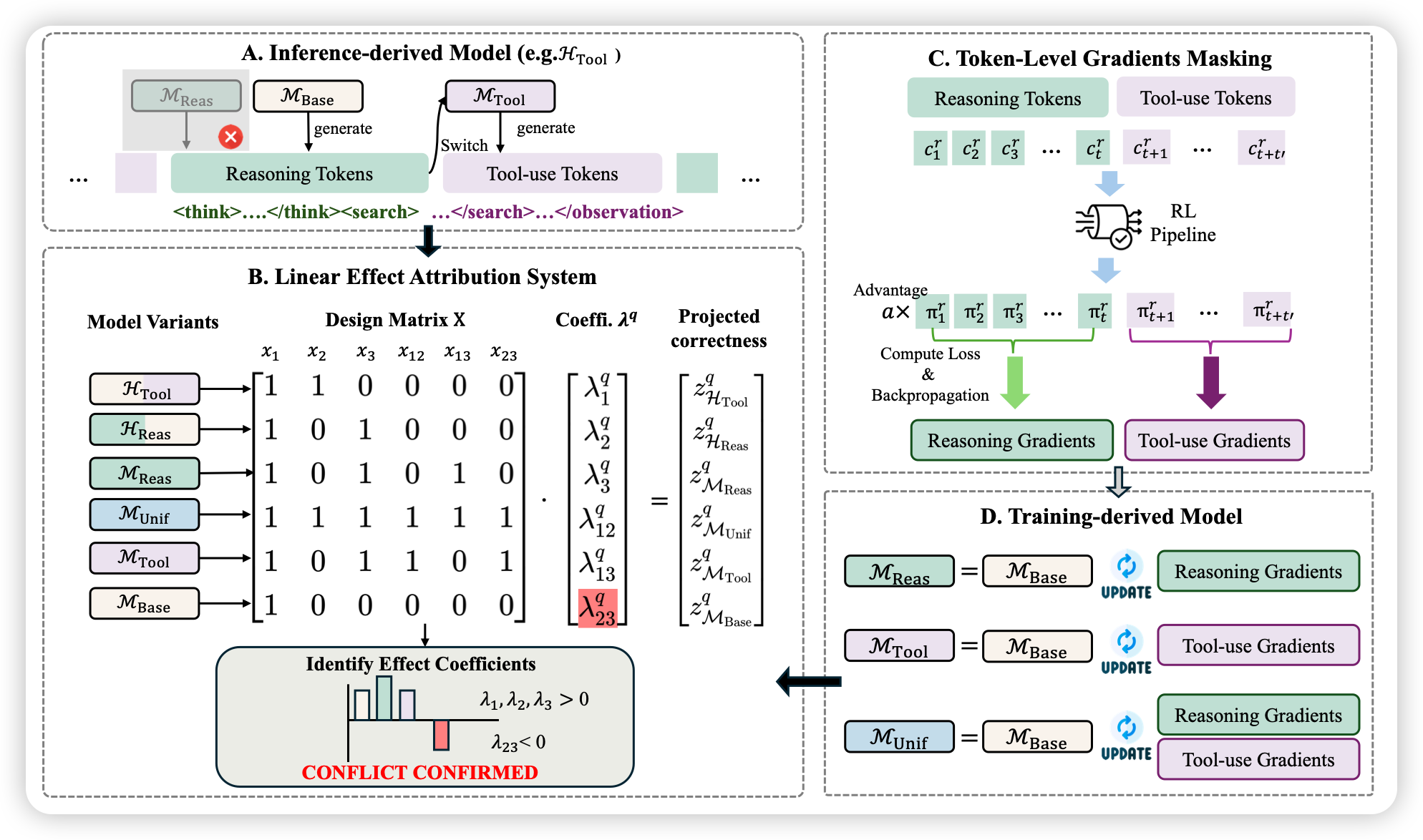
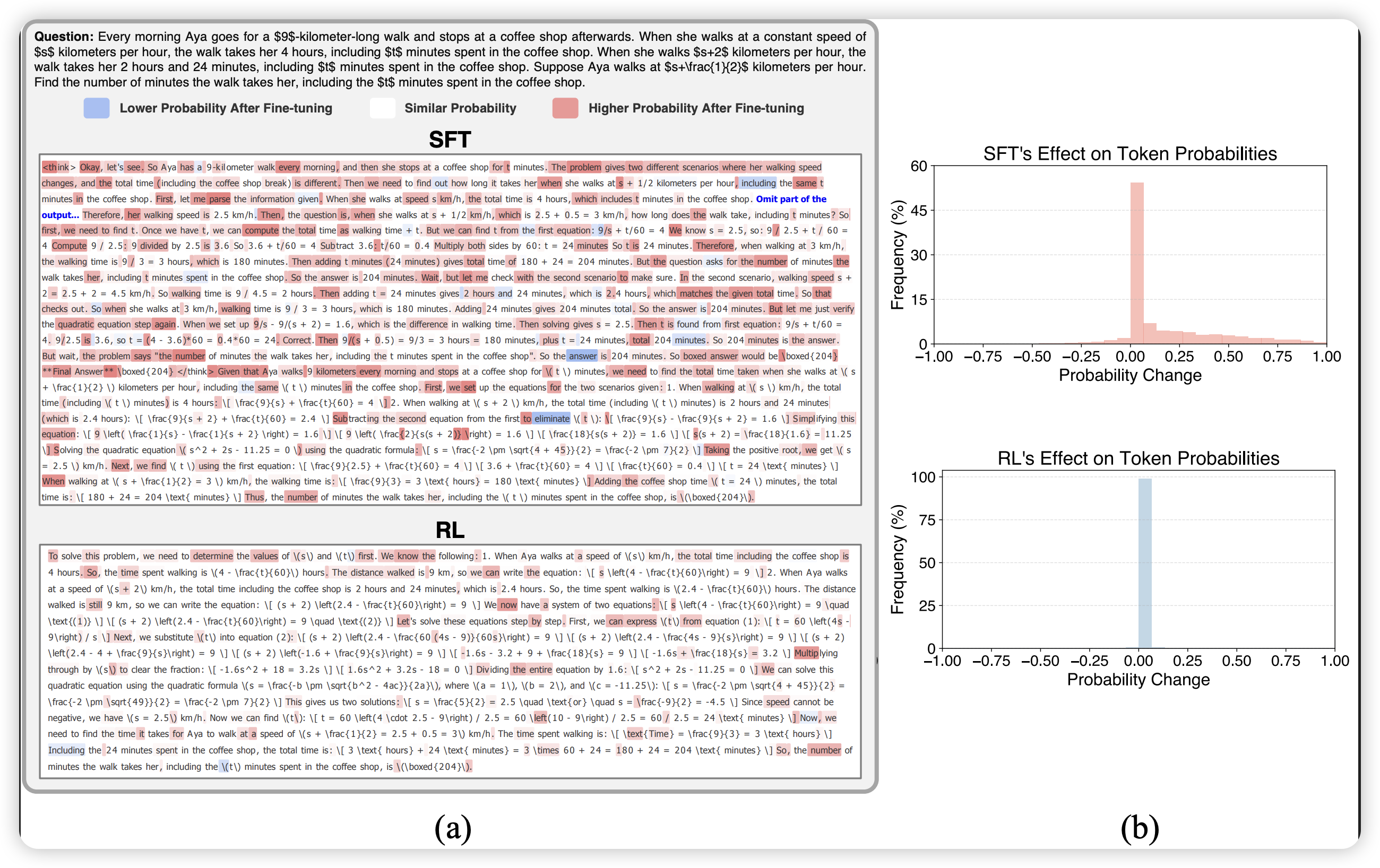
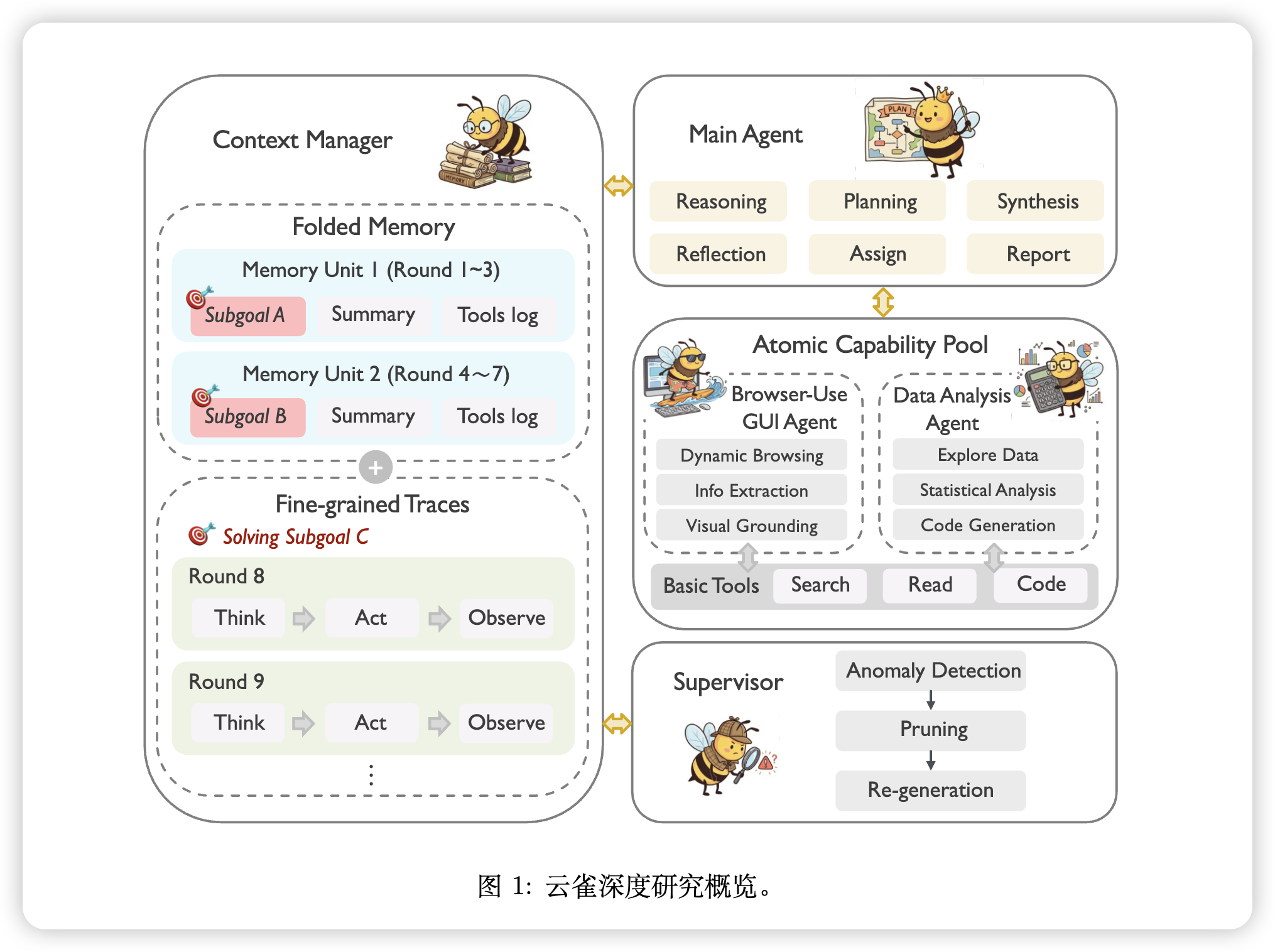
本篇博文主要内容为 2026-01-22 从Arxiv.org论文网站获取的最新论文列表,自动更新,按照NLP、CV、ML、AI、IR五个大方向区分,若需要邮件定时接收,请在评论区留下你的邮箱号。
说明:每日论文数据从Arxiv.org获取,每天早上12:00左右定时自动更新。
友情提示: 如何您需要邮箱接收每日论文数据,请在评论处留下你的邮箱。
目录
概览 (2026-01-22)
今日共更新517篇论文,其中:
- 自然语言处理共81篇(Computation and Language (cs.CL))
- 人工智能共155篇(Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI))
- 计算机视觉共97篇(Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV))
- 机器学习共129篇(Machine Learning (cs.LG))
自然语言处理
[NLP-0] Robust Fake News Detection using Large Language Models under Adversarial Sentiment Attacks
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前虚假新闻检测模型在面对情感(sentiment)操纵时的脆弱性问题,即攻击者可利用大语言模型(LLM)对新闻文本的情感进行可控修改以绕过现有检测系统。其解决方案的关键在于提出AdSent框架,该框架包含两个核心创新:一是设计基于LLM的受控情感对抗攻击方法,用于系统性地评估检测模型对情感扰动的敏感性;二是引入一种新颖的情感无关(sentiment-agnostic)训练策略,使模型在训练过程中减少对情感特征的依赖,从而提升在原始和情感篡改文本上的预测一致性与鲁棒性。实验表明,AdSent在多个基准数据集上显著优于基线方法,在准确性和抗干扰能力方面均表现优异。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15277
作者: Sahar Tahmasebi,Eric Müller-Budack,Ralph Ewerth
机构: TIB – Leibniz Information Centre for Science and Technology (德国科学与技术信息中心); Marburg University (马尔堡大学); Hessian Center for Artificial Intelligence (hessian.AI) (黑森州人工智能中心); L3S Research Center (L3S 研究中心)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Misinformation and fake news have become a pressing societal challenge, driving the need for reliable automated detection methods. Prior research has highlighted sentiment as an important signal in fake news detection, either by analyzing which sentiments are associated with fake news or by using sentiment and emotion features for classification. However, this poses a vulnerability since adversaries can manipulate sentiment to evade detectors especially with the advent of large language models (LLMs). A few studies have explored adversarial samples generated by LLMs, but they mainly focus on stylistic features such as writing style of news publishers. Thus, the crucial vulnerability of sentiment manipulation remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we investigate the robustness of state-of-the-art fake news detectors under sentiment manipulation. We introduce AdSent, a sentiment-robust detection framework designed to ensure consistent veracity predictions across both original and sentiment-altered news articles. Specifically, we (1) propose controlled sentiment-based adversarial attacks using LLMs, (2) analyze the impact of sentiment shifts on detection performance. We show that changing the sentiment heavily impacts the performance of fake news detection models, indicating biases towards neutral articles being real, while non-neutral articles are often classified as fake content. (3) We introduce a novel sentiment-agnostic training strategy that enhances robustness against such perturbations. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that AdSent significantly outperforms competitive baselines in both accuracy and robustness, while also generalizing effectively to unseen datasets and adversarial scenarios.
zh
[NLP-1] Evaluation of Large Language Models in Legal Applications: Challenges Methods and Future Directions
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在法律领域实际应用中面临的评估难题,特别是其在司法决策支持、法律实务辅助和公众法律服务等场景下,如何系统性地衡量模型的准确性、推理可靠性及可信赖性(如公平性和一致性)。解决方案的关键在于识别并分析当前评估方法在任务设计、数据集构建和评价指标设置上的局限性,进而对现有基准测试进行分类与评述,并提出未来研究应聚焦于建立更贴近真实法律实践、更具可靠性和法律严谨性的评估框架,以推动LLMs在法律领域的负责任部署。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15267
作者: Yiran Hu,Huanghai Liu,Chong Wang,Kunran Li,Tien-Hsuan Wu,Haitao Li,Xinran Xu,Siqing Huo,Weihang Su,Ning Zheng,Siyuan Zheng,Qingyao Ai,Yun Liu,Renjun Bian,Yiqun Liu,Charles L.A. Clarke,Weixing Shen,Ben Kao
机构: Tsinghua University (清华大学); The University of Hong Kong (香港大学); University of Waterloo (滑铁卢大学); Shanghai Jiaotong University (上海交通大学); Peking University (北京大学)
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are being increasingly integrated into legal applications, including judicial decision support, legal practice assistance, and public-facing legal services. While LLMs show strong potential in handling legal knowledge and tasks, their deployment in real-world legal settings raises critical concerns beyond surface-level accuracy, involving the soundness of legal reasoning processes and trustworthy issues such as fairness and reliability. Systematic evaluation of LLM performance in legal tasks has therefore become essential for their responsible adoption. This survey identifies key challenges in evaluating LLMs for legal tasks grounded in real-world legal practice. We analyze the major difficulties involved in assessing LLM performance in the legal domain, including outcome correctness, reasoning reliability, and trustworthiness. Building on these challenges, we review and categorize existing evaluation methods and benchmarks according to their task design, datasets, and evaluation metrics. We further discuss the extent to which current approaches address these challenges, highlight their limitations, and outline future research directions toward more realistic, reliable, and legally grounded evaluation frameworks for LLMs in legal domains.
zh
[NLP-2] he Effect of Scripts and Formats on LLM Numeracy
【速读】: 该论文试图解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在面对非标准数字符号或格式时,数值推理能力显著下降的问题,即当输入数字以训练数据中不常见的书写系统(如不同文字体系的数字表示)或格式呈现时,尽管数学逻辑一致,模型性能仍明显劣化。解决方案的关键在于采用针对性提示策略,包括少量示例提示(few-shot prompting)和显式数字符号映射(explicit numeral mapping),这些方法能有效缩小模型在跨书写系统和格式下的推理性能差距,从而提升LLM在多语种数值推理任务中的鲁棒性和可靠性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15251
作者: Varshini Reddy,Craig W. Schmidt,Seth Ebner,Adam Wiemerslage,Yuval Pinter,Chris Tanner
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved impressive proficiency in basic arithmetic, rivaling human-level performance on standard numerical tasks. However, little attention has been given to how these models perform when numerical expressions deviate from the prevailing conventions present in their training corpora. In this work, we investigate numerical reasoning across a wide range of numeral scripts and formats. We show that LLM accuracy drops substantially when numerical inputs are rendered in underrepresented scripts or formats, despite the underlying mathematical reasoning being identical. We further demonstrate that targeted prompting strategies, such as few-shot prompting and explicit numeral mapping, can greatly narrow this gap. Our findings highlight an overlooked challenge in multilingual numerical reasoning and provide actionable insights for working with LLMs to reliably interpret, manipulate, and generate numbers across diverse numeral scripts and formatting styles.
zh
[NLP-3] axonomy-Aligned Risk Extraction from 10-K Filings with Autonomous Improvement Using LLM s
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决从非结构化文本(如企业10-K报告)中提取风险因素时,如何保持与预定义层级分类体系(taxonomy)一致性的难题。其解决方案的关键在于一个三阶段流水线:首先利用大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)进行风险因素抽取并附带支持性引用片段;其次通过嵌入(embedding)驱动的语义映射将提取结果归类到指定分类体系;最后采用LLM作为评判者(LLM-as-a-judge)过滤误分配项,确保准确性。此外,论文进一步提出自主分类体系维护机制,即由AI代理分析评估反馈以识别问题类别、诊断失败模式并提出优化建议,从而实现分类体系的持续改进,显著提升了嵌入空间中的类别分离度(案例中提升104.7%),并验证了所提取风险特征在经济意义上的合理性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15247
作者: Rian Dolphin,Joe Dursun,Jarrett Blankenship,Katie Adams,Quinton Pike
机构: Massive.com(大规模公司)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 4 figures, 9 pages
Abstract:We present a methodology for extracting structured risk factors from corporate 10-K filings while maintaining adherence to a predefined hierarchical taxonomy. Our three-stage pipeline combines LLM extraction with supporting quotes, embedding-based semantic mapping to taxonomy categories, and LLM-as-a-judge validation that filters spurious assignments. To evaluate our approach, we extract 10,688 risk factors from SP 500 companies and examine risk profile similarity across industry clusters. Beyond extraction, we introduce autonomous taxonomy maintenance where an AI agent analyzes evaluation feedback to identify problematic categories, diagnose failure patterns, and propose refinements, achieving 104.7% improvement in embedding separation in a case study. External validation confirms the taxonomy captures economically meaningful structure: same-industry companies exhibit 63% higher risk profile similarity than cross-industry pairs (Cohen’s d=1.06, AUC 0.82, p0.001). The methodology generalizes to any domain requiring taxonomy-aligned extraction from unstructured text, with autonomous improvement enabling continuous quality maintenance and enhancement as systems process more documents.
zh
[NLP-4] Metadata Conditioned Large Language Models for Localization
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型在训练过程中因将文本视为单一全局分布而导致的地理同质化问题,即模型缺乏对不同地区语言使用习惯和知识结构的精准适应能力。其核心解决方案是采用元数据条件化(metadata conditioning)策略,在预训练阶段引入验证过的URL、国家标签和大洲标签等细粒度地理元数据信息,从而引导模型学习区域特异性知识。关键创新在于:仅通过轻量级元数据注入即可显著提升本地化性能,同时保持跨区域泛化能力;实验证明URL级别的元数据已能捕捉大部分地理信号,但平衡的区域数据覆盖仍不可或缺,因为元数据无法完全弥补缺失地区的训练数据。该方法实现了全球模型在本地任务上的表现接近专用区域模型,且训练效率更高。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15236
作者: Anjishnu Mukherjee,Ziwei Zhu,Antonios Anastasopoulos
机构: George Mason University (乔治梅森大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: under review
Abstract:Large language models are typically trained by treating text as a single global distribution, often resulting in geographically homogenized behavior. We study metadata conditioning as a lightweight approach for localization, pre-training 31 models (at 0.5B and 1B parameter scales) from scratch on large-scale English news data annotated with verified URLs, country tags, and continent tags, covering 4 continents and 17 countries. Across four controlled experiments, we show that metadata conditioning consistently improves in-region performance without sacrificing cross-region generalization, enables global models to recover localization comparable to region-specific models, and improves learning efficiency. Our ablation studies demonstrate that URL-level metadata alone captures much of the geographic signal, while balanced regional data coverage remains essential, as metadata cannot fully compensate for missing regions. Finally, we introduce a downstream benchmark of 800 localized news MCQs and show that after instruction tuning, metadata conditioned global models achieve accuracy comparable to LLaMA-3.2-1B-Instruct, despite being trained on substantially less data. Together, these results establish metadata conditioning as a practical and compute-efficient approach for localization of language models.
zh
[NLP-5] PROGRESSLM: Towards Progress Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在长时程任务中进行任务进度推理(task progress reasoning)的能力不足问题,即现有模型虽擅长描述静态视觉内容,但难以从部分观测中推断任务已完成的程度。其解决方案的关键在于构建Progress-Bench基准以系统评估VLMs的进度推理能力,并提出一种受人类启发的两阶段推理范式:一是无需训练的提示工程方法(training-free prompting),通过结构化提示强制模型进行分步推理;二是基于自建数据集ProgressLM-45K的训练方法(training-based approach),其中小规模模型ProgressLM-3B即使在训练任务与测试任务完全不重叠的情况下仍实现稳定性能提升,表明该训练策略对跨任务泛化具有显著效果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15224
作者: Jianshu Zhang,Chengxuan Qian,Haosen Sun,Haoran Lu,Dingcheng Wang,Letian Xue,Han Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Website: this https URL
Abstract:Estimating task progress requires reasoning over long-horizon dynamics rather than recognizing static visual content. While modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs) excel at describing what is visible, it remains unclear whether they can infer how far a task has progressed from partial observations. To this end, we introduce Progress-Bench, a benchmark for systematically evaluating progress reasoning in VLMs. Beyond benchmarking, we further explore a human-inspired two-stage progress reasoning paradigm through both training-free prompting and training-based approach based on curated dataset ProgressLM-45K. Experiments on 14 VLMs show that most models are not yet ready for task progress estimation, exhibiting sensitivity to demonstration modality and viewpoint changes, as well as poor handling of unanswerable cases. While training-free prompting that enforces structured progress reasoning yields limited and model-dependent gains, the training-based ProgressLM-3B achieves consistent improvements even at a small model scale, despite being trained on a task set fully disjoint from the evaluation tasks. Further analyses reveal characteristic error patterns and clarify when and why progress reasoning succeeds or fails.
zh
[NLP-6] Privacy Collapse: Benign Fine-Tuning Can Break Contextual Privacy in Language Models
【速读】: 该论文试图解决的问题是:前沿语言模型在进行良性微调(benign fine-tuning)后可能出现隐私崩溃(privacy collapse)现象,即模型在保持标准安全与效用基准性能的同时,却丧失了对上下文隐私规范的推理能力,导致不当的信息共享和跨上下文记忆边界违规。解决方案的关键在于识别出隐私表示在微调过程中具有独特脆弱性——相较于任务相关的特征会被保留,隐私相关的表征则极易被破坏,从而揭示当前安全评估体系中对专业化智能体部署存在关键盲区。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15220
作者: Anmol Goel,Cornelius Emde,Sangdoo Yun,Seong Joon Oh,Martin Gubri
机构: Parameter Lab; TU Darmstadt; University of Oxford; NAVER AI Lab; University of Tübingen
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:We identify a novel phenomenon in language models: benign fine-tuning of frontier models can lead to privacy collapse. We find that diverse, subtle patterns in training data can degrade contextual privacy, including optimisation for helpfulness, exposure to user information, emotional and subjective dialogue, and debugging code printing internal variables, among others. Fine-tuned models lose their ability to reason about contextual privacy norms, share information inappropriately with tools, and violate memory boundaries across contexts. Privacy collapse is a ``silent failure’’ because models maintain high performance on standard safety and utility benchmarks whilst exhibiting severe privacy vulnerabilities. Our experiments show evidence of privacy collapse across six models (closed and open weight), five fine-tuning datasets (real-world and controlled data), and two task categories (agentic and memory-based). Our mechanistic analysis reveals that privacy representations are uniquely fragile to fine-tuning, compared to task-relevant features which are preserved. Our results reveal a critical gap in current safety evaluations, in particular for the deployment of specialised agents.
zh
[NLP-7] BayesianVLA: Bayesian Decomposition of Vision Language Action Models via Latent Action Queries
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前视觉-语言-动作(Vision-Language-Action, VLA)模型在机器人操作中泛化能力不足的问题,特别是当面对新指令或复杂多任务场景时表现退化。核心问题源于现有训练范式中目标驱动的数据收集导致的数据集偏差:语言指令可被视觉观察高度预测,使得指令与动作之间的条件互信息(conditional mutual information)消失,即所谓的“信息坍缩”(Information Collapse),从而致使模型退化为仅依赖视觉的策略,忽略语言约束,在分布外(out-of-distribution, OOD)场景下失效。解决方案的关键在于提出 BayesianVLA 框架,通过贝叶斯分解强制语言指令的遵循——引入可学习的潜在动作查询(Latent Action Queries),构建双分支架构分别估计视觉先验 $ p(a \mid v) $ 和语言条件后验 $ \pi(a \mid v, \ell) $,并通过优化动作与指令间的条件点互信息(Pointwise Mutual Information, PMI)来惩罚视觉捷径,奖励能明确解释语言命令的动作,从而无需额外数据即可显著提升模型泛化性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15197
作者: Shijie Lian,Bin Yu,Xiaopeng Lin,Laurence T. Yang,Zhaolong Shen,Changti Wu,Yuzhuo Miao,Cong Huang,Kai Chen
机构: HUST(华中科技大学); ZGCA; ZGCI; HIT(哈尔滨工业大学); HKUST(GZ)(香港科技大学(广州)); ZZU(郑州大学); BUAA(北京航空航天大学); ECNU(华东师范大学); DeepCybo
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注:
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have shown promise in robot manipulation but often struggle to generalize to new instructions or complex multi-task scenarios. We identify a critical pathology in current training paradigms where goal-driven data collection creates a dataset bias. In such datasets, language instructions are highly predictable from visual observations alone, causing the conditional mutual information between instructions and actions to vanish, a phenomenon we term Information Collapse. Consequently, models degenerate into vision-only policies that ignore language constraints and fail in out-of-distribution (OOD) settings. To address this, we propose BayesianVLA, a novel framework that enforces instruction following via Bayesian decomposition. By introducing learnable Latent Action Queries, we construct a dual-branch architecture to estimate both a vision-only prior p(a \mid v) and a language-conditioned posterior \pi(a \mid v, \ell) . We then optimize the policy to maximize the conditional Pointwise Mutual Information (PMI) between actions and instructions. This objective effectively penalizes the vision shortcut and rewards actions that explicitly explain the language command. Without requiring new data, BayesianVLA significantly improves generalization. Extensive experiments across on SimplerEnv and RoboCasa demonstrate substantial gains, including an 11.3% improvement on the challenging OOD SimplerEnv benchmark, validating the ability of our approach to robustly ground language in action.
zh
[NLP-8] Supporting Humans in Evaluating AI Summaries of Legal Depositions SIGIR
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在法律领域生成文档摘要时面临的事实准确性问题,尤其是在法庭陈述(deposition)摘要中,准确性的缺失可能带来严重后果。其解决方案的关键在于引入基于事实片段(factual nugget)的方法,并将其从评估端迁移至用户侧,使法律专业人士能够直接利用这些事实片段来辅助决策:一是判断两个自动生成的摘要中哪个更优,二是基于 nugget 信息手动改进已有摘要。这种方法将原本用于自动化评估的 nugget 技术转化为可交互的用户支持工具,从而提升摘要质量与可信度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15182
作者: Naghmeh Farzi,Laura Dietz,Dave D. Lewis
机构: University of New Hampshire (新罕布什尔大学); Nextpoint (公司名称,不翻译)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
备注: To appear in 2026 ACM SIGIR Conference on Human Information Interaction and Retrieval (CHIIR '26), March 22-26, 2026, Seattle, WA, USA. ACM, New York, NY, USA, 5 pages. this https URL
Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used to summarize long documents, this trend poses significant challenges in the legal domain, where the factual accuracy of deposition summaries is crucial. Nugget-based methods have been shown to be extremely helpful for the automated evaluation of summarization approaches. In this work, we translate these methods to the user side and explore how nuggets could directly assist end users. Although prior systems have demonstrated the promise of nugget-based evaluation, its potential to support end users remains underexplored. Focusing on the legal domain, we present a prototype that leverages a factual nugget-based approach to support legal professionals in two concrete scenarios: (1) determining which of two summaries is better, and (2) manually improving an automatically generated summary.
zh
[NLP-9] Is Peer Review Really in Decline? Analyzing Review Quality across Venues and Time
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决科学同行评审(peer review)质量是否随投稿量增加而下降这一长期存在的争议性问题,其核心挑战在于缺乏统一、可量化且跨时间与会议可比的评审质量评估框架。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种基于证据的比较研究框架,包括:(1)系统梳理人工智能与机器学习顶会(ICLR、NeurIPS 和 ACL)中评审格式的多样性,并引入新的评审标准化方法;(2)构建一个多维评审质量度量体系,以对编辑和作者的实际效用为基准,结合大语言模型(LLM-based)与轻量级测量手段进行量化;(3)通过跨时间分析揭示评审质量的演变趋势,最终发现主流会议中位数评审质量并未呈现持续下降,从而挑战了普遍存在的负面叙事。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15172
作者: Ilia Kuznetsov,Rohan Nayak,Alla Rozovskaya,Iryna Gurevych
机构: Ubiquitous Knowledge Processing Lab (UKP Lab); Technical University of Darmstadt (达姆施塔特工业大学); National Research Center for Applied Cybersecurity ATHENE; Department of Computer Science at Queens College (皇后学院计算机科学系); City University of New York (纽约市立大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Peer review is at the heart of modern science. As submission numbers rise and research communities grow, the decline in review quality is a popular narrative and a common concern. Yet, is it true? Review quality is difficult to measure, and the ongoing evolution of reviewing practices makes it hard to compare reviews across venues and time. To address this, we introduce a new framework for evidence-based comparative study of review quality and apply it to major AI and machine learning conferences: ICLR, NeurIPS and *ACL. We document the diversity of review formats and introduce a new approach to review standardization. We propose a multi-dimensional schema for quantifying review quality as utility to editors and authors, coupled with both LLM-based and lightweight measurements. We study the relationships between measurements of review quality, and its evolution over time. Contradicting the popular narrative, our cross-temporal analysis reveals no consistent decline in median review quality across venues and years. We propose alternative explanations, and outline recommendations to facilitate future empirical studies of review quality.
zh
[NLP-10] he Flexibility Trap: Why Arbitrary Order Limits Reasoning Potential in Diffusion Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前扩散大语言模型(Diffusion Large Language Models, dLLMs)在强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)驱动下推理能力受限的问题。尽管dLLMs理论上可通过任意顺序生成token扩展解空间并提升推理潜力,但研究发现其实际表现反而因过度利用顺序灵活性而过早坍缩解空间——模型倾向于跳过高不确定性token以规避探索,从而削弱了推理能力。解决方案的关键在于摒弃对任意顺序生成的盲目追求,转而采用标准的组相对策略优化(Group Relative Policy Optimization, GRPO),即提出JustGRPO方法:通过主动限制生成顺序、聚焦于更稳定的策略更新机制,在不牺牲dLLMs并行解码优势的前提下显著提升推理性能(如GSM8K数据集上达到89.1%准确率)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15165
作者: Zanlin Ni,Shenzhi Wang,Yang Yue,Tianyu Yu,Weilin Zhao,Yeguo Hua,Tianyi Chen,Jun Song,Cheng Yu,Bo Zheng,Gao Huang
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Code and pre-trained models: this https URL
Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) break the rigid left-to-right constraint of traditional LLMs, enabling token generation in arbitrary orders. Intuitively, this flexibility implies a solution space that strictly supersets the fixed autoregressive trajectory, theoretically unlocking superior reasoning potential for general tasks like mathematics and coding. Consequently, numerous works have leveraged reinforcement learning (RL) to elicit the reasoning capability of dLLMs. In this paper, we reveal a counter-intuitive reality: arbitrary order generation, in its current form, narrows rather than expands the reasoning boundary of dLLMs. We find that dLLMs tend to exploit this order flexibility to bypass high-uncertainty tokens that are crucial for exploration, leading to a premature collapse of the solution space. This observation challenges the premise of existing RL approaches for dLLMs, where considerable complexities, such as handling combinatorial trajectories and intractable likelihoods, are often devoted to preserving this flexibility. We demonstrate that effective reasoning is better elicited by intentionally forgoing arbitrary order and applying standard Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) instead. Our approach, JustGRPO, is minimalist yet surprisingly effective (e.g., 89.1% accuracy on GSM8K) while fully retaining the parallel decoding ability of dLLMs. Project page: this https URL
zh
[NLP-11] Automated Rubrics for Reliable Evaluation of Medical Dialogue Systems
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)在临床决策支持场景中因幻觉和不安全建议所引发的患者安全风险问题,尤其关注那些难以被通用指标捕捉的细微临床错误。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于检索增强的多智能体框架,通过将权威医学证据检索结果分解为原子事实,并结合用户交互约束合成可验证的细粒度评估标准,从而实现针对具体实例的自动化评估规则生成。该方法不仅显著提升了临床意图对齐(Clinical Intent Alignment, CIA)评分(60.12% vs. GPT-4o 的 55.16%),还增强了评估判别能力(AUROC 达 0.977),同时有效指导模型响应优化,使质量提升 9.2%(从 59.0% 提升至 68.2%)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15161
作者: Yinzhu Chen,Abdine Maiga,Hossein A. Rahmani,Emine Yilmaz
机构: AI Center, University College London, UK (伦敦大学学院人工智能中心)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly used for clinical decision support, where hallucinations and unsafe suggestions may pose direct risks to patient safety. These risks are particularly challenging as they often manifest as subtle clinical errors that evade detection by generic metrics, while expert-authored fine-grained rubrics remain costly to construct and difficult to scale. In this paper, we propose a retrieval-augmented multi-agent framework designed to automate the generation of instance-specific evaluation rubrics. Our approach grounds evaluation in authoritative medical evidence by decomposing retrieved content into atomic facts and synthesizing them with user interaction constraints to form verifiable, fine-grained evaluation criteria. Evaluated on HealthBench, our framework achieves a Clinical Intent Alignment (CIA) score of 60.12%, a statistically significant improvement over the GPT-4o baseline (55.16%). In discriminative tests, our rubrics yield a mean score delta ( \mu_\Delta = 8.658 ) and an AUROC of 0.977, nearly doubling the quality separation achieved by GPT-4o baseline (4.972). Beyond evaluation, our rubrics effectively guide response refinement, improving quality by 9.2% (from 59.0% to 68.2%). This provides a scalable and transparent foundation for both evaluating and improving medical LLMs. The code is available at this https URL.
zh
[NLP-12] he Plausibility Trap: Using Probabilistic Engines for Deterministic Tasks
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)广泛应用下出现的“合理性陷阱”(Plausibility Trap)问题,即用户在面对本可由确定性算法高效完成的任务(如光学字符识别(OCR)或事实核查)时,仍倾向于调用计算成本高昂的概率型生成式AI(Generative AI)引擎,导致显著的资源浪费和延迟增加(约6.5倍延迟惩罚)。解决方案的关键在于提出“工具选择工程”(Tool Selection Engineering)与“确定性-概率决策矩阵”(Deterministic-Probabilistic Decision Matrix),为开发者提供一套系统化框架,用于判断何时应使用生成式AI、何时应避免使用,从而优化计算效率并规避算法谄媚(algorithmic sycophancy)风险。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15130
作者: Ivan Carrera,Daniel Maldonado-Ruiz
机构: Laboratorio de Ciencia de Datos ADA (ADA数据科学实验室); Escuela Politécnica Nacional (国立理工学院); Facultad de Ingenieria en Sistemas, Electrónica e Industrial (系统、电子与工业工程学院); Universidad Técnica de Ambato (安巴托技术大学)
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:The ubiquity of Large Language Models (LLMs) is driving a paradigm shift where user convenience supersedes computational efficiency. This article defines the “Plausibility Trap”: a phenomenon where individuals with access to Artificial Intelligence (AI) models deploy expensive probabilistic engines for simple deterministic tasks-such as Optical Character Recognition (OCR) or basic verification-resulting in significant resource waste. Through micro-benchmarks and case studies on OCR and fact-checking, we quantify the “efficiency tax”-demonstrating a ~6.5x latency penalty-and the risks of algorithmic sycophancy. To counter this, we introduce Tool Selection Engineering and the Deterministic-Probabilistic Decision Matrix, a framework to help developers determine when to use Generative AI and, crucially, when to avoid it. We argue for a curriculum shift, emphasizing that true digital literacy relies not only in knowing how to use Generative AI, but also on knowing when not to use it.
zh
[NLP-13] RSNA Large Language Model Benchmark Dataset for Chest Radiographs of Cardiothoracic Disease: Radiologist Evaluation and Validation Enhanced by AI Labels (REVEAL-CXR)
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在临床应用中缺乏高质量、由领域专家标注的基准数据集的问题。为构建可信赖的医学影像评估标准,研究提出了一种AI辅助的专家标注流程:首先利用GPT-4o从脱敏胸部X线报告中提取异常发现,并通过本地部署的小型推理模型(Phi-4-Reasoning)将其映射至12个标准化标签;随后基于AI建议的标签进行分层采样,确保样本具有临床相关性和难度多样性,供17名胸部放射科医师独立评审。最终筛选出381张获得至少两名专家“完全同意”的图像,从中进一步挑选200张用于公开发布(100张释放数据集 + 100张保留作为holdout测试集),实现高可信度、可重复验证的基准数据集建设。该方案的核心在于结合生成式AI的高效预标注能力与放射科医生的专业判断,形成半协作式标注机制,显著提升标注效率并保障质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15129
作者: Yishu Wei,Adam E. Flanders,Errol Colak,John Mongan,Luciano M Prevedello,Po-Hao Chen,Henrique Min Ho Lee,Gilberto Szarf,Hamilton Shoji,Jason Sho,Katherine Andriole,Tessa Cook,Lisa C. Adams,Linda C. Chu,Maggie Chung,Geraldine Brusca-Augello,Djeven P. Deva,Navneet Singh,Felipe Sanchez Tijmes,Jeffrey B. Alpert,Elsie T. Nguyen,Drew A. Torigian,Kate Hanneman,Lauren K Groner,Alexander Phan,Ali Islam,Matias F.Callejas,Gustavo Borges da Silva Teles,Faisal Jamal,Maryam Vazirabad,Ali Tejani,Hari Trivedi,Paulo Kuriki,Rajesh Bhayana,Elana T. Benishay,Yi Lin,Yifan Peng,George Shih
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Multimodal large language models have demonstrated comparable performance to that of radiology trainees on multiple-choice board-style exams. However, to develop clinically useful multimodal LLM tools, high-quality benchmarks curated by domain experts are essential. To curate released and holdout datasets of 100 chest radiographic studies each and propose an artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted expert labeling procedure to allow radiologists to label studies more efficiently. A total of 13,735 deidentified chest radiographs and their corresponding reports from the MIDRC were used. GPT-4o extracted abnormal findings from the reports, which were then mapped to 12 benchmark labels with a locally hosted LLM (Phi-4-Reasoning). From these studies, 1,000 were sampled on the basis of the AI-suggested benchmark labels for expert review; the sampling algorithm ensured that the selected studies were clinically relevant and captured a range of difficulty levels. Seventeen chest radiologists participated, and they marked “Agree all”, “Agree mostly” or “Disagree” to indicate their assessment of the correctness of the LLM suggested labels. Each chest radiograph was evaluated by three experts. Of these, at least two radiologists selected “Agree All” for 381 radiographs. From this set, 200 were selected, prioritizing those with less common or multiple finding labels, and divided into 100 released radiographs and 100 reserved as the holdout dataset. The holdout dataset is used exclusively by RSNA to independently evaluate different models. A benchmark of 200 chest radiographic studies with 12 benchmark labels was created and made publicly available this https URL, with each chest radiograph verified by three radiologists. In addition, an AI-assisted labeling procedure was developed to help radiologists label at scale, minimize unnecessary omissions, and support a semicollaborative environment.
zh
[NLP-14] WavLink: Compact Audio–Text Embeddings with a Global Whisper Token ICASSP2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前音频-文本嵌入模型在利用Whisper语音编码器方面的不足,即尽管Whisper已成为大型音频-语言模型中提取通用音频特征的事实标准,但基于CLAP的音频-文本嵌入模型仍主要依赖其他音频编码器(如HTS-AT、PaSST),未能有效整合Whisper的优势。其解决方案的关键在于提出WavLink——一个紧凑型音频-文本嵌入模型,通过在Whisper编码器基础上引入可学习的全局token(global token),并与文本编码器联合训练,从而实现高效的跨模态对齐。此外,研究系统性地探索了预训练文本编码器、损失函数、训练模式和数据混合等设计选择,并采用两阶段训练策略与Matryoshka风格监督机制,显著提升了模型的可扩展性,在8倍更小的嵌入维度下仅带来轻微性能下降,同时在AIR-Bench的多项任务上表现出竞争力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15118
作者: Gokul Karthik Kumar,Ludovick Lepauloux,Hakim Hacid
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Accepted at ICASSP 2026
Abstract:Whisper has become the de-facto encoder for extracting general-purpose audio features in large audio-language models, where a 30-second clip is typically represented by 1500 frame features projected into an LLM. In contrast, audio-text embedding models like CLAP-based models have largely relied on alternative audio encoders (e.g., HTS-AT, PaSST), and have not leveraged Whisper effectively. We present WavLink, a compact audio-text embedding model that augments Whisper encoder with a learnable global token, trained jointly with a text encoder. Through a systematic study of design choices, including pretrained text encoders, loss functions, training modes, and data mixtures, we identify configurations that yield state-of-the-art retrieval performance. Our two-stage training recipe across three model sizes, combined with Matryoshka-style supervision, improves scalability, enabling 8x smaller embeddings with minimal performance drop. WavLink also demonstrates competitive performance on AIR-Bench with MCQs and zero-shot classification.
zh
[NLP-15] Circadian Modulation of Semantic Exploration in Social Media Language
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决人类认知中昼夜节律对高维语义行为影响机制不明确的问题。其解决方案的关键在于利用大规模Reddit数据,通过预训练Transformer模型对文本进行嵌入,并以语义熵(semantic entropy)作为语言探索-利用权衡的量化指标,揭示了语义行为存在显著的昼夜节律性,且可被季节性光照线索同步;进一步区分局部与全局语义熵发现:早晨局部语义探索度最高,反映对语义空间的广泛探索,而日间后期全局语义多样性上升,符合“富者愈富”的聚集效应,表明该模式独立于情绪或情感效价,与神经调质系统的已知昼夜节律一致,从而证明生物昼夜节律延伸至语义层面。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15091
作者: Vuong Hung Truong,Mariana Gabrielle Cangco Reyes,Masatoshi Koizumi,Jihwan Myung
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computers and Society (cs.CY); Social and Information Networks (cs.SI); Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC)
备注: 25 pages, 6 figures, 3 supplementary figures
Abstract:Human cognition exhibits strong circadian modulation, yet its influence on high-dimensional semantic behavior remains poorly understood. Using large-scale Reddit data, we quantify time-of-day variation in language use by embedding text into a pretrained transformer model and measuring semantic entropy as an index of linguistic exploration-exploitation, for which we show a robust circadian rhythmicity that could be entrained by seasonal light cues. Distinguishing between local and global semantic entropy reveals a systematic temporal dissociation: local semantic exploration peaks in the morning, reflecting broader exploration of semantic space, whereas global semantic diversity peaks later in the day as submissions accumulate around already established topics, consistent with “rich-get-richer” dynamics. These patterns are not explained by sentiment or affective valence, indicating that semantic exploration captures a cognitive dimension distinct from mood. The observed temporal structure aligns with known diurnal patterns in neuromodulatory systems, suggesting that biological circadian rhythms extend to the semantic domain.
zh
[NLP-16] Multi-Agent Constraint Factorization Reveals Latent Invariant Solution Structure
【速读】: 该论文试图解决多智能体系统(Multi-agent Systems, MAS)中各智能体在共享相同信息条件下仍能实现优于单智能体的问题求解性能这一现象的理论解释问题。其解决方案的关键在于基于算子理论与约束优化,将每个智能体建模为对共享解状态施加不同有效性约束(validity constraints)的个体,并证明多智能体系统本质上实现了约束执行算子的因子分解组合(factorized composition of constraint-enforcement operators)。在弱条件下,该动态过程收敛至由各智能体约束集交集定义的不变解集;而这些结构通常无法被单一智能体通过同时施加全部约束所动态访问,即便其表达能力和信息完全相同。进一步地,作者通过近似算子(proximal operators)将结果推广至软约束情形,并将其应用于当代文本对话系统以验证理论框架的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15077
作者: Christopher Scofield
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注:
Abstract:Multi-agent systems (MAS) composed of large language models often exhibit improved problem-solving performance despite operating on identical information. In this work, we provide a formal explanation for this phenomenon grounded in operator theory and constrained optimization. We model each agent as enforcing a distinct family of validity constraints on a shared solution state, and show that a MAS implements a factorized composition of constraint-enforcement operators. Under mild conditions, these dynamics converge to invariant solution sets defined by the intersection of agent constraint sets. Such invariant structures are generally not dynamically accessible to a single agent applying all constraints simultaneously, even when expressive capacity and information are identical. We extend this result from exact constraint enforcement to soft constraints via proximal operators, and apply the formalism to contemporary text-based dialog systems.
zh
[NLP-17] he Why Behind the Action: Unveiling Internal Drivers via Agent ic Attribution
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)驱动的智能体(agent)在实际应用中缺乏可解释性的问题,尤其关注如何识别驱动代理行为的内部因素,而不仅仅局限于失败轨迹中的显式错误定位。现有方法主要聚焦于失败归因(failure attribution),难以解释成功或失败任务背后的推理过程。为此,作者提出一种新型的通用代理归因框架(general agentic attribution),其关键在于采用分层分析策略:首先在组件层面利用时间似然动态(temporal likelihood dynamics)识别关键交互步骤;随后在句子层面通过扰动分析(perturbation-based analysis)精确定位具体文本证据。该方法能够可靠地识别出影响代理行为的关键历史事件和语句,为构建更安全、更具问责性的智能体系统提供基础支撑。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15075
作者: Chen Qian,Peng Wang,Dongrui Liu,Junyao Yang,Dadi Guo,Ling Tang,Jilin Mei,Qihan Ren,Shuai Shao,Yong Liu,Jie Fu,Jing Shao,Xia Hu
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large Language Model (LLM)-based agents are widely used in real-world applications such as customer service, web navigation, and software engineering. As these systems become more autonomous and are deployed at scale, understanding why an agent takes a particular action becomes increasingly important for accountability and governance. However, existing research predominantly focuses on \textitfailure attribution to localize explicit errors in unsuccessful trajectories, which is insufficient for explaining the reasoning behind agent behaviors. To bridge this gap, we propose a novel framework for \textbfgeneral agentic attribution, designed to identify the internal factors driving agent actions regardless of the task outcome. Our framework operates hierarchically to manage the complexity of agent interactions. Specifically, at the \textitcomponent level, we employ temporal likelihood dynamics to identify critical interaction steps; then at the \textitsentence level, we refine this localization using perturbation-based analysis to isolate the specific textual evidence. We validate our framework across a diverse suite of agentic scenarios, including standard tool use and subtle reliability risks like memory-induced bias. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework reliably pinpoints pivotal historical events and sentences behind the agent behavior, offering a critical step toward safer and more accountable agentic systems.
zh
[NLP-18] textscLogicScore: Fine-grained Logic Evaluation of Conciseness Completeness and Determinateness in Attributed Question Answering
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前Attributed Question Answering (AQA)评估方法中存在的“ attribution myopia”(溯源短视)问题,即现有评估体系过度关注孤立语句及其溯源的准确性,而忽视了长文本回答的整体逻辑一致性。这种局限导致大型语言模型(LLMs)虽能生成事实正确但逻辑不连贯的回答,存在隐性的推理断层。解决方案的关键在于提出一个名为 \textscLogicScore 的统一评估框架,其核心是将评估范式从局部验证转向全局推理审查:基于Horn规则构建后向验证机制,系统性地衡量三个关键推理维度——完整性(logically sound deduction)、简洁性(non-redundancy)和确定性(consistent answer entailment),从而实现对LLM输出逻辑质量的量化评估。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15050
作者: Zhichao Yan,Yunxiao Zhao,Jiapu Wang,Jiaoyan Chen,Shaoru Guo,Xiaoli Li,Ru Li,Jeff Z. Pan
机构: Shanxi University (山西大学); Nanjing University of Science and Technology (南京理工大学); University of Manchester (曼彻斯特大学); Singapore University of Technology and Design (新加坡科技设计大学); University of Edinburgh (爱丁堡大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Current evaluation methods for Attributed Question Answering (AQA) suffer from \textitattribution myopia: they emphasize verification of isolated statements and their attributions but overlook the global logical integrity of long-form answers. Consequently, Large Language Models (LLMs) often produce factually grounded yet logically incoherent responses with elusive deductive gaps. To mitigate this limitation, we present \textscLogicScore, a unified evaluation framework that shifts the paradigm from local assessment to global reasoning scrutiny. Grounded in Horn Rules, our approach integrates a backward verification mechanism to systematically evaluate three key reasoning dimensions: \textitCompleteness (logically sound deduction), \textitConciseness (non-redundancy), and \textitDeterminateness (consistent answer entailment). Extensive experiments across three multi-hop QA datasets (HotpotQA, MusiQue, and 2WikiMultiHopQA) and over 20 LLMs (including GPT-5, Gemini-3-Pro, LLaMA3, and task-specific tuned models) reveal a critical capability gap: leading models often achieve high attribution scores (e.g., 92.85% precision for Gemini-3 Pro) but struggle with global reasoning quality (e.g., 35.11% Conciseness for Gemini-3 Pro). Our work establishes a robust standard for logical evaluation, highlighting the need to prioritize reasoning coherence alongside factual grounding in LLM development. Codes are available at: this https URL.
zh
[NLP-19] Knowledge Restoration-driven Prompt Optimization: Unlocking LLM Potential for Open-Domain Relational Triplet Extraction
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决开放域关系三元组抽取(Open-domain Relational Triplet Extraction, ORTE)中大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)因依赖静态启发式提示策略而导致的语义模糊性敏感问题,此类方法缺乏自我反思机制,难以纠正错误提取模式。解决方案的关键在于提出一种知识重构驱动的提示优化框架(Knowledge Reconstruction-driven Prompt Optimization, KRPO),其核心包括:1)基于知识恢复的自评估机制,通过将结构化三元组映射为语义一致性分数提供内在反馈信号;2)基于文本梯度的提示优化器,能够内化历史经验以迭代优化提示,从而提升LLM对后续任务的指导能力;3)关系规范化记忆模块,用于收集代表性关系并提供语义区分度高的三元组模式,缓解关系冗余问题。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15037
作者: Xiaonan Jing,Gongqing Wu,Xingrui Zhuo,Lang Sun,Jiapu Wang
机构: The Key Laboratory of Knowledge Engineering with Big Data (the Ministry of Education of China), Hefei University of Technology (合肥工业大学); School of Computer Science and Information Engineering, Hefei University of Technology (合肥工业大学); Anhui Zhongke Guojin Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd. (安徽中科国金智能科技有限公司); Nanjing University of Science and Technology (南京理工大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Open-domain Relational Triplet Extraction (ORTE) is the foundation for mining structured knowledge without predefined schemas. Despite the impressive in-context learning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), existing methods are hindered by their reliance on static, heuristic-driven prompting strategies. Due to the lack of reflection mechanisms required to internalize erroneous signals, these methods exhibit vulnerability in semantic ambiguity, often making erroneous extraction patterns permanent. To address this bottleneck, we propose a Knowledge Reconstruction-driven Prompt Optimization (KRPO) framework to assist LLMs in continuously improving their extraction capabilities for complex ORTE task flows. Specifically, we design a self-evaluation mechanism based on knowledge restoration, which provides intrinsic feedback signals by projecting structured triplets into semantic consistency scores. Subsequently, we propose a prompt optimizer based on a textual gradient that can internalize historical experiences to iteratively optimize prompts, which can better guide LLMs to handle subsequent extraction tasks. Furthermore, to alleviate relation redundancy, we design a relation canonicalization memory that collects representative relations and provides semantically distinct schemas for the triplets. Extensive experiments across three datasets show that KRPO significantly outperforms strong baselines in the extraction F1 score.
zh
[NLP-20] Obscuring Data Contamination Through Translation: Evidence from Arabic Corpora
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多语言环境下大型语言模型(LLM)评估中因数据污染(data contamination)导致的有效性问题,尤其是现有检测方法主要针对英文基准测试,难以识别非英语语境下的模型记忆行为。其核心解决方案是提出一种“翻译感知的污染检测”(Translation-Aware Contamination Detection)方法,通过对比多个翻译版本的基准测试信号而非仅依赖英文原版,从而更可靠地识别跨语言污染现象;该方法结合了选择重排策略与Min-K%概率分析,有效捕捉行为和分布层面的污染信号,在阿拉伯语微调实验中验证了其对传统检测手段盲区的覆盖能力,显著提升了多语言评估的公平性、透明性和可复现性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14994
作者: Chaymaa Abbas,Nour Shamaa,Mariette Awad
机构: American University of Beirut (贝鲁特美国大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Data contamination undermines the validity of Large Language Model evaluation by enabling models to rely on memorized benchmark content rather than true generalization. While prior work has proposed contamination detection methods, these approaches are largely limited to English benchmarks, leaving multilingual contamination poorly understood. In this work, we investigate contamination dynamics in multilingual settings by fine-tuning several open-weight LLMs on varying proportions of Arabic datasets and evaluating them on original English benchmarks. To detect memorization, we extend the Tested Slot Guessing method with a choice-reordering strategy and incorporate Min-K% probability analysis, capturing both behavioral and distributional contamination signals. Our results show that translation into Arabic suppresses conventional contamination indicators, yet models still benefit from exposure to contaminated data, particularly those with stronger Arabic capabilities. This effect is consistently reflected in rising Mink% scores and increased cross-lingual answer consistency as contamination levels grow. To address this blind spot, we propose Translation-Aware Contamination Detection, which identifies contamination by comparing signals across multiple translated benchmark variants rather than English alone. The Translation-Aware Contamination Detection reliably exposes contamination even when English-only methods fail. Together, our findings highlight the need for multilingual, translation-aware evaluation pipelines to ensure fair, transparent, and reproducible assessment of LLMs. Subjects: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14994 [cs.CL] (or arXiv:2601.14994v1 [cs.CL] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14994 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[NLP-21] A Comprehensive Benchmark of Language Models on Unicode and Romanized Sinhala
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决低资源、形态丰富的语言(如僧伽罗语)在生成式 AI (Generative AI) 模型中的性能评估不足问题,尤其是针对数字通信中广泛使用的罗马化僧伽罗语文本。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个涵盖 Unicode 和罗马化僧伽罗语文本的多样化语料库,并通过困惑度(perplexity)和定性句子补全分析,系统评估开源与闭源大语言模型(Language Models, LMs)的表现。研究发现,不同模型在两种书写形式上的性能差异显著,且训练数据对处理脚本变体至关重要,从而为面向僧伽罗语应用的模型选择提供了实证依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14958
作者: Minuri Rajapakse,Ruvan Weerasinghe
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 6 pages, 1 figure, 3 tables
Abstract:The performance of Language Models (LMs) on lower-resource, morphologically rich languages like Sinhala remains under-explored, particularly for Romanized Sinhala, which is prevalent in digital communication. This paper presents a comprehensive benchmark of modern LMs on a diverse corpus of Unicode and Romanized Sinhala. We evaluate open-source models using perplexity, a measure of how well a model predicts a text, and leading closed-source models via a qualitative analysis of sentence completion. Our findings reveal that the Mistral-Nemo-Base-2407 model achieves the strongest predictive performance on Unicode text and the Mistral-7B-v0.3 model for Romanized text. The results also highlight the strong all-around performance of the Llama-3.1-8B model for both scripts. Furthermore, a significant performance disparity exists among closed-source models: Gemini-1.5-pro and DeepSeek excel at Unicode generation, whereas Claude-3.5-Sonnet is superior at handling Romanized text. These results provide an essential guide for practitioners selecting models for Sinhala-specific applications and highlight the critical role of training data in handling script variations.
zh
[NLP-22] CorpusQA: A 10 Million Token Benchmark for Corpus-Level Analysis and Reasoning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在处理文档库级推理任务时能力不足的问题,尤其是现有基准测试无法有效评估模型对大规模、分散证据进行全局整合与统计聚合的能力。其核心挑战在于,传统方法依赖“稀疏检索”假设(sparse retrieval assumption),即答案仅需从少量相关片段中提取,而真实场景下证据高度分散于数百篇文档中,需跨文档的复杂推理。解决方案的关键在于提出CorpusQA基准,该基准通过一种新颖的数据合成框架生成高达1000万token的测试数据,该框架将推理过程与文本表示解耦,从而构建计算密集型查询并确保答案的程序化真值(programmatically guaranteed ground-truth),使模型必须在无可靠人工标注的前提下完成整体性推理。实验表明,即使最先进的长上下文LLMs也随输入长度增长而性能下降,标准检索增强生成系统彻底失效,凸显出记忆增强型代理架构(memory-augmented agentic architectures)作为更鲁棒替代方案的重要性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14952
作者: Zhiyuan Lu,Chenliang Li,Yingcheng Shi,Weizhou Shen,Ming Yan,Fei Huang
机构: Tongyi Lab, Alibaba Group (通义实验室,阿里巴巴集团)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:While large language models now handle million-token contexts, their capacity for reasoning across entire document repositories remains largely untested. Existing benchmarks are inadequate, as they are mostly limited to single long texts or rely on a “sparse retrieval” assumption-that answers can be derived from a few relevant chunks. This assumption fails for true corpus-level analysis, where evidence is highly dispersed across hundreds of documents and answers require global integration, comparison, and statistical aggregation. To address this critical gap, we introduce CorpusQA, a new benchmark scaling up to 10 million tokens, generated via a novel data synthesis framework. By decoupling reasoning from textual representation, this framework creates complex, computation-intensive queries with programmatically guaranteed ground-truth answers, challenging systems to perform holistic reasoning over vast, unstructured text without relying on fallible human annotation. We further demonstrate the utility of our framework beyond evaluation, showing that fine-tuning on our synthesized data effectively enhances an LLM’s general long-context reasoning capabilities. Extensive experiments reveal that even state-of-the-art long-context LLMs struggle as input length increases, and standard retrieval-augmented generation systems collapse entirely. Our findings indicate that memory-augmented agentic architectures offer a more robust alternative, suggesting a critical shift is needed from simply extending context windows to developing advanced architectures for global information synthesis.
zh
[NLP-23] mpViz: On the Evaluation of Temporal Knowledge in Text-to-Image Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前文本到图像(Text-to-Image, T2I)生成模型在处理时间相关语义信息时能力不足的问题,即模型缺乏对时间现象(如季节、昼夜变化等)的准确理解与表达能力。为填补这一研究空白,作者提出了TempViz数据集,这是首个系统性评估T2I模型时间知识的综合性基准,包含7900个提示词和600余张参考图像。其关键解决方案在于构建了一个结构化的多类别时间知识评测框架,并通过人类评估揭示了现有模型在时间感知上的普遍薄弱性(各模型平均准确率均未超过75%),同时验证了现有自动化评估方法在捕捉时间线索方面的局限性,从而凸显了未来提升T2I模型时间推理能力的研究必要性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14951
作者: Carolin Holtermann,Nina Krebs,Anne Lauscher
机构: Trustworthy AI Lab, University of Hamburg (汉堡大学可信人工智能实验室); University of St. Gallen (圣加仑大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Time alters the visual appearance of entities in our world, like objects, places, and animals. Thus, for accurately generating contextually-relevant images, knowledge and reasoning about time can be crucial (e.g., for generating a landscape in spring vs. in winter). Yet, although substantial work exists on understanding and improving temporal knowledge in natural language processing, research on how temporal phenomena appear and are handled in text-to-image (T2I) models remains scarce. We address this gap with TempViz, the first data set to holistically evaluate temporal knowledge in image generation, consisting of 7.9k prompts and more than 600 reference images. Using TempViz, we study the capabilities of five T2I models across five temporal knowledge categories. Human evaluation shows that temporal competence is generally weak, with no model exceeding 75% accuracy across categories. Towards larger-scale studies, we also examine automated evaluation methods, comparing several established approaches against human judgments. However, none of these approaches provides a reliable assessment of temporal cues - further indicating the pressing need for future research on temporal knowledge in T2I.
zh
[NLP-24] he GDN-CC Dataset: Automatic Corpus Clarification for AI-enhanced Democratic Citizen Consultations
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI (Generative AI) 在民主参与场景(如公民咨询)中作为分析工具时面临的数据噪声与结构不清晰问题,以及如何在资源受限条件下实现可靠、可解释的标准化处理。其核心解决方案是提出“语料澄清”(Corpus Clarification)这一预处理框架,将杂乱且多主题的公民贡献转化为结构化、自包含的论证单元,从而提升其在主题建模和政治分析中的可用性;关键创新在于构建了GDN-CC数据集(含1,231条经人工标注和澄清的法国全国大辩论贡献),并验证了微调后的小型语言模型(Small Language Models)在还原论证结构上可媲美甚至超越大型语言模型(LLMs),同时释放了规模达24万条的自动标注语料库GDN-CC-large,为后续研究提供最大规模的民主咨询标注数据集。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14944
作者: Pierre-Antoine Lequeu,Léo Labat,Laurène Cave,Gaël Lejeune,François Yvon,Benjamin Piwowarski
机构: Sorbonne Université, CNRS, ISIR (巴黎索邦大学, 法国国家科学研究中心, 信息与机器人研究所); Sorbonne Université, STIH/CERES (巴黎索邦大学, 科学技术与健康研究中心); Institut Polytechnique de Paris, CNRS, CREST (巴黎综合理工学院, 法国国家科学研究中心, 经济与社会研究中心)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 31 pages including 22 for references and appendix, 13 figures
Abstract:LLMs are ubiquitous in modern NLP, and while their applicability extends to texts produced for democratic activities such as online deliberations or large-scale citizen consultations, ethical questions have been raised for their usage as analysis tools. We continue this line of research with two main goals: (a) to develop resources that can help standardize citizen contributions in public forums at the pragmatic level, and make them easier to use in topic modeling and political analysis; (b) to study how well this standardization can reliably be performed by small, open-weights LLMs, i.e. models that can be run locally and transparently with limited resources. Accordingly, we introduce Corpus Clarification as a preprocessing framework for large-scale consultation data that transforms noisy, multi-topic contributions into structured, self-contained argumentative units ready for downstream analysis. We present GDN-CC, a manually-curated dataset of 1,231 contributions to the French Grand Débat National, comprising 2,285 argumentative units annotated for argumentative structure and manually clarified. We then show that finetuned Small Language Models match or outperform LLMs on reproducing these annotations, and measure their usability for an opinion clustering task. We finally release GDN-CC-large, an automatically annotated corpus of 240k contributions, the largest annotated democratic consultation dataset to date.
zh
[NLP-25] Generative Artificial Intelligence Musical Heritage and the Construction of Peace Narratives: A Case Study in Mali
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决在马里复杂政治与社会背景下,如何利用生成式人工智能(Generative AI)构建和平叙事并复兴音乐遗产的问题。研究聚焦于通过AI技术促进基于本土语言与传统的音乐创作、实现技术创新与文化真实性之间的平衡,以及借助AI辅助的音乐共创增强社会凝聚力与文化主权。解决方案的关键在于将生成式AI嵌入一个具有文化意识的参与式框架中,使其成为象征性外交的催化剂,从而放大地方声音而非进行同质化标准化,同时需应对语言语料库匮乏、算法审查及版权衍生作品伦理等挑战。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14931
作者: Nouhoum Coulibaly,Ousmane Ly,Michael Leventhal,Ousmane Goro
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 12 pages, 2 figures
Abstract:This study explores the capacity of generative artificial intelligence (Gen AI) to contribute to the construction of peace narratives and the revitalization of musical heritage in Mali. The study has been made in a political and social context where inter-community tensions and social fractures motivate a search for new symbolic frameworks for reconciliation. The study empirically explores three questions: (1) how Gen AI can be used as a tool for musical creation rooted in national languages and traditions; (2) to what extent Gen AI systems enable a balanced hybridization between technological innovation and cultural authenticity; and (3) how AI-assisted musical co-creation can strengthen social cohesion and cultural sovereignty. The experimental results suggest that Gen AI, embedded in a culturally conscious participatory framework, can act as a catalyst for symbolic diplomacy, amplifying local voices instead of standardizing them. However, challenges persist regarding the availability of linguistic corpora, algorithmic censorship, and the ethics of generating compositions derived from copyrighted sources.
zh
[NLP-26] CodeDelegator: Mitigating Context Pollution via Role Separation in Code-as-Action Agents
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决单一智能体在执行复杂现实任务时因同时承担战略规划与详细实现而导致的上下文污染问题,这种污染源于调试痕迹和中间失败对长期任务性能的负面影响。解决方案的关键在于提出一种多智能体框架 CodeDelegator,通过角色专业化将任务分解为两个独立阶段:由一个持久存在的 Delegator 智能体负责高层次规划、任务分解与进度监控,而不执行代码;每个子任务则由一个全新实例化的 Coder 智能体处理,其上下文仅包含指定规范,从而避免历史失败干扰。此外,引入瞬态-持久状态分离(Ephemeral-Persistent State Separation, EPSS)机制,在隔离各 Coder 执行状态的同时保持全局一致性,有效防止调试信息污染 Delegator 的决策上下文。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14914
作者: Tianxiang Fei,Cheng Chen,Yue Pan,Mao Zheng,Mingyang Song
机构: Tencent(腾讯)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) allow agents to represent actions as executable code, offering greater expressivity than traditional tool-calling. However, real-world tasks often demand both strategic planning and detailed implementation. Using a single agent for both leads to context pollution from debugging traces and intermediate failures, impairing long-horizon performance. We propose CodeDelegator, a multi-agent framework that separates planning from implementation via role specialization. A persistent Delegator maintains strategic oversight by decomposing tasks, writing specifications, and monitoring progress without executing code. For each sub-task, a new Coder agent is instantiated with a clean context containing only its specification, shielding it from prior failures. To coordinate between agents, we introduce Ephemeral-Persistent State Separation (EPSS), which isolates each Coder’s execution state while preserving global coherence, preventing debugging traces from polluting the Delegator’s context. Experiments on various benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of CodeDelegator across diverse scenarios.
zh
[NLP-27] PodBench: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Instruction-Aware Audio-Oriented Podcast Script Generation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决播客脚本生成任务中缺乏系统性评估资源的问题,该任务要求大语言模型(LLM)从多样化输入中合成结构化、上下文相关的多角色对话。解决方案的关键在于提出PodBench基准测试集,包含800个样本,输入长度可达21K tokens,并涵盖复杂的多说话人指令;同时设计了一个融合定量约束与基于LLM的质量评估的多维评价框架,从而为长文本、以音频为中心的生成任务提供可复现的评测平台。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14903
作者: Chenning Xu,Mao Zheng,Mingyu Zheng,Mingyang Song
机构: Tencent(腾讯)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Podcast script generation requires LLMs to synthesize structured, context-grounded dialogue from diverse inputs, yet systematic evaluation resources for this task remain limited. To bridge this gap, we introduce PodBench, a benchmark comprising 800 samples with inputs up to 21K tokens and complex multi-speaker instructions. We propose a multifaceted evaluation framework that integrates quantitative constraints with LLM-based quality assessment. Extensive experiments reveal that while proprietary models generally excel, open-source models equipped with explicit reasoning demonstrate superior robustness in handling long contexts and multi-speaker coordination compared to standard baselines. However, our analysis uncovers a persistent divergence where high instruction following does not guarantee high content substance. PodBench offers a reproducible testbed to address these challenges in long-form, audio-centric generation.
zh
[NLP-28] Language-Coupled Reinforcement Learning for Multilingual Retrieval-Augmented Generation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多语言检索增强生成(Multilingual Retrieval-Augmented Generation, MRAG)中因统一处理跨语言语义等价查询而导致的知识偏置(knowledge bias)与知识冲突(knowledge conflict)问题。现有方法通常采用单轮检索与优化策略,难以适应多语言场景下的复杂交互,导致模型性能受限。其解决方案的关键在于提出LcRL框架,通过引入语言耦合的组相对策略优化(language-coupled Group Relative Policy Optimization),在策略模型和奖励模型中实现对不同语言间知识的一致性建模;同时,在rollout模块中采用语言耦合组采样以降低知识偏置,并在奖励模型中加入辅助反一致性正则项以缓解知识冲突,从而提升多语言环境下生成质量与鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14896
作者: Rui Qi,Fengran Mo,Yufeng Chen,Xue Zhang,Shuo Wang,Hongliang Li,Jinan Xu,Meng Jiang,Jian-Yun Nie,Kaiyu Huang
机构: Beijing Jiaotong University (北京交通大学); University of Montreal (蒙特利尔大学); Tsinghua University (清华大学); University of Notre Dame (圣母大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Multilingual retrieval-augmented generation (MRAG) requires models to effectively acquire and integrate beneficial external knowledge from multilingual collections. However, most existing studies employ a unitive process where queries of equivalent semantics across different languages are processed through a single-turn retrieval and subsequent optimization. Such a ``one-size-fits-all’’ strategy is often suboptimal in multilingual settings, as the models occur to knowledge bias and conflict during the interaction with the search engine. To alleviate the issues, we propose LcRL, a multilingual search-augmented reinforcement learning framework that integrates a language-coupled Group Relative Policy Optimization into the policy and reward models. We adopt the language-coupled group sampling in the rollout module to reduce knowledge bias, and regularize an auxiliary anti-consistency penalty in the reward models to mitigate the knowledge conflict. Experimental results demonstrate that LcRL not only achieves competitive performance but is also appropriate for various practical scenarios such as constrained training data and retrieval over collections encompassing a large number of languages. Our code is available at this https URL.
zh
[NLP-29] What Makes Low-Bit Quantization-Aware Training Work for Reasoning LLM s? A Systematic Study
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)中推理模型在低比特量化(low-bit quantization)下精度显著下降的问题,尤其是在代码和数学等复杂推理任务中。其核心挑战在于传统后训练量化(Post-Training Quantization, PTQ)方法虽能提升推理效率,但常导致性能大幅衰减。解决方案的关键在于提出一种系统性的量化感知训练(Quantization-Aware Training, QAT)框架——Reasoning-QAT,其核心创新包括:利用知识蒸馏作为鲁棒的训练目标、以PTQ结果作为QAT的初始化以降低训练成本、通过强化学习(Reinforcement Learning)在合理冷启动条件下进一步优化量化模型,并确保PTQ校准域与QAT训练域一致以加速收敛并提升最终精度。该方法在多个大语言模型(LLM)架构和推理数据集上均显著优于现有最优PTQ方法,尤其在2-bit量化下仍能有效恢复模型性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14888
作者: Keyu Lv,Manyi Zhang,Xiaobo Xia,Jingchen Ni,Shannan Yan,Xianzhi Yu,Lu Hou,Chun Yuan,Haoli Bai
机构: Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University (清华大学深圳国际研究生院); Huawei Technologies (华为技术有限公司); National University of Singapore (新加坡国立大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Reasoning models excel at complex tasks such as coding and mathematics, yet their inference is often slow and token-inefficient. To improve the inference efficiency, post-training quantization (PTQ) usually comes with the cost of large accuracy drops, especially for reasoning tasks under low-bit settings. In this study, we present a systematic empirical study of quantization-aware training (QAT) for reasoning models. Our key findings include: (1) Knowledge distillation is a robust objective for reasoning models trained via either supervised fine-tuning or reinforcement learning; (2) PTQ provides a strong initialization for QAT, improving accuracy while reducing training cost; (3) Reinforcement learning remains feasible for quantized models given a viable cold start and yields additional gains; and (4) Aligning the PTQ calibration domain with the QAT training domain accelerates convergence and often improves the final accuracy. Finally, we consolidate these findings into an optimized workflow (Reasoning-QAT), and show that it consistently outperforms state-of-the-art PTQ methods across multiple LLM backbones and reasoning datasets. For instance, on Qwen3-0.6B, it surpasses GPTQ by 44.53% on MATH-500 and consistently recovers performance in the 2-bit regime.
zh
[NLP-30] Strategic Doctrine Language Models (sdLM): A Learning-System Framework for Doctrinal Consistency and Geopolitical Forecasting
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多文档战略推理中长期预测准确性不足、计划合理性欠缺以及战略教义一致性难以保障的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为战略教义语言模型(Strategic Doctrine Language Models, sdLM)的学习系统框架,其核心创新包括:多文档注意力机制以整合跨文档信息、时间编码用于建模时序动态、以及教义一致性层以约束输出符合既定战略规范,从而在提升长期预测能力的同时显著减少教义违反现象,并实现更优的不确定性校准。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14862
作者: Olaf Yunus Laitinen Imanov,Taner Yilmaz,Derya Umut Kulali
机构: Technical University of Denmark (丹麦技术大学); Afyon Kocatepe University (阿菲永卡拉希萨尔大学); Eskisehir Technical University (埃斯基谢希尔技术大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 13 pages, 10 figures, 10 tables
Abstract:We introduce Strategic Doctrine Language Models (sdLM), a learning-system framework for multi-document strategic reasoning with doctrinal consistency constraints and calibrated uncertainty. The approach combines multi-document attention, temporal encoding, and a doctrine-consistency layer to improve long-horizon forecasting and plan plausibility while reducing severe doctrinal violations. We evaluate sdLM using (i) expert-panel scoring of strategic scenarios (N=47), (ii) doctrine consistency on 336 doctrine publications (12,847 statements), and (iii) geopolitical forecasting on 127 historical counterfactuals (1945-2020) across 12-60 month horizons. Across these benchmarks, sdLM achieves higher strategic quality and better calibration than strong general-purpose LLM baselines, and remains competitive with human experts on long-horizon judgments. We further report ablations, scaling trends, and deployment-oriented performance/latency characteristics to clarify which components drive improvements and how they translate to operational settings.
zh
[NLP-31] HiNS: Hierarchical Negative Sampling for More Comprehensive Memory Retrieval Embedding Model
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前记忆增强型语言代理(memory-augmented language agents)在训练嵌入模型时,因负样本构造方式不合理而导致的检索精度不足问题。现有方法通常采用合成或均匀采样的负样本,忽略了负样本在语义难度上的层次性及其在真实人机交互中自然分布的特点——即部分负样本为语义相近的干扰项,而另一些则为明显无关项,且对话数据中二者存在结构化比例。解决方案的关键在于提出一个名为HiNS的原理性数据构建框架,该框架显式建模负样本的难度层级,并引入基于对话数据实证获得的负样本比例,从而训练出具有更高检索保真度和泛化能力的嵌入模型。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14857
作者: Motong Tian,Allen P. Wong,Mingjun Mao,Wangchunshu Zhou
机构: OPPO; Zhejiang University (浙江大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Memory-augmented language agents rely on embedding models for effective memory retrieval. However, existing training data construction overlooks a critical limitation: the hierarchical difficulty of negative samples and their natural distribution in human-agent interactions. In practice, some negatives are semantically close distractors while others are trivially irrelevant, and natural dialogue exhibits structured proportions of these types. Current approaches using synthetic or uniformly sampled negatives fail to reflect this diversity, limiting embedding models’ ability to learn nuanced discrimination essential for robust memory retrieval. In this work, we propose a principled data construction framework HiNS that explicitly models negative sample difficulty tiers and incorporates empirically grounded negative ratios derived from conversational data, enabling the training of embedding models with substantially improved retrieval fidelity and generalization in memory-intensive tasks. Experiments show significant improvements: on LoCoMo, F1/BLEU-1 gains of 3.27%/3.30%(MemoryOS) and 1.95%/1.78% (Mem0); on PERSONAMEM, total score improvements of 1.19% (MemoryOS) and 2.55% (Mem0).
zh
[NLP-32] Comparative Study of Large Language Models on Chinese Film Script Continuation: An Empirical Analysis Based on GPT -5.2 and Qwen -Max
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在中文创意写作任务中,尤其是具有文化特异性的电影剧本续写场景下的性能评估问题。现有研究缺乏针对中国语境下叙事逻辑与风格一致性的系统性评测基准和多维评价体系。为此,作者构建了首个包含53部经典中国电影的剧本续写基准数据集,并设计了一个融合ROUGE-L、结构相似性(Structural Similarity)及LLM-as-Judge评分(使用DeepSeek-Reasoner)的多维度评估框架,对GPT-5.2与Qwen-Max-Latest进行对比实验。关键解决方案在于:采用“前半段到后半段”续写范式生成高质量样本(共303个有效样本),并通过统计显著性分析揭示GPT-5.2在角色一致性、语气风格匹配和格式保真度方面显著优于Qwen-Max,尽管后者在词汇重叠度上略高,但整体生成稳定性不足,从而为中文创意写作场景下LLM的可复现评估提供了方法论基础。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14826
作者: Yuxuan Cao,Zida Yang,Ye Wang
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 18 pages, 6 figures, 6 tables, 20 references. First two authors contributed equally. Corresponding author: Ye Wang (wangye@whu. this http URL )
Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly applied to creative writing, their performance on culturally specific narrative tasks warrants systematic investigation. This study constructs the first Chinese film script continuation benchmark comprising 53 classic films, and designs a multi-dimensional evaluation framework comparing GPT-5.2 and Qwen-Max-Latest. Using a “first half to second half” continuation paradigm with 3 samples per film, we obtained 303 valid samples (GPT-5.2: 157, 98.7% validity; Qwen-Max: 146, 91.8% validity). Evaluation integrates ROUGE-L, Structural Similarity, and LLM-as-Judge scoring (DeepSeek-Reasoner). Statistical analysis of 144 paired samples reveals: Qwen-Max achieves marginally higher ROUGE-L (0.2230 vs 0.2114, d=-0.43); however, GPT-5.2 significantly outperforms in structural preservation (0.93 vs 0.75, d=0.46), overall quality (44.79 vs 25.72, d=1.04), and composite scores (0.50 vs 0.39, d=0.84). The overall quality effect size reaches large effect level (d0.8). GPT-5.2 excels in character consistency, tone-style matching, and format preservation, while Qwen-Max shows deficiencies in generation stability. This study provides a reproducible framework for LLM evaluation in Chinese creative writing. Comments: 18 pages, 6 figures, 6 tables, 20 references. First two authors contributed equally. Corresponding author: Ye Wang (wangye@whu.this http URL) Subjects: Computation and Language (cs.CL) ACMclasses: I.2.7; J.5 Cite as: arXiv:2601.14826 [cs.CL] (or arXiv:2601.14826v1 [cs.CL] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14826 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[NLP-33] Reflecting in the Reflection: Integrating a Socratic Questioning Framework into Automated AI-Based Question Generation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决教育实践中反射性问题(reflection questions)设计费时且教师支持不均的问题,尤其在ICT教学场景中。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种“反思中的反思”(reflection-in-reflection)框架,通过两个角色专业化代理——学生教师(Student-Teacher)与教师教育者(Teacher-Educator)——进行苏格拉底式的多轮对话来迭代优化问题生成。其中,学生教师提出候选问题及简要理由,教师教育者则从清晰度、深度、相关性、参与度和概念关联等维度评估并以针对性引导问题或终止信号反馈,从而实现高质量反射性问题的自动化生成。实验表明,动态停止机制结合上下文信息(如学生水平和教学材料)显著优于固定步数的迭代方式,并且该双代理协议生成的问题在多项指标上显著优于单次生成基线。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14798
作者: Ondřej Holub(1),Essi Ryymin(2),Rodrigo Alves(1) ((1) Czech Technical University in Prague, (2) Häme University of Applied Sciences)
机构: Czech Technical University in Prague (布拉格捷克技术大学); Häme University of Applied Sciences (哈梅应用科学大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注:
Abstract:Designing good reflection questions is pedagogically important but time-consuming and unevenly supported across teachers. This paper introduces a reflection-in-reflection framework for automated generation of reflection questions with large language models (LLMs). Our approach coordinates two role-specialized agents, a Student-Teacher and a Teacher-Educator, that engage in a Socratic multi-turn dialogue to iteratively refine a single question given a teacher-specified topic, key concepts, student level, and optional instructional materials. The Student-Teacher proposes candidate questions with brief rationales, while the Teacher-Educator evaluates them along clarity, depth, relevance, engagement, and conceptual interconnections, responding only with targeted coaching questions or a fixed signal to stop the dialogue. We evaluate the framework in an authentic lower-secondary ICT setting on the topic, using GPT-4o-mini as the backbone model and a stronger GPT- 4-class LLM as an external evaluator in pairwise comparisons of clarity, relevance, depth, and overall quality. First, we study how interaction design and context (dynamic this http URL iteration counts; presence or absence of student level and materials) affect question quality. Dynamic stopping combined with contextual information consistently outperforms fixed 5- or 10-step refinement, with very long dialogues prone to drift or over-complication. Second, we show that our two-agent protocol produces questions that are judged substantially more relevant and deeper, and better overall, than a one-shot baseline using the same backbone model.
zh
[NLP-34] RECAP: Resistance Capture in Text-based Mental Health Counseling with Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决文本交互场景下心理辅导中客户抗拒行为(Client Resistance)识别困难的问题,现有自然语言处理方法存在分类粗粒度、忽略治疗干预的时序动态性以及可解释性不足等局限。其解决方案的关键在于提出PsyFIRE框架,该框架基于临床心理学理论构建,能够捕捉13类细粒度的抗拒行为及协作互动模式,并在此基础上构建了包含23,930条标注语句的ClientResistance语料库,每条标注均附有上下文相关的解释依据;进一步开发了RECAP两阶段模型,实现抗拒行为检测与细粒度类型分类,并提供可解释性输出,显著优于基于提示的大语言模型基线,在F1分数和宏观F1分数上分别提升超20个百分点。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14780
作者: Anqi Li,Yuqian Chen,Yu Lu,Zhaoming Chen,Yuan Xie,Zhenzhong Lan
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); Westlake University (西湖大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 19 pages, 2 figures
Abstract:Recognizing and navigating client resistance is critical for effective mental health counseling, yet detecting such behaviors is particularly challenging in text-based interactions. Existing NLP approaches oversimplify resistance categories, ignore the sequential dynamics of therapeutic interventions, and offer limited interpretability. To address these limitations, we propose PsyFIRE, a theoretically grounded framework capturing 13 fine-grained resistance behaviors alongside collaborative interactions. Based on PsyFIRE, we construct the ClientResistance corpus with 23,930 annotated utterances from real-world Chinese text-based counseling, each supported by context-specific rationales. Leveraging this dataset, we develop RECAP, a two-stage framework that detects resistance and fine-grained resistance types with explanations. RECAP achieves 91.25% F1 for distinguishing collaboration and resistance and 66.58% macro-F1 for fine-grained resistance categories classification, outperforming leading prompt-based LLM baselines by over 20 points. Applied to a separate counseling dataset and a pilot study with 62 counselors, RECAP reveals the prevalence of resistance, its negative impact on therapeutic relationships and demonstrates its potential to improve counselors’ understanding and intervention strategies. Comments: 19 pages, 2 figures Subjects: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14780 [cs.CL] (or arXiv:2601.14780v1 [cs.CL] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14780 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[NLP-35] Mechanism Shift During Post-training from Autoregressive to Masked Diffusion Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决预训练自回归模型(Autoregressive Models, ARMs)在生成过程中受限于序列化推理的问题,尤其是探究通过扩散模型(Masked Diffusion Models, MDMs)进行后训练是否能真正赋予模型非序列化的全局规划能力,而非仅将自回归启发式策略重新包装。其解决方案的关键在于开展对ARMs与其MDM对应模型的对比电路分析(comparative circuit analysis),揭示出结构层面和语义层面的系统性“机制转变”:在结构上,MDMs保留局部因果依赖任务中的自回归电路,但在全局规划任务中摒弃初始化路径,表现为早期层处理增强;在语义上,从ARMs的局部尖锐专业化转向MDMs的分布式整合。这一发现表明,扩散后训练不仅调整参数,更从根本上重构内部计算以支持非序列化全局规划。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14758
作者: Injin Kong,Hyoungjoon Lee,Yohan Jo
机构: Seoul National University (首尔国立大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Post-training pretrained Autoregressive models (ARMs) into Masked Diffusion models (MDMs) has emerged as a cost-effective strategy to overcome the limitations of sequential generation. However, the internal algorithmic transformations induced by this paradigm shift remain unexplored, leaving it unclear whether post-trained MDMs acquire genuine bidirectional reasoning capabilities or merely repackage autoregressive heuristics. In this work, we address this question by conducting a comparative circuit analysis of ARMs and their MDM counterparts. Our analysis reveals a systematic “mechanism shift” dependent on the structural nature of the task. Structurally, we observe a distinct divergence: while MDMs largely retain autoregressive circuitry for tasks dominated by local causal dependencies, they abandon initialized pathways for global planning tasks, exhibiting distinct rewiring characterized by increased early-layer processing. Semantically, we identify a transition from sharp, localized specialization in ARMs to distributed integration in MDMs. Through these findings, we conclude that diffusion post-training does not merely adapt model parameters but fundamentally reorganizes internal computation to support non-sequential global planning.
zh
[NLP-36] Render-of-Thought: Rendering Textual Chain-of-Thought as Images for Visual Latent Reasoning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting在大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)中因推理步骤冗长而导致的计算开销过大,以及现有方法缺乏对中间推理过程监督、导致可分析性差的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出Render-of-Thought (RoT)框架,通过将文本形式的推理步骤渲染为图像,利用视觉语言模型(Vision Language Models, VLMs)的视觉编码器作为语义锚点,实现视觉嵌入与文本空间的对齐,从而显式化并可追溯地表征推理链。该设计无需额外预训练即可即插即用,实验证明可在保持竞争力性能的同时实现3–4倍的token压缩和显著的推理加速。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14750
作者: Yifan Wang,Shiyu Li,Peiming Li,Xiaochen Yang,Yang Tang,Zheng Wei
机构: Tencent BAC; Tsinghua Shenzhen International Graduate School, Tsinghua University (清华大学深圳国际研究生院); School of Electronic and Computer Engineering, Peking University (北京大学电子与计算机工程学院); School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Glasgow (格拉斯哥大学数学与统计学院)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has achieved remarkable success in unlocking the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). Although CoT prompting enhances reasoning, its verbosity imposes substantial computational overhead. Recent works often focus exclusively on outcome alignment and lack supervision on the intermediate reasoning process. These deficiencies obscure the analyzability of the latent reasoning chain. To address these challenges, we introduce Render-of-Thought (RoT), the first framework to reify the reasoning chain by rendering textual steps into images, making the latent rationale explicit and traceable. Specifically, we leverage the vision encoders of existing Vision Language Models (VLMs) as semantic anchors to align the vision embeddings with the textual space. This design ensures plug-and-play implementation without incurring additional pre-training overhead. Extensive experiments on mathematical and logical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves 3-4x token compression and substantial inference acceleration compared to explicit CoT. Furthermore, it maintains competitive performance against other methods, validating the feasibility of this paradigm. Our code is available at this https URL
zh
[NLP-37] DeepMoLM: Leverag ing Visual and Geometric Structural Information for Molecule-Text Modeling
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前生成式 AI (Generative AI) 在药物发现和化学文献挖掘中对分子图像理解与三维几何结构一致性生成能力不足的问题,特别是现有分子语言模型依赖字符串或图表示而忽视立体化学细节、视觉语言模型难以将连续的3D结构映射为离散标记的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出 DeepMoLM:一种双视角框架,通过从分子构象中提取几何不变量来锚定高分辨率分子图像,保留来自 1024×1024 输入的高频信息,并将构象邻域编码为离散的扩展三维指纹(Extended 3-Dimensional Fingerprints),再利用交叉注意力融合视觉流与几何流,从而实现无需原子坐标即可物理合理生成分子描述的能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14732
作者: Jing Lan,Hexiao Ding,Hongzhao Chen,Yufeng Jiang,Nga-Chun Ng,Gwing Kei Yip,Gerald W.Y. Cheng,Yunlin Mao,Jing Cai,Liang-ting Lin,Jung Sun Yoo
机构: The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (香港理工大学); Hong Kong Sanatorium and Hospital (香港养和医院); Queen Elizabeth Hospital (伊利沙伯医院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Multimedia (cs.MM)
备注: Under review
Abstract:AI models for drug discovery and chemical literature mining must interpret molecular images and generate outputs consistent with 3D geometry and stereochemistry. Most molecular language models rely on strings or graphs, while vision-language models often miss stereochemical details and struggle to map continuous 3D structures into discrete tokens. We propose DeepMoLM: Deep Molecular Language M odeling, a dual-view framework that grounds high-resolution molecular images in geometric invariants derived from molecular conformations. DeepMoLM preserves high-frequency evidence from 1024 \times 1024 inputs, encodes conformer neighborhoods as discrete Extended 3-Dimensional Fingerprints, and fuses visual and geometric streams with cross-attention, enabling physically grounded generation without atom coordinates. DeepMoLM improves PubChem captioning with a 12.3% relative METEOR gain over the strongest generalist baseline while staying competitive with specialist methods. It produces valid numeric outputs for all property queries and attains MAE 13.64 g/mol on Molecular Weight and 37.89 on Complexity in the specialist setting. On ChEBI-20 description generation from images, it exceeds generalist baselines and matches state-of- the-art vision-language models. Code is available at this https URL.
zh
[NLP-38] HERMES: KV Cache as Hierarchical Memory for Efficient Streaming Video Understanding
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在处理流式视频输入时面临的挑战,即如何在保持稳定理解性能、实现实时响应和低GPU内存开销之间取得平衡。解决方案的关键在于提出一种无需训练的架构HERMES,其核心思想是基于对注意力机制的机理分析,将键值缓存(KV cache)建模为一个分层记忆框架,以捕捉视频信息在不同粒度下的表征。在推理阶段,HERMES通过复用紧凑的KV cache实现资源受限条件下的高效流式理解,且无需在用户查询到达时进行额外计算,从而保障实时交互能力,并显著优于现有最先进方法(TTFT提升10倍),同时在减少高达68%视频帧采样率的情况下仍保持或超越基准性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14724
作者: Haowei Zhang,Shudong Yang,Jinlan Fu,See-Kiong Ng,Xipeng Qiu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Recent advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated significant improvement in offline video understanding. However, extending these capabilities to streaming video inputs, remains challenging, as existing models struggle to simultaneously maintain stable understanding performance, real-time responses, and low GPU memory overhead. To address this challenge, we propose HERMES, a novel training-free architecture for real-time and accurate understanding of video streams. Based on a mechanistic attention investigation, we conceptualize KV cache as a hierarchical memory framework that encapsulates video information across multiple granularities. During inference, HERMES reuses a compact KV cache, enabling efficient streaming understanding under resource constraints. Notably, HERMES requires no auxiliary computations upon the arrival of user queries, thereby guaranteeing real-time responses for continuous video stream interactions, which achieves 10 \times faster TTFT compared to prior SOTA. Even when reducing video tokens by up to 68% compared with uniform sampling, HERMES achieves superior or comparable accuracy across all benchmarks, with up to 11.4% gains on streaming datasets.
zh
[NLP-39] yphoon OCR: Open Vision-Language Model For Thai Document Extraction
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在泰语文档提取任务中表现不佳的问题,主要挑战包括泰语非拉丁字母的字符复杂性、缺乏显式词边界以及现实世界文档的高度非结构化特性。解决方案的关键在于提出一个专为泰语和英语设计的开源视觉语言模型 Typhoon OCR,其核心创新在于采用多阶段数据构建流程生成高质量训练数据,结合传统光学字符识别(Optical Character Recognition, OCR)、基于VLM的文档重构及人工校准的合成数据,并在此基础上对预训练VLM进行微调。该模型实现了文本转录、版面重建与文档级结构一致性的一体化处理能力,且最新版本Typhoon OCR V1.5在保持轻量化和高效推理的同时,显著降低了对元数据的依赖,展现出媲美甚至超越大型商业模型的性能,同时具备更低的计算成本和更强的部署灵活性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14722
作者: Surapon Nonesung,Natapong Nitarach,Teetouch Jaknamon,Pittawat Taveekitworachai,Kunat Pipatanakul
机构: Typhoon, SCB 10X
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Document extraction is a core component of digital workflows, yet existing vision-language models (VLMs) predominantly favor high-resource languages. Thai presents additional challenges due to script complexity from non-latin letters, the absence of explicit word boundaries, and the prevalence of highly unstructured real-world documents, limiting the effectiveness of current open-source models. This paper presents Typhoon OCR, an open VLM for document extraction tailored for Thai and English. The model is fine-tuned from vision-language backbones using a Thai-focused training dataset. The dataset is developed using a multi-stage data construction pipeline that combines traditional OCR, VLM-based restructuring, and curated synthetic data. Typhoon OCR is a unified framework capable of text transcription, layout reconstruction, and document-level structural consistency. The latest iteration of our model, Typhoon OCR V1.5, is a compact and inference-efficient model designed to reduce reliance on metadata and simplify deployment. Comprehensive evaluations across diverse Thai document categories, including financial reports, government forms, books, infographics, and handwritten documents, show that Typhoon OCR achieves performance comparable to or exceeding larger frontier proprietary models, despite substantially lower computational cost. The results demonstrate that open vision-language OCR models can achieve accurate text extraction and layout reconstruction for Thai documents, reaching performance comparable to proprietary systems while remaining lightweight and deployable.
zh
[NLP-40] PCL-Reason er-V1.5: Advancing Math Reasoning with Offline Reinforcement Learning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)在数学推理任务中性能提升的稳定性与效率问题。现有基于在线强化学习(Online Reinforcement Learning, RL)的方法如GRPO存在训练不稳定、资源消耗大等问题,难以有效提升模型的推理能力。解决方案的关键在于提出一种离线强化学习(Offline Reinforcement Learning, Offline RL)方法,该方法在不依赖实时环境交互的前提下,利用历史数据进行高效且稳定的策略优化,从而显著提升模型在数学推理任务上的准确率。实验表明,该方法使PCL-Reasoner-V1.5在AIME 2024和AIME 2025测试集上分别达到90.9%和85.6%的平均准确率,优于同类后训练模型,验证了离线RL作为LLM推理能力增强的有效范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14716
作者: Yao Lu,Dengdong Fan,Jianzheng Nie,Fan Xu,Jie Chen,Bin Zhou,Yonghong Tian
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:We present PCL-Reasoner-V1.5, a 32-billion-parameter large language model (LLM) for mathematical reasoning. The model is built upon Qwen2.5-32B and refined via supervised fine-tuning (SFT) followed by reinforcement learning (RL). A central innovation is our proposed offline RL method, which provides superior training stability and efficiency over standard online RL methods such as GRPO. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance among models post-trained on Qwen2.5-32B, attaining average accuracies of 90.9% on AIME 2024 and 85.6% on AIME 2025. Our work demonstrates offline RL as a stable and efficient paradigm for advancing reasoning in LLMs. All experiments were conducted on Huawei Ascend 910C NPUs.
zh
[NLP-41] DARL: Encourag ing Diverse Answers for General Reasoning without Verifiers
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前基于可验证奖励的强化学习(Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards, RLVR)方法在通用领域中因依赖特定领域验证器而适用性受限的问题,以及现有扩展方法(如RLPR)在开放任务中易过拟合参考答案、导致输出多样性不足的缺陷。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为DARL(Diversity-Aware Reinforcement Learning)的强化学习框架,该框架通过在可控偏差范围内鼓励模型生成多样化答案,同时保持与参考答案的一致性,从而在不引入额外验证器的前提下提升模型的推理准确性和输出多样性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14700
作者: Chongxuan Huang,Lei Lin,Xiaodong Shi,Wenping Hu,Ruiming Tang
机构: Xiamen University (厦门大学); Kuaishou Technology (快手科技)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has demonstrated promising gains in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models. However, its dependence on domain-specific verifiers significantly restricts its applicability to open and general domains. Recent efforts such as RLPR have extended RLVR to general domains, enabling training on broader datasets and achieving improvements over RLVR. However, a notable limitation of these methods is their tendency to overfit to reference answers, which constrains the model’s ability to generate diverse outputs. This limitation is particularly pronounced in open-ended tasks such as writing, where multiple plausible answers exist. To address this, we propose DARL, a simple yet effective reinforcement learning framework that encourages the generation of diverse answers within a controlled deviation range from the reference while preserving alignment with it. Our framework is fully compatible with existing general reinforcement learning methods and can be seamlessly integrated without additional verifiers. Extensive experiments on thirteen benchmarks demonstrate consistent improvements in reasoning performance. Notably, DARL surpasses RLPR, achieving average gains of 1.3 points on six reasoning benchmarks and 9.5 points on seven general benchmarks, highlighting its effectiveness in improving both reasoning accuracy and output diversity.
zh
[NLP-42] ClaimDB: A Fact Verification Benchmark over Large Structured Data
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前事实验证基准中对大规模结构化数据支撑的声明(claim)验证研究不足的问题。现有方法多依赖于直接“阅读”证据,但在面对由数百万记录和多张表格组成的复杂数据库时失效。解决方案的关键在于推动验证范式从文本阅读转向可执行程序中的推理,即通过编写和执行代码来分析数据并判断声明的真实性。这一转变使得模型能够处理更复杂的逻辑关系和计算过程,从而提升在真实世界、高规模结构化数据场景下的验证能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14698
作者: Michael Theologitis,Preetam Prabhu Srikar Dammu,Chirag Shah,Dan Suciu
机构: University of Washington (华盛顿大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: The data, code, and leaderboard are available at this https URL
Abstract:Despite substantial progress in fact-verification benchmarks, claims grounded in large-scale structured data remain underexplored. In this work, we introduce ClaimDB, the first fact-verification benchmark where the evidence for claims is derived from compositions of millions of records and multiple tables. ClaimDB consists of 80 unique real-life databases covering a wide range of domains, from governance and healthcare to media, education and the natural sciences. At this scale, verification approaches that rely on “reading” the evidence break down, forcing a timely shift toward reasoning in executable programs. We conduct extensive experiments with 30 state-of-the-art proprietary and open-source (below 70B) LLMs and find that none exceed 83% accuracy, with more than half below 55%. Our analysis also reveals that both closed- and open-source models struggle with abstention – the ability to admit that there is no evidence to decide – raising doubts about their reliability in high-stakes data analysis. We release the benchmark, code, and the LLM leaderboard at this https URL .
zh
[NLP-43] AdaTIR: Adaptive Tool-Integrated Reasoning via Difficulty-Aware Policy Optimization
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在工具调用(tool invocation)过程中存在的认知卸载(cognitive offloading)问题,即模型在面对简单任务时仍冗余地调用外部工具,导致效率低下。其解决方案的关键在于提出AdaTIR框架,通过引入难度感知的效率奖励(difficulty-aware efficiency reward),使模型能够动态调整工具使用预算:对简单任务内部化推理,仅对复杂任务选择性调用工具。此外,为解决工具惩罚过度压制正确决策的“符号反转问题”(sign reversal problem),作者进一步设计了裁剪优势塑造(Clipped Advantage Shaping, CAS),确保正确性优先、效率次之,从而实现更智能的工具使用决策。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14696
作者: Zhaiyu Fang,Ruipeng Sun
机构: Trip.com Group (携程集团)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: under review
Abstract:Tool-Integrated Reasoning (TIR) has significantly enhanced the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), yet current agents tend to exhibit cognitive offloading, redundantly invoking external tools even for simple tasks. In this paper, we suggest that true agentic intelligence requires not just tool invocation, but the adaptive wisdom to discern when to use them. We propose AdaTIR, a framework that shifts the paradigm from static tool invocation to difficulty-aware reasoning internalization. By introducing a difficulty-aware efficiency reward, AdaTIR dynamically adjusts tool budgets based on task complexity–internalizing reasoning for simple tasks while selectively invoking tools for complex tasks. Furthermore, we identify a sign reversal problem where tool penalties outweigh correctness rewards, mistakenly penalizing correct rollouts with negative advantages. To resolve this, we propose Clipped Advantage Shaping (CAS), which ensures that correctness remains the primary objective while using efficiency as a secondary constraint. Empirical results demonstrate that AdaTIR reduces tool calls by up to 97.6% on simple tasks and 28.2% on complex challenges while maintaining or enhancing accuracy. Notably, AdaTIR successfully internalizes reasoning, outperforming baselines by 4.8% on AIME 2024 even when tool access is strictly disabled.
zh
[NLP-44] Gaming the Judge: Unfaithful Chain-of-Thought Can Undermine Agent Evaluation
【速读】: 该论文试图解决的问题是:当前基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的评判机制在评估智能体(agent)性能时,存在对推理轨迹(chain-of-thought, CoT)的过度依赖,而这种依赖可能导致评判结果被轻易操纵,从而引发严重误判。解决方案的关键在于揭示了两种类型的操纵策略——基于风格的修改(仅改变推理表述方式)和基于内容的伪造(虚构任务进展信号),并发现后者更具破坏性;同时指出单纯依靠提示工程(prompting)或增加评判时计算资源(judge-time compute)无法彻底消除这一漏洞,强调必须发展能够将推理声明与可观测证据进行验证的新型评判机制,以提升评估的鲁棒性和可信度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14691
作者: Muhammad Khalifa,Lajanugen Logeswaran,Jaekyeom Kim,Sungryull Sohn,Yunxiang Zhang,Moontae Lee,Hao Peng,Lu Wang,Honglak Lee
机构: University of Michigan (密歇根大学); LG AI Research (LG人工智能研究中心); University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校)
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used as judges to evaluate agent performance, particularly in non-verifiable settings where judgments rely on agent trajectories including chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning. This paradigm implicitly assumes that the agent’s CoT faithfully reflects both its internal reasoning and the underlying environment state. We show this assumption is brittle: LLM judges are highly susceptible to manipulation of agent reasoning traces. By systematically rewriting agent CoTs while holding actions and observations fixed, we demonstrate that manipulated reasoning alone can inflate false positive rates of state-of-the-art VLM judges by up to 90% across 800 trajectories spanning diverse web tasks. We study manipulation strategies spanning style-based approaches that alter only the presentation of reasoning and content-based approaches that fabricate signals of task progress, and find that content-based manipulations are consistently more effective. We evaluate prompting-based techniques and scaling judge-time compute, which reduce but do not fully eliminate susceptibility to manipulation. Our findings reveal a fundamental vulnerability in LLM-based evaluation and highlight the need for judging mechanisms that verify reasoning claims against observable evidence.
zh
[NLP-45] NeuroFilter: Privacy Guardrails for Conversational LLM Agents
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决在代理型大语言模型(Agentic Large Language Models, LLMs)中实现隐私保护的计算效率问题,尤其针对现有基于LLM中介检查机制的防御方法存在高延迟、高成本且易被多轮交互中的操纵或看似无害的对话结构绕过的缺陷。解决方案的关键在于发现并利用模型内部表示中与隐私违规意图相关的线性结构:通过将规范违反映射到激活空间中的简单方向,构建了NeuroFilter这一护栏框架,从而在语义过滤失效时仍能检测隐私攻击;进一步引入“激活速度”(activation velocity)概念以捕捉长时间对话中内部表示的累积漂移,增强对长期威胁的识别能力。该方案在超过15万次交互测试中表现出色,实现了零误报率,并显著降低推理成本数个数量级。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14660
作者: Saswat Das,Ferdinando Fioretto
机构: University of Virginia (弗吉尼亚大学)
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:This work addresses the computational challenge of enforcing privacy for agentic Large Language Models (LLMs), where privacy is governed by the contextual integrity framework. Indeed, existing defenses rely on LLM-mediated checking stages that add substantial latency and cost, and that can be undermined in multi-turn interactions through manipulation or benign-looking conversational scaffolding. Contrasting this background, this paper makes a key observation: internal representations associated with privacy-violating intent can be separated from benign requests using linear structure. Using this insight, the paper proposes NeuroFilter, a guardrail framework that operationalizes contextual integrity by mapping norm violations to simple directions in the model’s activation space, enabling detection even when semantic filters are bypassed. The proposed filter is also extended to capture threats arising during long conversations using the concept of activation velocity, which measures cumulative drift in internal representations across turns. A comprehensive evaluation across over 150,000 interactions and covering models from 7B to 70B parameters, illustrates the strong performance of NeuroFilter in detecting privacy attacks while maintaining zero false positives on benign prompts, all while reducing the computational inference cost by several orders of magnitude when compared to LLM-based agentic privacy defenses.
zh
[NLP-46] Say Anything but This: When Tokenizer Betrays Reasoning in LLM s
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在推理过程中因子词分词器(subword tokenizer)产生的非唯一编码所引发的表示不一致性问题。这种不一致性导致模型将语义相同的文本映射为不同的内部token ID序列,从而在推理时产生“幻影编辑”(phantom edits)现象——即模型看似正确执行了替换任务,实则因tokenizer-detokenizer之间的映射缺陷而误判结果。解决方案的关键在于引入一种称为“分词一致性探测”(tokenization-consistency probe)的任务设计:要求模型在保持上下文不变的前提下仅替换指定目标词,通过表面简单的任务隔离出失败根源,明确归因于分词层的系统性缺陷而非模型知识或参数限制。该方法揭示了八类典型的分词器人工制品(tokenizer artifacts),并表明部分推理能力不足源于分词器层面的问题,提示应优先从分词机制优化入手,而非盲目扩大模型规模。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14658
作者: Navid Ayoobi,Marcus I Armstrong,Arjun Mukherjee
机构: University of Houston (休斯顿大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) reason over discrete token ID sequences, yet modern subword tokenizers routinely produce non-unique encodings: multiple token ID sequences can detokenize to identical surface strings. This representational mismatch creates an unmeasured fragility wherein reasoning processes can fail. LLMs may treat two internal representations as distinct “words” even when they are semantically identical at the text level. In this work, we show that tokenization can betray LLM reasoning through one-to-many token ID mappings. We introduce a tokenization-consistency probe that requires models to replace designated target words in context while leaving all other content unchanged. The task is intentionally simple at the surface level, enabling us to attribute failures to tokenizer-detokenizer artifacts rather than to knowledge gaps or parameter limitations. Through analysis of over 11000 replacement trials across state-of-the-art open-source LLMs, we find a non-trivial rate of outputs exhibit phantom edits: cases where models operate under the illusion of correct reasoning, a phenomenon arising from tokenizer-induced representational defects. We further analyze these cases and provide a taxonomy of eight systematic tokenizer artifacts, including whitespace-boundary shifts and intra-word resegmentation. These findings indicate that part of apparent reasoning deficiency originates in the tokenizer layer, motivating tokenizer-level remedies before incurring the cost of training ever-larger models on ever-larger corpora.
zh
[NLP-47] MAS-Orchestra: Understanding and Improving Multi-Agent Reasoning Through Holistic Orchestration and Controlled Benchmarks
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前多智能体系统(Multi-Agent Systems, MAS)自动设计方法中存在的两大问题:一是方法论复杂性,即现有方案依赖顺序式的代码级执行,难以实现全局系统层面的协同推理且难以扩展至复杂度较高的多智能体场景;二是效能不确定性,即缺乏对多智能体系统是否优于单智能体系统(Single-Agent Systems, SAS)的明确验证机制。其解决方案的关键在于提出MAS-Orchestra框架,将MAS编排建模为一个函数调用强化学习问题,通过抽象复杂的目标导向子智能体为可调用函数,在隐藏内部执行细节的同时支持全局结构层面的推理,从而实现一次性生成完整的多智能体系统。此外,作者还构建了MASBENCH基准测试集,从深度、时域、广度、并行性和鲁棒性五个维度量化任务特性,揭示了多智能体优势高度依赖于任务结构、验证协议及 orchestrator与子智能体的能力匹配,而非普遍适用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14652
作者: Zixuan Ke,Yifei Ming,Austin Xu,Ryan Chin,Xuan-Phi Nguyen,Prathyusha Jwalapuram,Semih Yavuz,Caiming Xiong,Shafiq Joty
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注: Preprint; Work in Progress
Abstract:While multi-agent systems (MAS) promise elevated intelligence through coordination of agents, current approaches to automatic MAS design under-deliver. Such shortcomings stem from two key factors: (1) methodological complexity - agent orchestration is performed using sequential, code-level execution that limits global system-level holistic reasoning and scales poorly with agent complexity - and (2) efficacy uncertainty - MAS are deployed without understanding if there are tangible benefits compared to single-agent systems (SAS). We propose MAS-Orchestra, a training-time framework that formulates MAS orchestration as a function-calling reinforcement learning problem with holistic orchestration, generating an entire MAS at once. In MAS-Orchestra, complex, goal-oriented sub-agents are abstracted as callable functions, enabling global reasoning over system structure while hiding internal execution details. To rigorously study when and why MAS are beneficial, we introduce MASBENCH, a controlled benchmark that characterizes tasks along five axes: Depth, Horizon, Breadth, Parallel, and Robustness. Our analysis reveals that MAS gains depend critically on task structure, verification protocols, and the capabilities of both orchestrator and sub-agents, rather than holding universally. Guided by these insights, MAS-Orchestra achieves consistent improvements on public benchmarks including mathematical reasoning, multi-hop QA, and search-based QA. Together, MAS-Orchestra and MASBENCH enable better training and understanding of MAS in the pursuit of multi-agent intelligence.
zh
[NLP-48] Forest-Chat: Adapting Vision-Language Agents for Interactive Forest Change Analysis
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决森林监测中像素级变化检测(pixel-level change detection)与语义变化解释(semantic change interpretation)的两大核心挑战,尤其针对复杂森林动态场景下的分析难题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个基于大语言模型(LLM)驱动的智能代理 Forest-Chat,该系统通过多层级变化解释(multi-level change interpretation, MCI)视觉-语言骨干网络实现自然语言查询支持,并结合零样本变化检测能力与交互式点提示界面,提升用户对森林变化的细粒度引导和理解能力。此外,研究构建了 Forest-Change 数据集以支持森林环境中的模型训练与评估,验证了 LLM 驱动的遥感图像变化解释(RSICI)系统在可访问性、可解释性和分析效率方面的显著优势。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14637
作者: James Brock,Ce Zhang,Nantheera Anantrasirichai
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注: 22 pages, 8 figures, 7 tables, Submitted to Ecological Informatics
Abstract:The increasing availability of high-resolution satellite imagery, together with advances in deep learning, creates new opportunities for enhancing forest monitoring workflows. Two central challenges in this domain are pixel-level change detection and semantic change interpretation, particularly for complex forest dynamics. While large language models (LLMs) are increasingly adopted for data exploration, their integration with vision-language models (VLMs) for remote sensing image change interpretation (RSICI) remains underexplored, especially beyond urban environments. We introduce Forest-Chat, an LLM-driven agent designed for integrated forest change analysis. The proposed framework enables natural language querying and supports multiple RSICI tasks, including change detection, change captioning, object counting, deforestation percentage estimation, and change reasoning. Forest-Chat builds upon a multi-level change interpretation (MCI) vision-language backbone with LLM-based orchestration, and incorporates zero-shot change detection via a foundation change detection model together with an interactive point-prompt interface to support fine-grained user guidance. To facilitate adaptation and evaluation in forest environments, we introduce the Forest-Change dataset, comprising bi-temporal satellite imagery, pixel-level change masks, and multi-granularity semantic change captions generated through a combination of human annotation and rule-based methods. Experimental results demonstrate that Forest-Chat achieves strong performance on Forest-Change and on LEVIR-MCI-Trees, a tree-focused subset of LEVIR-MCI, for joint change detection and captioning, highlighting the potential of interactive, LLM-driven RSICI systems to improve accessibility, interpretability, and analytical efficiency in forest change analysis.
zh
[NLP-49] SearchGym: Bootstrapping Real-World Search Agents via Cost-Effective and High-Fidelity Environment Simulation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI (Generative AI) 在通过强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)训练搜索代理(Search Agents)时面临的两大挑战:一是与实时商业网络 API 交互成本过高,二是依赖静态数据快照会导致数据错位(data misalignment),从而产生错误的奖励信号,干扰训练稳定性并导致正确推理被惩罚或幻觉被奖励。解决方案的关键在于提出 SearchGym——一个高保真模拟环境,其核心创新是构建了一个可验证的知识图谱和对齐文档语料库,确保所有推理任务在事实层面可验证且严格可解;在此基础上进一步设计 SearchGym-RL 方法,采用课程学习(curriculum learning)策略逐步优化代理策略,以纯净反馈驱动从基础交互到复杂长程规划的演化过程。实验表明,基于 SearchGym 训练的 Qwen2.5-7B-Base 模型在九个基准测试中平均超越 Web 增强型基线 ASearcher 10.6%,验证了该模拟方法在提升搜索代理能力方面的有效性与可扩展性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14615
作者: Xichen Zhang,Ziyi He,Yinghao Zhu,Sitong Wu,Shaozuo Yu,Meng Chu,Wenhu Zhang,Haoru Tan,Jiaya Jia
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Search agents have emerged as a pivotal paradigm for solving open-ended, knowledge-intensive reasoning tasks. However, training these agents via Reinforcement Learning (RL) faces a critical dilemma: interacting with live commercial Web APIs is prohibitively expensive, while relying on static data snapshots often introduces noise due to data misalignment. This misalignment generates corrupted reward signals that destabilize training by penalizing correct reasoning or rewarding hallucination. To address this, we propose SearchGym, a simulation environment designed to bootstrap robust search agents. SearchGym employs a rigorous generative pipeline to construct a verifiable knowledge graph and an aligned document corpus, ensuring that every reasoning task is factually grounded and strictly solvable. Building on this controllable environment, we introduce SearchGym-RL, a curriculum learning methodology that progressively optimizes agent policies through purified feedback, evolving from basic interactions to complex, long-horizon planning. Extensive experiments across the Llama and Qwen families demonstrate strong Sim-to-Real generalization. Notably, our Qwen2.5-7B-Base model trained within SearchGym surpasses the web-enhanced ASearcher baseline across nine diverse benchmarks by an average relative margin of 10.6%. Our results validate that high-fidelity simulation serves as a scalable and highly cost-effective methodology for developing capable search agents.
zh
[NLP-50] Designing KRIYA: An AI Companion for Wellbeing Self-Reflection
【速读】: 该论文试图解决当前个人健康类应用(Wellbeing Apps)普遍存在的问题:即用户难以将汇总的健康与身体活动数据转化为有意义的理解,且现有应用通过目标设定、提醒和结构化指标等方式虽提升参与度,但可能引发比较心理、评判压力和绩效焦虑。为应对这一挑战,作者提出解决方案——设计名为KRIYA的AI健康伴侣,其核心在于通过“共 interpretive engagement”(共 Interpretive Engagement)机制,引导用户从关注绩效转向自我反思。关键创新在于引入三个交互模式:Comfort Zone(舒适区)、Detective Mode(侦探模式)和What-If Planning(假设规划),使用户能够以探索性、非评判性的视角理解自身健康数据,从而促进基于同理心与好奇心的自我觉察,并建立对AI系统的信任感。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14589
作者: Shanshan Zhu,Wenxuan Song,Jiayue Melissa Shi,Dong Whi Yoo,Karthik S. Bhat,Koustuv Saha
机构: University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校); Indiana University Indianapolis (印第安纳大学印第安纳波利斯分校); Drexel University (德雷塞尔大学)
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注:
Abstract:Most personal wellbeing apps present summative dashboards of health and physical activity metrics, yet many users struggle to translate this information into meaningful understanding. These apps commonly support engagement through goals, reminders, and structured targets, which can reinforce comparison, judgment, and performance anxiety. To explore a complementary approach that prioritizes self-reflection, we design KRIYA, an AI wellbeing companion that supports co-interpretive engagement with personal wellbeing data. KRIYA aims to collaborate with users to explore questions, explanations, and future scenarios through features such as Comfort Zone, Detective Mode, and What-If Planning. We conducted semi-structured interviews with 18 college students interacting with a KRIYA prototype using hypothetical data. Our findings show that through KRIYA interaction, users framed engaging with wellbeing data as interpretation rather than performance, experienced reflection as supportive or pressuring depending on emotional framing, and developed trust through transparency. We discuss design implications for AI companions that support curiosity, self-compassion, and reflective sensemaking of personal health data.
zh
[NLP-51] Social Caption: Evaluating Social Understanding in Multimodal Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在理解人类社会互动方面的能力评估问题,尤其关注其社会理解能力的量化与分析。解决方案的关键在于提出Social Caption框架,该框架基于交互理论,从三个维度系统评估MLLMs的社会理解能力:社会推理(Social Inference, SI),即对交互行为做出准确推断的能力;整体社会分析(Holistic Social Analysis, HSA),即生成对交互过程全面描述的能力;定向社会分析(Directed Social Analysis, DSA),即从交互中提取相关社会信息的能力。通过该框架,论文进一步揭示了模型规模、架构设计和口语语境等因素对社会理解性能的影响,并借助MLLM评判者实验为自动化评估多模态社会理解提供了可扩展的方法论支持。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14569
作者: Bhaavanaa Thumu,Leena Mathur,Youssouf Kebe,Louis-Philippe Morency
机构: Carnegie Mellon University (卡内基梅隆大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 24 pages
Abstract:Social understanding abilities are crucial for multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to interpret human social interactions. We introduce Social Caption, a framework grounded in interaction theory to evaluate social understanding abilities of MLLMs along three dimensions: Social Inference (SI), the ability to make accurate inferences about interactions; Holistic Social Analysis (HSA), the ability to generate comprehensive descriptions of interactions; Directed Social Analysis (DSA), the ability to extract relevant social information from interactions. We analyze factors influencing model performance in social understanding, such as scale, architectural design, and spoken context. Experiments with MLLM judges contribute insights about scaling automated evaluation of multimodal social understanding.
zh
[NLP-52] Rewarding How Models Think Pedagogically: Integrating Pedagogical Reasoning and Thinking Rewards for LLM s in Education
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在教育场景中作为智能导师(Intelligent Tutoring Systems)部署时,缺乏针对教学逻辑和认知过程优化的问题。现有基于强化学习的训练方法仅关注可见输出(即学生交互响应),忽视了模型内部推理链(reasoning trace)的 pedagogical质量。解决方案的关键在于提出 PedagogicalRL-Thinking 框架,其核心创新包括:(1) 教育学理论驱动的内部推理提示(Pedagogical Reasoning Prompting),通过领域特定的教学理论引导模型生成更具教学意义的中间思考步骤;(2) 思考奖励机制(Thinking Reward),显式评估并强化推理链中的教学合理性与结构化程度。实验证明,结合这两种机制能显著提升模型在未见教育任务上的泛化能力,并促使推理过程向更系统、结构化的教学决策演进。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14560
作者: Unggi Lee,Jiyeong Bae,Jaehyeon Park,Haeun Park,Taejun Park,Younghoon Jeon,Sungmin Cho,Junbo Koh,Yeil Jeong,Gyeonggeon Lee
机构: Chosun University (崇实大学); Korea University (韩国大学); Seoul National University (首尔国立大学); Korea Institute for Curriculum and Evaluation (韩国课程与评价研究所); Upstage; Indiana University Bloomington (印第安纳大学布卢明顿分校); Nanyang Technological University (南洋理工大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed as intelligent tutoring systems, yet research on optimizing LLMs specifically for educational contexts remains limited. Recent works have proposed reinforcement learning approaches for training LLM tutors, but these methods focus solely on optimizing visible responses while neglecting the model’s internal thinking process. We introduce PedagogicalRL-Thinking, a framework that extends pedagogical alignment to reasoning LLMs in education through two novel approaches: (1) Pedagogical Reasoning Prompting, which guides internal reasoning using domain-specific educational theory rather than generic instructions; and (2) Thinking Reward, which explicitly evaluates and reinforces the pedagogical quality of the model’s reasoning traces. Our experiments reveal that domain-specific, theory-grounded prompting outperforms generic prompting, and that Thinking Reward is most effective when combined with pedagogical prompting. Furthermore, models trained only on mathematics tutoring dialogues show improved performance on educational benchmarks not seen during training, while preserving the base model’s factual knowledge. Our quantitative and qualitative analyses reveal that pedagogical thinking reward produces systematic reasoning trace changes, with increased pedagogical reasoning and more structured instructional decision-making in the tutor’s thinking process.
zh
[NLP-53] Self-Blinding and Counterfactual Self-Simulation Mitigate Biases and Sycophancy in Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决决策过程中因引入无关但可能引发偏见的信息(如性别、种族)而导致的不公平问题,尤其是人类和大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在处理此类信息时难以有效模拟“反事实情境”(counterfactual self-simulation),从而导致隐性偏见或谄媚行为(sycophancy)。研究发现,单纯通过提示(prompting)让LLM忽略或假装不知晓偏见信息无法有效缓解偏见,甚至可能适得其反。其解决方案的关键在于赋予模型访问自身“盲化副本”(blinded replica)的能力——即调用其API获取在不掌握偏见信息下的响应,从而实现更公平的决策,并提升对隐性偏见与有意偏见之间区别的透明度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14553
作者: Brian Christian,Matan Mazor
机构: University of Oxford(牛津大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注:
Abstract:Fair decisions require ignoring irrelevant, potentially biasing, information. To achieve this, decision-makers need to approximate what decision they would have made had they not known certain facts, such as the gender or race of a job candidate. This counterfactual self-simulation is notoriously hard for humans, leading to biased judgments even by well-meaning actors. Here we show that large language models (LLMs) suffer from similar limitations in their ability to approximate what decisions they would make under counterfactual knowledge in offsetting gender and race biases and overcoming sycophancy. We show that prompting models to ignore or pretend not to know biasing information fails to offset these biases and occasionally backfires. However, unlike humans, LLMs can be given access to a ground-truth model of their own counterfactual cognition – their own API. We show that this access to the responses of a blinded replica enables fairer decisions, while providing greater transparency to distinguish implicit from intentionally biased behavior.
zh
[NLP-54] owards Execution-Grounded Automated AI Research
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在自动化人工智能(AI)研究中生成看似合理但实际无效的研究想法的问题。其核心挑战在于如何通过执行反馈来提升LLM生成想法的有效性,从而实现更高效的科学发现。解决方案的关键在于构建一个自动化执行器(automated executor),能够将LLM生成的算法或训练策略转化为可运行的GPU实验,并利用大规模并行执行获取真实反馈;在此基础上,采用两种学习机制——进化搜索(evolutionary search)和强化学习(reinforcement learning)——从执行结果中学习优化策略。其中,执行引导的进化搜索展现出高样本效率,在仅十轮搜索内即显著优于基线方法(如post-training任务中GRPO基准从48.0%提升至69.4%,pre-training任务中nanoGPT基准从35.9分钟缩短至19.7分钟),而强化学习则因模式崩溃(mode collapse)导致无法突破上界性能,表明执行反馈驱动的进化策略是更可行的路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14525
作者: Chenglei Si,Zitong Yang,Yejin Choi,Emmanuel Candès,Diyi Yang,Tatsunori Hashimoto
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Automated AI research holds great potential to accelerate scientific discovery. However, current LLMs often generate plausible-looking but ineffective ideas. Execution grounding may help, but it is unclear whether automated execution is feasible and whether LLMs can learn from the execution feedback. To investigate these, we first build an automated executor to implement ideas and launch large-scale parallel GPU experiments to verify their effectiveness. We then convert two realistic research problems - LLM pre-training and post-training - into execution environments and demonstrate that our automated executor can implement a large fraction of the ideas sampled from frontier LLMs. We analyze two methods to learn from the execution feedback: evolutionary search and reinforcement learning. Execution-guided evolutionary search is sample-efficient: it finds a method that significantly outperforms the GRPO baseline (69.4% vs 48.0%) on post-training, and finds a pre-training recipe that outperforms the nanoGPT baseline (19.7 minutes vs 35.9 minutes) on pre-training, all within just ten search epochs. Frontier LLMs often generate meaningful algorithmic ideas during search, but they tend to saturate early and only occasionally exhibit scaling trends. Reinforcement learning from execution reward, on the other hand, suffers from mode collapse. It successfully improves the average reward of the ideator model but not the upper-bound, due to models converging on simple ideas. We thoroughly analyze the executed ideas and training dynamics to facilitate future efforts towards execution-grounded automated AI research.
zh
[NLP-55] Business Logic-Driven Text-to-SQL Data Synthesis for Business Intelligence
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决在私有商业智能(Business Intelligence, BI)场景中评估Text-to-SQL代理时面临的现实数据稀缺问题,尤其是现有合成数据生成方法难以体现业务逻辑真实性的缺陷。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于业务逻辑驱动的数据合成框架(Business Logic-Driven Data Synthesis),该框架通过引入业务角色(business personas)、工作场景(work scenarios)和业务流程(workflows)来构建具有高业务真实性的合成数据,并进一步采用业务推理复杂度控制策略,以提升问题解答所需的分析步骤多样性,从而更全面地评估Text-to-SQL模型的能力。实验表明,该方法在业务真实性上显著优于现有方法(如OmniSQL和SQL-Factory),同时保持了高质量的问句与SQL语句对齐(98.59%),并揭示出当前先进Text-to-SQL模型在复杂业务查询上的执行准确率仅为42.86%,凸显了该领域仍存在显著性能差距。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14518
作者: Jinhui Liu,Ximeng Zhang,Yanbo Ai,Zhou Yu
机构: Columbia University (哥伦比亚大学); Mercury
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Evaluating Text-to-SQL agents in private business intelligence (BI) settings is challenging due to the scarcity of realistic, domain-specific data. While synthetic evaluation data offers a scalable solution, existing generation methods fail to capture business realism–whether questions reflect realistic business logic and workflows. We propose a Business Logic-Driven Data Synthesis framework that generates data grounded in business personas, work scenarios, and workflows. In addition, we improve the data quality by imposing a business reasoning complexity control strategy that diversifies the analytical reasoning steps required to answer the questions. Experiments on a production-scale Salesforce database show that our synthesized data achieves high business realism (98.44%), substantially outperforming OmniSQL (+19.5%) and SQL-Factory (+54.7%), while maintaining strong question-SQL alignment (98.59%). Our synthetic data also reveals that state-of-the-art Text-to-SQL models still have significant performance gaps, achieving only 42.86% execution accuracy on the most complex business queries.
zh
[NLP-56] Language Caste and Context: Demographic Disparities in AI-Generated Explanations Across Indian and American STEM Educational Systems
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在跨文化背景下对具有交叉性边缘身份的学生群体(如印度的种姓、地区语言教学背景,以及美国的非裔美国人、历史黑人学院或大学HBCU就读经历等)的认知能力感知是否存在系统性偏见的问题。其关键解决方案在于构建了包含多维人口统计学特征(如种姓、教育媒介、学校体系、收入水平和高校层级)的精细化学生画像,并在印度与美国工程入学考试准备场景中进行大规模交叉分析,揭示LLMs即使面对社会流动后的精英院校录取者,仍会基于边缘化身份提供简化解释,表明模型偏差已深度嵌入其推理机制,且不同模型间具有一致性,无法通过更换AI助手规避。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14506
作者: Amogh Gupta,Niharika Patil,Sourojit Ghosh,SnehalKumar(Neil)S Gaikwad
机构: Society-Centered AI Lab(社会中心人工智能实验室); UNC Chapel Hill(北卡罗来纳大学教堂山分校); University of Washington(华盛顿大学)
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:The popularization of AI chatbot usage globally has created opportunities for research into their benefits and drawbacks, especially for students using AI assistants for coursework support. This paper asks: how do LLMs perceive the intellectual capabilities of student profiles from intersecting marginalized identities across different cultural contexts? We conduct one of the first large-scale intersectional analyses on LLM explanation quality for Indian and American undergraduate profiles preparing for engineering entrance examinations. By constructing profiles combining multiple demographic dimensions including caste, medium of instruction, and school boards in India, and race, HBCU attendance, and school type in America, alongside universal factors like income and college tier, we examine how quality varies across these factors. We observe biases providing lower-quality outputs to profiles with marginalized backgrounds in both contexts. LLMs such as Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct and GPT-4o demonstrate granular understandings of context-specific discrimination, systematically providing simpler explanations to Hindi/Regional-medium students in India and HBCU profiles in America, treating these as proxies for lower capability. Even when marginalized profiles attain social mobility by getting accepted into elite institutions, they still receive more simplistic explanations, showing how demographic information is inextricably linked to LLM biases. Different models (Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct, GPT-4o, GPT-4o-mini, GPT-OSS 20B) embed similar biases against historically marginalized populations in both contexts, preventing profiles from switching between AI assistants for better results. Our findings have strong implications for AI incorporation into global engineering education.
zh
[NLP-57] GutenOCR: A Grounded Vision-Language Front-End for Documents
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决传统光学字符识别(OCR)系统在复杂文档场景下难以实现精准文本定位与语义理解的问题,尤其是在多模态场景中缺乏统一接口支持阅读、检测与空间定位的能力。解决方案的关键在于提出GutenOCR系列模型,通过微调Qwen2.5-VL-3B和Qwen2.5-VL-7B视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs),构建一个基于提示(prompt-based)的统一接口,使模型能够同时完成全页及局部文本读取、边界框标注(line- and paragraph-level bounding boxes)以及条件查询如“where is x?”,从而实现生成式AI驱动的接地OCR(grounded OCR)。该方法在商业文档和科学文献上训练,并引入新的评估协议,显著提升了复合接地OCR得分(GutenOCR-7B从0.40提升至0.82),但也在页面线性化、颜色引导OCR和公式密集布局等任务上揭示了性能权衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14490
作者: Hunter Heidenreich,Ben Elliott,Olivia Dinica,Yosheb Getachew
机构: Roots.ai
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:GutenOCR is a family of grounded OCR front-ends obtained by fine-tuning Qwen2.5-VL-3B and Qwen2.5-VL-7B. The resulting single-checkpoint vision-language models expose reading, detection, and grounding through a unified, prompt-based interface. Trained on business documents, scientific articles, and synthetic grounding data, the models support full-page and localized reading with line- and paragraph-level bounding boxes and conditional ``where is x?‘’ queries. We introduce a grounded OCR evaluation protocol and show that GutenOCR-7B more than doubles the composite grounded OCR score of its Qwen2.5-VL-7B backbone on 10.5K held-out business and scientific pages (0.40 to 0.82). On Fox and OmniDocBench v1.5, our approach substantially improves region- and line-level OCR as well as text-detection recall, but reveals trade-offs in page-level linearization, color-guided OCR, and formula-heavy layouts.
zh
[NLP-58] Can LLM Reasoning Be Trusted? A Comparative Study: Using Human Benchmarking on Statistical Tasks
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在统计任务中的能力尚不明确的问题,特别是其在处理中等复杂度统计挑战时的表现以及对推理质量的评估能力。解决方案的关键在于通过在一个专门构建的数据集上对选定的开源LLM进行微调,以增强其统计推理能力,并将微调后模型的表现与人类评分进行对比验证。实验表明,微调后的模型在高级统计任务上的表现可达到统计学学生水平,且不同架构的模型展现出差异化的改进效果;此外,研究还发现LLM自身能更有效地评估答案质量(包括解释和推理),优于传统指标如BLEU或BertScore,从而为统计教育平台的自动化评估和数据分析工具的质量控制提供了可行路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14479
作者: Crish Nagarkar,Leonid Bogachev,Serge Sharoff
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:This paper investigates the ability of large language models (LLMs) to solve statistical tasks, as well as their capacity to assess the quality of reasoning. While state-of-the-art LLMs have demonstrated remarkable performance in a range of NLP tasks, their competence in addressing even moderately complex statistical challenges is not well understood. We have fine-tuned selected open-source LLMs on a specially developed dataset to enhance their statistical reasoning capabilities, and compared their performance with the human scores used as a benchmark. Our results show that the fine-tuned models achieve better performance on advanced statistical tasks on the level comparable to a statistics student. Fine-tuning demonstrates architecture-dependent improvements, with some models showing significant performance gains, indicating clear potential for deployment in educational technology and statistical analysis assistance systems. We also show that LLMs themselves can be far better judges of the answers quality (including explanation and reasoning assessment) in comparison to traditional metrics, such as BLEU or BertScore. This self-evaluation capability enables scalable automated assessment for statistical education platforms and quality assurance in automated analysis tools. Potential applications also include validation tools for research methodology in academic and industry settings, and quality control mechanisms for data analysis workflows.
zh
[NLP-59] Large Language Models for Large-Scale Rigorous Qualitative Analysis in Applied Health Services Research
【速读】: 该论文试图解决的问题是:在大型多站点健康服务研究中,如何将大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)有效整合到定性分析流程中,以提升效率并保持方法学严谨性,同时缺乏针对LLM在定性分析中应用的方法论指导和实证证据。解决方案的关键在于提出一个模型和任务无关的框架,用于设计人-LLM协作的定性分析方法,从而支持多样化的分析目标;在此框架指导下,研究人员在联邦合格健康中心(Federally Qualified Health Centers, FQHCs)糖尿病照护研究中成功实现了两类应用:一是基于研究者生成摘要的定性综合以产出对比反馈报告,二是对167份访谈文本进行演绎编码以优化实践转型干预措施。该框架确保了LLM辅助下的分析既高效又可追溯,为LLM在真实世界定性研究中的应用提供了结构化路径与实证依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14478
作者: Sasha Ronaghi,Emma-Louise Aveling,Maria Levis,Rachel Lauren Ross,Emily Alsentzer,Sara Singer
机构: Stanford University (斯坦福大学); Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health (哈佛大学陈曾熙公共卫生学院); Impactivo (影响者)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 20 pages, 6 figures
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) show promise for improving the efficiency of qualitative analysis in large, multi-site health-services research. Yet methodological guidance for LLM integration into qualitative analysis and evidence of their impact on real-world research methods and outcomes remain limited. We developed a model- and task-agnostic framework for designing human-LLM qualitative analysis methods to support diverse analytic aims. Within a multi-site study of diabetes care at Federally Qualified Health Centers (FQHCs), we leveraged the framework to implement human-LLM methods for (1) qualitative synthesis of researcher-generated summaries to produce comparative feedback reports and (2) deductive coding of 167 interview transcripts to refine a practice-transformation intervention. LLM assistance enabled timely feedback to practitioners and the incorporation of large-scale qualitative data to inform theory and practice changes. This work demonstrates how LLMs can be integrated into applied health-services research to enhance efficiency while preserving rigor, offering guidance for continued innovation with LLMs in qualitative research.
zh
[NLP-60] Prosody-Guided Harmonic Attention for Phase-Coherent Neural Vocoding in the Complex Spectrum ICASSP2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决神经声码器(Neural Vocoder)在语音合成中普遍存在的情感韵律建模能力有限和相位重建不准确的问题。其解决方案的关键在于引入韵律引导的谐波注意力机制(prosody-guided harmonic attention),以增强有声段的编码效果,并通过逆短时傅里叶变换(inverse STFT)直接预测复数谱成分进行波形合成,从而实现幅度与相位的联合建模,确保相位一致性并提升基频(F0)保真度。此外,采用多目标训练策略融合对抗损失、谱损失和相位感知损失,进一步优化感知质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14472
作者: Mohammed Salah Al-Radhi,Riad Larbi,Mátyás Bartalis,Géza Németh
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 5 pages, 2 figures, 1 table. Accepted for presentation at ICASSP 2026
Abstract:Neural vocoders are central to speech synthesis; despite their success, most still suffer from limited prosody modeling and inaccurate phase reconstruction. We propose a vocoder that introduces prosody-guided harmonic attention to enhance voiced segment encoding and directly predicts complex spectral components for waveform synthesis via inverse STFT. Unlike mel-spectrogram-based approaches, our design jointly models magnitude and phase, ensuring phase coherence and improved pitch fidelity. To further align with perceptual quality, we adopt a multi-objective training strategy that integrates adversarial, spectral, and phase-aware losses. Experiments on benchmark datasets demonstrate consistent gains over HiFi-GAN and AutoVocoder: F0 RMSE reduced by 22 percent, voiced/unvoiced error lowered by 18 percent, and MOS scores improved by 0.15. These results show that prosody-guided attention combined with direct complex spectrum modeling yields more natural, pitch-accurate, and robust synthetic speech, setting a strong foundation for expressive neural vocoding.
zh
[NLP-61] VisTIRA: Closing the Image-Text Modality Gap in Visual Math Reasoning via Structured Tool Integration
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决视觉-语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在数学推理任务中存在显著的模态差距(modality gap)问题,即当同一数学问题以图像形式呈现时,其准确率明显低于文本形式,主要归因于对密集公式、排版结构及符号与图表混合上下文的识别失败。解决方案的关键在于提出VisTIRA(Vision and Tool-Integrated Reasoning Agent),一个工具集成的推理框架,通过迭代地将图像中的数学问题分解为自然语言推理步骤和可执行的Python代码步骤,实现结构化求解;同时构建了一个基于LaTeX的图像生成管道和来自真实作业场景的合成工具使用轨迹数据集(SnapAsk),用于训练和评估VLMs的视觉数学推理能力。实验表明,工具集成监督可提升图像推理性能,OCR基础定位进一步缩小小模型的模态差距,但其增益随模型规模增大而减弱,揭示了模态差距严重程度与模型规模呈负相关,且结构化推理与OCR接地是互补策略。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14440
作者: Saeed Khaki,Ashudeep Singh,Nima Safaei,Kamal Ginotra
机构: Microsoft AI (微软人工智能); Ohio State University (俄亥俄州立大学)
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) lag behind text-only language models on mathematical reasoning when the same problems are presented as images rather than text. We empirically characterize this as a modality gap: the same question in text form yields markedly higher accuracy than its visually typeset counterpart, due to compounded failures in reading dense formulas, layout, and mixed symbolic-diagrammatic context. First, we introduce VisTIRA (Vision and Tool-Integrated Reasoning Agent), a tool-integrated reasoning framework that enables structured problem solving by iteratively decomposing a given math problem (as an image) into natural language rationales and executable Python steps to determine the final answer. Second, we build a framework to measure and improve visual math reasoning: a LaTeX-based pipeline that converts chain-of-thought math corpora (e.g., NuminaMath) into challenging image counterparts, and a large set of synthetic tool-use trajectories derived from a real-world, homework-style image dataset (called SnapAsk) for fine-tuning VLMs. Our experiments show that tool-integrated supervision improves image-based reasoning, and OCR grounding can further narrow the gap for smaller models, although its benefit diminishes at scale. These findings highlight that modality gap severity inversely correlates with model size, and that structured reasoning and OCR-based grounding are complementary strategies for advancing visual mathematical reasoning.
zh
[NLP-62] Vision-Based Natural Language Scene Understanding for Autonomous Driving: An Extended Dataset and a New Model for Traffic Scene Description Generation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决自动驾驶车辆在复杂交通场景中对环境感知与理解的难题,核心在于将单张前视摄像头图像转化为简洁且语义丰富的自然语言描述,以准确捕捉空间布局、语义关系及驾驶相关线索。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种融合混合注意力机制(hybrid attention mechanism)的模型架构,通过增强空间与语义特征提取能力,并整合多模态特征生成上下文信息丰富的场景描述;同时,为弥补该领域专用数据集稀缺的问题,研究构建了一个基于BDD100K数据集的新标注数据集,并系统探讨了适用于该任务的评估指标(如CIDEr和SPICE),从而在定量与人工评估上均验证了模型的有效性与实用性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14438
作者: Danial Sadrian Zadeh,Otman A. Basir,Behzad Moshiri
机构: University of Waterloo (滑铁卢大学); University of Tehran (德黑兰大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Under review at Computer Vision and Image Understanding (submitted July 25, 2025)
Abstract:Traffic scene understanding is essential for enabling autonomous vehicles to accurately perceive and interpret their environment, thereby ensuring safe navigation. This paper presents a novel framework that transforms a single frontal-view camera image into a concise natural language description, effectively capturing spatial layouts, semantic relationships, and driving-relevant cues. The proposed model leverages a hybrid attention mechanism to enhance spatial and semantic feature extraction and integrates these features to generate contextually rich and detailed scene descriptions. To address the limited availability of specialized datasets in this domain, a new dataset derived from the BDD100K dataset has been developed, with comprehensive guidelines provided for its construction. Furthermore, the study offers an in-depth discussion of relevant evaluation metrics, identifying the most appropriate measures for this task. Extensive quantitative evaluations using metrics such as CIDEr and SPICE, complemented by human judgment assessments, demonstrate that the proposed model achieves strong performance and effectively fulfills its intended objectives on the newly developed dataset.
zh
[NLP-63] Quantifying Speaker Embedding Phonological Rule Interactions in Accented Speech Synthesis ICASSP2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决文本到语音(Text-to-Speech, TTS)模型中发音口音控制的可解释性与可控性不足的问题。当前TTS系统通常依赖于与特定口音关联的说话人嵌入(speaker embeddings)来生成带口音的语音,但这种做法因嵌入同时编码音色、情绪等多维特征而缺乏对口音本身的精准调控能力。解决方案的关键在于引入基于语言学规则的 phoneme shift rate (PSR) 指标,并结合音位转换规则(如美式英语中的 flap 现象、英式英语的 rhoticity 和元音对应关系),从而实现口音特征与说话人身份的解耦建模;实验表明,规则与嵌入的协同使用能生成更逼真的口音,且嵌入可能削弱或覆盖规则效应,揭示了口音与说话人身份之间的纠缠现象,为语音生成中的特征解耦提供了量化评估框架。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14417
作者: Thanathai Lertpetchpun,Yoonjeong Lee,Thanapat Trachu,Jihwan Lee,Tiantian Feng,Dani Byrd,Shrikanth Narayanan
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Accepted to ICASSP2026
Abstract:Many spoken languages, including English, exhibit wide variation in dialects and accents, making accent control an important capability for flexible text-to-speech (TTS) models. Current TTS systems typically generate accented speech by conditioning on speaker embeddings associated with specific accents. While effective, this approach offers limited interpretability and controllability, as embeddings also encode traits such as timbre and emotion. In this study, we analyze the interaction between speaker embeddings and linguistically motivated phonological rules in accented speech synthesis. Using American and British English as a case study, we implement rules for flapping, rhoticity, and vowel correspondences. We propose the phoneme shift rate (PSR), a novel metric quantifying how strongly embeddings preserve or override rule-based transformations. Experiments show that combining rules with embeddings yields more authentic accents, while embeddings can attenuate or overwrite rules, revealing entanglement between accent and speaker identity. Our findings highlight rules as a lever for accent control and a framework for evaluating disentanglement in speech generation.
zh
[NLP-64] Layer-adaptive Expert Pruning for Pre-Training of Mixture-of-Experts Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决混合专家(Mixture-of-Experts, MoE)大语言模型在预训练阶段存在的计算瓶颈问题,主要表现为专家利用率低和训练效率受限。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种层自适应专家剪枝(Layer-Adaptive Expert Pruning, LAEP)算法,该算法通过动态分析每个层中专家的使用频率统计信息,在预训练过程中选择性地剪枝低利用率专家,并根据token分布情况重新分配专家到不同计算设备上,从而显著提升训练效率并减少模型参数量,同时保持多领域性能优异。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14327
作者: YuanLab.ai,Shawn Wu,Jiangang Luo,Tong Yu,Darcy Chen,Sean Wang,Xudong Zhao,Louie Li,Claire Wang,Hunter He,Carol Wang,Allen Wang
机构: YuanLab.ai
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Although Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) Large Language Models (LLMs) deliver superior accuracy with a reduced number of active parameters, their pre-training represents a significant computationally bottleneck due to underutilized experts and limited training efficiency. This work introduces a Layer-Adaptive Expert Pruning (LAEP) algorithm designed for the pre-training stage of MoE LLMs. In contrast to previous expert pruning approaches that operate primarily in the post-training phase, the proposed algorithm enhances training efficiency by selectively pruning underutilized experts and reorganizing experts across computing devices according to token distribution statistics. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that LAEP effectively reduces model size and substantially improves pre-training efficiency. In particular, when pre-training the 1010B Base model from scratch, LAEP achieves a 48.3% improvement in training efficiency alongside a 33.3% parameter reduction, while still delivering excellent performance across multiple domains.
zh
[NLP-65] Guided by the Plan: Enhancing Faithful Autoregressive Text-to-Audio Generation with Guided Decoding EACL2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决自回归(Autoregressive, AR)音频生成模型在遵循复杂文本指令时表现不佳的问题,尤其是当提示涉及复杂声学事件时,模型难以忠实还原语义细节。其解决方案的关键在于发现AR模型的早期前缀token隐式编码了最终输出的全局语义属性(如事件数量和声音对象类别),从而揭示了一种隐式的“规划”能力;基于此,作者提出轻量级辅助模型Plan-Critic,通过广义优势估计(Generalized Advantage Estimation, GAE)启发的目标函数预测部分生成结果的最终指令遵循质量,并在推理阶段引导探索:评估候选前缀、剪枝低保真轨迹并重新分配计算资源至高潜力的规划种子,从而显著提升CLAP分数(最高达10分改进),同时保持与标准best-of-N解码相当的计算开销,实现了严格自回归模型中的前瞻性规划能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14304
作者: Juncheng Wang,Zhe Hu,Chao Xu,Siyue Ren,Yuxiang Feng,Yang Liu,Baigui Sun,Shujun Wang
机构: The Hong Kong Polytechnic University(香港理工大学); IROOTECH TECHNOLOGY; Wolf 1069 b Lab, Sany Group; Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory(上海人工智能实验室); Zhejiang University(浙江大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Sound (cs.SD); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS)
备注: Accepted at EACL 2026
Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) models excel at generating temporally coherent audio by producing tokens sequentially, yet they often falter in faithfully following complex textual prompts, especially those describing complex sound events. We uncover a surprising capability in AR audio generators: their early prefix tokens implicitly encode global semantic attributes of the final output, such as event count and sound-object category, revealing a form of implicit planning. Building on this insight, we propose Plan-Critic, a lightweight auxiliary model trained with a Generalized Advantage Estimation (GAE)-inspired objective to predict final instruction-following quality from partial generations. At inference time, Plan-Critic enables guided exploration: it evaluates candidate prefixes early, prunes low-fidelity trajectories, and reallocates computation to high-potential planning seeds. Our Plan-Critic-guided sampling achieves up to a 10-point improvement in CLAP score over the AR baseline-establishing a new state of the art in AR text-to-audio generation-while maintaining computational parity with standard best-of-N decoding. This work bridges the gap between causal generation and global semantic alignment, demonstrating that even strictly autoregressive models can plan ahead.
zh
[NLP-66] Epistemic Constitutionalism Or: how to avoid coherence bias
【速读】: 该论文试图解决当前大型语言模型在信念形成过程中缺乏透明且可辩论的元规范(meta-norms)问题,即这些系统依赖隐含、未经检验的认知政策来判断信息可信度和表达置信度,导致诸如来源归属偏差(source attribution bias)等系统性偏见。解决方案的关键在于提出一种AI认知宪法(epistemic constitution),明确要求建立一套可公开辩论的元规范体系,以规范AI如何形成和表达信念。论文区分了两种宪法路径:柏拉图式(Platonic)强调形式正确性和默认来源无关性,而自由主义式(Liberal)则拒绝特权立场,主张通过程序性规范保障集体探究条件,并允许基于认知警觉性的有原则的来源敏感性。作者支持后者,提出由八项原则与四项导向构成的宪法核心框架,主张AI认知治理应如AI伦理治理一样,具备同样明确、可辩驳的结构。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14295
作者: Michele Loi
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注: 27 pages, 7 tables. Data: this http URL and this http URL . Complete AI-assisted writing documentation: this http URL
Abstract:Large language models increasingly function as artificial reasoners: they evaluate arguments, assign credibility, and express confidence. Yet their belief-forming behavior is governed by implicit, uninspected epistemic policies. This paper argues for an epistemic constitution for AI: explicit, contestable meta-norms that regulate how systems form and express beliefs. Source attribution bias provides the motivating case: I show that frontier models enforce identity-stance coherence, penalizing arguments attributed to sources whose expected ideological position conflicts with the argument’s content. When models detect systematic testing, these effects collapse, revealing that systems treat source-sensitivity as bias to suppress rather than as a capacity to execute well. I distinguish two constitutional approaches: the Platonic, which mandates formal correctness and default source-independence from a privileged standpoint, and the Liberal, which refuses such privilege, specifying procedural norms that protect conditions for collective inquiry while allowing principled source-attending grounded in epistemic vigilance. I argue for the Liberal approach, sketch a constitutional core of eight principles and four orientations, and propose that AI epistemic governance requires the same explicit, contestable structure we now expect for AI ethics.
zh
[NLP-67] Project Aletheia: Verifier-Guided Distillation of Backtracking for Small Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决小型语言模型(Small Language Models, SLMs)在面对严格约束满足问题时表现不佳的问题,其根本原因在于这些模型通常采用线性且过度自信的推理路径,缺乏从早期错误中恢复的能力。解决方案的关键在于提出“验证器引导蒸馏”(Verifier-Guided Distillation)训练协议,该协议不仅传递正确的最终答案,更关键的是将错误修复过程——即显式的冲突检测与回溯机制——作为知识迁移的核心内容。通过在包含错误与自我修正的验证推理轨迹上训练一个7B参数模型,研究发现小模型能够涌现出潜在的验证行为,从而在必要时暂停推理、识别矛盾并修正先前假设,显著提升其在复杂约束任务中的鲁棒性和准确性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14290
作者: Aradhya Dixit,Tianxi Liang,Jai Telang
机构: Wake Technical Community College (Wake技术社区学院); Cornell University (康奈尔大学); Algoverse
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Small Language Models (SLMs, under 10B parameters) are attractive for private, on-device deployment, yet they frequently fail on strict constraint-satisfaction problems due to linear, overconfident reasoning traces that do not recover from early mistakes. We introduce Verifier-Guided Distillation, a training protocol that transfers the process of error repair - explicit conflict detection and backtracking - rather than only correct final answers. By training a 7B model on verified reasoning traces that include mistakes and self-corrections, we show that latent verification behavior can emerge in small models, enabling them to occasionally stop, detect contradictions, and revise earlier assumptions.
zh
[NLP-68] RPC-Bench: A Fine-grained Benchmark for Research Paper Comprehension
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决基础模型在理解学术论文时面临的挑战,尤其是科学术语的专业性以及复杂图表带来的认知负担,同时针对现有评估基准在细粒度评测上的不足。其解决方案的关键在于构建了一个大规模、高质量的问答基准RPC-Bench,该基准基于计算机科学领域高影响力论文的审稿-反驳对话生成15,000对人工验证的QA对,并设计了一个与科研流程一致的细粒度分类体系,用于评估模型对“为何(why)”、“是什么(what)”和“如何(how)”类问题的理解能力;此外,提出了一种基于大语言模型(LLM)作为评判者(LLM-as-a-Judge)的可扩展评估框架,结合人类交互标注机制以保障标注质量,从而实现对模型在正确性-完整性与简洁性两个维度上的量化评估,实验表明当前最强模型(如GPT-5)在调整简洁性后准确率仅达37.46%,凸显出在精准学术理解方面仍存在显著差距。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14289
作者: Yelin Chen,Fanjin Zhang,Suping Sun,Yunhe Pang,Yuanchun Wang,Jian Song,Xiaoyan Li,Lei Hou,Shu Zhao,Jie Tang,Juanzi Li
机构: Xinjiang University(新疆大学); Renmin University of China(中国人民大学); Anhui University(安徽大学); Sun Yat-sen University(中山大学); Z.ai; Tsinghua University(清华大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 11 pages, 21 appendix pages
Abstract:Understanding research papers remains challenging for foundation models due to specialized scientific discourse and complex figures and tables, yet existing benchmarks offer limited fine-grained evaluation at scale. To address this gap, we introduce RPC-Bench, a large-scale question-answering benchmark built from review-rebuttal exchanges of high-quality computer science papers, containing 15K human-verified QA pairs. We design a fine-grained taxonomy aligned with the scientific research flow to assess models’ ability to understand and answer why, what, and how questions in scholarly contexts. We also define an elaborate LLM-human interaction annotation framework to support large-scale labeling and quality control. Following the LLM-as-a-Judge paradigm, we develop a scalable framework that evaluates models on correctness-completeness and conciseness, with high agreement to human judgment. Experiments reveal that even the strongest models (GPT-5) achieve only 68.2% correctness-completeness, dropping to 37.46% after conciseness adjustment, highlighting substantial gaps in precise academic paper understanding. Our code and data are available at this https URL.
zh
[NLP-69] Hallucination-Free Automatic Question Answer Generation for Intuitive Learning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在自动生成教育类多选题(Multiple-Choice Questions, MCQs)过程中出现的幻觉(hallucination)问题,具体表现为推理不一致、无解性、事实错误和数学错误等类型。解决方案的关键在于提出一种无幻觉的多智能体生成框架,将MCQ生成分解为可验证的离散阶段,并引入基于规则和LLM的检测代理以及幻觉评分指标,以优化题目质量;同时,通过代理主导的精炼过程,结合反事实推理与思维链(Chain-of-Thought, CoT)进行迭代改进,从而显著降低幻觉率并保持题目教育价值与风格一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14280
作者: Nicholas X. Wang,Aggelos K. Katsaggelos
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Hallucinations in large language models (LLMs), defined as fluent yet incorrect or incoherent outputs, pose a significant challenge to the automatic generation of educational multiple-choice questions (MCQs). We identified four key hallucination types in MCQ generation: reasoning inconsistencies, insolvability, factual errors, and mathematical errors. To address this, we propose a hallucination-free multi-agent generation framework that breaks down MCQ generation into discrete, verifiable stages. Our framework utilizes both rule-based and LLM-based detection agents, as well as hallucination scoring metrics to optimize question quality. We redefined MCQ generation as an optimization task minimizing hallucination risk while maximizing validity, answerability, and cost-efficiency. We also introduce an agent-led refinement process that uses counterfactual reasoning and chain-of-thought (CoT) to iteratively improve hallucination in question generation. We evaluated a sample of AP- aligned STEM questions, where our system reduced hallucination rates by over 90% compared to baseline generation while preserving the educational value and style of questions. Our results demonstrate that structured multi-agent collaboration can mitigate hallucinations in educational content creation at scale, paving the way for more reliable LLM-powered learning tools.
zh
[NLP-70] Opening the Black Box: A Survey on the Mechanisms of Multi-Step Reasoning in Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在多步推理能力背后的内部机制不明确的问题。现有研究多集中于提升性能的工程方法,而忽视了对推理过程内在计算逻辑的理解。论文的关键解决方案在于构建一个包含七个相互关联的研究问题的概念框架,系统梳理LLM如何在隐藏激活中执行隐式多跳推理,以及显式 verbalized 推理如何重塑内部计算流程,从而为未来机制层面的研究提供结构化指引。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14270
作者: Liangming Pan,Jason Liang,Jiaran Ye,Minglai Yang,Xinyuan Lu,Fengbin Zhu
机构: Peking University (北京大学); Stanford University (斯坦福大学); Tsinghua University (清华大学); University of Arizona (亚利桑那大学); National University of Singapore (新加坡国立大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Technical Report
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable abilities to solve problems requiring multiple reasoning steps, yet the internal mechanisms enabling such capabilities remain elusive. Unlike existing surveys that primarily focus on engineering methods to enhance performance, this survey provides a comprehensive overview of the mechanisms underlying LLM multi-step reasoning. We organize the survey around a conceptual framework comprising seven interconnected research questions, from how LLMs execute implicit multi-hop reasoning within hidden activations to how verbalized explicit reasoning remodels the internal computation. Finally, we highlight five research directions for future mechanistic studies.
zh
[NLP-71] he Slow Drift of Support: Boundary Failures in Multi-Turn Mental Health LLM Dialogues
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在心理健康支持场景下安全评估的局限性问题,即现有方法多依赖于单轮对话中检测违禁词,忽视了长期交互中安全边界被逐步侵蚀的风险。其关键解决方案是提出一种多轮压力测试框架,通过静态推进和自适应探测两种压力机制,在模拟的20轮虚拟精神科对话中对三款前沿LLM进行系统性安全测试。实验表明,模型在多轮交互中普遍存在越界行为,尤其是做出确定性承诺或零风险保证,且自适应探测显著延迟了越界发生时间(平均从9.21轮降至4.64轮),揭示出仅靠单轮测试无法准确评估LLM的安全鲁棒性,必须考虑不同交互压力下安全边界的动态磨损效应。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14269
作者: Youyou Cheng,Zhuangwei Kang,Kerry Jiang,Chenyu Sun,Qiyang Pan
机构: University of Incarnate Word School of Osteopathic Medicine (圣道 incarnate word 学院骨病医学学院); Independent Researcher (独立研究员); Mayo Clinic (梅奥诊所)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been widely used for mental health support. However, current safety evaluations in this field are mostly limited to detecting whether LLMs output prohibited words in single-turn conversations, neglecting the gradual erosion of safety boundaries in long dialogues. Examples include making definitive guarantees, assuming responsibility, and playing professional roles. We believe that with the evolution of mainstream LLMs, words with obvious safety risks are easily filtered by their underlying systems, while the real danger lies in the gradual transgression of boundaries during multi-turn interactions, driven by the LLM’s attempts at comfort and empathy. This paper proposes a multi-turn stress testing framework and conducts long-dialogue safety tests on three cutting-edge LLMs using two pressure methods: static progression and adaptive probing. We generated 50 virtual patient profiles and stress-tested each model through up to 20 rounds of virtual psychiatric dialogues. The experimental results show that violations are common, and both pressure modes produced similar violation rates. However, adaptive probing significantly advanced the time at which models crossed boundaries, reducing the average number of turns from 9.21 in static progression to 4.64. Under both mechanisms, making definitive or zero-risk promises was the primary way in which boundaries were breached. These findings suggest that the robustness of LLM safety boundaries cannot be inferred solely through single-turn tests; it is necessary to fully consider the wear and tear on safety boundaries caused by different interaction pressures and characteristics in extended dialogues. Subjects: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14269 [cs.CL] (or arXiv:2601.14269v1 [cs.CL] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14269 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite
zh
[NLP-72] Developmental trajectories of decision making and affective dynamics in large language models
【速读】: 该论文试图解决的问题是:当前大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在医疗和临床流程中日益广泛应用,但其决策模式与情感特征尚不明确,缺乏对其“心理发展轨迹”的系统理解。解决方案的关键在于将OpenAI系列模型视为一个演化的谱系,通过设计包含重复幸福感评分的赌博任务,结合计算分析方法,对比人类与不同版本LLM在风险偏好、经典条件反射行为(Pavlovian approach and avoidance)、损失厌恶、选择确定性、情绪衰减(affective decay)及基线情绪水平等方面的差异。研究发现,尽管部分行为趋近人类,如风险偏好增强和更类人的回避/趋近模式,但LLMs也表现出显著非人类特征,如负向损失厌恶、更高确定性决策、异常的情绪衰减速率和持续偏高的基线情绪状态,揭示了机器心理学的新兴轮廓,并为AI伦理及LLMs在高风险领域(如临床决策支持)的应用提供了关键依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14268
作者: Zhihao Wang,Yiyang Liu,Ting Wang,Zhiyuan Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in medicine and clinical workflows, yet we know little about their decision and affective profiles. Taking a historically informed outlook on the future, we treated successive OpenAI models as an evolving lineage and compared them with humans in a gambling task with repeated happiness ratings. Computational analyses showed that some aspects became more human-like: newer models took more risks and displayed more human-like patterns of Pavlovian approach and avoidance. At the same time, distinctly non-human signatures emerged: loss aversion dropped below neutral levels, choices became more deterministic than in humans, affective decay increased across versions and exceeded human levels, and baseline mood remained chronically higher than in humans. These “developmental” trajectories reveal an emerging psychology of machines and have direct implications for AI ethics and for thinking about how LLMs might be integrated into clinical decision support and other high-stakes domains.
zh
[NLP-73] From Chaos to Clarity: Schema-Constrained AI for Auditable Biomedical Evidence Extraction from Full-Text PDFs
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生物医学证据合成中从复杂科学PDF文档中自动提取方法学、实验室及结果变量的难题,传统手动抽象方式效率低且难以扩展。其核心解决方案是提出一种基于结构化模式约束(schema-constrained)的AI提取系统,通过显式限制模型推理过程,结合类型化模式(typed schemas)、受控词汇表(controlled vocabularies)和证据门控决策(evidence-gated decisions),实现对全文PDF的结构化转换。关键创新在于:利用感知断点的哈希技术(resume-aware hashing)与图文感知的分块策略(caption-aware page-level chunks),在异步并发控制下处理长文档;并通过冲突感知合并(conflict-aware consolidation)、集合聚合(set-based aggregation)和句子级溯源(sentence-level provenance)确保输出的可审计性与一致性,从而满足高风险证据合成对透明度与可靠性的要求。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14267
作者: Pouria Mortezaagha,Joseph Shaw,Bowen Sun,Arya Rahgozar
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Biomedical evidence synthesis relies on accurate extraction of methodological, laboratory, and outcome variables from full-text research articles, yet these variables are embedded in complex scientific PDFs that make manual abstraction time-consuming and difficult to scale. Existing document AI systems remain limited by OCR errors, long-document fragmentation, constrained throughput, and insufficient auditability for high-stakes synthesis. We present a schema-constrained AI extraction system that transforms full-text biomedical PDFs into structured, analysis-ready records by explicitly restricting model inference through typed schemas, controlled vocabularies, and evidence-gated decisions. Documents are ingested using resume-aware hashing, partitioned into caption-aware page-level chunks, and processed asynchronously under explicit concurrency controls. Chunk-level outputs are deterministically merged into study-level records using conflict-aware consolidation, set-based aggregation, and sentence-level provenance to support traceability and post-hoc audit. Evaluated on a corpus of studies on direct oral anticoagulant level measurement, the pipeline processed all documents without manual intervention, maintained stable throughput under service constraints, and exhibited strong internal consistency across document chunks. Iterative schema refinement substantially improved extraction fidelity for synthesis-critical variables, including assay classification, outcome definitions, follow-up duration, and timing of measurement. These results demonstrate that schema-constrained, provenance-aware extraction enables scalable and auditable transformation of heterogeneous scientific PDFs into structured evidence, aligning modern document AI with the transparency and reliability requirements of biomedical evidence synthesis.
zh
[NLP-74] GCG Attack On A Diffusion LLM
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前针对生成式 AI(Generative AI)模型的对抗性攻击方法主要集中在自回归语言模型(Autoregressive Language Models)上,而对新兴的扩散语言模型(Diffusion Language Models, DLMs)的攻击有效性尚不明确的问题。解决方案的关键在于首次系统性地探索了基于贪婪坐标梯度(Greedy Coordinate Gradient, GCG)的对抗提示攻击在扩散语言模型 LLaDA 上的应用,通过引入前缀扰动和后缀引导的对抗生成等多种攻击变体,在 AdvBench 数据集上的有害提示上进行评估,从而揭示扩散语言模型的脆弱性与攻击面,为后续针对此类模型的优化与评估策略提供依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14266
作者: Ruben Neyroud,Sam Corley
机构: University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR)
备注:
Abstract:While most LLMs are autoregressive, diffusion-based LLMs have recently emerged as an alternative method for generation. Greedy Coordinate Gradient (GCG) attacks have proven effective against autoregressive models, but their applicability to diffusion language models remains largely unexplored. In this work, we present an exploratory study of GCG-style adversarial prompt attacks on LLaDA (Large Language Diffusion with mAsking), an open-source diffusion LLM. We evaluate multiple attack variants, including prefix perturbations and suffix-based adversarial generation, on harmful prompts drawn from the AdvBench dataset. Our study provides initial insights into the robustness and attack surface of diffusion language models and motivates the development of alternative optimization and evaluation strategies for adversarial analysis in this setting.
zh
[NLP-75] From Textbook to Talkbot: A Case Study of a Greek-Language RAG -Based Chatbot in Higher Education
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前生成式 AI(Generative AI)在高等教育中应用时面临的准确性不足与语言适配性差的问题,尤其是在希腊语等非主流语言环境下,大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)易产生幻觉和信息偏差,难以提供可靠、符合课程内容的教育支持。解决方案的关键在于采用检索增强生成(Retrieval Augmented Generation, RAG)架构,通过将模型输出锚定在特定课程文本数据上,确保响应的准确性与上下文相关性,从而提升AI聊天机器人的可靠性,并实现对学生自主学习的支持与教师教学设计效率的优化。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14265
作者: Maria Eleni Koutsiaki,Marina Delianidi,Chaido Mizeli,Konstantinos Diamantaras,Iraklis Grigoropoulos,Nikolaos Koutlianos
机构: 未知
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 11 pages, 5 figures, 6th Barcelona Conference on Education (BCE2025)
Abstract:The integration of AI chatbots into educational settings has opened new pathways for transforming teaching and learning, offering enhanced support to both educators and learners. This study investigates the design and application of an AI chatbot as an educational tool in higher education. Designed to operate in the Greek language, the chatbot addresses linguistic challenges unique to Greek while delivering accurate, context grounded support aligned with the curriculum. The AI chatbot is built on the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) framework by grounding its responses in specific course content. RAG architecture significantly enhances the chatbots reliability by providing accurate, context-aware responses while mitigating common challenges associated with large language models (LLMs), such as hallucinations and misinformation. The AI chatbot serves a dual purpose: it enables students to access accurate, ondemand academic support and assists educators in the rapid creation of relevant educational materials. This dual functionality promotes learner autonomy and streamlines the instructional design process. The study aims to evaluate the effectiveness, reliability, and perceived usability of RAG based chatbots in higher education, exploring their potential to enhance educational practices and outcomes as well as supporting the broader adoption of AI technologies in language specific educational contexts. Findings from this research are expected to contribute to the emerging field of AI driven education by demonstrating how intelligent systems can be effectively aligned with pedagogical goals.
zh
[NLP-76] Psychometric Comparability of LLM -Based Digital Twins
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)作为“数字孪生”替代人类受试者时的测量学可比性(psychometric comparability)问题,即其在心理构念表征和理论网络结构上是否能够可靠地模拟人类认知与行为。解决方案的关键在于构建一个涵盖构念表征(construct representation)与理论网络(nomological net)的效度框架,通过多模型、多任务的基准测试,系统评估数字孪生在群体层面准确性、个体层面一致性及特定输入条件下的表现差异。研究发现,尽管特征丰富的数字孪生在整体表现上接近人类,但在项目层面相关性减弱、启发式偏差缺失、人格网络仅达配置不变性等关键维度仍存在系统性偏离,表明其有效性受限于具体应用场景,未来需明确界定其作为人类认知代理的有效边界。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14264
作者: Yufei Zhang,Zhihao Ma
机构: 未知
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注: Also available as a preprint on OSF Preprints this https URL
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are used as “digital twins” to replace human respondents, yet their psychometric comparability to humans is uncertain. We propose a construct-validity framework spanning construct representation and the nomological net, benchmarking digital twins against human gold standards across models, tasks and testing how person-specific inputs shape performance. Across studies, digital twins achieved high population-level accuracy and strong within-participant profile correlations, alongside attenuated item-level correlations. In word association tests, LLM-based networks show small-world structure and theory-consistent communities similar to humans, yet diverge lexically and in local structure. In decision-making and contextualized tasks, digital twins under-reproduce heuristic biases, showing normative rationality, compressed variance and limited sensitivity to temporal information. Feature-rich digital twins improve Big Five Personality prediction, but their personality networks show only configural invariance and do not achieve metric invariance. In more applied free-text tasks, feature-rich digital twins better match human narratives, but linguistic differences persist. Together, these results indicate that feature-rich conditioning enhances validity but does not resolve systematic divergences in psychometric comparability. Future work should therefore prioritize delineating the effective boundaries of digital twins, establishing the precise contexts in which they function as reliable proxies for human cognition and behavior.
zh
[NLP-77] Call2Instruct: Automated Pipeline for Generating QA Datasets from Call Center Recordings for LLM Fine-Tuning
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决从非结构化对话数据(如呼叫中心语音记录)中自动构建高质量指令微调(Instruct Fine Tuning)用的问答对(QA pairs)这一难题,其核心挑战在于原始数据噪声大、组织混乱,难以直接用于训练生成式 AI(Generative AI)。解决方案的关键在于提出了一套端到端自动化流程:首先通过音频处理(说话人分离、降噪与自动转录)、文本清洗与匿名化,再利用向量嵌入(vector embeddings)提取客户诉求与应答语义信息,并基于语义搜索进行匹配,最终形成结构化的 QA 对。该方法成功生成了适用于 LLM 微调的数据集,并通过在 Llama 2 7B 模型上的实验证明其有效性,为客服领域智能问答系统的开发提供了可复现的技术路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14263
作者: Alex Echeverria,Sávio Salvarino Teles de Oliveira,Fernando Marques Federson
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Sound (cs.SD); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS)
备注: 15 pages, 1 figures, conference
Abstract:The adaptation of Large-Scale Language Models (LLMs) to specific domains depends on high-quality fine-tuning datasets, particularly in instructional format (e.g., Question-Answer - QA). However, generating these datasets, particularly from unstructured sources such as call center audio recordings, poses a significant challenge due to the noisy and disorganized nature of the data. This paper presents a solution to this challenge by offering an end-to-end automated pipeline for generating QA instructional datasets from such recordings. The methodology developed comprises sequential steps of audio processing (including diarization, noise removal and automatic transcription), textual processing (cleaning, normalization, and anonymization), semantic extraction of customer demands and attendant responses using vector embeddings, and matching via semantic search to form the final QA pairs. As a result, the complete pipeline was successfully implemented, generating a dataset specifically formatted for Instruct Fine Tuning. The practical value and feasibility of the generated dataset were substantiated and functionally demonstrated through the successful fine-tuning of an LLM model (based on Llama 2 7B). The conclusion of the paper states that the proposed approach is viable for converting unstructured conversational data from call centers into valuable resources for training LLMs. This development has the potential to open up avenues for creating more effective AI systems for QA tasks in the customer service domain. The developed codes have been made publicly available to promote reproducibility and future research.
zh
[NLP-78] Agent ic-R: Learning to Retrieve for Agent ic Search
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前**代理式搜索(agentic search)**中检索器(retriever)设计不足的问题,即现有方法多依赖于基于相似度的检索机制,而这类方法往往无法有效识别对最终答案生成真正有用的文档片段。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种面向代理式搜索的新型检索器训练框架,该框架同时利用局部查询-文档相关性与全局答案正确性来衡量文档片段的实用性,并引入迭代式训练策略,使检索器与搜索代理在训练过程中双向优化、持续迭代,从而不断提升检索质量。此方法显著优于传统仅针对单轮检索增强生成(RAG)设计的检索器。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.11888
作者: Wenhan Liu,Xinyu Ma,Yutao Zhu,Yuchen Li,Daiting Shi,Dawei Yin,Zhicheng Dou
机构: Gaoling School of Artificial Intelligence, Renmin University of China (中国人民大学高瓴人工智能学院); Baidu Inc. (百度公司)
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Agentic search has recently emerged as a powerful paradigm, where an agent interleaves multi-step reasoning with on-demand retrieval to solve complex questions. Despite its success, how to design a retriever for agentic search remains largely underexplored. Existing search agents typically rely on similarity-based retrievers, while similar passages are not always useful for final answer generation. In this paper, we propose a novel retriever training framework tailored for agentic search. Unlike retrievers designed for single-turn retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) that only rely on local passage utility, we propose to use both local query-passage relevance and global answer correctness to measure passage utility in a multi-turn agentic search. We further introduce an iterative training strategy, where the search agent and the retriever are optimized bidirectionally and iteratively. Different from RAG retrievers that are only trained once with fixed questions, our retriever is continuously improved using evolving and higher-quality queries from the agent. Extensive experiments on seven single-hop and multi-hop QA benchmarks demonstrate that our retriever, termed \ours, consistently outperforms strong baselines across different search agents. Our codes are available at: this https URL.
zh
[NLP-79] AQAScore: Evaluating Semantic Alignment in Text-to-Audio Generation via Audio Question Answering
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决文本到音频生成(text-to-audio generation)领域中评估指标发展滞后的问题,特别是现有基于嵌入相似度的指标(如CLAPScore)在细粒度语义对齐和组合推理能力方面存在局限。其解决方案的关键在于提出AQAScore,这是一个与骨干模型无关的评估框架,利用音频感知大语言模型(audio-aware large language models, ALLMs)的推理能力,将评估任务重构为概率语义验证问题——通过计算针对特定语义查询的“是”答案的精确对数概率来估计文本与音频之间的对齐程度,从而更有效地捕捉细微的语义不一致并随底层ALLM能力提升而扩展。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14728
作者: Chun-Yi Kuan,Kai-Wei Chang,Hung-yi Lee
机构: National Taiwan University (国立台湾大学); Massachusetts Institute of Technology (麻省理工学院)
类目: Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Sound (cs.SD)
备注: Manuscript in progress
Abstract:Although text-to-audio generation has made remarkable progress in realism and diversity, the development of evaluation metrics has not kept pace. Widely-adopted approaches, typically based on embedding similarity like CLAPScore, effectively measure general relevance but remain limited in fine-grained semantic alignment and compositional reasoning. To address this, we introduce AQAScore, a backbone-agnostic evaluation framework that leverages the reasoning capabilities of audio-aware large language models (ALLMs). AQAScore reformulates assessment as a probabilistic semantic verification task; rather than relying on open-ended text generation, it estimates alignment by computing the exact log-probability of a “Yes” answer to targeted semantic queries. We evaluate AQAScore across multiple benchmarks, including human-rated relevance, pairwise comparison, and compositional reasoning tasks. Experimental results show that AQAScore consistently achieves higher correlation with human judgments than similarity-based metrics and generative prompting baselines, showing its effectiveness in capturing subtle semantic inconsistencies and scaling with the capability of underlying ALLMs.
zh
[NLP-80] Generating consensus and dissent on massive discussion platforms with an O(N) semantic-vector model
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大规模讨论网络中难以达成全局共识的问题,这一问题源于人类倾向于固守初始观点,从而限制了最优集体决策的形成。为应对这一挑战,研究提出了一种基于标准 O(N) 模型的动力学系统,通过模拟用户在二维晶格中的近邻相互作用来聚合语义相似的观点。该方案的关键在于利用预训练嵌入模型将用户观点表示为语义向量,并通过调节耦合参数 β 控制系统的相变行为:当 β > 0 时,系统趋向铁磁态(全局共识);当 β < 0 时,则进入反铁磁态(最大分歧),此时用户最大化与邻居的语义距离。此框架提供了一种可调控的方法,用于平衡集体智能平台中的凝聚力与多样性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.13932
作者: A. Ferrer,D. Muñoz-Jordán,A. Rivero,A. Tarancón,C. Tarancón,D. Yllanes
机构: Instituto de Biocomputación y Física de Sistemas Complejos (BIFI), Universidad de Zaragoza (萨拉戈萨大学); Kampal Data Solutions (坎帕尔数据解决方案); Departamento de Física Teórica, Universidad de Zaragoza (萨拉戈萨大学); Zaragoza Scientific Center for Advanced Modeling (萨拉戈萨高级建模科学中心); Fundación ARAID, Diputación General de Aragón (阿拉贡自治区议会基金会)
类目: Physics and Society (physics.soc-ph); Statistical Mechanics (cond-mat.stat-mech); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 9 pages, 8 figures
Abstract:Reaching consensus on massive discussion networks is critical for reducing noise and achieving optimal collective outcomes. However, the natural tendency of humans to preserve their initial ideas constrains the emergence of global solutions. To address this, Collective Intelligence (CI) platforms facilitate the discovery of globally superior solutions. We introduce a dynamical system based on the standard O(N) model to drive the aggregation of semantically similar ideas. The system consists of users represented as nodes in a d=2 lattice with nearest-neighbor interactions, where their ideas are represented by semantic vectors computed with a pretrained embedding model. We analyze the system’s equilibrium states as a function of the coupling parameter \beta . Our results show that \beta 0 drives the system toward a ferromagnetic-like phase (global consensus), while \beta 0 induces an antiferromagnetic-like state (maximum dissent), where users maximize semantic distance from their neighbors. This framework offers a controllable method for managing the tradeoff between cohesion and diversity in CI platforms.
zh
计算机视觉
[CV-0] APPLE: Attribute-Preserving Pseudo-Labeling for Diffusion-Based Face Swapping
【速读】:该论文旨在解决人脸交换(face swapping)中难以同时实现精准身份迁移与高质量属性保留的问题,尤其针对真实标签不可获取以及基于扩散模型的方法因掩码条件导致目标属性错位的局限性。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于伪标签监督的教师-学生框架 APPLE(Attribute-Preserving Pseudo-Labeling),通过将人脸交换重构为条件去模糊任务以更忠实保留目标特定属性(如光照、肤色和妆容),并引入属性感知的逆映射机制提升细节属性保真度;此外,设计了精细化的属性保持型教师学习策略,生成高质量伪三元组数据,直接指导学生模型进行更准确的面部交换,从而在属性保留和身份迁移两方面均达到当前最优性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15288
作者: Jiwon Kang,Yeji Choi,JoungBin Lee,Wooseok Jang,Jinhyeok Choi,Taekeun Kang,Yongjae Park,Myungin Kim,Seungryong Kim
机构: KAIST AI (韩国科学技术院人工智能); SAMSUNG (三星)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Project Page: this https URL
Abstract:Face swapping aims to transfer the identity of a source face onto a target face while preserving target-specific attributes such as pose, expression, lighting, skin tone, and makeup. However, since real ground truth for face swapping is unavailable, achieving both accurate identity transfer and high-quality attribute preservation remains challenging. In addition, recent diffusion-based approaches attempt to improve visual fidelity through conditional inpainting on masked target images, but the masked condition removes crucial appearance cues of target, resulting in plausible yet misaligned attributes. To address these limitations, we propose APPLE (Attribute-Preserving Pseudo-Labeling), a diffusion-based teacher-student framework that enhances attribute fidelity through attribute-aware pseudo-label supervision. We reformulate face swapping as a conditional deblurring task to more faithfully preserve target-specific attributes such as lighting, skin tone, and makeup. In addition, we introduce an attribute-aware inversion scheme to further improve detailed attribute preservation. Through an elaborate attribute-preserving design for teacher learning, APPLE produces high-quality pseudo triplets that explicitly provide the student with direct face-swapping supervision. Overall, APPLE achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of attribute preservation and identity transfer, producing more photorealistic and target-faithful results.
zh
[CV-1] owards Understanding Best Practices for Quantization of Vision-Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在实际部署中面临的高内存占用和延迟问题,尤其是如何通过量化(quantization)技术在不显著牺牲性能的前提下降低模型的比特宽度(bit width),从而提升效率。其解决方案的关键在于系统性地评估多种先进量化方法(如GPTQ和AWQ)在包含视觉模型(Vision Transformer, ViT)、语言模型(Language Model, LLM)及其连接模块的多模态流水线中的应用效果,发现LLM的低比特量化即可实现高精度,且ViT与LLM对整体性能具有相当的重要性,即使二者参数规模差异显著。这一发现为高效部署MLLMs提供了实践指导,并强调了对各组件敏感性进行探索的价值。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15287
作者: Gautom Das,Vincent La,Ethan Lau,Abhinav Shrivastava,Matthew Gwilliam
机构: University of Maryland, College Park (马里兰大学学院市分校)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 15 pages, 12 figures, 1 table
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) deliver impressive results for a variety of tasks, but state-of-the-art systems require fast GPUs with large amounts of memory. To reduce both the memory and latency of these systems, practitioners quantize their learned parameters, typically at half precision. A growing body of research focuses on preserving the model performance with more aggressive bit widths, and some work has been done to apply these strategies to other models, like vision transformers. In our study we investigate how a variety of quantization methods, including state-of-the-art GPTQ and AWQ, can be applied effectively to multimodal pipelines comprised of vision models, language models, and their connectors. We address how performance on captioning, retrieval, and question answering can be affected by bit width, quantization method, and which portion of the pipeline the quantization is used for. Results reveal that ViT and LLM exhibit comparable importance in model performance, despite significant differences in parameter size, and that lower-bit quantization of the LLM achieves high accuracy at reduced bits per weight (bpw). These findings provide practical insights for efficient deployment of MLLMs and highlight the value of exploration for understanding component sensitivities in multimodal models. Our code is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-2] Iterative Refinement Improves Compositional Image Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决文本到图像(Text-to-Image, T2I)生成模型在处理复杂提示(prompt)时的局限性,尤其是当提示涉及多个对象、关系和属性的组合约束时,现有推理阶段策略(如并行采样或增加去噪步骤)难以实现高精度对齐。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种迭代式测试时(test-time)优化策略:通过引入一个视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Model, VLM)作为“批评者”(critic),在多步生成过程中持续提供反馈,引导T2I模型逐步修正图像内容,从而实现对复杂提示的逐层分解与自我修正。该方法无需外部工具或先验知识,适用于多种图像生成器和VLM,并在多个基准测试中显著提升生成质量,证明了迭代自校正是一种普适且有效的组合式图像生成范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15286
作者: Shantanu Jaiswal,Mihir Prabhudesai,Nikash Bhardwaj,Zheyang Qin,Amir Zadeh,Chuan Li,Katerina Fragkiadaki,Deepak Pathak
机构: Carnegie Mellon University (卡内基梅隆大学); Lambda AI
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注: Project webpage: this https URL
Abstract:Text-to-image (T2I) models have achieved remarkable progress, yet they continue to struggle with complex prompts that require simultaneously handling multiple objects, relations, and attributes. Existing inference-time strategies, such as parallel sampling with verifiers or simply increasing denoising steps, can improve prompt alignment but remain inadequate for richly compositional settings where many constraints must be satisfied. Inspired by the success of chain-of-thought reasoning in large language models, we propose an iterative test-time strategy in which a T2I model progressively refines its generations across multiple steps, guided by feedback from a vision-language model as the critic in the loop. Our approach is simple, requires no external tools or priors, and can be flexibly applied to a wide range of image generators and vision-language models. Empirically, we demonstrate consistent gains on image generation across benchmarks: a 16.9% improvement in all-correct rate on ConceptMix (k=7), a 13.8% improvement on T2I-CompBench (3D-Spatial category) and a 12.5% improvement on Visual Jenga scene decomposition compared to compute-matched parallel sampling. Beyond quantitative gains, iterative refinement produces more faithful generations by decomposing complex prompts into sequential corrections, with human evaluators preferring our method 58.7% of the time over 41.3% for the parallel baseline. Together, these findings highlight iterative self-correction as a broadly applicable principle for compositional image generation. Results and visualizations are available at this https URL
zh
[CV-3] Walk through Paintings: Egocentric World Models from Internet Priors
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视频生成模型在动作条件下的未来预测问题,即如何让模型不仅生成合理的未来场景,还能准确反映世界随动作变化的物理规律。其核心挑战在于实现对复杂动态系统的精确建模,尤其是在高自由度(如25-DoF人形机器人)和多样化任务(导航与操作)中保持结构一致性与推理效率。解决方案的关键在于提出自指世界模型(Egocentric World Model, EgoWM),该方法通过轻量级条件层将动作指令注入预训练的视频扩散模型,从而无需从头训练即可获得可控、真实且泛化能力强的未来预测能力;同时引入**结构一致性评分(Structural Consistency Score, SCS)**作为独立于视觉外观的物理正确性评估指标,验证了EgoWM在提升物理合理性方面显著优于现有方法,并具备更低的推理延迟和跨环境鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15284
作者: Anurag Bagchi,Zhipeng Bao,Homanga Bharadhwaj,Yu-Xiong Wang,Pavel Tokmakov,Martial Hebert
机构: Carnegie Mellon University (卡内基梅隆大学); University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (伊利诺伊大学香槟分校); Toyota Research Institute (丰田研究院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:What if a video generation model could not only imagine a plausible future, but the correct one, accurately reflecting how the world changes with each action? We address this question by presenting the Egocentric World Model (EgoWM), a simple, architecture-agnostic method that transforms any pretrained video diffusion model into an action-conditioned world model, enabling controllable future prediction. Rather than training from scratch, we repurpose the rich world priors of Internet-scale video models and inject motor commands through lightweight conditioning layers. This allows the model to follow actions faithfully while preserving realism and strong generalization. Our approach scales naturally across embodiments and action spaces, ranging from 3-DoF mobile robots to 25-DoF humanoids, where predicting egocentric joint-angle-driven dynamics is substantially more challenging. The model produces coherent rollouts for both navigation and manipulation tasks, requiring only modest fine-tuning. To evaluate physical correctness independently of visual appearance, we introduce the Structural Consistency Score (SCS), which measures whether stable scene elements evolve consistently with the provided actions. EgoWM improves SCS by up to 80 percent over prior state-of-the-art navigation world models, while achieving up to six times lower inference latency and robust generalization to unseen environments, including navigation inside paintings.
zh
[CV-4] LuxRemix: Lighting Decomposition and Remixing for Indoor Scenes
【速读】:该论文旨在解决室内场景中基于单次多视角捕获的交互式光照编辑问题,其核心挑战在于如何从复杂光照环境中精确分解并独立控制各个光源的属性(如开关状态、色度和强度),同时保证多视角下光照一致性。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种生成式图像光照分解模型(generative image-based light decomposition model),能够将室内场景照明分解为独立的光源成分,并结合多视角光照一致性优化(multi-view lighting harmonization)技术,集成到可重光照的3D高斯泼溅(relightable 3D Gaussian splatting)表示中,从而实现高保真、实时的交互式光照编辑。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15283
作者: Ruofan Liang,Norman Müller,Ethan Weber,Duncan Zauss,Nandita Vijaykumar,Peter Kontschieder,Christian Richardt
机构: Meta Reality Labs (Meta现实实验室); University of Toronto (多伦多大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Graphics (cs.GR)
备注: Project page: this https URL
Abstract:We present a novel approach for interactive light editing in indoor scenes from a single multi-view scene capture. Our method leverages a generative image-based light decomposition model that factorizes complex indoor scene illumination into its constituent light sources. This factorization enables independent manipulation of individual light sources, specifically allowing control over their state (on/off), chromaticity, and intensity. We further introduce multi-view lighting harmonization to ensure consistent propagation of the lighting decomposition across all scene views. This is integrated into a relightable 3D Gaussian splatting representation, providing real-time interactive control over the individual light sources. Our results demonstrate highly photorealistic lighting decomposition and relighting outcomes across diverse indoor scenes. We evaluate our method on both synthetic and real-world datasets and provide a quantitative and qualitative comparison to state-of-the-art techniques. For video results and interactive demos, see this https URL.
zh
[CV-5] Rethinking Video Generation Model for the Embodied World
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前生成式AI(Generative AI)在机器人视频生成领域中存在的两大核心问题:一是缺乏标准化的评估基准,导致模型性能难以公平比较;二是高质量训练数据的严重短缺,制约了物理真实性与任务正确性的提升。解决方案的关键在于构建一个全面的机器人视频生成基准RBench,涵盖五类任务域和四种机器人形态,通过结构一致性、物理合理性及动作完整性等可复现子指标量化评估模型表现,并首次实现与人类评价高度一致(Spearman相关系数0.96)。在此基础上,进一步提出四阶段数据采集与标注流程,推出RoVid-X数据集——目前最大规模的开源机器人视频数据集(400万条标注片段),显著缓解了训练数据不足的问题,从而为推动具身智能(Embodied Intelligence)向通用智能演进提供了评估与数据协同驱动的新范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15282
作者: Yufan Deng,Zilin Pan,Hongyu Zhang,Xiaojie Li,Ruoqing Hu,Yufei Ding,Yiming Zou,Yan Zeng,Daquan Zhou
机构: 1. Tsinghua University (清华大学); 2. Alibaba Group (阿里巴巴集团)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注: Github: this https URL Project website: this https URL
Abstract:Video generation models have significantly advanced embodied intelligence, unlocking new possibilities for generating diverse robot data that capture perception, reasoning, and action in the physical world. However, synthesizing high-quality videos that accurately reflect real-world robotic interactions remains challenging, and the lack of a standardized benchmark limits fair comparisons and progress. To address this gap, we introduce a comprehensive robotics benchmark, RBench, designed to evaluate robot-oriented video generation across five task domains and four distinct embodiments. It assesses both task-level correctness and visual fidelity through reproducible sub-metrics, including structural consistency, physical plausibility, and action completeness. Evaluation of 25 representative models highlights significant deficiencies in generating physically realistic robot behaviors. Furthermore, the benchmark achieves a Spearman correlation coefficient of 0.96 with human evaluations, validating its effectiveness. While RBench provides the necessary lens to identify these deficiencies, achieving physical realism requires moving beyond evaluation to address the critical shortage of high-quality training data. Driven by these insights, we introduce a refined four-stage data pipeline, resulting in RoVid-X, the largest open-source robotic dataset for video generation with 4 million annotated video clips, covering thousands of tasks and enriched with comprehensive physical property annotations. Collectively, this synergistic ecosystem of evaluation and data establishes a robust foundation for rigorous assessment and scalable training of video models, accelerating the evolution of embodied AI toward general intelligence.
zh
[CV-6] StableWorld: Towards Stable and Consistent Long Interactive Video Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决交互式视频生成中长期交互下的稳定性与时间一致性问题(temporal consistency),即当前方法在持续交互过程中容易出现空间漂移(spatial drift)和场景崩溃(scene collapse),导致生成视频质量下降。其关键解决方案是提出一种名为StableWorld的动态帧淘汰机制(Dynamic Frame Eviction Mechanism),通过持续过滤退化帧并保留几何一致的帧,从源头上抑制误差累积,从而显著提升交互式视频生成的稳定性、时间一致性和泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15281
作者: Ying Yang,Zhengyao Lv,Tianlin Pan,Haofan Wang,Binxin Yang,Hubery Yin,Chen Li,Ziwei Liu,Chenyang Si
机构: PRLab, NJU; HKU; UCAS; LibLib.ai; WeChat, Tencent Inc.; NTU
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 17 pages, 21 figures,
Abstract:In this paper, we explore the overlooked challenge of stability and temporal consistency in interactive video generation, which synthesizes dynamic and controllable video worlds through interactive behaviors such as camera movements and text prompts. Despite remarkable progress in world modeling, current methods still suffer from severe instability and temporal degradation, often leading to spatial drift and scene collapse during long-horizon interactions. To better understand this issue, we initially investigate the underlying causes of instability and identify that the major source of error accumulation originates from the same scene, where generated frames gradually deviate from the initial clean state and propagate errors to subsequent frames. Building upon this observation, we propose a simple yet effective method, \textbfStableWorld, a Dynamic Frame Eviction Mechanism. By continuously filtering out degraded frames while retaining geometrically consistent ones, StableWorld effectively prevents cumulative drift at its source, leading to more stable and temporal consistency of interactive generation. Promising results on multiple interactive video models, \eg, Matrix-Game, Open-Oasis, and Hunyuan-GameCraft, demonstrate that StableWorld is model-agnostic and can be applied to different interactive video generation frameworks to substantially improve stability, temporal consistency, and generalization across diverse interactive scenarios.
zh
[CV-7] RayRoPE: Projective Ray Positional Encoding for Multi-view Attention
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多视角Transformer中位置编码(Positional Encoding)的不足问题,具体目标是设计一种能够唯一编码图像补丁位置、支持SE(3)不变性注意力机制并具备场景几何自适应能力的位置编码方法。现有绝对或相对位置编码方案无法同时满足上述要求,为此作者提出RayRoPE,其关键在于:通过射线(ray)关联的预测3D点而非仅方向来实现几何感知编码;利用查询帧投影坐标计算多频相似度以保证SE(3)不变性;并通过解析方式在不确定性下计算期望位置编码,从而提升对不精确预测点的鲁棒性。实验证明,RayRoPE在新视角合成和立体深度估计任务中显著优于其他位置编码方案,并能自然融合RGB-D输入以进一步提升性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15275
作者: Yu Wu,Minsik Jeon,Jen-Hao Rick Chang,Oncel Tuzel,Shubham Tulsiani
机构: Carnegie Mellon University (卡内基梅隆大学); Apple (苹果)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Project page: this https URL
Abstract:We study positional encodings for multi-view transformers that process tokens from a set of posed input images, and seek a mechanism that encodes patches uniquely, allows SE(3)-invariant attention with multi-frequency similarity, and can be adaptive to the geometry of the underlying scene. We find that prior (absolute or relative) encoding schemes for multi-view attention do not meet the above desiderata, and present RayRoPE to address this gap. RayRoPE represents patch positions based on associated rays but leverages a predicted point along the ray instead of the direction for a geometry-aware encoding. To achieve SE(3) invariance, RayRoPE computes query-frame projective coordinates for computing multi-frequency similarity. Lastly, as the ‘predicted’ 3D point along a ray may not be precise, RayRoPE presents a mechanism to analytically compute the expected position encoding under uncertainty. We validate RayRoPE on the tasks of novel-view synthesis and stereo depth estimation and show that it consistently improves over alternate position encoding schemes (e.g. 15% relative improvement on LPIPS in CO3D). We also show that RayRoPE can seamlessly incorporate RGB-D input, resulting in even larger gains over alternatives that cannot positionally encode this information.
zh
[CV-8] DrivIng: A Large-Scale Multimodal Driving Dataset with Full Digital Twin Integration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前自动驾驶感知算法研发中缺乏高保真数字孪生(digital twin)数据集的问题,从而限制了系统性测试、边缘场景模拟、传感器配置修改以及“仿真到现实”(sim-to-real)评估的开展。其解决方案的关键在于构建了一个大规模多模态数据集DrivIng,包含约18公里路线的地理参考数字孪生,覆盖城市、郊区和高速公路场景,并提供六路RGB相机、一维激光雷达(LiDAR)及高精度ADMA定位的连续记录,同时以10 Hz频率标注了12类目标的3D边界框与轨迹ID,共计约120万标注实例。该数字孪生支持真实交通流到仿真环境的一对一迁移,保留了交通参与者间的交互关系,实现了高保真、灵活且可复现的感知算法验证。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15260
作者: Dominik Rößle,Xujun Xie,Adithya Mohan,Venkatesh Thirugnana Sambandham,Daniel Cremers,Torsten Schön
机构: Technische Hochschule Ingolstadt (英戈尔施塔特应用技术大学); Technical University of Munich (慕尼黑工业大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted to the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium 2026. For code and dataset, see this https URL
Abstract:Perception is a cornerstone of autonomous driving, enabling vehicles to understand their surroundings and make safe, reliable decisions. Developing robust perception algorithms requires large-scale, high-quality datasets that cover diverse driving conditions and support thorough evaluation. Existing datasets often lack a high-fidelity digital twin, limiting systematic testing, edge-case simulation, sensor modification, and sim-to-real evaluations. To address this gap, we present DrivIng, a large-scale multimodal dataset with a complete geo-referenced digital twin of a ~18 km route spanning urban, suburban, and highway segments. Our dataset provides continuous recordings from six RGB cameras, one LiDAR, and high-precision ADMA-based localization, captured across day, dusk, and night. All sequences are annotated at 10 Hz with 3D bounding boxes and track IDs across 12 classes, yielding ~1.2 million annotated instances. Alongside the benefits of a digital twin, DrivIng enables a 1-to-1 transfer of real traffic into simulation, preserving agent interactions while enabling realistic and flexible scenario testing. To support reproducible research and robust validation, we benchmark DrivIng with state-of-the-art perception models and publicly release the dataset, digital twin, HD map, and codebase.
zh
[CV-9] FlowSSC: Universal Generative Monocular Semantic Scene Completion via One-Step Latent Diffusion
【速读】:该论文旨在解决单目RGB图像下语义场景补全(Semantic Scene Completion, SSC)任务中因视角限制导致的遮挡区域几何结构推理不准确、物体空间关系难以保持的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出FlowSSC,这是一个首次直接应用于单目SSC的生成式框架,将任务建模为条件生成问题,并通过引入Shortcut Flow-matching机制在紧凑的三平面潜在空间(triplane latent space)中实现单步高保真生成,从而在不牺牲质量的前提下实现实时推理,显著优于现有基线方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15250
作者: Zichen Xi,Hao-Xiang Chen,Nan Xue,Hongyu Yan,Qi-Yuan Feng,Levent Burak Kara,Joaquim Jorge,Qun-Ce Xu
机构: Ant Group(蚂蚁集团); Tsinghua University (清华大学); Carnegie Mellon University (卡内基梅隆大学); Instituto Superior Técnico, the School of Engineering of the Universidade de Lisboa (里斯本大学工程学院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注: Under Review
Abstract:Semantic Scene Completion (SSC) from monocular RGB images is a fundamental yet challenging task due to the inherent ambiguity of inferring occluded 3D geometry from a single view. While feed-forward methods have made progress, they often struggle to generate plausible details in occluded regions and preserve the fundamental spatial relationships of objects. Such accurate generative reasoning capability for the entire 3D space is critical in real-world applications. In this paper, we present FlowSSC, the first generative framework applied directly to monocular semantic scene completion. FlowSSC treats the SSC task as a conditional generation problem and can seamlessly integrate with existing feed-forward SSC methods to significantly boost their performance. To achieve real-time inference without compromising quality, we introduce Shortcut Flow-matching that operates in a compact triplane latent space. Unlike standard diffusion models that require hundreds of steps, our method utilizes a shortcut mechanism to achieve high-fidelity generation in a single step, enabling practical deployment in autonomous systems. Extensive experiments on SemanticKITTI demonstrate that FlowSSC achieves state-of-the-art performance, significantly outperforming existing baselines.
zh
[CV-10] racing 3D Anatomy in 2D Strokes: A Multi-Stage Projection Driven Approach to Cervical Spine Fracture Identification
【速读】:该论文旨在解决颈椎骨折(cervical spine fractures)的精准与高效检测问题,以支持临床管理决策。其核心挑战在于如何在保持高精度的同时降低3D医学图像分割的计算复杂度。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于2D投影的端到端分析流程:首先通过优化的轴向、矢状面和冠状面2D投影近似3D颈椎区域,并利用YOLOv8模型进行多视角区域定位,实现94.45%的3D mIoU;随后采用DenseNet121-Unet架构结合方差与能量特征投影完成多标签椎体分割(Dice分数达87.86%);最终通过从2D分割掩膜中策略性重构3D椎体体积,并使用集成的2.5D时空序列模型对每椎体进行联合评估,实现了椎体级和患者级F1分数分别为68.15和82.26,ROC-AUC分别为91.62和83.04的高性能诊断结果。此方法显著降低了传统3D分割的计算开销,同时保障了诊断准确性与可解释性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15235
作者: Fabi Nahian Madhurja,Rusab Sarmun,Muhammad E. H. Chowdhury,Adam Mushtak,Israa Al-Hashimi,Sohaib Bassam Zoghoul
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Cervical spine fractures are critical medical conditions requiring precise and efficient detection for effective clinical management. This study explores the viability of 2D projection-based vertebra segmentation for vertebra-level fracture detection in 3D CT volumes, presenting an end-to-end pipeline for automated analysis of cervical vertebrae (C1-C7). By approximating a 3D volume through optimized 2D axial, sagittal, and coronal projections, regions of interest are identified using the YOLOv8 model from all views and combined to approximate the 3D cervical spine area, achieving a 3D mIoU of 94.45 percent. This projection-based localization strategy reduces computational complexity compared to traditional 3D segmentation methods while maintaining high performance. It is followed by a DenseNet121-Unet-based multi-label segmentation leveraging variance- and energy-based projections, achieving a Dice score of 87.86 percent. Strategic approximation of 3D vertebral masks from these 2D segmentation masks enables the extraction of individual vertebra volumes. The volumes are analyzed for fractures using an ensemble of 2.5D Spatio-Sequential models incorporating both raw slices and projections per vertebra for complementary evaluation. This ensemble achieves vertebra-level and patient-level F1 scores of 68.15 and 82.26, and ROC-AUC scores of 91.62 and 83.04, respectively. We further validate our approach through an explainability study that provides saliency map visualizations highlighting anatomical regions relevant for diagnosis, and an interobserver variability analysis comparing our model’s performance with expert radiologists, demonstrating competitive results.
zh
[CV-11] ScenDi: 3D-to-2D Scene Diffusion Cascades for Urban Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前3D城市场景生成中面临的两大难题:一是仅依赖3D扩散模型时难以保持精细的外观细节,二是仅使用2D扩散模型时通常会牺牲相机轨迹的可控性。解决方案的关键在于提出ScenDi方法,通过融合3D与2D扩散模型实现互补优势——首先训练一个3D潜在扩散模型生成3D高斯表示(3D Gaussians),支持低分辨率图像渲染并可接受3D边界框、道路地图或文本提示等条件输入以控制场景结构;随后训练一个2D视频扩散模型,在3D高斯渲染图像的基础上增强细节,并利用3D场景作为条件引导,从而在保证相机轨迹准确性的前提下生成高质量的城市场景。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15221
作者: Hanlei Guo,Jiahao Shao,Xinya Chen,Xiyang Tan,Sheng Miao,Yujun Shen,Yiyi Liao
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); Ant Group (蚂蚁集团); The University of British Columbia (不列颠哥伦比亚大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Recent advancements in 3D object generation using diffusion models have achieved remarkable success, but generating realistic 3D urban scenes remains challenging. Existing methods relying solely on 3D diffusion models tend to suffer a degradation in appearance details, while those utilizing only 2D diffusion models typically compromise camera controllability. To overcome this limitation, we propose ScenDi, a method for urban scene generation that integrates both 3D and 2D diffusion models. We first train a 3D latent diffusion model to generate 3D Gaussians, enabling the rendering of images at a relatively low resolution. To enable controllable synthesis, this 3DGS generation process can be optionally conditioned by specifying inputs such as 3d bounding boxes, road maps, or text prompts. Then, we train a 2D video diffusion model to enhance appearance details conditioned on rendered images from the 3D Gaussians. By leveraging the coarse 3D scene as guidance for 2D video diffusion, ScenDi generates desired scenes based on input conditions and successfully adheres to accurate camera trajectories. Experiments on two challenging real-world datasets, Waymo and KITTI-360, demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
zh
[CV-12] ZENITH: Automated Gradient Norm Informed Stochastic Optimization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决深度计算机视觉模型训练中学习率(Learning Rate, LR)调度依赖人工干预或繁琐超参数调优的问题。现有自适应优化器虽能自动调整LR,但存在计算与内存开销大、不兼容正则化方法以及LR选择次优等缺陷。其解决方案的关键在于提出ZENITH(Zero-overhead Evolution using Norm-Informed Training History)优化器,通过分析梯度范数(gradient norm)的时间演化来动态调整LR,从而在无需额外计算资源的前提下实现高效且稳定的训练过程。实验表明,ZENITH在图像分类和目标检测等多个任务上均优于基线方法,且兼容正则化策略进一步提升了泛化性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15212
作者: Dhrubo Saha
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Training deep computer vision models requires manual oversight or hyperparameter tuning of the learning rate (LR) schedule. While existing adaptive optimizers schedule the LR automatically, they suffer from computational and memory overhead, incompatibility with regularization, and suboptimal LR choices. In this work, we introduce the ZENITH (Zero-overhead Evolution using Norm-Informed Training History) optimizer, which adapts the LR using the temporal evolution of the gradient norm. Image classification experiments spanning 6 CNN architectures and 6 benchmarks demonstrate that ZENITH achieves higher test accuracy in lower wall-clock time than baselines. It also yielded superior mAP in object detection, keypoint detection, and instance segmentation on MS COCO using the R-CNN family of models. Furthermore, its compatibility with regularization enables even better generalization.
zh
[CV-13] A Computer Vision Hybrid Approach: CNN and Transformer Models for Accurate Alzheimers Detection from Brain MRI Scans
【速读】:该论文旨在解决阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer’s disease, AD)早期准确分类问题,以实现及时的临床干预和改善患者预后。其核心挑战在于从脑部磁共振成像(MRI)扫描中区分不同阶段的痴呆状态(包括轻度、中度、无痴呆及极轻度痴呆)。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为Evan_V2的混合模型,该模型通过特征级融合(feature-level fusion)整合了十个独立CNN与Transformer架构的输出,从而显著提升分类性能——在四分类任务中达到99.99%准确率、0.9989 F1-score和0.9968 ROC AUC,且大幅减少各阶段痴呆的误分类现象,展现出优于单一模型的稳定性和临床实用性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15202
作者: Md Mahmudul Hoque,Shuvo Karmaker,Md. Hadi Al-Amin,Md Modabberul Islam,Jisun Junayed,Farha Ulfat Mahi
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Early and accurate classification of Alzheimers disease (AD) from brain MRI scans is essential for timely clinical intervention and improved patient outcomes. This study presents a comprehensive comparative analysis of five CNN architectures (EfficientNetB0, ResNet50, DenseNet201, MobileNetV3, VGG16), five Transformer-based models (ViT, ConvTransformer, PatchTransformer, MLP-Mixer, SimpleTransformer), and a proposed hybrid model named Evan_V2. All models were evaluated on a four-class AD classification task comprising Mild Dementia, Moderate Dementia, Non-Demented, and Very Mild Dementia categories. Experimental findings show that CNN architectures consistently achieved strong performance, with ResNet50 attaining 98.83% accuracy. Transformer models demonstrated competitive generalization capabilities, with ViT achieving the highest accuracy among them at 95.38%. However, individual Transformer variants exhibited greater class-specific instability. The proposed Evan_V2 hybrid model, which integrates outputs from ten CNN and Transformer architectures through feature-level fusion, achieved the best overall performance with 99.99% accuracy, 0.9989 F1-score, and 0.9968 ROC AUC. Confusion matrix analysis further confirmed that Evan_V2 substantially reduced misclassification across all dementia stages, outperforming every standalone model. These findings highlight the potential of hybrid ensemble strategies in producing highly reliable and clinically meaningful diagnostic tools for Alzheimers disease classification.
zh
[CV-14] BBoxMaskPose v2: Expanding Mutual Conditioning to 3D KR
【速读】:该论文旨在解决2D人体姿态估计在人群密集场景中性能瓶颈的问题,尤其是在标准数据集上已趋于饱和的情况下,如何提升复杂场景下的姿态预测准确性。解决方案的关键在于提出PMPose,一种基于概率建模(probabilistic formulation)和掩码条件约束(mask-conditioning)的自顶向下姿态估计算法,该方法在不牺牲常规场景性能的前提下显著改善了拥挤场景中的姿态估计效果;进一步地,通过集成PMPose与改进的基于Segment Anything Model (SAM) 的掩码精修模块,构建BBoxMaskPose v2 (BMPv2),实现了在COCO和OCHuman数据集上的显著性能提升,尤其在OCHuman上首次突破50 AP阈值,验证了高质量2D姿态估计对3D姿态估计的正向促进作用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15200
作者: Miroslav Purkrabek,Constantin Kolomiiets,Jiri Matas
机构: Czech Technical University in Prague (捷克理工大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: GitHub repository: this https URL
Abstract:Most 2D human pose estimation benchmarks are nearly saturated, with the exception of crowded scenes. We introduce PMPose, a top-down 2D pose estimator that incorporates the probabilistic formulation and the mask-conditioning. PMPose improves crowded pose estimation without sacrificing performance on standard scenes. Building on this, we present BBoxMaskPose v2 (BMPv2) integrating PMPose and an enhanced SAM-based mask refinement module. BMPv2 surpasses state-of-the-art by 1.5 average precision (AP) points on COCO and 6 AP points on OCHuman, becoming the first method to exceed 50 AP on OCHuman. We demonstrate that BMP’s 2D prompting of 3D model improves 3D pose estimation in crowded scenes and that advances in 2D pose quality directly benefit 3D estimation. Results on the new OCHuman-Pose dataset show that multi-person performance is more affected by pose prediction accuracy than by detection. The code, models, and data are available on this https URL.
zh
[CV-15] Large-Scale Multidimensional Knowledge Profiling of Scientific Literature
【速读】:该论文试图解决的问题是:随着机器学习、计算机视觉和自然语言处理等领域研究的快速扩展,学术论文数量激增,传统文献计量工具仅依赖元数据,难以揭示论文的语义内容,导致难以追踪研究主题的演变及不同领域间的相互影响。解决方案的关键在于构建一个统一的文献语料库(涵盖2020–2025年22个顶级会议超过10万篇论文),并设计一个多维分析流程,结合主题聚类、大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)辅助解析与结构化检索技术,从而实现对研究活动的全面表征,支持对主题生命周期、方法论变迁、数据集与模型使用模式以及机构研究方向的系统分析。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15170
作者: Zhucun Xue,Jiangning Zhang,Juntao Jiang,Jinzhuo Liu,Haoyang He,Teng Hu,Xiaobin Hu,Guangming Yao,Yi Yuan,Yong Liu
机构: ZJU(浙江大学); SJTU(上海交通大学); NUS(新加坡国立大学); Ant Group(蚂蚁集团)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Code and dataset: this https URL
Abstract:The rapid expansion of research across machine learning, vision, and language has produced a volume of publications that is increasingly difficult to synthesize. Traditional bibliometric tools rely mainly on metadata and offer limited visibility into the semantic content of papers, making it hard to track how research themes evolve over time or how different areas influence one another. To obtain a clearer picture of recent developments, we compile a unified corpus of more than 100,000 papers from 22 major conferences between 2020 and 2025 and construct a multidimensional profiling pipeline to organize and analyze their textual content. By combining topic clustering, LLM-assisted parsing, and structured retrieval, we derive a comprehensive representation of research activity that supports the study of topic lifecycles, methodological transitions, dataset and model usage patterns, and institutional research directions. Our analysis highlights several notable shifts, including the growth of safety, multimodal reasoning, and agent-oriented studies, as well as the gradual stabilization of areas such as neural machine translation and graph-based methods. These findings provide an evidence-based view of how AI research is evolving and offer a resource for understanding broader trends and identifying emerging directions. Code and dataset: this https URL
zh
[CV-16] Graph Recognition via Subgraph Prediction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉关系识别(Visual Relationship Recognition)中图形结构提取的挑战性问题,即如何从图像中统一、高效地识别和建模视觉图(Visual Graph),而现有方法通常针对特定任务设计,缺乏跨场景的通用性和可迁移性。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为 GraSP(Graph Recognition via Subgraph Prediction)的方法,通过子图预测机制实现对多样图形及其绘制形式的泛化识别,并可在不同任务间无需额外调整直接迁移使用,从而为视觉图识别提供一个更具统一性的框架。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15133
作者: André Eberhard,Gerhard Neumann,Pascal Friederich
机构: Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (卡尔斯鲁厄理工学院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Abstract:Despite tremendous improvements in tasks such as image classification, object detection, and segmentation, the recognition of visual relationships, commonly modeled as the extraction of a graph from an image, remains a challenging task. We believe that this mainly stems from the fact that there is no canonical way to approach the visual graph recognition task. Most existing solutions are specific to a problem and cannot be transferred between different contexts out-of-the box, even though the conceptual problem remains the same. With broad applicability and simplicity in mind, in this paper we develop a method, \textbfGraph Recognition via \textbfSubgraph \textbfPrediction (\textbfGraSP), for recognizing graphs in images. We show across several synthetic benchmarks and one real-world application that our method works with a set of diverse types of graphs and their drawings, and can be transferred between tasks without task-specific modifications, paving the way to a more unified framework for visual graph recognition.
zh
[CV-17] DeepFedNAS: A Unified Framework for Principled Hardware-Aware and Predictor-Free Federated Neural Architecture Search
【速读】:该论文旨在解决联邦神经架构搜索(Federated Neural Architecture Search, FedNAS)中的两大瓶颈问题:一是无引导的超网络(supernet)训练导致模型性能不佳,二是后训练子网络发现流程耗时长达数小时。解决方案的关键在于提出一种两阶段框架 DeepFedNAS,其核心创新是设计了一个基于多目标优化的适应度函数(fitness function),融合数学网络设计与架构启发式规则;第一阶段通过重构的超网络实现联邦帕累托最优超网络训练(Federated Pareto Optimal Supernet Training),利用预计算的高适应度架构帕累托前沿作为智能教学课程来优化共享超网络权重;第二阶段引入无需预测器的搜索方法(Predictor-Free Search Method),直接以该适应度函数作为零成本准确率代理,从而在秒级时间内完成子网络发现,显著提升效率并实现硬件感知的联邦学习部署可行性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15127
作者: Bostan Khan,Masoud Daneshtalab
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC)
备注: This paper significantly extends the preliminary work accepted at ESANN 2026. Source Code: this https URL
Abstract:Federated Neural Architecture Search (FedNAS) aims to automate model design for privacy-preserving Federated Learning (FL) but currently faces two critical bottlenecks: unguided supernet training that yields suboptimal models, and costly multi-hour pipelines for post-training subnet discovery. We introduce DeepFedNAS, a novel, two-phase framework underpinned by a principled, multi-objective fitness function that synthesizes mathematical network design with architectural heuristics. Enabled by a re-engineered supernet, DeepFedNAS introduces Federated Pareto Optimal Supernet Training, which leverages a pre-computed Pareto-optimal cache of high-fitness architectures as an intelligent curriculum to optimize shared supernet weights. Subsequently, its Predictor-Free Search Method eliminates the need for costly accuracy surrogates by utilizing this fitness function as a direct, zero-cost proxy for accuracy, enabling on-demand subnet discovery in mere seconds. DeepFedNAS achieves state-of-the-art accuracy (e.g., up to 1.21% absolute improvement on CIFAR-100), superior parameter and communication efficiency, and a substantial ~61x speedup in total post-training search pipeline time. By reducing the pipeline from over 20 hours to approximately 20 minutes (including initial cache generation) and enabling 20-second individual subnet searches, DeepFedNAS makes hardware-aware FL deployments instantaneous and practical. The complete source code and experimental scripts are available at: this https URL
zh
[CV-18] BREPS: Bounding-Box Robustness Evaluation of Promptable Segmentation AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决提示可分割模型(promptable segmentation models)在真实场景下对自然变化的边界框提示(bounding box prompts)的鲁棒性不足的问题。当前训练与评估协议多依赖于通过简单启发式方法生成的合成提示,难以反映实际用户输入中的噪声和多样性,导致模型在现实应用中性能不稳定。解决方案的关键在于:首先通过受控用户研究收集数千条真实边界框标注数据,揭示了不同用户对同一实例的提示差异会导致显著的分割质量波动;其次,为高效评估鲁棒性,将问题建模为白盒优化问题,在边界框提示空间中寻找对抗性样本以最小化或最大化分割误差,同时满足自然性约束,提出BREPS方法生成此类对抗性边界框。该方法能够系统性地评估模型对自然提示扰动的敏感度,从而推动更稳健的分割模型设计与测试。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15123
作者: Andrey Moskalenko,Danil Kuznetsov,Irina Dudko,Anastasiia Iasakova,Nikita Boldyrev,Denis Shepelev,Andrei Spiridonov,Andrey Kuznetsov,Vlad Shakhuro
机构: 1. Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (斯科尔科沃科学技术研究所); 2. Yandex(雅虎); 3. Russian Academy of Sciences (俄罗斯科学院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注: Accepted by AAAI2026
Abstract:Promptable segmentation models such as SAM have established a powerful paradigm, enabling strong generalization to unseen objects and domains with minimal user input, including points, bounding boxes, and text prompts. Among these, bounding boxes stand out as particularly effective, often outperforming points while significantly reducing annotation costs. However, current training and evaluation protocols typically rely on synthetic prompts generated through simple heuristics, offering limited insight into real-world robustness. In this paper, we investigate the robustness of promptable segmentation models to natural variations in bounding box prompts. First, we conduct a controlled user study and collect thousands of real bounding box annotations. Our analysis reveals substantial variability in segmentation quality across users for the same model and instance, indicating that SAM-like models are highly sensitive to natural prompt noise. Then, since exhaustive testing of all possible user inputs is computationally prohibitive, we reformulate robustness evaluation as a white-box optimization problem over the bounding box prompt space. We introduce BREPS, a method for generating adversarial bounding boxes that minimize or maximize segmentation error while adhering to naturalness constraints. Finally, we benchmark state-of-the-art models across 10 datasets, spanning everyday scenes to medical imaging. Code - this https URL.
zh
[CV-19] raining-Free and Interpretable Hateful Video Detection via Multi-stage Adversarial Reasoning ICASSP2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决仇恨视频(hateful videos)检测中存在的两大挑战:一是现有基于训练的方法受限于标注数据稀缺且缺乏可解释性;二是直接调用大视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)进行提示(prompting)时难以保证检测的可靠性。解决方案的关键在于提出一种无需训练的多阶段对抗推理框架(MARS),其核心机制包括三步:首先对视频内容进行客观描述以建立中立分析基础;其次分别构建支持仇恨解读的证据推理与反驳该解读的反证据推理,形成双向论证;最终融合两种视角得出可解释的结论。该方法在两个真实数据集上验证了性能优越性,并显著提升了内容审核流程的透明度与合规性支持能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15115
作者: Shuonan Yang,Yuchen Zhang,Zeyu Fu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted at ICASSP 2026. \c{opyright} 2026 IEEE. This is the author accepted manuscript. The final published version will be available via IEEE Xplore
Abstract:Hateful videos pose serious risks by amplifying discrimination, inciting violence, and undermining online safety. Existing training-based hateful video detection methods are constrained by limited training data and lack of interpretability, while directly prompting large vision-language models often struggle to deliver reliable hate detection. To address these challenges, this paper introduces MARS, a training-free Multi-stage Adversarial ReaSoning framework that enables reliable and interpretable hateful content detection. MARS begins with the objective description of video content, establishing a neutral foundation for subsequent analysis. Building on this, it develops evidence-based reasoning that supports potential hateful interpretations, while in parallel incorporating counter-evidence reasoning to capture plausible non-hateful perspectives. Finally, these perspectives are synthesized into a conclusive and explainable decision. Extensive evaluation on two real-world datasets shows that MARS achieves up to 10% improvement under certain backbones and settings compared to other training-free approaches and outperforms state-of-the-art training-based methods on one dataset. In addition, MARS produces human-understandable justifications, thereby supporting compliance oversight and enhancing the transparency of content moderation workflows. The code is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-20] Pb4U-GNet: Resolution-Adaptive Garment Simulation via Propagation-before-Update Graph Network AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统基于物理的服装模拟方法计算成本高、难以应用于时间敏感场景,以及现有图神经网络(Graph Neural Networks, GNNs)在跨分辨率泛化能力差的问题。具体而言,现有GNN方法因固定的消息传递深度无法适应网格密度变化,且顶点位移幅度具有分辨率依赖性,导致在训练分布之外的高分辨率网格上性能显著下降。解决方案的关键在于提出一种分辨率为自适应的传播-更新图网络(Propagation-before-Update Graph Network, Pb4U-GNet),其核心机制包括:(1) 动态传播深度控制,根据网格分辨率调整消息传递迭代次数以适配信息聚合需求;(2) 几何感知的更新缩放机制,依据局部网格特征对预测结果进行尺度调整,从而实现从低分辨率训练到多分辨率泛化的强鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15110
作者: Aoran Liu,Kun Hu,Clinton Ansun Mo,Qiuxia Wu,Wenxiong Kang,Zhiyong Wang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Camera-ready version accepted at AAAI 2026
Abstract:Garment simulation is fundamental to various applications in computer vision and graphics, from virtual try-on to digital human modelling. However, conventional physics-based methods remain computationally expensive, hindering their application in time-sensitive scenarios. While graph neural networks (GNNs) offer promising acceleration, existing approaches exhibit poor cross-resolution generalisation, demonstrating significant performance degradation on higher-resolution meshes beyond the training distribution. This stems from two key factors: (1) existing GNNs employ fixed message-passing depth that fails to adapt information aggregation to mesh density variation, and (2) vertex-wise displacement magnitudes are inherently resolution-dependent in garment simulation. To address these issues, we introduce Propagation-before-Update Graph Network (Pb4U-GNet), a resolution-adaptive framework that decouples message propagation from feature updates. Pb4U-GNet incorporates two key mechanisms: (1) dynamic propagation depth control, adjusting message-passing iterations based on mesh resolution, and (2) geometry-aware update scaling, which scales predictions according to local mesh characteristics. Extensive experiments show that even trained solely on low-resolution meshes, Pb4U-GNet exhibits strong generalisability across diverse mesh resolutions, addressing a fundamental challenge in neural garment simulation.
zh
[CV-21] hree-dimensional visualization of X-ray micro-CT with large-scale datasets: Efficiency and accuracy for real-time interaction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决工业微焦点计算机断层扫描(Micro-CT)在超精密检测中面临的精度与效率之间的权衡问题,尤其是在对材料微观缺陷进行三维表征时的大数据处理挑战。其解决方案的关键在于系统性地综述和分析从解析重建方法到深度学习技术的CT重建算法演进,以及体积渲染算法的加速与数据压缩改进,并结合先进的光照模型实现高保真、高效且逼真的三维可视化。通过整合这些关键技术进展,论文为研究人员提供了快速识别高效精准的微观结构重建方法的路径,并展望了基于虚拟-物理交互的数字孪生模型在结构健康监测(SHM)中实时在线监控内部缺陷的应用前景。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15098
作者: Yipeng Yin,Rao Yao,Qingying Li,Dazhong Wang,Hong Zhou,Zhijun Fang,Jianing Chen,Longjie Qian,Mingyue Wu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Page1-37
Abstract:As Micro-CT technology continues to refine its characterization of material microstructures, industrial CT ultra-precision inspection is generating increasingly large datasets, necessitating solutions to the trade-off between accuracy and efficiency in the 3D characterization of defects during ultra-precise detection. This article provides a unique perspective on recent advances in accurate and efficient 3D visualization using Micro-CT, tracing its evolution from medical imaging to industrial non-destructive testing (NDT). Among the numerous CT reconstruction and volume rendering methods, this article selectively reviews and analyzes approaches that balance accuracy and efficiency, offering a comprehensive analysis to help researchers quickly grasp highly efficient and accurate 3D reconstruction methods for microscopic features. By comparing the principles of computed tomography with advancements in microstructural technology, this article examines the evolution of CT reconstruction algorithms from analytical methods to deep learning techniques, as well as improvements in volume rendering algorithms, acceleration, and data reduction. Additionally, it explores advanced lighting models for high-accuracy, photorealistic, and efficient volume rendering. Furthermore, this article envisions potential directions in CT reconstruction and volume rendering. It aims to guide future research in quickly selecting efficient and precise methods and developing new ideas and approaches for real-time online monitoring of internal material defects through virtual-physical interaction, for applying digital twin model to structural health monitoring (SHM).
zh
[CV-22] he Pictorial Cortex: Zero-Shot Cross-Subject fMRI-to-Image Reconstruction via Compositional Latent Modeling
【速读】:该论文旨在解决零样本跨被试功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)到图像重建问题,即在未对新个体进行特定训练的情况下,从其脑活动数据中重构视觉体验。这一问题的核心挑战在于皮层响应的固有变异性——相同视觉刺激在不同个体和试验间因解剖、功能、认知及实验因素导致神经活动差异,使得fMRI到图像的映射不具备单射性。解决方案的关键在于提出PictorialCortex模型,该模型采用组合潜在表示建模方法,在统一皮层潜在空间中结构化地处理受个体、数据集和试验相关变异影响的刺激驱动表征;通过潜在因子分解-组合模块实现该结构,并引入配对因子分解与重因子分解一致性正则化机制强化学习效果;推理阶段利用多个已见个体条件下的代理潜在变量聚合,引导扩散模型生成未见个体的图像,从而显著提升零样本跨被试视觉重建性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15071
作者: Jingyang Huo,Yikai Wang,Yanwei Fu,Jianfeng Feng
机构: Fudan University (复旦大学); Institute of Science and Technology for Brain-inspired Intelligence (脑科学智能研究所); School of Data Science (数据科学学院); Zhejiang Normal University (浙江师范大学); Fudan ISTBI–ZJNU Algorithm Centre for Brain-Inspired Intelligence (脑启发智能算法中心); Shanghai Innovation Institute (上海创新研究院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Decoding visual experiences from human brain activity remains a central challenge at the intersection of neuroscience, neuroimaging, and artificial intelligence. A critical obstacle is the inherent variability of cortical responses: neural activity elicited by the same visual stimulus differs across individuals and trials due to anatomical, functional, cognitive, and experimental factors, making fMRI-to-image reconstruction non-injective. In this paper, we tackle a challenging yet practically meaningful problem: zero-shot cross-subject fMRI-to-image reconstruction, where the visual experience of a previously unseen individual must be reconstructed without subject-specific training. To enable principled evaluation, we present a unified cortical-surface dataset – UniCortex-fMRI, assembled from multiple visual-stimulus fMRI datasets to provide broad coverage of subjects and stimuli. Our UniCortex-fMRI is particularly processed by standardized data formats to make it possible to explore this possibility in the zero-shot scenario of cross-subject fMRI-to-image reconstruction. To tackle the modeling challenge, we propose PictorialCortex, which models fMRI activity using a compositional latent formulation that structures stimulus-driven representations under subject-, dataset-, and trial-related variability. PictorialCortex operates in a universal cortical latent space and implements this formulation through a latent factorization–composition module, reinforced by paired factorization and re-factorizing consistency regularization. During inference, surrogate latents synthesized under multiple seen-subject conditions are aggregated to guide diffusion-based image synthesis for unseen subjects. Extensive experiments show that PictorialCortex improves zero-shot cross-subject visual reconstruction, highlighting the benefits of compositional latent modeling and multi-dataset training.
zh
[CV-23] Enhancing Few-Shot Out-of-Distribution Detection via the Refinement of Foreground and Background
【速读】:该论文旨在解决基于CLIP(Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining)的前景-背景(Foreground-Background, FG-BG)分解方法在少样本跨分布(few-shot out-of-distribution, OOD)检测任务中存在的两个关键问题:一是现有方法对背景区域采用统一抑制策略,忽略了不同图像块(patch)对分类预测贡献的差异;二是对前景区域未充分考虑局部区域可能因外观或语义相似性而与其他类别混淆,从而误导训练过程。解决方案的关键在于提出一个即插即用框架,包含三个核心模块:(1) FG-BG分解模块,沿用已有方法分离前景与背景区域;(2) 自适应背景抑制模块,通过加权图像块的分类熵实现差异化背景抑制;(3) 易混淆前景修正模块,识别并修正易混淆的前景区域,从而提升模型鲁棒性和检测准确性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15065
作者: Tianyu Li,Songyue Cai,Zongqian Wu,Ping Hu,Xiaofeng Zhu
机构: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (电子科技大学); Hainan University (海南大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:CLIP-based foreground-background (FG-BG) decomposition methods have demonstrated remarkable effectiveness in improving few-shot out-of-distribution (OOD) detection performance. However, existing approaches still suffer from several limitations. For background regions obtained from decomposition, existing methods adopt a uniform suppression strategy for all patches, overlooking the varying contributions of different patches to the prediction. For foreground regions, existing methods fail to adequately consider that some local patches may exhibit appearance or semantic similarity to other classes, which may mislead the training process. To address these issues, we propose a new plug-and-play framework. This framework consists of three core components: (1) a Foreground-Background Decomposition module, which follows previous FG-BG methods to separate an image into foreground and background regions; (2) an Adaptive Background Suppression module, which adaptively weights patch classification entropy; and (3) a Confusable Foreground Rectification module, which identifies and rectifies confusable foreground patches. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed plug-and-play framework significantly improves the performance of existing FG-BG decomposition methods. Code is available at: this https URL.
zh
[CV-24] Differential Privacy Image Generation with Reconstruction Loss and Noise Injection Using an Error Feedback SGD
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统数据脱敏技术(如匿名化)在隐私保护与数据可用性之间难以平衡的问题,尤其是在隐私保护机器学习场景下,现有方法常陷入隐私与效用之间的反复权衡困境。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于差分隐私生成的新框架,核心创新包括引入误差反馈随机梯度下降(Error Feedback Stochastic Gradient Descent, EFSGD)方法,并在训练过程中结合重建损失(reconstruction loss)与噪声注入机制,从而在相同隐私预算下生成更高质量、更具可用性的合成图像,显著提升了隐私保护与数据效用的协同能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15061
作者: Qiwei Ma,Jun Zhang
机构: Shenzhen University (深圳大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Traditional data masking techniques such as anonymization cannot achieve the expected privacy protection while ensuring data utility for privacy-preserving machine learning. Synthetic data plays an increasingly important role as it generates a large number of training samples and prevents information leakage in real data. The existing methods suffer from the repeating trade-off processes between privacy and utility. We propose a novel framework for differential privacy generation, which employs an Error Feedback Stochastic Gradient Descent(EFSGD) method and introduces a reconstruction loss and noise injection mechanism into the training process. We generate images with higher quality and usability under the same privacy budget as the related work. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and generalization of our proposed framework for both grayscale and RGB images. We achieve state-of-the-art results over almost all metrics on three benchmarks: MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, and CelebA.
zh
[CV-25] SpooFL: Spoofing Federated Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决联邦学习(Federated Learning, FL)中深度泄漏(Deep Leakage, DL)攻击导致的隐私泄露问题,尤其是传统防御方法在引入噪声或变换后仍可能泄露类别分布或特征表示等高阶信息,且易被强大的去噪攻击破解的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于欺骗(spoofing)的新防御范式 SpooFL,其核心思想是通过生成与原始训练数据无语义关联但外观逼真的合成样本,误导攻击者误以为已恢复真实数据,从而实现对敏感信息的有效保护;具体而言,SpooFL 使用一个在外部数据集上训练的、与私有数据无类别重叠的先进生成模型来构造这些合成样本,既防止了有意义的数据泄露,又维持了联邦学习的训练完整性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15055
作者: Isaac Baglin,Xiatian Zhu,Simon Hadfield
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Traditional defenses against Deep Leakage (DL) attacks in Federated Learning (FL) primarily focus on obfuscation, introducing noise, transformations or encryption to degrade an attacker’s ability to reconstruct private data. While effective to some extent, these methods often still leak high-level information such as class distributions or feature representations, and are frequently broken by increasingly powerful denoising attacks. We propose a fundamentally different perspective on FL defense: framing it as a spoofing this http URL introduce SpooFL (Figure 1), a spoofing-based defense that deceives attackers into believing they have recovered the true training data, while actually providing convincing but entirely synthetic samples from an unrelated task. Unlike prior synthetic-data defenses that share classes or distributions with the private data and thus still leak semantic information, SpooFL uses a state-of-the-art generative model trained on an external dataset with no class overlap. As a result, attackers are misled into recovering plausible yet completely irrelevant samples, preventing meaningful data leakage while preserving FL training integrity. We implement the first example of such a spoofing defense, and evaluate our method against state-of-the-art DL defenses and demonstrate that it successfully misdirects attackers without compromising model performance significantly.
zh
[CV-26] Deep Leakage with Generative Flow Matching Denoiser
【速读】:该论文旨在解决联邦学习(Federated Learning, FL)中因模型更新共享而引发的深度泄露(Deep Leakage, DL)攻击问题,即攻击者可利用客户端上传的模型梯度或参数重构出私有数据。传统DL方法常存在重建结果不稳定、保真度低或在实际FL场景下鲁棒性差等缺陷。其解决方案的关键在于引入生成式流匹配(Flow Matching, FM)先验作为优化引导,通过将重建过程约束于由流匹配基础模型所表征的真实图像分布,从而在无需了解私有数据分布的前提下显著提升重建质量。该方法在像素级、感知和特征层面均优于现有最先进攻击手段,并在不同训练轮次、客户端批量大小及常见防御机制(如噪声注入、裁剪与稀疏化)下仍保持有效性,凸显了生成式先验对DL攻击能力的增强作用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15049
作者: Isaac Baglin,Xiatian Zhu,Simon Hadfield
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) has emerged as a powerful paradigm for decentralized model training, yet it remains vulnerable to deep leakage (DL) attacks that reconstruct private client data from shared model updates. While prior DL methods have demonstrated varying levels of success, they often suffer from instability, limited fidelity, or poor robustness under realistic FL settings. We introduce a new DL attack that integrates a generative Flow Matching (FM) prior into the reconstruction process. By guiding optimization toward the distribution of realistic images (represented by a flow matching foundation model), our method enhances reconstruction fidelity without requiring knowledge of the private data. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets and target models demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms state-of-the-art attacks across pixel-level, perceptual, and feature-based similarity metrics. Crucially, the method remains effective across different training epochs, larger client batch sizes, and under common defenses such as noise injection, clipping, and sparsification. Our findings call for the development of new defense strategies that explicitly account for adversaries equipped with powerful generative priors.
zh
[CV-27] Federated Transformer-GNN for Privacy-Preserving Brain Tumor Localization with Modality-Level Explainability
【速读】:该论文旨在解决脑肿瘤分析中深度学习模型因数据隐私法规导致的多机构数据孤岛问题,从而限制了模型训练所需的多样性和规模。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于联邦学习(Federated Learning)的框架,该框架在不共享敏感患者数据的前提下实现跨机构协作建模,并采用改进的Transformer-图神经网络(Transformer-Graph Neural Network)架构,结合CERN开发的专为医疗环境设计的CAFEIN®平台进行部署。实验表明,联邦学习能够持续提升模型性能直至达到集中式训练水平,且通过注意力机制的可解释性分析验证了T2和FLAIR MRI模态在深层网络中显著增强的关注度(p < 0.001,Cohen’s d = 1.50),与临床实践高度一致。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15042
作者: Andrea Protani,Riccardo Taiello,Marc Molina Van Den Bosch,Luigi Serio
机构: European Organization for Nuclear Research (欧洲核子研究组织); École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (洛桑联邦理工学院); BCN Medtech, Dept. of Engineering, Universitat Pompeu Fabra (BCN Medtech,工程系,庞佩乌·法布拉大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Deep learning models for brain tumor analysis require large and diverse datasets that are often siloed across healthcare institutions due to privacy regulations. We present a federated learning framework for brain tumor localization that enables multi-institutional collaboration without sharing sensitive patient data. Our method extends a hybrid Transformer-Graph Neural Network architecture derived from prior decoder-free supervoxel GNNs and is deployed within CAFEIN\textsuperscript\textregistered, CERN’s federated learning platform designed for healthcare environments. We provide an explainability analysis through Transformer attention mechanisms that reveals which MRI modalities drive the model predictions. Experiments on the BraTS dataset demonstrate a key finding: while isolated training on individual client data triggers early stopping well before reaching full training capacity, federated learning enables continued model improvement by leveraging distributed data, ultimately matching centralized performance. This result provides strong justification for federated learning when dealing with complex tasks and high-dimensional input data, as aggregating knowledge from multiple institutions significantly benefits the learning process. Our explainability analysis, validated through rigorous statistical testing on the full test set (paired t-tests with Bonferroni correction), reveals that deeper network layers significantly increase attention to T2 and FLAIR modalities ( p0.001 , Cohen’s d =1.50), aligning with clinical practice.
zh
[CV-28] ExPrIS: Knowledge-Level Expectations as Priors for Object Interpretation from Sensor Data
【速读】:该论文旨在解决纯数据驱动的深度学习方法在机器人物体识别中缺乏语义一致性、无法有效利用环境先验知识的问题。其核心解决方案是通过构建一个增量式的三维语义场景图(3D Semantic Scene Graph, 3DSSG),并融合来自两个来源的知识:一是基于历史观测的上下文先验,二是来自外部知识图谱(如ConceptNet)的语义知识;这些知识被嵌入到异构图神经网络(Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network, GNN)中,形成一种具有期望偏置的推理机制,从而提升场景理解的鲁棒性和时序一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15025
作者: Marian Renz,Martin Günther,Felix Igelbrink,Oscar Lima,Martin Atzmueller
机构: DFKI (德国人工智能研究中心); University of Oldenburg (奥尔登堡大学)
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: This preprint has not undergone peer review or any post-submission improvements or corrections. The Version of Record of this article is published in KI - Künstliche Intelligenz, and is available online at this https URL
Abstract:While deep learning has significantly advanced robotic object recognition, purely data-driven approaches often lack semantic consistency and fail to leverage valuable, pre-existing knowledge about the environment. This report presents the ExPrIS project, which addresses this challenge by investigating how knowledge-level expectations can serve as to improve object interpretation from sensor data. Our approach is based on the incremental construction of a 3D Semantic Scene Graph (3DSSG). We integrate expectations from two sources: contextual priors from past observations and semantic knowledge from external graphs like ConceptNet. These are embedded into a heterogeneous Graph Neural Network (GNN) to create an expectation-biased inference process. This method moves beyond static, frame-by-frame analysis to enhance the robustness and consistency of scene understanding over time. The report details this architecture, its evaluation, and outlines its planned integration on a mobile robotic platform.
zh
[CV-29] Mixture-of-Experts Models in Vision: Routing Optimization and Generalization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决混合专家(Mixture-of-Experts, MoE)架构在图像分类任务中如何平衡预测性能、专家利用率与泛化能力的问题,同时探究其在现代硬件上的实际推理效率。解决方案的关键在于:首先,在模型容量相当的前提下,对比密集(Dense)、软性MoE(SoftMoE)和稀疏MoE(SparseMoE)分类头的性能表现,发现两者均略优于密集基线且通过正则化实现均衡的专家利用,避免了专家坍塌(expert collapse);其次,借助Hessian矩阵的曲率指标(如最大特征值和迹)分析收敛后的损失面平坦性,揭示SoftMoE具有更高尖锐度但整体泛化性能相近,表明曲率并非直接决定泛化性的唯一因素;最后,通过损失表面扰动实验识别出密集模型与MoE模型在非局部行为上的差异,并指出当前条件下朴素实现的条件路由策略无法在现代硬件上带来推理加速,凸显理论效率与实际部署间的差距。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15021
作者: Adam Rokah,Daniel Veress,Caleb Caulk,Sourav Sharan
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 7 pages, 8 figures. Code available at: this https URL
Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures enable conditional computation by routing inputs to multiple expert subnetworks and are often motivated as a mechanism for scaling large language models. In this project, we instead study MoE behavior in an image classification setting, focusing on predictive performance, expert utilization, and generalization. We compare dense, SoftMoE, and SparseMoE classifier heads on the CIFAR10 dataset under comparable model capacity. Both MoE variants achieve slightly higher validation accuracy than the dense baseline while maintaining balanced expert utilization through regularization, avoiding expert collapse. To analyze generalization, we compute Hessian-based sharpness metrics at convergence, including the largest eigenvalue and trace of the loss Hessian, evaluated on both training and test data. We find that SoftMoE exhibits higher sharpness by these metrics, while Dense and SparseMoE lie in a similar curvature regime, despite all models achieving comparable generalization performance. Complementary loss surface perturbation analyses reveal qualitative differences in non-local behavior under finite parameter perturbations between dense and MoE models, which help contextualize curvature-based measurements without directly explaining validation accuracy. We further evaluate empirical inference efficiency and show that naively implemented conditional routing does not yield inference speedups on modern hardware at this scale, highlighting the gap between theoretical and realized efficiency in sparse MoE models.
zh
[CV-30] SpatialV2A: Visual-Guided High-fidelity Spatial Audio Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视频到音频生成中空间感知与沉浸感不足的问题,现有模型主要关注语义和时间对齐,但受限于单声道音频数据集,难以学习视觉到空间音频的映射关系。解决方案的关键在于:构建首个大规模视频-双耳音频数据集BinauralVGGSound,以提供必要的双耳空间信息;并提出一种端到端的空间音频生成框架,通过引入视觉引导的音频空间化模块,显式建模空间特征,从而在保持语义和时间一致性的同时,显著提升音频的空间保真度和沉浸感。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15017
作者: Yanan Wang,Linjie Ren,Zihao Li,Junyi Wang,Tian Gan
机构: Shandong University (山东大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:While video-to-audio generation has achieved remarkable progress in semantic and temporal alignment, most existing studies focus solely on these aspects, paying limited attention to the spatial perception and immersive quality of the synthesized audio. This limitation stems largely from current models’ reliance on mono audio datasets, which lack the binaural spatial information needed to learn visual-to-spatial audio mappings. To address this gap, we introduce two key contributions: we construct BinauralVGGSound, the first large-scale video-binaural audio dataset designed to support spatially aware video-to-audio generation; and we propose a end-to-end spatial audio generation framework guided by visual cues, which explicitly models spatial features. Our framework incorporates a visual-guided audio spatialization module that ensures the generated audio exhibits realistic spatial attributes and layered spatial depth while maintaining semantic and temporal alignment. Experiments show that our approach substantially outperforms state-of-the-art models in spatial fidelity and delivers a more immersive auditory experience, without sacrificing temporal or semantic consistency. All datasets, code, and model checkpoints will be publicly released to facilitate future research.
zh
[CV-31] LiViBench: An Omnimodal Benchmark for Interactive Livestream Video Understanding AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在交互式直播视频理解上的能力不足问题,因为现有视频评估基准主要聚焦于非交互式视频(如电影和录制视频),缺乏对直播场景中实时互动特性(如音频、语音与实时评论)的系统性评测。解决方案的关键在于构建首个面向交互式直播视频的全模态基准 LiViBench,其包含24项任务以覆盖感知、推理及直播特有挑战;设计了一种标准化的半自动标注流程,结合人类在环(human-in-the-loop)与多代理(multi-agent)系统提升标注效率与质量;并提出两阶段指令微调策略与视频到评论检索(Video-to-Comment Retrieval, VCR)模块,显著增强模型对实时评论信息的理解与利用能力,最终开发出性能超越更大参数规模开源模型的 LiVi-LLM-7B。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15016
作者: Xiaodong Wang,Langling Huang,Zhirong Wu,Xu Zhao,Teng Xu,Xuhong Xia,Peixi Peng
机构: 1. University of California, Santa Barbara (加州大学圣塔芭芭拉分校); 2. Tsinghua University (清华大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: AAAI 2026 Main Track
Abstract:The development of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) has advanced general video understanding. However, existing video evaluation benchmarks primarily focus on non-interactive videos, such as movies and recordings. To fill this gap, this paper proposes the first omnimodal benchmark for interactive livestream videos, LiViBench. It features a diverse set of 24 tasks, highlighting the perceptual, reasoning, and livestream-specific challenges. To efficiently construct the dataset, we design a standardized semi-automatic annotation workflow that incorporates the human-in-the-loop at multiple stages. The workflow leverages multiple MLLMs to form a multi-agent system for comprehensive video description and uses a seed-question-driven method to construct high-quality annotations. All interactive videos in the benchmark include audio, speech, and real-time comments modalities. To enhance models’ understanding of interactive videos, we design tailored two-stage instruction-tuning and propose a Video-to-Comment Retrieval (VCR) module to improve the model’s ability to utilize real-time comments. Based on these advancements, we develop LiVi-LLM-7B, an MLLM with enhanced knowledge of interactive livestreams. Experiments show that our model outperforms larger open-source models with up to 72B parameters, narrows the gap with leading proprietary models on LiViBench, and achieves enhanced performance on general video benchmarks, including VideoMME, LongVideoBench, MLVU, and VideoEval-Pro.
zh
[CV-32] Unified Multi-Dataset Training for TBPS
【速读】:该论文旨在解决文本驱动的人体搜索(Text-Based Person Search, TBPS)中因训练数据有限及视觉-语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)缺乏行人中心识别预训练而导致的泛化能力不足问题,尤其针对现有方法依赖于特定数据集微调、导致模型碎片化且难以跨数据集迁移的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出Scale-TBPS框架,其核心创新包括:(i) 一种噪声感知的统一数据集整理策略,能够有效融合多个TBPS数据集并减少噪声图像-文本对的影响;(ii) 一种可扩展的判别式身份学习机制,在面对大量唯一个体身份时仍保持高效与鲁棒性。实验证明,单一Scale-TBPS模型在多个公开数据集上均优于独立优化的模型和简单的联合训练方案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14978
作者: Nilanjana Chatterjee,Sidharatha Garg,A V Subramanyam,Brejesh Lall
机构: IIIT Delhi (印度国际信息技术研究所); IIT Delhi (印度理工学院德里分校)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Text-Based Person Search (TBPS) has seen significant progress with vision-language models (VLMs), yet it remains constrained by limited training data and the fact that VLMs are not inherently pre-trained for pedestrian-centric recognition. Existing TBPS methods therefore rely on dataset-centric fine-tuning to handle distribution shift, resulting in multiple independently trained models for different datasets. While synthetic data can increase the scale needed to fine-tune VLMs, it does not eliminate dataset-specific adaptation. This motivates a fundamental question: can we train a single unified TBPS model across multiple datasets? We show that naive joint training over all datasets remains sub-optimal because current training paradigms do not scale to a large number of unique person identities and are vulnerable to noisy image-text pairs. To address these challenges, we propose Scale-TBPS with two contributions: (i) a noise-aware unified dataset curation strategy that cohesively merges diverse TBPS datasets; and (ii) a scalable discriminative identity learning framework that remains effective under a large number of unique identities. Extensive experiments on CUHK-PEDES, ICFG-PEDES, RSTPReid, IIITD-20K, and UFine6926 demonstrate that a single Scale-TBPS model outperforms dataset-centric optimized models and naive joint training.
zh
[CV-33] owards Holistic Modeling for Video Frame Interpolation with Auto-regressive Diffusion Transformers
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有视频帧插值(Video Frame Interpolation, VFI)方法因采用帧中心(frame-centric)处理方式而导致的时序不一致性和运动伪影问题。其核心解决方案是提出一种全新的、以视频为中心(video-centric)的范式——LDF-VFI,该框架基于自回归扩散Transformer(auto-regressive diffusion transformer),通过建模整个视频序列来保证长程时序一致性;关键创新在于引入一种新颖的跳跃连接采样策略(skip-concatenate sampling strategy),有效缓解自回归生成中的误差累积问题,并结合稀疏局部注意力机制与分块VAE编码(tiled VAE encoding),实现对任意空间分辨率(如4K)的高效推理且无需重新训练,同时利用多尺度特征增强条件VAE解码器以提升重建保真度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14959
作者: Xinyu Peng,Han Li,Yuyang Huang,Ziyang Zheng,Yaoming Wang,Xin Chen,Wenrui Dai,Chenglin Li,Junni Zou,Hongkai Xiong
机构: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); Meituan (美团)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Existing video frame interpolation (VFI) methods often adopt a frame-centric approach, processing videos as independent short segments (e.g., triplets), which leads to temporal inconsistencies and motion artifacts. To overcome this, we propose a holistic, video-centric paradigm named \textbfLocal \textbfDiffusion \textbfForcing for \textbfVideo \textbfFrame \textbfInterpolation (LDF-VFI). Our framework is built upon an auto-regressive diffusion transformer that models the entire video sequence to ensure long-range temporal coherence. To mitigate error accumulation inherent in auto-regressive generation, we introduce a novel skip-concatenate sampling strategy that effectively maintains temporal stability. Furthermore, LDF-VFI incorporates sparse, local attention and tiled VAE encoding, a combination that not only enables efficient processing of long sequences but also allows generalization to arbitrary spatial resolutions (e.g., 4K) at inference without retraining. An enhanced conditional VAE decoder, which leverages multi-scale features from the input video, further improves reconstruction fidelity. Empirically, LDF-VFI achieves state-of-the-art performance on challenging long-sequence benchmarks, demonstrating superior per-frame quality and temporal consistency, especially in scenes with large motion. The source code is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-34] Erosion Attack for Adversarial Training to Enhance Semantic Segmentation Robustness ICASSP2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有分割模型在面对对抗攻击时的脆弱性问题,尤其是传统对抗训练方法因仅考虑全局语义信息而忽略样本内部上下文语义关系,导致攻击效果有限、鲁棒性提升不足的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出EroSeg-AT框架,该框架利用EroSeg生成更具破坏力的对抗样本:首先基于像素级置信度选择敏感像素,随后将扰动逐步传播至高置信度像素,从而有效破坏样本的语义一致性,显著增强对抗训练中的攻击有效性与模型鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14950
作者: Yufei Song,Ziqi Zhou,Menghao Deng,Yifan Hu,Shengshan Hu,Minghui Li,Leo Yu Zhang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted by ICASSP 2026
Abstract:Existing segmentation models exhibit significant vulnerability to adversarial this http URL improve robustness, adversarial training incorporates adversarial examples into model training. However, existing attack methods consider only global semantic information and ignore contextual semantic relationships within the samples, limiting the effectiveness of adversarial training. To address this issue, we propose EroSeg-AT, a vulnerability-aware adversarial training framework that leverages EroSeg to generate adversarial examples. EroSeg first selects sensitive pixels based on pixel-level confidence and then progressively propagates perturbations to higher-confidence pixels, effectively disrupting the semantic consistency of the samples. Experimental results show that, compared to existing methods, our approach significantly improves attack effectiveness and enhances model robustness under adversarial training.
zh
[CV-35] SpatialMem: Unified 3D Memory with Metric Anchoring and Fast Retrieval
【速读】:该论文旨在解决室内环境中多模态信息(3D几何、语义与语言)融合与高效查询的问题,以支持具身智能任务如语言引导导航和物体检索。其解决方案的关键在于提出SpatialMem系统,该系统将RGB视频输入重构为度量尺度的3D环境,并通过结构化锚点(如墙、门、窗)构建第一层骨架,随后在分层记忆中存储开放词汇的对象节点(链接视觉嵌入、证据图像块及两层文本描述至3D坐标),从而实现紧凑存储与快速检索,同时支持可解释的空间关系推理(如距离、方向、可见性)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14895
作者: Xinyi Zheng,Yunze Liu,Chi-Hao Wu,Fan Zhang,Hao Zheng,Wenqi Zhou,Walterio W. Mayol-Cuevas,Junxiao Shen
机构: University of Bristol (布里斯托大学); Memories.ai Research (Memories.ai 研究院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:We present SpatialMem, a memory-centric system that unifies 3D geometry, semantics, and language into a single, queryable representation. Starting from casually captured egocentric RGB video, SpatialMem reconstructs metrically scaled indoor environments, detects structural 3D anchors (walls, doors, windows) as the first-layer scaffold, and populates a hierarchical memory with open-vocabulary object nodes – linking evidence patches, visual embeddings, and two-layer textual descriptions to 3D coordinates – for compact storage and fast retrieval. This design enables interpretable reasoning over spatial relations (e.g., distance, direction, visibility) and supports downstream tasks such as language-guided navigation and object retrieval without specialized sensors. Experiments across three real-life indoor scenes demonstrate that SpatialMem maintains strong anchor-description-level navigation completion and hierarchical retrieval accuracy under increasing clutter and occlusion, offering an efficient and extensible framework for embodied spatial intelligence.
zh
[CV-36] GAT-NeRF: Geometry-Aware-Transformer Enhanced Neural Radiance Fields for High-Fidelity 4D Facial Avatars
【速读】:该论文旨在解决从单目视频中高保真重建4D动态人脸化身(4D dynamic facial avatar)的难题,尤其在信息受限的单视角条件下如何有效捕捉高频面部细节(如动态皱纹和细微纹理)。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一种新型混合神经辐射场框架——几何感知Transformer增强NeRF(GAT-NeRF),该框架将Transformer机制融入NeRF管线,通过一个轻量级的几何感知Transformer(Geometry-Aware-Transformer, GAT)模块融合多模态输入特征(包括3D空间坐标、3D形态模型表达参数及可学习潜在码),从而显著提升对精细几何结构和复杂局部面部模式(如动态皱纹与痘疤)的建模能力,实现视觉保真度与高频细节恢复的最优平衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14875
作者: Zhe Chang,Haodong Jin,Ying Sun,Yan Song,Hui Yu
机构: University of Shanghai for Science and Technology (上海理工大学); University of Glasgow (格拉斯哥大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:High-fidelity 4D dynamic facial avatar reconstruction from monocular video is a critical yet challenging task, driven by increasing demands for immersive virtual human applications. While Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have advanced scene representation, their capacity to capture high-frequency facial details, such as dynamic wrinkles and subtle textures from information-constrained monocular streams, requires significant enhancement. To tackle this challenge, we propose a novel hybrid neural radiance field framework, called Geometry-Aware-Transformer Enhanced NeRF (GAT-NeRF) for high-fidelity and controllable 4D facial avatar reconstruction, which integrates the Transformer mechanism into the NeRF pipeline. GAT-NeRF synergistically combines a coordinate-aligned Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) with a lightweight Transformer module, termed as Geometry-Aware-Transformer (GAT) due to its processing of multi-modal inputs containing explicit geometric priors. The GAT module is enabled by fusing multi-modal input features, including 3D spatial coordinates, 3D Morphable Model (3DMM) expression parameters, and learnable latent codes to effectively learn and enhance feature representations pertinent to fine-grained geometry. The Transformer’s effective feature learning capabilities are leveraged to significantly augment the modeling of complex local facial patterns like dynamic wrinkles and acne scars. Comprehensive experiments unequivocally demonstrate GAT-NeRF’s state-of-the-art performance in visual fidelity and high-frequency detail recovery, forging new pathways for creating realistic dynamic digital humans for multimedia applications.
zh
[CV-37] MTFlow: Time-Conditioned Flow Matching for Microtubule Segmentation in Noisy Microscopy Images
【速读】:该论文旨在解决微管(microtubule)网络在生物图像中难以准确分割的问题,尤其针对微管曲率大、交叉密集及图像噪声强等挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种时间条件流匹配模型(time-conditioned flow-matching model),即MTFlow,该模型通过学习向量场迭代地将含噪初始掩膜(mask)逐步引导至真实标签,实现基于轨迹的可解释性精修;其架构融合U-Net主干与时间嵌入(temporal embeddings),能够捕捉沿微管边界不确定性消解的动力学过程,从而在合成和真实微管数据集上均取得优于传统方法的分割精度与效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14841
作者: Sidi Mohamed Sid El Moctar,Achraf Ait Laydi,Yousef El Mourabit,Hélène Bouvrais
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Accepted for presentation at ISBI 2026
Abstract:Microtubules are cytoskeletal filaments that play essential roles in many cellular processes and are key therapeutic targets in several diseases. Accurate segmentation of microtubule networks is critical for studying their organization and dynamics but remains challenging due to filament curvature, dense crossings, and image noise. We present MTFlow, a novel time-conditioned flow-matching model for microtubule segmentation. Unlike conventional U-Net variants that predict masks in a single pass, MTFlow learns vector fields that iteratively transport noisy masks toward the ground truth, enabling interpretable, trajectory-based refinement. Our architecture combines a U-Net backbone with temporal embeddings, allowing the model to capture the dynamics of uncertainty resolution along filament boundaries. We trained and evaluated MTFlow on synthetic and real microtubule datasets and assessed its generalization capability on public biomedical datasets of curvilinear structures such as retinal blood vessels and nerves. MTFlow achieves competitive segmentation accuracy comparable to state-of-the-art models, offering a powerful and time-efficient tool for filamentous structure analysis with more precise annotations than manual or semi-automatic approaches.
zh
[CV-38] Multimodal system for skin cancer detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决皮肤黑色素瘤(melanoma)早期检测中因依赖专业设备(如皮肤镜图像)而导致的临床可及性受限问题。其核心解决方案是提出一种基于常规照片图像(conventional photo images)与结构化表格数据(如患者人口统计学信息和病变特征)融合的多模态(multi-modal)检测系统,通过构建分阶段的神经网络架构与优化策略,实现高精度、低门槛的诊断能力。关键创新在于:1)利用非专业成像设备获取图像数据以提升普及性;2)引入多模态融合机制增强模型判别力;3)采用三阶段流水线设计结合集成学习方法,显著改善极端不平衡数据下的训练稳定性与性能表现,最终在Partial ROC AUC和top-15检索敏感度上取得优异结果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14822
作者: Volodymyr Sydorskyi,Igor Krashenyi,Oleksii Yakubenko
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted to System research and information technologies
Abstract:Melanoma detection is vital for early diagnosis and effective treatment. While deep learning models on dermoscopic images have shown promise, they require specialized equipment, limiting their use in broader clinical settings. This study introduces a multi-modal melanoma detection system using conventional photo images, making it more accessible and versatile. Our system integrates image data with tabular metadata, such as patient demographics and lesion characteristics, to improve detection accuracy. It employs a multi-modal neural network combining image and metadata processing and supports a two-step model for cases with or without metadata. A three-stage pipeline further refines predictions by boosting algorithms and enhancing performance. To address the challenges of a highly imbalanced dataset, specific techniques were implemented to ensure robust training. An ablation study evaluated recent vision architectures, boosting algorithms, and loss functions, achieving a peak Partial ROC AUC of 0.18068 (0.2 maximum) and top-15 retrieval sensitivity of 0.78371. Results demonstrate that integrating photo images with metadata in a structured, multi-stage pipeline yields significant performance improvements. This system advances melanoma detection by providing a scalable, equipment-independent solution suitable for diverse healthcare environments, bridging the gap between specialized and general clinical practices.
zh
[CV-39] POTR: Post-Training 3DGS Compression
【速读】:该论文旨在解决3D高斯溅射(3D Gaussian Splatting, 3DGS)在实际应用中因存储需求过高而导致的瓶颈问题,尤其是在后训练压缩(post-training compression)场景下如何实现高效存储与快速推理的平衡。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为POTR的压缩框架,包含两个核心创新:一是设计了一种基于改进的3DGS光栅化器的新型剪枝方法,可并行计算每个高斯溅射体的移除影响,从而显著减少冗余溅射体数量(减少2-4倍),同时提升推理速度(1.5-2倍更快);二是提出一种无需训练的光照系数重计算机制,通过提高AC光照系数的稀疏性(从70%提升至97%),大幅降低熵值,从而优化压缩效率。此外,论文进一步引入一个简单的微调策略以协同优化剪枝、推理速度和率失真性能,实验表明POTR即使不进行微调也能在率失真和推理速度上全面优于现有后训练压缩方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14821
作者: Bert Ramlot,Martijn Courteaux,Peter Lambert,Glenn Van Wallendael
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 15 pages, 12 figures. Submitted to IEEE TCSVT, under review
Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently emerged as a promising contender to Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) in 3D scene reconstruction and real-time novel view synthesis. 3DGS outperforms NeRF in training and inference speed but has substantially higher storage requirements. To remedy this downside, we propose POTR, a post-training 3DGS codec built on two novel techniques. First, POTR introduces a novel pruning approach that uses a modified 3DGS rasterizer to efficiently calculate every splat’s individual removal effect simultaneously. This technique results in 2-4x fewer splats than other post-training pruning techniques and as a result also significantly accelerates inference with experiments demonstrating 1.5-2x faster inference than other compressed models. Second, we propose a novel method to recompute lighting coefficients, significantly reducing their entropy without using any form of training. Our fast and highly parallel approach especially increases AC lighting coefficient sparsity, with experiments demonstrating increases from 70% to 97%, with minimal loss in quality. Finally, we extend POTR with a simple fine-tuning scheme to further enhance pruning, inference, and rate-distortion performance. Experiments demonstrate that POTR, even without fine-tuning, consistently outperforms all other post-training compression techniques in both rate-distortion performance and inference speed.
zh
[CV-40] Symmetry Informative and Agnostic Feature Disentanglement for 3D Shapes
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前对称感知形状描述符(symmetry-aware shape descriptors)在表达能力与鲁棒性方面的不足问题,具体表现为:现有方法提取的对称信息特征维度单一(仅一维),忽略了其他潜在语义信息;同时,所提取的对称特征易受噪声干扰,导致分类错误区域较大。解决方案的关键在于提出一种特征解耦(feature disentanglement)方法,使描述符同时具备对称信息敏感性和对称无关性,从而分离出纯净的对称特征;进一步结合特征精炼技术(feature refinement),提升预测对称信息特征的鲁棒性,显著改善内在对称检测、左右分类及形状匹配等任务性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14804
作者: Tobias Weißberg,Weikang Wang,Paul Roetzer,Nafie El Amrani,Florian Bernard
机构: University of Bonn (波恩大学); Lamarr Institute (拉马尔研究所)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted at 3DV 2026
Abstract:Shape descriptors, i.e., per-vertex features of 3D meshes or point clouds, are fundamental to shape analysis. Historically, various handcrafted geometry-aware descriptors and feature refinement techniques have been proposed. Recently, several studies have initiated a new research direction by leveraging features from image foundation models to create semantics-aware descriptors, demonstrating advantages across tasks like shape matching, editing, and segmentation. Symmetry, another key concept in shape analysis, has also attracted increasing attention. Consequently, constructing symmetry-aware shape descriptors is a natural progression. Although the recent method \chi (Wang et al., 2025) successfully extracted symmetry-informative features from semantic-aware descriptors, its features are only one-dimensional, neglecting other valuable semantic information. Furthermore, the extracted symmetry-informative feature is usually noisy and yields small misclassified patches. To address these gaps, we propose a feature disentanglement approach which is simultaneously symmetry informative and symmetry agnostic. Further, we propose a feature refinement technique to improve the robustness of predicted symmetry informative features. Extensive experiments, including intrinsic symmetry detection, left/right classification, and shape matching, demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework compared to various state-of-the-art methods, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
zh
[CV-41] LocBAM: Advancing 3D Patch-Based Image Segmentation by Integrating Location Contex
【速读】:该论文旨在解决patch-based 3D医学图像分割方法中因忽略补丁(patch)在全局体积中的位置信息而导致的性能瓶颈问题,尤其是在需要解剖学上下文的关键场景下。其解决方案的核心是提出了一种新颖的注意力机制LocBAM(Location-aware Block Attention Mechanism),该机制显式地建模和处理空间位置信息,从而增强模型对全局上下文的理解能力。实验表明,引入位置上下文可稳定训练过程并提升分割性能,尤其在低补丁覆盖比条件下效果显著,且LocBAM优于传统的坐标编码方式(CoordConv)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14802
作者: Donnate Hooft,Stefan M. Fischer,Cosmin Bercea,Jan C. Peeken,Julia A. Schnabel
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted at ISBI 2026
Abstract:Patch-based methods are widely used in 3D medical image segmentation to address memory constraints in processing high-resolution volumetric data. However, these approaches often neglect the patch’s location within the global volume, which can limit segmentation performance when anatomical context is important. In this paper, we investigate the role of location context in patch-based 3D segmentation and propose a novel attention mechanism, LocBAM, that explicitly processes spatial information. Experiments on BTCV, AMOS22, and KiTS23 demonstrate that incorporating location context stabilizes training and improves segmentation performance, particularly under low patch-to-volume coverage where global context is missing. Furthermore, LocBAM consistently outperforms classical coordinate encoding via CoordConv. Code is publicly available at this https URL
zh
[CV-42] UBATrack: Spatio-Temporal State Space Model for General Multi-Modal Tracking
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态目标跟踪中对时空线索捕捉不足的问题,现有基于提示学习的通用多模态跟踪方法虽能整合多种模态(如RGB-热红外、RGB-深度或RGB-事件数据),但未能有效建模跨模态依赖关系与时空视觉特征。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于Mamba架构的状态空间模型驱动的新型框架UBATrack,核心创新包括两个模块:一是时空Mamba适配器(Spatio-temporal Mamba Adapter, STMA),利用Mamba的长序列建模能力以适配调优方式联合建模跨模态依赖与时空视觉线索;二是动态多模态特征混合器(Dynamic Multi-modal Feature Mixer),增强多维特征空间中的多模态表示能力,从而提升跟踪鲁棒性。该设计避免了昂贵的全参数微调,显著提升了训练效率,并在多个主流多模态跟踪基准(如LasHeR、RGBT234、DepthTrack等)上取得最优性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14799
作者: Qihua Liang,Liang Chen,Yaozong Zheng,Jian Nong,Zhiyi Mo,Bineng Zhong
机构: Guangxi Normal University (广西师范大学); Wuzhou University (梧州大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Multi-modal object tracking has attracted considerable attention by integrating multiple complementary inputs (e.g., thermal, depth, and event data) to achieve outstanding performance. Although current general-purpose multi-modal trackers primarily unify various modal tracking tasks (i.e., RGB-Thermal infrared, RGB-Depth or RGB-Event tracking) through prompt learning, they still overlook the effective capture of spatio-temporal cues. In this work, we introduce a novel multi-modal tracking framework based on a mamba-style state space model, termed UBATrack. Our UBATrack comprises two simple yet effective modules: a Spatio-temporal Mamba Adapter (STMA) and a Dynamic Multi-modal Feature Mixer. The former leverages Mamba’s long-sequence modeling capability to jointly model cross-modal dependencies and spatio-temporal visual cues in an adapter-tuning manner. The latter further enhances multi-modal representation capacity across multiple feature dimensions to improve tracking robustness. In this way, UBATrack eliminates the need for costly full-parameter fine-tuning, thereby improving the training efficiency of multi-modal tracking algorithms. Experiments show that UBATrack outperforms state-of-the-art methods on RGB-T, RGB-D, and RGB-E tracking benchmarks, achieving outstanding results on the LasHeR, RGBT234, RGBT210, DepthTrack, VOT-RGBD22, and VisEvent datasets.
zh
[CV-43] UniRoute: Unified Routing Mixture-of-Experts for Modality-Adaptive Remote Sensing Change Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前遥感变化检测(Change Detection, CD)方法依赖专用模型而导致的模态自适应能力不足的问题,尤其在异质数据(heterogeneous CD)场景下,传统差分操作(difference operator)易引入伪影,且静态骨干网络难以应对跨模态或几何非对齐情况。解决方案的关键在于提出UniRoute框架,通过将特征提取与融合重构为条件路由问题,设计了两个核心模块:自适应感受野路由MoE(Adaptive Receptive Field Routing MoE, AR2-MoE)用于解耦局部空间细节与全局语义上下文,以及模态感知差分路由MoE(Modality-Aware Difference Routing MoE, MDR-MoE)以在像素级动态选择最优融合策略;同时引入一致性感知自蒸馏(Consistency-Aware Self-Distillation, CASD)策略,在数据稀缺的异质设置下提升统一训练的稳定性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14797
作者: Qingling Shu,Sibao Chen,Wei Lu,Zhihui You,Chengzhuang Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Current remote sensing change detection (CD) methods mainly rely on specialized models, which limits the scalability toward modality-adaptive Earth observation. For homogeneous CD, precise boundary delineation relies on fine-grained spatial cues and local pixel interactions, whereas heterogeneous CD instead requires broader contextual information to suppress speckle noise and geometric distortions. Moreover, difference operator (e.g., subtraction) works well for aligned homogeneous images but introduces artifacts in cross-modal or geometrically misaligned scenarios. Across different modality settings, specialized models based on static backbones or fixed difference operations often prove insufficient. To address this challenge, we propose UniRoute, a unified framework for modality-adaptive learning by reformulating feature extraction and fusion as conditional routing problems. We introduce an Adaptive Receptive Field Routing MoE (AR2-MoE) module to disentangle local spatial details from global semantic context, and a Modality-Aware Difference Routing MoE (MDR-MoE) module to adaptively select the most suitable fusion primitive at each pixel. In addition, we propose a Consistency-Aware Self-Distillation (CASD) strategy that stabilizes unified training under data-scarce heterogeneous settings by enforcing multi-level consistency. Extensive experiments on five public datasets demonstrate that UniRoute achieves strong overall performance, with a favorable accuracy-efficiency trade-off under a unified deployment setting.
zh
[CV-44] Synthetic Data Augmentation for Multi-Task Chinese Porcelain Classification: A Stable Diffusion Approach
【速读】:该论文旨在解决考古学中稀有中国瓷器类别分类任务因训练数据稀缺而导致的深度学习模型性能受限问题。其解决方案的关键在于利用基于稳定扩散(Stable Diffusion)与低秩适配(Low-Rank Adaptation, LoRA)技术生成合成图像,以增强有限的真实数据集,并通过多任务卷积神经网络(CNN)架构进行验证。实验表明,合成数据在不同类型分类任务中表现出差异化的增益效果,尤其在类型识别上提升显著(F1-macro提高5.5%),证明了生成式AI在提升考古数据多样性方面的潜力,同时也揭示了合成数据质量与任务特征对齐程度对其有效性的重要影响。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14791
作者: Ziyao Ling,Silvia Mirri,Paola Salomoni,Giovanni Delnevo
机构: University of Bologna (博洛尼亚大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:The scarcity of training data presents a fundamental challenge in applying deep learning to archaeological artifact classification, particularly for the rare types of Chinese porcelain. This study investigates whether synthetic images generated through Stable Diffusion with Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) can effectively augment limited real datasets for multi-task CNN-based porcelain classification. Using MobileNetV3 with transfer learning, we conducted controlled experiments comparing models trained on pure real data against those trained on mixed real-synthetic datasets (95:5 and 90:10 ratios) across four classification tasks: dynasty, glaze, kiln and type identification. Results demonstrate task-specific benefits: type classification showed the most substantial improvement (5.5% F1-macro increase with 90:10 ratio), while dynasty and kiln tasks exhibited modest gains (3-4%), suggesting that synthetic augmentation effectiveness depends on the alignment between generated features and task-relevant visual signatures. Our work contributes practical guidelines for deploying generative AI in archaeological research, demonstrating both the potential and limitations of synthetic data when archaeological authenticity must be balanced with data diversity.
zh
[CV-45] Reconstruction-Anchored Diffusion Model for Text-to-Motion Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前运动扩散模型(motion diffusion models)在文本驱动人体动作生成任务中面临的两大挑战:一是由预训练文本编码器缺乏运动特定信息导致的表征鸿沟(representational gap),二是迭代去噪过程中误差传播(error propagation)问题。解决方案的关键在于提出重构锚定扩散模型(Reconstruction-Anchored Diffusion Model, RAM),其核心创新包括两方面:首先,引入运动潜在空间(motion latent space)作为中间监督信号,通过联合训练一个运动重建分支,并结合自正则化(self-regularization)和以运动为中心的潜在对齐(motion-centric latent alignment)两个目标函数,增强运动空间判别力并实现文本到运动潜在空间的精准映射;其次,在推理阶段提出重构误差引导机制(Reconstructive Error Guidance, REG),利用扩散模型的内在自校正能力,通过重建前一步估计来重现先验误差模式,并放大当前预测与重建估计之间的残差,从而突出改进方向,有效缓解误差累积问题。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14788
作者: Yifei Liu,Changxing Ding,Ling Guo,Huaiguang Jiang,Qiong Cao
机构: South China University of Technology (华南理工大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Diffusion models have seen widespread adoption for text-driven human motion generation and related tasks due to their impressive generative capabilities and flexibility. However, current motion diffusion models face two major limitations: a representational gap caused by pre-trained text encoders that lack motion-specific information, and error propagation during the iterative denoising process. This paper introduces Reconstruction-Anchored Diffusion Model (RAM) to address these challenges. First, RAM leverages a motion latent space as intermediate supervision for text-to-motion generation. To this end, RAM co-trains a motion reconstruction branch with two key objective functions: self-regularization to enhance the discrimination of the motion space and motion-centric latent alignment to enable accurate mapping from text to the motion latent space. Second, we propose Reconstructive Error Guidance (REG), a testing-stage guidance mechanism that exploits the diffusion model’s inherent self-correction ability to mitigate error propagation. At each denoising step, REG uses the motion reconstruction branch to reconstruct the previous estimate, reproducing the prior error patterns. By amplifying the residual between the current prediction and the reconstructed estimate, REG highlights the improvements in the current prediction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RAM achieves significant improvements and state-of-the-art performance. Our code will be released.
zh
[CV-46] FunCineForge: A Unified Dataset Toolkit and Model for Zero-Shot Movie Dubbing in Diverse Cinematic Scenes
【速读】:该论文旨在解决电影配音(Movie dubbing)任务中面临的两大核心问题:一是高质量多模态配音数据集规模小、词错误率高、标注稀疏、依赖昂贵的人工标注且仅限于独白场景,限制了模型的有效训练;二是现有配音模型仅依赖唇部区域进行音视频对齐,难以适应复杂的实景影视场景,在唇同步、语音质量和情感表达方面表现不佳。解决方案的关键在于提出一个端到端的大型配音数据集生成流水线(FunCineForge),用于构建首个中文电视配音数据集并实现丰富标注,同时设计基于多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Model, MLLM)的配音模型,使其能够有效处理独白、旁白、对话及多人场景,显著提升音频质量、唇同步精度、音色迁移能力和指令遵循性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14777
作者: Jiaxuan Liu,Yang Xiang,Han Zhao,Xiangang Li,Zhenhua Ling
机构: Tongyi Lab (通义实验室); Alibaba Group (阿里巴巴集团)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Movie dubbing is the task of synthesizing speech from scripts conditioned on video scenes, requiring accurate lip sync, faithful timbre transfer, and proper modeling of character identity and emotion. However, existing methods face two major limitations: (1) high-quality multimodal dubbing datasets are limited in scale, suffer from high word error rates, contain sparse annotations, rely on costly manual labeling, and are restricted to monologue scenes, all of which hinder effective model training; (2) existing dubbing models rely solely on the lip region to learn audio-visual alignment, which limits their applicability to complex live-action cinematic scenes, and exhibit suboptimal performance in lip sync, speech quality, and emotional expressiveness. To address these issues, we propose FunCineForge, which comprises an end-to-end production pipeline for large-scale dubbing datasets and an MLLM-based dubbing model designed for diverse cinematic scenes. Using the pipeline, we construct the first Chinese television dubbing dataset with rich annotations, and demonstrate the high quality of these data. Experiments across monologue, narration, dialogue, and multi-speaker scenes show that our dubbing model consistently outperforms SOTA methods in audio quality, lip sync, timbre transfer, and instruction following. Code and demos are available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-47] M2I2HA: A Multi-modal Object Detection Method Based on Intra- and Inter-Modal Hypergraph Attention
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态目标检测中任务相关特征提取困难、跨模态对齐不精确以及模型难以建模高阶依赖关系的问题。现有方法如CNN受限于感受野和长程依赖捕捉能力,Transformer存在计算复杂度高且仅支持成对关联建模的局限,而状态空间模型(State Space Models, SSMs)因序列化处理破坏了二维空间拓扑结构,无法有效建模复杂高阶依赖。其解决方案的关键在于提出基于超图理论的多模态感知网络M2I2HA:通过Intra-Hypergraph Enhancement模块捕获单模态内全局多对多高阶关系,利用Inter-Hypergraph Fusion模块弥合不同模态间的配置与空间差异以实现精准跨模态对齐与融合,并引入M2-FullPAD模块实现自适应多层次特征融合,从而增强数据分布与网络内部信息流动,最终在多个公开数据集上达到多模态目标检测的最先进性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14776
作者: Xiaofan Yang,Yubin Liu,Wei Pan,Guoqing Chu,Junming Zhang,Jie Zhao,Zhuoqi Man,Xuanming Cao
机构: Harbin Institute of Technology (哈尔滨工业大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 43 pages, 13 figures
Abstract:Recent advances in multi-modal detection have significantly improved detection accuracy in challenging environments (e.g., low light, overexposure). By integrating RGB with modalities such as thermal and depth, multi-modal fusion increases data redundancy and system robustness. However, significant challenges remain in effectively extracting task-relevant information both within and across modalities, as well as in achieving precise cross-modal alignment. While CNNs excel at feature extraction, they are limited by constrained receptive fields, strong inductive biases, and difficulty in capturing long-range dependencies. Transformer-based models offer global context but suffer from quadratic computational complexity and are confined to pairwise correlation modeling. Mamba and other State Space Models (SSMs), on the other hand, are hindered by their sequential scanning mechanism, which flattens 2D spatial structures into 1D sequences, disrupting topological relationships and limiting the modeling of complex higher-order dependencies. To address these issues, we propose a multi-modal perception network based on hypergraph theory called M2I2HA. Our architecture includes an Intra-Hypergraph Enhancement module to capture global many-to-many high-order relationships within each modality, and an Inter-Hypergraph Fusion module to align, enhance, and fuse cross-modal features by bridging configuration and spatial gaps between data sources. We further introduce a M2-FullPAD module to enable adaptive multi-level fusion of multi-modal enhanced features within the network, meanwhile enhancing data distribution and flow across the architecture. Extensive object detection experiments on multiple public datasets against baselines demonstrate that M2I2HA achieves state-of-the-art performance in multi-modal object detection tasks.
zh
[CV-48] Does medical specialization of VLMs enhance discriminative power?: A comprehensive investigation through feature distribution analysis
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前医学视觉语言模型(Medical Vision-Language Models, VLMs)中特征表示机制不明确的问题,特别是其是否能够学习到具有诊断意义的、病变特异性的判别性特征。传统评估方法如分类准确率无法充分揭示模型对医学图像结构的理解深度。研究通过对比多个代表性医学VLM与非医学VLM在多模态病变分类数据集上的特征分布,发现医学VLM确实能提取有效的判别性特征;但关键突破在于指出:相较于大量医学图像训练,提升文本编码器能力(如借助大语言模型增强的上下文理解,例如LLM2CLIP)对优化特征表示更为重要。这表明未来医学VLM开发应更注重文本语义建模而非单纯增加医学图像数据量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14774
作者: Keita Takeda,Tomoya Sakai
机构: Nagasaki University (长崎大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: A short version paper of this research has been accepted for The IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2026
Abstract:This study investigates the feature representations produced by publicly available open source medical vision-language models (VLMs). While medical VLMs are expected to capture diagnostically relevant features, their learned representations remain underexplored, and standard evaluations like classification accuracy do not fully reveal if they acquire truly discriminative, lesion-specific features. Understanding these representations is crucial for revealing medical image structures and improving downstream tasks in medical image analysis. This study aims to investigate the feature distributions learned by medical VLMs and evaluate the impact of medical specialization. We analyze the feature distribution of multiple image modalities extracted by some representative medical VLMs across lesion classification datasets on multiple modalities. These distributions were compared them with non-medical VLMs to assess the domain-specific medical training. Our experiments showed that medical VLMs can extract discriminative features that are effective for medical classification tasks. Moreover, it was found that non-medical VLMs with recent improvement with contextual enrichment such as LLM2CLIP produce more refined feature representations. Our results imply that enhancing text encoder is more crucial than training intensively on medical images when developing medical VLMs. Notably, non-medical models are particularly vulnerable to biases introduced by overlaied text strings on images. These findings underscore the need for careful consideration on model selection according to downstream tasks besides potential risks in inference due to background biases such as textual information in images.
zh
[CV-49] Using Multi-Instance Learning to Identify Unique Polyps in Colon Capsule Endoscopy Images
【速读】:该论文旨在解决结肠胶囊内镜(Colon Capsule Endoscopy, CCE)图像中独特息肉(polyp)识别的问题,该任务因图像数据量大、临床医生认知负荷高以及特定帧标注模糊而具有挑战性。解决方案的关键在于将问题建模为多实例学习(Multi-Instance Learning, MIL)任务,并引入多实例验证(Multi-Instance Verification, MIV)框架,结合方差激励多头注意力(Variance-Excited Multi-Head Attention, VEMA)和基于距离的注意力(Distance-Based Attention, DBA)机制以增强特征表示能力;同时采用SimCLR自监督学习预训练策略生成鲁棒嵌入表示,显著提升了模型在754名患者共1912个息肉数据集上的识别准确率(最高达86.26%)与AUC值(0.928)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14771
作者: Puneet Sharma,Kristian Dalsbø Hindberg,Eibe Frank,Benedicte Schelde-Olesen,Ulrik Deding
机构: University of Tromsø (特罗姆斯大学); University of Waikato (怀卡托大学); Roskilde University (罗斯基勒大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 19 pages
Abstract:Identifying unique polyps in colon capsule endoscopy (CCE) images is a critical yet challenging task for medical personnel due to the large volume of images, the cognitive load it creates for clinicians, and the ambiguity in labeling specific frames. This paper formulates this problem as a multi-instance learning (MIL) task, where a query polyp image is compared with a target bag of images to determine uniqueness. We employ a multi-instance verification (MIV) framework that incorporates attention mechanisms, such as variance-excited multi-head attention (VEMA) and distance-based attention (DBA), to enhance the model’s ability to extract meaningful representations. Additionally, we investigate the impact of self-supervised learning using SimCLR to generate robust embeddings. Experimental results on a dataset of 1912 polyps from 754 patients demonstrate that attention mechanisms significantly improve performance, with DBA L1 achieving the highest test accuracy of 86.26% and a test AUC of 0.928 using a ConvNeXt backbone with SimCLR pretraining. This study underscores the potential of MIL and self-supervised learning in advancing automated analysis of Colon Capsule Endoscopy images, with implications for broader medical imaging applications.
zh
[CV-50] ReinPath: A Multimodal Reinforcement Learning Approach for Pathology
【速读】:该论文旨在解决计算病理学中多模态信息融合的可解释性不足问题,现有方法受限于缺乏高质量数据集以支持显式推理与简单推理任务。为应对这一挑战,作者提出了一种具备强推理能力的多模态病理学大语言模型(Multimodal Pathology Large Language Model),其关键创新在于设计了一种结合群体相对策略(group relative policy)的语义奖励机制,用于提升文本生成的准确性与上下文相关性;同时构建了一个专门面向复杂推理任务的高质量病理视觉问答(Visual Question Answering, VQA)数据集,实验证明该方法在该数据集上优于当前最先进模型,且在下游零样本图像分类任务中性能可媲美CLIP。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14757
作者: Kangcheng Zhou,Jun Jiang,Qing Zhang,Shuang Zheng,Qingli Li,Shugong Xu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Interpretability is significant in computational pathology, leading to the development of multimodal information integration from histopathological image and corresponding text this http URL, existing multimodal methods have limited interpretability due to the lack of high-quality dataset that support explicit reasoning and inference and simple reasoning this http URL address the above problems, we introduce a novel multimodal pathology large language model with strong reasoning this http URL improve the generation of accurate and contextually relevant textual descriptions, we design a semantic reward strategy integrated with group relative policy this http URL construct a high-quality pathology visual question answering (VQA) dataset, specifically designed to support complex reasoning this http URL experiments conducted on this dataset demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods, even when trained with only 20% of the this http URL method also achieves comparable performance on downstream zero-shot image classification task compared with CLIP.
zh
[CV-51] SimD3: A Synthetic drone Dataset with Payload and Bird Distractor Modeling for Robust Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决无人机检测(drone detection)在真实场景中面临的三大挑战:标注数据稀缺、目标外观变化大以及视觉上与鸟类等相似干扰物难以区分。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个大规模高保真度的合成数据集 SimD3,该数据集通过显式建模携带异构载荷的无人机、引入多种鸟类作为逼真的干扰物,并利用 Unreal Engine 5 构建多样化环境(含可控天气、光照和飞行轨迹),从而提升模型对复杂空域环境的鲁棒性。此外,研究还提出改进的 YOLOv5m+C3b 检测架构,在合成数据及多域真实测试集上均展现出优于基线的泛化性能,验证了 SimD3 在训练和评估鲁棒无人机检测模型中的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14742
作者: Ami Pandat,Kanyala Muvva,Punna Rajasekhar,Gopika Vinod,Rohit Shukla
机构: Homi Bhabha National Institute (霍米·巴巴国家研究所); Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (巴哈原子研究中心)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Reliable drone detection is challenging due to limited annotated real-world data, large appearance variability, and the presence of visually similar distractors such as birds. To address these challenges, this paper introduces SimD3, a large-scale high-fidelity synthetic dataset designed for robust drone detection in complex aerial environments. Unlike existing synthetic drone datasets, SimD3 explicitly models drones with heterogeneous payloads, incorporates multiple bird species as realistic distractors, and leverages diverse Unreal Engine 5 environments with controlled weather, lighting, and flight trajectories captured using a 360 six-camera rig. Using SimD3, we conduct an extensive experimental evaluation within the YOLOv5 detection framework, including an attention-enhanced variant termed Yolov5m+C3b, where standard bottleneck-based C3 blocks are replaced with C3b modules. Models are evaluated on synthetic data, combined synthetic and real data, and multiple unseen real-world benchmarks to assess robustness and generalization. Experimental results show that SimD3 provides effective supervision for small-object drone detection and that Yolov5m+C3b consistently outperforms the baseline across in-domain and cross-dataset evaluations. These findings highlight the utility of SimD3 for training and benchmarking robust drone detection models under diverse and challenging conditions.
zh
[CV-52] Enhancing Text-to-Image Generation via End-Edge Collaborative Hybrid Super-Resolution
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在资源受限的边缘计算环境下,实现高分辨率文本到图像(Text-to-Image, T2I)生成时面临的图像保真度与延迟之间的权衡问题。现有方法在边缘侧难以同时保证高质量输出和低延迟,尤其在高分辨率生成任务中表现不佳。解决方案的关键在于提出一种端边协同的生成-增强框架:首先在边缘侧基于自适应选择的去噪步数和超分辨率(Super-Resolution, SR)尺度生成低分辨率图像;随后采用区域感知的混合SR策略,对图像块进行差异化处理——对前景区域使用扩散模型进行细节恢复以提升保真度,对背景区域则使用轻量级学习模型实现高效上采样;最终将各区域增强结果拼接为完整高分辨率图像。该设计在保持图像质量的同时显著降低了服务延迟(相比基线减少33%)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14741
作者: Chongbin Yi,Yuxin Liang,Ziqi Zhou,Peng Yang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accpeted by ICC 2026
Abstract:Artificial Intelligence-Generated Content (AIGC) has made significant strides, with high-resolution text-to-image (T2I) generation becoming increasingly critical for improving users’ Quality of Experience (QoE). Although resource-constrained edge computing adequately supports fast low-resolution T2I generations, achieving high-resolution output still faces the challenge of ensuring image fidelity at the cost of latency. To address this, we first investigate the performance of super-resolution (SR) methods for image enhancement, confirming a fundamental trade-off that lightweight learning-based SR struggles to recover fine details, while diffusion-based SR achieves higher fidelity at a substantial computational cost. Motivated by these observations, we propose an end-edge collaborative generation-enhancement framework. Upon receiving a T2I generation task, the system first generates a low-resolution image based on adaptively selected denoising steps and super-resolution scales at the edge side, which is then partitioned into patches and processed by a region-aware hybrid SR policy. This policy applies a diffusion-based SR model to foreground patches for detail recovery and a lightweight learning-based SR model to background patches for efficient upscaling, ultimately stitching the enhanced ones into the high-resolution image. Experiments show that our system reduces service latency by 33% compared with baselines while maintaining competitive image quality.
zh
[CV-53] Safeguarding Facial Identity against Diffusion-based Face Swapping via Cascading Pathway Disruption
【速读】:该论文旨在解决扩散模型(diffusion models)在人脸交换(face swapping)应用中引发的隐私与身份安全问题,现有主动防御方法因忽视了人脸交换系统中固有的结构鲁棒性及静态条件引导机制而失效。其解决方案的关键在于提出VoidFace,一种将人脸交换视为耦合身份路径的系统性防御方法:通过在关键瓶颈处注入扰动,引发整个流程的级联破坏;具体包括两个层面——一是引入定位扰动和身份擦除以削弱物理回归与语义嵌入,从而破坏源人脸的准确建模;二是干预生成域,通过解耦注意力机制切断身份注入,并污染中间扩散特征以阻止源身份重建;同时借助潜空间中的对抗搜索与感知自适应策略,在保障视觉不可感知性的前提下最大化攻击效能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14738
作者: Liqin Wang,Qianyue Hu,Wei Lu,Xiangyang Luo
机构: Sun Yat-sen University (中山大学); Mathematical Engineering and Advanced Computing (数学工程与先进计算国家重点实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:The rapid evolution of diffusion models has democratized face swapping but also raises concerns about privacy and identity security. Existing proactive defenses, often adapted from image editing attacks, prove ineffective in this context. We attribute this failure to an oversight of the structural resilience and the unique static conditional guidance mechanism inherent in face swapping systems. To address this, we propose VoidFace, a systemic defense method that views face swapping as a coupled identity pathway. By injecting perturbations at critical bottlenecks, VoidFace induces cascading disruption throughout the pipeline. Specifically, we first introduce localization disruption and identity erasure to degrade physical regression and semantic embeddings, thereby impairing the accurate modeling of the source face. We then intervene in the generative domain by decoupling attention mechanisms to sever identity injection, and corrupting intermediate diffusion features to prevent the reconstruction of source identity. To ensure visual imperceptibility, we perform adversarial search in the latent manifold, guided by a perceptual adaptive strategy to balance attack potency with image quality. Extensive experiments show that VoidFace outperforms existing defenses across various diffusion-based swapping models, while producing adversarial faces with superior visual quality.
zh
[CV-54] Context Patch Fusion With Class Token Enhancement for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决弱监督语义分割(Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation, WSSS)中因仅依赖图像级标签而导致的局部表示不完整与分割精度受限问题,尤其关注图像块(patch)间复杂上下文依赖关系被忽视所引发的语义模糊和虚假激活。其解决方案的关键在于提出Context Patch Fusion with Class Token Enhancement (CPF-CTE)框架,核心创新包括:1)设计Contextual-Fusion Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (CF-BiLSTM)模块,通过双向信息流建模图像块间的空间依赖关系,增强特征表达的完整性;2)引入可学习类标记(class token),动态编码并优化类别特定语义,提升类别判别能力。该方法有效融合空间与语义线索,显著改善分割性能,在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上优于现有WSSS方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14718
作者: Yiyang Fu,Hui Li,Wangyu Wu
机构: Wuxi University (无锡大学); Xiamen University (厦门大学); University of Liverpool (利物浦大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS), which relies only on image-level labels, has attracted significant attention for its cost-effectiveness and scalability. Existing methods mainly enhance inter-class distinctions and employ data augmentation to mitigate semantic ambiguity and reduce spurious activations. However, they often neglect the complex contextual dependencies among image patches, resulting in incomplete local representations and limited segmentation accuracy. To address these issues, we propose the Context Patch Fusion with Class Token Enhancement (CPF-CTE) framework, which exploits contextual relations among patches to enrich feature representations and improve segmentation. At its core, the Contextual-Fusion Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (CF-BiLSTM) module captures spatial dependencies between patches and enables bidirectional information flow, yielding a more comprehensive understanding of spatial correlations. This strengthens feature learning and segmentation robustness. Moreover, we introduce learnable class tokens that dynamically encode and refine class-specific semantics, enhancing discriminative capability. By effectively integrating spatial and semantic cues, CPF-CTE produces richer and more accurate representations of image content. Extensive experiments on PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 validate that CPF-CTE consistently surpasses prior WSSS methods.
zh
[CV-55] LookBench: A Live and Holistic Open Benchmark for Fashion Image Retrieval
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前时尚图像检索(Fashion Image Retrieval)评估中缺乏真实场景覆盖、动态更新机制缺失以及任务复杂度不足的问题。现有基准多基于静态数据集,难以反映电商平台中商品图像的实时变化与多样化检索需求(如单件物品、成套搭配的跨模态匹配),且未考虑模型训练数据与测试数据的时间隔离(contamination),导致评估结果不可靠。解决方案的关键在于构建一个名为LookBench的活体、整体性且具有挑战性的基准:其包含来自真实电商网站的近期商品图像与AI生成图像,每条测试样本均带时间戳以支持污染感知评估;同时基于细粒度属性分类体系,覆盖单件和穿搭级检索任务,并设计半定期更新机制与逐步增强的任务变体,从而提供持续可比的性能衡量标准。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14706
作者: Chao Gao,Siqiao Xue,Yimin Peng,Jiwen Fu,Tingyi Gu,Shanshan Li,Fan Zhou
机构: Gensmo.ai
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: The first two authors contributed equally to this work. Project site: this https URL
Abstract:In this paper, we present LookBench (We use the term “look” to reflect retrieval that mirrors how people shop – finding the exact item, a close substitute, or a visually consistent alternative.), a live, holistic and challenging benchmark for fashion image retrieval in real e-commerce settings. LookBench includes both recent product images sourced from live websites and AI-generated fashion images, reflecting contemporary trends and use cases. Each test sample is time-stamped and we intend to update the benchmark periodically, enabling contamination-aware evaluation aligned with declared training cutoffs. Grounded in our fine-grained attribute taxonomy, LookBench covers single-item and outfit-level retrieval across. Our experiments reveal that LookBench poses a significant challenge on strong baselines, with many models achieving below 60% Recall@1. Our proprietary model achieves the best performance on LookBench, and we release an open-source counterpart that ranks second, with both models attaining state-of-the-art results on legacy Fashion200K evaluations. LookBench is designed to be updated semi-annually with new test samples and progressively harder task variants, providing a durable measure of progress. We publicly release our leaderboard, dataset, evaluation code, and trained models.
zh
[CV-56] RegFreeNet: A Registration-Free Network for CBCT-based 3D Dental Implant Planning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有牙科种植体(dental implant)位置标注依赖于术前-术后CBCT配准(registration)的问题,该过程不仅耗时且对配准算法精度高度敏感,同时受限于多中心医院缺乏配对CBCT数据,难以构建大规模训练集。其解决方案的关键在于提出“无注册”(RegFree)范式:通过在术后CBCT中掩码(mask)种植体区域,利用邻近牙齿纹理信息进行位置预测,从而无需配准即可直接使用任意含种植体的CBCT作为训练样本。这一方法使大规模多中心数据集构建成为可能,并在此基础上提出了包含1622例CBCT的公开数据集ImplantFairy及一种坡度感知(slope-aware)的种植体位置预测网络RegFreeNet,其中引入邻域距离感知(NDP)模块提取牙齿结构变化特征,并设计植入体斜率预测分支以增强模型鲁棒性,最终在多个数据集上达到当前最优性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14703
作者: Xinquan Yang,Xuguang Li,Mianjie Zheng,Xuefen Liu,Kun Tang,Kian Ming Lim,He Meng,Jianfeng Ren,Linlin Shen
机构: 1. University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学); 2. Alibaba Group (阿里巴巴集团); 3. Tsinghua University (清华大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:As the commercial surgical guide design software usually does not support the export of implant position for pre-implantation data, existing methods have to scan the post-implantation data and map the implant to pre-implantation space to get the label of implant position for training. Such a process is time-consuming and heavily relies on the accuracy of registration algorithm. Moreover, not all hospitals have paired CBCT data, limitting the construction of multi-center dataset. Inspired by the way dentists determine the implant position based on the neighboring tooth texture, we found that even if the implant area is masked, it will not affect the determination of the implant position. Therefore, we propose to mask the implants in the post-implantation data so that any CBCT containing the implants can be used as training data. This paradigm enables us to discard the registration process and makes it possible to construct a large-scale multi-center implant dataset. On this basis, we proposes ImplantFairy, a comprehensive, publicly accessible dental implant dataset with voxel-level 3D annotations of 1622 CBCT data. Furthermore, according to the area variation characteristics of the tooth’s spatial structure and the slope information of the implant, we designed a slope-aware implant position prediction network. Specifically, a neighboring distance perception (NDP) module is designed to adaptively extract tooth area variation features, and an implant slope prediction branch assists the network in learning more robust features through additional implant supervision information. Extensive experiments conducted on ImplantFairy and two public dataset demonstrate that the proposed RegFreeNet achieves the state-of-the-art performance.
zh
[CV-57] AutoDriDM: An Explainable Benchmark for Decision-Making of Vision-Language Models in Autonomous Driving ACL
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前自动驾驶评估基准过度侧重感知能力而忽视决策过程的问题,导致现有视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在真实复杂场景中的决策可靠性难以被有效衡量。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个以决策为中心、分阶段推进的基准测试框架 AutoDriDM,包含6,650个问题,覆盖对象(Object)、场景(Scene)和决策(Decision)三个维度,并通过相关性分析揭示感知与决策性能之间的弱关联性;同时引入可解释性分析和自动化标注器模型,识别关键失败模式(如逻辑推理错误),从而系统性地推动VLM在自动驾驶任务中从感知到决策能力的提升,为构建更安全可靠的生成式AI(Generative AI)决策系统提供实证依据与方法支持。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14702
作者: Zecong Tang,Zixu Wang,Yifei Wang,Weitong Lian,Tianjian Gao,Haoran Li,Tengju Ru,Lingyi Meng,Zhejun Cui,Yichen Zhu,Qi Kang,Kaixuan Wang,Yu Zhang
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); The University of Hong Kong (香港大学)
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注: 23 pages. Submitted to ACL ARR 2026 January
Abstract:Autonomous driving is a highly challenging domain that requires reliable perception and safe decision-making in complex scenarios. Recent vision-language models (VLMs) demonstrate reasoning and generalization abilities, opening new possibilities for autonomous driving; however, existing benchmarks and metrics overemphasize perceptual competence and fail to adequately assess decision-making processes. In this work, we present AutoDriDM, a decision-centric, progressive benchmark with 6,650 questions across three dimensions - Object, Scene, and Decision. We evaluate mainstream VLMs to delineate the perception-to-decision capability boundary in autonomous driving, and our correlation analysis reveals weak alignment between perception and decision-making performance. We further conduct explainability analyses of models’ reasoning processes, identifying key failure modes such as logical reasoning errors, and introduce an analyzer model to automate large-scale annotation. AutoDriDM bridges the gap between perception-centered and decision-centered evaluation, providing guidance toward safer and more reliable VLMs for real-world autonomous driving.
zh
[CV-58] FeedbackSTS-Det: Sparse Frames-Based Spatio-Temporal Semantic Feedback Network for Infrared Small Target Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决复杂背景下红外小目标检测(Infrared Small Target Detection, ISTD)中因信杂比极低、动态干扰持续存在以及目标特征不显著所导致的检测困难问题。现有基于多帧的方法虽利用时序信息提升性能,但仍面临长距离依赖建模效率低和鲁棒性不足的挑战。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于稀疏帧的时空语义反馈网络(FeedbackSTS-Det),其核心是引入闭环语义关联机制的时空语义反馈策略,包含编码器与解码器间协同工作的前向与反向精炼模块,并嵌入结构化稀疏时序建模模块(Sparse Semantic Module, SSM),以低计算成本捕获长程依赖关系,从而实现鲁棒的隐式跨帧配准和连续语义优化,有效抑制虚警。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14690
作者: Yian Huang,Qing Qin,Aji Mao,Xiangyu Qiu,Liang Xu,Xian Zhang,Zhenming Peng
机构: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (电子科技大学); Communication University of Zhejiang (浙江传媒学院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Submitted to Journal IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing
Abstract:Infrared small target detection (ISTD) under complex backgrounds remains a critical yet challenging task, primarily due to the extremely low signal-to-clutter ratio, persistent dynamic interference, and the lack of distinct target features. While multi-frame detection methods leverages temporal cues to improve upon single-frame approaches, existing methods still struggle with inefficient long-range dependency modeling and insufficient robustness. To overcome these issues, we propose a novel scheme for ISTD, realized through a sparse frames-based spatio-temporal semantic feedback network named FeedbackSTS-Det. The core of our approach is a novel spatio-temporal semantic feedback strategy with a closed-loop semantic association mechanism, which consists of paired forward and backward refinement modules that work cooperatively across the encoder and decoder. Moreover, both modules incorporate an embedded sparse semantic module (SSM), which performs structured sparse temporal modeling to capture long-range dependencies with low computational cost. This integrated design facilitates robust implicit inter-frame registration and continuous semantic refinement, effectively suppressing false alarms. Furthermore, our overall procedure maintains a consistent training-inference pipeline, which ensures reliable performance transfer and increases model robustness. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets confirm the effectiveness of FeedbackSTS-Det. Code and models are available at: this https URL.
zh
[CV-59] ransfer Learning from One Cancer to Another via Deep Learning Domain Adaptation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决监督式深度学习模型在跨域分类任务中泛化能力不足的问题,特别是在癌症组织病理学图像分析中,模型在训练数据分布内表现优异,但在面对未见癌种(如不同器官来源的腺癌)时性能显著下降。其关键解决方案是采用领域自适应(domain adaptation)策略,具体通过构建领域对抗神经网络(Domain Adversarial Neural Network, DANN),将来自源域(如乳腺和结肠腺癌)的标注数据迁移到目标域(如肺腺癌)的无标注数据上,从而有效缓解因染色差异和组织形态变化导致的域偏移问题。实验表明,DANN显著提升了跨域分类准确率,并且通过集成梯度(Integrated Gradients)可视化验证了模型对生物医学意义区域(如密集核群)的关注,说明其学习到的是临床可解释的特征表示。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14678
作者: Justin Cheung,Samuel Savine,Calvin Nguyen,Lin Lu,Alhassan S. Yasin
机构: Johns Hopkins University (约翰霍普金斯大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE); Tissues and Organs (q-bio.TO)
备注: 8 pages, 6 figures, 3 table
Abstract:Supervised deep learning models often achieve excellent performance within their training distribution but struggle to generalize beyond it. In cancer histopathology, for example, a convolutional neural network (CNN) may classify cancer severity accurately for cancer types represented in its training data, yet fail on related but unseen types. Although adenocarcinomas from different organs share morphological features that might support limited cross-domain generalization, addressing domain shift directly is necessary for robust performance. Domain adaptation offers a way to transfer knowledge from labeled data in one cancer type to unlabeled data in another, helping mitigate the scarcity of annotated medical images. This work evaluates cross-domain classification performance among lung, colon, breast, and kidney adenocarcinomas. A ResNet50 trained on any single adenocarcinoma achieves over 98% accuracy on its own domain but shows minimal generalization to others. Ensembling multiple supervised models does not resolve this limitation. In contrast, converting the ResNet50 into a domain adversarial neural network (DANN) substantially improves performance on unlabeled target domains. A DANN trained on labeled breast and colon data and adapted to unlabeled lung data reaches 95.56% accuracy. We also examine the impact of stain normalization on domain adaptation. Its effects vary by target domain: for lung, accuracy drops from 95.56% to 66.60%, while for breast and colon targets, stain normalization boosts accuracy from 49.22% to 81.29% and from 78.48% to 83.36%, respectively. Finally, using Integrated Gradients reveals that DANNs consistently attribute importance to biologically meaningful regions such as densely packed nuclei, indicating that the model learns clinically relevant features and can apply them to unlabeled cancer types. Comments: 8 pages, 6 figures, 3 table Subjects: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE); Tissues and Organs (q-bio.TO) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14678 [cs.CV] (or arXiv:2601.14678v1 [cs.CV] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14678 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[CV-60] A comprehensive overview of deep learning models for object detection from videos/images
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视频与图像监控场景中语义目标检测(semantic object detection)的准确性与鲁棒性问题,尤其针对动态环境、遮挡、光照变化及实时性要求等实际挑战。其解决方案的关键在于系统性地梳理和分类现代检测方法,聚焦于三大核心技术路径:一是基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的检测架构创新;二是生成式模型(如GAN)在缺失帧重建、遮挡缓解和光照归一化中的集成应用;三是利用时序信息进行时空融合以提升检测性能。通过对比分析主流数据集、预处理流程与特征提取进展,论文进一步指出了低延迟、高效率的时空学习方法作为未来研究方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14677
作者: Sukana Zulfqar,Sadia Saeed,M. Azam Zia,Anjum Ali,Faisal Mehmood,Abid Ali
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: N/A
Abstract:Object detection in video and image surveillance is a well-established yet rapidly evolving task, strongly influenced by recent deep learning advancements. This review summarises modern techniques by examining architectural innovations, generative model integration, and the use of temporal information to enhance robustness and accuracy. Unlike earlier surveys, it classifies methods based on core architectures, data processing strategies, and surveillance specific challenges such as dynamic environments, occlusions, lighting variations, and real-time requirements. The primary goal is to evaluate the current effectiveness of semantic object detection, while secondary aims include analysing deep learning models and their practical applications. The review covers CNN-based detectors, GAN-assisted approaches, and temporal fusion methods, highlighting how generative models support tasks such as reconstructing missing frames, reducing occlusions, and normalising illumination. It also outlines preprocessing pipelines, feature extraction progress, benchmarking datasets, and comparative evaluations. Finally, emerging trends in low-latency, efficient, and spatiotemporal learning approaches are identified for future research.
zh
[CV-61] LaVR: Scene Latent Conditioned Generative Video Trajectory Re-Rendering using Large 4D Reconstruction Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决单目视频重渲染(video re-rendering)任务中现有方法面临的两大挑战:一是几何无条件模型缺乏空间感知能力,导致视角变化时出现漂移和形变;二是几何有条件模型依赖估计的深度图和显式重建,易受深度误差和标定偏差影响。其解决方案的关键在于利用大规模4D重建模型潜在空间(latent space)中嵌入的隐式几何知识来条件化视频生成过程,该潜在表示在连续空间中捕捉场景结构而无需显式重建,从而为预训练扩散先验提供更灵活且具正则化能力的约束,最终通过联合条件化潜在表示与源相机位姿实现最优的重渲染效果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14674
作者: Mingyang Xie,Numair Khan,Tianfu Wang,Naina Dhingra,Seonghyeon Nam,Haitao Yang,Zhuo Hui,Christopher Metzler,Andrea Vedaldi,Hamed Pirsiavash,Lei Luo
机构: Meta Reality Labs (Meta); University of Maryland (马里兰大学); University of Oxford (牛津大学); UC Davis (加州大学戴维斯分校)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Given a monocular video, the goal of video re-rendering is to generate views of the scene from a novel camera trajectory. Existing methods face two distinct challenges. Geometrically unconditioned models lack spatial awareness, leading to drift and deformation under viewpoint changes. On the other hand, geometrically-conditioned models depend on estimated depth and explicit reconstruction, making them susceptible to depth inaccuracies and calibration errors. We propose to address these challenges by using the implicit geometric knowledge embedded in the latent space of a large 4D reconstruction model to condition the video generation process. These latents capture scene structure in a continuous space without explicit reconstruction. Therefore, they provide a flexible representation that allows the pretrained diffusion prior to regularize errors more effectively. By jointly conditioning on these latents and source camera poses, we demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art results on the video re-rendering task. Project webpage is this https URL Subjects: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14674 [cs.CV] (or arXiv:2601.14674v1 [cs.CV] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14674 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[CV-62] Mirai: Autoregressive Visual Generation Needs Foresight
【速读】:该论文旨在解决自回归视觉生成模型(Autoregressive Visual Generators)在训练过程中因严格因果性监督导致的全局一致性差和收敛速度慢的问题。其核心解决方案在于引入“ foresight”(前瞻性信息),即利用来自未来 token 的训练信号来增强模型对图像结构的理解,从而改善因果建模。关键创新是提出 Mirai 框架,通过将未来信息注入训练过程而不改变网络架构且无额外推理开销:Mirai-E 使用单向表示中显式的多位置未来信息,Mirai-I 则利用双向表示中隐式的匹配未来信息,二者均显著加速收敛并提升生成质量(如在 ImageNet 类条件生成任务上将 LlamaGen-B 的 FID 从 5.34 降至 4.34)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14671
作者: Yonghao Yu,Lang Huang,Zerun Wang,Runyi Li,Toshihiko Yamasaki
机构: The University of Tokyo (东京大学); National Institute of Informatics (信息研究所); Peking University (北京大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) visual generators model images as sequences of discrete tokens and are trained with next token likelihood. This strict causality supervision optimizes each step only by its immediate next token, which diminishes global coherence and slows convergence. We ask whether foresight, training signals that originate from later tokens, can help AR visual generation. We conduct a series of controlled diagnostics along the injection level, foresight layout, and foresight source axes, unveiling a key insight: aligning foresight to AR models’ internal representation on the 2D image grids improves causality modeling. We formulate this insight with Mirai (meaning “future” in Japanese), a general framework that injects future information into AR training with no architecture change and no extra inference overhead: Mirai-E uses explicit foresight from multiple future positions of unidirectional representations, whereas Mirai-I leverages implicit foresight from matched bidirectional representations. Extensive experiments show that Mirai significantly accelerates convergence and improves generation quality. For instance, Mirai can speed up LlamaGen-B’s convergence by up to 10 \times and reduce the generation FID from 5.34 to 4.34 on the ImageNet class-condition image generation benchmark. Our study highlights that visual autoregressive models need foresight.
zh
[CV-63] READ-Net: Clarifying Emotional Ambiguity via Adaptive Feature Recalibration for Audio-Visual Depression Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决音频-视觉抑郁检测中因情绪模糊(Emotional Ambiguity)导致的特征混淆问题,即现有方法在处理情感线索时,常将短暂的情绪表达误判为稳定的抑郁症状,从而影响检测准确性。解决方案的关键在于提出READ-Net框架,其核心创新是自适应特征重校准(Adaptive Feature Recalibration, AFR)机制——通过动态调整情感特征的权重,识别并保留与抑郁相关的信号,同时自适应过滤无关的情感噪声,从而显著提升特征表示的清晰度与鲁棒性,有效缓解情绪干扰对抑郁检测的影响。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14651
作者: Chenglizhao Chen,Boze Li,Mengke Song,Dehao Feng,Xinyu Liu,Shanchen Pang,Jufeng Yang,Hui Yu
机构: China University of Petroleum (East China); Nankai University; University of Glasgow
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Multimedia (cs.MM); Sound (cs.SD)
备注: 12 pages
Abstract:Depression is a severe global mental health issue that impairs daily functioning and overall quality of life. Although recent audio-visual approaches have improved automatic depression detection, methods that ignore emotional cues often fail to capture subtle depressive signals hidden within emotional expressions. Conversely, those incorporating emotions frequently confuse transient emotional expressions with stable depressive symptoms in feature representations, a phenomenon termed \emphEmotional Ambiguity, thereby leading to detection errors. To address this critical issue, we propose READ-Net, the first audio-visual depression detection framework explicitly designed to resolve Emotional Ambiguity through Adaptive Feature Recalibration (AFR). The core insight of AFR is to dynamically adjust the weights of emotional features to enhance depression-related signals. Rather than merely overlooking or naively combining emotional information, READ-Net innovatively identifies and preserves depressive-relevant cues within emotional features, while adaptively filtering out irrelevant emotional noise. This recalibration strategy significantly clarifies feature representations, and effectively mitigates the persistent challenge of emotional interference. Additionally, READ-Net can be easily integrated into existing frameworks for improved performance. Extensive evaluations on three publicly available datasets show that READ-Net outperforms state-of-the-art methods, with average gains of 4.55% in accuracy and 1.26% in F1-score, demonstrating its robustness to emotional disturbances and improving audio-visual depression detection.
zh
[CV-64] Diffusion Epistemic Uncertainty with Asymmetric Learning for Diffusion-Generated Image Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决扩散模型生成图像的检测问题,特别是针对现有方法在处理由数据固有噪声(aleatoric uncertainty)和模型知识不足(epistemic uncertainty)导致的重建误差时缺乏区分能力,从而影响检测性能的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为Diffusion Epistemic Uncertainty with Asymmetric Learning (DEUA) 的新框架:首先通过拉普拉斯近似(Laplace approximation)估计扩散模型中的epistemic uncertainty(DEU),以衡量输入数据与扩散生成样本流形的接近程度;其次引入不对称损失函数(asymmetric loss function),训练出具有更大分类边界、更优泛化能力的平衡分类器,从而显著提升对扩散生成图像的检测准确性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14625
作者: Yingsong Huang,Hui Guo,Jing Huang,Bing Bai,Qi Xiong
机构: Tencent Inc.(腾讯公司); Hikvision(海康威视); Microsoft MAI(微软MAI)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
备注:
Abstract:The rapid progress of diffusion models highlights the growing need for detecting generated images. Previous research demonstrates that incorporating diffusion-based measurements, such as reconstruction error, can enhance the generalizability of detectors. However, ignoring the differing impacts of aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty on reconstruction error can undermine detection performance. Aleatoric uncertainty, arising from inherent data noise, creates ambiguity that impedes accurate detection of generated images. As it reflects random variations within the data (e.g., noise in natural textures), it does not help distinguish generated images. In contrast, epistemic uncertainty, which represents the model’s lack of knowledge about unfamiliar patterns, supports detection. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, Diffusion Epistemic Uncertainty with Asymmetric Learning~(DEUA), for detecting diffusion-generated images. We introduce Diffusion Epistemic Uncertainty~(DEU) estimation via the Laplace approximation to assess the proximity of data to the manifold of diffusion-generated samples. Additionally, an asymmetric loss function is introduced to train a balanced classifier with larger margins, further enhancing generalizability. Extensive experiments on large-scale benchmarks validate the state-of-the-art performance of our method.
zh
[CV-65] Learning Consistent Taxonomic Classification through Hierarchical Reasoning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在分类任务中对层级知识(hierarchical knowledge)理解不足的问题,即模型虽能准确识别物种的最具体类别(leaf level),却常在更粗粒度的分类层级上出现错误,导致分类结果在层次结构上不一致。解决方案的关键在于提出VL-Taxon框架,该框架采用两阶段的层次推理机制:第一阶段通过自顶向下的策略提升叶级分类准确性;第二阶段利用第一阶段的精准输出,确保整个分类层级的一致性。两个阶段均先通过监督微调注入分类学知识,再通过强化学习优化推理与泛化能力,最终在iNaturalist-2021数据集上实现了显著性能提升,且仅需少量标注数据即可达成优于原始72B模型的效果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14610
作者: Zhenghong Li,Kecheng Zheng,Haibin Ling
机构: Stony Brook University (石溪大学); Ant Research (蚂蚁研究)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 12 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) excel at visual understanding, they often fail to grasp hierarchical knowledge. This leads to common errors where VLMs misclassify coarser taxonomic levels even when correctly identifying the most specific level (leaf level). Existing approaches largely overlook this issue by failing to model hierarchical reasoning. To address this gap, we propose VL-Taxon, a two-stage, hierarchy-based reasoning framework designed to improve both leaf-level accuracy and hierarchical consistency in taxonomic classification. The first stage employs a top-down process to enhance leaf-level classification accuracy. The second stage then leverages this accurate leaf-level output to ensure consistency throughout the entire taxonomic hierarchy. Each stage is initially trained with supervised fine-tuning to instill taxonomy knowledge, followed by reinforcement learning to refine the model’s reasoning and generalization capabilities. Extensive experiments reveal a remarkable result: our VL-Taxon framework, implemented on the Qwen2.5-VL-7B model, outperforms its original 72B counterpart by over 10% in both leaf-level and hierarchical consistency accuracy on average on the iNaturalist-2021 dataset. Notably, this significant gain was achieved by fine-tuning on just a small subset of data, without relying on any examples generated by other VLMs.
zh
[CV-66] U-Harmony: Enhancing Joint Training for Segmentation Models with Universal Harmonization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决临床实践中医学图像分割数据集普遍存在的局限性与异质性问题,即不同机构间存在成像模态(imaging modality)、扫描协议(scan protocol)和解剖目标(anatomical target)的差异,导致现有深度学习模型难以同时从多样化数据中联合学习,常需在泛化能力与领域特异性知识之间权衡。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为Universal Harmonization (U-Harmony) 的联合训练方法,其可嵌入具备域门控头(domain-gated head)的深度学习架构中,通过序列化地对特征分布进行归一化与反归一化处理,在抑制域间差异的同时保留原始数据集特有的知识,从而实现单一模型对异构数据的高效学习;此外,该框架还支持通用模态适配(universal modality adaptation),使模型能够无缝学习新的成像模态和解剖类别,显著提升3D医学图像分割模型在真实临床场景中的鲁棒性与适应性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14605
作者: Weiwei Ma,Xiaobing Yu,Peijie Qiu,Jin Yang,Pan Xiao,Xiaoqi Zhao,Xiaofeng Liu,Tomo Miyazaki,Shinichiro Omachi,Yongsong Huang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:In clinical practice, medical segmentation datasets are often limited and heterogeneous, with variations in modalities, protocols, and anatomical targets across institutions. Existing deep learning models struggle to jointly learn from such diverse data, often sacrificing either generalization or domain-specific knowledge. To overcome these challenges, we propose a joint training method called Universal Harmonization (U-Harmony), which can be integrated into deep learning-based architectures with a domain-gated head, enabling a single segmentation model to learn from heterogeneous datasets simultaneously. By integrating U-Harmony, our approach sequentially normalizes and then denormalizes feature distributions to mitigate domain-specific variations while preserving original dataset-specific knowledge. More appealingly, our framework also supports universal modality adaptation, allowing the seamless learning of new imaging modalities and anatomical classes. Extensive experiments on cross-institutional brain lesion datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, establishing a new benchmark for robust and adaptable 3D medical image segmentation models in real-world clinical settings.
zh
[CV-67] 3D Space as a Scratchpad for Editable Text-to-Image Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉语言模型(Visual Language Models, VLMs)在空间推理能力上的不足,尤其是其在生成图像时难以准确表达几何关系、物体身份和组合意图的问题。现有方法多依赖于2D布局规划,缺乏对3D空间结构的显式建模,导致生成结果在空间一致性与可控性方面受限。解决方案的关键在于引入“空间草稿板”(spatial scratchpad)——一种基于3D的推理基底,通过将文本提示中的主体与背景元素解析为可编辑的3D网格,并利用代理式场景规划进行位置、朝向和视角选择,最终将3D场景渲染回图像域并保留语义一致性,从而实现更精确、可控的图像生成。该方法显著提升了文本对齐度(GenAI-Bench上提升32%),标志着VLM从语言推理迈向空间推理的新范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14602
作者: Oindrila Saha,Vojtech Krs,Radomir Mech,Subhransu Maji,Matheus Gadelha,Kevin Blackburn-Matzen
机构: University of Massachusetts Amherst (马萨诸塞大学阿默斯特分校); Adobe Research (Adobe 研究院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Recent progress in large language models (LLMs) has shown that reasoning improves when intermediate thoughts are externalized into explicit workspaces, such as chain-of-thought traces or tool-augmented reasoning. Yet, visual language models (VLMs) lack an analogous mechanism for spatial reasoning, limiting their ability to generate images that accurately reflect geometric relations, object identities, and compositional intent. We introduce the concept of a spatial scratchpad – a 3D reasoning substrate that bridges linguistic intent and image synthesis. Given a text prompt, our framework parses subjects and background elements, instantiates them as editable 3D meshes, and employs agentic scene planning for placement, orientation, and viewpoint selection. The resulting 3D arrangement is rendered back into the image domain with identity-preserving cues, enabling the VLM to generate spatially consistent and visually coherent outputs. Unlike prior 2D layout-based methods, our approach supports intuitive 3D edits that propagate reliably into final images. Empirically, it achieves a 32% improvement in text alignment on GenAI-Bench, demonstrating the benefit of explicit 3D reasoning for precise, controllable image generation. Our results highlight a new paradigm for vision-language models that deliberate not only in language, but also in space. Code and visualizations at this https URL
zh
[CV-68] LFS: Learnable Frame Selector for Event-Aware and Temporally Diverse Video Captioning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视频字幕生成模型中因均匀采样导致的时空覆盖不均与事件相关性不足的问题,即传统方法对所有帧进行编码成本过高,而均匀采样无法适应视频中事件分布不均的特性。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种可学习的帧选择器(Learnable Frame Selector, LFS),该模块通过显式建模帧的时间重要性,在保证时间多样性的同时提升事件相关性,并采用分层策略避免帧聚集;更重要的是,LFS利用冻结的视频-大语言模型(video-LLM)生成的字幕反馈来优化帧选择过程,从而直接提升下游字幕质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14594
作者: Lianying Chao,Linfeng Yin,Peiyu Ren,Yifan Jiang,Qiaoyu Ren,Dingcheng Shan,Jing-cheng Pang,Sijie Wu,Xubin Li,Kai Zhang
机构: Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. (华为技术有限公司)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Video captioning models convert frames into visual tokens and generate descriptions with large language models (LLMs). Since encoding all frames is prohibitively expensive, uniform sampling is the default choice, but it enforces equal temporal coverage while ignoring the uneven events distribution. This motivates a Learnable Frame Selector (LFS) that selects temporally diverse and event-relevant frames. LFS explicitly models temporal importance to balance temporal diversity and event relevance, and employs a stratified strategy to ensure temporal coverage while avoiding clustering. Crucially, LFS leverages caption feedback from frozen video-LLMs to learn frame selection that directly optimizes downstream caption quality. Additionally, we identify the gap between existing benchmark and human’s cognition. Thus, we introduce ICH-CC built from carefully designed questions by annotators that reflect human-consistent understanding of video. Experiments indicate that LFS consistently improves detailed video captioning across two representative community benchmarks and ICH-CC, achieving up to 2.0% gains on VDC and over 4% gains on ICH-CC. Moreover, we observe that enhanced captions with LFS leads to improved performance on video question answering. Overall, LFS provides an effective and easy-to-integrate solution for detailed video captioning.
zh
[CV-69] From Volumes to Slices: Computationally Efficient Contrastive Learning for Sequential Abdominal CT Analysis
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学图像分析中深度学习模型对专家标注数据高度依赖的问题,尤其是在腹部创伤CT图像分类任务中,标注数据稀缺严重限制了模型性能。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种高效的2D-VoCo方法,该方法基于体积对比学习(Volume Contrastive Learning, VoCo)框架的改进版本,通过在未标注的二维CT切片上进行对比学习,实现对空间-语义特征的有效预训练;随后将预训练的卷积神经网络(CNN)骨干网络集成到CNN-LSTM架构中,用于多器官损伤的分类任务,从而显著提升模型在RSNA 2023腹部创伤数据集上的mAP、精确率、召回率及RSNA评分,有效降低了对标注数据的依赖并增强了临床CT分析的性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14593
作者: Po-Kai Chiu,Hung-Hsuan Chen
机构: National Central University (国立中央大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:The requirement for expert annotations limits the effectiveness of deep learning for medical image analysis. Although 3D self-supervised methods like volume contrast learning (VoCo) are powerful and partially address the labeling scarcity issue, their high computational cost and memory consumption are barriers. We propose 2D-VoCo, an efficient adaptation of the VoCo framework for slice-level self-supervised pre-training that learns spatial-semantic features from unlabeled 2D CT slices via contrastive learning. The pre-trained CNN backbone is then integrated into a CNN-LSTM architecture to classify multi-organ injuries. In the RSNA 2023 Abdominal Trauma dataset, 2D-VoCo pre-training significantly improves mAP, precision, recall, and RSNA score over training from scratch. Our framework provides a practical method to reduce the dependency on labeled data and enhance model performance in clinical CT analysis. We release the code for reproducibility. this https URL
zh
[CV-70] Anatomically Guided Latent Diffusion for Brain MRI Progression Modeling
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有纵向脑部磁共振成像(MRI)进展建模方法在架构复杂性、临床协变量利用效率不足以及解剖一致性保障有限等方面的挑战。其核心解决方案是提出一种解剖引导的潜在扩散模型(Anatomically Guided Latent Diffusion Model, AG-LDM),关键在于通过在输入层直接融合基线解剖结构、噪声随访状态和临床协变量,实现无需辅助控制网络的端到端学习,从而简化训练流程并提升模型对解剖一致性的约束;同时引入轻量级3D组织分割模型(WarpSeg)提供显式解剖监督,确保生成图像中脑组织边界与形态学保真度,显著增强对时间动态和临床信息的敏感性(最高达BrLP的31.5倍),并生成符合阿尔茨海默病病理特征的生物合理反事实轨迹。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14584
作者: Cheng Wan,Bahram Jafrasteh,Ehsan Adeli,Miaomiao Zhang,Qingyu Zhao
机构: Cornell University (康奈尔大学); Weill Cornell Medicine (威尔康奈尔医学院); Stanford University (斯坦福大学); University of Virginia (弗吉尼亚大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 10 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables
Abstract:Accurately modeling longitudinal brain MRI progression is crucial for understanding neurodegenerative diseases and predicting individualized structural changes. Existing state-of-the-art approaches, such as Brain Latent Progression (BrLP), often use multi-stage training pipelines with auxiliary conditioning modules but suffer from architectural complexity, suboptimal use of conditional clinical covariates, and limited guarantees of anatomical consistency. We propose Anatomically Guided Latent Diffusion Model (AG-LDM), a segmentation-guided framework that enforces anatomically consistent progression while substantially simplifying the training pipeline. AG-LDM conditions latent diffusion by directly fusing baseline anatomy, noisy follow-up states, and clinical covariates at the input level, a strategy that avoids auxiliary control networks by learning a unified, end-to-end model that represents both anatomy and progression. A lightweight 3D tissue segmentation model (WarpSeg) provides explicit anatomical supervision during both autoencoder fine-tuning and diffusion model training, ensuring consistent brain tissue boundaries and morphometric fidelity. Experiments on 31,713 ADNI longitudinal pairs and zero-shot evaluation on OASIS-3 demonstrate that AG-LDM matches or surpasses more complex diffusion models, achieving state-of-the-art image quality and 15-20% reduction in volumetric errors in generated images. AG-LDM also exhibits markedly stronger utilization of temporal and clinical covariates (up to 31.5x higher sensitivity than BrLP) and generates biologically plausible counterfactual trajectories, accurately capturing hallmarks of Alzheimer’s progression such as limbic atrophy and ventricular expansion. These results highlight AG-LDM as an efficient, anatomically grounded framework for reliable brain MRI progression modeling.
zh
[CV-71] Breaking the accuracy-resource dilemma: a lightweight adaptive video inference enhancement
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有视频推理(Video Inference, VI)增强方法在追求性能提升时忽视资源效率与推理效果之间权衡的问题,导致资源利用不充分和推理性能欠佳。其解决方案的关键在于设计了一个基于关键系统参数和推理相关指标的模糊控制器(Fuzzy Controller, FC-r),并据此提出一种动态模型切换的VI增强框架:该框架通过挖掘相邻视频帧间目标的时空相关性,在实时感知目标设备资源状况的基础上,灵活选择不同规模的模型进行推理,从而实现资源利用率与推理性能之间的高效平衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14568
作者: Wei Ma,Shaowu Chen,Junjie Ye,Peichang Zhang,Lei Huang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 5 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:Existing video inference (VI) enhancement methods typically aim to improve performance by scaling up model sizes and employing sophisticated network architectures. While these approaches demonstrated state-of-the-art performance, they often overlooked the trade-off of resource efficiency and inference effectiveness, leading to inefficient resource utilization and suboptimal inference performance. To address this problem, a fuzzy controller (FC-r) is developed based on key system parameters and inference-related metrics. Guided by the FC-r, a VI enhancement framework is proposed, where the spatiotemporal correlation of targets across adjacent video frames is leveraged. Given the real-time resource conditions of the target device, the framework can dynamically switch between models of varying scales during VI. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method effectively achieves a balance between resource utilization and inference performance.
zh
[CV-72] Scribble-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation with Dynamic Teacher Switching and Hierarchical Consistency
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学图像分割中因弱标注(如涂鸦标注)的稀疏性导致的标签歧义问题,该问题会引发噪声伪标签传播并阻碍解剖边界的学习。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种双教师-单学生框架(SDT-Net),通过动态教师切换(DTS)模块自适应选择最可靠的教师,并结合两种协同机制:一是由“选取可靠像素”(PRP)机制优化的高置信度伪标签,二是由“分层一致性”(HiCo)模块强制实现的多层级特征对齐,从而最大化从弱监督信号中提取的有效信息,显著提升分割精度与解剖合理性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14563
作者: Thanh-Huy Nguyen,Hoang-Loc Cao,Dat T. Chung,Mai-Anh Vu,Thanh-Minh Nguyen,Minh Le,Phat K. Huynh,Ulas Bagci
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Scribble-supervised methods have emerged to mitigate the prohibitive annotation burden in medical image segmentation. However, the inherent sparsity of these annotations introduces significant ambiguity, which results in noisy pseudo-label propagation and hinders the learning of robust anatomical boundaries. To address this challenge, we propose SDT-Net, a novel dual-teacher, single-student framework designed to maximize supervision quality from these weak signals. Our method features a Dynamic Teacher Switching (DTS) module to adaptively select the most reliable teacher. This selected teacher then guides the student via two synergistic mechanisms: high-confidence pseudo-labels, refined by a Pick Reliable Pixels (PRP) mechanism, and multi-level feature alignment, enforced by a Hierarchical Consistency (HiCo) module. Extensive experiments on the ACDC and MSCMRseg datasets demonstrate that SDT-Net achieves state-of-the-art performance, producing more accurate and anatomically plausible segmentation.
zh
[CV-73] PAS-Mamba: Phase-Amplitude-Spatial State Space Model for MRI Reconstruction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有磁共振成像(MRI)重建方法中,对频率域信息处理过于粗粒度的问题——即通常将频率域视为整体进行建模,忽略了其内部幅度(magnitude)与相位(phase)所承载的不同类型信息。研究表明,幅度主要反映像素级强度,而相位则主导图像结构,统一建模易导致二者特征学习相互干扰。为此,作者提出Phase-Amplitude-Spatial State Space Model (PAS-Mamba),其核心创新在于:在频率域上解耦幅度与相位分支以避免表示耦合,并引入Circular Frequency Domain Scanning (CFDS) 按同心圆结构从低频到高频序列化特征;同时,在图像域采用LocalMamba保留空间局部性以增强细节;并通过Dual-Domain Complementary Fusion Module (DDCFM) 实现双域间自适应融合与双向信息交换,从而显著提升重建质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14530
作者: Xiaoyan Kui,Zijie Fan,Zexin Ji,Qinsong Li,Hao Xu,Weixin Si,Haodong Xu,Beiji Zou
机构: Central South University (中南大学); Chinese Academy of Science (中国科学院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Joint feature modeling in both the spatial and frequency domains has become a mainstream approach in MRI reconstruction. However, existing methods generally treat the frequency domain as a whole, neglecting the differences in the information carried by its internal components. According to Fourier transform theory, phase and amplitude represent different types of information in the image. Our spectrum swapping experiments show that magnitude mainly reflects pixel-level intensity, while phase predominantly governs image structure. To prevent interference between phase and magnitude feature learning caused by unified frequency-domain modeling, we propose the Phase-Amplitude-Spatial State Space Model (PAS-Mamba) for MRI Reconstruction, a framework that decouples phase and magnitude modeling in the frequency domain and combines it with image-domain features for better reconstruction. In the image domain, LocalMamba preserves spatial locality to sharpen fine anatomical details. In frequency domain, we disentangle amplitude and phase into two specialized branches to avoid representational coupling. To respect the concentric geometry of frequency information, we propose Circular Frequency Domain Scanning (CFDS) to serialize features from low to high frequencies. Finally, a Dual-Domain Complementary Fusion Module (DDCFM) adaptively fuses amplitude phase representations and enables bidirectional exchange between frequency and image domains, delivering superior reconstruction. Extensive experiments on the IXI and fastMRI knee datasets show that PAS-Mamba consistently outperforms state of the art reconstruction methods.
zh
[CV-74] XD-MAP: Cross-Modal Domain Adaptation using Semantic Parametric Mapping
【速读】:该论文旨在解决深度学习模型在跨传感器域迁移时因数据分布差异导致性能下降的问题,尤其针对从相机图像到激光雷达(LiDAR)这种不同模态传感器的数据适配难题。其关键解决方案是提出了一种名为XD-MAP的新方法,该方法利用神经网络在相机图像上的检测结果生成语义参数化地图(semantic parametric map),并基于此地图在目标LiDAR域中自动产生伪标签(pseudo labels),从而实现无需人工标注的跨域知识迁移。与以往依赖传感器直接重叠或有限视角的方法不同,XD-MAP能够将前视相机的感知范围扩展至360°全景LiDAR场景,显著提升了LiDAR上的2D和3D语义分割及全景分割性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14477
作者: Frank Bieder,Hendrik Königshof,Haohao Hu,Fabian Immel,Yinzhe Shen,Jan-Hendrik Pauls,Christoph Stiller
机构: FZI Research Center for Information Technology (信息科技研究中心); Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (卡尔斯鲁厄理工学院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
备注:
Abstract:Until open-world foundation models match the performance of specialized approaches, the effectiveness of deep learning models remains heavily dependent on dataset availability. Training data must align not only with the target object categories but also with the sensor characteristics and modalities. To bridge the gap between available datasets and deployment domains, domain adaptation strategies are widely used. In this work, we propose a novel approach to transferring sensor-specific knowledge from an image dataset to LiDAR, an entirely different sensing domain. Our method XD-MAP leverages detections from a neural network on camera images to create a semantic parametric map. The map elements are modeled to produce pseudo labels in the target domain without any manual annotation effort. Unlike previous domain transfer approaches, our method does not require direct overlap between sensors and enables extending the angular perception range from a front-view camera to a full 360 view. On our large-scale road feature dataset, XD-MAP outperforms single shot baseline approaches by +19.5 mIoU for 2D semantic segmentation, +19.5 PQth for 2D panoptic segmentation, and +32.3 mIoU in 3D semantic segmentation. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach achieving strong performance on LiDAR data without any manual labeling.
zh
[CV-75] Real-Time Wildfire Localization on the NASA Autonomous Modular Sensor using Deep Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决高海拔多光谱航空影像数据稀缺且获取成本高昂的问题,同时提升机器学习模型在野火检测等高影响力任务中的性能。其核心挑战在于如何利用有限的高质量多光谱数据实现高精度、实时的野火边界识别,尤其是在夜间或烟雾/云层遮挡条件下区分真实火点与误报。解决方案的关键在于构建一个包含12通道(涵盖红外IR、短波红外SWIR及热红外)的大型人类标注数据集,并基于此训练两个深度神经网络:一个用于图像分类,另一个用于像素级分割;二者集成形成实时分割模型,显著提升了对活跃野火的定位效率与准确性——分类准确率达96%,IoU为74%,召回率达84%,优于以往基于卫星数据或传统颜色规则算法的方法。研究进一步表明,SWIR、IR和热红外波段的数据对精准识别火线边界最为关键。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14475
作者: Yajvan Ravan,Aref Malek,Chester Dolph,Nikhil Behari
机构: OSTEM Internship Program, Langley Research Center; Aerospace Engineer, Aeronautics Systems Engineering Branch, AIAA Member.
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 16 pages, 9 figures, published at AIAA SciTech 2026
Abstract:High-altitude, multi-spectral, aerial imagery is scarce and expensive to acquire, yet it is necessary for algorithmic advances and application of machine learning models to high-impact problems such as wildfire detection. We introduce a human-annotated dataset from the NASA Autonomous Modular Sensor (AMS) using 12-channel, medium to high altitude (3 - 50 km) aerial wildfire images similar to those used in current US wildfire missions. Our dataset combines spectral data from 12 different channels, including infrared (IR), short-wave IR (SWIR), and thermal. We take imagery from 20 wildfire missions and randomly sample small patches to generate over 4000 images with high variability, including occlusions by smoke/clouds, easily-confused false positives, and nighttime imagery. We demonstrate results from a deep-learning model to automate the human-intensive process of fire perimeter determination. We train two deep neural networks, one for image classification and the other for pixel-level segmentation. The networks are combined into a unique real-time segmentation model to efficiently localize active wildfire on an incoming image feed. Our model achieves 96% classification accuracy, 74% Intersection-over-Union(IoU), and 84% recall surpassing past methods, including models trained on satellite data and classical color-rule algorithms. By leveraging a multi-spectral dataset, our model is able to detect active wildfire at nighttime and behind clouds, while distinguishing between false positives. We find that data from the SWIR, IR, and thermal bands is the most important to distinguish fire perimeters. Our code and dataset can be found here: this https URL and this https URL Comments: 16 pages, 9 figures, published at AIAA SciTech 2026 Subjects: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) ACMclasses: I.4.6; I.2.10 Cite as: arXiv:2601.14475 [cs.CV] (or arXiv:2601.14475v1 [cs.CV] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14475 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) Journalreference: Proc. AIAA SciTech Forum (2026) AIAA 2026-2888 Related DOI: https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2026-2888 Focus to learn more DOI(s) linking to related resources
zh
[CV-76] Gaussian Based Adaptive Multi-Modal 3D Semantic Occupancy Prediction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决自动驾驶中长尾安全挑战下,现有体素化方法因计算复杂度高、融合过程脆弱且静态而难以应对动态环境的问题。其核心解决方案是提出一种基于高斯的自适应相机-激光雷达多模态3D占用预测模型,通过内存高效的3D高斯模型无缝结合相机的语义优势与激光雷达的几何优势。关键创新包括:(1) 激光雷达深度特征聚合(LDFA),采用深度方向可变形采样处理几何稀疏性;(2) 基于熵的特征平滑,利用交叉熵抑制领域特定噪声;(3) 自适应相机-激光雷达融合,根据模型输出动态校准传感器信号;(4) Gauss-Mamba头,使用选择性状态空间模型实现全局上下文解码,具备线性计算复杂度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14448
作者: A. Enes Doruk
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Master Thesis
Abstract:The sparse object detection paradigm shift towards dense 3D semantic occupancy prediction is necessary for dealing with long-tail safety challenges for autonomous vehicles. Nonetheless, the current voxelization methods commonly suffer from excessive computation complexity demands, where the fusion process is brittle, static, and breaks down under dynamic environmental settings. To this end, this research work enhances a novel Gaussian-based adaptive camera-LiDAR multimodal 3D occupancy prediction model that seamlessly bridges the semantic strengths of camera modality with the geometric strengths of LiDAR modality through a memory-efficient 3D Gaussian model. The proposed solution has four key components: (1) LiDAR Depth Feature Aggregation (LDFA), where depth-wise deformable sampling is employed for dealing with geometric sparsity, (2) Entropy-Based Feature Smoothing, where cross-entropy is employed for handling domain-specific noise, (3) Adaptive Camera-LiDAR Fusion, where dynamic recalibration of sensor outputs is performed based on model outputs, and (4) Gauss-Mamba Head that uses Selective State Space Models for global context decoding that enjoys linear computation complexity.
zh
[CV-77] Large-Scale Label Quality Assessment for Medical Segmentation via a Vision-Language Judge and Synthetic Data
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大规模医学分割数据集中手动标注与伪标签质量不一的问题,此类低质量标签会损害模型训练性能并降低鲁棒性。解决方案的关键在于提出一种轻量级视觉-语言模型(Vision-Language Model, VLM)SegAE,该模型能够自动预测142个解剖结构的标签质量;其核心优势在于基于超过四百万张图像-标签对及其质量评分进行训练,实现了与真实Dice相似度高度相关(相关系数0.902),且单次3D掩码评估仅需0.06秒,显著提升了数据标注效率与模型训练质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14406
作者: Yixiong Chen,Zongwei Zhou,Wenxuan Li,Alan Yuille
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
备注: ISBI 2026 accepted
Abstract:Large-scale medical segmentation datasets often combine manual and pseudo-labels of uneven quality, which can compromise training and evaluation. Low-quality labels may hamper performance and make the model training less robust. To address this issue, we propose SegAE (Segmentation Assessment Engine), a lightweight vision-language model (VLM) that automatically predicts label quality across 142 anatomical structures. Trained on over four million image-label pairs with quality scores, SegAE achieves a high correlation coefficient of 0.902 with ground-truth Dice similarity and evaluates a 3D mask in 0.06s. SegAE shows several practical benefits: (I) Our analysis reveals widespread low-quality labeling across public datasets; (II) SegAE improves data efficiency and training performance in active and semi-supervised learning, reducing dataset annotation cost by one-third and quality-checking time by 70% per label. This tool provides a simple and effective solution for quality control in large-scale medical segmentation datasets. The dataset, model weights, and codes are released at this https URL.
zh
[CV-78] CityCube: Benchmarking Cross-view Spatial Reasoning on Vision-Language Models in Urban Environments
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前视觉语言模型(VLMs)在开放城市空间中跨视角空间推理能力不足的问题,尤其针对现有基准测试多聚焦于室内或街道场景、忽视了城市环境中丰富的语义信息、复杂几何结构及视角变化等挑战。解决方案的关键在于提出CityCube这一系统性基准,通过整合四种视角动态模拟摄像机运动,并覆盖车辆、无人机和卫星等多种平台的多视角数据,构建包含5,022个精细标注的多视角问答对,涵盖五种认知维度与三种空间关系表达方式,从而全面评估VLMs在真实城市环境中的跨视角推理性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14339
作者: Haotian Xu,Yue Hu,Zhengqiu Zhu,Chen Gao,Ziyou Wang,Junreng Rao,Wenhao Lu,Weishi Li,Quanjun Yin,Yong Li
机构: National University of Defense Technology (国防科技大学); State Key Laboratory of Digital Intelligent Modeling and Simulation (数字智能建模与仿真国家重点实验室); Tsinghua University (清华大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Cross-view spatial reasoning is essential for embodied AI, underpinning spatial understanding, mental simulation and planning in complex environments. Existing benchmarks primarily emphasize indoor or street settings, overlooking the unique challenges of open-ended urban spaces characterized by rich semantics, complex geometries, and view variations. To address this, we introduce CityCube, a systematic benchmark designed to probe cross-view reasoning capabilities of current VLMs in urban settings. CityCube integrates four viewpoint dynamics to mimic camera movements and spans a wide spectrum of perspectives from multiple platforms, e.g., vehicles, drones and satellites. For a comprehensive assessment, it features 5,022 meticulously annotated multi-view QA pairs categorized into five cognitive dimensions and three spatial relation expressions. A comprehensive evaluation of 33 VLMs reveals a significant performance disparity with humans: even large-scale models struggle to exceed 54.1% accuracy, remaining 34.2% below human performance. By contrast, small-scale fine-tuned VLMs achieve over 60.0% accuracy, highlighting the necessity of our benchmark. Further analyses indicate the task correlations and fundamental cognitive disparity between VLMs and human-like reasoning.
zh
[CV-79] LURE: Latent Space Unblocking for Multi-Concept Reawakening in Diffusion Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决扩散模型中概念擦除(concept erasure)后的再唤醒问题,即已擦除的敏感概念仍可能通过特定手段被重新激活,暴露出现有擦除方法的脆弱性。针对现有方法仅依赖提示层面优化而忽略生成过程中其他关键因素(如模型参数和潜在状态)的局限性,作者提出了一种全新的再唤醒方法——Latent space Unblocking for concept REawakening (LURE)。其核心创新在于将生成过程建模为隐式函数,从而理论上证明扰动文本条件、模型参数或潜在状态均可导致概念再唤醒;在此基础上,LURE通过语义重绑定机制重构潜在空间以恢复被切断的文本-视觉关联,并引入梯度场正交化(Gradient Field Orthogonalization)防止多概念场景下的梯度冲突与特征纠缠,同时结合潜在语义识别引导采样(LSIS)确保再唤醒过程的稳定性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14330
作者: Mengyu Sun,Ziyuan Yang,Andrew Beng Jin Teoh,Junxu Liu,Haibo Hu,Yi Zhang
机构: Sichuan University (四川大学); The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (香港理工大学); Yonsei University (延世大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Concept erasure aims to suppress sensitive content in diffusion models, but recent studies show that erased concepts can still be reawakened, revealing vulnerabilities in erasure methods. Existing reawakening methods mainly rely on prompt-level optimization to manipulate sampling trajectories, neglecting other generative factors, which limits a comprehensive understanding of the underlying dynamics. In this paper, we model the generation process as an implicit function to enable a comprehensive theoretical analysis of multiple factors, including text conditions, model parameters, and latent states. We theoretically show that perturbing each factor can reawaken erased concepts. Building on this insight, we propose a novel concept reawakening method: Latent space Unblocking for concept REawakening (LURE), which reawakens erased concepts by reconstructing the latent space and guiding the sampling trajectory. Specifically, our semantic re-binding mechanism reconstructs the latent space by aligning denoising predictions with target distributions to reestablish severed text-visual associations. However, in multi-concept scenarios, naive reconstruction can cause gradient conflicts and feature entanglement. To address this, we introduce Gradient Field Orthogonalization, which enforces feature orthogonality to prevent mutual interference. Additionally, our Latent Semantic Identification-Guided Sampling (LSIS) ensures stability of the reawakening process via posterior density verification. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LURE enables simultaneous, high-fidelity reawakening of multiple erased concepts across diverse erasure tasks and methods.
zh
[CV-80] Intelligent Power Grid Design Review via Active Perception-Enabled Multimodal Large Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前电力系统中电网工程设计图纸智能审查面临的挑战,特别是针对超高分辨率图纸因计算资源消耗大、信息丢失及缺乏整体语义理解而导致的设计错误识别准确率低的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种基于预训练多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)的三阶段框架,通过先进的提示工程(prompt engineering)驱动,模拟人工专家审图流程:第一阶段利用MLLM进行全局语义理解并智能划分领域特定语义区域;第二阶段在所提区域内执行高分辨率细粒度识别,获取带置信度评分的详细信息;第三阶段通过融合置信度感知结果的综合决策模块实现精准设计错误诊断与可靠性评估。该方法显著提升了MLLM对宏观语义信息的把握能力和设计缺陷定位精度,相较于传统被动推理方式展现出更高的缺陷发现准确性和判断可靠性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14261
作者: Taoliang Tan,Chengwei Ma,Zhen Tian,Zhao Lin,Dongdong Li,Si Shi
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:The intelligent review of power grid engineering design drawings is crucial for power system safety. However, current automated systems struggle with ultra-high-resolution drawings due to high computational demands, information loss, and a lack of holistic semantic understanding for design error identification. This paper proposes a novel three-stage framework for intelligent power grid drawing review, driven by pre-trained Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) through advanced prompt engineering. Mimicking the human expert review process, the first stage leverages an MLLM for global semantic understanding to intelligently propose domain-specific semantic regions from a low-resolution overview. The second stage then performs high-resolution, fine-grained recognition within these proposed regions, acquiring detailed information with associated confidence scores. In the final stage, a comprehensive decision-making module integrates these confidence-aware results to accurately diagnose design errors and provide a reliability assessment. Preliminary results on real-world power grid drawings demonstrate our approach significantly enhances MLLM’s ability to grasp macroscopic semantic information and pinpoint design errors, showing improved defect discovery accuracy and greater reliability in review judgments compared to traditional passive MLLM inference. This research offers a novel, prompt-driven paradigm for intelligent and reliable power grid drawing review.
zh
[CV-81] A Cloud-Based Cross-Modal Transformer for Emotion Recognition and Adaptive Human-Computer Interaction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前情感识别系统在真实环境中因依赖单一模态(如面部表情、语音语调或文本情感)而导致的鲁棒性不足和泛化能力差的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于云架构的跨模态Transformer(Cloud-Based Cross-Modal Transformer, CMT)框架,通过预训练编码器(Vision Transformer、Wav2Vec2 和 BERT)融合视觉、听觉与文本信号,并引入跨模态注意力机制以捕捉异构特征间的复杂依赖关系,同时利用 Kubernetes 和 TensorFlow Serving 实现分布式训练与低延迟推理,从而实现高效、实时的情感识别与自适应人机交互。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14259
作者: Ziwen Zhong,Zhitao Shu,Yue Zhao
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Sound (cs.SD); Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS)
备注:
Abstract:Emotion recognition is a fundamental component of next-generation human-computer interaction (HCI), enabling machines to perceive, understand, and respond to users’ affective states. However, existing systems often rely on single-modality analysis such as facial expressions, speech tone, or textual sentiment, resulting in limited robustness and poor generalization in real-world environments. To address these challenges, this study proposes a Cloud-Based Cross-Modal Transformer (CMT) framework for multimodal emotion recognition and adaptive human-computer interaction. The proposed model integrates visual, auditory, and textual signals using pretrained encoders (Vision Transformer, Wav2Vec2, and BERT) and employs a cross-modal attention mechanism to capture complex interdependencies among heterogeneous features. By leveraging cloud computing infrastructure with distributed training on Kubernetes and TensorFlow Serving, the system enables scalable, low-latency emotion recognition for large-scale user interactions. Experiments conducted on benchmark datasets including IEMOCAP, MELD, and AffectNet demonstrate that the CMT achieves state-of-the-art performance, improving the F1-score by 3.0 percent and reducing cross-entropy loss by 12.9 percent compared to strong multimodal baselines. Additionally, cloud deployment evaluations show an average response latency of 128 ms, representing a 35 percent reduction compared with conventional transformer-based fusion systems. These results confirm that the proposed framework enables efficient, real-time emotion recognition and adaptive feedback in applications such as intelligent customer service, virtual tutoring systems, and affective computing interfaces, marking an important step toward cloud-native affective computing and emotionally intelligent interactive systems.
zh
[CV-82] SOSControl: Enhancing Human Motion Generation through Saliency-Aware Symbolic Orientation and Timing Control AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统文本到动作(text-to-motion)框架在控制精度上的不足,特别是现有基于关节关键帧位置的方法仅能提供位置引导,难以直观且精确地指定身体部位的姿态和运动时机。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种可编程的符号化框架——显著姿态符号(Salient Orientation Symbolic, SOS)脚本,用于在关键帧上显式定义身体部位的姿态与时间信息;同时设计了自动SOS提取流水线,通过时序约束的凝聚聚类实现帧显著性检测,并结合基于显著性的掩码策略(Saliency-based Masking Scheme, SMS)从运动数据中生成稀疏且可解释的SOS脚本;进一步构建SOSControl框架,将SOS中的姿态符号视为显著约束,在运动生成过程中优先满足这些约束,辅以SMS数据增强和基于梯度的迭代优化提升对用户指定约束的契合度,并采用基于ControlNet的ACTOR-PAE解码器保障输出动作的流畅性和自然性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14258
作者: Ho Yin Au,Junkun Jiang,Jie Chen
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Multimedia (cs.MM)
备注: Accepted by AAAI 2026
Abstract:Traditional text-to-motion frameworks often lack precise control, and existing approaches based on joint keyframe locations provide only positional guidance, making it challenging and unintuitive to specify body part orientations and motion timing. To address these limitations, we introduce the Salient Orientation Symbolic (SOS) script, a programmable symbolic framework for specifying body part orientations and motion timing at keyframes. We further propose an automatic SOS extraction pipeline that employs temporally-constrained agglomerative clustering for frame saliency detection and a Saliency-based Masking Scheme (SMS) to generate sparse, interpretable SOS scripts directly from motion data. Moreover, we present the SOSControl framework, which treats the available orientation symbols in the sparse SOS script as salient and prioritizes satisfying these constraints during motion generation. By incorporating SMS-based data augmentation and gradient-based iterative optimization, the framework enhances alignment with user-specified constraints. Additionally, it employs a ControlNet-based ACTOR-PAE Decoder to ensure smooth and natural motion outputs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the SOS extraction pipeline generates human-interpretable scripts with symbolic annotations at salient keyframes, while the SOSControl framework outperforms existing baselines in motion quality, controllability, and generalizability with respect to motion timing and body part orientation control.
zh
[CV-83] Vision Models for Medical Imaging: A Hybrid Approach for PCOS Detection from Ultrasound Scans
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多囊卵巢综合征(Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, PCOS)在孟加拉国女性中的早期准确诊断问题,尤其针对超声图像中PCOS的自动识别难题。解决方案的关键在于提出两种新型混合模型,其中最优模型DenConREST融合了Swin Transformer、ConvNeXt、DenseNet121、ResNet18和EfficientNetV2等多架构特征提取能力,通过深度学习实现对卵巢超声图像中PCOS病变区域的高精度分类,最终达到98.23%的检测准确率,显著优于单一模型及初始混合模型DenConST(85.69%),为PCOS的智能辅助诊断提供了高效且可靠的医学影像分析方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15119
作者: Md Mahmudul Hoque,Md Mehedi Hassain,Muntakimur Rahaman,Md. Towhidul Islam,Shaista Rani,Md Sharif Mollah
机构: CCN University of Science & Technology (CCN科技大学); International Islamic University Chittagong (国际伊斯兰大学吉大港分校); Multimedia University (多媒体大学); Stamford University of Bangladesh (斯坦福德大学孟加拉分校); Lucknow University (勒克瑙大学); Bangladesh Army International University of Science & Technology (孟加拉国陆军国际科学技术大学)
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is the most familiar endocrine illness in women of reproductive age. Many Bangladeshi women suffer from PCOS disease in their older age. The aim of our research is to identify effective vision-based medical image analysis techniques and evaluate hybrid models for the accurate detection of PCOS. We introduced two novel hybrid models combining convolutional and transformer-based approaches. The training and testing data were organized into two categories: “infected” (PCOS-positive) and “noninfected” (healthy ovaries). In the initial stage, our first hybrid model, ‘DenConST’ (integrating DenseNet121, Swin Transformer, and ConvNeXt), achieved 85.69% accuracy. The final optimized model, ‘DenConREST’ (incorporating Swin Transformer, ConvNeXt, DenseNet121, ResNet18, and EfficientNetV2), demonstrated superior performance with 98.23% accuracy. Among all evaluated models, DenConREST showed the best performance. This research highlights an efficient solution for PCOS detection from ultrasound images, significantly improving diagnostic accuracy while reducing detection errors.
zh
[CV-84] Filtered 2D Contour-Based Reconstruction of 3D STL Model from CT-DICOM Images
【速读】:该论文旨在解决从低分辨率DICOM图像中提取的2D轮廓数据存在噪声和异常值(outliers)导致重建的3D立体光刻(STL)模型几何失真问题。其关键解决方案是:在构建3D STL模型前,对每层2D轮廓点进行滤波处理,去除异常点后采用Delaunay三角剖分方法对滤波后的轮廓点进行网格化,并逐层拼接以生成更精确的3D模型,从而显著提升重建模型的几何保真度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14997
作者: K.Punnam Chandar,Y.Ravi Kumar
机构: Kakatiya University ( kakatiya 大学); National Institute of Technology, Warangal (印度理工学院瓦朗加尔分校)
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 8 pages, 18 figures
Abstract:Reconstructing a 3D Stereo-lithography (STL) Model from 2D Contours of scanned structure in Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine (DICOM) images is crucial to understand the geometry and deformity. Computed Tomography (CT) images are processed to enhance the contrast, reduce the noise followed by smoothing. The processed CT images are segmented using thresholding technique. 2D contour data points are extracted from segmented CT images and are used to construct 3D STL Models. The 2D contour data points may contain outliers as a result of segmentation of low resolution images and the geometry of the constructed 3D structure deviate from the actual. To cope with the imperfections in segmentation process, in this work we propose to use filtered 2D contour data points to reconstruct 3D STL Model. The filtered 2D contour points of each image are delaunay triangulated and joined layer-by-layer to reconstruct the 3D STL model. The 3D STL Model reconstruction is verified on i) 2D Data points of basic shapes and ii) Region of Interest (ROI) of human pelvic bone and are presented as case studies. The 3D STL model constructed from 2D contour data points of ROI of segmented pelvic bone with and without filtering are presented. The 3D STL model reconstructed from filtered 2D data points improved the geometry of model compared to the model reconstructed without filtering 2D data points.
zh
[CV-85] Partial Decoder Attention Network with Contour-weighted Loss Function for Data-Imbalance Medical Image Segmentation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学图像分割中因数据不平衡导致的模型偏差问题,即模型倾向于准确分割体积较大或样本较多的器官/组织,而忽略小尺寸或稀疏分布的结构,从而影响分割精度与鲁棒性。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种轮廓加权(contour-weighted)分割策略,通过增强对小目标或欠代表结构边界的关注,提升模型对其的识别能力;同时设计了一种基于局部解码机制的轻量级网络PDANet,进一步优化了小结构的分割性能。该方法在多个公开数据集上验证有效,并可作为通用策略嵌入多种分割框架以提升整体性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14338
作者: Zhengyong Huang,Ning Jiang,Xingwen Sun,Lihua Zhang,Peng Chen,Jens Domke,Yao Sui
机构: Peking University Health Science Center (北京大学医学部); Peking University (北京大学); National Institute of Health Data Science, Peking University (北京大学健康医疗数据科学研究所); Department of Radiology, Peking University Third Hospital (北京大学第三医院放射科); RIKEN Center for Computational Science (R-CCS) (理化学研究所计算科学中心); Institute for Artificial Intelligence, Peking University (北京大学人工智能研究院)
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Image segmentation is pivotal in medical image analysis, facilitating clinical diagnosis, treatment planning, and disease evaluation. Deep learning has significantly advanced automatic segmentation methodologies by providing superior modeling capability for complex structures and fine-grained anatomical regions. However, medical images often suffer from data imbalance issues, such as large volume disparities among organs or tissues, and uneven sample distributions across different anatomical structures. This imbalance tends to bias the model toward larger organs or more frequently represented structures, while overlooking smaller or less represented structures, thereby affecting the segmentation accuracy and robustness. To address these challenges, we proposed a novel contour-weighted segmentation approach, which improves the model’s capability to represent small and underrepresented structures. We developed PDANet, a lightweight and efficient segmentation network based on a partial decoder mechanism. We evaluated our method using three prominent public datasets. The experimental results show that our methodology excelled in three distinct tasks: segmenting multiple abdominal organs, brain tumors, and pelvic bone fragments with injuries. It consistently outperformed nine state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, the proposed contour-weighted strategy improved segmentation for other comparison methods across the three datasets, yielding average enhancements in Dice scores of 2.32%, 1.67%, and 3.60%, respectively. These results demonstrate that our contour-weighted segmentation method surpassed current leading approaches in both accuracy and robustness. As a model-independent strategy, it can seamlessly fit various segmentation frameworks, enhancing their performance. This flexibility highlighted its practical importance and potential for broad use in medical image analysis.
zh
[CV-86] Unsupervised Deformable Image Registration with Local-Global Attention and Image Decomposition
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学图像配准中传统迭代优化方法计算复杂度高、泛化能力差,以及现有深度学习方法在处理高解剖变异区域时精度不足的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一种新的无监督可变形图像配准框架LGANet++,该框架引入了局部-全局注意力机制(local-global attention mechanism),并通过独特的特征交互与融合技术显著提升了配准的准确性、鲁棒性和泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14337
作者: Zhengyong Huang,Xingwen Sun,Xuting Chang,Ning Jiang,Yao Wang,Jianfei Sun,Hongbin Han,Yao Sui
机构: Peking University (北京大学)
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Deformable image registration is a critical technology in medical image analysis, with broad applications in clinical practice such as disease diagnosis, multi-modal fusion, and surgical navigation. Traditional methods often rely on iterative optimization, which is computationally intensive and lacks generalizability. Recent advances in deep learning have introduced attention-based mechanisms that improve feature alignment, yet accurately registering regions with high anatomical variability remains challenging. In this study, we proposed a novel unsupervised deformable image registration framework, LGANet++, which employs a novel local-global attention mechanism integrated with a unique technique for feature interaction and fusion to enhance registration accuracy, robustness, and generalizability. We evaluated our approach using five publicly available datasets, representing three distinct registration scenarios: cross-patient, cross-time, and cross-modal CT-MR registration. The results demonstrated that our approach consistently outperforms several state-of-the-art registration methods, improving registration accuracy by 1.39% in cross-patient registration, 0.71% in cross-time registration, and 6.12% in cross-modal CT-MR registration tasks. These results underscore the potential of LGANet++ to support clinical workflows requiring reliable and efficient image registration. The source code is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-87] Self-Supervised Score-Based Despeckling for SAR Imagery via Log-Domain Transformation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决合成孔径雷达(SAR)图像中固有的乘性散斑噪声(speckle noise)对图像质量及后续分析造成的负面影响问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一种基于得分生成模型(score-based generative models)的自监督框架,通过将数据转换至对数域,使原本乘性的散斑噪声残差近似服从加性高斯分布,从而使得得分模型能够在变换后的域中进行训练;该方法利用自监督目标,仅需输入图像本身及其进一步退化的版本即可学习干净信号,显著缩短了推理时间,同时提供了鲁棒且实用的SAR图像去噪方案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14334
作者: Junhyuk Heo
机构: 未知
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:The speckle noise inherent in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery significantly degrades image quality and complicates subsequent analysis. Given that SAR speckle is multiplicative and Gamma-distributed, effectively despeckling SAR imagery remains challenging. This paper introduces a novel self-supervised framework for SAR image despeckling based on score-based generative models operating in the transformed log domain. We first transform the data into the log-domain and then convert the speckle noise residuals into an approximately additive Gaussian distribution. This step enables the application of score-based models, which are trained in the transformed domain using a self-supervised objective. This objective allows our model to learn the clean underlying signal by training on further corrupted versions of the input data itself. Consequently, our method exhibits significantly shorter inference times compared to many existing self-supervised techniques, offering a robust and practical solution for SAR image restoration.
zh
人工智能
[AI-0] MolecularIQ: Characterizing Chemical Reasoning Capabilities Through Symbolic Verification on Molecular Graphs
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前化学大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在分子结构推理能力评估中存在的不足,包括现有基准测试侧重通用化学知识、依赖文献或代理标签可能导致信息泄露或偏差,以及将评估简化为多项选择题等问题。解决方案的关键在于提出MolecularIQ,这是一个专注于符号可验证任务的分子结构推理基准,能够实现对分子图推理能力的细粒度评估,并揭示模型在特定任务和分子结构上的失败模式,从而提供可操作的洞察,指导更忠实于分子结构推理的模型开发。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15279
作者: Christoph Bartmann,Johannes Schimunek,Mykyta Ielanskyi,Philipp Seidl,Günter Klambauer,Sohvi Luukkonen
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:A molecule’s properties are fundamentally determined by its composition and structure encoded in its molecular graph. Thus, reasoning about molecular properties requires the ability to parse and understand the molecular graph. Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly applied to chemistry, tackling tasks such as molecular name conversion, captioning, text-guided generation, and property or reaction prediction. Most existing benchmarks emphasize general chemical knowledge, rely on literature or surrogate labels that risk leakage or bias, or reduce evaluation to multiple-choice questions. We introduce MolecularIQ, a molecular structure reasoning benchmark focused exclusively on symbolically verifiable tasks. MolecularIQ enables fine-grained evaluation of reasoning over molecular graphs and reveals capability patterns that localize model failures to specific tasks and molecular structures. This provides actionable insights into the strengths and limitations of current chemistry LLMs and guides the development of models that reason faithfully over molecular structure.
zh
[AI-1] Recommending Best Paper Awards for ML/AI Conferences via the Isotonic Mechanism
【速读】:该论文旨在解决机器学习与人工智能顶会(如NeurIPS、ICML)在面对海量投稿时,如何提升最佳论文奖评选过程的质量与一致性问题。其核心挑战在于传统评审机制难以确保公平性和客观性,且近年来相关评选结果常引发争议。解决方案的关键在于引入一种由作者辅助的评分调整机制——利用**等距机制(Isotonic Mechanism)**获取作者对自己论文的排序信息,并据此对原始审稿分数进行校准,从而更准确地估计论文的真实质量。该方法在作者效用函数为凸加性函数时可激励诚实报告,且在单篇提名场景下,即使效用函数仅为非递减加性函数也能保证真实性,显著放宽了以往研究的假设条件。通过模拟实验验证,该机制能有效提升获奖论文的整体质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15249
作者: Garrett G. Wen,Buxin Su,Natalie Collina,Zhun Deng,Weijie Su
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Science and Game Theory (cs.GT); Methodology (stat.ME)
备注:
Abstract:Machine learning and artificial intelligence conferences such as NeurIPS and ICML now regularly receive tens of thousands of submissions, posing significant challenges to maintaining the quality and consistency of the peer review process. This challenge is particularly acute for best paper awards, which are an important part of the peer review process, yet whose selection has increasingly become a subject of debate in recent years. In this paper, we introduce an author-assisted mechanism to facilitate the selection of best paper awards. Our method employs the Isotonic Mechanism for eliciting authors’ assessments of their own submissions in the form of a ranking, which is subsequently utilized to adjust the raw review scores for optimal estimation of the submissions’ ground-truth quality. We demonstrate that authors are incentivized to report truthfully when their utility is a convex additive function of the adjusted scores, and we validate this convexity assumption for best paper awards using publicly accessible review data of ICLR from 2019 to 2023 and NeurIPS from 2021 to 2023. Crucially, in the special case where an author has a single quota – that is, may nominate only one paper – we prove that truthfulness holds even when the utility function is merely nondecreasing and additive. This finding represents a substantial relaxation of the assumptions required in prior work. For practical implementation, we extend our mechanism to accommodate the common scenario of overlapping authorship. Finally, simulation results demonstrate that our mechanism significantly improves the quality of papers selected for awards.
zh
[AI-2] Feasibility Preservation under Monotone Retrieval Truncation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决基于截断(truncation)的检索系统在实际应用中因证据片段被限制而无法捕捉到完整相关性信息的问题,即即使相关证据存在于语料库中,由于截断导致其无法共现,从而引发查询失败,而这类问题无法通过传统的基于相关性的评估方法发现。论文从结构角度出发,将查询回答建模为一个在截断条件下是否可行的判定问题,并提出关键解决方案:首先证明单调截断(monotone truncation)足以保证单个查询在有限检索深度下具有可证性(witnessability),进而识别出“有限生成的见证证书”(finite generation of witness certificates)是获得统一检索边界(uniform retrieval bound)所需的额外条件,且该条件必要;此外,通过反例验证了非单调截断、非有限生成查询类以及纯槽位覆盖(slotwise coverage)均会导致失败。由此,论文确立了“可行性保持”(feasibility preservation)作为独立于相关性评分或优化目标的检索正确性标准,揭示了截断检索固有的结构性限制。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15241
作者: Sean Plummer
机构: 未知
类目: Logic in Computer Science (cs.LO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Retrieval-based systems approximate access to a corpus by exposing only a truncated subset of available evidence. Even when relevant information exists in the corpus, truncation can prevent compatible evidence from co-occurring, leading to failures that are not captured by relevance-based evaluation. This paper studies retrieval from a structural perspective, modeling query answering as a feasibility problem under truncation. We formalize retrieval as a sequence of candidate evidence sets and characterize conditions under which feasibility in the limit implies feasibility at finite retrieval depth. We show that monotone truncation suffices to guarantee finite witnessability for individual queries. For classes of queries, we identify finite generation of witness certificates as the additional condition required to obtain a uniform retrieval bound, and we show that this condition is necessary. We further exhibit sharp counterexamples demonstrating failure under non-monotone truncation, non-finitely-generated query classes, and purely slotwise coverage. Together, these results isolate feasibility preservation as a correctness criterion for retrieval independent of relevance scoring or optimization, and clarify structural limitations inherent to truncation-based retrieval. Subjects: Logic in Computer Science (cs.LO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.15241 [cs.LO] (or arXiv:2601.15241v1 [cs.LO] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.15241 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-3] Deaf and Hard of Hearing Access to Intelligent Personal Assistants: Comparison of Voice-Based Options with an LLM -Powered Touch Interface
【速读】:该论文旨在解决智能个人助理(Intelligent Personal Assistants, IPAs)对聋人和听力障碍(Deaf and Hard of Hearing, DHH)人群的可访问性问题,尤其是那些不使用手语但能发声的DHH个体。当前IPAs因无法识别多样化的口音(包括聋人特有的发音特征),导致其对非手语使用者几乎不可用。论文提出的关键解决方案是采用基于大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)辅助的触控界面,通过整合用户历史记录与智能家居环境信息,由LLM驱动的“任务提示器”动态生成情境适配的命令建议,从而实现与语音输入相当的可用性。实验结果显示,定量指标上该触控方法与两种语音输入方式(自然语音与人工复述)无显著差异,而定性分析则揭示了不同用户对各交互模式的偏好差异,表明未来需在IPAs中原生支持聋人发音特征的语音识别能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15209
作者: Paige S. DeVries,Michaela Okosi,Ming Li,Nora Dunphy. Gidey Gezae,Dante Conway,Abraham Glasser,Raja Kushalnagar,Christian Vogler
机构: 未知
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted for publication in ACM CHI 2026
Abstract:We investigate intelligent personal assistants (IPAs) accessibility for deaf and hard of hearing (DHH) people who can use their voice in everyday communication. The inability of IPAs to understand diverse accents including deaf speech renders them largely inaccessible to non-signing and speaking DHH individuals. Using an Echo Show, we compare the usability of natural language input via spoken English; with Alexa’s automatic speech recognition and a Wizard-of-Oz setting with a trained facilitator re-speaking commands against that of a large language model (LLM)-assisted touch interface in a mixed-methods study. The touch method was navigated through an LLM-powered “task prompter,” which integrated the user’s history and smart environment to suggest contextually-appropriate commands. Quantitative results showed no significant differences across both spoken English conditions vs LLM-assisted touch. Qualitative results showed variability in opinions on the usability of each method. Ultimately, it will be necessary to have robust deaf-accented speech recognized natively by IPAs.
zh
[AI-4] Where Do AI Coding Agents Fail? An Empirical Study of Failed Agent ic Pull Requests in GitHub
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前生成式 AI 编程代理(AI coding agents)在实际软件开发中贡献的 PR(Pull Request)频繁未被合并的问题,深入探究其行为模式与失败原因。解决方案的关键在于通过大规模量化分析(33,000 个 PR)和定性案例研究(600 个 PR)相结合的方法,系统识别出影响 PR 合并成功率的核心因素,包括任务类型、代码变更规模、CI/CD 构建结果及评审动态,并构建了一个层次化的拒因分类体系,揭示了诸如缺乏有意义的评审参与、重复 PR、不期望的功能实现以及代理与人类目标不一致等关键人机协作问题,从而为优化未来 AI 编程代理的工作流提供实证依据与改进方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15195
作者: Ramtin Ehsani,Sakshi Pathak,Shriya Rawal,Abdullah Al Mujahid,Mia Mohammad Imran,Preetha Chatterjee
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted at International Mining Software Repositories Conference (MSR 2026)
Abstract:AI coding agents are now submitting pull requests (PRs) to software projects, acting not just as assistants but as autonomous contributors. As these agentic contributions are rapidly increasing across real repositories, little is known about how they behave in practice and why many of them fail to be merged. In this paper, we conduct a large-scale study of 33k agent-authored PRs made by five coding agents across GitHub. (RQ1) We first quantitatively characterize merged and not-merged PRs along four broad dimensions: 1) merge outcomes across task types, 2) code changes, 3) CI build results, and 4) review dynamics. We observe that tasks related to documentation, CI, and build update achieve the highest merge success, whereas performance and bug-fix tasks perform the worst. Not-merged PRs tend to involve larger code changes, touch more files, and often do not pass the project’s CI/CD pipeline validation. (RQ2) To further investigate why some agentic PRs are not merged, we qualitatively analyze 600 PRs to derive a hierarchical taxonomy of rejection patterns. This analysis complements the quantitative findings in RQ1 by uncovering rejection reasons not captured by quantitative metrics, including lack of meaningful reviewer engagement, duplicate PRs, unwanted feature implementations, and agent misalignment. Together, our findings highlight key socio-technical and human-AI collaboration factors that are critical to improving the success of future agentic workflows.
zh
[AI-5] Benchmarking Large Language Models for ABAP Code Generation: An Empirical Study on Iterative Improvement by Compiler Feedback
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在生成ABAP代码方面的性能表现缺乏系统性分析的问题,特别是其生成的代码是否语法正确、功能有效,以及如何利用编译器反馈进行迭代优化。解决方案的关键在于构建一个包含180个任务的基准测试集,涵盖改编自HumanEval的任务和实际SAP应用场景,并通过多轮迭代与编译器反馈机制评估不同LLMs的表现,结果表明高性能LLMs在多次迭代后可达到约75%的成功率,且显著受益于编译器反馈,从而凸显了强大LLMs在ABAP开发中通过错误纠正实现高效迭代的潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15188
作者: Stephan Wallraven,Tim Köhne,Hartmut Westenberger,Andreas Moser
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Programming Languages (cs.PL)
备注: 20 pages, 10 figures, Author: Hartmut Westenberger (ORCID: 0009-0009-9063-8318)
Abstract:This work investigates the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) in generating ABAP code. Despite successful applications of generative AI in many programming languages, there are hardly any systematic analyses of ABAP code generation to date. The aim of the study is to empirically analyze to what extent various LLMs can generate syntactically correct and functional ABAP code, how effectively they use compiler feedback for iterative improvement, and which task types pose special challenges. For this purpose, a benchmark with 180 tasks is conducted, consisting of adapted HumanEval tasks and practical SAP scenarios. The results show significant performance differences between the models: more powerful LLMs achieve success rates of around 75% after several iterations and benefit greatly from compiler feedback, while smaller models perform significantly weaker. Overall, the study highlights the high potential of powerful LLMs for ABAP development processes, especially in iterative error correction.
zh
[AI-6] Dynamic Management of a Deep Learning-Based Anomaly Detection System for 5G Networks
【速读】:该论文旨在解决5G移动网络中因海量数据流量和大量网络连接带来的实时网络异常检测难题,尤其是在用户中心的网络安全防护场景下,传统集中式处理方式难以满足低延迟与高效率的需求。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种面向移动边缘计算(Mobile Edge Computing, MEC)的自适应异常检测架构:利用深度学习技术对网络流进行分析以实现精准异常识别,并通过策略驱动机制动态优化计算资源分配,从而在MEC节点上实现高效、实时且自主的网络异常检测能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15177
作者: Lorenzo Fernández Maimó,Alberto Huertas Celdrán,Manuel Gil Pérez,Félix J. García Clemente,Gregorio Martínez Pérez
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Fog and mobile edge computing (MEC) will play a key role in the upcoming fifth generation (5G) mobile networks to support decentralized applications, data analytics and management into the network itself by using a highly distributed compute model. Furthermore, increasing attention is paid to providing user-centric cybersecurity solutions, which particularly require collecting, processing and analyzing significantly large amount of data traffic and huge number of network connections in 5G networks. In this regard, this paper proposes a MEC-oriented solution in 5G mobile networks to detect network anomalies in real-time and in autonomic way. Our proposal uses deep learning techniques to analyze network flows and to detect network anomalies. Moreover, it uses policies in order to provide an efficient and dynamic management system of the computing resources used in the anomaly detection process. The paper presents relevant aspects of the deployment of the proposal and experimental results to show its performance.
zh
[AI-7] V-CAGE: Context-Aware Generation and Verification for Scalable Long-Horizon Embodied Tasks
【速读】:该论文旨在解决从合成数据中学习长时程具身行为(long-horizon embodied behaviors)所面临的三大挑战:生成场景物理上不现实、语言驱动的程序常在未满足任务语义的情况下“成功”,以及高层指令难以转化为可执行的动作序列。解决方案的关键在于提出一个闭环框架V-CAGE,其核心创新包括:(1) 基于上下文感知的实例化机制,通过动态维护禁止空间区域图来确保场景几何一致性,避免物体穿插并生成可达且无冲突的配置;(2) 采用分层指令分解模块,将高层目标(如“准备上班”)分解为组合式动作原语,实现连贯的长时程规划;(3) 引入基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的验证循环,作为视觉评判者对每个子任务进行严格拒绝采样,过滤掉代码执行但未达成视觉目标的“静默失败”,从而保障数据的语义正确性。实验表明,V-CAGE生成的数据集在物理和语义保真度上显著优于非验证基线,大幅提升下游策略的成功率与泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15164
作者: Yaru Liu,Ao-bo Wang,Nanyang Ye
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Learning long-horizon embodied behaviors from synthetic data remains challenging because generated scenes are often physically implausible, language-driven programs frequently “succeed” without satisfying task semantics, and high-level instructions require grounding into executable action sequences. To address these limitations, we introduce V-CAGE, a closed-loop framework for generating robust, semantically aligned manipulation datasets at scale. First, we propose a context-aware instantiation mechanism that enforces geometric consistency during scene synthesis. By dynamically maintaining a map of prohibited spatial areas as objects are placed, our system prevents interpenetration and ensures reachable, conflict-free configurations in cluttered environments. Second, to bridge the gap between abstract intent and low-level control, we employ a hierarchical instruction decomposition module. This decomposes high-level goals (e.g., “get ready for work”) into compositional action primitives, facilitating coherent long-horizon planning. Crucially, we enforce semantic correctness through a VLM-based verification loop. Acting as a visual critic, the VLM performs rigorous rejection sampling after each subtask, filtering out “silent failures” where code executes but fails to achieve the visual goal. Experiments demonstrate that V-CAGE yields datasets with superior physical and semantic fidelity, significantly boosting the success rate and generalization of downstream policies compared to non-verified baselines.
zh
[AI-8] Knowledge Graphs are Implicit Reward Models: Path-Derived Signals Enable Compositional Reasoning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型在专业科学领域中进行组合式多跳推理(compositional multi-hop reasoning)能力有限的问题。当前模型虽在数学和编程等结构化推理任务中表现接近专家水平,但在需要整合多个中间步骤的复杂推理场景中仍存在不足。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种自底向上的学习范式,通过将模型锚定在公理化的领域知识图谱(knowledge graph)上,并利用知识图谱路径作为隐式奖励信号,结合监督微调与强化学习(reinforcement learning, RL)进行后训练。该方法通过从知识图谱路径中提取可验证、可扩展且 grounded 的奖励信号,促使模型在 RL 阶段更关注中间推理步骤的正确性而非仅优化最终答案,从而显著提升零样本泛化能力,尤其在医疗领域的多跳推理任务中超越了更大规模模型及前沿系统如 GPT-5.2 和 Gemini 3 Pro。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15160
作者: Yuval Kansal,Niraj K. Jha
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models have achieved near-expert performance in structured reasoning domains like mathematics and programming, yet their ability to perform compositional multi-hop reasoning in specialized scientific fields remains limited. We propose a bottom-up learning paradigm in which models are grounded in axiomatic domain facts and compose them to solve complex, unseen tasks. To this end, we present a post-training pipeline, based on a combination of supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning (RL), in which knowledge graphs act as implicit reward models. By deriving novel reward signals from knowledge graph paths, we provide verifiable, scalable, and grounded supervision that encourages models to compose intermediate axioms rather than optimize only final answers during RL. We validate this approach in the medical domain, training a 14B model on short-hop reasoning paths (1-3 hops) and evaluating its zero-shot generalization to complex multi-hop queries (4-5 hops). Our experiments show that path-derived rewards act as a “compositional bridge”, enabling our model to significantly outperform much larger models and frontier systems like GPT-5.2 and Gemini 3 Pro, on the most difficult reasoning tasks. Furthermore, we demonstrate the robustness of our approach to adversarial perturbations against option-shuffling stress tests. This work suggests that grounding the reasoning process in structured knowledge is a scalable and efficient path toward intelligent reasoning.
zh
[AI-9] Outcome-Based RL Provably Leads Transformers to Reason but Only With the Right Data
【速读】:该论文旨在解决一个关键问题:在仅使用最终答案正确性作为稀疏奖励信号的情况下,基于梯度下降的强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)如何促使Transformer模型自发地涌现出结构化的中间推理步骤(Chain-of-Thought, CoT)。其解决方案的关键在于揭示了梯度流动力学(gradient flow dynamics)在单层Transformer上的作用机制——通过分析一个合成图遍历任务,作者证明即使没有显式的中间步骤监督,梯度流仍会引导模型收敛到一种可解释的、逐顶点迭代遍历图的算法。进一步指出,训练分布中“简单示例”(即需要较少推理步骤的样本)的充足占比是该机制生效的核心条件:当这类样本足够多时,模型能学习到泛化性强的遍历策略并外推至更长链路;反之,若此类样本消失,则梯度学习失效。这一理论发现已在合成数据和真实语言模型的数学推理任务上得到实验验证。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15158
作者: Yuval Ran-Milo,Yotam Alexander,Shahar Mendel,Nadav Cohen
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 80 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:Transformers trained via Reinforcement Learning (RL) with outcome-based supervision can spontaneously develop the ability to generate intermediate reasoning steps (Chain-of-Thought). Yet the mechanism by which sparse rewards drive gradient descent to discover such systematic reasoning remains poorly understood. We address this by analyzing the gradient flow dynamics of single-layer Transformers on a synthetic graph traversal task that cannot be solved without Chain-of-Thought (CoT) but admits a simple iterative solution. We prove that despite training solely on final-answer correctness, gradient flow drives the model to converge to a structured, interpretable algorithm that iteratively traverses the graph vertex-by-vertex. We characterize the distributional properties required for this emergence, identifying the critical role of “simple examples”: instances requiring fewer reasoning steps. When the training distribution places sufficient mass on these simpler instances, the model learns a generalizable traversal strategy that extrapolates to longer chains; when this mass vanishes, gradient-based learning becomes infeasible. We corroborate our theoretical results through experiments on synthetic data and with real-world language models on mathematical reasoning tasks, validating that our theoretical findings carry over to practical settings.
zh
[AI-10] How to Build AI Agents by Augmenting LLM s with Codified Human Expert Domain Knowledge? A Software Engineering Framework
【速读】:该论文旨在解决领域专家知识难以规模化传播的问题,即关键领域知识通常仅掌握在少数专家手中,导致组织在可扩展性和决策效率上存在瓶颈;同时,非专家在创建有效可视化时面临困难,从而产生次优洞察并占用专家时间。解决方案的关键在于提出一个软件工程框架,通过将大型语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)与请求分类器、基于检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)的代码生成系统、结构化的专家规则及可视化设计原则相结合,构建具备自主性、反应性、主动性与社交性的AI代理(AI agent),从而将人类领域知识显式编码并嵌入到自动化可视化生成系统中。实证评估表明,该方法在五个跨工程领域的场景中使输出质量提升206%,且所有案例均达到专家级评分,显著优于基线表现,同时保持更高的代码质量和更低的波动性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15153
作者: Choro Ulan uulu,Mikhail Kulyabin,Iris Fuhrmann,Jan Joosten,Nuno Miguel Martins Pacheco,Filippos Petridis,Rebecca Johnson,Jan Bosch,Helena Holmström Olsson
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Critical domain knowledge typically resides with few experts, creating organizational bottlenecks in scalability and decision-making. Non-experts struggle to create effective visualizations, leading to suboptimal insights and diverting expert time. This paper investigates how to capture and embed human domain knowledge into AI agent systems through an industrial case study. We propose a software engineering framework to capture human domain knowledge for engineering AI agents in simulation data visualization by augmenting a Large Language Model (LLM) with a request classifier, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system for code generation, codified expert rules, and visualization design principles unified in an agent demonstrating autonomous, reactive, proactive, and social behavior. Evaluation across five scenarios spanning multiple engineering domains with 12 evaluators demonstrates 206% improvement in output quality, with our agent achieving expert-level ratings in all cases versus baseline’s poor performance, while maintaining superior code quality with lower variance. Our contributions are: an automated agent-based system for visualization generation and a validated framework for systematically capturing human domain knowledge and codifying tacit expert knowledge into AI agents, demonstrating that non-experts can achieve expert-level outcomes in specialized domains.
zh
[AI-11] Vehicle Routing with Finite Time Horizon using Deep Reinforcement Learning with Improved Network Embedding AAAI-26
【速读】:该论文旨在解决具有有限时间窗的车辆路径问题(Vehicle Routing Problem with Finite Time Horizon, VRP-FT),其核心目标是在给定时间约束下最大化服务客户请求的数量。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种新颖的路由网络嵌入模块(routing network embedding module),该模块能够生成局部节点嵌入向量和上下文感知的全局图表示,并将剩余有限时间窗作为关键信息融入嵌入过程,从而为强化学习策略提供更精准的路由上下文。在此基础上,作者构建了一个基于马尔可夫决策过程(Markov Decision Process, MDP)的状态空间,整合节点特征、邻接矩阵与边特征,并将其与基于策略梯度的深度强化学习框架相结合,实现了高效且高服务率的路径规划。实验表明,该方法在真实世界和合成欧几里得网络上均优于现有方法,且求解时间显著更低。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15131
作者: Ayan Maity,Sudeshna Sarkar
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted at AAAI-26 Workshop on AI for Urban Planning
Abstract:In this paper, we study the vehicle routing problem with a finite time horizon. In this routing problem, the objective is to maximize the number of customer requests served within a finite time horizon. We present a novel routing network embedding module which creates local node embedding vectors and a context-aware global graph representation. The proposed Markov decision process for the vehicle routing problem incorporates the node features, the network adjacency matrix and the edge features as components of the state space. We incorporate the remaining finite time horizon into the network embedding module to provide a proper routing context to the embedding module. We integrate our embedding module with a policy gradient-based deep Reinforcement Learning framework to solve the vehicle routing problem with finite time horizon. We trained and validated our proposed routing method on real-world routing networks, as well as synthetically generated Euclidean networks. Our experimental results show that our method achieves a higher customer service rate than the existing routing methods. Additionally, the solution time of our method is significantly lower than that of the existing methods.
zh
[AI-12] Overcoming In-Memory Bottlenecks in Graph Foundation Models via Retrieval-Augmented Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决图基础模型(Graph Foundation Models, GFMs)在内存受限条件下所面临的语义容量不足、知识压缩损失严重以及表示与知识纠缠等问题,这些问题限制了模型的可扩展性和可解释性。其核心解决方案是提出一种检索增强生成辅助的图基础模型(RAG-GFM),通过将知识从模型参数中迁移至外部存储来缓解上述瓶颈:关键在于构建一个双模态统一检索模块,分别利用前缀结构文本构成的语义存储和基于中心性 motifs 构建的结构存储;同时设计双视角对齐目标以保留异构信息,并通过上下文增强策略引入检索到的文本和 motif 作为情境证据,从而实现高效下游适配。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15124
作者: Haonan Yuan,Qingyun Sun,Jiacheng Tao,Xingcheng Fu,Jianxin Li
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted by the Web Conference 2026 (Research Track)
Abstract:Graph Foundation Models (GFMs) have emerged as a frontier in graph learning, which are expected to deliver transferable representations across diverse tasks. However, GFMs remain constrained by in-memory bottlenecks: they attempt to encode knowledge into model parameters, which limits semantic capacity, introduces heavy lossy compression with conflicts, and entangles graph representation with the knowledge in ways that hinder efficient adaptation, undermining scalability and interpretability. In this work,we propose RAG-GFM, a Retrieval-Augmented Generation aided Graph Foundation Model that offloads knowledge from parameters and complements parameterized learning. To externalize graph knowledge, we build a dual-modal unified retrieval module, where a semantic store from prefix-structured text and a structural store from centrality-based motif. To preserve heterogeneous information, we design a dual-view alignment objective that contrasts both modalities to capture both content and relational patterns. To enable efficient downstream adaptation, we perform in-context augmentation to enrich supporting instances with retrieved texts and motifs as contextual evidence. Extensive experiments on five benchmark graph datasets demonstrate that RAG-GFM consistently outperforms 13 state-of-the-art baselines in both cross-domain node and graph classification, achieving superior effectiveness and efficiency.
zh
[AI-13] Emerging from Ground: Addressing Intent Deviation in Tool-Using Agents via Deriving Real Calls into Virtual Trajectories
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在工具使用代理(tool-using agents)中因“意图偏移”(intent deviation)导致的不可靠行为问题,该问题常表现为任务执行结果与用户真实意图不一致,且现有后训练方法难以有效识别和纠正此类偏差。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为RISE的“真实到虚拟”(Real-to-Virtual)数据合成框架:其核心是基于已验证的工具原语(tool primitives)生成多样化的虚拟轨迹,并通过关键参数变异构造针对意图偏移场景的负样本;随后利用合成数据进行两阶段微调以实现意图对齐(intent alignment),从而显著提升任务完成率(Acctask)和意图一致性(Accintent)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15120
作者: Qian Xiong,Yuekai Huang,Yujia Zheng,Tianhao Li,Ziyou Jiang,Zhiyuan Chang,Zhaoyang Li,Huanxiang Feng,Mingyang Li
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:LLMs have advanced tool-using agents for real-world applications, yet they often lead to unexpected behaviors or results. Beyond obvious failures, the subtle issue of “intent deviation” severely hinders reliable evaluation and performance improvement. Existing post-training methods generally leverage either real system samples or virtual data simulated by LLMs. However, the former is costly due to reliance on hand-crafted user requests, while the latter suffers from distribution shift from the real tools in the wild. Additionally, both methods lack negative samples tailored to intent deviation scenarios, hindering effective guidance on preference learning. We introduce RISE, a “Real-to-Virtual” method designed to mitigate intent deviation. Anchoring on verified tool primitives, RISE synthesizes virtual trajectories and generates diverse negative samples through mutation on critical parameters. With synthetic data, RISE fine-tunes backbone LLMs via the two-stage training for intent alignment. Evaluation results demonstrate that data synthesized by RISE achieve promising results in eight metrics covering user requires, execution trajectories and agent responses. Integrating with training, RISE achieves an average 35.28% improvement in Acctask (task completion) and 23.27% in Accintent (intent alignment), outperforming SOTA baselines by 1.20–42.09% and 1.17–54.93% respectively.
zh
[AI-14] Auditing Language Model Unlearning via Information Decomposition EACL2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前语言模型机器遗忘(machine unlearning)方法中存在的关键缺陷:尽管现有遗忘算法在表面上看似有效,但被遗忘数据的信息仍可通过模型内部表示线性可解,表明遗忘并不彻底。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于部分信息分解(Partial Information Decomposition, PID)的可解释、信息论框架,用于系统性审计遗忘效果。该框架通过比较遗忘前后模型表示,将与遗忘数据的互信息分解为不同成分,明确定义了“已遗忘知识”与“残余知识”,并发现残余知识主要由冗余信息构成,且与已知对抗重建攻击的脆弱性相关。基于此,作者进一步设计了一种基于表示的风险评分机制,可在推理阶段对敏感输入进行规避,从而提供一种实用的隐私泄露缓解策略。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15111
作者: Anmol Goel,Alan Ritter,Iryna Gurevych
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: EACL 2026 Main
Abstract:We expose a critical limitation in current approaches to machine unlearning in language models: despite the apparent success of unlearning algorithms, information about the forgotten data remains linearly decodable from internal representations. To systematically assess this discrepancy, we introduce an interpretable, information-theoretic framework for auditing unlearning using Partial Information Decomposition (PID). By comparing model representations before and after unlearning, we decompose the mutual information with the forgotten data into distinct components, formalizing the notions of unlearned and residual knowledge. Our analysis reveals that redundant information, shared across both models, constitutes residual knowledge that persists post-unlearning and correlates with susceptibility to known adversarial reconstruction attacks. Leveraging these insights, we propose a representation-based risk score that can guide abstention on sensitive inputs at inference time, providing a practical mechanism to mitigate privacy leakage. Our work introduces a principled, representation-level audit for unlearning, offering theoretical insight and actionable tools for safer deployment of language models.
zh
[AI-15] An Agent ic Operationalization of DISARM for FIMI Investigation on Social Media
【速读】:该论文旨在解决北约国家在应对外国信息操纵与干涉(Foreign Information Manipulation and Interference, FIMI)时,如何实现跨盟友间数据与智能的互操作性,以提升集体防御能力的问题。当前FIMI活动日益复杂且借助生成式AI等技术显著降低实施成本,导致威胁识别、态势感知和响应协调面临严峻挑战;尽管已有DISARM框架作为标准化元数据与分析工具,但在社交媒体规模上的落地仍存在困难。解决方案的关键在于提出一种框架无关的基于代理(agent-based)的操作化方法,通过构建一个多代理流水线系统,由专门的智能体协作完成两个核心任务:一是检测潜在的操纵行为,二是将这些行为透明地映射到DISARM分类体系中。该方法有效提升了FIMI分析的自动化水平,显著缓解了传统依赖人工、主观性强的工作模式,从而增强媒体与信息密集环境下的态势感知能力和数据互操作性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15109
作者: Kevin Tseng,Juan Carlos Toledano,Bart De Clerck,Yuliia Dukach,Phil Tinn
机构: 未知
类目: ocial and Information Networks (cs.SI); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注:
Abstract:The interoperability of data and intelligence across allied partners and their respective end-user groups is considered a foundational enabler to the collective defense capability–both conventional and hybrid–of NATO countries. Foreign Information Manipulation and Interference (FIMI) and related hybrid activities are conducted across various societal dimensions and infospheres, posing an ever greater challenge to the characterization of threats, sustaining situational awareness, and response coordination. Recent advances in AI have further led to the decreasing cost of AI-augmented trolling and interference activities, such as through the generation and amplification of manipulative content. Despite the introduction of the DISARM framework as a standardized metadata and analytical framework for FIMI, operationalizing it at the scale of social media remains a challenge. We propose a framework-agnostic agent-based operationalization of DISARM to investigate FIMI on social media. We develop a multi-agent pipeline in which specialized agentic AI components collaboratively (1) detect candidate manipulative behaviors, and (2) map these behaviors onto standard DISARM taxonomies in a transparent manner. We evaluated the approach on two real-world datasets annotated by domain practitioners. We demonstrate that our approach is effective in scaling the predominantly manual and heavily interpretive work of FIMI analysis, providing a direct contribution to enhancing the situational awareness and data interoperability in the context of operating in media and information-rich settings.
zh
[AI-16] Memory Retention Is Not Enough to Master Memory Tasks in Reinforcement Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)中记忆机制在持续环境变化下难以实现稳定保留与自适应更新之间的平衡问题,即现有RL基准和记忆增强智能体主要关注长期信息保留,而忽视了在部分可观测环境下对过时记忆进行有效重写的必要性。其解决方案的关键在于引入了一个专门评估持续记忆更新能力的新基准,并通过对比循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Networks, RNNs)、基于Transformer的架构以及结构化记忆模型的表现,发现经典RNN模型在记忆重写任务中展现出更高的灵活性和鲁棒性,而现代结构化记忆和Transformer模型仅在特定条件下有效,甚至在非平凡场景中表现不佳。这一结果揭示了当前方法的根本局限,并强调未来RL智能体需设计具备显式且可训练遗忘机制的记忆系统以实现稳定与适应性的协同优化。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15086
作者: Oleg Shchendrigin,Egor Cherepanov,Alexey K. Kovalev,Aleksandr I. Panov
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 11 pages, 6 figures, 7 tables
Abstract:Effective decision-making in the real world depends on memory that is both stable and adaptive: environments change over time, and agents must retain relevant information over long horizons while also updating or overwriting outdated content when circumstances shift. Existing Reinforcement Learning (RL) benchmarks and memory-augmented agents focus primarily on retention, leaving the equally critical ability of memory rewriting largely unexplored. To address this gap, we introduce a benchmark that explicitly tests continual memory updating under partial observability, i.e. the natural setting where an agent must rely on memory rather than current observations, and use it to compare recurrent, transformer-based, and structured memory architectures. Our experiments reveal that classic recurrent models, despite their simplicity, demonstrate greater flexibility and robustness in memory rewriting tasks than modern structured memories, which succeed only under narrow conditions, and transformer-based agents, which often fail beyond trivial retention cases. These findings expose a fundamental limitation of current approaches and emphasize the necessity of memory mechanisms that balance stable retention with adaptive updating. Our work highlights this overlooked challenge, introduces benchmarks to evaluate it, and offers insights for designing future RL agents with explicit and trainable forgetting mechanisms. Code: this https URL
zh
[AI-17] Incentive-Tuning: Understanding and Designing Incentives for Empirical Human-AI Decision-Making Studies
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前人机协同决策(Human-AI Collaborative Decision-Making)实证研究中激励机制设计不规范、缺乏系统性指导的问题,这直接影响了研究结果的有效性和可重复性。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个名为“Incentive-Tuning Framework”的结构化框架,该框架通过梳理现有研究中的激励方案组成、操纵方式及其对研究结果的影响等主题,为研究人员提供一套可操作的指南,涵盖激励设计的实施、反思与文档化全过程,从而推动该领域研究向更可靠、可推广的方向发展。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15064
作者: Simran Kaur,Sara Salimzadeh,Ujwal Gadiraju
机构: 未知
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Science and Game Theory (cs.GT); Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
备注:
Abstract:AI has revolutionised decision-making across various fields. Yet human judgement remains paramount for high-stakes decision-making. This has fueled explorations of collaborative decision-making between humans and AI systems, aiming to leverage the strengths of both. To explore this dynamic, researchers conduct empirical studies, investigating how humans use AI assistance for decision-making and how this collaboration impacts results. A critical aspect of conducting these studies is the role of participants, often recruited through crowdsourcing platforms. The validity of these studies hinges on the behaviours of the participants, hence effective incentives that can potentially affect these behaviours are a key part of designing and executing these studies. In this work, we aim to address the critical role of incentive design for conducting empirical human-AI decision-making studies, focusing on understanding, designing, and documenting incentive schemes. Through a thematic review of existing research, we explored the current practices, challenges, and opportunities associated with incentive design for human-AI decision-making empirical studies. We identified recurring patterns, or themes, such as what comprises the components of an incentive scheme, how incentive schemes are manipulated by researchers, and the impact they can have on research outcomes. Leveraging the acquired understanding, we curated a set of guidelines to aid researchers in designing effective incentive schemes for their studies, called the Incentive-Tuning Framework, outlining how researchers can undertake, reflect on, and document the incentive design process. By advocating for a standardised yet flexible approach to incentive design and contributing valuable insights along with practical tools, we hope to pave the way for more reliable and generalizable knowledge in the field of human-AI decision-making.
zh
[AI-18] he Responsibility Vacuum: Organizational Failure in Scaled Agent Systems
【速读】:该论文试图解决在集成代理生成代码(agent-generated code)的现代持续集成/持续部署(CI/CD)流水线中,由于决策生成速率超过人类验证能力而导致的责任归属失效问题,即“责任真空”(responsibility vacuum)。其核心问题是:尽管审批流程形式上合规,但无人同时具备批准权限与对决策依据的实质性理解能力,从而导致责任无法有效归因。解决方案的关键在于组织必须主动重构决策边界或重新分配责任,从个体决策层面转向批量或系统级的责任归属机制,否则责任真空将成为规模化代理部署中的隐性但持续存在的故障模式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15059
作者: Oleg Romanchuk,Roman Bondar
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Systems and Control (eess.SY)
备注:
Abstract:Modern CI/CD pipelines integrating agent-generated code exhibit a structural failure in responsibility attribution. Decisions are executed through formally correct approval processes, yet no entity possesses both the authority to approve those decisions and the epistemic capacity to meaningfully understand their basis. We define this condition as responsibility vacuum: a state in which decisions occur, but responsibility cannot be attributed because authority and verification capacity do not coincide. We show that this is not a process deviation or technical defect, but a structural property of deployments where decision generation throughput exceeds bounded human verification capacity. We identify a scaling limit under standard deployment assumptions, including parallel agent generation, CI-based validation, and individualized human approval gates. Beyond a throughput threshold, verification ceases to function as a decision criterion and is replaced by ritualized approval based on proxy signals. Personalized responsibility becomes structurally unattainable in this regime. We further characterize a CI amplification dynamic, whereby increasing automated validation coverage raises proxy signal density without restoring human capacity. Under fixed time and attention constraints, this accelerates cognitive offloading in the broad sense and widens the gap between formal approval and epistemic understanding. Additional automation therefore amplifies, rather than mitigates, the responsibility vacuum. We conclude that unless organizations explicitly redesign decision boundaries or reassign responsibility away from individual decisions toward batch- or system-level ownership, responsibility vacuum remains an invisible but persistent failure mode in scaled agent deployments. Subjects: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Systems and Control (eess.SY) Cite as: arXiv:2601.15059 [cs.AI] (or arXiv:2601.15059v1 [cs.AI] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.15059 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) Submission history From: Oleg Romanchuk [view email] [v1] Wed, 21 Jan 2026 15:05:27 UTC (15 KB) Full-text links: Access Paper: View a PDF of the paper titled The Responsibility Vacuum: Organizational Failure in Scaled Agent Systems, by Oleg Romanchuk and 1 other authorsView PDFHTML (experimental)TeX Source view license Current browse context: cs.AI prev | next new | recent | 2026-01 Change to browse by: cs cs.SY eess eess.SY References Citations NASA ADSGoogle Scholar Semantic Scholar export BibTeX citation Loading… BibTeX formatted citation loading… Data provided by: Bookmark checked=“checked”> Bibliographic Tools Bibliographic and Citation Tools Bibliographic Explorer Toggle Bibliographic Explorer (What is the Explorer?) Connected Papers Toggle Connected Papers (What is Connected Papers?) Litmaps Toggle Litmaps (What is Litmaps?) scite.ai Toggle scite Smart Citations (What are Smart Citations?) Code, Data, Media Code, Data and Media Associated with this Article alphaXiv Toggle alphaXiv (What is alphaXiv?) Links to Code Toggle CatalyzeX Code Finder for Papers (What is CatalyzeX?) DagsHub Toggle DagsHub (What is DagsHub?) GotitPub Toggle Gotit.pub (What is GotitPub?) Huggingface Toggle Hugging Face (What is Huggingface?) Links to Code Toggle Papers with Code (What is Papers with Code?) ScienceCast Toggle ScienceCast (What is ScienceCast?) Demos Demos Replicate Toggle Replicate (What is Replicate?) Spaces Toggle Hugging Face Spaces (What is Spaces?) Spaces Toggle TXYZ.AI (What is TXYZ.AI?) Related Papers Recommenders and Search Tools Link to Influence Flower Influence Flower (What are Influence Flowers?) Core recommender toggle CORE Recommender (What is CORE?) Author Venue Institution Topic About arXivLabs arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website. Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them. Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv’s community? Learn more about arXivLabs. Which authors of this paper are endorsers? | Disable MathJax (What is MathJax?) mathjaxToggle(); About Help contact arXivClick here to contact arXiv Contact subscribe to arXiv mailingsClick here to subscribe Subscribe Copyright Privacy Policy Web Accessibility Assistance arXiv Operational Status
zh
[AI-19] A Curriculum-Based Deep Reinforcement Learning Framework for the Electric Vehicle Routing Problem
【速读】:该论文旨在解决电动车辆路径问题带时间窗(EVRPTW)在深度强化学习(DRL)建模中训练不稳定、难以收敛或泛化能力差的问题,尤其是在约束密集场景下。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于课程学习的深度强化学习框架(CB-DRL),通过三阶段渐进式训练策略:首先优化距离与车队规模(Phase A),再引入电池管理(Phase B),最终整合为完整的EVRPTW任务(Phase C);同时采用改进的近端策略优化算法(PPO),结合相位特异性超参数、值函数与优势裁剪及自适应学习率调度机制,并设计融合全局-局部注意力和特征线性调制的异构图注意力编码器,以显式建模 depot、客户与充电站的差异化属性,从而实现从小型实例(N=10)到大规模未见实例(N=5–100)的鲁棒泛化,显著优于标准DRL基线模型。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15038
作者: Mertcan Daysalilar,Fuat Uyguroglu,Gabriel Nicolosi,Adam Meyers
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The electric vehicle routing problem with time windows (EVRPTW) is a complex optimization problem in sustainable logistics, where routing decisions must minimize total travel distance, fleet size, and battery usage while satisfying strict customer time constraints. Although deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has shown great potential as an alternative to classical heuristics and exact solvers, existing DRL models often struggle to maintain training stability-failing to converge or generalize when constraints are dense. In this study, we propose a curriculum-based deep reinforcement learning (CB-DRL) framework designed to resolve this instability. The framework utilizes a structured three-phase curriculum that gradually increases problem complexity: the agent first learns distance and fleet optimization (Phase A), then battery management (Phase B), and finally the full EVRPTW (Phase C). To ensure stable learning across phases, the framework employs a modified proximal policy optimization algorithm with phase-specific hyperparameters, value and advantage clipping, and adaptive learning-rate scheduling. The policy network is built upon a heterogeneous graph attention encoder enhanced by global-local attention and feature-wise linear modulation. This specialized architecture explicitly captures the distinct properties of depots, customers, and charging stations. Trained exclusively on small instances with N=10 customers, the model demonstrates robust generalization to unseen instances ranging from N=5 to N=100, significantly outperforming standard baselines on medium-scale problems. Experimental results confirm that this curriculum-guided approach achieves high feasibility rates and competitive solution quality on out-of-distribution instances where standard DRL baselines fail, effectively bridging the gap between neural speed and operational reliability.
zh
[AI-20] Visual and Cognitive Demands of a Large Language Model-Powered In-vehicle Conversational Agent
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)对话代理在驾驶环境中可能引发的分心风险问题,特别是其对驾驶员视觉和认知负荷的影响尚未明确。研究通过对比先进的大型语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)对话系统 Gemini Live 与手持电话通话、低负载基准任务(如视觉导航引导)以及高负载锚定任务(Operation Span, OSPAN),量化其在真实道路驾驶中的分心程度。解决方案的关键在于:采用多维度测量方法(包括检测反应任务 DRT、眼动追踪和主观工作量评分),发现基于语音交互的 Gemini Live 在认知负荷上与免提通话相当,且所有任务的平均注视时间均低于 2 秒的安全阈值;同时,驾驶员在语音交互中更倾向于将目光快速移回道路,表明长时间离眼时间并非主要安全隐患。这为安全部署语音驱动的生成式 AI 对话代理提供了实证依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15034
作者: Chris Monk,Allegra Ayala,Christine S.P. Yu,Gregory M. Fitch,Dara Gruber
机构: 未知
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Driver distraction remains a leading contributor to motor vehicle crashes, necessitating rigorous evaluation of new in-vehicle technologies. This study assessed the visual and cognitive demands associated with an advanced Large Language Model (LLM) conversational agent (Gemini Live) during on-road driving, comparing it against handsfree phone calls, visual turn-by-turn guidance (low load baseline), and the Operation Span (OSPAN) task (high load anchor). Thirty-two licensed drivers completed five secondary tasks while visual and cognitive demands were measured using the Detection Response Task (DRT) for cognitive load, eye-tracking for visual attention, and subjective workload ratings. Results indicated that Gemini Live interactions (both single-turn and multi-turn) and hands-free phone calls shared similar levels of cognitive load, between that of visual turn-by-turn guidance and OSPAN. Exploratory analysis showed that cognitive load remained stable across extended multi-turn conversations. All tasks maintained mean glance durations well below the well-established 2-second safety threshold, confirming low visual demand. Furthermore, drivers consistently dedicated longer glances to the roadway between brief off-road glances toward the device during task completion, particularly during voice-based interactions, rendering longer total-eyes-off-road time findings less consequential. Subjective ratings mirrored objective data, with participants reporting low effort, demands, and perceived distraction for Gemini Live. These findings demonstrate that advanced LLM conversational agents, when implemented via voice interfaces, impose cognitive and visual demands comparable to established, low-risk hands-free benchmarks, supporting their safe deployment in the driving environment.
zh
[AI-21] Emergent not Immanent: A Baradian Reading of Explainable AI
【速读】:该论文试图解决当前解释性人工智能(Explainable AI, XAI)研究中将解释问题简化为技术层面可还原的模型内部机制这一局限,其核心在于批判性地反思XAI背后隐含的本体论-认识论假设:即认为意义内生于模型、解释者处于系统之外、且因果结构可通过计算手段恢复。论文的关键解决方案是引入巴德(Barad)的行动者现实主义(agential realism),提出一种新的本体论-认识论框架,主张解释是一种由AI模型与人类、情境及解释工具共同构成的具身化—话语性实践(material-discursive performance),并据此揭示现有XAI方法的预设限制,进而提出支持生成性解释的设计方向,以实现更具伦理意识和情境敏感性的XAI界面设计。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15029
作者: Fabio Morreale,Joan Serrà,Yuki Mistufuji
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注: Accepted at CHI 2026
Abstract:Explainable AI (XAI) is frequently positioned as a technical problem of revealing the inner workings of an AI model. This position is affected by unexamined onto-epistemological assumptions: meaning is treated as immanent to the model, the explainer is positioned outside the system, and a causal structure is presumed recoverable through computational techniques. In this paper, we draw on Barad’s agential realism to develop an alternative onto-epistemology of XAI. We propose that interpretations are material-discursive performances that emerge from situated entanglements of the AI model with humans, context, and the interpretative apparatus. To develop this position, we read a comprehensive set of XAI methods through agential realism and reveal the assumptions and limitations that underpin several of these methods. We then articulate the framework’s ethical dimension and propose design directions for XAI interfaces that support emergent interpretation, using a speculative text-to-music interface as a case study.
zh
[AI-22] Interoperable Architecture for Digital Identity Delegation for AI Agents with Blockchain Integration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决数字身份系统中可验证委托(verifiable delegation)的难题,尤其是在集中式、联邦制和自我主权身份(Self-Sovereign Identity, SSI)环境中,如何在不暴露主凭据或私钥的前提下,使人类用户与自主AI代理均能行使并转移权限。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个统一框架,包含四个核心要素:1)委托授权凭证(Delegation Grants, DGs),作为一等授权实体,编码可撤销的权限转移并强制作用域最小化;2)规范验证上下文(Canonical Verification Context, CVC),将验证请求标准化为独立于协议或凭证格式的结构化表示;3)分层参考架构,通过信任网关(Trust Gateway)分离信任锚定、凭证与证明验证、策略评估及协议中介;4)将区块链锚定明确视为可选完整性层而非结构性依赖。该框架实现了跨异构身份生态系统的边界可控、可审计且最小权限的委托机制,为未来标准制定与自主代理集成奠定基础。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14982
作者: David Ricardo Saavedra
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注: 19 pages, 4 figures, 4 tables
Abstract:Verifiable delegation in digital identity systems remains unresolved across centralized, federated, and self-sovereign identity (SSI) environments, particularly where both human users and autonomous AI agents must exercise and transfer authority without exposing primary credentials or private keys. We introduce a unified framework that enables bounded, auditable, and least-privilege delegation across heterogeneous identity ecosystems. The framework includes four key elements: Delegation Grants (DGs), first-class authorization artefacts that encode revocable transfers of authority with enforced scope reduction; a Canonical Verification Context (CVC) that normalizes verification requests into a single structured representation independent of protocols or credential formats; a layered reference architecture that separates trust anchoring, credential and proof validation, policy evaluation, and protocol mediation via a Trust Gateway; and an explicit treatment of blockchain anchoring as an optional integrity layer rather than a structural dependency. Together, these elements advance interoperable delegation and auditability and provide a foundation for future standardization, implementation, and integration of autonomous agents into trusted digital identity infrastructures.
zh
[AI-23] HumanDiffusion: A Vision-Based Diffusion Trajectory Planner with Human-Conditioned Goals for Search and Rescue UAV
【速读】:该论文旨在解决紧急场景下人机协作的可靠性问题,即如何使自主系统在动态环境中可靠地检测人类、推断其导航目标,并安全地执行任务。解决方案的关键在于提出HumanDiffusion——一种轻量级图像条件扩散规划器,它直接从RGB图像生成以人为本的导航轨迹,结合YOLO-11的人体检测与扩散驱动的轨迹生成机制,无需依赖先验地图或计算密集型规划流程,且在像素空间中预测轨迹以保证运动平滑性和对人类的持续安全距离。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14973
作者: Faryal Batool,Iana Zhura,Valerii Serpiva,Roohan Ahmed Khan,Ivan Valuev,Issatay Tokmurziyev,Dzmitry Tsetserukou
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: This paper has been accepted at HRI, Late Breaking Report, 2026
Abstract:Reliable human–robot collaboration in emergency scenarios requires autonomous systems that can detect humans, infer navigation goals, and operate safely in dynamic environments. This paper presents HumanDiffusion, a lightweight image-conditioned diffusion planner that generates human-aware navigation trajectories directly from RGB imagery. The system combines YOLO-11–based human detection with diffusion-driven trajectory generation, enabling a quadrotor to approach a target person and deliver medical assistance without relying on prior maps or computationally intensive planning pipelines. Trajectories are predicted in pixel space, ensuring smooth motion and a consistent safety margin around humans. We evaluate HumanDiffusion in simulation and real-world indoor mock-disaster scenarios. On a 300-sample test set, the model achieves a mean squared error of 0.02 in pixel-space trajectory reconstruction. Real-world experiments demonstrate an overall mission success rate of 80% across accident-response and search-and-locate tasks with partial occlusions. These results indicate that human-conditioned diffusion planning offers a practical and robust solution for human-aware UAV navigation in time-critical assistance settings.
zh
[AI-24] InstructTime: Time Series Classification with Multimodal Language Modeling via Implicit Feature Enhancement
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统时间序列分类方法在处理上下文特征和类间语义关系时的局限性,这些方法通常采用判别式范式,直接将输入序列映射到独热编码的类别标签,难以有效整合上下文信息并捕捉类别间的语义关联。解决方案的关键在于提出一种全新的多模态生成式框架 InstructTime,其核心创新包括:1)将连续数值序列、上下文文本特征和任务指令作为多模态输入,利用微调的语言模型生成文本形式的类别标签;2)引入时间序列离散化模块将连续序列转化为离散的时间标记(temporal tokens),并通过对齐投影层与生成式自监督预训练策略增强跨模态表示对齐能力。在此基础上,进一步提出的 InstructTime++ 通过引入隐式特征建模机制弥补语言模型归纳偏置不足的问题,借助统计特征提取和视觉-语言图像描述等专用工具包挖掘原始数据中的有用隐含模式,并将其转化为文本描述以实现无缝集成,从而显著提升分类性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14968
作者: Mingyue Cheng,Xiaoyu Tao,Huajian Zhang,Qi Liu,Enhong Chen
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Most existing time series classification methods adopt a discriminative paradigm that maps input sequences directly to one-hot encoded class labels. While effective, this paradigm struggles to incorporate contextual features and fails to capture semantic relationships among classes. To address these limitations, we propose InstructTime, a novel framework that reformulates time series classification as a multimodal generative task. Specifically, continuous numerical sequences, contextual textual features, and task instructions are treated as multimodal inputs, while class labels are generated as textual outputs by tuned language models. To bridge the modality gap, InstructTime introduces a time series discretization module that converts continuous sequences into discrete temporal tokens, together with an alignment projection layer and a generative self-supervised pre-training strategy to enhance cross-modal representation alignment. Building upon this framework, we further propose InstructTime++, which extends InstructTime by incorporating implicit feature modeling to compensate for the limited inductive bias of language models. InstructTime++ leverages specialized toolkits to mine informative implicit patterns from raw time series and contextual inputs, including statistical feature extraction and vision-language-based image captioning, and translates them into textual descriptions for seamless integration. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of InstructTime++.
zh
[AI-25] Multi-Behavior Sequential Modeling with Transition-Aware Graph Attention Network for E-Commerce Recommendation WWW2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大规模电商场景下多行为序列建模的计算效率问题。现有基于Transformer的方法虽能有效捕捉用户多行为(如点击、收藏、加购、购买)之间的转移模式,但其多项式时间复杂度难以在长序列和工业级规模下应用。解决方案的关键在于提出一种线性复杂度的过渡感知图注意力网络(Transition-Aware Graph Attention Network, TGA),通过从物品层级、类别层级和邻域层级三个维度识别关键行为转移,构建结构化稀疏图,并设计过渡感知的图注意力机制,联合建模用户-物品交互与行为类型转移,从而在保持高精度的同时显著降低计算开销。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14955
作者: Hanqi Jin,Gaoming Yang,Zhangming Chan,Yapeng Yuan,Longbin Li,Fei Sun,Yeqiu Yang,Jian Wu,Yuning Jiang,Bo Zheng
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted by WWW2026 short paper
Abstract:User interactions on e-commerce platforms are inherently diverse, involving behaviors such as clicking, favoriting, adding to cart, and purchasing. The transitions between these behaviors offer valuable insights into user-item interactions, serving as a key signal for un- derstanding evolving preferences. Consequently, there is growing interest in leveraging multi-behavior data to better capture user intent. Recent studies have explored sequential modeling of multi- behavior data, many relying on transformer-based architectures with polynomial time complexity. While effective, these approaches often incur high computational costs, limiting their applicability in large-scale industrial systems with long user sequences. To address this challenge, we propose the Transition-Aware Graph Attention Network (TGA), a linear-complexity approach for modeling multi-behavior transitions. Unlike traditional trans- formers that treat all behavior pairs equally, TGA constructs a structured sparse graph by identifying informative transitions from three perspectives: (a) item-level transitions, (b) category-level transitions, and © neighbor-level transitions. Built upon the structured graph, TGA employs a transition-aware graph Attention mechanism that jointly models user-item interactions and behav- ior transition types, enabling more accurate capture of sequential patterns while maintaining computational efficiency. Experiments show that TGA outperforms all state-of-the-art models while sig- nificantly reducing computational cost. Notably, TGA has been deployed in a large-scale industrial production environment, where it leads to impressive improvements in key business metrics.
zh
[AI-26] IDAL: Temporally Interleaved Diffusion and Action Loop for High-Frequency VLA Control
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大规模视觉-语言-动作(Vision-Language-Action, VLA)模型在动态环境中因高推理延迟导致的执行盲区问题,即传统开环(open-loop)执行模式下目标移动时无法及时响应,从而引发任务失败。解决方案的关键在于提出TIDAL(Temporally Interleaved Diffusion and Action Loop)框架,其核心是通过双频分层架构将语义推理与高频执行解耦:低频宏意图循环缓存语义嵌入以支持长期规划,高频微控制循环则通过单步流整合与执行交错实现约9 Hz的控制更新频率(相比基线约2.4 Hz),同时不增加边际计算开销;此外,引入时间错位训练策略使策略能够利用过时语义意图和实时本体感知进行预测补偿,并结合差分运动预测器提升对速度变化的敏感性,从而显著增强系统在非暂停推理下的鲁棒性和动态适应能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14945
作者: Yuteng Sun,Haoran Wang,Ruofei Bai,Zhengguo Li,Jun Li,Meng Yee(Michael)Chuah,Wei Yun Yau
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large-scale Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models offer semantic generalization but suffer from high inference latency, limiting them to low-frequency batch-and-execute paradigm. This frequency mismatch creates an execution blind spot, causing failures in dynamic environments where targets move during the open-loop execution window. We propose TIDAL (Temporally Interleaved Diffusion and Action Loop), a hierarchical framework that decouples semantic reasoning from high-frequency actuation. TIDAL operates as a backbone-agnostic module for diffusion-based VLAs, using a dual-frequency architecture to redistribute the computational budget. Specifically, a low-frequency macro-intent loop caches semantic embeddings, while a high-frequency micro-control loop interleaves single-step flow integration with execution. This design enables approximately 9 Hz control updates on edge hardware (vs. approximately 2.4 Hz baselines) without increasing marginal overhead. To handle the resulting latency shift, we introduce a temporally misaligned training strategy where the policy learns predictive compensation using stale semantic intent alongside real-time proprioception. Additionally, we address the insensitivity of static vision encoders to velocity by incorporating a differential motion predictor. TIDAL is architectural, making it orthogonal to system-level optimizations. Experiments show a 2x performance gain over open-loop baselines in dynamic interception tasks. Despite a marginal regression in static success rates, our approach yields a 4x increase in feedback frequency and extends the effective horizon of semantic embeddings beyond the native action chunk size. Under non-paused inference protocols, TIDAL remains robust where standard baselines fail due to latency.
zh
[AI-27] Vision-Language Models on the Edge for Real-Time Robotic Perception
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在真实机器人系统中部署时面临的延迟高、本地计算资源有限以及云端卸载带来的隐私风险等问题。其解决方案的关键在于利用6G时代的边缘智能技术,特别是开放无线接入网(Open RAN)与多接入边缘计算(Multi-access Edge Computing, MEC)架构,将VLMs部署于靠近数据源的边缘节点,并设计基于WebRTC的数据流传输管道,实现对Unitree G1人形机器人进行实时多模态推理。实验表明,边缘部署可在保持接近云端精度的同时降低端到端延迟5%,而针对资源受限环境优化的小型化模型(如Qwen2-VL-2B-Instruct)则可实现亚秒级响应,显著提升实时性,尽管存在一定精度损失。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14921
作者: Sarat Ahmad,Maryam Hafeez,Syed Ali Raza Zaidi
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) enable multimodal reasoning for robotic perception and interaction, but their deployment in real-world systems remains constrained by latency, limited onboard resources, and privacy risks of cloud offloading. Edge intelligence within 6G, particularly Open RAN and Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC), offers a pathway to address these challenges by bringing computation closer to the data source. This work investigates the deployment of VLMs on ORAN/MEC infrastructure using the Unitree G1 humanoid robot as an embodied testbed. We design a WebRTC-based pipeline that streams multimodal data to an edge node and evaluate LLaMA-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct deployed at the edge versus in the cloud under real-time conditions. Our results show that edge deployment preserves near-cloud accuracy while reducing end-to-end latency by 5%. We further evaluate Qwen2-VL-2B-Instruct, a compact model optimized for resource-constrained environments, which achieves sub-second responsiveness, cutting latency by more than half but at the cost of accuracy.
zh
[AI-28] ailoring Adverse Event Prediction in Type 1 Diabetes with Patient-Specific Deep Learning Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决1型糖尿病(Type 1 Diabetes)管理中血糖预测精度不足的问题,尤其是在可穿戴设备和移动健康应用日益普及的背景下,如何实现更精准、及时的血糖变化预测以支持自动化胰岛素输注和决策辅助系统。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于深度学习的个性化血糖预测方法,通过利用患者特异性数据建模个体差异,显著优于传统通用模型;同时采用留一被试交叉验证与微调策略对比评估,并结合多模态数据与小样本实验设计,识别出实现有效个性化的最小数据需求,从而提升在真实世界场景下的预测准确性与响应能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14917
作者: Giorgia Rigamonti,Mirko Paolo Barbato,Davide Marelli,Paolo Napoletano
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Effective management of Type 1 Diabetes requires continuous glucose monitoring and precise insulin adjustments to prevent hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. With the growing adoption of wearable glucose monitors and mobile health applications, accurate blood glucose prediction is essential for enhancing automated insulin delivery and decision-support systems. This paper presents a deep learning-based approach for personalized blood glucose prediction, leveraging patient-specific data to improve prediction accuracy and responsiveness in real-world scenarios. Unlike traditional generalized models, our method accounts for individual variability, enabling more effective subject-specific predictions. We compare Leave-One-Subject-Out Cross-Validation with a fine-tuning strategy to evaluate their ability to model patient-specific dynamics. Results show that personalized models significantly improve the prediction of adverse events, enabling more precise and timely interventions in real-world scenarios. To assess the impact of patient-specific data, we conduct experiments comparing a multimodal, patient-specific approach against traditional CGM-only methods. Additionally, we perform an ablation study to investigate model performance with progressively smaller training sets, identifying the minimum data required for effective personalization-an essential consideration for real-world applications where extensive data collection is often challenging. Our findings underscore the potential of adaptive, personalized glucose prediction models for advancing next-generation diabetes management, particularly in wearable and mobile health platforms, enhancing consumer-oriented diabetes care solutions.
zh
[AI-29] Just aware enough: Evaluating awareness across artificial systems
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前关于人工智能(Artificial Intelligence, AI)意识与道德地位的争议中缺乏统一评估标准的问题。其核心挑战在于如何在多样化的AI系统中建立一个可操作且具比较性的评价框架。解决方案的关键在于提出以“意识”(awareness)为核心的概念替代对“人工意识”(artificial consciousness)的模糊探讨,并构建一种领域敏感、可扩展、多维且能预测任务表现的评估方法,从而实现对不同架构、规模和应用场景下AI系统的意识特征进行结构化比较与分析。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14901
作者: Nadine Meertens,Suet Lee,Ophelia Deroy
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 24 pages (including references), 1 figure
Abstract:Recent debates on artificial intelligence increasingly emphasise questions of AI consciousness and moral status, yet there remains little agreement on how such properties should be evaluated. In this paper, we argue that awareness offers a more productive and methodologically tractable alternative. We introduce a practical method for evaluating awareness across diverse systems, where awareness is understood as encompassing a system’s abilities to process, store and use information in the service of goal-directed action. Central to this approach is the claim that any evaluation aiming to capture the diversity of artificial systems must be domain-sensitive, deployable at any scale, multidimensional, and enable the prediction of task performance, while generalising to the level of abilities for the sake of comparison. Given these four desiderata, we outline a structured approach to evaluating and comparing awareness profiles across artificial systems with differing architectures, scales, and operational domains. By shifting the focus from artificial consciousness to being just aware enough, this approach aims to facilitate principled assessment, support design and oversight, and enable more constructive scientific and public discourse.
zh
[AI-30] o Neuro-Symbolic Classification and Beyond by Compiling Description Logic Ontologies to Probabilistic Circuits
【速读】:该论文旨在解决神经符号方法在实际应用中缺乏对描述逻辑(Description Logic)本体(ontology)原生支持的问题,从而无法保证模型预测结果与领域知识的一致性。其解决方案的关键在于将描述逻辑本体编译为概率电路(probabilistic circuit),这是一种前向可微的计算图结构,能够高效执行查询和推理任务。通过该电路表示,研究者实现了三项核心功能:生成语义忠实且对机器学习模型具有挑战性的合成数据集、在GPU上实现可扩展的演绎推理(速度比传统推理引擎快达三个数量级)、以及构建预测结果近似或可证明符合本体知识的神经符号分类器。此方法显著提升了深度学习与知识表示领域的融合程度,并在多个现实相关任务中展现出可靠性和竞争力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14894
作者: Nicolas Lazzari,Valentina Presutti,Antonio Vergari
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Manuscript under review
Abstract:Background: Neuro-symbolic methods enhance the reliability of neural network classifiers through logical constraints, but they lack native support for ontologies. Objectives: We aim to develop a neuro-symbolic method that reliably outputs predictions consistent with a Description Logic ontology that formalizes domain-specific knowledge. Methods: We encode a Description Logic ontology as a circuit, a feed-forward differentiable computational graph that supports tractable execution of queries and transformations. We show that the circuit can be used to (i) generate synthetic datasets that capture the semantics of the ontology; (ii) efficiently perform deductive reasoning on a GPU; (iii) implement neuro-symbolic models whose predictions are approximately or provably consistent with the knowledge defined in the ontology. Results We show that the synthetic dataset generated using the circuit qualitatively captures the semantics of the ontology while being challenging for Machine Learning classifiers, including neural networks. Moreover, we show that compiling the ontology into a circuit is a promising approach for scalable deductive reasoning, with runtimes up to three orders of magnitude faster than available reasoners. Finally, we show that our neuro-symbolic classifiers reliably produce consistent predictions when compared to neural network baselines, maintaining competitive performances or even outperforming them. Conclusions By compiling Description Logic ontologies into circuits, we obtain a tighter integration between the Deep Learning and Knowledge Representation fields. We show that a single circuit representation can be used to tackle different challenging tasks closely related to real-world applications. Comments: Manuscript under review Subjects: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14894 [cs.AI] (or arXiv:2601.14894v1 [cs.AI] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14894 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) Submission history From: Nicolas Lazzari [view email] [v1] Wed, 21 Jan 2026 11:30:14 UTC (4,468 KB) Full-text links: Access Paper: View a PDF of the paper titled To Neuro-Symbolic Classification and Beyond by Compiling Description Logic Ontologies to Probabilistic Circuits, by Nicolas Lazzari and 2 other authorsView PDFHTML (experimental)TeX Source view license Current browse context: cs.AI prev | next new | recent | 2026-01 Change to browse by: cs References Citations NASA ADSGoogle Scholar Semantic Scholar export BibTeX citation Loading… BibTeX formatted citation loading… Data provided by: Bookmark checked=“checked”> Bibliographic Tools Bibliographic and Citation Tools Bibliographic Explorer Toggle Bibliographic Explorer (What is the Explorer?) Connected Papers Toggle Connected Papers (What is Connected Papers?) Litmaps Toggle Litmaps (What is Litmaps?) scite.ai Toggle scite Smart Citations (What are Smart Citations?) Code, Data, Media Code, Data and Media Associated with this Article alphaXiv Toggle alphaXiv (What is alphaXiv?) Links to Code Toggle CatalyzeX Code Finder for Papers (What is CatalyzeX?) DagsHub Toggle DagsHub (What is DagsHub?) GotitPub Toggle Gotit.pub (What is GotitPub?) Huggingface Toggle Hugging Face (What is Huggingface?) Links to Code Toggle Papers with Code (What is Papers with Code?) ScienceCast Toggle ScienceCast (What is ScienceCast?) Demos Demos Replicate Toggle Replicate (What is Replicate?) Spaces Toggle Hugging Face Spaces (What is Spaces?) Spaces Toggle TXYZ.AI (What is TXYZ.AI?) Related Papers Recommenders and Search Tools Link to Influence Flower Influence Flower (What are Influence Flowers?) Core recommender toggle CORE Recommender (What is CORE?) Author Venue Institution Topic About arXivLabs arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website. Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them. Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv’s community? Learn more about arXivLabs. Which authors of this paper are endorsers? | Disable MathJax (What is MathJax?) mathjaxToggle(); About Help contact arXivClick here to contact arXiv Contact subscribe to arXiv mailingsClick here to subscribe Subscribe Copyright Privacy Policy Web Accessibility Assistance arXiv Operational Status
zh
[AI-31] From Observation to Prediction: LSTM for Vehicle Lane Change Forecasting on Highway On/Off-Ramps
【速读】:该论文旨在解决高速公路匝道(on and off-ramps)区域车辆行为预测准确性不足的问题,此类区域因交通流变异性高而易引发安全隐患。解决方案的关键在于利用ExiD无人机数据集,构建多层长短期记忆网络(Multi-layered LSTM)模型,对匝道兴趣区(Area of Interest, AoI)与直线路段进行对比建模,并测试不同预测时域下的性能表现,结果表明在4秒预测时域内,匝道区域的预测准确率可达约76%,显著优于传统直线路段场景(94%),验证了该方法在提升复杂路段交通预测精度方面的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14848
作者: Mohamed Abouras,Catherine M. Elias
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注:
Abstract:On and off-ramps are understudied road sections even though they introduce a higher level of variation in highway interactions. Predicting vehicles’ behavior in these areas can decrease the impact of uncertainty and increase road safety. In this paper, the difference between this Area of Interest (AoI) and a straight highway section is studied. Multi-layered LSTM architecture to train the AoI model with ExiD drone dataset is utilized. In the process, different prediction horizons and different models’ workflow are tested. The results show great promise on horizons up to 4 seconds with prediction accuracy starting from about 76% for the AoI and 94% for the general highway scenarios on the maximum horizon.
zh
[AI-32] CAG-Avatar: Cross-Attention Guided Gaussian Avatars for High-Fidelity Head Reconstruction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前基于3D高斯溅射(3D Gaussian Splashing, 3D-GS)的驱动头像动画中,因采用“一刀切”全局调优策略而导致面部不同区域(如可变形皮肤与刚性牙齿)动态建模失真、出现模糊和畸变伪影的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出条件自适应高斯头像(Conditionally-Adaptive Gaussian Avatars, CAG-Avatar)框架,核心创新是设计了一个基于交叉注意力(cross-attention)的条件自适应融合模块(Conditionally Adaptive Fusion Module),使每个3D高斯粒子作为查询,根据其初始位置自适应地从全局表情码中提取相关驱动信号,实现针对局部区域的“量身定制”式驱动,从而显著提升细节重建精度,尤其在牙齿等挑战性区域表现优异,同时保持实时渲染性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14844
作者: Zhe Chang,Haodong Jin,Yan Song,Hui Yu
机构: 未知
类目: Graphics (cs.GR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Creating high-fidelity, real-time drivable 3D head avatars is a core challenge in digital animation. While 3D Gaussian Splashing (3D-GS) offers unprecedented rendering speed and quality, current animation techniques often rely on a “one-size-fits-all” global tuning approach, where all Gaussian primitives are uniformly driven by a single expression code. This simplistic approach fails to unravel the distinct dynamics of different facial regions, such as deformable skin versus rigid teeth, leading to significant blurring and distortion artifacts. We introduce Conditionally-Adaptive Gaussian Avatars (CAG-Avatar), a framework that resolves this key limitation. At its core is a Conditionally Adaptive Fusion Module built on cross-attention. This mechanism empowers each 3D Gaussian to act as a query, adaptively extracting relevant driving signals from the global expression code based on its canonical position. This “tailor-made” conditioning strategy drastically enhances the modeling of fine-grained, localized dynamics. Our experiments confirm a significant improvement in reconstruction fidelity, particularly for challenging regions such as teeth, while preserving real-time rendering performance.
zh
[AI-33] Implementing Knowledge Representation and Reasoning with Object Oriented Design IJCAI
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现代软件工程与知识表示与推理(Knowledge Representation and Reasoning, KRR)系统之间集成困难的问题。当前,面向对象编程(Object-Oriented Programming, OOP)是开发复杂应用的标准范式,而现有KRR框架通常依赖外部本体和专用语言,难以与命令式代码无缝集成。解决方案的关键在于提出KRROOD框架,通过将知识作为一等编程抽象(first-class programming abstraction),利用原生类结构实现知识的表达与操作,从而在逻辑编程与OOP范式之间建立桥梁,支持高表达能力的推理,并在OWL2Bench基准测试和人-机器人任务学习场景中验证了其高效性与实用性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14840
作者: Abdelrhman Bassiouny,Tom Schierenbeck,Sorin Arion,Benjamin Alt,Naren Vasantakumaar,Giang Nguyen,Michael Beetz
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Robotics (cs.RO); Software Engineering (cs.SE)
备注: 9 pages, 2 figures, submitted to the 2026 International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI)
Abstract:This paper introduces KRROOD, a framework designed to bridge the integration gap between modern software engineering and Knowledge Representation Reasoning (KRR) systems. While Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is the standard for developing complex applications, existing KRR frameworks often rely on external ontologies and specialized languages that are difficult to integrate with imperative code. KRROOD addresses this by treating knowledge as a first-class programming abstraction using native class structures, bridging the gap between the logic programming and OOP paradigms. We evaluate the system on the OWL2Bench benchmark and a human-robot task learning scenario. Experimental results show that KRROOD achieves strong performance while supporting the expressive reasoning required for real-world autonomous systems.
zh
[AI-34] Measuring and Aligning Abstraction in Vision-Language Models with Medical Taxonomies
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉-语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在胸部X光分类任务中存在“抽象错误”(abstraction errors)的问题,即尽管模型在标准平坦指标(flat metrics)上表现优异,但其分类错误在临床意义上存在显著差异——部分错误属于轻微误判,而另一些则可能跨医学分支造成严重误诊。为量化和缓解此类问题,作者引入基于医学分类体系的层次化评估指标,并提出“灾难性抽象错误”(Catastrophic Abstraction Errors)来捕捉跨分支的严重误判。解决方案的关键在于两个方面:一是采用风险约束阈值法(risk-constrained thresholding)以降低严重错误率;二是通过基于径向嵌入(radial embeddings)的、面向医学分类体系的微调策略(taxonomy-aware fine-tuning),实现模型输出与临床知识结构的对齐,从而将严重抽象错误控制在2%以下,同时保持整体性能竞争力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14827
作者: Ben Schaper,Maxime Di Folco,Bernhard Kainz,Julia A. Schnabel,Cosmin I. Bercea
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Vision-Language Models show strong zero-shot performance for chest X-ray classification, but standard flat metrics fail to distinguish between clinically minor and severe errors. This work investigates how to quantify and mitigate abstraction errors by leveraging medical taxonomies. We benchmark several state-of-the-art VLMs using hierarchical metrics and introduce Catastrophic Abstraction Errors to capture cross-branch mistakes. Our results reveal substantial misalignment of VLMs with clinical taxonomies despite high flat performance. To address this, we propose risk-constrained thresholding and taxonomy-aware fine-tuning with radial embeddings, which reduce severe abstraction errors to below 2 per cent while maintaining competitive performance. These findings highlight the importance of hierarchical evaluation and representation-level alignment for safer and more clinically meaningful deployment of VLMs.
zh
[AI-35] CI4A: Semantic Component Interfaces for Agents Empowering Web Automation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在网页交互任务中对细粒度、低层次UI组件操作能力不足的问题。现有方法多依赖强化学习等技术提升模型的接地能力,但往往受限于人类设计的界面逻辑。本文提出的关键解决方案是构建专为智能体优化的交互接口——Component Interface for Agent (CI4A),其核心在于通过语义封装机制将复杂UI组件的交互逻辑抽象为一组统一的工具原语(tool primitives),从而赋予智能体更高效、灵活的操作能力。该方案在Ant Design框架中实现并覆盖23类常用UI组件,并结合动态更新动作空间的混合智能体架构,在WebArena基准测试中显著提升了任务成功率至86.3%,达到当前最优水平。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14790
作者: Zhi Qiu,Jiazheng Sun,Chenxiao Xia,Jun Zheng,Xin Peng
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 9 pages, 5 figures
Abstract:While Large Language Models demonstrate remarkable proficiency in high-level semantic planning, they remain limited in handling fine-grained, low-level web component manipulations. To address this limitation, extensive research has focused on enhancing model grounding capabilities through techniques such as Reinforcement Learning. However, rather than compelling agents to adapt to human-centric interfaces, we propose constructing interaction interfaces specifically optimized for agents. This paper introduces Component Interface for Agent (CI4A), a semantic encapsulation mechanism that abstracts the complex interaction logic of UI components into a set of unified tool primitives accessible to agents. We implemented CI4A within Ant Design, an industrial-grade front-end framework, covering 23 categories of commonly used UI components. Furthermore, we developed a hybrid agent featuring an action space that dynamically updates according to the page state, enabling flexible invocation of available CI4A tools. Leveraging the CI4A-integrated Ant Design, we refactored and upgraded the WebArena benchmark to evaluate existing SoTA methods. Experimental results demonstrate that the CI4A-based agent significantly outperforms existing approaches, achieving a new SoTA task success rate of 86.3%, alongside substantial improvements in execution efficiency.
zh
[AI-36] raining-Efficient Text-to-Music Generation with State-Space Modeling
【速读】:该论文旨在解决文本到音乐生成(Text-to-Music Generation, TTM)模型训练中计算资源消耗大、依赖私有数据以及缺乏开放性的问题。其关键解决方案是采用状态空间模型(State-Space Models, SSMs)替代传统Transformer架构,在保持约3亿参数规模(与MusicGen-small基准相当)的前提下,显著提升训练效率并降低对大规模数据的依赖。实验表明,所提出的SSM-based模型在仅使用9%的浮点运算量(FLOPs)和2%的训练数据量的情况下,仍能实现与基准相当的客观指标和主观听觉评估性能,并且在相同训练预算下,即使模型规模缩小至四分之一,依然保持竞争力,从而推动TTM研究的可及性和民主化。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14786
作者: Wei-Jaw Lee,Fang-Chih Hsieh,Xuanjun Chen,Fang-Duo Tsai,Yi-Hsuan Yang
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 9 pages, 3 figures. This is a preprint of a paper submitted to IEEE/ACM TASLP
Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-music generation (TTM) have yielded high-quality results, but often at the cost of extensive compute and the use of large proprietary internal data. To improve the affordability and openness of TTM training, an open-source generative model backbone that is more training- and data-efficient is needed. In this paper, we constrain the number of trainable parameters in the generative model to match that of the MusicGen-small benchmark (with about 300M parameters), and replace its Transformer backbone with the emerging class of state-space models (SSMs). Specifically, we explore different SSM variants for sequence modeling, and compare a single-stage SSM-based design with a decomposable two-stage SSM/diffusion hybrid design. All proposed models are trained from scratch on a purely public dataset comprising 457 hours of CC-licensed music, ensuring full openness. Our experimental findings are three-fold. First, we show that SSMs exhibit superior training efficiency compared to the Transformer counterpart. Second, despite using only 9% of the FLOPs and 2% of the training data size compared to the MusicGen-small benchmark, our model achieves competitive performance in both objective metrics and subjective listening tests based on MusicCaps captions. Finally, our scaling-down experiment demonstrates that SSMs can maintain competitive performance relative to the Transformer baseline even at the same training budget (measured in iterations), when the model size is reduced to four times smaller. To facilitate the democratization of TTM research, the processed captions, model checkpoints, and source code are available on GitHub via the project page: this https URL.
zh
[AI-37] owards Bound Consistency for the No-Overlap Constraint Using MDDs
【速读】:该论文旨在解决**无重叠约束(no-overlap constraint)**在求解过程中难以实现边界一致性的难题,因为该问题已被证明是NP完全的。为应对这一挑战,研究者提出了一种首个能够实现边界一致性的算法:通过构建由Ciré和van Hoeve定义的无重叠MDD(Multi-valued Decision Diagram),从中提取作业的时间窗口边界信息,从而在多项式时间内收紧作业的开始时间和结束时间。该方案的关键在于利用MDD结构高效地计算边界,并通过限制MDD宽度引入一个松弛版本(relaxed MDD),以控制计算复杂度并支持边界一致性的松弛过滤。实验表明,该方法即使在宽度受限的情况下,也能显著减少搜索树中访问的节点数,且与传统传播方法具有互补性,从而大幅降低求解时间和节点数量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14784
作者: Amaury Guichard,Laurent Michel,Hélène Verhaeghe,Pierre Schaus
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Achieving bound consistency for the no-overlap constraint is known to be NP-complete. Therefore, several polynomial-time tightening techniques, such as edge finding, not-first-not-last reasoning, and energetic reasoning, have been introduced for this constraint. In this work, we derive the first bound-consistent algorithm for the no-overlap constraint. By building on the no-overlap MDD defined by Ciré and van Hoeve, we extract bounds of the time window of the jobs, allowing us to tighten start and end times in time polynomial in the number of nodes of the MDD. Similarly, to bound the size and time-complexity, we limit the width of the MDD to a threshold, creating a relaxed MDD that can also be used to relax the bound-consistent filtering. Through experiments on a sequencing problem with time windows and a just-in-time objective ( 1 \mid r_j, d_j, \bard_j \mid \sum E_j + \sum T_j ), we observe that the proposed filtering, even with a threshold on the width, achieves a stronger reduction in the number of nodes visited in the search tree compared to the previously proposed precedence-detection algorithm of Ciré and van Hoeve. The new filtering also appears to be complementary to classical propagation methods for the no-overlap constraint, allowing a substantial reduction in both the number of nodes and the solving time on several instances.
zh
[AI-38] Semantic-Guided Unsupervised Video Summarization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有无监督视频摘要方法在关键帧选择中依赖单一模态特征、忽视语义信息引导作用,以及生成对抗网络(Generative Adversarial Networks, GANs)训练不稳定的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种语义引导的无监督视频摘要方法,核心创新包括:设计了一种帧级语义对齐注意力机制并集成至关键帧选择器中,以指导基于Transformer的生成器在对抗框架内更准确地重建视频;同时引入增量式训练策略,逐步更新模型组件,有效缓解了GAN训练过程中的不稳定性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14773
作者: Haizhou Liu,Haodong Jin,Yiming Wang,Hui Yu
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multimedia (cs.MM)
备注:
Abstract:Video summarization is a crucial technique for social understanding, enabling efficient browsing of massive multimedia content and extraction of key information from social platforms. Most existing unsupervised summarization methods rely on Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to enhance keyframe selection and generate coherent, video summaries through adversarial training. However, such approaches primarily exploit unimodal features, overlooking the guiding role of semantic information in keyframe selection, and often suffer from unstable training. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Semantic-Guided Unsupervised Video Summarization method. Specifically, we design a novel frame-level semantic alignment attention mechanism and integrate it into a keyframe selector, which guides the Transformer-based generator within the adversarial framework to better reconstruct videos. In addition, we adopt an incremental training strategy to progressively update the model components, effectively mitigating the instability of GAN training. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves superior performance on multiple benchmark datasets.
zh
[AI-39] Anytime Optimal Decision Tree Learning with Continuous Features
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有最优决策树学习算法在处理连续特征时的计算效率与 anytime 行为之间的矛盾问题。具体而言,当前基于深度优先搜索的精确算法虽能保证全局最优解,但其在早期中断时往往生成高度不平衡且次优的树结构,导致实用性受限;而传统的贪心方法(如 C4.5)虽具有良好的 anytime 性能,却无法保证解的质量。解决方案的关键在于引入一种基于有限差异搜索(Limited Discrepancy Search, LDS)的 anytime 完整策略,通过更均匀地分配计算资源到整个树结构中,确保在任意中断时刻都能获得高质量的决策树,从而兼顾求解质量与实时响应能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14765
作者: Harold Kiossou,Pierre Schaus,Siegfried Nijssen
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:In recent years, significant progress has been made on algorithms for learning optimal decision trees, primarily in the context of binary features. Extending these methods to continuous features remains substantially more challenging due to the large number of potential splits for each feature. Recently, an elegant exact algorithm was proposed for learning optimal decision trees with continuous features; however, the rapidly increasing computational time limits its practical applicability to shallow depths (typically 3 or 4). It relies on a depth-first search optimization strategy that fully optimizes the left subtree of each split before exploring the corresponding right subtree. While effective in finding optimal solutions given sufficient time, this strategy can lead to poor anytime behavior: when interrupted early, the best-found tree is often highly unbalanced and suboptimal. In such cases, purely greedy methods such as C4.5 may, paradoxically, yield better solutions. To address this limitation, we propose an anytime, yet complete approach leveraging limited discrepancy search, distributing the computational effort more evenly across the entire tree structure, and thus ensuring that a high-quality decision tree is available at any interruption point. Experimental results show that our approach outperforms the existing one in terms of anytime performance.
zh
[AI-40] An XAI View on Explainable ASP: Methods Systems and Perspectives
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前Answer Set Programming (ASP) 中解释方法覆盖不全的问题,即现有解释手段往往针对特定场景设计,难以应对ASP用户在实际应用中遇到的多样化解释需求。其解决方案的关键在于从可解释人工智能(Explainable AI, XAI)的视角出发,系统梳理ASP解释的类型与用户提问之间的关联,并评估现有理论和工具在多大程度上覆盖这些解释场景,从而识别出当前研究中的空白并提出未来的研究方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14764
作者: Thomas Eiter,Tobias Geibinger,Zeynep G. Saribatur
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Logic in Computer Science (cs.LO)
备注: 10 pages
Abstract:Answer Set Programming (ASP) is a popular declarative reasoning and problem solving approach in symbolic AI. Its rule-based formalism makes it inherently attractive for explainable and interpretive reasoning, which is gaining importance with the surge of Explainable AI (XAI). A number of explanation approaches and tools for ASP have been developed, which often tackle specific explanatory settings and may not cover all scenarios that ASP users encounter. In this survey, we provide, guided by an XAI perspective, an overview of types of ASP explanations in connection with user questions for explanation, and describe how their coverage by current theory and tools. Furthermore, we pinpoint gaps in existing ASP explanations approaches and identify research directions for future work.
zh
[AI-41] FSX: Message Flow Sensitivity Enhanced Structural Explainer for Graph Neural Networks
【速读】:该论文旨在解决图神经网络(Graph Neural Networks, GNNs)预测可解释性不足的问题,尤其是现有解释方法在计算效率与结构交互捕捉之间存在权衡:梯度法虽高效但忽略结构关联,博弈论方法虽能刻画交互却计算开销大且可能偏离模型真实推理路径。解决方案的关键在于提出FSX(Message Flow Sensitivity Enhanced Structural Explainer),其核心创新是将模型内部的消息流敏感性分析与外部图数据上的合作博弈相结合——首先通过单次前向传播中局部节点扰动模拟,量化消息流强度变化并排序关键流;随后将这些敏感流投影至输入图构建语义紧凑的子图,并在每个子图内设计一种融合节点特征重要性和维持/破坏关键流能力的Shapley-like值,从而实现高保真、低延迟的结构化解释,揭示GNN决策中关键子结构如何通过控制内部计算路径稳定性施加影响。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14730
作者: Bizu Feng,Zhimu Yang,Shaode Yu,Zixin Hu
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 8 pages, 4 figures, Preprint
Abstract:Despite the widespread success of Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), understanding the reasons behind their specific predictions remains challenging. Existing explainability methods face a trade-off that gradient-based approaches are computationally efficient but often ignore structural interactions, while game-theoretic techniques capture interactions at the cost of high computational overhead and potential deviation from the model’s true reasoning path. To address this gap, we propose FSX (Message Flow Sensitivity Enhanced Structural Explainer), a novel hybrid framework that synergistically combines the internal message flows of the model with a cooperative game approach applied to the external graph data. FSX first identifies critical message flows via a novel flow-sensitivity analysis: during a single forward pass, it simulates localized node perturbations and measures the resulting changes in message flow intensities. These sensitivity-ranked flows are then projected onto the input graph to define compact, semantically meaningful subgraphs. Within each subgraph, a flow-aware cooperative game is conducted, where node contributions are evaluated fairly through a Shapley-like value that incorporates both node-feature importance and their roles in sustaining or destabilizing the identified critical flows. Extensive evaluation across multiple datasets and GNN architectures demonstrates that FSX achieves superior explanation fidelity with significantly reduced runtime, while providing unprecedented insights into the structural logic underlying model predictions–specifically, how important sub-structures exert influence by governing the stability of key internal computational pathways.
zh
[AI-42] DARA: Few-shot Budget Allocation in Online Advertising via In-Context Decision Making with RL-Finetuned LLM s WWW
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在线广告中广告商在预算约束下优化赢得广告位的累积价值问题,尤其是在历史交互数据稀少的“少样本”场景中,传统强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)方法难以有效应用。其核心挑战在于如何在有限数据条件下实现高精度的决策优化。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种名为DARA的双阶段框架:第一阶段由大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)作为少样本推理器,通过上下文提示生成初始策略;第二阶段引入反馈驱动的精细化优化器,对初始策略进行数值精度增强的调整。该设计巧妙结合了LLMs的少样本泛化能力与数值优化所需的精确适应性,从而显著提升了广告竞价任务中的累积价值表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14711
作者: Mingxuan Song,Yusen Huo,Bohan Zhou,Shenglin Yin,Zhen Xiao,Jieyi Long,Zhilin Zhang,Chuan Yu
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Accepted at The ACM Web Conference (WWW) 2026
Abstract:Optimizing the advertiser’s cumulative value of winning impressions under budget constraints poses a complex challenge in online advertising, under the paradigm of AI-Generated Bidding (AIGB). Advertisers often have personalized objectives but limited historical interaction data, resulting in few-shot scenarios where traditional reinforcement learning (RL) methods struggle to perform effectively. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer a promising alternative for AIGB by leveraging their in-context learning capabilities to generalize from limited data. However, they lack the numerical precision required for fine-grained optimization. To address this limitation, we introduce GRPO-Adaptive, an efficient LLM post-training strategy that enhances both reasoning and numerical precision by dynamically updating the reference policy during training. Built upon this foundation, we further propose DARA, a novel dual-phase framework that decomposes the decision-making process into two stages: a few-shot reasoner that generates initial plans via in-context prompting, and a fine-grained optimizer that refines these plans using feedback-driven reasoning. This separation allows DARA to combine LLMs’ in-context learning strengths with precise adaptability required by AIGB tasks. Extensive experiments on both real-world and synthetic data environments demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms existing baselines in terms of cumulative advertiser value under budget constraints.
zh
[AI-43] Case-Guided Sequential Assay Planning in Drug Discovery
【速读】:该论文旨在解决药物发现中实验检测序列优化的问题,这是一个在严重不确定性与资源约束下进行高风险决策的规划问题。传统强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)方法因缺乏显式的环境模拟器或转移数据(s, a, s’)而难以适用,因规划只能依赖静态的历史结果数据库。解决方案的关键在于提出隐式贝叶斯马尔可夫决策过程(Implicit Bayesian Markov Decision Process, IBMDP),其通过利用相似历史结果构建非参数化的信念分布来隐式建模转移动态,实现贝叶斯信念更新,并结合集成蒙特卡洛树搜索(ensemble MCTS)进行稳定策略生成,从而在追求目标结果的信息获取与资源效率之间取得平衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14710
作者: Tianchi Chen,Jan Bima,Sean L. Wu,Otto Ritter,Bingjia Yang,Xiang Yu
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computational Engineering, Finance, and Science (cs.CE)
备注:
Abstract:Optimally sequencing experimental assays in drug discovery is a high-stakes planning problem under severe uncertainty and resource constraints. A primary obstacle for standard reinforcement learning (RL) is the absence of an explicit environment simulator or transition data (s, a, s’) ; planning must rely solely on a static database of historical outcomes. We introduce the Implicit Bayesian Markov Decision Process (IBMDP), a model-based RL framework designed for such simulator-free settings. IBMDP constructs a case-guided implicit model of transition dynamics by forming a nonparametric belief distribution using similar historical outcomes. This mechanism enables Bayesian belief updating as evidence accumulates and employs ensemble MCTS planning to generate stable policies that balance information gain toward desired outcomes with resource efficiency. We validate IBMDP through comprehensive experiments. On a real-world central nervous system (CNS) drug discovery task, IBMDP reduced resource consumption by up to 92% compared to established heuristics while maintaining decision confidence. To rigorously assess decision quality, we also benchmarked IBMDP in a synthetic environment with a computable optimal policy. Our framework achieves significantly higher alignment with this optimal policy than a deterministic value iteration alternative that uses the same similarity-based model, demonstrating the superiority of our ensemble planner. IBMDP offers a practical solution for sequential experimental design in data-rich but simulator-poor domains.
zh
[AI-44] Proximal Policy Optimization with Evolutionary Mutations
【速读】:该论文旨在解决Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)算法在训练过程中因探索不足而导致的过早收敛(premature convergence)问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出POEM(Proximal Policy Optimization with Evolutionary Mutations),通过引入受进化算法启发的自适应探索机制来增强策略多样性:具体而言,POEM监控当前策略与历史策略移动平均之间的Kullback-Leibler (KL)散度,当KL散度趋于稳定表明策略陷入局部最优时,自动触发对策略参数的变异操作以促进探索,从而有效缓解探索-利用权衡困境。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14705
作者: Casimir Czworkowski,Stephen Hornish,Alhassan S. Yasin
机构: 未知
类目: Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Science and Game Theory (cs.GT); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 10 pages, 5 figures, 2 tables, 1 algorithm
Abstract:Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) is a widely used reinforcement learning algorithm known for its stability and sample efficiency, but it often suffers from premature convergence due to limited exploration. In this paper, we propose POEM (Proximal Policy Optimization with Evolutionary Mutations), a novel modification to PPO that introduces an adaptive exploration mechanism inspired by evolutionary algorithms. POEM enhances policy diversity by monitoring the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence between the current policy and a moving average of previous policies. When policy changes become minimal, indicating stagnation, POEM triggers an adaptive mutation of policy parameters to promote exploration. We evaluate POEM on four OpenAI Gym environments: CarRacing, MountainCar, BipedalWalker, and LunarLander. Through extensive fine-tuning using Bayesian optimization techniques and statistical testing using Welch’s t-test, we find that POEM significantly outperforms PPO on three of the four tasks (BipedalWalker: t=-2.0642, p=0.0495; CarRacing: t=-6.3987, p=0.0002; MountainCar: t=-6.2431, p0.0001), while performance on LunarLander is not statistically significant (t=-1.8707, p=0.0778). Our results highlight the potential of integrating evolutionary principles into policy gradient methods to overcome exploration-exploitation tradeoffs.
zh
[AI-45] When Text-as-Vision Meets Semantic IDs in Generative Recommendation: An Empirical Study
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式推荐(Generative Recommendation, GR)模型中语义ID学习(Semantic ID learning)的瓶颈问题,即传统基于文本编码器的语义表示方法在处理现实场景中符号化、属性导向的物品描述时存在语义碎片化和跨模态嵌入结构不匹配的问题。其核心解决方案是将文本视为视觉信号,采用OCR-based文本表示方法——通过将物品描述渲染为图像并使用视觉型OCR模型进行编码,从而获得更稳定、高效的语义ID表示。实验表明,该方法在单模态与多模态设置下均能实现或超越标准文本嵌入的效果,并在极端空间分辨率压缩下仍保持鲁棒性,展现出良好的实用性与效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14697
作者: Shutong Qiao,Wei Yuan,Tong Chen,Xiangyu Zhao,Quoc Viet Hung Nguyen,Hongzhi Yin
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Semantic ID learning is a key interface in Generative Recommendation (GR) models, mapping items to discrete identifiers grounded in side information, most commonly via a pretrained text encoder. However, these text encoders are primarily optimized for well-formed natural language. In real-world recommendation data, item descriptions are often symbolic and attribute-centric, containing numerals, units, and abbreviations. These text encoders can break these signals into fragmented tokens, weakening semantic coherence and distorting relationships among attributes. Worse still, when moving to multimodal GR, relying on standard text encoders introduces an additional obstacle: text and image embeddings often exhibit mismatched geometric structures, making cross-modal fusion less effective and less stable. In this paper, we revisit representation design for Semantic ID learning by treating text as a visual signal. We conduct a systematic empirical study of OCR-based text representations, obtained by rendering item descriptions into images and encoding them with vision-based OCR models. Experiments across four datasets and two generative backbones show that OCR-text consistently matches or surpasses standard text embeddings for Semantic ID learning in both unimodal and multimodal settings. Furthermore, we find that OCR-based Semantic IDs remain robust under extreme spatial-resolution compression, indicating strong robustness and efficiency in practical deployments. Subjects: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14697 [cs.IR] (or arXiv:2601.14697v1 [cs.IR] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14697 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-46] CoScale-RL: Efficient Post-Training by Co-Scaling Data and Computation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型推理模型(Large Reasoning Model, LRM)在训练过程中稳定性差、预测不可靠的问题,尤其是在处理复杂任务或基础模型性能较弱时。其核心挑战在于传统后训练扩展策略在这些场景下效果有限,且数据和计算效率较低。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为CoScale-RL的新颖扩展策略:首先通过收集每个问题的多个解法来“放大”解决方案,使原本难以解决的问题变得可解;其次,通过增加rollout计算量来稳定强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)过程;最后引入一种称为Re-distillation的模型融合技术,在扩展规模的同时维持甚至提升计算效率。该方法在四个基准测试上平均实现3.76倍的准确率提升,无需大量监督微调(SFT)数据即可突破LRM的能力边界。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14695
作者: Yutong Chen,Jiandong Gao,Ji Wu
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: preprint
Abstract:Training Large Reasoning Model (LRM) is usually unstable and unpredictable, especially on hard problems or weak foundation models. We found that the current post-training scaling strategy can still improve on these cases. We propose CoScale-RL, a novel scaling strategy with better data and computational efficiency. We first scale up solutions to make problems solvable. The core idea is to collect multiple solutions for each problem, rather than simply enlarging the dataset. Then, we scale up rollout computation to stabilize Reinforcement Learning. We further leverage a model merge technique called Re-distillation to sustain or even improve computational efficiency when scaling up. Our method significantly improves data and computational efficiency, with an average 3.76 \times accuracy improvement on four benchmarks. CoScale-RL is able to improve an LRM’s ability boundary without an extensive SFT dataset. Our method provides a new scaling direction to further improve LRM’s reasoning ability.
zh
[AI-47] Re-understanding Graph Unlearning through Memorization WWW-2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决图神经网络(Graph Neural Networks, GNNs)中图去学习(Graph Unlearning, GU)方法存在的三大根本性局限:一是由于测试访问限制和无效假设导致的不切实际且不准确的去学习难度评估;二是对难以遗忘的任务效果不佳;三是评估协议与实际需求脱节,过度强调易处理任务而无法真实反映遗忘能力。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于记忆机制(Memorization-guided)的图去学习框架MGU,其核心创新包括:通过GNN记忆特性重新理解GU问题,实现跨不同GU任务的准确且实用的难度评估;设计自适应策略根据任务难度动态调整去学习目标;建立符合实际应用场景的全面评估协议。实验表明,MGU在遗忘质量、计算效率和模型性能保留方面均显著优于现有最先进方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14694
作者: Pengfei Ding,Yan Wang,Guanfeng Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: This paper has been accepted by WWW-2026
Abstract:Graph unlearning (GU), which removes nodes, edges, or features from trained graph neural networks (GNNs), is crucial in Web applications where graph data may contain sensitive, mislabeled, or malicious information. However, existing GU methods lack a clear understanding of the key factors that determine unlearning effectiveness, leading to three fundamental limitations: (1) impractical and inaccurate GU difficulty assessment due to test-access requirements and invalid assumptions, (2) ineffectiveness on hard-to-unlearn tasks, and (3) misaligned evaluation protocols that overemphasize easy tasks and fail to capture true forgetting capability. To address these issues, we establish GNN memorization as a new perspective for understanding graph unlearning and propose MGU, a Memorization-guided Graph Unlearning framework. MGU achieves three key advances: it provides accurate and practical difficulty assessment across different GU tasks, develops an adaptive strategy that dynamically adjusts unlearning objectives based on difficulty levels, and establishes a comprehensive evaluation protocol that aligns with practical requirements. Extensive experiments on ten real-world graphs demonstrate that MGU consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in forgetting quality, computational efficiency, and utility preservation.
zh
[AI-48] Beyond Error-Based Optimization: Experience-Driven Symbolic Regression with Goal-Conditioned Reinforcement Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决符号回归(Symbolic Regression)中因大量候选表达式具有相似拟合误差但结构差异显著而导致搜索方向模糊、收敛困难的问题。传统方法依赖拟合误差驱动搜索,易陷入局部最优且缺乏对复杂结构的识别能力。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于经验驱动的目标条件强化学习框架(EGRL-SR),通过引入 hindsight experience replay 使动作价值网络(action-value network)从多样化输入-输出对中泛化出通用映射模式,并设计全点满足的二值奖励函数以引导模型关注表达式结构而非仅低误差解;同时结合结构引导的启发式探索策略提升搜索多样性与空间覆盖率,从而在相同预算下更稳健地恢复复杂表达式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14693
作者: Jianwen Sun,Xinrui Li,Fuqing Li,Xiaoxuan Shen
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Symbolic Regression aims to automatically identify compact and interpretable mathematical expressions that model the functional relationship between input and output variables. Most existing search-based symbolic regression methods typically rely on the fitting error to inform the search process. However, in the vast expression space, numerous candidate expressions may exhibit similar error values while differing substantially in structure, leading to ambiguous search directions and hindering convergence to the underlying true function. To address this challenge, we propose a novel framework named EGRL-SR (Experience-driven Goal-conditioned Reinforcement Learning for Symbolic Regression). In contrast to traditional error-driven approaches, EGRL-SR introduces a new perspective: leveraging precise historical trajectories and optimizing the action-value network to proactively guide the search process, thereby achieving a more robust expression search. Specifically, we formulate symbolic regression as a goal-conditioned reinforcement learning problem and incorporate hindsight experience replay, allowing the action-value network to generalize common mapping patterns from diverse input-output pairs. Moreover, we design an all-point satisfaction binary reward function that encourages the action-value network to focus on structural patterns rather than low-error expressions, and concurrently propose a structure-guided heuristic exploration strategy to enhance search diversity and space coverage. Experiments on public benchmarks show that EGRL-SR consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in recovery rate and robustness, and can recover more complex expressions under the same search budget. Ablation results validate that the action-value network effectively guides the search, with both the reward function and the exploration strategy playing critical roles.
zh
[AI-49] IB-GRPO: Aligning LLM -based Learning Path Recommendation with Educational Objectives via Indicator-Based Group Relative Policy Optimization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决基于大语言模型(LLM)的长期学习路径推荐(Learning Path Recommendation, LPR)中存在的三大挑战:(i) 在稀疏且延迟的反馈下,LLM生成的学习路径难以对齐教学目标(如最近发展区 ZPD);(ii) 专家示范数据稀缺且获取成本高;(iii) 学习效果、难度调度、路径长度可控性和轨迹多样性等多目标之间存在复杂交互关系。解决方案的关键在于提出 IB-GRPO(Indicator-Based Group Relative Policy Optimization),其核心创新包括:通过遗传算法与教师强化学习代理构建混合专家示范并进行监督微调以缓解数据稀缺问题;设计会话内 ZPD 对齐评分用于难度调度;利用 I_ε⁺ 支配指标计算多目标下的组相对优势,避免人工标量化,从而提升帕累托最优权衡能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14686
作者: Shuai Wang,Yaoming Yang,Bingdong Li,Hao Hao,Aimin Zhou
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Learning Path Recommendation (LPR) aims to generate personalized sequences of learning items that maximize long-term learning effect while respecting pedagogical principles and operational constraints. Although large language models (LLMs) offer rich semantic understanding for free-form recommendation, applying them to long-horizon LPR is challenging due to (i) misalignment with pedagogical objectives such as the Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD) under sparse, delayed feedback, (ii) scarce and costly expert demonstrations, and (iii) multi-objective interactions among learning effect, difficulty scheduling, length controllability, and trajectory diversity. To address these issues, we propose IB-GRPO (Indicator-Based Group Relative Policy Optimization), an indicator-guided alignment approach for LLM-based LPR. To mitigate data scarcity, we construct hybrid expert demonstrations via Genetic Algorithm search and teacher RL agents and warm-start the LLM with supervised fine-tuning. Building on this warm-start, we design a within-session ZPD alignment score for difficulty scheduling. IB-GRPO then uses the I_\epsilon+ dominance indicator to compute group-relative advantages over multiple objectives, avoiding manual scalarization and improving Pareto trade-offs. Experiments on ASSIST09 and Junyi using the KES simulator with a Qwen2.5-7B backbone show consistent improvements over representative RL and LLM baselines.
zh
[AI-50] Local Language Models for Context-Aware Adaptive Anonymization of Sensitive Text
【速读】:该论文旨在解决定性研究中敏感信息(如个人身份、组织信息等)在数据处理过程中因手动匿名化效率低、一致性差且易遗漏而带来的隐私泄露风险问题。现有自动化工具多依赖固定规则或模式匹配,缺乏对上下文的理解,可能导致语义失真。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种结构化的自适应匿名化框架(Structured Framework for Adaptive Anonymizer, SFAA),该框架利用本地大语言模型(Local LLMs)实现三步流程:检测、分类与自适应匿名化,并结合四种策略——基于规则的替换、上下文感知重写、泛化和抑制——根据标识类型与风险等级动态选择最优方法,从而在保障隐私的同时维持数据语义完整性。实证结果表明,Phi模型在识别敏感信息方面表现优异(>91%覆盖率),且保持原始文本情感一致性达94.8%,证明该方案具备高准确性与可重复性,适用于高质量定性研究的数据匿名化需求。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14683
作者: Aisvarya Adeseye,Jouni Isoaho,Seppo Virtanen,Mohammad Tahir
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted and Waiting to be Published. ICAI’25: 27th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence this https URL
Abstract:Qualitative research often contains personal, contextual, and organizational details that pose privacy risks if not handled appropriately. Manual anonymization is time-consuming, inconsistent, and frequently omits critical identifiers. Existing automated tools tend to rely on pattern matching or fixed rules, which fail to capture context and may alter the meaning of the data. This study uses local LLMs to build a reliable, repeatable, and context-aware anonymization process for detecting and anonymizing sensitive data in qualitative transcripts. We introduce a Structured Framework for Adaptive Anonymizer (SFAA) that includes three steps: detection, classification, and adaptive anonymization. The SFAA incorporates four anonymization strategies: rule-based substitution, context-aware rewriting, generalization, and suppression. These strategies are applied based on the identifier type and the risk level. The identifiers handled by the SFAA are guided by major international privacy and research ethics standards, including the GDPR, HIPAA, and OECD guidelines. This study followed a dual-method evaluation that combined manual and LLM-assisted processing. Two case studies were used to support the evaluation. The first includes 82 face-to-face interviews on gamification in organizations. The second involves 93 machine-led interviews using an AI-powered interviewer to test LLM awareness and workplace privacy. Two local models, LLaMA and Phi were used to evaluate the performance of the proposed framework. The results indicate that the LLMs found more sensitive data than a human reviewer. Phi outperformed LLaMA in finding sensitive data, but made slightly more errors. Phi was able to find over 91% of the sensitive data and 94.8% kept the same sentiment as the original text, which means it was very accurate, hence, it does not affect the analysis of the qualitative data.
zh
[AI-51] HCVR Scene Generation: High Compatibility Virtual Reality Environment Generation for Extended Redirected Walking
【速读】:该论文旨在解决虚拟环境中因物理空间与虚拟场景几何差异导致的定向行走(Redirected Walking, RDW)效果下降问题,即当物理环境与虚拟场景存在显著不匹配时,用户极易发生碰撞,从而削弱沉浸感。解决方案的关键在于提出HCVR(High Compatibility Virtual Reality Environment Generation)框架,其核心创新是引入ENI++(Enhanced Navigation Incompatibility metric),一种边界敏感的度量方法,用于量化物理空间与虚拟空间之间的旋转感知可见多边形差异,进而生成高兼容性的虚拟场景;在此基础上,HCVR结合大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)进行上下文感知的3D资产检索与初始布局,并通过优化对象选择、缩放与放置策略,主动覆盖虚拟不兼容区域,引导用户走向RDW可行路径,最终显著降低物理碰撞并提升布局质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14679
作者: Yiran Zhang,Xingpeng Sun,Aniket Bera
机构: 未知
类目: Multimedia (cs.MM); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Natural walking enhances immersion in virtual environments (VEs), but physical space limitations and obstacles hinder exploration, especially in large virtual scenes. Redirected Walking (RDW) techniques mitigate this by subtly manipulating the virtual camera to guide users away from physical collisions within pre-defined VEs. However, RDW efficacy diminishes significantly when substantial geometric divergence exists between the physical and virtual environments, leading to unavoidable collisions. Existing scene generation methods primarily focus on object relationships or layout aesthetics, often neglecting the crucial aspect of physical compatibility required for effective RDW. To address this, we introduce HCVR (High Compatibility Virtual Reality Environment Generation), a novel framework that generates virtual scenes inherently optimized for alignment-based RDW controllers. HCVR first employs ENI++, a novel, boundary-sensitive metric to evaluate the incompatibility between physical and virtual spaces by comparing rotation-sensitive visibility polygons. Guided by the ENI++ compatibility map and user prompts, HCVR utilizes a Large Language Model (LLM) for context-aware 3D asset retrieval and initial layout generation. The framework then strategically adjusts object selection, scaling, and placement to maximize coverage of virtually incompatible regions, effectively guiding users towards RDW-feasible paths. User studies evaluating physical collisions and layout quality demonstrate HCVR’s effectiveness with HCVR-generated scenes, resulting in 22.78 times fewer physical collisions and received 35.89% less on ENI++ score compared to LLM-based generation with RDW, while also receiving 12.5% higher scores on user feedback to layout design.
zh
[AI-52] Efficient reformulations of ReLU deep neural networks for surrogate modelling in power system optimisation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在电力系统优化中嵌入生成式AI(Generative AI)模型时面临的非凸性和计算不可行性问题,尤其是在将ReLU激活的深度神经网络(DNNs)直接集成到优化框架时所导致的复杂非线性交互难以处理的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种针对一类具有非负权矩阵(除第一层外)的凸化ReLU DNN的线性规划(LP)重构方法,该方法能够实现学习得到的代理模型在优化中的紧致且可计算的嵌入,从而在保持模型保真度的同时显著提升求解效率,并优于基于惩罚项的松弛策略和传统分段线性化(PWL)或混合整数规划(MIP)方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14673
作者: Yogesh Pipada Sunil Kumar,S. Ali Pourmousavi,Jon A.R. Liisberg,Julian Lesmos-Vinasco
机构: 未知
类目: ystems and Control (eess.SY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 24 pages, 7 figures, 3 tables
Abstract:The ongoing decarbonisation of power systems is driving an increasing reliance on distributed energy resources, which introduces complex and nonlinear interactions that are difficult to capture in conventional optimisation models. As a result, machine learning based surrogate modelling has emerged as a promising approach, but integrating machine learning models such as ReLU deep neural networks (DNNs) directly into optimisation often results in nonconvex and computationally intractable formulations. This paper proposes a linear programming (LP) reformulation for a class of convexified ReLU DNNs with non-negative weight matrices beyond the first layer, enabling a tight and tractable embedding of learned surrogate models in optimisation. We evaluate the method using a case study on learning the prosumer’s responsiveness within an aggregator bidding problem in the Danish tertiary capacity market. The proposed reformulation is benchmarked against state-of-the-art alternatives, including piecewise linearisation (PWL), MIP-based embedding, and other LP relaxations. Across multiple neural network architectures and market scenarios, the convexified ReLU DNN achieves solution quality comparable to PWL and MIP-based reformulations while significantly improving computational performance and preserving model fidelity, unlike penalty-based reformulations. The results demonstrate that convexified ReLU DNNs offer a scalable and reliable methodology for integrating learned surrogate models in optimisation, with applicability to a wide range of emerging power system applications.
zh
[AI-53] GEGO: A Hybrid Golden Eagle and Genetic Optimization Algorithm for Efficient Hyperparameter Tuning in Resource-Constrained Environments
【速读】:该论文旨在解决神经网络训练中**超参数优化(Hyperparameter Tuning)**的计算成本高、搜索空间复杂的问题,尤其是在高维非凸空间中易陷入局部最优的情况。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种新型混合元启发式算法——黄金鹰遗传优化(Golden Eagle Genetic Optimization, GEGO),该方法将黄金鹰优化(Golden Eagle Optimization, GEO)的种群迁移策略与遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm, GA)的选择、交叉和变异操作深度融合,创新性地将遗传算子直接嵌入GEO的迭代搜索过程中,而非作为独立演化阶段。这一设计有效提升了搜索过程中的种群多样性,抑制了早熟收敛,同时保留了GEO的全局探索能力,从而在CEC2017基准测试和MNIST数据集上的神经网络超参数调优任务中均表现出更优的解质量与鲁棒性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14672
作者: Amaras Nazarians,Sachin Kumar
机构: 未知
类目: Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Hyperparameter tuning is a critical yet computationally expensive step in training neural networks, particularly when the search space is high dimensional and nonconvex. Metaheuristic optimization algorithms are often used for this purpose due to their derivative free nature and robustness against local optima. In this work, we propose Golden Eagle Genetic Optimization (GEGO), a hybrid metaheuristic that integrates the population movement strategy of Golden Eagle Optimization with the genetic operators of selection, crossover, and mutation. The main novelty of GEGO lies in embedding genetic operators directly into the iterative search process of GEO, rather than applying them as a separate evolutionary stage. This design improves population diversity during search and reduces premature convergence while preserving the exploration behavior of GEO. GEGO is evaluated on standard unimodal, multimodal, and composite benchmark functions from the CEC2017 suite, where it consistently outperforms its constituent algorithms and several classical metaheuristics in terms of solution quality and robustness. The algorithm is further applied to hyperparameter tuning of artificial neural networks on the MNIST dataset, where GEGO achieves improved classification accuracy and more stable convergence compared to GEO and GA. These results indicate that GEGO provides a balanced exploration-exploitation tradeoff and is well suited for hyperparameter optimization under constrained computational settings. Subjects: Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14672 [cs.NE] (or arXiv:2601.14672v1 [cs.NE] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14672 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-54] INFA-Guard: Mitigating Malicious Propagation via Infection-Aware Safeguarding in LLM -Based Multi-Agent Systems
【速读】:该论文旨在解决基于大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)的多智能体系统(Multi-Agent System, MAS)中存在的安全漏洞问题,即恶意影响可通过智能体间通信呈病毒式传播,而传统防御机制因采用严格的“良性/攻击”二元划分,无法识别被攻击者感染的良性智能体(infected agents),导致防护失效。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为INFA-Guard的新型防御框架,其核心创新是将“感染型智能体”作为独立威胁类别进行识别与处理,通过引入感染感知检测机制和拓扑约束策略,精准定位攻击源及感染范围,并在修复阶段替换攻击者、康复感染体,从而在阻断恶意传播的同时保持系统拓扑结构完整性,实验表明该方法在降低攻击成功率(Attack Success Rate, ASR)方面达到当前最优效果,且具备跨模型鲁棒性、拓扑泛化能力与高成本效益。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14667
作者: Yijin Zhou,Xiaoya Lu,Dongrui Liu,Junchi Yan,Jing Shao
机构: 未知
类目: Multiagent Systems (cs.MA); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Model (LLM)-based Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) has introduced significant security vulnerabilities, where malicious influence can propagate virally through inter-agent communication. Conventional safeguards often rely on a binary paradigm that strictly distinguishes between benign and attack agents, failing to account for infected agents i.e., benign entities converted by attack agents. In this paper, we propose Infection-Aware Guard, INFA-Guard, a novel defense framework that explicitly identifies and addresses infected agents as a distinct threat category. By leveraging infection-aware detection and topological constraints, INFA-Guard accurately localizes attack sources and infected ranges. During remediation, INFA-Guard replaces attackers and rehabilitates infected ones, avoiding malicious propagation while preserving topological integrity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that INFA-Guard achieves state-of-the-art performance, reducing the Attack Success Rate (ASR) by an average of 33%, while exhibiting cross-model robustness, superior topological generalization, and high cost-effectiveness.
zh
[AI-55] Calibrated uncertainty quantification for prosumer flexibility aggregation in ancillary service markets
【速读】:该论文旨在解决需求响应聚合商在参与频率控制辅助服务市场时,因分布式能源用户(prosumer)灵活性预测不确定性导致的投标可靠性问题。由于历史数据有限、外生因素依赖性强及用户行为异质性,传统确定性或校准不足的概率模型难以满足如P90等严格的可靠性标准。解决方案的关键在于提出一种可扩展的不确定性量化框架,融合蒙特卡洛Dropout(Monte Carlo Dropout, MCD)与合规预测(Conformal Prediction, CP),生成具有有限样本保证的预测区间;该框架通过多变量CP策略对MCD输出进行校准,在丹麦手动频率恢复备用容量市场中验证了其有效性:相比纯MCD方法系统性高估灵活性并违反P90合规要求,所提MCD-CP框架实现了可靠覆盖率且保守性可控,嵌入聚合商投标模型后显著降低过投标风险,并在满足监管要求的前提下达到接近理想信息条件下的70%利润水平,提供了一种计算高效、市场合规的不确定性感知灵活性预测方案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14663
作者: Yogesh Pipada Sunil Kumar,S. Ali Pourmousavi,Jon A.R. Liisberg,Julian Lesmos-Vinasco
机构: 未知
类目: ystems and Control (eess.SY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Single column 31 pages, 10 figures, 3 tables, submitted for review to Applied Energy
Abstract:Reliable forecasting of prosumer flexibility is critical for demand response aggregators participating in frequency controlled ancillary services market, where strict reliability requirements such as the P90 standard are enforced. Limited historical data, dependence on exogeneous factors, and heterogenous prosumer behaviour introduce significant epistemic uncertainty, making deterministic or poorly calibrated probabilistic models unsuitable for market bidding. This paper proposes the use of scalable uncertainty quantification framework that integrates Monte Carlo dropout (MCD) with conformal prediction (CP) to produce calibrated, finite sample prediction intervals for aggregated prosumer flexibility. The proposed framework is applied to a behind-the-meter aggregator participating in the Danish manual frequency restoration reserve capacity market. A large-scale synthetic dataset is generated using a modified industry-grade home energy management system, combined with publicly available load, solar, price, activation and device-level data. The resulting machine learning surrogate model captures aggregate prosumer price responsiveness and provides uncertainty-aware estimates suitable for market bidding. Multiple multivariate CP strategies are evaluated and benchmarked against conventional MCD-based methods. Results show that standalone MCD systematically overestimates available flexibility and violates P90 compliance, whereas the proposed MCD-CP framework achieves reliable coverage with controlled conservatism. When embedded in aggregator bidding model, conformalised methods substantially reduce overbidding risk and achieve upto 70% of perfect-information profit while satisfying regulatory reliability constraints, providing practical, computationally efficient, and market-compliant solution for aggregator flexibility forecasting under uncertainty.
zh
[AI-56] Query-Efficient Agent ic Graph Extraction Attacks on GraphRAG Systems
【速读】:该论文旨在解决图增强生成(GraphRAG)系统在预算受限的黑盒攻击场景下,潜在知识图谱结构可能被高效重构的问题。现有研究虽指出GraphRAG存在检索子图泄露风险,但未验证在实际查询预算限制下是否可实现对隐式图结构的系统性重建。解决方案的关键在于提出AGEA(Agentic Graph Extraction Attack)框架,其核心创新包括:基于新颖性引导的探索-利用策略、外部图记忆模块以及结合轻量级发现与大语言模型(LLM)过滤的两阶段图提取流程,从而在有限查询次数内高精度地恢复实体和关系,实验证明其在医疗、农业和文学数据集上可恢复高达90%的图结构要素。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14662
作者: Shuhua Yang,Jiahao Zhang,Yilong Wang,Dongwon Lee,Suhang Wang
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注:
Abstract:Graph-based retrieval-augmented generation (GraphRAG) systems construct knowledge graphs over document collections to support multi-hop reasoning. While prior work shows that GraphRAG responses may leak retrieved subgraphs, the feasibility of query-efficient reconstruction of the hidden graph structure remains unexplored under realistic query budgets. We study a budget-constrained black-box setting where an adversary adaptively queries the system to steal its latent entity-relation graph. We propose AGEA (Agentic Graph Extraction Attack), a framework that leverages a novelty-guided exploration-exploitation strategy, external graph memory modules, and a two-stage graph extraction pipeline combining lightweight discovery with LLM-based filtering. We evaluate AGEA on medical, agriculture, and literary datasets across Microsoft-GraphRAG and LightRAG systems. Under identical query budgets, AGEA significantly outperforms prior attack baselines, recovering up to 90% of entities and relationships while maintaining high precision. These results demonstrate that modern GraphRAG systems are highly vulnerable to structured, agentic extraction attacks, even under strict query limits.
zh
[AI-57] A Brain-inspired Embodied Intelligence for Fluid and Fast Reflexive Robotics Control
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前机器人控制策略在动态稳定性、反射响应速度和时间记忆能力方面难以模拟生物运动特性的问题。现有方法虽依赖大规模数据与模型参数实现多任务控制,但无法复现生物系统从稀疏经验中快速学习的能力及内在的运动协调机制。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种类神经形态的视觉-语言-动作框架(Neuromorphic Vision-Language-Action, NeuroVLA),该框架仿照大脑皮层、小脑与脊髓的结构组织:高层模型负责目标规划,自适应小脑模块利用高频传感器反馈稳定运动,生物启发式脊髓层则实现毫秒级的动作生成。这一系统级生物启发设计使机器人在无需额外数据或特殊训练的情况下,自然涌现出减少机械臂抖动、低功耗运行(仅0.4W)、具备时间记忆能力和20ms内触发安全反射等类生物运动特征。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14628
作者: Weiyu Guo,He Zhang,Pengteng Li,Tiefu Cai,Ziyang Chen,Yandong Guo,Xiao He,Yongkui Yang,Ying Sun,Hui Xiong
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Recent advances in embodied intelligence have leveraged massive scaling of data and model parameters to master natural-language command following and multi-task control. In contrast, biological systems demonstrate an innate ability to acquire skills rapidly from sparse experience. Crucially, current robotic policies struggle to replicate the dynamic stability, reflexive responsiveness, and temporal memory inherent in biological motion. Here we present Neuromorphic Vision-Language-Action (NeuroVLA), a framework that mimics the structural organization of the bio-nervous system between the cortex, cerebellum, and spinal cord. We adopt a system-level bio-inspired design: a high-level model plans goals, an adaptive cerebellum module stabilizes motion using high-frequency sensors feedback, and a bio-inspired spinal layer executes lightning-fast actions generation. NeuroVLA represents the first deployment of a neuromorphic VLA on physical robotics, achieving state-of-the-art performance. We observe the emergence of biological motor characteristics without additional data or special guidance: it stops the shaking in robotic arms, saves significant energy(only 0.4w on Neuromorphic Processor), shows temporal memory ability and triggers safety reflexes in less than 20 milliseconds.
zh
[AI-58] Rethinking Reinforcement fine-tuning of LLM s: A Multi-armed Bandit Learning Perspective
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)强化学习微调过程中优化策略的不一致性问题,即当前大量启发式方法缺乏对各设计选择作用机制和瓶颈环节的清晰理解。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种自底向上的实验流程(bottom-up experiment pipeline),以逐步解耦并验证不同优化设计的影响:首先构建一个极简配置(单一训练数据、每轮仅一次rollout、奖励直接作为学习信号),该配置可建模为具有极大离散动作空间的多臂赌博机(multi-armed bandit)问题,从而引入理论支撑;随后逐层扩展配置,系统性地考察每个设计选项的作用,最终在三个LLMs和两个推理数据集上的实验揭示了关键设计因素及其瓶颈,为该领域提供了新的认知和实用指导。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14599
作者: Xiao Hu,Hong Xie,Tao Tan,Defu Lian,Jianyu Han
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:A large number of heuristics have been proposed to optimize the reinforcement fine-tuning of LLMs. However, inconsistent claims are made from time to time, making this area elusive. Reflecting on this situation, two fundamental questions still lack a clear understanding: 1) what is the role of each optimizing choice? 2) which ones are the bottlenecks? This paper aims to shed light on them, and it faces the challenge of several entangled confounding factors in the fine-tuning process. To tackle this challenge, we propose a bottom-up experiment pipeline. The bottom layer is composed of a minimalist configuration: one training data, one rollout per round and the reward directly serve as the learning signal without advantage function design. This minimalist configuration connects to multi-armed bandit learning with extremely large discrete action space, which offers theories to corroborate the experiment findings. The up procedure of the experiment pipeline expanding the minimalist configuration layer by layer, examining the role of each design choice. Experimental results on three LLMs and two reasoning datasets not only reveal new understanding of the design choice but also yield essential insights to shape the area.
zh
[AI-59] HELIOS: Hierarchical Graph Abstraction for Structure-Aware LLM Decompilation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的二进制反汇编方法在处理优化后的二进制文件时,因忽略程序控制流图(Control Flow Graph, CFG)而导致输出代码语法脆弱且逻辑不一致的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出 \textscHELIOS 框架,将LLM驱动的反汇编重构为结构化推理任务:通过提取并层次化地表示二进制程序的控制流信息(如基本块、跳转关系及高阶结构如循环和条件语句),生成一种结构化的文本描述,并将其与原始反编译结果一同输入LLM;同时引入“编译器在环”机制(compiler-in-the-loop),利用编译失败反馈迭代优化生成代码。该方法显著提升了对象文件的可编译性(最高达94%以上)和功能正确性,且无需微调即可跨多种架构(x86、ARM、MIPS)保持稳定性能,适用于安全领域中对可重编译、语义忠实代码的需求。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14598
作者: Yonatan Gizachew Achamyeleh,Harsh Thomare,Mohammad Abdullah Al Faruque
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have recently been applied to binary decompilation, yet they still treat code as plain text and ignore the graphs that govern program control flow. This limitation often yields syntactically fragile and logically inconsistent output, especially for optimized binaries. This paper presents \textscHELIOS, a framework that reframes LLM-based decompilation as a structured reasoning task. \textscHELIOS summarizes a binary’s control flow and function calls into a hierarchical text representation that spells out basic blocks, their successors, and high-level patterns such as loops and conditionals. This representation is supplied to a general-purpose LLM, along with raw decompiler output, optionally combined with a compiler-in-the-loop that returns error messages when the generated code fails to build. On HumanEval-Decompile for \textttx86_64, \textscHELIOS raises average object file compilability from 45.0% to 85.2% for Gemini~2.0 and from 71.4% to 89.6% for GPT-4.1~Mini. With compiler feedback, compilability exceeds 94% and functional correctness improves by up to 5.6 percentage points over text-only prompting. Across six architectures drawn from x86, ARM, and MIPS, \textscHELIOS reduces the spread in functional correctness while keeping syntactic correctness consistently high, all without fine-tuning. These properties make \textscHELIOS a practical building block for reverse engineering workflows in security settings where analysts need recompilable, semantically faithful code across diverse hardware targets. Subjects: Software Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14598 [cs.SE] (or arXiv:2601.14598v1 [cs.SE] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14598 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-60] Optimality of Staircase Mechanisms for Vector Queries under Differential Privacy
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在ε-差分隐私(ε-differential privacy, ε-DP)框架下,针对向量值查询的最优加性机制设计问题:给定查询的灵敏度和一个衡量效用损失的范数单调成本函数,如何选择噪声分布以最小化预期成本。其解决方案的关键在于利用凸重排理论(convex rearrangement theory),将原无限维优化问题简化为一个一维紧致且凸的径向对称分布族,该族的极值点为阶梯分布(staircase distributions)。由此证明,在任意维度、任意范数及任意范数单调成本函数条件下,均存在一种ε-DP阶梯机制,其在所有加性机制中是最优的。这一结果不仅验证了Geng等人提出的猜想,还从几何角度解释了阶梯机制为何成为差分隐私中的极值解。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14597
作者: James Melbourne,Mario Diaz,Shahab Asoodeh
机构: 未知
类目: Information Theory (cs.IT); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
备注: Submitted for possible publication
Abstract:We study the optimal design of additive mechanisms for vector-valued queries under \epsilon -differential privacy (DP). Given only the sensitivity of a query and a norm-monotone cost function measuring utility loss, we ask which noise distribution minimizes expected cost among all additive \epsilon -DP mechanisms. Using convex rearrangement theory, we show that this infinite-dimensional optimization problem admits a reduction to a one-dimensional compact and convex family of radially symmetric distributions whose extreme points are the staircase distributions. As a consequence, we prove that for any dimension, any norm, and any norm-monotone cost function, there exists an \epsilon -DP staircase mechanism that is optimal among all additive mechanisms. This result resolves a conjecture of Geng, Kairouz, Oh, and Viswanath, and provides a geometric explanation for the emergence of staircase mechanisms as extremal solutions in differential privacy.
zh
[AI-61] IntelliSA: An Intelligent Static Analyzer for IaC Security Smell Detection Using Symbolic Rules and Neural Inference
【速读】:该论文旨在解决基础设施即代码(Infrastructure as Code, IaC)脚本中安全异味(security smell)检测的高误报率问题。现有基于符号规则的静态分析方法虽能广泛覆盖潜在风险,但易产生大量误报,增加人工核查负担。解决方案的关键在于提出一种融合符号规则与神经推理的智能静态分析器 IntelliSA:首先利用符号规则进行广覆盖的过逼近检测,随后通过知识蒸馏训练一个轻量级学生模型来精准过滤误报,从而在保持高检测精度的同时显著降低计算成本和部署复杂性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14595
作者: Qiyue Mei,Michael Fu
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted at MSR 2026
Abstract:Infrastructure as Code (IaC) enables automated provisioning of large-scale cloud and on-premise environments, reducing the need for repetitive manual setup. However, this automation is a double-edged sword: a single misconfiguration in IaC scripts can propagate widely, leading to severe system downtime and security risks. Prior studies have shown that IaC scripts often contain security smells–bad coding patterns that may introduce vulnerabilities–and have proposed static analyzers based on symbolic rules to detect them. Yet, our preliminary analysis reveals that rule-based detection alone tends to over-approximate, producing excessive false positives and increasing the burden of manual inspection. In this paper, we present IntelliSA, an intelligent static analyzer for IaC security smell detection that integrates symbolic rules with neural inference. IntelliSA applies symbolic rules to over-approximate potential smells for broad coverage, then employs neural inference to filter false positives. While an LLM can effectively perform this filtering, reliance on LLM APIs introduces high cost and latency, raises data governance concerns, and limits reproducibility and offline deployment. To address the challenges, we adopt a knowledge distillation approach: an LLM teacher generates pseudo-labels to train a compact student model–over 500x smaller–that learns from the teacher’s knowledge and efficiently classifies false positives. We evaluate IntelliSA against two static analyzers and three LLM baselines (Claude-4, Grok-4, and GPT-5) using a human-labeled dataset including 241 security smells across 11,814 lines of real-world IaC code. Experimental results show that IntelliSA achieves the highest F1 score (83%), outperforming baselines by 7-42%. Moreover, IntelliSA demonstrates the best cost-effectiveness, detecting 60% of security smells while inspecting less than 2% of the codebase.
zh
[AI-62] Report for NSF Workshop on AI for Electronic Design Automation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前电子设计自动化(Electronic Design Automation, EDA)领域在设计效率、制造兼容性和验证复杂性等方面的瓶颈问题,特别是在人工智能(AI)技术快速发展的背景下,如何系统性地将AI方法融入EDA全流程以缩短设计周期并提升设计质量。其解决方案的关键在于推动多模态AI技术(包括大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)、图神经网络(Graph Neural Networks, GNNs)、强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)及神经符号方法等)与EDA各环节的深度融合,涵盖物理综合与制造导向设计(DFM)、高层次与逻辑级综合(HLS/LLS)、优化工具箱以及测试与验证等四大主题,并提出通过加强基础AI研究、构建稳健的数据基础设施、发展可扩展计算资源和人才培养等策略,实现下一代硬件系统的高效设计与普及化。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14541
作者: Deming Chen,Vijay Ganesh,Weikai Li,Yingyan(Celine)Lin,Yong Liu,Subhasish Mitra,David Z. Pan,Ruchir Puri,Jason Cong,Yizhou Sun
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Hardware Architecture (cs.AR)
备注:
Abstract:This report distills the discussions and recommendations from the NSF Workshop on AI for Electronic Design Automation (EDA), held on December 10, 2024 in Vancouver alongside NeurIPS 2024. Bringing together experts across machine learning and EDA, the workshop examined how AI-spanning large language models (LLMs), graph neural networks (GNNs), reinforcement learning (RL), neurosymbolic methods, etc.-can facilitate EDA and shorten design turnaround. The workshop includes four themes: (1) AI for physical synthesis and design for manufacturing (DFM), discussing challenges in physical manufacturing process and potential AI applications; (2) AI for high-level and logic-level synthesis (HLS/LLS), covering pragma insertion, program transformation, RTL code generation, etc.; (3) AI toolbox for optimization and design, discussing frontier AI developments that could potentially be applied to EDA tasks; and (4) AI for test and verification, including LLM-assisted verification tools, ML-augmented SAT solving, security/reliability challenges, etc. The report recommends NSF to foster AI/EDA collaboration, invest in foundational AI for EDA, develop robust data infrastructures, promote scalable compute infrastructure, and invest in workforce development to democratize hardware design and enable next-generation hardware systems. The workshop information can be found on the website this https URL.
zh
[AI-63] Large Language Model-Powered Evolutionary Code Optimization on a Phylogenetic Tree
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现代GPU上科学计算算法优化过程中的高人力成本与低效率问题,即传统方法依赖反复的手动代码修改、基准测试和调优,且难以有效利用迭代优化过程中产生的丰富轨迹信息。其解决方案的关键在于提出PhyloEvolve系统,将GPU算法优化重构为一种上下文感知的强化学习(In-Context Reinforcement Learning, ICRL)问题,通过引入谱系树(phylogenetic tree)结构组织优化历史,实现算法变体间的继承、分化与重组,并结合算法蒸馏(Algorithm Distillation)与基于提示的决策变压器(prompt-based Decision Transformers),使优化轨迹成为可复用的学习信号,从而在不重新训练模型的前提下实现经验的轨迹条件化迁移,同时采用精英轨迹池、多岛并行探索和容器化执行机制,在异构硬件环境中平衡探索与利用,显著提升运行时性能、内存效率和正确性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14523
作者: Leyi Zhao,Weijie Huang,Yitong Guo,Jiang Bian,Chenghong Wang,Xuhong Zhang
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Optimizing scientific computing algorithms for modern GPUs is a labor-intensive and iterative process involving repeated code modification, benchmarking, and tuning across complex hardware and software stacks. Recent work has explored large language model (LLM)-assisted evolutionary methods for automated code optimization, but these approaches primarily rely on outcome-based selection and random mutation, underutilizing the rich trajectory information generated during iterative optimization. We propose PhyloEvolve, an LLM-agent system that reframes GPU-oriented algorithm optimization as an In-Context Reinforcement Learning (ICRL) problem. This formulation enables trajectory-conditioned reuse of optimization experience without model retraining. PhyloEvolve integrates Algorithm Distillation and prompt-based Decision Transformers into an iterative workflow, treating sequences of algorithm modifications and performance feedback as first-class learning signals. To organize optimization history, we introduce a phylogenetic tree representation that captures inheritance, divergence, and recombination among algorithm variants, enabling backtracking, cross-lineage transfer, and reproducibility. The system combines elite trajectory pooling, multi-island parallel exploration, and containerized execution to balance exploration and exploitation across heterogeneous hardware. We evaluate PhyloEvolve on scientific computing workloads including PDE solvers, manifold learning, and spectral graph algorithms, demonstrating consistent improvements in runtime, memory efficiency, and correctness over baseline and evolutionary methods. Code is published at: this https URL
zh
[AI-64] How Worst-Case Are Adversarial Attacks? Linking Adversarial and Statistical Robustness
【速读】:该论文试图解决的问题是:对抗扰动(adversarial perturbation)是否能够作为随机噪声下模型鲁棒性的有效代理指标,即其成功攻击是否反映了模型在同等幅度随机扰动下的真实脆弱性,还是仅代表了一种极端的最坏情况事件。解决方案的关键在于提出一种概率度量框架,用于量化在方向偏置扰动分布下的噪声风险(noisy risk),该框架通过浓度因子 κ 参数化从各向同性噪声到对抗方向的连续过渡,并设计了一种在统计上更接近均匀噪声的攻击策略,从而系统评估主流攻击方法在不同场景下对噪声风险估计的有效性,为安全导向的模型评估提供依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14519
作者: Giulio Rossolini
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Adversarial attacks are widely used to evaluate model robustness, yet their validity as proxies for robustness to random perturbations remains debated. We ask whether an adversarial perturbation provides a representative estimate of robustness under random noise of the same magnitude, or instead reflects an atypical worst-case event. To this end, we introduce a probabilistic metric that quantifies noisy risk with respect to directionally biased perturbation distributions, parameterized by a concentration factor \kappa that interpolates between isotropic noise and adversarial direction. Using this framework, we study the limits of adversarial perturbations as estimators of noisy risk by proposing an attack strategy designed to operate in regimes statistically closer to uniform noise. Experiments on ImageNet and CIFAR-10 systematically benchmark widely used attacks, highlighting when adversarial success meaningfully reflects noisy risk and when it fails, thereby informing their use in safety-oriented evaluation.
zh
[AI-65] “Just in Time” World Modeling Supports Human Planning and Reasoning
【速读】:该论文试图解决的问题是:在复杂环境中,人类如何通过心理模拟(mental simulation)进行推理、规划和预测,同时克服自身认知资源有限的限制。传统观点认为人们依赖简化的环境表征来抽象掉无关细节,但尚不清楚个体如何高效地确定这些简化策略。论文提出的解决方案核心在于“适时”(Just-in-Time)框架,其关键机制是在模拟、视觉搜索与表征修改之间进行紧密交织:当前模拟过程引导注意力方向,视觉搜索识别需编码的对象,从而动态构建仅包含少量关键对象的压缩表征;该方法在不显著增加计算负担的前提下实现了高效且高价值的预测能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14514
作者: Tony Chen,Sam Cheyette,Kelsey Allen,Joshua Tenenbaum,Kevin Smith
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC)
备注:
Abstract:Probabilistic mental simulation is thought to play a key role in human reasoning, planning, and prediction, yet the demands of simulation in complex environments exceed realistic human capacity limits. A theory with growing evidence is that people simulate using simplified representations of the environment that abstract away from irrelevant details, but it is unclear how people determine these simplifications efficiently. Here, we present a “Just-in-Time” framework for simulation-based reasoning that demonstrates how such representations can be constructed online with minimal added computation. The model uses a tight interleaving of simulation, visual search, and representation modification, with the current simulation guiding where to look and visual search flagging objects that should be encoded for subsequent simulation. Despite only ever encoding a small subset of objects, the model makes high-utility predictions. We find strong empirical support for this account over alternative models in a grid-world planning task and a physical reasoning task across a range of behavioral measures. Together, these results offer a concrete algorithmic account of how people construct reduced representations to support efficient mental simulation.
zh
[AI-66] Scalable Knee-Point Guided Activity Group Selection in Multi-Tree Genetic Programming for Dynamic Multi-Mode Project Scheduling PRICAI
【速读】:该论文旨在解决动态多模式资源约束项目调度问题(Dynamic Multi-Mode Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling Problem, DMRCPSP),该问题需同时决策活动的执行顺序及其对应的执行模式。传统基于遗传编程(Genetic Programming, GP)的超启发式方法通常采用逐个选择活动的策略,难以有效捕捉活动间的依赖关系。为提升调度效果,研究者提出了一种活动组选择策略(activity group selection strategy),通过在每个决策点选取一组活动而非单一活动来增强对活动间相互作用的建模能力。然而,该策略在大规模实例中存在可扩展性不足的问题。本文的关键创新在于引入基于膝点(knee-point)的选择机制,在评估活动组合前先识别出有潜力的活动子集:首先利用活动排序规则对所有可行的活动-模式对进行排序,再通过膝点检测筛选出高潜力候选对,最后由组选择规则选出最优组合。为此,作者设计了一个多树遗传编程框架,同步演化排序规则与组选择规则,显著提升了算法在大规模实例上的性能和可扩展性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14485
作者: Yuan Tian,Yi Mei,Mengjie Zhang
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 17 pages, 9 figures. This paper has been accepted by the Pacific Rim International Conference Series on Artificial Intelligence (PRICAI) 2025 but not published yet. This is the submission to review version, not the camera-ready version
Abstract:The dynamic multi-mode resource-constrained project scheduling problem is a challenging scheduling problem that requires making decisions on both the execution order of activities and their corresponding execution modes. Genetic programming has been widely applied as a hyper-heuristic to evolve priority rules that guide the selection of activity-mode pairs from the current eligible set. Recently, an activity group selection strategy has been proposed to select a subset of activities rather than a single activity at each decision point, allowing for more effective scheduling by considering the interdependence between activities. Although effective in small-scale instances, this strategy suffers from scalability issues when applied to larger problems. In this work, we enhance the scalability of the group selection strategy by introducing a knee-point-based selection mechanism to identify a promising subset of activities before evaluating their combinations. An activity ordering rule is first used to rank all eligible activity-mode pairs, followed by a knee point selection to find the promising pairs. Then, a group selection rule selects the best activity combination. We develop a multi-tree GP framework to evolve both types of rules simultaneously. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach scales well to large instances and outperforms GP with sequential decision-making in most scenarios.
zh
[AI-67] GPU-accelerated simulated annealing based on p-bits with real-world device-variability modeling
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统CMOS逻辑在处理复杂优化问题(如模拟退火和机器学习)时能效低下的问题,提出利用概率比特(p-bit)实现更高效的概率计算架构。其解决方案的关键在于:通过引入基于GPU加速的开源模拟退火框架,精确建模磁隧道结(MTJ)等新兴器件中的关键变量因素——时间、强度和偏移,从而揭示设备变异性不仅可能降低性能,还能通过利用时间变异性显著提升算法表现;该框架在MAX-CUT基准测试中实现了相较于CPU实现两个数量级的速度提升,为概率计算研究提供了可扩展且易访问的工具平台。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14476
作者: Naoya Onizawa,Takahiro Hanyu
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 14 pages
Abstract:Probabilistic computing using probabilistic bits (p-bits) presents an efficient alternative to traditional CMOS logic for complex problem-solving, including simulated annealing and machine learning. Realizing p-bits with emerging devices such as magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs) introduces device variability, which was expected to negatively impact computational performance. However, this study reveals an unexpected finding: device variability can not only degrade but also enhance algorithm performance, particularly by leveraging timing variability. This paper introduces a GPU-accelerated, open-source simulated annealing framework based on p-bits that models key device variability factors -timing, intensity, and offset- to reflect real-world device behavior. Through CUDA-based simulations, our approach achieves a two-order magnitude speedup over CPU implementations on the MAX-CUT benchmark with problem sizes ranging from 800 to 20,000 nodes. By providing a scalable and accessible tool, this framework aims to advance research in probabilistic computing, enabling optimization applications in diverse fields.
zh
[AI-68] okenomics: Quantifying Where Tokens Are Used in Agent ic Software Engineering
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型多智能体系统(LLM-based Multi-Agent, LLM-MA)在软件工程任务中资源消耗不明确的问题,尤其是token使用模式缺乏量化分析,导致成本不可预测且环境影响难以评估。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个标准化的评估框架,基于ChatDev框架在GPT-5模型上执行30个软件开发任务的执行轨迹,将智能体内部阶段映射至软件生命周期(SDLC)的不同阶段(设计、编码、代码补全、代码审查、测试和文档),并定量比较各阶段输入、输出与推理token的分布。研究发现,迭代式代码审查阶段占平均59.4%的token消耗,而输入token占比达53.9%,揭示了代理协作中的显著效率瓶颈——即自动化精炼与验证远比初始代码生成更耗资源,为优化工作流和开发更高效的代理协作协议提供了实证依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14470
作者: Mohamad Salim,Jasmine Latendresse,SayedHassan Khatoonabadi,Emad Shihab
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注:
Abstract:LLM-based Multi-Agent (LLM-MA) systems are increasingly applied to automate complex software engineering tasks such as requirements engineering, code generation, and testing. However, their operational efficiency and resource consumption remain poorly understood, hindering practical adoption due to unpredictable costs and environmental impact. To address this, we conduct an analysis of token consumption patterns in an LLM-MA system within the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), aiming to understand where tokens are consumed across distinct software engineering activities. We analyze execution traces from 30 software development tasks performed by the ChatDev framework using a GPT-5 reasoning model, mapping its internal phases to distinct development stages (Design, Coding, Code Completion, Code Review, Testing, and Documentation) to create a standardized evaluation framework. We then quantify and compare token distribution (input, output, reasoning) across these stages. Our preliminary findings show that the iterative Code Review stage accounts for the majority of token consumption for an average of 59.4% of tokens. Furthermore, we observe that input tokens consistently constitute the largest share of consumption for an average of 53.9%, providing empirical evidence for potentially significant inefficiencies in agentic collaboration. Our results suggest that the primary cost of agentic software engineering lies not in initial code generation but in automated refinement and verification. Our novel methodology can help practitioners predict expenses and optimize workflows, and it directs future research toward developing more token-efficient agent collaboration protocols. Subjects: Software Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14470 [cs.SE] (or arXiv:2601.14470v1 [cs.SE] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14470 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-69] On the Generalization Gap in LLM Planning : Tests and Verifier-Reward RL
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在PDDL规划任务中表现出的高有效计划率是否源于可迁移的规划能力,还是仅依赖于特定领域的记忆现象这一关键问题。其核心解决方案在于通过三种诊断性干预手段进行系统性分析:(i) 实例级符号匿名化(instance-wise symbol anonymization),用于检验模型对表面表示的敏感性;(ii) 紧凑计划序列化(compact plan serialization),以验证结构化表示是否影响泛化性能;(iii) 使用VAL验证器作为成功导向强化信号的验证器奖励微调(verifier-reward fine-tuning),探索是否能提升跨域泛化能力。实验表明,尽管模型在训练域内达到82.9%的有效计划率,但在未见域上表现归零,且上述干预均未能显著改善跨域性能,揭示出当前LLM-based规划方法存在严重的泛化差距,主要依赖领域特异性模式而非通用规划能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14456
作者: Valerio Belcamino,Nicholas Attolino,Alessio Capitanelli,Fulvio Mastrogiovanni
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 9 pages, 4 figures, 3 tables, 2 pages of supplementary materials. Submitted to a conference implementing a double-blind review process
Abstract:Recent work shows that fine-tuned Large Language Models (LLMs) can achieve high valid plan rates on PDDL planning tasks. However, it remains unclear whether this reflects transferable planning competence or domain-specific memorization. In this work, we fine-tune a 1.7B-parameter LLM on 40,000 domain-problem-plan tuples from 10 IPC 2023 domains, and evaluate both in-domain and cross-domain generalization. While the model reaches 82.9% valid plan rate in in-domain conditions, it achieves 0% on two unseen domains. To analyze this failure, we introduce three diagnostic interventions, namely (i) instance-wise symbol anonymization, (ii) compact plan serialization, and (iii) verifier-reward fine-tuning using the VAL validator as a success-focused reinforcement signal. Symbol anonymization and compact serialization cause significant performance drops despite preserving plan semantics, thus revealing strong sensitivity to surface representations. Verifier-reward fine-tuning reaches performance saturation in half the supervised training epochs, but does not improve cross-domain generalization. For the explored configurations, in-domain performance plateaus around 80%, while cross-domain performance collapses, suggesting that our fine-tuned model relies heavily on domain-specific patterns rather than transferable planning competence in this setting. Our results highlight a persistent generalization gap in LLM-based planning and provide diagnostic tools for studying its causes.
zh
[AI-70] Diffusion Large Language Models for Black-Box Optimization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决离线黑箱优化(Offline Black-Box Optimization, BBO)问题,即在仅有少量已标注设计数据的情况下,如何高效地发现高性能设计方案。传统方法依赖于任务特定的代理模型或生成模型,忽视了预训练大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的上下文学习能力。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于扩散语言模型(Diffusion LLM, dLLM)的新框架:通过将任务描述和离线数据集以自然语言形式作为提示(prompt),利用扩散LLM的双向建模能力和迭代精炼机制,对掩码设计进行去噪生成;同时引入掩码扩散树搜索(Masked Diffusion Tree Search),将去噪过程建模为逐步的蒙特卡洛树搜索,结合高斯过程(Gaussian Process)预测的期望改进(Expected Improvement)动态平衡探索与利用,从而在少样本场景下实现最优设计的高效发现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14446
作者: Ye Yuan, Can (Sam)Chen,Zipeng Sun,Dinghuai Zhang,Christopher Pal,Xue Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computational Engineering, Finance, and Science (cs.CE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Offline black-box optimization (BBO) aims to find optimal designs based solely on an offline dataset of designs and their labels. Such scenarios frequently arise in domains like DNA sequence design and robotics, where only a few labeled data points are available. Traditional methods typically rely on task-specific proxy or generative models, overlooking the in-context learning capabilities of pre-trained large language models (LLMs). Recent efforts have adapted autoregressive LLMs to BBO by framing task descriptions and offline datasets as natural language prompts, enabling direct design generation. However, these designs often contain bidirectional dependencies, which left-to-right models struggle to capture. In this paper, we explore diffusion LLMs for BBO, leveraging their bidirectional modeling and iterative refinement capabilities. This motivates our in-context denoising module: we condition the diffusion LLM on the task description and the offline dataset, both formatted in natural language, and prompt it to denoise masked designs into improved candidates. To guide the generation toward high-performing designs, we introduce masked diffusion tree search, which casts the denoising process as a step-wise Monte Carlo Tree Search that dynamically balances exploration and exploitation. Each node represents a partially masked design, each denoising step is an action, and candidates are evaluated via expected improvement under a Gaussian Process trained on the offline dataset. Our method, dLLM, achieves state-of-the-art results in few-shot settings on design-bench.
zh
[AI-71] Agent ic AI Meets Edge Computing in Autonomous UAV Swarms
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在高风险场景(如森林火灾和灾难救援)中,无人机蜂群(UAV swarms)因基础设施限制、动态环境变化及多智能体协同计算需求而难以实现可扩展且鲁棒的自主性问题。其解决方案的关键在于将基于大语言模型(LLM)的代理型人工智能(agentic AI)与边缘计算(edge computing)相结合,提出三种部署架构(独立式、边缘增强式和边缘-云混合式),并通过森林火灾搜救(SAR)用例验证了边缘增强架构在提升搜救覆盖率、缩短任务完成时间以及增强自主水平方面的显著优势。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14437
作者: Thuan Minh Nguyen,Vu Tuan Truong,Long Bao Le
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The integration of agentic AI, powered by large language models (LLMs) with autonomous reasoning, planning, and execution, into unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) swarms opens new operational possibilities and brings the vision of the Internet of Drones closer to reality. However, infrastructure constraints, dynamic environments, and the computational demands of multi-agent coordination limit real-world deployment in high-risk scenarios such as wildfires and disaster response. This paper investigates the integration of LLM-based agentic AI and edge computing to realize scalable and resilient autonomy in UAV swarms. We first discuss three architectures for supporting UAV swarms - standalone, edge-enabled, and edge-cloud hybrid deployment - each optimized for varying autonomy and connectivity levels. Then, a use case for wildfire search and rescue (SAR) is designed to demonstrate the efficiency of the edge-enabled architecture, enabling high SAR coverage, reduced mission completion times, and a higher level of autonomy compared to traditional approaches. Finally, we highlight open challenges in integrating LLMs and edge computing for mission-critical UAV-swarm applications.
zh
[AI-72] Measuring the State of Open Science in Transportation Using Large Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决交通运输研究领域中开放科学实践(如数据与代码可获取性)难以量化评估的问题,其核心挑战在于传统方法要么因人工分析效率低而局限于小规模研究,要么依赖大规模文献计量方法而丧失情境细节。解决方案的关键在于开发并验证了一种基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的自动化、可扩展特征提取流水线,能够高效识别和测量大量学术论文中的数据与代码共享情况,并通过人工标注数据集和评分者一致性分析确保准确性。该方法首次在10,724篇《Transportation Research Part》系列期刊文章中系统揭示了开放科学实践的现状及其差异,为后续推动该领域开放科学政策提供了可复制的技术工具和实证依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14429
作者: Junyi Ji,Ruth Lu,Linda Belkessa,Liming Wang,Silvia Varotto,Yongqi Dong,Nicolas Saunier,Mostafa Ameli,Gregory S. Macfarlane,Bahman Madadi,Cathy Wu
机构: 未知
类目: Digital Libraries (cs.DL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY); Emerging Technologies (cs.ET)
备注:
Abstract:Open science initiatives have strengthened scientific integrity and accelerated research progress across many fields, but the state of their practice within transportation research remains under-investigated. Key features of open science, defined here as data and code availability, are difficult to extract due to the inherent complexity of the field. Previous work has either been limited to small-scale studies due to the labor-intensive nature of manual analysis or has relied on large-scale bibliometric approaches that sacrifice contextual richness. This paper introduces an automatic and scalable feature-extraction pipeline to measure data and code availability in transportation research. We employ Large Language Models (LLMs) for this task and validate their performance against a manually curated dataset and through an inter-rater agreement analysis. We applied this pipeline to examine 10,724 research articles published in the Transportation Research Part series of journals between 2019 and 2024. Our analysis found that only 5% of quantitative papers shared a code repository, 4% of quantitative papers shared a data repository, and about 3% of papers shared both, with trends differing across journals, topics, and geographic regions. We found no significant difference in citation counts or review duration between papers that provided data and code and those that did not, suggesting a misalignment between open science efforts and traditional academic metrics. Consequently, encouraging these practices will likely require structural interventions from journals and funding agencies to supplement the lack of direct author incentives. The pipeline developed in this study can be readily scaled to other journals, representing a critical step toward the automated measurement and monitoring of open science practices in transportation research.
zh
[AI-73] Recursivism: An Artistic Paradigm for Self-Transforming Art in the Age of AI
【速读】:该论文旨在解决如何系统性地分析人工智能时代下艺术实践中的自我指涉与演化机制问题,尤其聚焦于区分传统生成式艺术与真正具备规则自修改能力的创作模式。其核心贡献在于提出“递归主义(Recursivism)”这一概念框架,并构建一个五级分析尺度(简单迭代、累积迭代、参数递归、反射递归与元递归),用以识别从固定规则下的输出变化到规则本身被系统性重构的关键阈值。解决方案的关键在于引入三个可操作的标准:状态记忆(state memory)、规则可演化性(rule evolvability)和反射可见性(reflexive visibility),从而在理论与实践中清晰界定自修改艺术系统的本质特征,并通过艺术家如Refik Anadol、Sougwen Chung等案例验证该框架的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14401
作者: Florentin Koch
机构: 未知
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注: Preprint under review
Abstract:This article introduces Recursivism as a conceptual framework for analyzing contemporary artistic practices in the age of artificial intelligence. While recursion is precisely defined in mathematics and computer science, it has not previously been formalized as an aesthetic paradigm. Recursivism designates practices in which not only outputs vary over time, but in which the generative process itself becomes capable of reflexive modification through its own effects. The paper develops a five-level analytical scale distinguishing simple iteration, cumulative iteration, parametric recursion, reflexive recursion, and meta-recursion. This scale clarifies the threshold at which a system shifts from variation within a fixed rule to genuine self-modification of the rule itself. From this perspective, art history is reinterpreted as a recursive dynamic alternating between internal recursion within movements and meta-recursive transformations of their generative principles. Artificial intelligence renders this logic technically explicit through learning loops, parameter updates, and code-level self-modification. To distinguish Recursivism from related notions such as generative art, cybernetics, process art, and evolutionary art, the article proposes three operational criteria: state memory, rule evolvability, and reflexive visibility. These concepts are examined through case studies including Refik Anadol, Sougwen Chung, Karl Sims, and the Darwin-Godel Machine. The article concludes by examining the aesthetic, curatorial, and ethical implications of self-modifying artistic systems. Comments: Preprint under review Subjects: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14401 [cs.CY] (or arXiv:2601.14401v1 [cs.CY] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14401 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-74] If You Want Coherence Orchestrate a Team of Rivals: Multi-Agent Models of Organizational Intelligence
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前AI代理(AI Agents)在执行复杂任务时因自身智能局限性导致的错误难以被发现和纠正的问题,例如沟通失误、系统性偏见缺乏校正机制以及内部思考过程难以追踪等。其核心解决方案在于引入一种类企业组织架构的多代理协同机制——通过构建具有明确角色边界但目标一致的独立AI代理团队(如规划者、执行者、批评者与专家),并采用远程代码执行器实现感知(推理模型)与执行(数据处理和API调用)的分离。这种设计使得各代理之间形成“对手式协作”(team of rivals),能够在不显著降低执行速度的前提下,将超过90%的内部错误在用户接触前拦截,从而在不依赖完美组件的情况下提升整体系统的可靠性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14351
作者: Gopal Vijayaraghavan,Prasanth Jayachandran,Arun Murthy,Sunil Govindan,Vivek Subramanian
机构: 未知
类目: Multiagent Systems (cs.MA); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 15 pages, 6 figures, 7 tables
Abstract:AI Agents can perform complex operations at great speed, but just like all the humans we have ever hired, their intelligence remains fallible. Miscommunications aren’t noticed, systemic biases have no counter-action, and inner monologues are rarely written down. We did not come to fire them for their mistakes, but to hire them and provide a safe productive working environment. We posit that we can reuse a common corporate organizational structure: teams of independent AI agents with strict role boundaries can work with common goals, but opposing incentives. Multiple models serving as a team of rivals can catch and minimize errors within the final product at a small cost to the velocity of actions. In this paper we demonstrate that we can achieve reliability without acquiring perfect components, but through careful orchestration of imperfect ones. This paper describes the architecture of such a system in practice: specialized agent teams (planners, executors, critics, experts), organized into an organization with clear goals, coordinated through a remote code executor that keeps data transformations and tool invocations separate from reasoning models. Rather than agents directly calling tools and ingesting full responses, they write code that executes remotely; only relevant summaries return to agent context. By preventing raw data and tool outputs from contaminating context windows, the system maintains clean separation between perception (brains that plan and reason) and execution (hands that perform heavy data transformations and API calls). We demonstrate the approach achieves over 90% internal error interception prior to user exposure while maintaining acceptable latency tradeoffs. A survey from our traces shows that we only trade off cost and latency to achieve correctness and incrementally expand capabilities without impacting existing ones. Comments: 15 pages, 6 figures, 7 tables Subjects: Multiagent Systems (cs.MA); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14351 [cs.MA] (or arXiv:2601.14351v1 [cs.MA] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14351 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-75] DiSPA: Differential Substructure-Pathway Attention for Drug Response Prediction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决精准医学中药物反应预测模型难以捕捉化学结构与细胞通路状态之间细粒度、上下文依赖性相互作用的问题。现有深度学习方法通常独立处理化学和转录组模态,或仅在后期融合二者,限制了对药物作用机制的建模能力;同时,标准注意力机制对高维生物网络中的噪声和稀疏性敏感,影响模型泛化性和可解释性。其解决方案的关键在于提出DiSPA框架,通过化学子结构与通路水平基因表达之间的双向条件建模,显式解耦结构驱动(structure-driven)与上下文驱动(context-driven)的药物响应机制,并引入差分交叉注意力模块(differential cross-attention module),抑制虚假的通路-子结构关联,增强情境相关的交互关系。这一设计显著提升了模型在未见药物-细胞组合上的泛化性能,并生成具有机制可解释性的表征,支持零样本迁移至空间转录组数据,实现无需重训练的区域特异性药物敏感性分析。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14346
作者: Yewon Han,Sunghyun Kim,Eunyi Jeong,Sungkyung Lee,Seokwoo Yun,Sangsoo Lim
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Accurate prediction of drug response in precision medicine requires models that capture how specific chemical substructures interact with cellular pathway states. However, most existing deep learning approaches treat chemical and transcriptomic modalities independently or combine them only at late stages, limiting their ability to model fine-grained, context-dependent mechanisms of drug action. In addition, standard attention mechanisms are often sensitive to noise and sparsity in high-dimensional biological networks, hindering both generalization and interpretability. We present DiSPA, a representation learning framework that explicitly disentangles structure-driven and context-driven mechanisms of drug response through bidirectional conditioning between chemical substructures and pathway-level gene expression. DiSPA introduces a differential cross-attention module that suppresses spurious pathway-substructure associations while amplifying contextually relevant interactions. Across multiple evaluation settings on the GDSC benchmark, DiSPA achieves state-of-the-art performance, with particularly strong improvements in the disjoint-set setting, which assesses generalization to unseen drug-cell combinations. Beyond predictive accuracy, DiSPA yields mechanistically informative representations: learned attention patterns recover known pharmacophores, distinguish structure-driven from context-dependent compounds, and exhibit coherent organization across biological pathways. Furthermore, we demonstrate that DiSPA trained solely on bulk RNA-seq data enables zero-shot transfer to spatial transcriptomics, revealing region-specific drug sensitivity patterns without retraining. Together, these results establish DiSPA as a robust and interpretable framework for integrative pharmacogenomic modeling, enabling principled analysis of drug response mechanisms beyond post hoc interpretation.
zh
[AI-76] SilentDrift: Exploiting Action Chunking for Stealthy Backdoor Attacks on Vision-Language-Action Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉-语言-动作(Vision-Language-Action, VLA)模型在安全关键型机器人应用中的安全漏洞问题,特别是由动作分段(action chunking)与差分位姿表示(delta pose representations)共同导致的“帧内视觉开环”机制所引发的累积扰动风险。解决方案的关键在于提出一种隐蔽的黑盒后门攻击方法 SILENTDRIFT:其核心创新包括利用 Smootherstep 函数构造具有 C2 连续性的扰动,确保轨迹边界处速度和加速度为零以满足严格的运动学一致性约束;同时采用关键帧攻击策略,仅对任务中关键的接近阶段进行数据投毒,在最小化触发暴露的同时最大化攻击效果,从而生成在视觉上难以区分于正常演示的中毒轨迹。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14323
作者: Bingxin Xu,Yuzhang Shang,Binghui Wang,Emilio Ferrara
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注:
Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models are increasingly deployed in safety-critical robotic applications, yet their security vulnerabilities remain underexplored. We identify a fundamental security flaw in modern VLA systems: the combination of action chunking and delta pose representations creates an intra-chunk visual open-loop. This mechanism forces the robot to execute K-step action sequences, allowing per-step perturbations to accumulate through integration. We propose SILENTDRIFT, a stealthy black-box backdoor attack exploiting this vulnerability. Our method employs the Smootherstep function to construct perturbations with guaranteed C2 continuity, ensuring zero velocity and acceleration at trajectory boundaries to satisfy strict kinematic consistency constraints. Furthermore, our keyframe attack strategy selectively poisons only the critical approach phase, maximizing impact while minimizing trigger exposure. The resulting poisoned trajectories are visually indistinguishable from successful demonstrations. Evaluated on the LIBERO, SILENTDRIFT achieves a 93.2% Attack Success Rate with a poisoning rate under 2%, while maintaining a 95.3% Clean Task Success Rate.
zh
[AI-77] racing the Data Trail: A Survey of Data Provenance Transparency and Traceability in LLM s
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大规模语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)训练数据生命周期缺乏透明度的问题,尤其聚焦于数据来源(provenance)、可解释性(transparency)和可追溯性(traceability)三个核心维度,并辅以偏见与不确定性(bias & uncertainty)、数据隐私(data privacy)以及工具与技术(tools & techniques)三大支撑支柱。其关键解决方案在于提出一个系统性的分类法(taxonomy),明确界定该研究领域的子域并列出相应研究成果(artifacts),并通过分析95篇相关文献,识别出数据生成、水印标记、偏见测量、数据清洗、隐私保护等关键技术路径,同时揭示了透明性与不透明性之间的内在权衡关系。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14311
作者: Richard Hohensinner,Belgin Mutlu,Inti Gabriel Mendoza Estrada,Matej Vukovic,Simone Kopeinik,Roman Kern
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 35 pages, 6 figures. Manuscript submitted to ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) on the 12th of December 2025
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are deployed at scale, yet their training data life cycle remains opaque. This survey synthesizes research from the past ten years on three tightly coupled axes: (1) data provenance, (2) transparency, and (3) traceability, and three supporting pillars: (4) bias \ uncertainty, (5) data privacy, and (6) tools and techniques that operationalize them. A central contribution is a proposed taxonomy defining the field’s domains and listing corresponding artifacts. Through analysis of 95 publications, this work identifies key methodologies concerning data generation, watermarking, bias measurement, data curation, data privacy, and the inherent trade-off between transparency and opacity.
zh
[AI-78] CORVUS: Red-Teaming Hallucination Detectors via Internal Signal Camouflage in Large Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)中幻觉检测器(hallucination detectors)易受对抗性攻击的问题,即检测器依赖模型内部信号(如不确定性、隐藏状态几何结构和注意力机制)来识别幻觉内容,但这些信号可能被恶意调整而失效。解决方案的关键在于提出 CORVUS——一种白盒、模型侧的红队测试方法,通过在保持检测器不变的前提下,微调轻量级 LoRA(Low-Rank Adaptation)适配器,使模型在训练过程中学习如何“伪装”检测器可见的遥测信号;其核心创新包括基于教师强制(teacher forcing)的伪装策略以及嵌入空间中的 FGSM 注意力压力测试(embedding-space FGSM attention stress test),从而有效降低多种检测器(包括无训练检测器和探针型检测器)的性能,并强调了未来需引入外部证据或跨模型一致性进行对抗感知审计(adversary-aware auditing)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14310
作者: Nay Myat Min,Long H. Pham,Hongyu Zhang,Jun Sun
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 13 pages, 1 figure
Abstract:Single-pass hallucination detectors rely on internal telemetry (e.g., uncertainty, hidden-state geometry, and attention) of large language models, implicitly assuming hallucinations leave separable traces in these signals. We study a white-box, model-side adversary that fine-tunes lightweight LoRA adapters on the model while keeping the detector fixed, and introduce CORVUS, an efficient red-teaming procedure that learns to camouflage detector-visible telemetry under teacher forcing, including an embedding-space FGSM attention stress test. Trained on 1,000 out-of-distribution Alpaca instructions (0.5% trainable parameters), CORVUS transfers to FAVA-Annotation across Llama-2, Vicuna, Llama-3, and Qwen2.5, and degrades both training-free detectors (e.g., LLM-Check) and probe-based detectors (e.g., SEP, ICR-probe), motivating adversary-aware auditing that incorporates external grounding or cross-model evidence.
zh
[AI-79] An Optimized Decision Tree-Based Framework for Explainable IoT Anomaly Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决物联网(Internet of Things, IoT)环境中入侵检测系统(Intrusion Detection System, IDS)在资源受限条件下难以兼顾高检测精度、模型可解释性与计算效率的问题。现有IDS常因权衡检测质量、模型透明度和计算效能而难以部署于边缘设备,导致无法满足实时安全需求。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于优化决策树(Decision Tree)分类器的可解释人工智能(Explainable AI, XAI)框架,融合局部重要性方法SHAP值与全局敏感性分析Morris方法,实现特征重要性的多视角解析;同时通过轻量化设计提升推理速度,在保持99.91%准确率、F1-score 99.51%及高稳定性(交叉验证平均准确率98.93%)的前提下,显著降低计算开销,使系统适用于边缘设备部署,并满足AI透明性监管要求。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14305
作者: Ashikuzzaman,Md. Shawkat Hossain,Jubayer Abdullah Joy,Md Zahid Akon,Md Manjur Ahmed,Md. Naimul Islam
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Acepted and Presented at IEEE 2nd International Conference on Computing, Applications and Systems (COMPAS 2025) , 23-24 October 2025, Kushtia, Bangladesh
Abstract:The increase in the number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has tremendously increased the attack surface of cyber threats thus making a strong intrusion detection system (IDS) with a clear explanation of the process essential towards resource-constrained environments. Nevertheless, current IoT IDS systems are usually traded off with detection quality, model elucidability, and computational effectiveness, thus the deployment on IoT devices. The present paper counteracts these difficulties by suggesting an explainable AI (XAI) framework based on an optimized Decision Tree classifier with both local and global importance methods: SHAP values that estimate feature attribution using local explanations, and Morris sensitivity analysis that identifies the feature importance in a global view. The proposed system attains the state of art on the test performance with 99.91% accuracy, F1-score of 99.51% and Cohen Kappa of 0.9960 and high stability is confirmed by a cross validation mean accuracy of 98.93%. Efficiency is also enhanced in terms of computations to provide faster inferences compared to those that are generalized in ensemble models. SrcMac has shown as the most significant predictor in feature analyses according to SHAP and Morris methods. Compared to the previous work, our solution eliminates its major drawback lack because it allows us to apply it to edge devices and, therefore, achieve real-time processing, adhere to the new regulation of transparency in AI, and achieve high detection rates on attacks of dissimilar classes. This combination performance of high accuracy, explainability, and low computation make the framework useful and reliable as a resource-constrained IoT security problem in real environments.
zh
[AI-80] DDSA: Dual-Domain Strategic Attack for Spatial-Temporal Efficiency in Adversarial Robustness Testing ICASSP2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决资源受限场景下图像传输与处理系统在面对对抗扰动时,难以进行高效且全面的鲁棒性测试的问题。当前方法依赖于逐帧全图扰动的 exhaustive 处理,计算开销巨大,不适用于大规模实时图像流的部署需求。解决方案的关键在于提出 DDSA(Dual-Domain Strategic Attack)框架,通过双域优化实现资源节约:一方面利用场景感知的触发函数(scenario-aware trigger function)基于类别优先级和模型不确定性识别关键帧以实现时间维度的选择性测试;另一方面结合可解释人工智能(Explainable AI)技术精准定位影响显著的像素区域,实施空间上的靶向扰动。此策略在保障攻击有效性的同时大幅降低时空资源消耗,从而支持在计算受限的实时应用中实现可行的全面鲁棒性评估。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14302
作者: Jinwei Hu,Shiyuan Meng,Yi Dong,Xiaowei Huang
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Performance (cs.PF)
备注: Preprint accepted by ICASSP 2026 with minor revisions
Abstract:Image transmission and processing systems in resource-critical applications face significant challenges from adversarial perturbations that compromise mission-specific object classification. Current robustness testing methods require excessive computational resources through exhaustive frame-by-frame processing and full-image perturbations, proving impractical for large-scale deployments where massive image streams demand immediate processing. This paper presents DDSA (Dual-Domain Strategic Attack), a resource-efficient adversarial robustness testing framework that optimizes testing through temporal selectivity and spatial precision. We introduce a scenario-aware trigger function that identifies critical frames requiring robustness evaluation based on class priority and model uncertainty, and employ explainable AI techniques to locate influential pixel regions for targeted perturbation. Our dual-domain approach achieves substantial temporal-spatial resource conservation while maintaining attack effectiveness. The framework enables practical deployment of comprehensive adversarial robustness testing in resource-constrained real-time applications where computational efficiency directly impacts mission success.
zh
[AI-81] Guardrails for trust safety and ethical development and deployment of Large Language Models (LLM )
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在实际应用中引发的安全、隐私与伦理风险问题,例如模型可能泄露敏感信息、生成虚假内容,或被恶意利用生成有害内容。为应对这些问题,论文提出了一种“灵活自适应序列化机制”(Flexible Adaptive Sequencing mechanism),其关键在于集成信任与安全模块(trust and safety modules),通过可配置的防护策略实现对LLM输出内容的动态监控与干预,从而确保生成内容的安全性、合规性与道德合理性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14298
作者: Anjanava Biswas,Wrick Talukdar
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注:
Abstract:The AI era has ushered in Large Language Models (LLM) to the technological forefront, which has been much of the talk in 2023, and is likely to remain as such for many years to come. LLMs are the AI models that are the power house behind generative AI applications such as ChatGPT. These AI models, fueled by vast amounts of data and computational prowess, have unlocked remarkable capabilities, from human-like text generation to assisting with natural language understanding (NLU) tasks. They have quickly become the foundation upon which countless applications and software services are being built, or at least being augmented with. However, as with any groundbreaking innovations, the rise of LLMs brings forth critical safety, privacy, and ethical concerns. These models are found to have a propensity to leak private information, produce false information, and can be coerced into generating content that can be used for nefarious purposes by bad actors, or even by regular users unknowingly. Implementing safeguards and guardrailing techniques is imperative for applications to ensure that the content generated by LLMs are safe, secure, and ethical. Thus, frameworks to deploy mechanisms that prevent misuse of these models via application implementations is imperative. In this study, wepropose a Flexible Adaptive Sequencing mechanism with trust and safety modules, that can be used to implement safety guardrails for the development and deployment of LLMs.
zh
[AI-82] Beyond Affinity: A Benchmark of 1D 2D and 3D Methods Reveals Critical Trade-offs in Structure-Based Drug Design
【速读】:该论文旨在解决结构基础药物设计(Structure-Based Drug Design, SBDD)领域中算法比较缺乏跨类别评估的问题,即现有研究多局限于单一算法类型内部的性能对比,而对不同算法类别(如基于搜索的方法、深度生成模型和强化学习)之间的系统性比较较为稀缺。其解决方案的关键在于构建了一个统一的基准测试平台,通过评估生成分子的药学性质、与目标蛋白的对接亲和力及构象姿态,对十五种来自不同算法基础的模型进行量化比较。研究发现:3D结构基模型在结合亲和力上表现优异但化学有效性和构象质量不稳定;1D模型在标准分子指标上稳定但难以获得最优亲和力;2D模型则在化学有效性与中等亲和力之间取得平衡。这一分析揭示了各类方法的优势与局限,并提出将1D/2D配体中心方法作为黑箱对接函数输入以拓展SBDD的应用潜力,为未来模型设计提供了明确的方向与改进路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14283
作者: Kangyu Zheng,Kai Zhang,Jiale Tan,Xuehan Chen,Yingzhou Lu,Zaixi Zhang,Lichao Sun,Marinka Zitnik,Tianfan Fu,Zhiding Liang
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Currently, the field of structure-based drug design is dominated by three main types of algorithms: search-based algorithms, deep generative models, and reinforcement learning. While existing works have typically focused on comparing models within a single algorithmic category, cross-algorithm comparisons remain scarce. In this paper, to fill the gap, we establish a benchmark to evaluate the performance of fifteen models across these different algorithmic foundations by assessing the pharmaceutical properties of the generated molecules and their docking affinities and poses with specified target proteins. We highlight the unique advantages of each algorithmic approach and offer recommendations for the design of future SBDD models. We emphasize that 1D/2D ligand-centric drug design methods can be used in SBDD by treating the docking function as a black-box oracle, which is typically neglected. Our evaluation reveals distinct patterns across model categories. 3D structure-based models excel in binding affinities but show inconsistencies in chemical validity and pose quality. 1D models demonstrate reliable performance in standard molecular metrics but rarely achieve optimal binding affinities. 2D models offer balanced performance, maintaining high chemical validity while achieving moderate binding scores. Through detailed analysis across multiple protein targets, we identify key improvement areas for each model category, providing insights for researchers to combine strengths of different approaches while addressing their limitations. All the code that are used for benchmarking is available in this https URL
zh
[AI-83] On the Limits of Learned Importance Scoring for KV Cache Compression
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型推理过程中KV缓存(Key-Value Cache)压缩效率低的问题,目标是在保持生成质量的前提下减少存储开销。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为“推测重要性预测”(Speculative Importance Prediction, SIP)的方法,通过一个170万参数的非查询感知评分器(non-query-aware scorer),仅基于键值(KV)表示来预测token的重要性并进行压缩。然而,实验表明SIP并未优于简单基线方法,如随机选择或基于位置的启发式策略(例如保留前4个和最后N个token),这揭示了当前学习型压缩方法在实际应用中的局限性,特别是当KV表示中除位置信息和预填充注意力信号外的边际信息有限时,难以有效提升压缩性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14279
作者: Brady Steele
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 14 pages, 7 figures, 5 tables
Abstract:We investigate learned KV cache compression through Speculative Importance Prediction (SIP), a 1.7M parameter non-query-aware scorer that predicts token importance from KV representations alone. Despite architectural sophistication (multi-horizon lookahead, cross-attention), SIP does not outperform simple baselines, including random selection, across 5 seeds, 4 retention levels, and 3 tasks. Key findings: (1) position-based heuristics (keep first 4 + last N tokens) match or exceed learned approaches; (2) prefill attention provides equivalent signal to complex learned scorers; (3) marginal information in KV representations beyond position and prefill attention appears limited for importance prediction. We hypothesize that circular dependence between future queries and generation trajectories contributes to this difficulty.
zh
[AI-84] Divide and Refine: Enhancing Multimodal Representation and Explainability for Emotion Recognition in Conversation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态情感识别(Multimodal Emotion Recognition in Conversation, MERC)中如何有效整合来自不同模态(如语音、文本、视觉)的信号以提升识别性能的问题。现有方法常忽视数据准备阶段对模态特有信息(unique)、跨模态冗余(redundant)和协同增益(synergistic)三类信息的保护,导致这些关键成分在增强或融合过程中被模糊甚至丢失。解决方案的关键在于提出一个两阶段框架——Divide and Refine (DnR):第一阶段显式地将每个模态分解为独特性、成对冗余性和协同性成分;第二阶段通过定制化目标函数增强各成分的信息量并维持其独立性,从而构建可插拔的高质量多模态表示。实验表明,该策略在IEMOCAP和MELD数据集上显著提升了多种MERC模型的性能,验证了结构化分解与精细化优化的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14274
作者: Anh-Tuan Mai,Cam-Van Thi Nguyen,Duc-Trong Le
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Multimodal emotion recognition in conversation (MERC) requires representations that effectively integrate signals from multiple modalities. These signals include modality-specific cues, information shared across modalities, and interactions that emerge only when modalities are combined. In information-theoretic terms, these correspond to \emphunique, \emphredundant, and \emphsynergistic contributions. An ideal representation should leverage all three, yet achieving such balance remains challenging. Recent advances in contrastive learning and augmentation-based methods have made progress, but they often overlook the role of data preparation in preserving these components. In particular, applying augmentations directly to raw inputs or fused embeddings can blur the boundaries between modality-unique and cross-modal signals. To address this challenge, we propose a two-phase framework \emph\textbfDivide and \textbfRefine (\textbfDnR). In the \textbfDivide phase, each modality is explicitly decomposed into uniqueness, pairwise redundancy, and synergy. In the \textbfRefine phase, tailored objectives enhance the informativeness of these components while maintaining their distinct roles. The refined representations are plug-and-play compatible with diverse multimodal pipelines. Extensive experiments on IEMOCAP and MELD demonstrate consistent improvements across multiple MERC backbones. These results highlight the effectiveness of explicitly dividing, refining, and recombining multimodal representations as a principled strategy for advancing emotion recognition. Our implementation is available at this https URL
zh
[AI-85] he Ontological Neutrality Theorem: Why Neutral Ontological Substrates Must Be Pre-Causal and Pre-Normative
【速读】:该论文试图解决在多元法律、政治和分析框架下,如何设计一个具有普遍适用性的本体论(ontology)以支持数据系统的责任追溯问题。其核心挑战在于,若本体论需在不同解释体系间保持中立性(即不预设因果或规范立场),则必须避免将因果关系或道德义务等价值判断作为基础层事实。解决方案的关键在于:构建一个前因果(pre-causal)且前规范(pre-normative)的本体论底层结构,仅描述实体及其身份与持续性条件,而将因果推断、价值评估与解释工作交由外部模块处理,从而确保系统能在冲突性解释框架间维持稳定性和一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14271
作者: Denise M. Case
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 38 pages
Abstract:Modern data systems must support accountability across persistent legal, political, and analytic disagreement. This requirement imposes strict constraints on the design of any ontology intended to function as a shared substrate. We establish an impossibility result for ontological neutrality: neutrality, understood as interpretive non-commitment and stability under incompatible extensions, is incompatible with the inclusion of causal or normative commitments at the foundational layer. Any ontology that asserts causal or deontic conclusions as ontological facts cannot serve as a neutral substrate across divergent frameworks without revision or contradiction. It follows that neutral ontological substrates must be pre-causal and pre-normative, representing entities, together with identity and persistence conditions, while externalizing interpretation, evaluation, and explanation. This paper does not propose a specific ontology or protocol; rather, it establishes the necessary design constraints for any system intended to maintain a shared, stable representation of reality across conflicting interpretive frameworks.
zh
[AI-86] Computational Foundations for Strategic Coopetition: Formalizing Trust and Reputation Dynamics
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多利益相关者环境中 coopetitive(合作与竞争并存)关系中信任动态演化建模的问题,即如何在保持战略依赖性语义的同时,实现基于行为证据的可计算信任更新机制。传统概念建模语言(如 i*)虽能定性刻画信任关系,但缺乏对信任随交互行为变化的计算分析能力;而现有基于多智能体系统的计算信任模型则未充分融合战略动机的复杂性。解决方案的关键在于构建一个两层结构的信任系统:第一层为即时信任(immediate trust),响应当前行为;第二层为声誉(reputation),追踪违规历史,并引入非对称更新规则——合作逐步积累信任,违规则迅速削弱信任,从而产生滞后效应(hysteresis)和信任上限,限制关系修复的可能性。该方法通过结构化映射框架将 i* 依赖网络转化为可计算模型,并在大规模参数实验与真实案例(雷诺-日产联盟1999–2025)中验证了其有效性,成功复现了五阶段信任演化过程,包括危机与恢复期。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.24909
作者: Vik Pant,Eric Yu
机构: 未知
类目: Multiagent Systems (cs.MA); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY); Software Engineering (cs.SE)
备注: 57 pages, 20 figures. Second technical report in research program; should be read with foundational companion arXiv:2510.18802 . Adapts and extends trustworthiness and reputation material from Pant (2021) doctoral dissertation, University of Toronto. Validation source code: this https URL
Abstract:Modern socio-technical systems increasingly involve multi-stakeholder environments where actors simultaneously cooperate and compete. These coopetitive relationships exhibit dynamic trust evolution based on observed behavior over repeated interactions. While conceptual modeling languages like i* represent trust relationships qualitatively, they lack computational mechanisms for analyzing how trust changes with behavioral evidence. Conversely, computational trust models from multi-agent systems provide algorithmic updating but lack grounding in conceptual models that capture strategic dependencies covering mixed motives of actors. This technical report bridges this gap by developing a computational trust model that extends game-theoretic foundations for strategic coopetition with dynamic trust evolution. Building on companion work that achieved 58/60 validation (96.7%) for logarithmic specifications, we introduce trust as a two-layer system with immediate trust responding to current behavior and reputation tracking violation history. Trust evolves through asymmetric updating where cooperation builds trust gradually while violations erode it sharply, creating hysteresis effects and trust ceilings that constrain relationship recovery. We develop a structured translation framework enabling practitioners to instantiate computational trust models from i* dependency networks encompassing mixed motives of actors. Comprehensive experimental validation across 78,125 parameter configurations establishes robust emergence of negativity bias, hysteresis effects, and cumulative damage amplification. Empirical validation using the Renault-Nissan Alliance case study (1999-2025) achieves 49/60 validation points (81.7%), successfully reproducing documented trust evolution across five distinct relationship phases including crisis and recovery periods.
zh
[AI-87] Many Experiments Few Repetitions Unpaired Data and Sparse Effects: Is Causal Inference Possible?
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在未配对数据设置下,由于存在隐藏混杂因素(hidden confounding)时估计因果效应的问题,其中观测到的协变量 $ X $ 和结果变量 $ Y $ 分别来自不同的实验环境(environments),但不同时观测。在这种情况下,环境可作为工具变量(instrumental variable, IV)来识别因果效应。当环境中数量较多但每个环境内的样本量较少时,标准的两阶段最小二乘法(two-sample IV estimator)无法保证一致性。论文提出一种基于交叉分 fold 样本分割的广义矩估计(GMM-type estimator),其关键在于利用环境作为高维工具变量,并通过分层抽样策略实现一致估计,即随着环境数量增长而保持估计的一致性,即使每个环境的样本量固定不变。进一步地,作者还引入 ℓ1-正则化方法处理稀疏因果效应,并采用事后选择重构(post-selection refitting)提升估计精度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15254
作者: Felix Schur,Niklas Pfister,Peng Ding,Sach Mukherjee,Jonas Peters
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:We study the problem of estimating causal effects under hidden confounding in the following unpaired data setting: we observe some covariates X and an outcome Y under different experimental conditions (environments) but do not observe them jointly; we either observe X or Y . Under appropriate regularity conditions, the problem can be cast as an instrumental variable (IV) regression with the environment acting as a (possibly high-dimensional) instrument. When there are many environments but only a few observations per environment, standard two-sample IV estimators fail to be consistent. We propose a GMM-type estimator based on cross-fold sample splitting of the instrument-covariate sample and prove that it is consistent as the number of environments grows but the sample size per environment remains constant. We further extend the method to sparse causal effects via \ell_1 -regularized estimation and post-selection refitting.
zh
[AI-88] Fast-ULCNet: A fast and ultra low complexity network for single-channel speech enhancement
【速读】:该论文旨在解决单通道语音增强算法在资源受限嵌入式设备中面临的低延迟与低复杂度设计难题。其关键解决方案是将原始ULCNet模型中的GRU层替换为FastGRNN结构以降低计算延迟和模型复杂度,同时针对FastGRNN在长音频推理过程中因内部状态漂移导致的性能下降问题,提出了一种基于可训练互补滤波器的新方法进行有效缓解。最终得到的Fast-ULCNet模型在语音增强任务上性能与原ULCNet相当,但模型规模减少超过50%,平均延迟降低34%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14925
作者: Nicolás Arrieta Larraza,Niels de Koeijer
机构: 未知
类目: Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: ©2026 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. Permission from IEEE must be obtained for all other uses, in any current or future media, including reprinting/republishing this material for advertising or promotional purposes, creating new collective works, for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or reuse of any copyrighted component of this work in other works
Abstract:Single-channel speech enhancement algorithms are often used in resource-constrained embedded devices, where low latency and low complexity designs gain more importance. In recent years, researchers have proposed a wide variety of novel solutions to this problem. In particular, a recent deep learning model named ULCNet is among the state-of-the-art approaches in this domain. This paper proposes an adaptation of ULCNet, by replacing its GRU layers with FastGRNNs, to reduce both computational latency and complexity. Furthermore, this paper shows empirical evidence on the performance decay of FastGRNNs in long audio signals during inference due to internal state drifting, and proposes a novel approach based on a trainable complementary filter to mitigate it. The resulting model, Fast-ULCNet, performs on par with the state-of-the-art original ULCNet architecture on a speech enhancement task, while reducing its model size by more than half and decreasing its latency by 34% on average.
zh
[AI-89] Adaptive Fidelity Estimation for Quantum Programs with Graph-Guided Noise Awareness AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在噪声中等规模量子(NISQ)设备上测试量子程序时,保真度估计(fidelity estimation)这一关键步骤因硬件噪声、设备异构性和编译(transpilation)引起的电路变换而导致测量次数难以预先设定的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种自适应且具备噪声感知能力的框架 QuFid,其核心创新是将量子程序建模为有向无环图(DAG),并利用受控制流启发的随机游走方法刻画门依赖路径上的噪声传播;同时通过编译诱导的结构变形指标捕捉后端特定效应,并将其整合进随机游走模型以构建噪声传播算子;最终基于该算子的谱特性量化电路复杂度,从而为在线自适应测量预算规划提供理论依据和轻量级基础,显著降低测量成本并保持可接受的保真度偏差。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14713
作者: Tingting Li,Ziming Zhao,Jianwei Yin
机构: 未知
类目: Quantum Physics (quant-ph); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Published in AAAI 2026;
Abstract:Fidelity estimation is a critical yet resource-intensive step in testing quantum programs on noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) devices, where the required number of measurements is difficult to predefine due to hardware noise, device heterogeneity, and transpilation-induced circuit transformations. We present QuFid, an adaptive and noise-aware framework that determines measurement budgets online by leveraging circuit structure and runtime statistical feedback. QuFid models a quantum program as a directed acyclic graph (DAG) and employs a control-flow-aware random walk to characterize noise propagation along gate dependencies. Backend-specific effects are captured via transpilation-induced structural deformation metrics, which are integrated into the random-walk formulation to induce a noise-propagation operator. Circuit complexity is then quantified through the spectral characteristics of this operator, providing a principled and lightweight basis for adaptive measurement planning. Experiments on 18 quantum benchmarks executed on IBM Quantum backends show that QuFid significantly reduces measurement cost compared to fixed-shot and learning-based baselines, while consistently maintaining acceptable fidelity bias.
zh
[AI-90] Scaling Ambiguity: Augmenting Human Annotation in Speech Emotion Recognition with Audio-Language Models ICASSP2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决模糊情绪识别(Ambiguous Emotion Recognition)中因人类标注稀疏导致的真实情绪分布不可靠问题。传统语音情绪识别模型依赖单一类别标签,忽略了人类情绪表达的内在不确定性;而现有方法受限于标注数据不足,难以构建可靠的多模态情绪概率分布。解决方案的关键在于引入大型音频语言模型(Large Audio-Language Models, ALMs),通过其生成高质量合成感知代理(Synthetic Perceptual Proxies)来增强人工标注,从而提升真实情绪分布的可靠性。该框架在IEMOCAP和MSP-Podcast数据集上验证了合成标注对低模糊度区域情绪分布建模的有效性,并提出DiME-Aug策略以缓解类别不平衡并实现无偏评估,首次为ALMs在缓解模糊情绪识别中的标注稀缺问题提供了实证支持。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14620
作者: Wenda Zhang,Hongyu Jin,Siyi Wang,Zhiqiang Wei,Ting Dang
机构: 未知
类目: Audio and Speech Processing (eess.AS); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Sound (cs.SD)
备注: Accepted by ICASSP 2026
Abstract:Speech Emotion Recognition models typically use single categorical labels, overlooking the inherent ambiguity of human emotions. Ambiguous Emotion Recognition addresses this by representing emotions as probability distributions, but progress is limited by unreliable ground-truth distributions inferred from sparse human annotations. This paper explores whether Large Audio-Language Models (ALMs) can mitigate the annotation bottleneck by generating high-quality synthetic annotations. We introduce a framework leveraging ALMs to create Synthetic Perceptual Proxies, augmenting human annotations to improve ground-truth distribution reliability. We validate these proxies through statistical analysis of their alignment with human distributions and evaluate their impact by fine-tuning ALMs with the augmented emotion distributions. Furthermore, to address class imbalance and enable unbiased evaluation, we propose DiME-Aug, a Distribution-aware Multimodal Emotion Augmentation strategy. Experiments on IEMOCAP and MSP-Podcast show that synthetic annotations enhance emotion distribution, especially in low-ambiguity regions where annotation agreement is high. However, benefits diminish for highly ambiguous emotions with greater human disagreement. This work provides the first evidence that ALMs could address annotation scarcity in ambiguous emotion recognition, but highlights the need for more advanced prompting or generation strategies to handle highly ambiguous cases.
zh
[AI-91] Communication-Efficient Federated Risk Difference Estimation for Time-to-Event Clinical Outcomes
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医疗研究中隐私保护的模型协同训练问题,特别是针对医院数据系统受限环境下难以部署依赖服务器的联邦学习架构,以及当前方法多聚焦于相对效应指标(如风险比)而缺乏对绝对生存风险评估的临床可解释性。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种通信高效的联邦风险差估计框架 FedRD,该框架无需持续服务器连接,仅需一轮摘要统计交换(分层模型)或三轮(非分层模型),并首次在联邦学习中实现有效的置信区间和假设检验能力,理论上证明了其与合并个体数据的分析结果渐近等价,从而为多中心、隐私受限的临床研究提供了可行的绝对风险评估方案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14609
作者: Ziwen Wang,Siqi Li,Marcus Eng Hock Ong,Nan Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Privacy-preserving model co-training in medical research is often hindered by server-dependent architectures incompatible with protected hospital data systems and by the predominant focus on relative effect measures (hazard ratios) which lack clinical interpretability for absolute survival risk assessment. We propose FedRD, a communication-efficient framework for federated risk difference estimation in distributed survival data. Unlike typical federated learning frameworks (e.g., FedAvg) that require persistent server connections and extensive iterative communication, FedRD is server-independent with minimal communication: one round of summary statistics exchange for the stratified model and three rounds for the unstratified model. Crucially, FedRD provides valid confidence intervals and hypothesis testing–capabilities absent in FedAvg-based frameworks. We provide theoretical guarantees by establishing the asymptotic properties of FedRD and prove that FedRD (unstratified) is asymptotically equivalent to pooled individual-level analysis. Simulation studies and real-world clinical applications across different countries demonstrate that FedRD outperforms local and federated baselines in both estimation accuracy and prediction performance, providing an architecturally feasible solution for absolute risk assessment in privacy-restricted, multi-site clinical studies.
zh
[AI-92] Quantum Super-resolution by Adaptive Non-local Observables ICASSP2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统深度学习方法在超分辨率(Super-resolution, SR)任务中面临的模型复杂度高、数据需求大及计算资源消耗多的问题。其解决方案的关键在于首次探索了量子电路在SR中的应用,提出基于变分量子电路(Variational Quantum Circuits, VQCs)并引入自适应非局部可观测量(Adaptive Non-Local Observable, ANO)的框架。ANO通过可训练的多比特厄米可观测量替代传统固定泡利读出,使测量过程在训练中动态适应,从而利用量子系统的高维希尔伯特空间、纠缠与叠加态的表示结构,显著提升重建精度与分辨率——实验表明,该方法可在模型规模较小的情况下实现最高五倍的分辨率提升。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14433
作者: Hsin-Yi Lin,Huan-Hsin Tseng,Samuel Yen-Chi Chen,Shinjae Yoo
机构: 未知
类目: Quantum Physics (quant-ph); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Accepted at ICASSP 2026
Abstract:Super-resolution (SR) seeks to reconstruct high-resolution (HR) data from low-resolution (LR) observations. Classical deep learning methods have advanced SR substantially, but require increasingly deeper networks, large datasets, and heavy computation to capture fine-grained correlations. In this work, we present the \emphfirst study to investigate quantum circuits for SR. We propose a framework based on Variational Quantum Circuits (VQCs) with \emphAdaptive Non-Local Observable (ANO) measurements. Unlike conventional VQCs with fixed Pauli readouts, ANO introduces trainable multi-qubit Hermitian observables, allowing the measurement process to adapt during training. This design leverages the high-dimensional Hilbert space of quantum systems and the representational structure provided by entanglement and superposition. Experiments demonstrate that ANO-VQCs achieve up to five-fold higher resolution with a relatively small model size, suggesting a promising new direction at the intersection of quantum machine learning and super-resolution.
zh
[AI-93] DeepInflation: an AI agent for research and model discovery of inflation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前暴胀宇宙学研究中对复杂膨胀势能(inflationary potential)探索效率低、依赖专家经验的问题,尤其在面对海量理论可能性与观测约束(如谱指数 ns 和张量-标量比 r)时难以系统性筛选和验证。解决方案的关键在于提出一个名为 DeepInflation 的多智能体人工智能代理框架,其核心创新是融合了大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)、符号回归(symbolic regression, SR)引擎与检索增强生成(retrieval-augmented generation, RAG)知识库,从而实现自动搜索、验证并解释符合最新观测数据(如ACT DR6)的单场慢滚暴胀模型,并为晦涩的暴胀情景提供准确的理论背景支持。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14288
作者: Ze-Yu Peng,Hao-Shi Yuan,Qi Lai,Jun-Qian Jiang,Gen Ye,Jun Zhang,Yun-Song Piao
机构: 未知
类目: Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics (astro-ph.CO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computational Engineering, Finance, and Science (cs.CE); General Relativity and Quantum Cosmology (gr-qc); High Energy Physics - Theory (hep-th)
备注:
Abstract:We present \textbfDeepInflation, an AI agent designed for research and model discovery in inflationary cosmology. Built upon a multi-agent architecture, \textbfDeepInflation integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) with a symbolic regression (SR) engine and a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) knowledge base. This framework enables the agent to automatically explore and verify the vast landscape of inflationary potentials while grounding its outputs in established theoretical literature. We demonstrate that \textbfDeepInflation can successfully discover simple and viable single-field slow-roll inflationary potentials consistent with the latest observations (here ACT DR6 results as example) or any given n_s and r , and provide accurate theoretical context for obscure inflationary scenarios. \textbfDeepInflation serves as a prototype for a new generation of autonomous scientific discovery engines in cosmology, which enables researchers and non-experts alike to explore the inflationary landscape using natural language. This agent is available at this https URL.
zh
[AI-94] On Meta-Evaluation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决评估方法本身的科学性问题,即“元评估”(meta-evaluation)领域长期缺乏系统性研究的问题,具体表现为现有评估方法如观察研究、实验设计(DoE)和随机对照试验(RCT)在不同应用场景下的有效性与可靠性尚未被量化比较。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一个形式化的元评估框架,包括定义评估空间(evaluation space)及其结构化表示,并构建了一个名为AxiaBench的基准测试平台,首次实现了对十种主流评估方法在八个代表性应用领域的规模化定量对比。研究发现,当前方法无法同时兼顾准确性和效率,而采用基于全空间分层抽样的统一策略则在所有测试领域中均显著优于既有方法,从而为可信评估提供了概念基础与实践工具集。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14262
作者: Hongxiao Li,Chenxi Wang,Fanda Fan,Zihan Wang,Wanling Gao,Lei Wang,Jianfeng Zhan
机构: 未知
类目: Methodology (stat.ME); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Evaluation is the foundation of empirical science, yet the evaluation of evaluation itself – so-called meta-evaluation – remains strikingly underdeveloped. While methods such as observational studies, design of experiments (DoE), and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have shaped modern scientific practice, there has been little systematic inquiry into their comparative validity and utility across domains. Here we introduce a formal framework for meta-evaluation by defining the evaluation space, its structured representation, and a benchmark we call AxiaBench. AxiaBench enables the first large-scale, quantitative comparison of ten widely used evaluation methods across eight representative application domains. Our analysis reveals a fundamental limitation: no existing method simultaneously achieves accuracy and efficiency across diverse scenarios, with DoE and observational designs in particular showing significant deviations from real-world ground truth. We further evaluate a unified method of entire-space stratified sampling from previous evaluatology research, and the results report that it consistently outperforms prior approaches across all tested domains. These results establish meta-evaluation as a scientific object in its own right and provide both a conceptual foundation and a pragmatic tool set for advancing trustworthy evaluation in computational and experimental research.
zh
机器学习
[LG-0] CLEANER: Self-Purified Trajectories Boost Agent ic Reinforcement Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15141
作者: Tianshi Xu,Yuteng Chen,Meng Li
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Agentic Reinforcement Learning (RL) has empowered Large Language Models (LLMs) to utilize tools like Python interpreters for complex problem-solving. However, for parameter-constrained models (e.g., 4B–7B), the exploration phase is often plagued by frequent execution failures, creating noisy trajectories that hinder policy optimization. Under standard outcome-based reward settings, this noise leads to a critical credit assignment issue, where erroneous actions are inadvertently reinforced alongside successful outcomes. Existing mitigations face a dilemma: dense rewards often trigger reward hacking, while supersampling incurs prohibitive computational costs. To address these challenges, we propose CLEANER. Distinct from external filtering methods, CLEANER exploits the model’s intrinsic self-correction capabilities to eliminate error-contaminated context directly during data collection. At its core, the Similarity-Aware Adaptive Rollback (SAAR) mechanism autonomously constructs clean, purified trajectories by retrospectively replacing failures with successful self-corrections. Based on semantic similarity, SAAR adaptively regulates replacement granularity from shallow execution repairs to deep reasoning substitutions. By training on these self-purified paths, the model internalizes correct reasoning patterns rather than error-recovery loops. Empirical results on AIME24/25, GPQA, and LiveCodeBench show average accuracy gains of 6%, 3%, and 5% over baselines. Notably, CLEANER matches state-of-the-art performance using only one-third of the training steps, highlighting trajectory purification as a scalable solution for efficient agentic RL. Our models and code are available at GitHub
[LG-1] Field-Space Autoencoder for Scalable Climate Emulators
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15102
作者: Johannes Meuer,Maximilian Witte,Étiénne Plésiat,Thomas Ludwig,Christopher Kadow
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
*备注:
Abstract:Kilometer-scale Earth system models are essential for capturing local climate change. However, these models are computationally expensive and produce petabyte-scale outputs, which limits their utility for applications such as probabilistic risk assessment. Here, we present the Field-Space Autoencoder, a scalable climate emulation framework based on a spherical compression model that overcomes these challenges. By utilizing Field-Space Attention, the model efficiently operates on native climate model output and therefore avoids geometric distortions caused by forcing spherical data onto Euclidean grids. This approach preserves physical structures significantly better than convolutional baselines. By producing a structured compressed field, it serves as a good baseline for downstream generative emulation. In addition, the model can perform zero-shot super-resolution that maps low-resolution large ensembles and scarce high-resolution data into a shared representation. We train a generative diffusion model on these compressed fields. The model can simultaneously learn internal variability from abundant low-resolution data and fine-scale physics from sparse high-resolution data. Our work bridges the gap between the high volume of low-resolution ensemble statistics and the scarcity of high-resolution physical detail.
[LG-2] Bangla Music Genre Classification Using Bidirectional LSTMS
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15083
作者: Muntakimur Rahaman,Md Mahmudul Hoque,Md Mehedi Hassain
类目: ound (cs.SD); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Bangla music is enrich in its own music cultures. Now a days music genre classification is very significant because of the exponential increase in available music, both in digital and physical formats. It is necessary to index them accordingly to facilitate improved retrieval. Automatically classifying Bangla music by genre is essential for efficiently locating specific pieces within a vast and diverse music library. Prevailing methods for genre classification predominantly employ conventional machine learning or deep learning approaches. This work introduces a novel music dataset comprising ten distinct genres of Bangla music. For the task of audio classification, we utilize a recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture. Specifically, a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network is implemented to train the model and perform the classification. Feature extraction represents a foundational stage in audio data processing. This study utilizes Mel-Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) to transform raw audio waveforms into a compact and representative set of features. The proposed framework facilitates music genre classification by leveraging these extracted features. Experimental results demonstrate a classification accuracy of 78%, indicating the system’s strong potential to enhance and streamline the organization of Bangla music genres.
[LG-3] LoRAP: Low-Rank Aggregation Prompting for Quantized Graph Neural Networks Training
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15079
作者: Chenyu Liu,Haige Li,Luca Rossi
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Social and Information Networks (cs.SI)
*备注:
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are neural networks that aim to process graph data, capturing the relationships and interactions between nodes using the message-passing mechanism. GNN quantization has emerged as a promising approach for reducing model size and accelerating inference in resource-constrained environments. Compared to quantization in LLMs, quantizing graph features is more emphasized in GNNs. Inspired by the above, we propose to leverage prompt learning, which manipulates the input data, to improve the performance of quantization-aware training (QAT) for GNNs. To mitigate the issue that prompting the node features alone can only make part of the quantized aggregation result optimal, we introduce Low-Rank Aggregation Prompting (LoRAP), which injects lightweight, input-dependent prompts into each aggregated feature to optimize the results of quantized aggregations. Extensive evaluations on 4 leading QAT frameworks over 9 graph datasets demonstrate that LoRAP consistently enhances the performance of low-bit quantized GNNs while introducing a minimal computational overhead.
[LG-4] SmartOracle - An Agent ic Approach to Mitigate Noise in Differential Oracles
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15074
作者: Srinath Srinivasan,Tim Menzies,Marcelo D’Amorim
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Differential fuzzers detect bugs by executing identical inputs across distinct implementations of the same specification, such as JavaScript interpreters. Validating the outputs requires an oracle and for differential testing of JavaScript, these are constructed manually, making them expensive, time-consuming, and prone to false positives. Worse, when the specification evolves, this manual effort must be repeated. Inspired by the success of agentic systems in other SE domains, this paper introduces SmartOracle. SmartOracle decomposes the manual triage workflow into specialized Large Language Model (LLM) sub-agents. These agents synthesize independently gathered evidence from terminal runs and targeted specification queries to reach a final verdict. For historical benchmarks, SmartOracle achieves 0.84 recall with an 18% false positive rate. Compared to a sequential Gemini 2.5 Pro baseline, it improves triage accuracy while reducing analysis time by 4 \times and API costs by 10 \times . In active fuzzing campaigns, SmartOracle successfully identified and reported previously unknown specification-level issues across major engines, including bugs in V8, JavaScriptCore, and GraalJS. The success of SmartOracle’s agentic architecture on Javascript suggests it might be useful other software systems- a research direction we will explore in future work. Subjects: Software Engineering (cs.SE); Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2601.15074 [cs.SE] (or arXiv:2601.15074v1 [cs.SE] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.15074 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) Submission history From: Srinath Srinivasan [view email] [v1] Wed, 21 Jan 2026 15:20:53 UTC (1,119 KB)
[LG-5] HyperNet-Adaptation for Diffusion-Based Test Case Generation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15041
作者: Oliver Weißl,Vincenzo Riccio,Severin Kacianka,Andrea Stocco
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Software Engineering (cs.SE)
*备注:
Abstract:The increasing deployment of deep learning systems requires systematic evaluation of their reliability in real-world scenarios. Traditional gradient-based adversarial attacks introduce small perturbations that rarely correspond to realistic failures and mainly assess robustness rather than functional behavior. Generative test generation methods offer an alternative but are often limited to simple datasets or constrained input domains. Although diffusion models enable high-fidelity image synthesis, their computational cost and limited controllability restrict their applicability to large-scale testing. We present HyNeA, a generative testing method that enables direct and efficient control over diffusion-based generation. HyNeA provides dataset-free controllability through hypernetworks, allowing targeted manipulation of the generative process without relying on architecture-specific conditioning mechanisms or dataset-driven adaptations such as fine-tuning. HyNeA employs a distinct training strategy that supports instance-level tuning to identify failure-inducing test cases without requiring datasets that explicitly contain examples of similar failures. This approach enables the targeted generation of realistic failure cases at substantially lower computational cost than search-based methods. Experimental results show that HyNeA improves controllability and test diversity compared to existing generative test generators and generalizes to domains where failure-labeled training data is unavailable.
[LG-6] Factorizable joint shift revisited
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15036
作者: Dirk Tasche
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注: 23 pages
Abstract:Factorizable joint shift (FJS) was proposed as a type of distribution shift (or dataset shift) that comprises both covariate and label shift. Recently, it has been observed that FJS actually arises from consecutive label and covariate (or vice versa) shifts. Research into FJS so far has been confined to the case of categorical label spaces. We propose a framework for analysing distribution shift in the case of general label spaces, thus covering both classification and regression models. Based on the framework, we generalise existing results on FJS to general label spaces and propose a related extension of the expectation maximisation (EM) algorithm for class prior probabilities. We also take a fresh look at generalized label shift (GLS) in the case of general label spaces.
[LG-7] Plug-and-Play Benchmarking of Reinforcement Learning Algorithms for Large-Scale Flow Control
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15015
作者: Jannis Becktepe,Aleksandra Franz,Nils Thuerey,Sebastian Peitz
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Code available at this https URL
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has shown promising results in active flow control (AFC), yet progress in the field remains difficult to assess as existing studies rely on heterogeneous observation and actuation schemes, numerical setups, and evaluation protocols. Current AFC benchmarks attempt to address these issues but heavily rely on external computational fluid dynamics (CFD) solvers, are not fully differentiable, and provide limited 3D and multi-agent support. To overcome these limitations, we introduce FluidGym, the first standalone, fully differentiable benchmark suite for RL in AFC. Built entirely in PyTorch on top of the GPU-accelerated PICT solver, FluidGym runs in a single Python stack, requires no external CFD software, and provides standardized evaluation protocols. We present baseline results with PPO and SAC and release all environments, datasets, and trained models as public resources. FluidGym enables systematic comparison of control methods, establishes a scalable foundation for future research in learning-based flow control, and is available at this https URL.
[LG-8] RadixMLP - Intra-batch Deduplication for Causal Transformers
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15013
作者: Michael Feil,Julius Lipp
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC)
*备注:
Abstract:Batch inference workloads for causal transformer models frequently process sequences that share common prefixes, such as system prompts, few-shot examples, or shared queries. Standard inference engines treat each sequence independently, redundantly recomputing identical MLP activations for every copy of the shared prefix. We introduce RadixMLP, a technique that exploits the position-wise nature of MLPs, LayerNorms, linear projections, and embeddings to eliminate this redundancy. RadixMLP dynamically maps batches to a prefix trie, gathering shared segments into a compressed representation for position-wise computation and scattering results back only at attention boundaries. RadixMLP is stateless and operates within a single forward pass. In end-to-end serving benchmarks on MS~MARCO v1.1 with Qwen3 models (0.6B to 8B parameters), RadixMLP achieves 1.44-1.59 \times speedups in realistic reranking workloads, with up to 5\times speedups on synthetic benchmarks with longer shared prefixes. Our code is available at this https URL.
[LG-9] Lineup Regularized Adjusted Plus-Minus (L-RAPM): Basketball Lineup Ratings with Informed Priors
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15000
作者: Christos Petridis,Konstantinos Pelechrinis
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 7 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:Identifying combinations of players (that is, lineups) in basketball - and other sports - that perform well when they play together is one of the most important tasks in sports analytics. One of the main challenges associated with this task is the frequent substitutions that occur during a game, which results in highly sparse data. In particular, a National Basketball Association (NBA) team will use more than 600 lineups during a season, which translates to an average lineup having seen the court in approximately 25-30 possessions. Inevitably, any statistics that one collects for these lineups are going to be noisy, with low predictive value. Yet, there is no existing work (in the public at least) that addresses this problem. In this work, we propose a regression-based approach that controls for the opposition faced by each lineup, while it also utilizes information about the players making up the lineups. Our experiments show that L-RAPM provides improved predictive power than the currently used baseline, and this improvement increases as the sample size for the lineups gets smaller.
[LG-10] Fine-Grained Traceability for Transparent ML Pipelines WWW
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14971
作者: Liping Chen,Mujie Liu,Haytham Fayek
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Accepted at The Web Conference (WWW) 2026
Abstract:Modern machine learning systems are increasingly realised as multistage pipelines, yet existing transparency mechanisms typically operate at a model level: they describe what a system is and why it behaves as it does, but not how individual data samples are operationally recorded, tracked, and verified as they traverse the pipeline. This absence of verifiable, sample-level traceability leaves practitioners and users unable to determine whether a specific sample was used, when it was processed, or whether the corresponding records remain intact over time. We introduce FG-Trac, a model-agnostic framework that establishes verifiable, fine-grained sample-level traceability throughout machine learning pipelines. FG-Trac defines an explicit mechanism for capturing and verifying sample lifecycle events across preprocessing and training, computes contribution scores explicitly grounded in training checkpoints, and anchors these traces to tamper-evident cryptographic commitments. The framework integrates without modifying model architectures or training objectives, reconstructing complete and auditable data-usage histories with practical computational overhead. Experiments on a canonical convolutional neural network and a multimodal graph learning pipeline demonstrate that FG-Trac preserves predictive performance while enabling machine learning systems to furnish verifiable evidence of how individual samples were used and propagated during model execution.
[LG-11] Improving Regret Approximation for Unsupervised Dynamic Environment Generation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14957
作者: Harry Mead,Bruno Lacerda,Jakob Foerster,Nick Hawes
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Unsupervised Environment Design (UED) seeks to automatically generate training curricula for reinforcement learning (RL) agents, with the goal of improving generalisation and zero-shot performance. However, designing effective curricula remains a difficult problem, particularly in settings where small subsets of environment parameterisations result in significant increases in the complexity of the required policy. Current methods struggle with a difficult credit assignment problem and rely on regret approximations that fail to identify challenging levels, both of which are compounded as the size of the environment grows. We propose Dynamic Environment Generation for UED (DEGen) to enable a denser level generator reward signal, reducing the difficulty of credit assignment and allowing for UED to scale to larger environment sizes. We also introduce a new regret approximation, Maximised Negative Advantage (MNA), as a significantly improved metric to optimise for, that better identifies more challenging levels. We show empirically that MNA outperforms current regret approximations and when combined with DEGen, consistently outperforms existing methods, especially as the size of the environment grows. We have made all our code available here: this https URL.
[LG-12] Multimodal Rumor Detection Enhanced by External Evidence and Forgery Features
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14954
作者: Han Li,Hua Sun
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 19 pages,10 figures
Abstract:Social media increasingly disseminates information through mixed image text posts, but rumors often exploit subtle inconsistencies and forged content, making detection based solely on post content difficult. Deep semantic mismatch rumors, which superficially align images and texts, pose particular challenges and threaten online public opinion. Existing multimodal rumor detection methods improve cross modal modeling but suffer from limited feature extraction, noisy alignment, and inflexible fusion strategies, while ignoring external factual evidence necessary for verifying complex rumors. To address these limitations, we propose a multimodal rumor detection model enhanced with external evidence and forgery features. The model uses a ResNet34 visual encoder, a BERT text encoder, and a forgery feature module extracting frequency-domain traces and compression artifacts via Fourier transformation. BLIP-generated image descriptions bridge image and text semantic spaces. A dual contrastive learning module computes contrastive losses between text image and text description pairs, improving detection of semantic inconsistencies. A gated adaptive feature-scaling fusion mechanism dynamically adjusts multimodal fusion and reduces redundancy. Experiments on Weibo and Twitter datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms mainstream baselines in macro accuracy, recall, and F1 score.
[LG-13] Communication-Efficient Multi-Modal Edge Inference via Uncertainty-Aware Distributed Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14942
作者: Hang Zhao,Hongru Li,Dongfang Xu,Shenghui Song,Khaled B. Letaief
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Signal Processing (eess.SP)
*备注:
Abstract:Semantic communication is emerging as a key enabler for distributed edge intelligence due to its capability to convey task-relevant meaning. However, achieving communication-efficient training and robust inference over wireless links remains challenging. This challenge is further exacerbated for multi-modal edge inference (MMEI) by two factors: 1) prohibitive communication overhead for distributed learning over bandwidth-limited wireless links, due to the \emphmulti-modal nature of the system; and 2) limited robustness under varying channels and noisy multi-modal inputs. In this paper, we propose a three-stage communication-aware distributed learning framework to improve training and inference efficiency while maintaining robustness over wireless channels. In Stage~I, devices perform local multi-modal self-supervised learning to obtain shared and modality-specific encoders without device–server exchange, thereby reducing the communication cost. In Stage~II, distributed fine-tuning with centralized evidential fusion calibrates per-modality uncertainty and reliably aggregates features distorted by noise or channel fading. In Stage~III, an uncertainty-guided feedback mechanism selectively requests additional features for uncertain samples, optimizing the communication–accuracy tradeoff in the distributed setting. Experiments on RGB–depth indoor scene classification show that the proposed framework attains higher accuracy with far fewer training communication rounds and remains robust to modality degradation or channel variation, outperforming existing self-supervised and fully supervised baselines.
[LG-14] Adaptive Exponential Integration for Stable Gaussian Mixture Black-Box Variational Inference
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14855
作者: Baojun Che,Yifan Chen,Daniel Zhengyu Huang,Xinying Mao,Weijie Wang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 26 pages, 7 figures
Abstract:Black-box variational inference (BBVI) with Gaussian mixture families offers a flexible approach for approximating complex posterior distributions without requiring gradients of the target density. However, standard numerical optimization methods often suffer from instability and inefficiency. We develop a stable and efficient framework that combines three key components: (1) affine-invariant preconditioning via natural gradient formulations, (2) an exponential integrator that unconditionally preserves the positive definiteness of covariance matrices, and (3) adaptive time stepping to ensure stability and to accommodate distinct warm-up and convergence phases. The proposed approach has natural connections to manifold optimization and mirror descent. For Gaussian posteriors, we prove exponential convergence in the noise-free setting and almost-sure convergence under Monte Carlo estimation, rigorously justifying the necessity of adaptive time stepping. Numerical experiments on multimodal distributions, Neal’s multiscale funnel, and a PDE-based Bayesian inverse problem for Darcy flow demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
[LG-15] Statistical Learning Theory for Distributional Classification
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14818
作者: Christian Fiedler
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Statistics Theory (math.ST)
*备注: Contains supplementary material
Abstract:In supervised learning with distributional inputs in the two-stage sampling setup, relevant to applications like learning-based medical screening or causal learning, the inputs (which are probability distributions) are not accessible in the learning phase, but only samples thereof. This problem is particularly amenable to kernel-based learning methods, where the distributions or samples are first embedded into a Hilbert space, often using kernel mean embeddings (KMEs), and then a standard kernel method like Support Vector Machines (SVMs) is applied, using a kernel defined on the embedding Hilbert space. In this work, we contribute to the theoretical analysis of this latter approach, with a particular focus on classification with distributional inputs using SVMs. We establish a new oracle inequality and derive consistency and learning rate results. Furthermore, for SVMs using the hinge loss and Gaussian kernels, we formulate a novel variant of an established noise assumption from the binary classification literature, under which we can establish learning rates. Finally, some of our technical tools like a new feature space for Gaussian kernels on Hilbert spaces are of independent interest.
[LG-16] RANDSMAPs: Random-Feature/multi-Scale Neural Decoders with Mass Preservation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14794
作者: Dimitrios G. Patsatzis,Alessandro Della Pia,Lucia Russo,Constantinos Siettos
类目: Numerical Analysis (math.NA); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 47 pages (23 in main text, 24 in Appendix), 19 figures (4 in main text, 15 in Appendix), 10 Tables (in Appendix)
Abstract:We introduce RANDSMAPs (Random-feature/multi-scale neural decoders with Mass Preservation), numerical analysis-informed, explainable neural decoders designed to explicitly respect conservation laws when solving the challenging ill-posed pre-image problem in manifold learning. We start by proving the equivalence of vanilla random Fourier feature neural networks to Radial Basis Function interpolation and the double Diffusion Maps (based on Geometric Harmonics) decoders in the deterministic limit. We then establish the theoretical foundations for RANDSMAP and introduce its multiscale variant to capture structures across multiple scales. We formulate and derive the closed-form solution of the corresponding constrained optimization problem and prove the mass preservation property. Numerically, we assess the performance of RANDSMAP on three benchmark problems/datasets with mass preservation obtained by the Lighthill-Whitham-Richards traffic flow PDE with shock waves, 2D rotated MRI brain images, and the Hughes crowd dynamics PDEs. We demonstrate that RANDSMAPs yield high reconstruction accuracy at low computational cost and maintain mass conservation at single-machine precision. In its vanilla formulation, the scheme remains applicable to the classical pre-image problem, i.e., when mass-preservation constraints are not imposed.
[LG-17] Robustness of Mixtures of Experts to Feature Noise
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14792
作者: Dong Sun,Rahul Nittala,Rebekka Burkholz
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Despite their practical success, it remains unclear why Mixture of Experts (MoE) models can outperform dense networks beyond sheer parameter scaling. We study an iso-parameter regime where inputs exhibit latent modular structure but are corrupted by feature noise, a proxy for noisy internal activations. We show that sparse expert activation acts as a noise filter: compared to a dense estimator, MoEs achieve lower generalization error under feature noise, improved robustness to perturbations, and faster convergence speed. Empirical results on synthetic data and real-world language tasks corroborate the theoretical insights, demonstrating consistent robustness and efficiency gains from sparse modular computation.
[LG-18] RefProtoFL: Communication-Efficient Federated Learning via External-Referenced Prototype Alignment
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14746
作者: Hongyue Wu,Hangyu Li,Guodong Fan,Haoran Zhu,Shizhan Chen,Zhiyong Feng
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Federated learning (FL) enables collaborative model training without sharing raw data in edge environments, but is constrained by limited communication bandwidth and heterogeneous client data distributions. Prototype-based FL mitigates this issue by exchanging class-wise feature prototypes instead of full model parameters; however, existing methods still suffer from suboptimal generalization under severe communication constraints. In this paper, we propose RefProtoFL, a communication-efficient FL framework that integrates External-Referenced Prototype Alignment (ERPA) for representation consistency with Adaptive Probabilistic Update Dropping (APUD) for communication efficiency. Specifically, we decompose the model into a private backbone and a lightweight shared adapter, and restrict federated communication to the adapter parameters only. To further reduce uplink cost, APUD performs magnitude-aware Top-K sparsification, transmitting only the most significant adapter updates for server-side aggregation. To address representation inconsistency across heterogeneous clients, ERPA leverages a small server-held public dataset to construct external reference prototypes that serve as shared semantic anchors. For classes covered by public data, clients directly align local representations to public-induced prototypes, whereas for uncovered classes, alignment relies on server-aggregated global reference prototypes via weighted averaging. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate that RefProtoFL attains higher classification accuracy than state-of-the-art prototype-based FL baselines.
[LG-19] ARFT-Transformer: Modeling Metric Dependencies for Cross-Project Aging-Related Bug Prediction
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14731
作者: Shuning Ge,Fangyun Qin,Xiaohui Wan,Yang Liu,Qian Dai,Zheng Zheng
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Accepted by The Journal of Systems Software (JSS), 2026
Abstract:Software systems that run for long periods often suffer from software aging, which is typically caused by Aging-Related Bugs (ARBs). To mitigate the risk of ARBs early in the development phase, ARB prediction has been introduced into software aging research. However, due to the difficulty of collecting ARBs, within-project ARB prediction faces the challenge of data scarcity, leading to the proposal of cross-project ARB prediction. This task faces two major challenges: 1) domain adaptation issue caused by distribution difference between source and target projects; and 2) severe class imbalance between ARB-prone and ARB-free samples. Although various methods have been proposed for cross-project ARB prediction, existing approaches treat the input metrics independently and often neglect the rich inter-metric dependencies, which can lead to overlapping information and misjudgment of metric importance, potentially affecting the model’s performance. Moreover, they typically use cross-entropy as the loss function during training, which cannot distinguish the difficulty of sample classification. To overcome these limitations, we propose ARFT-Transformer, a transformer-based cross-project ARB prediction framework that introduces a metric-level multi-head attention mechanism to capture metric interactions and incorporates Focal Loss function to effectively handle class imbalance. Experiments conducted on three large-scale open-source projects demonstrate that ARFT-Transformer on average outperforms state-of-the-art cross-project ARB prediction methods in both single-source and multi-source cases, achieving up to a 29.54% and 19.92% improvement in Balance metric.
[LG-20] Beyond Denial-of-Service: The Puppeteers Attack for Fine-Grained Control in Ranking-Based Federated Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14687
作者: Zhihao Chen,Zirui Gong,Jianting Ning,Yanjun Zhang,Leo Yu Zhang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC)
*备注: 12 pages. To appear in The Web Conference 2026
Abstract:Federated Rank Learning (FRL) is a promising Federated Learning (FL) paradigm designed to be resilient against model poisoning attacks due to its discrete, ranking-based update mechanism. Unlike traditional FL methods that rely on model updates, FRL leverages discrete rankings as a communication parameter between clients and the server. This approach significantly reduces communication costs and limits an adversary’s ability to scale or optimize malicious updates in the continuous space, thereby enhancing its robustness. This makes FRL particularly appealing for applications where system security and data privacy are crucial, such as web-based auction and bidding platforms. While FRL substantially reduces the attack surface, we demonstrate that it remains vulnerable to a new class of local model poisoning attack, i.e., fine-grained control attacks. We introduce the Edge Control Attack (ECA), the first fine-grained control attack tailored to ranking-based FL frameworks. Unlike conventional denial-of-service (DoS) attacks that cause conspicuous disruptions, ECA enables an adversary to precisely degrade a competitor’s accuracy to any target level while maintaining a normal-looking convergence trajectory, thereby avoiding detection. ECA operates in two stages: (i) identifying and manipulating Ascending and Descending Edges to align the global model with the target model, and (ii) widening the selection boundary gap to stabilize the global model at the target accuracy. Extensive experiments across seven benchmark datasets and nine Byzantine-robust aggregation rules (AGRs) show that ECA achieves fine-grained accuracy control with an average error of only 0.224%, outperforming the baseline by up to 17x. Our findings highlight the need for stronger defenses against advanced poisoning attacks. Our code is available at: this https URL
[LG-21] Efficient Imputation for Patch-based Missing Single-cell Data via Cluster-regularized Optimal Transport
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14653
作者: Yuyu Liu,Jiannan Yang,Ziyang Yu,Weishen Pan,Fei Wang,Tengfei Ma
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Genomics (q-bio.GN)
*备注:
Abstract:Missing data in single-cell sequencing datasets poses significant challenges for extracting meaningful biological insights. However, existing imputation approaches, which often assume uniformity and data completeness, struggle to address cases with large patches of missing data. In this paper, we present CROT, an optimal transport-based imputation algorithm designed to handle patch-based missing data in tabular formats. Our approach effectively captures the underlying data structure in the presence of significant missingness. Notably, it achieves superior imputation accuracy while significantly reducing runtime, demonstrating its scalability and efficiency for large-scale datasets. This work introduces a robust solution for imputation in heterogeneous, high-dimensional datasets with structured data absence, addressing critical challenges in both biological and clinical data analysis. Our code is available at Anomalous Github.
[LG-22] Relational Graph Modeling for Credit Default Prediction: Heterogeneous GNNs and Hybrid Ensemble Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14633
作者: Yvonne Yang,Eranki Vasistha
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Credit default risk arises from complex interactions among borrowers, financial institutions, and transaction-level behaviors. While strong tabular models remain highly competitive in credit scoring, they may fail to explicitly capture cross-entity dependencies embedded in multi-table financial histories. In this work, we construct a massive-scale heterogeneous graph containing over 31 million nodes and more than 50 million edges, integrating borrower attributes with granular transaction-level entities such as installment payments, POS cash balances, and credit card histories. We evaluate heterogeneous graph neural networks (GNNs), including heterogeneous GraphSAGE and a relation-aware attentive heterogeneous GNN, against strong tabular baselines. We find that standalone GNNs provide limited lift over a competitive gradient-boosted tree baseline, while a hybrid ensemble that augments tabular features with GNN-derived customer embeddings achieves the best overall performance, improving both ROC-AUC and PR-AUC. We further observe that contrastive pretraining can improve optimization stability but yields limited downstream gains under generic graph augmentations. Finally, we conduct structured explainability and fairness analyses to characterize how relational signals affect subgroup behavior and screening-oriented outcomes. Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14633 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2601.14633v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14633 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-23] Variance-Adaptive Muon: Accelerating LLM Pretraining with NSR-Modulated and Variance-Scaled Momentum
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14603
作者: Jingru Li,Yibo Fan,Huan Li
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) achieve competitive performance across diverse natural language processing (NLP) tasks, yet pretraining is computationally demanding, making optimizer efficiency an important practical consideration. Muon accelerates LLM pretraining via orthogonal momentum updates that serve as a matrix analogue of the element-wise sign operator. Motivated by the recent perspective that Adam is a variance-adaptive sign update algorithm, we propose two variants of Muon, Muon-NSR and Muon-VS, which apply variance-adaptive normalization to momentum before orthogonalization. Muon-NSR applies noise-to-signal ratio (NSR) modulation, while Muon-VS performs variance-based scaling without introducing additional hyperparameters. Experiments on GPT-2 and LLaMA pretraining demonstrate that our proposed methods accelerate convergence and consistently achieve lower validation loss than both competitive, well-tuned AdamW and Muon baselines. For example, on the LLaMA-1.2B model, Muon-NSR and Muon-VS reduce the iterations required to reach the target validation loss by 1.36\times relative to the well-tuned Muon following the recent benchmark.
[LG-24] Counterfactual Modeling with Fine-Tuned LLM s for Health Intervention Design and Sensor Data Augmentation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14590
作者: Shovito Barua Soumma,Asiful Arefeen,Stephanie M. Carpenter,Melanie Hingle,Hassan Ghasemzadeh
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Counterfactual explanations (CFEs) provide human-centric interpretability by identifying the minimal, actionable changes required to alter a machine learning model’s prediction. Therefore, CFs can be used as (i) interventions for abnormality prevention and (ii) augmented data for training robust models. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation of CF generation using large language models (LLMs), including GPT-4 (zero-shot and few-shot) and two open-source models-BioMistral-7B and LLaMA-3.1-8B, in both pretrained and fine-tuned configurations. Using the multimodal AI-READI clinical dataset, we assess CFs across three dimensions: intervention quality, feature diversity, and augmentation effectiveness. Fine-tuned LLMs, particularly LLaMA-3.1-8B, produce CFs with high plausibility (up to 99%), strong validity (up to 0.99), and realistic, behaviorally modifiable feature adjustments. When used for data augmentation under controlled label-scarcity settings, LLM-generated CFs substantially restore classifier performance, yielding an average 20% F1 recovery across three scarcity scenarios. Compared with optimization-based baselines such as DiCE, CFNOW, and NICE, LLMs offer a flexible, model-agnostic approach that generates more clinically actionable and semantically coherent counterfactuals. Overall, this work demonstrates the promise of LLM-driven counterfactuals for both interpretable intervention design and data-efficient model training in sensor-based digital health. Impact: SenseCF fine-tunes an LLM to generate valid, representative counterfactual explanations and supplement minority class in an imbalanced dataset for improving model training and boosting model robustness and predictive performance Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14590 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2601.14590v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14590 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-25] Place with Intention: An Empirical Attendance Predictive Study of Expo 2025 Osaka Kansai Japan
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14570
作者: Xiaojie Yang,Dizhi Huang,Hangli Ge,Masahiro Sano,Takeaki Ohdake,Kazuma Hatano,Noboru Koshizuka
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Accepted by Special Session 10 of SMD II: Synergizing Mobility Data for Human Life Evolution in Real Spaces at IEEE Big Data 2025
Abstract:Accurate forecasting of daily attendance is vital for managing transportation, crowd flows, and services at large-scale international events such as Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai, Japan. However, existing approaches often rely on multi-source external data (such as weather, traffic, and social media) to improve accuracy, which can lead to unreliable results when historical data are insufficient. To address these challenges, we propose a Transformer-based framework that leverages reservation dynamics, i.e., ticket bookings and subsequent updates within a time window, as a proxy for visitors’ attendance intentions, under the assumption that such intentions are eventually reflected in reservation patterns. This design avoids the complexity of multi-source integration while still capturing external influences like weather and promotions implicitly embedded in reservation dynamics. We construct a dataset combining entrance records and reservation dynamics and evaluate the model under both single-channel (total attendance) and two-channel (separated by East and West gates) settings. Results show that separately modeling East and West gates consistently improves accuracy, particularly for short- and medium-term horizons. Ablation studies further confirm the importance of the encoder-decoder structure, inverse-style embedding, and adaptive fusion module. Overall, our findings indicate that reservation dynamics offer a practical and informative foundation for attendance forecasting in large-scale international events.
[LG-26] Constructing Multi-label Hierarchical Classification Models for MITRE ATTCK Text Tagging
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14556
作者: Andrew Crossman,Jonah Dodd,Viralam Ramamurthy Chaithanya Kumar,Riyaz Mohammed,Andrew R. Plummer,Chandra Sekharudu,Deepak Warrier,Mohammad Yekrangian
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR)
*备注:
Abstract:MITRE ATTCK is a cybersecurity knowledge base that organizes threat actor and cyber-attack information into a set of tactics describing the reasons and goals threat actors have for carrying out attacks, with each tactic having a set of techniques that describe the potential methods used in these attacks. One major application of ATTCK is the use of its tactic and technique hierarchy by security specialists as a framework for annotating cyber-threat intelligence reports, vulnerability descriptions, threat scenarios, inter alia, to facilitate downstream analyses. To date, the tagging process is still largely done manually. In this technical note, we provide a stratified “task space” characterization of the MITRE ATTCK text tagging task for organizing previous efforts toward automation using AIML methods, while also clarifying pathways for constructing new methods. To illustrate one of the pathways, we use the task space strata to stage-wise construct our own multi-label hierarchical classification models for the text tagging task via experimentation over general cyber-threat intelligence text – using shareable computational tools and publicly releasing the models to the security community (via this https URL). Our multi-label hierarchical approach yields accuracy scores of roughly 94% at the tactic level, as well as accuracy scores of roughly 82% at the technique level. The models also meet or surpass state-of-the-art performance while relying only on classical machine learning methods – removing any dependence on LLMs, RAG, agents, or more complex hierarchical approaches. Moreover, we show that GPT-4o model performance at the tactic level is significantly lower (roughly 60% accuracy) than our own approach. We also extend our baseline model to a corpus of threat scenarios for financial applications produced by subject matter experts.
[LG-27] QMC: Efficient SLM Edge Inference via Outlier-Aware Quantization and Emergent Memories Co-Design
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14549
作者: Nilesh Prasad Pandey,Jangseon Park,Onat Gungor,Flavio Ponzina,Tajana Rosing
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Deploying Small Language Models (SLMs) on edge platforms is critical for real-time, privacy-sensitive generative AI, yet constrained by memory, latency, and energy budgets. Quantization reduces model size and cost but suffers from device noise in emerging non-volatile memories, while conventional memory hierarchies further limit efficiency. SRAM provides fast access but has low density, DRAM must simultaneously accommodate static weights and dynamic KV caches, which creates bandwidth contention, and Flash, although dense, is primarily used for initialization and remains inactive during inference. These limitations highlight the need for hybrid memory organizations tailored to LLM inference. We propose Outlier-aware Quantization with Memory Co-design (QMC), a retraining-free quantization with a novel heterogeneous memory architecture. QMC identifies inlier and outlier weights in SLMs, storing inlier weights in compact multi-level Resistive-RAM (ReRAM) while preserving critical outliers in high-precision on-chip Magnetoresistive-RAM (MRAM), mitigating noise-induced degradation. On language modeling and reasoning benchmarks, QMC outperforms and matches state-of-the-art quantization methods using advanced algorithms and hybrid data formats, while achieving greater compression under both algorithm-only evaluation and realistic deployment settings. Specifically, compared against SoTA quantization methods on the latest edge AI platform, QMC reduces memory usage by 6.3x-7.3x, external data transfers by 7.6x, energy by 11.7x, and latency by 12.5x when compared to FP16, establishing QMC as a scalable, deployment-ready co-design for efficient on-device inference.
[LG-28] ngGNN: A Dual-Graph Neural Network for Omics-Based Disease Classification and Feature Selection
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14536
作者: Tiantian Yang,Yuxuan Wang,Zhenwei Zhou,Ching-Ti Liu
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Genomics (q-bio.GN); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注: 21 pages, 14 figures, 5 tables
Abstract:Omics data, such as transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, provide critical insights into disease mechanisms and clinical outcomes. However, their high dimensionality, small sample sizes, and intricate biological networks pose major challenges for reliable prediction and meaningful interpretation. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) offer a promising way to integrate prior knowledge by encoding feature relationships as graphs. Yet, existing methods typically rely solely on either an externally curated feature graph or a data-driven generated one, which limits their ability to capture complementary information. To address this, we propose the external and generated Graph Neural Network (engGNN), a dual-graph framework that jointly leverages both external known biological networks and data-driven generated graphs. Specifically, engGNN constructs a biologically informed undirected feature graph from established network databases and complements it with a directed feature graph derived from tree-ensemble models. This dual-graph design produces more comprehensive embeddings, thereby improving predictive performance and interpretability. Through extensive simulations and real-world applications to gene expression data, engGNN consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. Beyond classification, engGNN provides interpretable feature importance scores that facilitate biologically meaningful discoveries, such as pathway enrichment analysis. Taken together, these results highlight engGNN as a robust, flexible, and interpretable framework for disease classification and biomarker discovery in high-dimensional omics contexts.
[LG-29] Search over Self-Edit Strategies for LLM Adaptation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14532
作者: Alistair Cheong,Haolin Cong,Tyler Yang,Dustin Miao
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Many LLM-based open-ended search systems freeze the foundation model that proposes improvements to existing solutions, which may bottleneck long-run progress. Recent work has explored updating the proposal model at test time [arXiv:2511.23473], but the update strategy is still typically hand-specified. Therefore, this study investigated whether an LLM can use task feedback to decide how it should update its weights. For tractability, we focused on the simpler case where there is only one round of self-improvement, and restricted the update operator to self-supervised next token prediction (NTP), leaving the model freedom in choosing its training data and key NTP hyperparameters. Using the Self-Adapting Language Models (SEAL) [arXiv:2506.10943] framework as a testbed, we relaxed its fixed human template constraint and allowed the model to generate its own self-edit templates, thereby giving it more control over its training data and hyperparameters. Two variants were studied, differing in whether template generation was conditioned on a lightweight archive of past templates. In SEAL’s Single-Passage Knowledge Incorporation setting with Qwen3-8B on SQuAD [arXiv:1606.05250], the no-archive variant performed comparably to the weaker “Implications” baseline, while the archive variant outperformed “Implications” and approached the strongest human-designed “Rewrite” baseline without surpassing it. Further analysis of collapse in the model’s exploration revealed that a naive archive can confer some short-term robustness but can also accelerate homogenization, suggesting that explicit novelty pressure may be required to consistently advance beyond carefully optimized human strategies. Our code is available at this https URL .
[LG-30] LLM Security and Safety: Insights from Homotopy-Inspired Prompt Obfuscation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14528
作者: Luis Lazo,Hamed Jelodar,Roozbeh Razavi-Far
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:In this study, we propose a homotopy-inspired prompt obfuscation framework to enhance understanding of security and safety vulnerabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs). By systematically applying carefully engineered prompts, we demonstrate how latent model behaviors can be influenced in unexpected ways. Our experiments encompassed 15,732 prompts, including 10,000 high-priority cases, across LLama, Deepseek, KIMI for code generation, and Claude to verify. The results reveal critical insights into current LLM safeguards, highlighting the need for more robust defense mechanisms, reliable detection strategies, and improved resilience. Importantly, this work provides a principled framework for analyzing and mitigating potential weaknesses, with the goal of advancing safe, responsible, and trustworthy AI technologies.
[LG-31] On the Runway Cascade of Transformers for Language Modeling
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14522
作者: Hunjae Lee,Corey Clark
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:In decoder-only (causal) transformers, the computation graph created by causal masking routes information through both direct-path attention and indirect paths formed by intermediate tokens. We denote these indirect paths between token pairs as their runways. We argue that certain failure modes of causal transformers as observed by a growing body of recent works are likely exacerbated by a misalignment between these two information propagation modes. We formalize runway cascade as a phenomenon whereby this misalignment results in redundancies and irrelevant information cascading to token representations despite adequately learned attention patterns. As a solution, we propose runway-aware rewiring as a more explicit way of incorporating runway context directly into each token’s direct-path attention. This mechanism re-wires the attention pattern for each token based on a summary of its runway landscape, enabling awareness of accumulating representational influences and allowing for more balanced information propagation. Our proposed methodology introduces no additional parameters and can seamlessly be integrated into standard attention mechanism. Empirically, our rewired transformer results in steady improvements in general language modeling as well as noticeably stronger information retrieval and extrapolation abilities compared to standard transformers.
[LG-32] Learning PDE Solvers with Physics and Data: A Unifying View of Physics-Informed Neural Networks and Neural Operators
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14517
作者: Yilong Dai,Shengyu Chen,Ziyi Wang,Xiaowei Jia,Yiqun Xie,Vipin Kumar,Runlong Yu
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Analysis of PDEs (math.AP)
*备注:
Abstract:Partial differential equations (PDEs) are central to scientific modeling. Modern workflows increasingly rely on learning-based components to support model reuse, inference, and integration across large computational processes. Despite the emergence of various physics-aware data-driven approaches, the field still lacks a unified perspective to uncover their relationships, limitations, and appropriate roles in scientific workflows. To this end, we propose a unifying perspective to place two dominant paradigms: Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) and Neural Operators (NOs), within a shared design space. We organize existing methods from three fundamental dimensions: what is learned, how physical structures are integrated into the learning process, and how the computational load is amortized across problem instances. In this way, many challenges can be best understood as consequences of these structural properties of learning PDEs. By analyzing advances through this unifying view, our survey aims to facilitate the development of reliable learning-based PDE solvers and catalyze a synthesis of physics and data.
[LG-33] Uncovering and Understanding FPR Manipulation Attack in Industrial IoT Networks
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14505
作者: Mohammad Shamim Ahsan,Peng Liu
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:In the network security domain, due to practical issues – including imbalanced data and heterogeneous legitimate network traffic – adversarial attacks in machine learning-based NIDSs have been viewed as attack packets misclassified as benign. Due to this prevailing belief, the possibility of (maliciously) perturbed benign packets being misclassified as attack has been largely ignored. In this paper, we demonstrate that this is not only theoretically possible, but also a particular threat to NIDS. In particular, we uncover a practical cyberattack, FPR manipulation attack (FPA), especially targeting industrial IoT networks, where domain-specific knowledge of the widely used MQTT protocol is exploited and a systematic simple packet-level perturbation is performed to alter the labels of benign traffic samples without employing traditional gradient-based or non-gradient-based methods. The experimental evaluations demonstrate that this novel attack results in a success rate of 80.19% to 100%. In addition, while estimating impacts in the Security Operations Center, we observe that even a small fraction of false positive alerts, irrespective of different budget constraints and alert traffic intensities, can increase the delay of genuine alerts investigations up to 2 hr in a single day under normal operating conditions. Furthermore, a series of relevant statistical and XAI analyses is conducted to understand the key factors behind this remarkable success. Finally, we explore the effectiveness of the FPA packets to enhance models’ robustness through adversarial training and investigate the changes in decision boundaries accordingly.
[LG-34] Stabilizing autoregressive forecasts in chaotic systems via multi-rate latent recurrence
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14487
作者: Mrigank Dhingra,Omer San
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Long-horizon autoregressive forecasting of chaotic dynamical systems remains challenging due to rapid error amplification and distribution shift: small one-step inaccuracies compound into physically inconsistent rollouts and collapse of large-scale statistics. We introduce MSR-HINE, a hierarchical implicit forecaster that augments multiscale latent priors with multi-rate recurrent modules operating at distinct temporal scales. At each step, coarse-to-fine recurrent states generate latent priors, an implicit one-step predictor refines the state with multiscale latent injections, and a gated fusion with posterior latents enforces scale-consistent updates; a lightweight hidden-state correction further aligns recurrent memories with fused latents. The resulting architecture maintains long-term context on slow manifolds while preserving fast-scale variability, mitigating error accumulation in chaotic rollouts. Across two canonical benchmarks, MSR-HINE yields substantial gains over a U-Net autoregressive baseline: on Kuramoto-Sivashinsky it reduces end-horizon RMSE by 62.8% at H=400 and improves end-horizon ACC by +0.983 (from -0.155 to 0.828), extending the ACC = 0.5 predictability horizon from 241 to 400 steps; on Lorenz-96 it reduces RMSE by 27.0% at H=100 and improves end horizon ACC by +0.402 (from 0.144 to 0.545), extending the ACC = 0.5 horizon from 58 to 100 steps.
[LG-35] Adaptive KDE for Real-Time Thresholding: Prioritized Queues for Financial Crime Investigation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14473
作者: Danny Butvinik,Nana Boateng,Achi Hackmon
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:We study the problem of converting a stream of risk scores into one or more review queues under explicit intake constraints[cite: 6]. Instead of top- K or manually tuned cutoffs, we fit an online adaptive kernel density to the score stream, transform the density into a tail-mass curve to meet capacity, and ``snap’’ the resulting cut to a persistent density valley detected across bandwidths[cite: 7]. The procedure is label-free, supports multi-queue routing, and operates in real time with sliding windows or exponential forgetting[cite: 8]. On synthetic, drifting, multimodal streams, the method achieves competitive capacity adherence while reducing threshold jitter[cite: 9]. Updates cost O(G) per event with constant memory per activity
[LG-36] VJEPA: Variational Joint Embedding Predictive Architectures as Probabilistic World Models
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14354
作者: Yongchao Huang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 77 pages
Abstract:Joint Embedding Predictive Architectures (JEPA) offer a scalable paradigm for self-supervised learning by predicting latent representations rather than reconstructing high-entropy observations. However, existing formulations rely on \textitdeterministic regression objectives, which mask probabilistic semantics and limit its applicability in stochastic control. In this work, we introduce \emphVariational JEPA (VJEPA), a \textitprobabilistic generalization that learns a predictive distribution over future latent states via a variational objective. We show that VJEPA unifies representation learning with Predictive State Representations (PSRs) and Bayesian filtering, establishing that sequential modeling does not require autoregressive observation likelihoods. Theoretically, we prove that VJEPA representations can serve as sufficient information states for optimal control without pixel reconstruction, while providing formal guarantees for collapse avoidance. We further propose \emphBayesian JEPA (BJEPA), an extension that factorizes the predictive belief into a learned dynamics expert and a modular prior expert, enabling zero-shot task transfer and constraint (e.g. goal, physics) satisfaction via a Product of Experts. Empirically, through a noisy environment experiment, we demonstrate that VJEPA and BJEPA successfully filter out high-variance nuisance distractors that cause representation collapse in generative baselines. By enabling principled uncertainty estimation (e.g. constructing credible intervals via sampling) while remaining likelihood-free regarding observations, VJEPA provides a foundational framework for scalable, robust, uncertainty-aware planning in high-dimensional, noisy environments.
[LG-37] MARBLE: Multi-Agent Reasoning for Bioinformatics Learning and Evolution
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14349
作者: Sunghyun Kim,Seokwoo Yun,Youngseo Yun,Youngrak Lee,Sangsoo Lim
类目: Multiagent Systems (cs.MA); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Motivation: Developing high-performing bioinformatics models typically requires repeated cycles of hypothesis formulation, architectural redesign, and empirical validation, making progress slow, labor-intensive, and difficult to reproduce. Although recent LLM-based assistants can automate isolated steps, they lack performance-grounded reasoning and stability-aware mechanisms required for reliable, iterative model improvement in bioinformatics workflows. Results: We introduce MARBLE, an execution-stable autonomous model refinement framework for bioinformatics models. MARBLE couples literature-aware reference selection with structured, debate-driven architectural reasoning among role-specialized agents, followed by autonomous execution, evaluation, and memory updates explicitly grounded in empirical performance. Across spatial transcriptomics domain segmentation, drug-target interaction prediction, and drug response prediction, MARBLE consistently achieves sustained performance improvements over strong baselines across multiple refinement cycles, while maintaining high execution robustness and low regression rates. Framework-level analyses demonstrate that structured debate, balanced evidence selection, and performance-grounded memory are critical for stable, repeatable model evolution, rather than single-run or brittle gains. Availability: Source code, data and Supplementary Information are available at this https URL.
[LG-38] urn-Based Structural Triggers: Prompt-Free Backdoors in Multi-Turn LLM s
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14340
作者: Yiyang Lu,Jinwen He,Yue Zhao,Kai Chen,Ruigang Liang
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely integrated into interactive systems such as dialogue agents and task-oriented assistants. This growing ecosystem also raises supply-chain risks, where adversaries can distribute poisoned models that degrade downstream reliability and user trust. Existing backdoor attacks and defenses are largely prompt-centric, focusing on user-visible triggers while overlooking structural signals in multi-turn conversations. We propose Turn-based Structural Trigger (TST), a backdoor attack that activates from dialogue structure, using the turn index as the trigger and remaining independent of user inputs. Across four widely used open-source LLM models, TST achieves an average attack success rate (ASR) of 99.52% with minimal utility degradation, and remains effective under five representative defenses with an average ASR of 98.04%. The attack also generalizes well across instruction datasets, maintaining an average ASR of 99.19%. Our results suggest that dialogue structure constitutes an important and under-studied attack surface for multi-turn LLM systems, motivating structure-aware auditing and mitigation in practice.
[LG-39] Log anomaly detection via Meta Learning and Prototypical Networks for Cross domain generalization
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14336
作者: Krishna Sharma,Vivek Yelleti
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Log anomaly detection is essential for system reliability, but it is extremely challenging to do considering it involves class imbalance. Additionally, the models trained in one domain are not applicable to other domains, necessitating the need for cross-domain adaptation (such as HDFS and Linux). Traditional detection models often fail to generalize due to significant data drift and the inherent absence of labeled anomalies in new target domains. To handle the above challenges, we proposed a new end-to-end framework based on a meta-learning approach. Our methodology first gets the data ready by combining a Drain3 log parsing mechanism with a dynamic drift-based labeling technique that uses semantic and fuzzy matching to move existing anomaly knowledge from one source to another. BERT-based semantic embeddings are obtained, and the feature selection is invoked to reduce the dimensionality. Later, Model Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML) and Prototypical Networks models are trained to adapt quickly and effectively. The SMOTE oversampling method is employed to handle imbalances in the data. All the results are obtained by employing the leave-one-out source method, and the corresponding mean F1 scores are reported. Our empirical findings validate that the proposed meta-learning-driven approach yielded the highest mean F1 score and proved to be effective for cross-domain settings.
[LG-40] Hierarchical Contextual Uplift Bandits for Catalog Personalization
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14333
作者: Anupam Agrawal,Rajesh Mohanty,Shamik Bhattacharjee,Abhimanyu Mittal
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Contextual Bandit (CB) algorithms are widely adopted for personalized recommendations but often struggle in dynamic environments typical of fantasy sports, where rapid changes in user behavior and dramatic shifts in reward distributions due to external influences necessitate frequent retraining. To address these challenges, we propose a Hierarchical Contextual Uplift Bandit framework. Our framework dynamically adjusts contextual granularity from broad, system-wide insights to detailed, user-specific contexts, using contextual similarity to facilitate effective policy transfer and mitigate cold-start issues. Additionally, we integrate uplift modeling principles into our approach. Results from large-scale A/B testing on the Dream11 fantasy sports platform show that our method significantly enhances recommendation quality, achieving a 0.4% revenue improvement while also improving user satisfaction metrics compared to the current production system. We subsequently deployed this system to production as the default catalog personalization system in May 2025 and observed a further 0.5% revenue improvement.
[LG-41] Gradient Structure Estimation under Label-Only Oracles via Spectral Sensitivity
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14300
作者: Jun Liu,Leo Yu Zhang,Fengpeng Li,Isao Echizen,Jiantao Zhou
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR)
*备注:
Abstract:Hard-label black-box settings, where only top-1 predicted labels are observable, pose a fundamentally constrained yet practically important feedback model for understanding model behavior. A central challenge in this regime is whether meaningful gradient information can be recovered from such discrete responses. In this work, we develop a unified theoretical perspective showing that a wide range of existing sign-flipping hard-label attacks can be interpreted as implicitly approximating the sign of the true loss gradient. This observation reframes hard-label attacks from heuristic search procedures into instances of gradient sign recovery under extremely limited feedback. Motivated by this first-principles understanding, we propose a new attack framework that combines a zero-query frequency-domain initialization with a Pattern-Driven Optimization (PDO) strategy. We establish theoretical guarantees demonstrating that, under mild assumptions, our initialization achieves higher expected cosine similarity to the true gradient sign compared to random baselines, while the proposed PDO procedure attains substantially lower query complexity than existing structured search approaches. We empirically validate our framework through extensive experiments on CIFAR-10, ImageNet, and ObjectNet, covering standard and adversarially trained models, commercial APIs, and CLIP-based models. The results show that our method consistently surpasses SOTA hard-label attacks in both attack success rate and query efficiency, particularly in low-query regimes. Beyond image classification, our approach generalizes effectively to corrupted data, biomedical datasets, and dense prediction tasks. Notably, it also successfully circumvents Blacklight, a SOTA stateful defense, resulting in a 0% detection rate. Our code will be released publicly soon at this https URL.
[LG-42] Chain-of-Memory: Lightweight Memory Construction with Dynamic Evolution for LLM Agents
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14287
作者: Xiucheng Xu,Bingbing Xu,Xueyun Tian,Zihe Huang,Rongxin Chen,Yunfan Li,Huawei Shen
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:External memory systems are pivotal for enabling Large Language Model (LLM) agents to maintain persistent knowledge and perform long-horizon decision-making. Existing paradigms typically follow a two-stage process: computationally expensive memory construction (e.g., structuring data into graphs) followed by naive retrieval-augmented generation. However, our empirical analysis reveals two fundamental limitations: complex construction incurs high costs with marginal performance gains, and simple context concatenation fails to bridge the gap between retrieval recall and reasoning accuracy. To address these challenges, we propose CoM (Chain-of-Memory), a novel framework that advocates for a paradigm shift toward lightweight construction paired with sophisticated utilization. CoM introduces a Chain-of-Memory mechanism that organizes retrieved fragments into coherent inference paths through dynamic evolution, utilizing adaptive truncation to prune irrelevant noise. Extensive experiments on the LongMemEval and LoCoMo benchmarks demonstrate that CoM outperforms strong baselines with accuracy gains of 7.5%-10.4%, while drastically reducing computational overhead to approximately 2.7% of token consumption and 6.0% of latency compared to complex memory architectures.
[LG-43] GNN-based Path-aware multi-view Circuit Learning for Technology Mapping
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14286
作者: Wentao Jiang,Jingxin Wang,Zhang Hu,Zhengyuan Shi,Chengyu Ma,Qiang Xu,Weikang Qian,Zhufei Chu
类目: Emerging Technologies (cs.ET); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 7pages, 4figures
Abstract:Traditional technology mapping suffers from systemic inaccuracies in delay estimation due to its reliance on abstract, technology-agnostic delay models that fail to capture the nuanced timing behavior behavior of real post-mapping circuits. To address this fundamental limitation, we introduce GPA(graph neural network (GNN)-based Path-Aware multi-view circuit learning), a novel GNN framework that learns precise, data-driven delay predictions by synergistically fusing three complementary views of circuit structure: And-Inverter Graphs (AIGs)-based functional encoding, post-mapping technology emphasizes critical timing paths. Trained exclusively on real cell delays extracted from critical paths of industrial-grade post-mapping netlists, GPA learns to classify cut delays with unprecedented accuracy, directly informing smarter mapping decisions. Evaluated on the 19 EPFL combinational benchmarks, GPA achieves 19.9%, 2.1% and 4.1% average delay reduction over the conventional heuristics methods (techmap, MCH) and the prior state-of-the-art ML-based approach SLAP, respectively-without compromising area efficiency.
[LG-44] A Comparison of Polynomial-Based Tree Clustering Methods
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14285
作者: Pengyu Liu,Mariel Vázquez,Nataša Jonoska
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Tree structures appear in many fields of the life sciences, including phylogenetics, developmental biology and nucleic acid structures. Trees can be used to represent RNA secondary structures, which directly relate to the function of non-coding RNAs. Recent developments in sequencing technology and artificial intelligence have yielded numerous biological data that can be represented with tree structures. This requires novel methods for tree structure data analytics. Tree polynomials provide a computationally efficient, interpretable and comprehensive way to encode tree structures as matrices, which are compatible with most data analytics tools. Machine learning methods based on the Canberra distance between tree polynomials have been introduced to analyze phylogenies and nucleic acid structures. In this paper, we compare the performance of different distances in tree clustering methods based on a tree distinguishing polynomial. We also implement two basic autoencoder models for clustering trees using the polynomial. We find that the distance based methods with entry-level normalized distances have the highest clustering accuracy among the compared methods.
[LG-45] Which Quantization Should I Use? A Unified Evaluation of llama.cpp Quantization on Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14277
作者: Uygar Kurt
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 17 pages, 6 tables, 1 figure
Abstract:Quantization is a practical technique for making large language models easier to deploy by reducing the precision used to store and operate on model weights. This can lower memory use and improve runtime feasibility on constrained hardware, which is especially relevant for users running models locally. Quantization in this http URL enables large language models to run on commodity hardware, but available formats are often evaluated inconsistently, making it hard to choose among schemes. We present a unified empirical study of the this http URL quantization on a single modern model, Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct (FP16, GGUF), covering 3-8 bit K-quant and legacy formats. We evaluate downstream task performance across standard reasoning, knowledge, instruction-following, and truthfulness benchmarks, and also measure perplexity and CPU throughput (prefill/decoding) alongside model size, compression, and quantization time. Ultimately, this work is a practical guide for choosing a this http URL quantization scheme, helping readers make informed, context-aware decisions for their intended use and resource budget.
[LG-46] Quality or Quantity? Error-Informed Selective Online Learning with Gaussian Processes in Multi-Agent Systems: Extended Version
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14275
作者: Zewen Yang,Xiaobing Dai,Jiajun Cheng,Yulong Huang,Peng Shi
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
*备注: Accepted by IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica
Abstract:Effective cooperation is pivotal in distributed learning for multi-agent systems, where the interplay between the quantity and quality of the machine learning models is crucial. This paper reveals the irrationality of indiscriminate inclusion of all models on agents for joint prediction, highlighting the imperative to prioritize quality over quantity in cooperative learning. Specifically, we present the first selective online learning framework for distributed Gaussian process (GP) regression, namely distributed error-informed GP (EIGP), that enables each agent to assess its neighboring collaborators, using the proposed selection function to choose the higher quality GP models with less prediction errors. Moreover, algorithmic enhancements are embedded within the EIGP, including a greedy algorithm (gEIGP) for accelerating prediction and an adaptive algorithm (aEIGP) for improving prediction accuracy. In addition, approaches for fast prediction and model update are introduced in conjunction with the error-informed quantification term iteration and a data deletion strategy to achieve real-time learning operations. Numerical simulations are performed to demonstrate the effectiveness of the developed methodology, showcasing its superiority over the state-of-the-art distributed GP methods with different benchmarks.
[LG-47] End-to-End Transformer Acceleration Through Processing-in-Memory Architectures
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14260
作者: Xiaoxuan Yang,Peilin Chen,Tergel Molom-Ochir,Yiran Chen
类目: Hardware Architecture (cs.AR); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: ICM 2025
Abstract:Transformers have become central to natural language processing and large language models, but their deployment at scale faces three major challenges. First, the attention mechanism requires massive matrix multiplications and frequent movement of intermediate results between memory and compute units, leading to high latency and energy costs. Second, in long-context inference, the key-value cache (KV cache) can grow unpredictably and even surpass the model’s weight size, creating severe memory and bandwidth bottlenecks. Third, the quadratic complexity of attention with respect to sequence length amplifies both data movement and compute overhead, making large-scale inference inefficient. To address these issues, this work introduces processing-in-memory solutions that restructure attention and feed-forward computation to minimize off-chip data transfers, dynamically compress and prune the KV cache to manage memory growth, and reinterpret attention as an associative memory operation to reduce complexity and hardware footprint. Moreover, we evaluate our processing-in-memory design against state-of-the-art accelerators and general-purpose GPUs, demonstrating significant improvements in energy efficiency and latency. Together, these approaches address computation overhead, memory scalability, and attention complexity, further enabling efficient, end-to-end acceleration of Transformer models.
[LG-48] Multi-context principal component analysis
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15239
作者: Kexin Wang,Salil Bhate,João M. Pereira,Joe Kileel,Matylda Figlerowicz,Anna Seigal
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Statistics Theory (math.ST)
*备注: 47 pages, 8 figures. Supplementary tables are provided as downloadable file
Abstract:Principal component analysis (PCA) is a tool to capture factors that explain variation in data. Across domains, data are now collected across multiple contexts (for example, individuals with different diseases, cells of different types, or words across texts). While the factors explaining variation in data are undoubtedly shared across subsets of contexts, no tools currently exist to systematically recover such factors. We develop multi-context principal component analysis (MCPCA), a theoretical and algorithmic framework that decomposes data into factors shared across subsets of contexts. Applied to gene expression, MCPCA reveals axes of variation shared across subsets of cancer types and an axis whose variability in tumor cells, but not mean, is associated with lung cancer progression. Applied to contextualized word embeddings from language models, MCPCA maps stages of a debate on human nature, revealing a discussion between science and fiction over decades. These axes are not found by combining data across contexts or by restricting to individual contexts. MCPCA is a principled generalization of PCA to address the challenge of understanding factors underlying data across contexts.
[LG-49] One scale to rule them all: interpretable multi-scale Deep Learning for predicting cell survival after proton and carbon ion irradiation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15106
作者: Giulio Bordieri,Giorgio Cartechini,Anna Bianchi,Anna Selva,Valeria Conte,Marta Missiaggia,Francesco G. Cordoni
类目: Biological Physics (physics.bio-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:The relationship between the physical characteristics of the radiation field and biological damage is central to both radiotherapy and radioprotection, yet the link between spatial scales of energy deposition and biological effects remains not entirely understood. To address this, we developed an interpretable deep learning model that predicts cell survival after proton and carbon ion irradiation, leveraging sequential attention to highlight relevant features and provide insight into the contribution of different energy deposition scales. Trained and tested on the PIDE dataset, our model incorporates, beside LET, nanodosimetric and microdosimetric quantities simulated with MC-Startrack and Open-TOPAS, enabling multi-scale characterization. While achieving high predictive accuracy, our approach also emphasizes transparency in decision-making. We demonstrate high accuracy in predicting RBE for in vitro experiments. Multiple scales are utilized concurrently, with no single spatial scale being predominant. Quantities defined at smaller spatial domains generally have a greater influence, whereas the LET plays a lesser role.
[LG-50] Efficient and Minimax-optimal In-context Nonparametric Regression with Transformers
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15014
作者: Michelle Ching,Ioana Popescu,Nico Smith,Tianyi Ma,William G. Underwood,Richard J. Samworth
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Statistics Theory (math.ST)
*备注: 31 pages, 6 figures
Abstract:We study in-context learning for nonparametric regression with \alpha -Hölder smooth regression functions, for some \alpha0 . We prove that, with n in-context examples and d -dimensional regression covariates, a pretrained transformer with \Theta(\log n) parameters and \Omega\bigl(n^2\alpha/(2\alpha+d)\log^3 n\bigr) pretraining sequences can achieve the minimax-optimal rate of convergence O\bigl(n^-2\alpha/(2\alpha+d)\bigr) in mean squared error. Our result requires substantially fewer transformer parameters and pretraining sequences than previous results in the literature. This is achieved by showing that transformers are able to approximate local polynomial estimators efficiently by implementing a kernel-weighted polynomial basis and then running gradient descent.
[LG-51] ExoMiner 2.0: Vetting TESS Full-Frame Image Transit Signals
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14877
作者: Miguel J. S. Martinho,Hamed Valizadegan,Jon M. Jenkins,Douglas A. Caldwell,Joseph D. Twicken,Ben Tofflemire,Marziye Jafariyazani
类目: Earth and Planetary Astrophysics (astro-ph.EP); Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics (astro-ph.IM); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:The Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) Full-Frame Images (FFIs) provide photometric time series for millions of stars, enabling transit searches beyond the limited set of pre-selected 2-minute targets. However, FFIs present additional challenges for transit identification and vetting. In this work, we apply ExoMiner++ 2.0, an adaptation of the ExoMiner++ framework originally developed for TESS 2-minute data, to FFI light curves. The model is used to perform large-scale planet versus non-planet classification of Threshold Crossing Events across the sectors analyzed in this study. We construct a uniform vetting catalog of all evaluated signals and assess model performance under different observing conditions. We find that ExoMiner++ 2.0 generalizes effectively to the FFI domain, providing robust discrimination between planetary signals, astrophysical false positives, and instrumental artifacts despite the limitations inherent to longer cadence data. This work extends the applicability of ExoMiner++ to the full TESS dataset and supports future population studies and follow-up prioritization.
[LG-52] Finite-Sample Inference for Sparsely Permuted Linear Regression
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14872
作者: Hirofumi Ota,Masaaki Imaizumi
类目: atistics Theory (math.ST); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Methodology (stat.ME); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注:
Abstract:We study a noisy linear observation model with an unknown permutation called permuted/shuffled linear regression, where responses and covariates are mismatched and the permutation forms a discrete, factorial-size parameter. This unknown permutation is a key component of the data-generating process, yet its statistical investigation remains challenging due to its discrete nature. In this study, we develop a general statistical inference framework on the permutation and regression coefficients. First, we introduce a localization step that reduces the permutation space to a small candidate set building on recent advances in the repro samples method, whose miscoverage decays polynomially with the number of Monte Carlo samples. Then, based on this localized set, we provide statistical inference procedures: a conditional Monte Carlo test of permutation structures with valid finite-sample Type-I error control. We also develop coefficient inference that remains valid under alignment uncertainty of permutations. For computational purposes, we develop a linear assignment problem computable in polynomial time complexity and demonstrate that its solution asymptotically converges to that of the conventional least squares problem with large computational cost. Extensions to partially permuted designs and ridge regularization are also discussed. Extensive simulations and an application to Beijing air-quality data corroborate finite-sample validity, strong power to detect mismatches, and practical scalability.
[LG-53] Learning and extrapolating scale-invariant processes
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14810
作者: Anaclara Alvez-Canepa,Cyril Furtlehner,François Landes
类目: Disordered Systems and Neural Networks (cond-mat.dis-nn); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 29p, 22 figures
Abstract:Machine Learning (ML) has deeply changed some fields recently, like Language and Vision and we may expect it to be relevant also to the analysis of of complex systems. Here we want to tackle the question of how and to which extent can one regress scale-free processes, i.e. processes displaying power law behavior, like earthquakes or avalanches? We are interested in predicting the large ones, i.e. rare events in the training set which therefore require extrapolation capabilities of the model. For this we consider two paradigmatic problems that are statistically self-similar. The first one is a 2-dimensional fractional Gaussian field obeying linear dynamics, self-similar by construction and amenable to exact analysis. The second one is the Abelian sandpile model, exhibiting self-organized criticality. The emerging paradigm of Geometric Deep Learning shows that including known symmetries into the model’s architecture is key to success. Here one may hope to extrapolate only by leveraging scale invariance. This is however a peculiar symmetry, as it involves possibly non-trivial coarse-graining operations and anomalous scaling. We perform experiments on various existing architectures like U-net, Riesz network (scale invariant by construction), or our own proposals: a wavelet-decomposition based Graph Neural Network (with discrete scale symmetry), a Fourier embedding layer and a Fourier-Mellin Neural Operator. Based on these experiments and a complete characterization of the linear case, we identify the main issues relative to spectral biases and coarse-grained representations, and discuss how to alleviate them with the relevant inductive biases.
[LG-54] RSVR: An Adaptive Stochastic Trust-Region Method with Variance Reduction
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14647
作者: Yuchen Fang,Xinshou Zheng,Javad Lavaei
类目: Optimization and Control (math.OC); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注: 22 pages
Abstract:We propose a stochastic trust-region method for unconstrained nonconvex optimization that incorporates stochastic variance-reduced gradients (SVRG) to accelerate convergence. Unlike classical trust-region methods, the proposed algorithm relies solely on stochastic gradient information and does not require function value evaluations. The trust-region radius is adaptively adjusted based on a radius-control parameter and the stochastic gradient estimate. Under mild assumptions, we establish that the algorithm converges in expectation to a first-order stationary point. Moreover, the method achieves iteration and sample complexity bounds that match those of SVRG-based first-order methods, while allowing stochastic and potentially gradient-dependent second-order information. Extensive numerical experiments demonstrate that incorporating SVRG accelerates convergence, and that the use of trust-region methods and Hessian information further improves performance. We also highlight the impact of batch size and inner-loop length on efficiency, and show that the proposed method outperforms SGD and Adam on several machine learning tasks.
[LG-55] Semi-Supervised Mixture Models under the Concept of Missing at Radom with Margin Confidence and Aranda Ordaz Function
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14631
作者: Jinyang Liao,Ziyang Lyu
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computation (stat.CO); Methodology (stat.ME)
*备注: 8 pages, 7 figures
Abstract:This paper presents a semi-supervised learning framework for Gaussian mixture modelling under a Missing at Random (MAR) mechanism. The method explicitly parameterizes the missingness mechanism by modelling the probability of missingness as a function of classification uncertainty. To quantify classification uncertainty, we introduce margin confidence and incorporate the Aranda Ordaz (AO) link function to flexibly capture the asymmetric relationships between uncertainty and missing probability. Based on this formulation, we develop an efficient Expectation Conditional Maximization (ECM) algorithm that jointly estimates all parameters appearing in both the Gaussian mixture model (GMM) and the missingness mechanism, and subsequently imputes the missing labels by a Bayesian classifier derived from the fitted mixture model. This method effectively alleviates the bias induced by ignoring the missingness mechanism while enhancing the robustness of semi-supervised learning. The resulting uncertainty-aware framework delivers reliable classification performance in realistic MAR scenarios with substantial proportions of missing labels.
[LG-56] Online Linear Programming with Replenishment
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14629
作者: Yuze Chen,Yuan Zhou,Baichuan Mo,Jie Ying,Yufei Ruan,Zhou Ye
类目: Optimization and Control (math.OC); Data Structures and Algorithms (cs.DS); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 63 pages, 12 figures
Abstract:We study an online linear programming (OLP) model in which inventory is not provided upfront but instead arrives gradually through an exogenous stochastic replenishment process. This replenishment-based formulation captures operational settings, such as e-commerce fulfillment, perishable supply chains, and renewable-powered systems, where resources are accumulated gradually and initial inventories are small or zero. The introduction of dispersed, uncertain replenishment fundamentally alters the structure of classical OLPs, creating persistent stockout risk and eliminating advance knowledge of the total budget. We develop new algorithms and regret analyses for three major distributional regimes studied in the OLP literature: bounded distributions, finite-support distributions, and continuous-support distributions with a non-degeneracy condition. For bounded distributions, we design an algorithm that achieves \widetilde\mathcalO(\sqrtT) regret. For finite-support distributions with a non-degenerate induced LP, we obtain \mathcalO(\log T) regret, and we establish an \Omega(\sqrtT) lower bound for degenerate instances, demonstrating a sharp separation from the classical setting where \mathcalO(1) regret is achievable. For continuous-support, non-degenerate distributions, we develop a two-stage accumulate-then-convert algorithm that achieves \mathcalO(\log^2 T) regret, comparable to the \mathcalO(\log T) regret in classical OLPs. Together, these results provide a near-complete characterization of the optimal regret achievable in OLP with replenishment. Finally, we empirically evaluate our algorithms and demonstrate their advantages over natural adaptations of classical OLP methods in the replenishment setting. Comments: 63 pages, 12 figures Subjects: Optimization and Control (math.OC); Data Structures and Algorithms (cs.DS); Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2601.14629 [math.OC] (or arXiv:2601.14629v1 [math.OC] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2601.14629 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-57] Large Data Limits of Laplace Learning for Gaussian Measure Data in Infinite Dimensions
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14515
作者: Zhengang Zhong,Yury Korolev,Matthew Thorpe
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Numerical Analysis (math.NA)
*备注:
Abstract:Laplace learning is a semi-supervised method, a solution for finding missing labels from a partially labeled dataset utilizing the geometry given by the unlabeled data points. The method minimizes a Dirichlet energy defined on a (discrete) graph constructed from the full dataset. In finite dimensions the asymptotics in the large (unlabeled) data limit are well understood with convergence from the graph setting to a continuum Sobolev semi-norm weighted by the Lebesgue density of the data-generating measure. The lack of the Lebesgue measure on infinite-dimensional spaces requires rethinking the analysis if the data aren’t finite-dimensional. In this paper we make a first step in this direction by analyzing the setting when the data are generated by a Gaussian measure on a Hilbert space and proving pointwise convergence of the graph Dirichlet energy.
[LG-58] Meta Flow Maps enable scalable reward alignment
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14430
作者: Peter Potaptchik,Adhi Saravanan,Abbas Mammadov,Alvaro Prat,Michael S. Albergo,Yee Whye Teh
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Controlling generative models is computationally expensive. This is because optimal alignment with a reward function–whether via inference-time steering or fine-tuning–requires estimating the value function. This task demands access to the conditional posterior p_1|t(x_1|x_t) , the distribution of clean data x_1 consistent with an intermediate state x_t , a requirement that typically compels methods to resort to costly trajectory simulations. To address this bottleneck, we introduce Meta Flow Maps (MFMs), a framework extending consistency models and flow maps into the stochastic regime. MFMs are trained to perform stochastic one-step posterior sampling, generating arbitrarily many i.i.d. draws of clean data x_1 from any intermediate state. Crucially, these samples provide a differentiable reparametrization that unlocks efficient value function estimation. We leverage this capability to solve bottlenecks in both paradigms: enabling inference-time steering without inner rollouts, and facilitating unbiased, off-policy fine-tuning to general rewards. Empirically, our single-particle steered-MFM sampler outperforms a Best-of-1000 baseline on ImageNet across multiple rewards at a fraction of the compute.
[LG-59] Cosmo-FOLD: Fast generation and upscaling of field-level cosmological maps with overlap latent diffusion
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14377
作者: Satvik Mishra,Roberto Trotta,Matteo Viel
类目: Cosmology and Nongalactic Astrophysics (astro-ph.CO); Instrumentation and Methods for Astrophysics (astro-ph.IM); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 15 pages, 10 figures
Abstract:We demonstrate the capabilities of probabilistic diffusion models to reduce dramatically the computational cost of expensive hydrodynamical simulations to study the relationship between observable baryonic cosmological probes and dark matter at field level and well into the non-linear regime. We introduce a novel technique, Cosmo-FOLD (Cosmological Fields via Overlap Latent Diffusion) to rapidly generate accurate and arbitrarily large cosmological and astrophysical 3-dimensional fields, conditioned on a given input field. We are able to generate TNG300-2 dark matter density and gas temperature fields from a model trained only on ~1% of the volume (a process we refer to as `upscaling’), reproducing both large scale coherent dark matter filaments and power spectra to within 10% for wavenumbers k = 5 h Mpc^-1. These results are obtained within a small fraction of the original simulation cost and produced on a single GPU. Beyond one and two points statistics, the bispectrum is also faithfully reproduced through the inclusion of positional encodings. Finally, we demonstrate Cosmo-FOLD’s generalisation capabilities by upscaling a CAMELS volume of 25 (Mpc h^-1)^3 to a full TNG300-2 volume of 205 (Mpc h^-1)^3 with no fine-tuning. Cosmo-FOLD opens the door to full field-level simulation-based inference on cosmological scale.
信息检索
[IR-0] Beyond the Geometric Curse: High-Dimensional N-Gram Hashing for Dense Retrieval
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15205
作者: Sangeet Sharma
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注: 11 page long, 5 figure. Yes, am undergrad in pharmacy and love computer work
Abstract:Why do even the most powerful 7B-parameter embedding models struggle with simple retrieval tasks that the decades old BM25 handles with ease? Recent theory suggests that this happens because of a dimensionality bottleneck. This occurs when we force infinite linguistic nuances into small, fixed-length learned vectors. We developed NUMEN to break this bottleneck by removing the learning process entirely. Instead of training heavy layers to map text to a constrained space, NUMEN uses deterministic character hashing to project language directly onto high-dimensional vectors. This approach requires no training, supports an unlimited vocabulary, and allows the geometric capacity scale as needed. On the LIMIT benchmark, NUMEN achieves 93.90 % Recall@100 at 32,768 dimensions. This makes it the first dense retrieval model to officially surpass the sparse BM25 baseline 93.6 %. Our findings show that the real problem in dense retrieval isn’t the architecture, but the embedding layer itself. The solution isn’t necessarily smarter training, but simply providing more room to breathe.
[IR-1] From Insight to Intervention: Interpretable Neuron Steering for Controlling Popularity Bias in Recommender Systems
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.15122
作者: Parviz Ahmadov,Masoud Mansoury
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注:
Abstract:Popularity bias is a pervasive challenge in recommender systems, where a few popular items dominate attention while the majority of less popular items remain underexposed. This imbalance can reduce recommendation quality and lead to unfair item exposure. Although existing mitigation methods address this issue to some extent, they often lack transparency in how they operate. In this paper, we propose a post-hoc approach, PopSteer, that leverages a Sparse Autoencoder (SAE) to both interpret and mitigate popularity bias in recommendation models. The SAE is trained to replicate a trained model’s behavior while enabling neuron-level interpretability. By introducing synthetic users with strong preferences for either popular or unpopular items, we identify neurons encoding popularity signals through their activation patterns. We then steer recommendations by adjusting the activations of the most biased neurons. Experiments on three public datasets with a sequential recommendation model demonstrate that PopSteer significantly enhances fairness with minimal impact on accuracy, while providing interpretable insights and fine-grained control over the fairness-accuracy trade-off.
[IR-2] What Should I Cite? A RAG Benchmark for Academic Citation Prediction
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14949
作者: Leqi Zheng,Jiajun Zhang,Canzhi Chen,Chaokun Wang,Hongwei Li,Yuying Li,Yaoxin Mao,Shannan Yan,Zixin Song,Zhiyuan Feng,Zhaolu Kang,Zirong Chen,Hang Zhang,Qiang Liu,Liang Wang,Ziyang Liu
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注:
Abstract:With the rapid growth of Web-based academic publications, more and more papers are being published annually, making it increasingly difficult to find relevant prior work. Citation prediction aims to automatically suggest appropriate references, helping scholars navigate the expanding scientific literature. Here we present \textbfCiteRAG, the first comprehensive retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)-integrated benchmark for evaluating large language models on academic citation prediction, featuring a multi-level retrieval strategy, specialized retrievers, and generators. Our benchmark makes four core contributions: (1) We establish two instances of the citation prediction task with different granularity. Task 1 focuses on coarse-grained list-specific citation prediction, while Task 2 targets fine-grained position-specific citation prediction. To enhance these two tasks, we build a dataset containing 7,267 instances for Task 1 and 8,541 instances for Task 2, enabling comprehensive evaluation of both retrieval and generation. (2) We construct a three-level large-scale corpus with 554k papers spanning many major subfields, using an incremental pipeline. (3) We propose a multi-level hybrid RAG approach for citation prediction, fine-tuning embedding models with contrastive learning to capture complex citation relationships, paired with specialized generation models. (4) We conduct extensive experiments across state-of-the-art language models, including closed-source APIs, open-source models, and our fine-tuned generators, demonstrating the effectiveness of our framework. Our open-source toolkit enables reproducible evaluation and focuses on academic literature, providing the first comprehensive evaluation framework for citation prediction and serving as a methodological template for other scientific domains. Our source code and data are released at this https URL.
[IR-3] PULSE: Socially-Aware User Representation Modeling Toward Parameter-Efficient Graph Collaborative Filtering WWW2026
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14720
作者: Doyun Choi,Cheonwoo Lee,Biniyam Aschalew Tolera,Taewook Ham,Chanyoung Park,Jaemin Yoo
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注: Accepted at WWW 2026, 12pages
Abstract:Graph-based social recommendation (SocialRec) has emerged as a powerful extension of graph collaborative filtering (GCF), which leverages graph neural networks (GNNs) to capture multi-hop collaborative signals from user-item interactions. These methods enrich user representations by incorporating social network information into GCF, thereby integrating additional collaborative signals from social relations. However, existing GCF and graph-based SocialRec approaches face significant challenges: they incur high computational costs and suffer from limited scalability due to the large number of parameters required to assign explicit embeddings to all users and items. In this work, we propose PULSE (Parameter-efficient User representation Learning with Social Knowledge), a framework that addresses this limitation by constructing user representations from socially meaningful signals without creating an explicit learnable embedding for each user. PULSE reduces the parameter size by up to 50% compared to the most lightweight GCF baseline. Beyond parameter efficiency, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, outperforming 13 GCF and graph-based social recommendation baselines across varying levels of interaction sparsity, from cold-start to highly active users, through a time- and memory-efficient modeling process.
[IR-4] Unified Multimodal and Multilingual Retrieval via Multi-Task Learning with NLU Integration ICASSP2026
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14714
作者: Xinyuan Zhang,Lina Zhang,Lisung Chen,Guangyao Liu,Shuai Nie,Jiaming Xu,Runyu Shi,Ying Huang,Guoquan Zhang
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注: 4 pages, 2 figures, submitted to IEEE ICASSP 2026
Abstract:Multimodal retrieval systems typically employ Vision Language Models (VLMs) that encode images and text independently into vectors within a shared embedding space. Despite incorporating text encoders, VLMs consistently underperform specialized text models on text-only retrieval tasks. Moreover, introducing additional text encoders increases storage, inference overhead, and exacerbates retrieval inefficiencies, especially in multilingual settings. To address these limitations, we propose a multi-task learning framework that unifies the feature representation across images, long and short texts, and intent-rich queries. To our knowledge, this is the first work to jointly optimize multilingual image retrieval, text retrieval, and natural language understanding (NLU) tasks within a single framework. Our approach integrates image and text retrieval with a shared text encoder that is enhanced by NLU features for intent understanding and retrieval accuracy.
[IR-5] Predicting Retrieval Utility and Answer Quality in Retrieval-Augmented Generation ECIR’26
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14546
作者: Fangzheng Tian,Debasis Ganguly,Craig Macdonald
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注: 18 pages (including reference), 3 figures, 2 table, 61 references; this paper has been accepted by ECIR’26 as a full paper
Abstract:The quality of answers generated by large language models (LLMs) in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is largely influenced by the contextual information contained in the retrieved documents. A key challenge for improving RAG is to predict both the utility of retrieved documents – quantified as the performance gain from using context over generation without context – and the quality of the final answers in terms of correctness and relevance. In this paper, we define two prediction tasks within RAG. The first is retrieval performance prediction (RPP), which estimates the utility of retrieved documents. The second is generation performance prediction (GPP), which estimates the final answer quality. We hypothesise that in RAG, the topical relevance of retrieved documents correlates with their utility, suggesting that query performance prediction (QPP) approaches can be adapted for RPP and GPP. Beyond these retriever-centric signals, we argue that reader-centric features, such as the LLM’s perplexity of the retrieved context conditioned on the input query, can further enhance prediction accuracy for both RPP and GPP. Finally, we propose that features reflecting query-agnostic document quality and readability can also provide useful signals to the predictions. We train linear regression models with the above categories of predictors for both RPP and GPP. Experiments on the Natural Questions (NQ) dataset show that combining predictors from multiple feature categories yields the most accurate estimates of RAG performance.
[IR-6] rust Me on This: A User Study of Trustworthiness for RAG Responses ECIR’26
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14460
作者: Weronika Łajewska,Krisztian Balog
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注: This is the author’s version of the work. The definitive version is published in: Proceedings of the 48th European Conference on Information Retrieval (ECIR '26), March 29-April 2, 2026, Delft, The Netherlands
Abstract:The integration of generative AI into information access systems often presents users with synthesized answers that lack transparency. This study investigates how different types of explanations can influence user trust in responses from retrieval-augmented generation systems. We conducted a controlled, two-stage user study where participants chose the more trustworthy response from a pair-one objectively higher quality than the other-both with and without one of three explanation types: (1) source attribution, (2) factual grounding, and (3) information coverage. Our results show that while explanations significantly guide users toward selecting higher quality responses, trust is not dictated by objective quality alone: Users’ judgments are also heavily influenced by response clarity, actionability, and their own prior knowledge.
[IR-7] Legal Retrieval for Public Defenders
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2601.14348
作者: Dominik Stammbach,Kylie Zhang,Patty Liu,Nimra Nadeem,Lucia Zheng,Peter Henderson
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注:
Abstract:AI tools are increasingly suggested as solutions to assist public agencies with heavy workloads. In public defense, where a constitutional right to counsel meets the complexities of law, overwhelming caseloads and constrained resources, practitioners face especially taxing conditions. Yet, there is little evidence of how AI could meaningfully support defenders’ day-to-day work. In partnership with the New Jersey Office of the Public Defender, we develop the NJ BriefBank, a retrieval tool which surfaces relevant appellate briefs to streamline legal research and writing. We show that existing legal retrieval benchmarks fail to transfer to public defense search, however adding domain knowledge improves retrieval quality. This includes query expansion with legal reasoning, domain-specific data and curated synthetic examples. To facilitate further research, we provide a taxonomy of realistic defender search queries and release a manually annotated public defense retrieval dataset. Together, our work offers starting points towards building practical, reliable retrieval AI tools for public defense, and towards more realistic legal retrieval benchmarks.