remains fundamentally limited by a critical vulnerability: the learned gating network itself suffers from catastrophic forgetting. We introduce Mixture of Bidders (MoB), a novel framework that reconceptualizes expert routing as a decentralized economic mechanism. MoB replaces learned gating networks with Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG) auctions, where experts compete for each data batch by bidding their true cost – a principled combination of execution cost (predicted loss) and forgetting cost (Elastic Weight Consolidation penalty). This game-theoretic approach provides three key advantages: (1) stateless routing that is immune to catastrophic forgetting, (2) \textbftruthful bidding guaranteed by dominant-strategy incentive compatibility, and (3) emergent specialization without explicit task boundaries. On Split-MNIST benchmarks, MoB achieves 88.77% average accuracy compared to 19.54% for Gated MoE and 27.96% for Monolithic EWC, representing a 4.5 times improvement over the strongest baseline. We further extend MoB with autonomous self-monitoring experts that detect their own knowledge consolidation boundaries, eliminating the need for explicit task demarcation.
[LG-45] Learning Minimal Representations of Fermionic Ground States
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11767
作者: Felix Frohnert,Emiel Koridon,Stefano Polla
类目: Quantum Physics (quant-ph); Strongly Correlated Electrons (cond-mat.str-el); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:We introduce an unsupervised machine-learning framework that discovers optimally compressed representations of quantum many-body ground states. Using an autoencoder neural network architecture on data from L -site Fermi-Hubbard models, we identify minimal latent spaces with a sharp reconstruction quality threshold at L-1 latent dimensions, matching the system’s intrinsic degrees of freedom. We demonstrate the use of the trained decoder as a differentiable variational ansatz to minimize energy directly within the latent space. Crucially, this approach circumvents the N -representability problem, as the learned manifold implicitly restricts the optimization to physically valid quantum states.
[LG-46] Stable spectral neural operator for learning stiff PDE systems from limited data
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11686
作者: Rui Zhang,Han Wan,Yang Liu,Hao Sun
类目: Computational Physics (physics.comp-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Accurate modeling of spatiotemporal dynamics is crucial to understanding complex phenomena across science and engineering. However, this task faces a fundamental challenge when the governing equations are unknown and observational data are sparse. System stiffness, the coupling of multiple time-scales, further exacerbates this problem and hinders long-term prediction. Existing methods fall short: purely data-driven methods demand massive datasets, whereas physics-aware approaches are constrained by their reliance on known equations and fine-grained time steps. To overcome these limitations, we introduce an equation-free learning framework, namely, the Stable Spectral Neural Operator (SSNO), for modeling stiff partial differential equation (PDE) systems based on limited data. Instead of encoding specific equation terms, SSNO embeds spectrally inspired structures in its architecture, yielding strong inductive biases for learning the underlying physics. It automatically learns local and global spatial interactions in the frequency domain, while handling system stiffness with a robust integrating factor time-stepping scheme. Demonstrated across multiple 2D and 3D benchmarks in Cartesian and spherical geometries, SSNO achieves prediction errors one to two orders of magnitude lower than leading models. Crucially, it shows remarkable data efficiency, requiring only very few (2–5) training trajectories for robust generalization to out-of-distribution conditions. This work offers a robust and generalizable approach to learning stiff spatiotemporal dynamics from limited data without explicit \textita priori knowledge of PDE terms.
[LG-47] Neural Network-based Partial-Linear Single-Index Models for Environmental Mixtures Analysis
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11593
作者: Hyungrok Do,Yuyan Wang,Mengling Liu,Myeonggyun Lee
类目: Applications (stat.AP); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Evaluating the health effects of complex environmental mixtures remains a central challenge in environmental health research. Existing approaches vary in their flexibility, interpretability, scalability, and support for diverse outcome types, often limiting their utility in real-world applications. To address these limitations, we propose a neural network-based partial-linear single-index (NeuralPLSI) modeling framework that bridges semiparametric regression modeling interpretability with the expressive power of deep learning. The NeuralPLSI model constructs an interpretable exposure index via a learnable projection and models its relationship with the outcome through a flexible neural network. The framework accommodates continuous, binary, and time-to-event outcomes, and supports inference through a bootstrap-based procedure that yields confidence intervals for key model parameters. We evaluated NeuralPLSI through simulation studies under a range of scenarios and applied it to data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) to demonstrate its practical utility. Together, our contributions establish NeuralPLSI as a scalable, interpretable, and versatile modeling tool for mixture analysis. To promote adoption and reproducibility, we release a user-friendly open-source software package that implements the proposed methodology and supports downstream visualization and inference (\textttthis https URL).
[LG-48] Safe Bayesian optimization across noise models via scenario programming
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11580
作者: Abdullah Tokmak,Thomas B. Schön,Dominik Baumann
类目: Optimization and Control (math.OC); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Systems and Control (eess.SY)
*备注: Accepted for publication (IEEE Control System Letters)
Abstract:Safe Bayesian optimization (BO) with Gaussian processes is an effective tool for tuning control policies in safety-critical real-world systems, specifically due to its sample efficiency and safety guarantees. However, most safe BO algorithms assume homoscedastic sub-Gaussian measurement noise, an assumption that does not hold in many relevant applications. In this article, we propose a straightforward yet rigorous approach for safe BO across noise models, including homoscedastic sub-Gaussian and heteroscedastic heavy-tailed distributions. We provide a high-probability bound on the measurement noise via the scenario approach, integrate these bounds into high probability confidence intervals, and prove safety and optimality for our proposed safe BO algorithm. We deploy our algorithm in synthetic examples and in tuning a controller for the Franka Emika manipulator in simulation.
[LG-49] FRQI Pairs method for image classification using Quantum Recurrent Neural Network
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11499
作者: Rafał Potempa,Michał Kordasz,Sundas Naqeeb Khan,Krzysztof Werner,Kamil Wereszczyński,Krzysztof Simiński,Krzysztof A. Cyran
类目: Quantum Physics (quant-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: This is a preprint of a paper submitted to the 2025 11th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT). Copyright may be transferred to IEEE upon acceptance
Abstract:This study aims to introduce the FRQI Pairs method to a wider audience, a novel approach to image classification using Quantum Recurrent Neural Networks (QRNN) with Flexible Representation for Quantum Images (FRQI). The study highlights an innovative approach to use quantum encoded data for an image classification task, suggesting that such quantum-based approaches could significantly reduce the complexity of quantum algorithms. Comparison of the FRQI Pairs method with contemporary techniques underscores the promise of integrating quantum computing principles with neural network architectures for the development of quantum machine learning. Comments: This is a preprint of a paper submitted to the 2025 11th International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies (CoDIT). Copyright may be transferred to IEEE upon acceptance Subjects: Quantum Physics (quant-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2512.11499 [quant-ph] (or arXiv:2512.11499v1 [quant-ph] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.11499 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-50] Emergence of Nonequilibrium Latent Cycles in Unsupervised Generative Modeling
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11415
作者: Marco Baiesi,Alberto Rosso
类目: atistical Mechanics (cond-mat.stat-mech); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 8 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:We show that nonequilibrium dynamics can play a constructive role in unsupervised machine learning by inducing the spontaneous emergence of latent-state cycles. We introduce a model in which visible and hidden variables interact through two independently parametrized transition matrices, defining a Markov chain whose steady state is intrinsically out of equilibrium. Likelihood maximization drives this system toward nonequilibrium steady states with finite entropy production, reduced self-transition probabilities, and persistent probability currents in the latent space. These cycles are not imposed by the architecture but arise from training, and models that develop them avoid the low-log-likelihood regime associated with nearly reversible dynamics while more faithfully reproducing the empirical distribution of data classes. Compared with equilibrium approaches such as restricted Boltzmann machines, our model breaks the detailed balance between the forward and backward conditional transitions and relies on a log-likelihood gradient that depends explicitly on the last two steps of the Markov chain. Hence, this exploration of the interface between nonequilibrium statistical physics and modern machine learning suggests that introducing irreversibility into latent-variable models can enhance generative performance.
[LG-51] Maritime object classification with SAR imagery using quantum kernel methods
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11367
作者: John Tanner,Nicholas Davies,Pascal Elahi,Casey R. Myers,Du Huynh,Wei Liu,Mark Reynolds,Jingbo Wang
类目: Quantum Physics (quant-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 15 + 5 pages, 5 figures, 4 tables
Abstract:Illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing causes global economic losses of \ 10-25 billion annually and undermines marine sustainability and governance. Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) provides reliable maritime surveillance under all weather and lighting conditions, but classifying small maritime objects in SAR imagery remains challenging. We investigate quantum machine learning for this task, focusing on Quantum Kernel Methods (QKMs) applied to real and complex SAR chips extracted from the SARFish dataset. We tackle two binary classification problems, the first for distinguishing vessels from non-vessels, and the second for distinguishing fishing vessels from other types of vessels. We compare QKMs applied to real and complex SAR chips against classical Laplacian, RBF, and linear kernels applied to real SAR chips. Using noiseless numerical simulations of the quantum kernels, we find that QKMs are capable of obtaining equal or better performance than the classical kernel on these tasks in the best case, but do not demonstrate a clear advantage for the complex SAR data. This work presents the first application of QKMs to maritime classification in SAR imagery and offers insight into the potential and current limitations of quantum-enhanced learning for maritime surveillance.
[LG-52] Data-Driven Model Reduction using WeldNet: Windowed Encoders for Learning Dynamics
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11090
作者: Biraj Dahal,Jiahui Cheng,Hao Liu,Rongjie Lai,Wenjing Liao
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Numerical Analysis (math.NA)
*备注:
Abstract:Many problems in science and engineering involve time-dependent, high dimensional datasets arising from complex physical processes, which are costly to simulate. In this work, we propose WeldNet: Windowed Encoders for Learning Dynamics, a data-driven nonlinear model reduction framework to build a low-dimensional surrogate model for complex evolution systems. Given time-dependent training data, we split the time domain into multiple overlapping windows, within which nonlinear dimension reduction is performed by auto-encoders to capture latent codes. Once a low-dimensional representation of the data is learned, a propagator network is trained to capture the evolution of the latent codes in each window, and a transcoder is trained to connect the latent codes between adjacent windows. The proposed windowed decomposition significantly simplifies propagator training by breaking long-horizon dynamics into multiple short, manageable segments, while the transcoders ensure consistency across windows. In addition to the algorithmic framework, we develop a mathematical theory establishing the representation power of WeldNet under the manifold hypothesis, justifying the success of nonlinear model reduction via deep autoencoder-based architectures. Our numerical experiments on various differential equations indicate that WeldNet can capture nonlinear latent structures and their underlying dynamics, outperforming both traditional projection-based approaches and recently developed nonlinear model reduction methods.
[LG-53] PV: Parameter Perturbations Through the Lens of Test Prediction Variance
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11089
作者: Devansh Arpit
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:We identify test prediction variance (TPV) – the first-order sensitivity of model outputs to parameter perturbations around a trained solution – as a unifying quantity that links several classical observations about generalization in deep networks. TPV is a fully label-free object whose trace form separates the geometry of the trained model from the specific perturbation mechanism, allowing a broad family of parameter perturbations like SGD noise, label noise, finite-precision noise, and other post-training perturbations to be analyzed under a single framework. Theoretically, we show that TPV estimated on the training set converges to its test-set value in the overparameterized limit, providing the first result that prediction variance under local parameter perturbations can be inferred from training inputs alone. Empirically, TPV exhibits a striking stability across datasets and architectures – including extremely narrow networks – and correlates well with clean test loss. Finally, we demonstrate that modeling pruning as a TPV perturbation yields a simple label-free importance measure that performs competitively with state-of-the-art pruning methods, illustrating the practical utility of TPV. Code available at this http URL.
[LG-54] Provable Recovery of Locally Important Signed Features and Interactions from Random Forest
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11081
作者: Kata Vuk,Nicolas Alexander Ihlo,Merle Behr
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Methodology (stat.ME)
*备注:
Abstract:Feature and Interaction Importance (FII) methods are essential in supervised learning for assessing the relevance of input variables and their interactions in complex prediction models. In many domains, such as personalized medicine, local interpretations for individual predictions are often required, rather than global scores summarizing overall feature importance. Random Forests (RFs) are widely used in these settings, and existing interpretability methods typically exploit tree structures and split statistics to provide model-specific insights. However, theoretical understanding of local FII methods for RF remains limited, making it unclear how to interpret high importance scores for individual predictions. We propose a novel, local, model-specific FII method that identifies frequent co-occurrences of features along decision paths, combining global patterns with those observed on paths specific to a given test point. We prove that our method consistently recovers the true local signal features and their interactions under a Locally Spike Sparse (LSS) model and also identifies whether large or small feature values drive a prediction. We illustrate the usefulness of our method and theoretical results through simulation studies and a real-world data example.
[LG-55] An Efficient Variant of One-Class SVM with Lifelong Online Learning Guarantees
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11052
作者: Joe Suk,Samory Kpotufe
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:We study outlier (a.k.a., anomaly) detection for single-pass non-stationary streaming data. In the well-studied offline or batch outlier detection problem, traditional methods such as kernel One-Class SVM (OCSVM) are both computationally heavy and prone to large false-negative (Type II) errors under non-stationarity. To remedy this, we introduce SONAR, an efficient SGD-based OCSVM solver with strongly convex regularization. We show novel theoretical guarantees on the Type I/II errors of SONAR, superior to those known for OCSVM, and further prove that SONAR ensures favorable lifelong learning guarantees under benign distribution shifts. In the more challenging problem of adversarial non-stationary data, we show that SONAR can be used within an ensemble method and equipped with changepoint detection to achieve adaptive guarantees, ensuring small Type I/II errors on each phase of data. We validate our theoretical findings on synthetic and real-world datasets.
[LG-56] Boosted Random Forests for Predicting Treatment Failure of Chemotherapy Regimens
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10995
作者: Muhammad Usamah Shahid,Muddassar Farooq
类目: Quantitative Methods (q-bio.QM); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, 2023
Abstract:Cancer patients may undergo lengthy and painful chemotherapy treatments, comprising several successive regimens or plans. Treatment inefficacy and other adverse events can lead to discontinuation (or failure) of these plans, or prematurely changing them, which results in a significant amount of physical, financial, and emotional toxicity to the patients and their families. In this work, we build treatment failure models based on the Real World Evidence (RWE) gathered from patients’ profiles available in our oncology EMR/EHR system. We also describe our feature engineering pipeline, experimental methods, and valuable insights obtained about treatment failures from trained models. We report our findings on five primary cancer types with the most frequent treatment failures (or discontinuations) to build unique and novel feature vectors from the clinical notes, diagnoses, and medications that are available in our oncology EMR. After following a novel three axes - performance, complexity and explainability - design exploration framework, boosted random forests are selected because they provide a baseline accuracy of 80% and an F1 score of 75%, with reduced model complexity, thus making them more interpretable to and usable by oncologists.
[LG-57] STARK denoises spatial transcriptomics images via adaptive regularization
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10994
作者: Sharvaj Kubal,Naomi Graham,Matthieu Heitz,Andrew Warren,Michael P. Friedlander,Yaniv Plan,Geoffrey Schiebinger
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Optimization and Control (math.OC); Statistics Theory (math.ST)
*备注: 34 pages, 10 figures
Abstract:We present an approach to denoising spatial transcriptomics images that is particularly effective for uncovering cell identities in the regime of ultra-low sequencing depths, and also allows for interpolation of gene expression. The method – Spatial Transcriptomics via Adaptive Regularization and Kernels (STARK) – augments kernel ridge regression with an incrementally adaptive graph Laplacian regularizer. In each iteration, we (1) perform kernel ridge regression with a fixed graph to update the image, and (2) update the graph based on the new image. The kernel ridge regression step involves reducing the infinite dimensional problem on a space of images to finite dimensions via a modified representer theorem. Starting with a purely spatial graph, and updating it as we improve our image makes the graph more robust to noise in low sequencing depth regimes. We show that the aforementioned approach optimizes a block-convex objective through an alternating minimization scheme wherein the sub-problems have closed form expressions that are easily computed. This perspective allows us to prove convergence of the iterates to a stationary point of this non-convex objective. Statistically, such stationary points converge to the ground truth with rate \mathcalO(R^-1/2) where R is the number of reads. In numerical experiments on real spatial transcriptomics data, the denoising performance of STARK, evaluated in terms of label transfer accuracy, shows consistent improvement over the competing methods tested.
[LG-58] Generalization of Long-Range Machine Learning Potentials in Complex Chemical Spaces
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10989
作者: Michal Sanocki,Julija Zavadlav
类目: Chemical Physics (physics.chem-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:The vastness of chemical space makes generalization a central challenge in the development of machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs). While MLIPs could enable large-scale atomistic simulations with near-quantum accuracy, their usefulness is often limited by poor transferability to out-of-distribution samples. Here, we systematically evaluate different MLIP architectures with long-range corrections across diverse chemical spaces and show that such schemes are essential, not only for improving in-distribution performance but, more importantly, for enabling significant gains in transferability to unseen regions of chemical space. To enable a more rigorous benchmarking, we introduce biased train-test splitting strategies, which explicitly test the model performance in significantly different regions of chemical space. Together, our findings highlight the importance of long-range modeling for achieving generalizable MLIPs and provide a framework for diagnosing systematic failures across chemical space. Although we demonstrate our methodology on metal-organic frameworks, it is broadly applicable to other materials, offering insights into the design of more robust and transferable MLIPs.
[LG-59] RMSup: Physics-Informed Radio Map Super-Resolution for Compute-Enhanced Integrated Sensing and Communications
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.10965
作者: Qiming Zhang,Xiucheng Wang,Nan Cheng,Zhisheng Yin,Xiang Li
类目: ignal Processing (eess.SP); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Systems and Control (eess.SY)
*备注:
Abstract:Radio maps (RMs) provide a spatially continuous description of wireless propagation, enabling cross-layer optimization and unifying communication and sensing for integrated sensing and communications (ISAC). However, constructing high-fidelity RMs at operational scales is difficult, since physics-based solvers are time-consuming and require precise scene models, while learning methods degrade under incomplete priors and sparse measurements, often smoothing away critical discontinuities. We present RMSup, a physics-informed super-resolution framework that functions with uniform sparse sampling and imperfect environment priors. RMSup extracts Helmholtz equation-informed boundary and singularity prompts from the measurements, fuses them with base-station side information and coarse scene descriptors as conditional inputs, and employs a boundary-aware dual-head network to reconstruct a high-fidelity RM and recover environmental contours jointly. Experimental results show the proposed RMsup achieves state-of-the-art performance both in RM construction and ISAC-related environment sensing.
信息检索
[IR-0] FAIR: Focused Attention Is All You Need for Generative Recommendation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.11254
作者: Longtao Xiao,Haolin Zhang,Guohao Cai,Jieming Zhu,Yifan Wang,Heng Chang,Zhenhua Dong,Xiu Li,Ruixuan Li
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注:
Abstract:Recently, transformer-based generative recommendation has garnered significant attention for user behavior modeling. However, it often requires discretizing items into multi-code representations (e.g., typically four code tokens or more), which sharply increases the length of the original item sequence. This expansion poses challenges to transformer-based models for modeling user behavior sequences with inherent noises, since they tend to overallocate attention to irrelevant or noisy context. To mitigate this issue, we propose FAIR, the first generative recommendation framework with focused attention, which enhances attention scores to relevant context while suppressing those to irrelevant ones. Specifically, we propose (1) a focused attention mechanism integrated into the standard Transformer, which learns two separate sets of Q and K attention weights and computes their difference as the final attention scores to eliminate attention noise while focusing on relevant contexts; (2) a noise-robustness objective, which encourages the model to maintain stable attention patterns under stochastic perturbations, preventing undesirable shifts toward irrelevant context due to noise; and (3) a mutual information maximization objective, which guides the model to identify contexts that are most informative for next-item prediction. We validate the effectiveness of FAIR on four public benchmarks, demonstrating its superior performance compared to existing methods.
附件下载