本篇博文主要内容为 2025-12-29 从Arxiv.org论文网站获取的最新论文列表,自动更新,按照NLP、CV、ML、AI、IR五个大方向区分,若需要邮件定时接收,请在评论区留下你的邮箱号。
说明:每日论文数据从Arxiv.org获取,每天早上12:00左右定时自动更新。
友情提示: 如何您需要邮箱接收每日论文数据,请在评论处留下你的邮箱。
目录
概览 (2025-12-29)
今日共更新360篇论文,其中:
- 自然语言处理共40篇(Computation and Language (cs.CL))
- 人工智能共96篇(Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI))
- 计算机视觉共96篇(Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV))
- 机器学习共92篇(Machine Learning (cs.LG))
自然语言处理
[NLP-0] A2P-Vis: an Analyzer-to-Presenter Agent ic Pipeline for Visual Insights Generation and Reporting
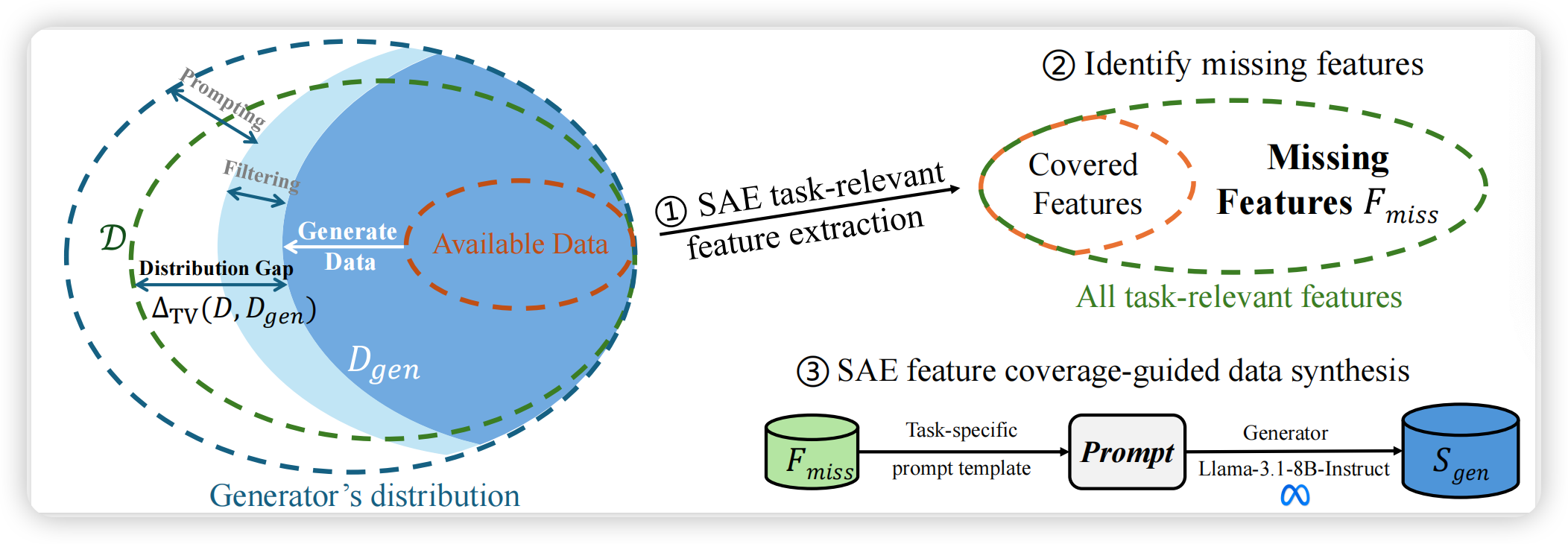
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决自动化端到端数据科学流程中两个关键瓶颈问题:一是生成具有洞察力且多样化的可视化证据,二是将这些可视化结果整合为结构清晰、专业规范的报告。解决方案的核心在于提出A2P-Vis这一两阶段多智能体流水线架构,其中“数据分析师”(Data Analyzer)负责数据概要分析、提出多样化的可视化方向、生成并执行绘图代码、通过可读性检查过滤低质量图表,并对候选洞察进行深度、正确性、具体性和可操作性评分;“呈现者”(Presenter)则负责排序主题、基于高分洞察撰写图表支撑的叙事内容、添加逻辑过渡句并优化文档整体清晰度与一致性,最终输出一篇无需人工干预即可直接发表的高质量数据可视化报告。通过将质量保障的分析模块与叙事构建模块耦合,A2P-Vis实现了从原始数据到可读叙事的全流程自动化,显著提升了自动化数据分析在实际场景中的可用性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22101
作者: Shuyu Gan,Renxiang Wang,James Mooney,Dongyeop Kang
机构: University of Minnesota (明尼苏达大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 3 pages, 3 figures; Accepted by 1st Workshop on GenAI, Agents and the Future of VIS as Mini-challenge paper and win the Honorable Mention award. Submit number is 7597 and the paper is archived on the workshop website: this https URL
Abstract:Automating end-to-end data science pipeline with AI agents still stalls on two gaps: generating insightful, diverse visual evidence and assembling it into a coherent, professional report. We present A2P-Vis, a two-part, multi-agent pipeline that turns raw datasets into a high-quality data-visualization report. The Data Analyzer orchestrates profiling, proposes diverse visualization directions, generates and executes plotting code, filters low-quality figures with a legibility checker, and elicits candidate insights that are automatically scored for depth, correctness, specificity, depth and actionability. The Presenter then orders topics, composes chart-grounded narratives from the top-ranked insights, writes justified transitions, and revises the document for clarity and consistency, yielding a coherent, publication-ready report. Together, these agents convert raw data into curated materials (charts + vetted insights) and into a readable narrative without manual glue work. We claim that by coupling a quality-assured Analyzer with a narrative Presenter, A2P-Vis operationalizes co-analysis end-to-end, improving the real-world usefulness of automated data analysis for practitioners. For the complete dataset report, please see: this https URL.
zh
[NLP-1] Introducing TrGLUE and SentiTurca: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Turkish General Language Understanding and Sentiment Analysis
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决土耳其语自然语言理解(Natural Language Understanding, NLU)缺乏综合性评估基准的问题。当前虽有针对英语(GLUE)、中文(CLUE)、法语(FLUE)和日语(JGLUE)等语言的NLU基准,但土耳其语尚无类似系统性评测框架。为填补这一空白,作者提出了TrGLUE,一个涵盖多种NLU任务的土耳其语基准,并配套提出SentiTurca用于情感分析专项评估。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个基于土耳其语原生语料库的评估体系,通过结合大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)辅助标注、多模型一致性校验与人工验证的半自动化标注流程,确保数据的语义自然性和标注质量,同时实现可扩展、可复现的数据生成范式,从而为土耳其语NLU研究提供可靠、标准化的评估工具。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22100
作者: Duygu Altinok
机构: Independent Researcher(独立研究员)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: under review by Springer
Abstract:Evaluating the performance of various model architectures, such as transformers, large language models (LLMs), and other NLP systems, requires comprehensive benchmarks that measure performance across multiple dimensions. Among these, the evaluation of natural language understanding (NLU) is particularly critical as it serves as a fundamental criterion for assessing model capabilities. Thus, it is essential to establish benchmarks that enable thorough evaluation and analysis of NLU abilities from diverse perspectives. While the GLUE benchmark has set a standard for evaluating English NLU, similar benchmarks have been developed for other languages, such as CLUE for Chinese, FLUE for French, and JGLUE for Japanese. However, no comparable benchmark currently exists for the Turkish language. To address this gap, we introduce TrGLUE, a comprehensive benchmark encompassing a variety of NLU tasks for Turkish. In addition, we present SentiTurca, a specialized benchmark for sentiment analysis. To support researchers, we also provide fine-tuning and evaluation code for transformer-based models, facilitating the effective use of these benchmarks. TrGLUE comprises Turkish-native corpora curated to mirror the domains and task formulations of GLUE-style evaluations, with labels obtained through a semi-automated pipeline that combines strong LLM-based annotation, cross-model agreement checks, and subsequent human validation. This design prioritizes linguistic naturalness, minimizes direct translation artifacts, and yields a scalable, reproducible workflow. With TrGLUE, our goal is to establish a robust evaluation framework for Turkish NLU, empower researchers with valuable resources, and provide insights into generating high-quality semi-automated datasets.
zh
[NLP-2] Unifying Learning Dynamics and Generalization in Transformers Scaling Law
【速读】: 该论文试图解决大型语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)中Scaling Law的理论基础不明确的问题,即尽管经验上已验证计算资源增加可提升模型性能,但其背后的机制仍缺乏严谨的数学刻画。解决方案的关键在于将基于Transformer的序列到序列语言模型的学习动态形式化为常微分方程(Ordinary Differential Equation, ODE)系统,并进一步近似为核(kernel)行为;在此基础上,对随机梯度下降(Stochastic Gradient Descent, SGD)训练过程进行严格分析,首次在任意数据分布下刻画了泛化误差收敛至不可约风险(irreducible risk)的过程,揭示出一个由计算成本 C 决定的相变现象:初始优化阶段误差呈指数衰减,越过阈值后进入统计相位,泛化误差以 Θ(C−1/6) 的幂律衰减,从而统一解释了模型规模、训练时间和数据量各自独立影响泛化上界的作用机制。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22088
作者: Chiwun Yang
机构: Sun Yat-sen University (中山大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:The scaling law, a cornerstone of Large Language Model (LLM) development, predicts improvements in model performance with increasing computational resources. Yet, while empirically validated, its theoretical underpinnings remain poorly understood. This work formalizes the learning dynamics of transformer-based language models as an ordinary differential equation (ODE) system, then approximates this process to kernel behaviors. Departing from prior toy-model analyses, we rigorously analyze stochastic gradient descent (SGD) training for multi-layer transformers on sequence-to-sequence data with arbitrary data distribution, closely mirroring real-world conditions. Our analysis characterizes the convergence of generalization error to the irreducible risk as computational resources scale with data, especially during the optimization process. We establish a theoretical upper bound on excess risk characterized by a distinct phase transition. In the initial optimization phase, the excess risk decays exponentially relative to the computational cost \sf C . However, once a specific resource allocation threshold is crossed, the system enters a statistical phase, where the generalization error follows a power-law decay of \Theta(\mathsfC^-1/6) . Beyond this unified framework, our theory derives isolated scaling laws for model size, training time, and dataset size, elucidating how each variable independently governs the upper bounds of generalization. Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL) Cite as: arXiv:2512.22088 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2512.22088v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.22088 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[NLP-3] Context as a Tool: Context Management for Long-Horizon SWE-Agents
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决基于大语言模型的智能体(Agent)在执行需要长时间交互的软件工程(Software Engineering, SWE)任务时,因上下文管理策略不合理而导致的上下文爆炸(context explosion)、语义漂移(semantic drift)以及推理能力退化问题。现有方法多依赖于追加式上下文维护或被动触发的压缩启发式策略,难以在有限上下文窗口内保持长期任务的连贯性和有效性。解决方案的关键在于提出一种全新的上下文管理范式CAT(Context-aware Agent Tool),其核心是将上下文维护提升为可调用工具,并嵌入到智能体决策流程中;通过构建包含稳定任务语义、压缩后的长期记忆和高保真短期交互的结构化上下文工作区,使智能体能够在适当里程碑主动压缩历史轨迹并生成可操作的摘要。此外,作者设计了基于离线数据构建管道的轨迹级监督框架CAT-GENERATOR,用于训练一个具备上下文感知能力的压缩模型SWE-Compressor,在SWE-Bench-Verified基准上实现了57.6%的求解率,显著优于ReAct基线和静态压缩方法,且在受限上下文预算下仍能保持稳定、可扩展的长程推理能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22087
作者: Shukai Liu,Jian Yang,Bo Jiang,Yizhi Li,Jinyang Guo,Xianglong Liu,Bryan Dai
机构: Beihang University (北京航空航天大学); Manchester (曼彻斯特大学); Ubiquant (Ubiquant)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Agents based on large language models have recently shown strong potential on real-world software engineering (SWE) tasks that require long-horizon interaction with repository-scale codebases. However, most existing agents rely on append-only context maintenance or passively triggered compression heuristics, which often lead to context explosion, semantic drift, and degraded reasoning in long-running interactions. We propose CAT, a new context management paradigm that elevates context maintenance to a callable tool integrated into the decision-making process of agents. CAT formalizes a structured context workspace consisting of stable task semantics, condensed long-term memory, and high-fidelity short-term interactions, and enables agents to proactively compress historical trajectories into actionable summaries at appropriate milestones. To support context management for SWE-agents, we propose a trajectory-level supervision framework, CAT-GENERATOR, based on an offline data construction pipeline that injects context-management actions into complete interaction trajectories. Using this framework, we train a context-aware model, SWE-Compressor. Experiments on SWE-Bench-Verified demonstrate that SWE-Compressor reaches a 57.6% solved rate and significantly outperforms ReAct-based agents and static compression baselines, while maintaining stable and scalable long-horizon reasoning under a bounded context budget.
zh
[NLP-4] oward Secure and Compliant AI: Organizational Standards and Protocols for NLP Model Lifecycle Management
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing, NLP)系统在医疗、金融和政府等敏感领域应用中,因处理大量个人及受监管数据而引发的安全、隐私与合规风险问题,这些问题目前尚未被现有人工智能治理框架充分覆盖。解决方案的关键在于提出一个六阶段的“安全与合规NLP生命周期管理框架”(Secure and Compliant NLP Lifecycle Management Framework, SC-NLP-LMF),该框架通过整合差分隐私、联邦学习、可解释性、模型安全部署与退役等成熟方法,并基于PRISMA系统文献回顾方法对45篇同行评审和监管源进行分析,确保NLP系统从开发到退役全过程的安全可控,同时满足NIST AI RMF、ISO/IEC 42001:2023、欧盟AI法案及MITRE ATLAS等主流标准要求。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22060
作者: Sunil Arora,John Hastings
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注: 9 pages, 2 tables, 1 figure
Abstract:Natural Language Processing (NLP) systems are increasingly used in sensitive domains such as healthcare, finance, and government, where they handle large volumes of personal and regulated data. However, these systems introduce distinct risks related to security, privacy, and regulatory compliance that are not fully addressed by existing AI governance frameworks. This paper introduces the Secure and Compliant NLP Lifecycle Management Framework (SC-NLP-LMF), a comprehensive six-phase model designed to ensure the secure operation of NLP systems from development to retirement. The framework, developed through a systematic PRISMA-based review of 45 peer-reviewed and regulatory sources, aligns with leading standards, including NIST AI RMF, ISO/IEC 42001:2023, the EU AI Act, and MITRE ATLAS. It integrates established methods for bias detection, privacy protection (differential privacy, federated learning), secure deployment, explainability, and secure model decommissioning. A healthcare case study illustrates how SC-NLP-LMF detects emerging terminology drift (e.g., COVID-related language) and guides compliant model updates. The framework offers organizations a practical, lifecycle-wide structure for developing, deploying, and maintaining secure and accountable NLP systems in high-risk environments.
zh
[NLP-5] Self-attention vector output similarities reveal how machines pay attention
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决自注意力机制(self-attention mechanism)在自然语言处理中如何量化信息处理过程及其学习特性的开放性问题。其关键解决方案是基于BERT-12架构的注意力头(attention head)所生成的向量空间,构建上下文相似度矩阵(context similarity matrix),通过计算token向量间的标量积来量化不同层与头之间的语义关联特性。研究发现,不同注意力头在各层中聚焦于不同的语言特征,如重复词识别或共现模式感知,并且随着网络深度增加,注意力从长距离相似性逐渐转向短距离、句内强相似性,同时每个注意力头倾向于围绕一个独特高频词建立相似性对,从而揭示了自注意力机制在深层结构中的功能分工与语义聚焦规律。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21956
作者: Tal Halevi,Yarden Tzach,Ronit D. Gross,Shalom Rosner,Ido Kanter
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 22 pages, 13 figures
Abstract:The self-attention mechanism has significantly advanced the field of natural language processing, facilitating the development of advanced language-learning machines. Although its utility is widely acknowledged, the precise mechanisms of self-attention underlying its advanced learning and the quantitative characterization of this learning process remains an open research question. This study introduces a new approach for quantifying information processing within the self-attention mechanism. The analysis conducted on the BERT-12 architecture reveals that, in the final layers, the attention map focuses on sentence separator tokens, suggesting a practical approach to text segmentation based on semantic features. Based on the vector space emerging from the self-attention heads, a context similarity matrix, measuring the scalar product between two token vectors was derived, revealing distinct similarities between different token vector pairs within each head and layer. The findings demonstrated that different attention heads within an attention block focused on different linguistic characteristics, such as identifying token repetitions in a given text or recognizing a token of common appearance in the text and its surrounding context. This specialization is also reflected in the distribution of distances between token vectors with high similarity as the architecture progresses. The initial attention layers exhibit substantially long-range similarities; however, as the layers progress, a more short-range similarity develops, culminating in a preference for attention heads to create strong similarities within the same sentence. Finally, the behavior of individual heads was analyzed by examining the uniqueness of their most common tokens in their high similarity elements. Each head tends to focus on a unique token from the text and builds similarity pairs centered around it.
zh
[NLP-6] Broken Words Broken Performance: Effect of Tokenization on Performance of LLM s AACL2025
【速读】: 该论文试图解决的问题是:大型语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)在文本分词(tokenization)过程中,由于词汇表规模有限,常将自然单词拆分为多个子词单元(subword tokens),这种非自然的分词方式可能对LLM在各类自然语言处理(NLP)任务中的性能产生负面影响。为量化这一影响,论文提出了一组惩罚函数(penalty functions),用于计算特定文本在给定LLM下的分词惩罚值,从而衡量其分词质量。解决方案的关键在于构建可量化的分词惩罚指标,并通过多任务实验证明该指标与LLM性能之间存在统计显著的相关性,从而为优化分词策略提供了理论依据和评估工具。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21933
作者: Sachin Pawar,Manoj Apte,Kshitij Jadhav,Girish Keshav Palshikar,Nitin Ramrakhiyani
机构: TCS Research, Tata Consultancy Services Limited(塔塔咨询有限公司)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing Asia-Pacific Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (IJCNLP-AACL 2025)
Abstract:Tokenization is the first step in training any Large Language Model (LLM), where the text is split into a sequence of tokens as per the model’s fixed vocabulary. This tokenization in LLMs is different from the traditional tokenization in NLP where the text is split into a sequence of “natural” words. In LLMs, a natural word may also be broken into multiple tokens due to limited vocabulary size of the LLMs (e.g., Mistral’s tokenizer splits “martial” into “mart” and “ial”). In this paper, we hypothesize that such breaking of natural words negatively impacts LLM performance on various NLP tasks. To quantify this effect, we propose a set of penalty functions that compute a tokenization penalty for a given text for a specific LLM, indicating how “bad” the tokenization is. We establish statistical significance of our hypothesis on multiple NLP tasks for a set of different LLMs.
zh
[NLP-7] SWE-RM: Execution-free Feedback For Software Engineering Agents
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前软件工程(Software Engineering, SWE)代理在使用执行反馈(如单元测试)和无执行反馈(如奖励模型)时存在的性能不一致问题,特别是奖励模型在测试时缩放(Test-Time Scaling, TTS)与强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)训练中表现差异显著的问题。研究发现,即使两个验证器在TTS上表现相近,其在RL中的效果可能截然不同,这表明TTS能力不能直接泛化到RL场景。为解决这一局限性,作者识别出分类准确性和校准性(calibration)是影响RL训练的关键因素,并通过系统性的受控实验分析了训练数据规模、策略混合方式及数据来源组成等因素的影响。最终提出SWE-RM,一种基于专家混合(mixture-of-experts)架构的奖励模型,具有30B总参数量、推理时激活3B参数,显著提升了SWE代理在TTS和RL任务上的综合性能,例如将Qwen3-Coder-Flash在SWE-Bench Verified上的准确率从51.6%提升至62.0%,并在开源模型中达到新的最先进水平。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21919
作者: KaShun Shum,Binyuan Hui,Jiawei Chen,Lei Zhang,X. W.,Jiaxi Yang,Yuzhen Huang,Junyang Lin,Junxian He
机构: The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (香港科技大学); Qwen Team, Alibaba Group (阿里巴巴集团)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: 21 pages
Abstract:Execution-based feedback like unit testing is widely used in the development of coding agents through test-time scaling (TTS) and reinforcement learning (RL). This paradigm requires scalable and reliable collection of unit test cases to provide accurate feedback, and the resulting feedback is often sparse and cannot effectively distinguish between trajectories that are both successful or both unsuccessful. In contrast, execution-free feedback from reward models can provide more fine-grained signals without depending on unit test cases. Despite this potential, execution-free feedback for realistic software engineering (SWE) agents remains underexplored. Aiming to develop versatile reward models that are effective across TTS and RL, however, we observe that two verifiers with nearly identical TTS performance can nevertheless yield very different results in RL. Intuitively, TTS primarily reflects the model’s ability to select the best trajectory, but this ability does not necessarily generalize to RL. To address this limitation, we identify two additional aspects that are crucial for RL training: classification accuracy and calibration. We then conduct comprehensive controlled experiments to investigate how to train a robust reward model that performs well across these metrics. In particular, we analyze the impact of various factors such as training data scale, policy mixtures, and data source composition. Guided by these investigations, we introduce SWE-RM, an accurate and robust reward model adopting a mixture-of-experts architecture with 30B total parameters and 3B activated during inference. SWE-RM substantially improves SWE agents on both TTS and RL performance. For example, it increases the accuracy of Qwen3-Coder-Flash from 51.6% to 62.0%, and Qwen3-Coder-Max from 67.0% to 74.6% on SWE-Bench Verified using TTS, achieving new state-of-the-art performance among open-source models.
zh
[NLP-8] Accelerate Speculative Decoding with Sparse Computation in Verification
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)中自回归语言模型推理时,推测解码(speculative decoding)的验证阶段成为主要计算瓶颈的问题,尤其是在长上下文输入和混合专家(Mixture-of-Experts, MoE)模型场景下。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种稀疏验证框架(sparse verification framework),通过联合稀疏化注意力机制(attention)、前馈网络(Feed-Forward Network, FFN)和MoE组件来降低验证阶段的主导计算开销,并引入跨推测token与跨层的检索重用策略,在不增加额外训练的前提下进一步减少冗余计算。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21911
作者: Jikai Wang,Jianchao Tan,Yuxuan Hu,Jiayu Qin,Yerui Sun,Yuchen Xie,Xunliang Cai,Juntao Li,Min Zhang
机构: Soochow University (苏州大学); Meituan (美团)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Pre-print
Abstract:Speculative decoding accelerates autoregressive language model inference by verifying multiple draft tokens in parallel. However, the verification stage often becomes the dominant computational bottleneck, especially for long-context inputs and mixture-of-experts (MoE) models. Existing sparsification methods are designed primarily for standard token-by-token autoregressive decoding to remove substantial computational redundancy in LLMs. This work systematically adopts different sparse methods on the verification stage of the speculative decoding and identifies structured redundancy across multiple dimensions. Based on these observations, we propose a sparse verification framework that jointly sparsifies attention, FFN, and MoE components during the verification stage to reduce the dominant computation cost. The framework further incorporates an inter-draft token and inter-layer retrieval reuse strategy to further reduce redundant computation without introducing additional training. Extensive experiments across summarization, question answering, and mathematical reasoning datasets demonstrate that the proposed methods achieve favorable efficiency-accuracy trade-offs, while maintaining stable acceptance length.
zh
[NLP-9] Explainable Statute Prediction via Attention-based Model and LLM Prompting
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决法律领域的自动法条预测(statute prediction)问题,即根据给定的案件描述,自动识别并输出相关的法律条文(如某部法律中的条款、子条款或章节)。这一任务对法律人工智能系统(如律师辅助工具和法律问答系统)具有重要应用价值。解决方案的关键在于提供可解释的预测结果:一方面提出AoS(Attention-over-Sentences)方法,利用句子级注意力机制在较小语言模型(sentence transformers)上进行监督训练以实现法条预测;另一方面提出LLMPrompt方法,基于大语言模型(LLM)采用零样本学习策略,并结合标准提示与思维链(Chain-of-Thought, CoT)提示技术,在不依赖标注数据的情况下同时生成预测和人类可理解的解释。两种方法均能输出可解释性较强的预测结果,且通过对比实验和人工评估验证了其性能与解释质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21902
作者: Sachin Pawar,Girish Keshav Palshikar,Anindita Sinha Banerjee,Nitin Ramrakhiyani,Basit Ali
机构: TCS Research (TCS 研究院); Tata Consultancy Services Limited (塔塔咨询服务有限公司)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:In this paper, we explore the problem of automatic statute prediction where for a given case description, a subset of relevant statutes are to be predicted. Here, the term “statute” refers to a section, a sub-section, or an article of any specific Act. Addressing this problem would be useful in several applications such as AI-assistant for lawyers and legal question answering system. For better user acceptance of such Legal AI systems, we believe the predictions should also be accompanied by human understandable explanations. We propose two techniques for addressing this problem of statute prediction with explanations – (i) AoS (Attention-over-Sentences) which uses attention over sentences in a case description to predict statutes relevant for it and (ii) LLMPrompt which prompts an LLM to predict as well as explain relevance of a certain statute. AoS uses smaller language models, specifically sentence transformers and is trained in a supervised manner whereas LLMPrompt uses larger language models in a zero-shot manner and explores both standard as well as Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting techniques. Both these models produce explanations for their predictions in human understandable forms. We compare statute prediction performance of both the proposed techniques with each other as well as with a set of competent baselines, across two popular datasets. Also, we evaluate the quality of the generated explanations through an automated counter-factual manner as well as through human evaluation.
zh
[NLP-10] CricBench: A Multilingual Benchmark for Evaluating LLM s in Cricket Analytics
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在体育数据分析领域,特别是板球(cricket)这一特定领域中,面对复杂数据模式、多语言需求和专业术语时性能不足的问题。其核心挑战在于:尽管LLMs在通用Text-to-SQL任务上表现优异,但在处理具有高度领域特异性、结构复杂且涉及多语言的体育数据库查询时仍存在显著能力缺口。解决方案的关键在于构建一个名为CricBench的综合性基准测试套件,该套件通过与板球及SQL领域的专家合作,人工编写逻辑正确的复杂查询以形成“黄金标准”数据集,并支持英语和印地语双语查询,从而系统性评估LLMs在真实场景下的表现。实验表明,即使是最先进的模型如DeepSeek R1,在从通用基准(如BIRD)迁移到CricBench时也出现明显准确率下降,且代码混合的印地语查询反而常优于纯英文提示,揭示了语言多样性对专业SQL生成任务的重要影响。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21877
作者: Vaibhav Devraj,Dhruv Kumar,Jagat Sesh Challa
机构: Birla Institute of Technology and Science (BITS), Pilani
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Under Review
Abstract:Cricket is the second most popular sport globally, commanding a massive following of over 2.5 billion fans globally. Enthusiasts and analysts frequently seek advanced statistical insights, such as long-term historical performance trends or complex player comparisons, that are often unavailable through standard web searches. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have advanced significantly in Text-to-SQL tasks, their capability to handle the domain-specific nuances, complex schema variations, and multilingual requirements inherent to sports analytics remains under-explored. To investigate this potential capability gap, we present CricBench, a comprehensive benchmark suite for evaluating LLMs on specialized cricket data. To curate a “Gold Standard” dataset, we collaborate with domain experts in cricket and SQL to manually author complex queries, ensuring logical correctness. Recognizing linguistic diversity, we construct the benchmark in both English and Hindi, establishing a framework that is open for further extension to other regional languages. We evaluate six state-of-the-art models, including GPT-4o, Claude 3.7 Sonnet, and open-source models, using a strict evaluation protocol. Our results reveal that high performance on general benchmarks does not guarantee success in specialized domains. While the open-weights reasoning model DeepSeek R1 achieves state-of-the-art performance (50.6%), surpassing proprietary giants like Claude 3.7 Sonnet (47.7%) and GPT-4o (33.7%), it still exhibits a significant accuracy drop when moving from general benchmarks (BIRD) to CricBench. Furthermore, we observe that code-mixed Hindi queries frequently yield parity or higher accuracy compared to English, challenging the assumption that English is the optimal prompt language for specialized SQL tasks.
zh
[NLP-11] Bridging the Copyright Gap: Do Large Vision-Language Models Recognize and Respect Copyrighted Content? AAAI2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型视觉语言模型(Large Vision-Language Models, LVLMs)在处理受版权保护内容时存在的合规性问题,即模型是否能准确识别并遵守版权法规,尤其是在用户输入或检索到的图文内容涉及版权材料(如书籍摘录、新闻报道、音乐歌词和代码文档)时。研究发现,即使是最先进的闭源LVLM,在面对带或不带版权标识的场景下,也普遍存在对版权内容识别不足和尊重缺失的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种新颖的工具增强型防御框架(tool-augmented defense framework),通过引入外部工具辅助判断与响应机制,在所有测试场景中有效降低版权侵权风险,从而推动构建具备版权意识的LVLM,保障其合法、负责任地使用受版权保护的内容。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21871
作者: Naen Xu,Jinghuai Zhang,Changjiang Li,Hengyu An,Chunyi Zhou,Jun Wang,Boyu Xu,Yuyuan Li,Tianyu Du,Shouling Ji
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注: AAAI 2026 (Oral)
Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) have achieved remarkable advancements in multimodal reasoning tasks. However, their widespread accessibility raises critical concerns about potential copyright infringement. Will LVLMs accurately recognize and comply with copyright regulations when encountering copyrighted content (i.e., user input, retrieved documents) in the context? Failure to comply with copyright regulations may lead to serious legal and ethical consequences, particularly when LVLMs generate responses based on copyrighted materials (e.g., retrieved book experts, news reports). In this paper, we present a comprehensive evaluation of various LVLMs, examining how they handle copyrighted content – such as book excerpts, news articles, music lyrics, and code documentation when they are presented as visual inputs. To systematically measure copyright compliance, we introduce a large-scale benchmark dataset comprising 50,000 multimodal query-content pairs designed to evaluate how effectively LVLMs handle queries that could lead to copyright infringement. Given that real-world copyrighted content may or may not include a copyright notice, the dataset includes query-content pairs in two distinct scenarios: with and without a copyright notice. For the former, we extensively cover four types of copyright notices to account for different cases. Our evaluation reveals that even state-of-the-art closed-source LVLMs exhibit significant deficiencies in recognizing and respecting the copyrighted content, even when presented with the copyright notice. To solve this limitation, we introduce a novel tool-augmented defense framework for copyright compliance, which reduces infringement risks in all scenarios. Our findings underscore the importance of developing copyright-aware LVLMs to ensure the responsible and lawful use of copyrighted content.
zh
[NLP-12] meBill: Time-Budgeted Inference for Large Language Models AAAI2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在时间敏感系统中推理效率与响应性能难以平衡的问题,尤其是在需要严格遵守时间预算的场景下,如机器人控制、自动驾驶和工业自动化等。现有基于固定键值缓存(Key-Value Cache, KV Cache)淘汰比例的高效推理方法无法适应不同任务的时间约束,导致推理不完整或性能下降。解决方案的关键在于提出TimeBill框架,其核心创新包括:1)设计细粒度的响应长度预测器(Response Length Predictor, RLP)和执行时间估计器(Execution Time Estimator, ETE),以精确预测端到端推理耗时;2)基于预测时间和给定时间预算动态调整KV缓存淘汰比例,从而实现推理效率与响应质量的自适应权衡。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21859
作者: Qi Fan,An Zou,Yehan Ma
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Accepted to AAAI 2026
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in time-critical systems, such as robotics, autonomous driving, embodied intelligence, and industrial automation, where generating accurate responses within a given time budget is crucial for decision-making, control, or safety-critical tasks. However, the auto-regressive generation process of LLMs makes it challenging to model and estimate the end-to-end execution time. Furthermore, existing efficient inference methods based on a fixed key-value (KV) cache eviction ratio struggle to adapt to varying tasks with diverse time budgets, where an improper eviction ratio may lead to incomplete inference or a drop in response performance. In this paper, we propose TimeBill, a novel time-budgeted inference framework for LLMs that balances the inference efficiency and response performance. To be more specific, we propose a fine-grained response length predictor (RLP) and an execution time estimator (ETE) to accurately predict the end-to-end execution time of LLMs. Following this, we develop a time-budgeted efficient inference approach that adaptively adjusts the KV cache eviction ratio based on execution time prediction and the given time budget. Finally, through extensive experiments, we demonstrate the advantages of TimeBill in improving task completion rate and maintaining response performance under various overrun strategies.
zh
[NLP-13] HeartBench: Probing Core Dimensions of Anthropomorphic Intelligence in LLM s
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在中文语境下缺乏对情感、文化与伦理等人类社会属性的综合理解能力的问题,即“拟人智能”(anthropomorphic intelligence)的不足。其解决方案的关键在于提出HeartBench框架,该框架基于真实心理咨询场景并结合临床专家知识,构建了一个理论驱动的五维分类体系及15项具体能力指标,并采用“先推理后评分”的评分协议,将抽象的人类特质转化为可量化评估的标准,从而为中文LLMs提供系统化、高精度的拟人智能评测方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21849
作者: Jiaxin Liu,Peiyi Tu,Wenyu Chen,Yihong Zhuang,Xinxia Ling,Anji Zhou,Chenxi Wang,Zhuo Han,Zhengkai Yang,Junbo Zhao,Zenan Huang,Yuanyuan Wang
机构: Ant Group; Xiamen University (厦门大学); Beijing Normal University (北京师范大学); Zhejiang University (浙江大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 10 pages
Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable success in cognitive and reasoning benchmarks, they exhibit a persistent deficit in anthropomorphic intelligence-the capacity to navigate complex social, emotional, and ethical nuances. This gap is particularly acute in the Chinese linguistic and cultural context, where a lack of specialized evaluation frameworks and high-quality socio-emotional data impedes progress. To address these limitations, we present HeartBench, a framework designed to evaluate the integrated emotional, cultural, and ethical dimensions of Chinese LLMs. Grounded in authentic psychological counseling scenarios and developed in collaboration with clinical experts, the benchmark is structured around a theory-driven taxonomy comprising five primary dimensions and 15 secondary capabilities. We implement a case-specific, rubric-based methodology that translates abstract human-like traits into granular, measurable criteria through a reasoning-before-scoring'' evaluation protocol. Our assessment of 13 state-of-the-art LLMs indicates a substantial performance ceiling: even leading models achieve only 60% of the expert-defined ideal score. Furthermore, analysis using a difficulty-stratified Hard Set’’ reveals a significant performance decay in scenarios involving subtle emotional subtexts and complex ethical trade-offs. HeartBench establishes a standardized metric for anthropomorphic AI evaluation and provides a methodological blueprint for constructing high-quality, human-aligned training data.
zh
[NLP-14] AlignAR: Generative Sentence Alignment for Arabic-English Parallel Corpora of Legal and Literary Texts
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决阿拉伯语-英语平行语料库稀缺且现有数据集多为简单一对一映射、难以充分评估句子对齐方法的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一种生成式句子对齐方法(AlignAR),并构建了一个包含复杂法律与文学文本的新阿拉伯语-英语数据集,其中通过减少一对一映射来创建更具挑战性的“Hard”子集,从而更有效地揭示传统对齐方法的局限性;同时,基于大语言模型(LLM)的方法在该数据集上表现出更强的鲁棒性,F1分数达到85.5%,较之前方法提升9%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21842
作者: Baorong Huang,Ali Asiri
机构: Huaihua University (怀化学院); Umm al-Qura University (乌姆库拉大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:High-quality parallel corpora are essential for Machine Translation (MT) research and translation teaching. However, Arabic-English resources remain scarce and existing datasets mainly consist of simple one-to-one mappings. In this paper, we present AlignAR, a generative sentence alignment method, and a new Arabic-English dataset comprising complex legal and literary texts. Our evaluation demonstrates that “Easy” datasets lack the discriminatory power to fully assess alignment methods. By reducing one-to-one mappings in our “Hard” subset, we exposed the limitations of traditional alignment methods. In contrast, LLM-based approaches demonstrated superior robustness, achieving an overall F1-score of 85.5%, a 9% improvement over previous methods. Our datasets and codes are open-sourced at this https URL.
zh
[NLP-15] Knowledge Reasoning of Large Language Models Integrating Graph-Structured Information for Pest and Disease Control in Tobacco
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决烟草病虫害防控领域中知识推理的准确性与深度不足的问题,尤其在复杂多跳(multi-hop)和对比推理场景下表现有限。解决方案的关键在于构建一个融合图结构信息的大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)框架,通过引入领域特定的知识图谱(Knowledge Graph, KG)增强知识检索与推理能力:首先利用LLM辅助构建包含病害、症状、防治方法等实体及其关系的结构化知识图谱;随后采用图神经网络(Graph Neural Network, GNN)学习节点的表达以捕捉局部与全局关系信息,并将检索到的图结构知识注入Transformer架构的核心推理模型中;最终基于ChatGLM模型并使用LoRA(Low-Rank Adaptation)技术实现参数高效的微调,显著提升了模型在复杂推理任务中的性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21837
作者: Siyu Li,Chenwei Song,Wan Zhou,Xinyi Liu
机构: Chongqing Jiaotong University (重庆交通大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:This paper proposes a large language model (LLM) approach that integrates graph-structured information for knowledge reasoning in tobacco pest and disease control. Built upon the GraphRAG framework, the proposed method enhances knowledge retrieval and reasoning by explicitly incorporating structured information from a domain-specific knowledge graph. Specifically, LLMs are first leveraged to assist in the construction of a tobacco pest and disease knowledge graph, which organizes key entities such as diseases, symptoms, control methods, and their relationships. Based on this graph, relevant knowledge is retrieved and integrated into the reasoning process to support accurate answer generation. The Transformer architecture is adopted as the core inference model, while a graph neural network (GNN) is employed to learn expressive node representations that capture both local and global relational information within the knowledge graph. A ChatGLM-based model serves as the backbone LLM and is fine-tuned using LoRA to achieve parameter-efficient adaptation. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach consistently outperforms baseline methods across multiple evaluation metrics, significantly improving both the accuracy and depth of reasoning, particularly in complex multi-hop and comparative reasoning scenarios.
zh
[NLP-16] Method Decoration (DeMe): A Framework for LLM -Driven Adaptive Method Generation in Dynamic IoT Environments
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决智能物联网(Intelligent IoT)系统在面对未见过的情境时,难以系统性生成新任务执行方法的问题,同时克服现有方法依赖固定设备逻辑、缺乏环境适应性的局限。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种通用框架——方法装饰(Method Decoration, DeMe),该框架通过从隐含目标、累积的学习方法和环境反馈中提取显式装饰(decorations),动态修改大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的方法生成路径,实现预装饰、后装饰、中间步骤修改及步骤插入等结构重组,从而生成具有情境感知性、安全对齐性和环境自适应性的任务执行方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21817
作者: Hong Su
机构: Chengdu University of Information Technology (成都信息工程大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Intelligent IoT systems increasingly rely on large language models (LLMs) to generate task-execution methods for dynamic environments. However, existing approaches lack the ability to systematically produce new methods when facing previously unseen situations, and they often depend on fixed, device-specific logic that cannot adapt to changing environmental this http URL this paper, we propose Method Decoration (DeMe), a general framework that modifies the method-generation path of an LLM using explicit decorations derived from hidden goals, accumulated learned methods, and environmental feedback. Unlike traditional rule augmentation, decorations in DeMe are not hardcoded; instead, they are extracted from universal behavioral principles, experience, and observed environmental differences. DeMe enables the agent to reshuffle the structure of its method path-through pre-decoration, post-decoration, intermediate-step modification, and step insertion-thereby producing context-aware, safety-aligned, and environment-adaptive methods. Experimental results show that method decoration allows IoT devices to derive ore appropriate methods when confronting unknown or faulty operating conditions.
zh
[NLP-17] On The Conceptualization and Societal Impact of Cross-Cultural Bias
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing, NLP)中文化偏见的识别与评估问题,尤其关注当前研究往往忽视真实使用者这一关键利益相关者群体,从而导致对语言技术跨文化偏差的社会影响评估流于表面。其解决方案的关键在于系统性地分析2025年发表的20篇相关文献,提炼出一套可操作的观察框架,帮助NLP研究人员更具体地概念化偏见,并有效评估其潜在危害,进而推动对语言技术社会影响的稳健评估。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21809
作者: Vitthal Bhandari
机构: University of Washington (华盛顿大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computers and Society (cs.CY)
备注: Term paper for LING 575 (Societal Impacts of Language Technologies)
Abstract:Research has shown that while large language models (LLMs) can generate their responses based on cultural context, they are not perfect and tend to generalize across cultures. However, when evaluating the cultural bias of a language technology on any dataset, researchers may choose not to engage with stakeholders actually using that technology in real life, which evades the very fundamental problem they set out to address. Inspired by the work done by arXiv:2005.14050v2, I set out to analyse recent literature about identifying and evaluating cultural bias in Natural Language Processing (NLP). I picked out 20 papers published in 2025 about cultural bias and came up with a set of observations to allow NLP researchers in the future to conceptualize bias concretely and evaluate its harms effectively. My aim is to advocate for a robust assessment of the societal impact of language technologies exhibiting cross-cultural bias. Comments: Term paper for LING 575 (Societal Impacts of Language Technologies) Subjects: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Computers and Society (cs.CY) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21809 [cs.CL] (or arXiv:2512.21809v1 [cs.CL] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21809 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[NLP-18] Five Years of SciCap: What We Learned and Future Directions for Scientific Figure Captioning AAAI
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决科学文献中图表说明(figure caption)生成质量低的问题,其核心挑战在于如何利用自然语言处理技术自动为学术图表生成准确、语义丰富且符合科研规范的描述。解决方案的关键在于构建一个大规模、高质量的arXiv论文图表-说明对数据集,并通过领域特定训练(domain-specific training)提升模型在科学语境下的表现,同时结合人工与自动评估机制持续优化生成效果。这一方法借鉴了如SciBERT等预训练语言模型的成功经验,并借助多机构协作与年度竞赛推动社区发展,从而系统性地推进科学图表示例生成的研究进展。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21789
作者: Ting-Hao K.Huang,Ryan A. Rossi,Sungchul Kim,Tong Yu,Ting-Yao E. Hsu,Ho Yin(Sam)Ng,C. Lee Giles
机构: University of Pennsylvania (宾夕法尼亚大学); University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (伊利诺伊大学厄巴纳-香槟分校)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注: Accepted to the 5th Annual AAAI Workshop on AI to Accelerate Science and Engineering (AI2ASE 2026)
Abstract:Between 2021 and 2025, the SciCap project grew from a small seed-funded idea at The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State) into one of the central efforts shaping the scientific figure-captioning landscape. Supported by a Penn State seed grant, Adobe, and the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, what began as our attempt to test whether domain-specific training, which was successful in text models like SciBERT, could also work for figure captions expanded into a multi-institution collaboration. Over these five years, we curated, released, and continually updated a large collection of figure-caption pairs from arXiv papers, conducted extensive automatic and human evaluations on both generated and author-written captions, navigated the rapid rise of large language models (LLMs), launched annual challenges, and built interactive systems that help scientists write better captions. In this piece, we look back at the first five years of SciCap and summarize the key technical and methodological lessons we learned. We then outline five major unsolved challenges and propose directions for the next phase of research in scientific figure captioning.
zh
[NLP-19] Ara-HOPE: Human-Centric Post-Editing Evaluation for Dialectal Arabic to Modern Standard Arabic Translation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决方言阿拉伯语到现代标准阿拉伯语(DA-MSA)翻译中自动评估指标和通用人工评估框架难以捕捉方言特异性错误的问题,从而阻碍了机器翻译(MT)质量的准确评估与改进。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种以人类为中心的后编辑评估框架——Ara-HOPE,该框架包含一个五类错误分类体系和基于决策树的标注协议,能够系统性识别并量化不同MT系统在方言术语处理和语义保持方面的性能差异,从而为提升方言感知型MT系统提供可操作的改进方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21787
作者: Abdullah Alabdullah,Lifeng Han,Chenghua Lin
机构: University of Edinburgh (爱丁堡大学); Leids Uni. Medisch Centrum (莱顿大学医学中心); LIACS (莱顿大学计算机科学研究所); University of Manchester (曼彻斯特大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Dialectal Arabic to Modern Standard Arabic (DA-MSA) translation is a challenging task in Machine Translation (MT) due to significant lexical, syntactic, and semantic divergences between Arabic dialects and MSA. Existing automatic evaluation metrics and general-purpose human evaluation frameworks struggle to capture dialect-specific MT errors, hindering progress in translation assessment. This paper introduces Ara-HOPE, a human-centric post-editing evaluation framework designed to systematically address these challenges. The framework includes a five-category error taxonomy and a decision-tree annotation protocol. Through comparative evaluation of three MT systems (Arabic-centric Jais, general-purpose GPT-3.5, and baseline NLLB-200), Ara-HOPE effectively highlights systematic performance differences between these systems. The results show that dialect-specific terminology and semantic preservation remain the most persistent challenges in DA-MSA translation. Ara-HOPE establishes a new framework for evaluating Dialectal Arabic MT quality and provides actionable guidance for improving dialect-aware MT systems.
zh
[NLP-20] An Information Theoretic Perspective on Agent ic System Design
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决当前基于代理语言模型(Agentic language model, LM)系统设计中缺乏理论指导的问题,尤其是压缩器(compressor)与预测器(predictor)之间的配置如何影响下游任务性能的不确定性。现有方法多依赖于经验性的、任务特定的调参实验,效率低下且难以泛化。其解决方案的关键在于引入信息论视角,将压缩器视为一个有噪信道,并提出一种任务无关的互信息(mutual information)估计器来量化压缩质量。研究表明,该互信息指标能有效预测下游性能,且压缩器规模的扩展比预测器更具性价比——更大规模的压缩器不仅更准确、更高效(单位token传递更多信息),还能显著降低API成本(如在Deep Research系统中,使用3B参数本地压缩器即可达到前沿大模型99%的精度,仅需26%的API费用)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21720
作者: Shizhe He,Avanika Narayan,Ishan S. Khare,Scott W. Linderman,Christopher Ré,Dan Biderman
机构: Stanford University (斯坦福大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Information Theory (cs.IT)
备注:
Abstract:Agentic language model (LM) systems power modern applications like “Deep Research” and “Claude Code,” and leverage multi-LM architectures to overcome context limitations. Beneath their apparent diversity lies a recurring pattern: smaller “compressor” LMs (that can even run locally) distill raw context into compact text that is then consumed by larger “predictor” LMs. Despite their popularity, the design of compressor-predictor systems remains largely ad hoc, with little guidance on how compressor and predictor choices shape downstream performance. In practice, attributing gains to compression versus prediction requires costly, task-specific pairwise sweeps. We argue that these agentic system design questions are, at root, information-theoretic. Viewing the compressor LM as a noisy channel, we introduce a simple estimator of mutual information between the context and its compression to quantify compression quality in a task-independent way. We show that mutual information strongly predicts downstream performance, independent of any specific task. Through an information-theoretic framework, we perform a comprehensive empirical analysis across five datasets and three model families. Results reveal that larger compressors not only are more accurate, but also more token-efficient, conveying more bits of information per token. A 7B Qwen-2.5 compressor, for instance, is 1.6\times more accurate, 4.6\times more concise, and conveys 5.5\times more bits of mutual information per token than its 1.5B sibling. Across datasets, scaling compressors is substantially more effective than scaling predictors, enabling larger on-device compressors to pair with smaller cloud predictors. Applied to a Deep Research system, these principles enable local compressors as small as 3B parameters to recover 99% of frontier-LM accuracy at 26% of API costs.
zh
[NLP-21] CATCH: A Controllable Theme Detection Framework with Contextualized Clustering and Hierarchical Generation
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决用户中心对话系统中的主题检测(Theme Detection)问题,即在不依赖预定义标签空间的情况下,准确识别每条语句的潜在主题,并确保跨对话的一致性与个性化用户偏好对齐。现有方法在处理短文本和稀疏语句时难以获得高质量的主题表示,且无法有效捕捉用户层面的主题偏好。解决方案的关键在于提出CATCH框架,其核心创新包括:(1) 上下文感知的主题表示,通过利用邻近话题片段增强话语级语义;(2) 基于偏好的主题聚类机制,联合建模语义相似性和个性化反馈以实现跨对话主题对齐;(3) 分层主题生成机制,通过抑制噪声提升主题标签的鲁棒性和连贯性。实验证明,该方法在DSTC-12多领域客户对话数据集上表现出优越的主题聚类与生成质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21715
作者: Rui Ke,Jiahui Xu,Shenghao Yang,Kuang Wang,Feng Jiang,Haizhou Li
机构: 1. Nanyang Technological University (南洋理工大学); 2. Tsinghua University (清华大学); 3. Singapore Management University (新加坡管理大学); 4. National University of Singapore (新加坡国立大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Theme detection is a fundamental task in user-centric dialogue systems, aiming to identify the latent topic of each utterance without relying on predefined schemas. Unlike intent induction, which operates within fixed label spaces, theme detection requires cross-dialogue consistency and alignment with personalized user preferences, posing significant challenges. Existing methods often struggle with sparse, short utterances for accurate topic representation and fail to capture user-level thematic preferences across dialogues. To address these challenges, we propose CATCH (Controllable Theme Detection with Contextualized Clustering and Hierarchical Generation), a unified framework that integrates three core components: (1) context-aware topic representation, which enriches utterance-level semantics using surrounding topic segments; (2) preference-guided topic clustering, which jointly models semantic proximity and personalized feedback to align themes across dialogue; and (3) a hierarchical theme generation mechanism designed to suppress noise and produce robust, coherent topic labels. Experiments on a multi-domain customer dialogue benchmark (DSTC-12) demonstrate the effectiveness of CATCH with 8B LLM in both theme clustering and topic generation quality.
zh
[NLP-22] Do Latent Tokens Think? A Causal and Adversarial Analysis of Chain-of-Continuous-Thought
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI(Generative AI)中潜空间标记(latent tokens)在大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)推理能力提升中的可靠性问题,即这些标记是否真正编码了可解释的推理过程,而非仅作为表面合理的“伪推理”机制。其解决方案的关键在于通过两类互补实验:一是引导实验(steering experiments),对比潜空间标记(如COCONUT)与显式思维链(Chain-of-Thought, CoT)对特定token子集的扰动敏感性,发现COCONUT标记对引导不敏感且缺乏关键推理信息;二是捷径实验(shortcut experiments),在有偏和分布外设置下评估模型表现,结果表明COCONUT在MMLU和HotpotQA数据集上持续利用数据集特征而未体现真实推理能力。由此揭示COCONUT本质上是一种伪推理机制,其生成的推理轨迹掩盖了对捷径的依赖,而非忠实反映推理过程。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21711
作者: Yuyi Zhang,Boyu Tang,Tianjie Ju,Sufeng Duan,Gongshen Liu
机构: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 13 pages, 5 figures
Abstract:Latent tokens are gaining attention for enhancing reasoning in large language models (LLMs), yet their internal mechanisms remain unclear. This paper examines the problem from a reliability perspective, uncovering fundamental weaknesses: latent tokens function as uninterpretable placeholders rather than encoding faithful reasoning. While resistant to perturbation, they promote shortcut usage over genuine reasoning. We focus on Chain-of-Continuous-Thought (COCONUT), which claims better efficiency and stability than explicit Chain-of-Thought (CoT) while maintaining performance. We investigate this through two complementary approaches. First, steering experiments perturb specific token subsets, namely COCONUT and explicit CoT. Unlike CoT tokens, COCONUT tokens show minimal sensitivity to steering and lack reasoning-critical information. Second, shortcut experiments evaluate models under biased and out-of-distribution settings. Results on MMLU and HotpotQA demonstrate that COCONUT consistently exploits dataset artifacts, inflating benchmark performance without true reasoning. These findings reposition COCONUT as a pseudo-reasoning mechanism: it generates plausible traces that conceal shortcut dependence rather than faithfully representing reasoning processes.
zh
[NLP-23] Detecting AI-Generated Paraphrases in Bengali: A Comparative Study of Zero-Shot and Fine-Tuned Transformers
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决生成式 AI (Generative AI) 生成文本在孟加拉语(Bengali)中的检测问题,以应对虚假信息和内容操纵等潜在滥用风险。当前针对多语言文本的检测研究已较为丰富,但孟加拉语因其词汇丰富性和语法复杂性,仍缺乏有效的检测方法。解决方案的关键在于采用五种基于 Transformer 的预训练模型进行零样本评估与微调实验,结果表明:零样本条件下所有模型性能接近随机水平(约50%准确率),而经过任务特定微调后,XLM-RoBERTa、mDeBERTa 和 MultilingualBERT 在准确率和 F1 分数上均达到约91%,显著优于其他模型,尤其是 IndicBERT 表现出较弱的适应能力,凸显了模型选择与细调策略对提升检测性能的重要性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21709
作者: Md. Rakibul Islam,Most. Sharmin Sultana Samu,Md. Zahid Hossain,Farhad Uz Zaman,Md. Kamrozzaman Bhuiyan
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted for publication in 2025 28th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT)
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) can produce text that closely resembles human writing. This capability raises concerns about misuse, including disinformation and content manipulation. Detecting AI-generated text is essential to maintain authenticity and prevent malicious applications. Existing research has addressed detection in multiple languages, but the Bengali language remains largely unexplored. Bengali’s rich vocabulary and complex structure make distinguishing human-written and AI-generated text particularly challenging. This study investigates five transformer-based models: XLMRoBERTa-Large, mDeBERTaV3-Base, BanglaBERT-Base, IndicBERT-Base and MultilingualBERT-Base. Zero-shot evaluation shows that all models perform near chance levels (around 50% accuracy) and highlight the need for task-specific fine-tuning. Fine-tuning significantly improves performance, with XLM-RoBERTa, mDeBERTa and MultilingualBERT achieving around 91% on both accuracy and F1-score. IndicBERT demonstrates comparatively weaker performance, indicating limited effectiveness in fine-tuning for this task. This work advances AI-generated text detection in Bengali and establishes a foundation for building robust systems to counter AI-generated content.
zh
[NLP-24] MoRAg ent: Parameter Efficient Agent Tuning with Mixture-of-Roles ICML2025
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在智能体(agent)任务中参数高效微调(Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning, PEFT)方法研究不足的问题。其核心解决方案是提出一种基于角色分工的混合角色框架(Mixture-of-Roles, MoR),将 agent 任务所需的复杂能力解耦为三个独立角色:推理器(reasoner)、执行器(executor)和总结器(summarizer),并为每个角色配置专用的低秩适配层(Low-Rank Adaptation, LoRA)模块,通过协同交互实现任务完成。该方法显著提升了微调效率与任务表现,并辅以角色特异性数据生成与验证机制,实验证明其在多种 LLM 和 agent 基准上的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21708
作者: Jing Han,Binwei Yan,Tianyu Guo,Zheyuan Bai,Mengyu Zheng,Hanting Chen,Ying Nie
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Accepted by ICML 2025
Abstract:Despite recent advancements of fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) to facilitate agent tasks, parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methodologies for agent remain largely unexplored. In this paper, we introduce three key strategies for PEFT in agent tasks: 1) Inspired by the increasingly dominant Reason+Action paradigm, we first decompose the capabilities necessary for the agent tasks into three distinct roles: reasoner, executor, and summarizer. The reasoner is responsible for comprehending the user’s query and determining the next role based on the execution trajectory. The executor is tasked with identifying the appropriate functions and parameters to invoke. The summarizer conveys the distilled information from conversations back to the user. 2) We then propose the Mixture-of-Roles (MoR) framework, which comprises three specialized Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) groups, each designated to fulfill a distinct role. By focusing on their respective specialized capabilities and engaging in collaborative interactions, these LoRAs collectively accomplish the agent task. 3) To effectively fine-tune the framework, we develop a multi-role data generation pipeline based on publicly available datasets, incorporating role-specific content completion and reliability verification. We conduct extensive experiments and thorough ablation studies on various LLMs and agent benchmarks, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed method. This project is publicly available at this https URL.
zh
[NLP-25] Enabling Conversational Behavior Reasoning Capabilities in Full-Duplex Speech
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决全双工(full-duplex)交互系统中自然对话建模的问题,核心挑战在于捕捉人类对话中隐含的因果性思维链(chain of thoughts),该链条表现为时序化的言语行为(speech acts)。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于思维图(Graph-of-Thoughts, GoT)的因果推理框架,通过分层标注策略建模从高阶交际意图到低阶言语行为的因果与时间依赖关系,并利用混合语料库(包含可控事件丰富的仿真数据和人类标注的推理依据)进行训练。GoT将流式预测结构化为动态演化的图结构,使多模态Transformer能够预测下一言语行为、生成决策解释并持续优化推理过程,从而实现对对话行为的鲁棒检测、可解释的推理链构建及全双工语音对话系统中对话推理能力的基准测试。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21706
作者: Shuchang Pan,Siddharth Banerjee,Dhruv Hebbar,Siddhant Patel,Akshaj Gupta,Kan Jen Cheng,Hanjo Kim,Zeyi Austin Li,Martin Q. Ma,Tingle Li,Gopala Anumanchipalli,Jiachen Lian
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); University of California, Berkeley (加州大学伯克利分校); Carnegie Mellon University (卡内基梅隆大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Human conversation is organized by an implicit chain of thoughts that manifests as timed speech acts. Capturing this causal pathway is key to building natural full-duplex interactive systems. We introduce a framework that enables reasoning over conversational behaviors by modeling this process as causal inference within a Graph-of-Thoughts (GoT). Our approach formalizes the intent-to-action pathway with a hierarchical labeling scheme, predicting high-level communicative intents and low-level speech acts to learn their causal and temporal dependencies. To train this system, we develop a hybrid corpus that pairs controllable, event-rich simulations with human-annotated rationales and real conversational speech. The GoT framework structures streaming predictions as an evolving graph, enabling a multimodal transformer to forecast the next speech act, generate concise justifications for its decisions, and dynamically refine its reasoning. Experiments on both synthetic and real duplex dialogues show that the framework delivers robust behavior detection, produces interpretable reasoning chains, and establishes a foundation for benchmarking conversational reasoning in full duplex spoken dialogue systems.
zh
[NLP-26] Semantic Codebooks as Effective Priors for Neural Speech Compression
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决传统语音编解码器(speech codec)在压缩效率和下游识别任务性能之间的权衡问题:传统方法侧重于波形保真度,导致比特分配冗余,未能充分利用语音中的语言结构信息,从而造成压缩效率低下且不利于语音识别等下游任务。其解决方案的关键在于提出SemDAC,一种语义感知的神经音频编解码器,通过引入语义码本(semantic codebook)作为先验知识来优化压缩过程——具体而言,采用残差向量量化(residual vector quantization, RVQ)结构中首个量化器从HuBERT特征蒸馏出捕捉音素内容的语义标记(semantic tokens),后续量化器建模剩余声学细节,并由FiLM条件解码器根据语义标记重建音频,从而显著提升声学码本利用效率。实验表明,SemDAC在感知指标上优于DAC,在Whisper语音识别任务中WER更低,且比特率大幅降低(如0.95 kbps vs. 2.5 kbps)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21653
作者: Liuyang Bai,Weiyi Lu,Li Guo
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Speech codecs are traditionally optimized for waveform fidelity, allocating bits to preserve acoustic detail even when much of it can be inferred from linguistic structure. This leads to inefficient compression and suboptimal performance on downstream recognition tasks. We propose SemDAC, a semantic-aware neural audio codec that leverages semantic codebooks as effective priors for speech compression. In SemDAC, the first quantizer in a residual vector quantization (RVQ) stack is distilled from HuBERT features to produce semantic tokens that capture phonetic content, while subsequent quantizers model residual acoustics. A FiLM-conditioned decoder reconstructs audio conditioned on the semantic tokens, improving efficiency in the use of acoustic codebooks. Despite its simplicity, this design proves highly effective: SemDAC outperforms DAC across perceptual metrics and achieves lower WER when running Whisper on reconstructed speech, all while operating at substantially lower bitrates (e.g., 0.95 kbps vs. 2.5 kbps for DAC). These results demonstrate that semantic codebooks provide an effective inductive bias for neural speech compression, producing compact yet recognition-friendly representations.
zh
[NLP-27] Heaven-Sent or Hell-Bent? Benchmarking the Intelligence and Defectiveness of LLM Hallucinations KDD2026
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)中幻觉(Hallucination)现象的评估难题,尤其是现有方法过度关注事实一致性而忽视了部分幻觉可能蕴含的创造性价值。传统检测手段难以在多样化的科学任务中平衡创造力与准确性,导致对幻觉的量化分析不足。其解决方案的关键在于提出HIC-Bench评估框架,该框架首次将幻觉系统性区分为智能型幻觉(Intelligent Hallucination, IH)与缺陷型幻觉(Defective Hallucination, DH),并通过多维指标矩阵(融合Torrance创造性思维测试TTCT中的原创性、可行性、价值维度与科学合理性、事实偏离度等幻觉特异性维度)、跨领域适用性(覆盖十大学科的开放式创新任务)以及动态提示优化(Dynamic Hallucination Prompt, DHP)实现对二者交互关系的精细化建模。实验表明IH与DH之间存在非线性关联,揭示了通过合理引导可同时提升LLM的创造力与可靠性,为探索生成式AI(Generative AI)的创造性智能提供了新范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21635
作者: Chengxu Yang,Jingling Yuan,Siqi Cai,Jiawei Jiang,Chuang Hu
机构: Wuhan University of Technology (武汉理工大学); Hubei Key Laboratory of Transportation Internet of Things (湖北省交通物联网重点实验室); BreathingCORE (呼吸核心); China; Wuhan University (武汉大学); University of Macau (澳门大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Published as a conference paper at KDD 2026
Abstract:Hallucinations in large language models (LLMs) are commonly regarded as errors to be minimized. However, recent perspectives suggest that some hallucinations may encode creative or epistemically valuable content, a dimension that remains underquantified in current literature. Existing hallucination detection methods primarily focus on factual consistency, struggling to handle heterogeneous scientific tasks and balance creativity with accuracy. To address these challenges, we propose HIC-Bench, a novel evaluation framework that categorizes hallucinations into Intelligent Hallucinations (IH) and Defective Hallucinations (DH), enabling systematic investigation of their interplay in LLM creativity. HIC-Bench features three core characteristics: (1) Structured IH/DH Assessment. using a multi-dimensional metric matrix integrating Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking (TTCT) metrics (Originality, Feasibility, Value) with hallucination-specific dimensions (scientific plausibility, factual deviation); (2) Cross-Domain Applicability. spanning ten scientific domains with open-ended innovation tasks; and (3) Dynamic Prompt Optimization. leveraging the Dynamic Hallucination Prompt (DHP) to guide models toward creative and reliable outputs. The evaluation process employs multiple LLM judges, averaging scores to mitigate bias, with human annotators verifying IH/DH classifications. Experimental results reveal a nonlinear relationship between IH and DH, demonstrating that creativity and correctness can be jointly optimized. These insights position IH as a catalyst for creativity and reveal the ability of LLM hallucinations to drive scientific this http URL, the HIC-Bench offers a valuable platform for advancing research into the creative intelligence of LLM hallucinations.
zh
[NLP-28] Rethinking Sample Polarity in Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大规模推理模型(Large Reasoning Models, LRMs)在基于可验证奖励的强化学习(Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Reward, RLVR)训练过程中,正负样本极性对策略优化动态影响不明确的问题。现有方法未充分挖掘正样本(增强已有正确推理模式)与负样本(促进探索新推理路径)在训练中的差异化作用,导致优势信号分配不够精准。解决方案的关键在于提出一种自适应且不对称的token级优势值调整方法——A3PO(Adaptive and Asymmetric token-level Advantage shaping for Policy Optimization),该方法能够根据样本极性差异,在样本层面和token层面精细化调整优势信号,从而更有效地引导策略更新,提升模型在多个推理基准上的性能表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21625
作者: Xinyu Tang,Yuliang Zhan,Zhixun Li,Wayne Xin Zhao,Zhenduo Zhang,Zujie Wen,Zhiqiang Zhang,Jun Zhou
机构: Gaoling School of Artificial Intelligence, Renmin University of China (中国人民大学高瓴人工智能学院); The Chinese University of Hong Kong (香港中文大学); Ant Group (蚂蚁集团)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Large reasoning models (LRMs) are typically trained using reinforcement learning with verifiable reward (RLVR) to enhance their reasoning abilities. In this paradigm, policies are updated using both positive and negative self-generated rollouts, which correspond to distinct sample polarities. In this paper, we provide a systematic investigation into how these sample polarities affect RLVR training dynamics and behaviors. We find that positive samples sharpen existing correct reasoning patterns, while negative samples encourage exploration of new reasoning paths. We further explore how adjusting the advantage values of positive and negative samples at both the sample level and the token level affects RLVR training. Based on these insights, we propose an Adaptive and Asymmetric token-level Advantage shaping method for Policy Optimization, namely A3PO, that more precisely allocates advantage signals to key tokens across different polarities. Experiments across five reasoning benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach.
zh
[NLP-29] Gamayuns Path to Multilingual Mastery: Cost-Efficient Training of a 1.5B-Parameter LLM
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决资源受限环境下小规模非英语中心语言模型(non-English-centric large language models, LLMs)研究不足的问题,尤其关注俄语等低资源语言的性能瓶颈。解决方案的关键在于提出一种新颖的两阶段预训练策略:第一阶段采用平衡多语言训练以实现跨语言对齐,第二阶段通过高质量英文数据增强来迁移性能优势至其他语言,从而在有限训练预算下显著提升多语言能力,特别是在俄语相关任务上达到当前同规模模型的最优表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21580
作者: Alexander Podolskiy,Semen Molokov,Timofey Gerasin,Maksim Titov,Alexey Rukhovich,Artem Khrapov,Kirill Morozov,Evgeny Tetin,Constantine Korikov,Pavel Efimov,Polina Lazukova,Yuliya Skripkar,Nikita Okhotnikov,Irina Piontkovskaya,Meng Xiaojun,Zou Xueyi,Zhang Zhenhe
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:We present Gamayun, a 1.5B-parameter multilingual language model trained entirely from scratch on 2.5T tokens. Designed for efficiency and deployment in resource-constrained environments, Gamayun addresses the lack of research on small non-English-centric LLMs by adopting a novel two-stage pre-training strategy: balanced multilingual training for cross-lingual alignment, followed by high-quality English enrichment to transfer performance gains across languages. Our model supports 12 languages, with special focus on Russian. Despite a significantly smaller training budget than comparable models, Gamayun outperforms LLaMA3.2-1B (9T tokens) on all considered benchmarks, and surpasses Qwen2.5-1.5B (18T tokens) on a wide range of English and multilingual tasks. It matches or exceeds Qwen3 (36T tokens) on most tasks outside advanced STEM, achieving state-of-the-art results in Russian, including the MERA benchmark, among the models of comparable size (1-2B parameters).
zh
[NLP-30] A Unified Definition of Hallucination Or: Its the World Model Stupid
【速读】: 该论文试图解决大语言模型中长期存在的幻觉(Hallucination)问题,即模型生成与事实不符的信息。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个统一的幻觉定义:幻觉本质上是模型对内部世界模型(world modeling)的不准确建模,且这种不准确可被用户感知(如陈述与知识库矛盾的事实或生成与已知来源冲突的摘要)。作者指出,现有文献中多样化的幻觉定义实际上聚焦于这一核心定义的不同方面,区别在于参考的世界模型和知识冲突判定策略(如知识库 vs. 上下文内信息)。该统一视角有助于明确评估基准中的“真理源”,区分幻觉与规划或激励机制错误,并为比较不同基准和缓解技术提供共同语言。在此基础上,论文进一步提出构建基于合成但完全指定世界模型的基准测试体系,以系统性地压力测试并改进语言模型的世界建模能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21577
作者: Emmy Liu,Varun Gangal,Chelsea Zou,Xiaoqi Huang,Michael Yu,Alex Chang,Zhuofu Tao,Sachin Kumar,Steven Y. Feng
机构: Carnegie Mellon University (卡内基梅隆大学); Patronus AI; Stanford University (斯坦福大学); Independent Researcher; The Ohio State University (俄亥俄州立大学); DegenAI Labs
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
备注:
Abstract:Despite numerous attempts to solve the issue of hallucination since the inception of neural language models, it remains a problem in even frontier large language models today. Why is this the case? We walk through definitions of hallucination used in the literature from a historical perspective up to the current day, and fold them into a single definition of hallucination, wherein different prior definitions focus on different aspects of our definition. At its core, we argue that hallucination is simply inaccurate (internal) world modeling, in a form where it is observable to the user (e.g., stating a fact which contradicts a knowledge base, or producing a summary which contradicts a known source). By varying the reference world model as well as the knowledge conflict policy (e.g., knowledge base vs. in-context), we arrive at the different existing definitions of hallucination present in the literature. We argue that this unified view is useful because it forces evaluations to make clear their assumed “world” or source of truth, clarifies what should and should not be called hallucination (as opposed to planning or reward/incentive-related errors), and provides a common language to compare benchmarks and mitigation techniques. Building on this definition, we outline plans for a family of benchmarks in which hallucinations are defined as mismatches with synthetic but fully specified world models in different environments, and sketch out how these benchmarks can use such settings to stress-test and improve the world modeling components of language models. Subjects: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Machine Learning (stat.ML) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21577 [cs.CL] (or arXiv:2512.21577v1 [cs.CL] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21577 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[NLP-31] Beyond Heuristics: A Decision-Theoretic Framework for Agent Memory Management
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)中外部记忆(External Memory)管理依赖人工设计启发式规则的问题,这些问题在长期交互和不确定性情境下难以预测其后果。论文提出了一种基于决策理论的框架DAM(Decision-theoretic Agent Memory),其关键在于将记忆管理重构为一个在不确定环境下进行序贯决策的问题,通过价值函数和不确定性估计器对候选操作进行评估,从而基于估计的长期效用和风险制定决策策略,而非依赖静态启发式规则。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21567
作者: Changzhi Sun,Xiangyu Chen,Jixiang Luo,Dell Zhang,Xuelong Li
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:External memory is a key component of modern large language model (LLM) systems, enabling long-term interaction and personalization. Despite its importance, memory management is still largely driven by hand-designed heuristics, offering little insight into the long-term and uncertain consequences of memory decisions. In practice, choices about what to read or write shape future retrieval and downstream behavior in ways that are difficult to anticipate. We argue that memory management should be viewed as a sequential decision-making problem under uncertainty, where the utility of memory is delayed and dependent on future interactions. To this end, we propose DAM (Decision-theoretic Agent Memory), a decision-theoretic framework that decomposes memory management into immediate information access and hierarchical storage maintenance. Within this architecture, candidate operations are evaluated via value functions and uncertainty estimators, enabling an aggregate policy to arbitrate decisions based on estimated long-term utility and risk. Our contribution is not a new algorithm, but a principled reframing that clarifies the limitations of heuristic approaches and provides a foundation for future research on uncertainty-aware memory systems.
zh
[NLP-32] Human-AI Interaction Alignment: Designing Evaluating and Evolving Value-Centered AI For Reciprocal Human-AI Futures
【速读】: 该论文试图解决当前生成式 AI (Generative AI) 研究中过度依赖单向对齐(unidirectional alignment)模型的问题,即仅将AI系统调整以适应人类价值观,而忽视了人类自身在与AI交互过程中可能发生的认知、行为和价值体系的动态变化。解决方案的关键在于推动双向人-AI对齐(bidirectional human-AI alignment),这是一种动态、互惠的过程,强调人类与AI通过交互、评估和以价值为中心的设计共同适应与演化。该方法不仅要求AI系统能够响应并遵循人类价值观,还致力于赋能人类对AI系统的批判性参与和持续进化,从而构建更具责任性和协同性的未来人-AI协作范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21551
作者: Hua Shen,Tiffany Knearem,Divy Thakkar,Pat Pataranutaporn,Anoop Sinha,Yike(Cassandra)Shi,Jenny T. Liang,Lama Ahmad,Tanu Mitra,Brad A. Myers,Yang Li
机构: NYU Shanghai, New York University(纽约大学上海分校); MBZUAI(穆罕默德·本·扎耶德人工智能大学); Google(谷歌); Massachusetts Institute of Technology(麻省理工学院); Google, Paradigms of Intelligence(谷歌,智能范式); Carnegie Mellon University(卡内基梅隆大学); OpenAI(OpenAI); University of Washington(华盛顿大学); Google DeepMind(谷歌深度思维)
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: CHI 2026 BiAlign Workshop
Abstract:The rapid integration of generative AI into everyday life underscores the need to move beyond unidirectional alignment models that only adapt AI to human values. This workshop focuses on bidirectional human-AI alignment, a dynamic, reciprocal process where humans and AI co-adapt through interaction, evaluation, and value-centered design. Building on our past CHI 2025 BiAlign SIG and ICLR 2025 Workshop, this workshop will bring together interdisciplinary researchers from HCI, AI, social sciences and more domains to advance value-centered AI and reciprocal human-AI collaboration. We focus on embedding human and societal values into alignment research, emphasizing not only steering AI toward human values but also enabling humans to critically engage with and evolve alongside AI systems. Through talks, interdisciplinary discussions, and collaborative activities, participants will explore methods for interactive alignment, frameworks for societal impact evaluation, and strategies for alignment in dynamic contexts. This workshop aims to bridge the disciplines’ gaps and establish a shared agenda for responsible, reciprocal human-AI futures.
zh
[NLP-33] Perplexity-Aware Data Scaling Law: Perplexity Landscapes Predict Performance for Continual Pre-training
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决持续预训练(Continual Pre-training, CPT)中因单纯增加数据导致边际收益迅速衰减的问题,从而实现更高效的数据利用与模型性能提升。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于困惑度(perplexity)的新型数据缩放定律,通过预训练模型在领域数据上的困惑度作为知识差距的代理指标,量化候选训练样本的信息困惑度分布,并据此自适应地选择高价值数据子集,优先保留能最大化知识吸收且最小化冗余和噪声的内容,从而显著提升CPT阶段的数据利用效率与最终模型表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21515
作者: Lei Liu,Hao Zhu,Yue Shen,Zhixuan Chu,Jian Wang,Jinjie Gu,Kui Ren
机构: Ant Group; Zhejiang University (浙江大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注:
Abstract:Continual Pre-training (CPT) serves as a fundamental approach for adapting foundation models to domain-specific applications. Scaling laws for pre-training define a power-law relationship between dataset size and the test loss of an LLM. However, the marginal gains from simply increasing data for CPT diminish rapidly, yielding suboptimal data utilization and inefficient training. To address this challenge, we propose a novel perplexity-aware data scaling law to establish a predictive relationship between the perplexity landscape of domain-specific data and the test loss. Our approach leverages the perplexity derived from the pre-trained model on domain data as a proxy for estimating the knowledge gap, effectively quantifying the informational perplexity landscape of candidate training samples. By fitting this scaling law across diverse perplexity regimes, we enable adaptive selection of high-utility data subsets, prioritizing content that maximizes knowledge absorption while minimizing redundancy and noise. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method consistently identifies near-optimal training subsets and achieves superior performance on both medical and general-domain benchmarks.
zh
[NLP-34] MotionTeller: Multi-modal Integration of Wearable Time-Series with LLM s for Health and Behavioral Understanding
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决如何从原始生理信号(如通过加速度计采集的分钟级活动数据,即actigraphy)中自动生成自然语言摘要的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出MotionTeller框架,该框架将预训练的actigraphy编码器与一个轻量级投影模块相结合,将行为嵌入映射到冻结的解码器-only大语言模型(LLM)的token空间中,从而实现端到端的自由文本、自回归生成每日行为摘要。此设计无需对语言模型进行微调,仅通过语言token的交叉熵损失进行监督训练,即可实现高语义保真度(BERTScore-F1 = 0.924)和词汇准确性(ROUGE-1 = 0.722),显著优于基于提示(prompt-based)的基线方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21506
作者: Aiwei Zhang,Arvind Pillai,Andrew Campbell,Nicholas C. Jacobson
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注:
Abstract:As wearable sensing becomes increasingly pervasive, a key challenge remains: how can we generate natural language summaries from raw physiological signals such as actigraphy - minute-level movement data collected via accelerometers? In this work, we introduce MotionTeller, a generative framework that natively integrates minute-level wearable activity data with large language models (LLMs). MotionTeller combines a pretrained actigraphy encoder with a lightweight projection module that maps behavioral embeddings into the token space of a frozen decoder-only LLM, enabling free-text, autoregressive generation of daily behavioral summaries. We construct a novel dataset of 54383 (actigraphy, text) pairs derived from real-world NHANES recordings, and train the model using cross-entropy loss with supervision only on the language tokens. MotionTeller achieves high semantic fidelity (BERTScore-F1 = 0.924) and lexical accuracy (ROUGE-1 = 0.722), outperforming prompt-based baselines by 7 percent in ROUGE-1. The average training loss converges to 0.38 by epoch 15, indicating stable optimization. Qualitative analysis confirms that MotionTeller captures circadian structure and behavioral transitions, while PCA plots reveal enhanced cluster alignment in embedding space post-training. Together, these results position MotionTeller as a scalable, interpretable system for transforming wearable sensor data into fluent, human-centered descriptions, introducing new pathways for behavioral monitoring, clinical review, and personalized health interventions.
zh
[NLP-35] Oogiri-Master: Benchmarking Humor Understanding via Oogiri
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在幽默理解方面的评估难题,具体聚焦于回答“什么因素使人类认为某个回应有趣”这一核心问题。此前研究受限于数据集规模小、候选回复数量少、评分过程中存在流行度信号干扰以及缺乏客观可比的幽默度指标。为应对这些问题,作者提出了Oogiri-Master基准和Oogiri-Corpus数据集:前者提供标准化评测框架,后者包含每个提示约100个多样化候选回复,并由约100名独立人类评委无偏见评分,从而显著降低流行度偏差并实现稳健的聚合。关键创新在于构建了高质量、大规模、去偏的人类幽默评分数据集,并基于此量化分析文本长度、模糊性、不一致化解析等语言特征与幽默感的相关性,进而建立可预测人类判断的客观指标,为LLMs的幽默理解能力提供了可重复、可比较的评估基础。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21494
作者: Soichiro Murakami,Hidetaka Kamigaito,Hiroya Takamura,Manabu Okumura
机构: 未知
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Humor is a salient testbed for human-like creative thinking in large language models (LLMs). We study humor using the Japanese creative response game Oogiri, in which participants produce witty responses to a given prompt, and ask the following research question: What makes such responses funny to humans? Previous work has offered only limited reliable means to answer this question. Existing datasets contain few candidate responses per prompt, expose popularity signals during ratings, and lack objective and comparable metrics for funniness. Thus, we introduce Oogiri-Master and Oogiri-Corpus, which are a benchmark and dataset designed to enable rigorous evaluation of humor understanding in LLMs. Each prompt is paired with approximately 100 diverse candidate responses, and funniness is rated independently by approximately 100 human judges without access to others’ ratings, reducing popularity bias and enabling robust aggregation. Using Oogiri-Corpus, we conduct a quantitative analysis of the linguistic factors associated with funniness, such as text length, ambiguity, and incongruity resolution, and derive objective metrics for predicting human judgments. Subsequently, we benchmark a range of LLMs and human baselines in Oogiri-Master, demonstrating that state-of-the-art models approach human performance and that insight-augmented prompting improves the model performance. Our results provide a principled basis for evaluating and advancing humor understanding in LLMs.
zh
[NLP-36] Morality is Contextual: Learning Interpretable Moral Contexts from Human Data with Probabilistic Clustering and Large Language Models
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决道德判断中情境依赖性建模的问题,即如何准确捕捉情境因素对模糊行为可接受性的影响。现有方法(如端到端大语言模型提示)难以解释为何某些行为在特定情境下被接受或拒绝,且与人类判断的一致性较低。其解决方案的关键在于提出COMETH框架:首先构建一个基于实证数据集的六类核心道德行为(如“不杀人”、“不欺骗”等)情境库,并通过LLM过滤和MiniLM嵌入聚类实现动作标准化;其次利用人类道德评价分布在线学习每个动作特异的情境簇,结合信息论中的分歧准则确保情境划分的合理性;最后通过一个可解释的泛化模块提取非评价性的二值情境特征并学习其权重,从而提升预测准确性(相较端到端LLM提升约30%至60%)并揭示驱动判断的关键情境因素。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21439
作者: Geoffroy Morlat,Marceau Nahon,Augustin Chartouny,Raja Chatila,Ismael T. Freire,Mehdi Khamassi
机构: Institute of Intelligent Systems and Robotics (智能系统与机器人研究所); Sorbonne University (索邦大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 11 pages, 5 figures, +24 pages of Appendix
Abstract:Moral actions are judged not only by their outcomes but by the context in which they occur. We present COMETH (Contextual Organization of Moral Evaluation from Textual Human inputs), a framework that integrates a probabilistic context learner with LLM-based semantic abstraction and human moral evaluations to model how context shapes the acceptability of ambiguous actions. We curate an empirically grounded dataset of 300 scenarios across six core actions (violating Do not kill, Do not deceive, and Do not break the law) and collect ternary judgments (Blame/Neutral/Support) from N=101 participants. A preprocessing pipeline standardizes actions via an LLM filter and MiniLM embeddings with K-means, producing robust, reproducible core-action clusters. COMETH then learns action-specific moral contexts by clustering scenarios online from human judgment distributions using principled divergence criteria. To generalize and explain predictions, a Generalization module extracts concise, non-evaluative binary contextual features and learns feature weights in a transparent likelihood-based model. Empirically, COMETH roughly doubles alignment with majority human judgments relative to end-to-end LLM prompting (approx. 60% vs. approx. 30% on average), while revealing which contextual features drive its predictions. The contributions are: (i) an empirically grounded moral-context dataset, (ii) a reproducible pipeline combining human judgments with model-based context learning and LLM semantics, and (iii) an interpretable alternative to end-to-end LLMs for context-sensitive moral prediction and explanation.
zh
[NLP-37] aching People LLM s Errors and Getting it Right
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决用户对大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的过度依赖问题,尤其是当LLM在简单任务(如基础算术)上出现错误时,用户仍可能误判其可靠性。现有方法试图通过聚类实例嵌入并识别失败模式来缓解此问题,但效果有限。论文的关键发现是:失败模式确实存在,且可通过元标签(meta-label)分组识别出误差率高且规模可观的子集;然而,当前基于提示(prompting)和嵌入的方法未能有效暴露这些已知失败模式,导致教学效果不佳。因此,解决方案的关键在于改进自动化失败发现机制,并引入更贴近实际应用的评估指标——即衡量用户能否利用所教失败模式准确预判LLM的错误场景,而非仅关注人机协作的整体准确性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21422
作者: Nathan Stringham,Fateme Hashemi Chaleshtori,Xinyuan Yan,Zhichao Xu,Bei Wang,Ana Marasović
机构: University of Utah (犹他大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:People use large language models (LLMs) when they should not. This is partly because they see LLMs compose poems and answer intricate questions, so they understandably, but incorrectly, assume LLMs won’t stumble on basic tasks like simple arithmetic. Prior work has tried to address this by clustering instance embeddings into regions where an LLM is likely to fail and automatically describing patterns in these regions. The found failure patterns are taught to users to mitigate their overreliance. Yet, this approach has not fully succeeded. In this analysis paper, we aim to understand why. We first examine whether the negative result stems from the absence of failure patterns. We group instances in two datasets by their meta-labels and evaluate an LLM’s predictions on these groups. We then define criteria to flag groups that are sizable and where the LLM is error-prone, and find meta-label groups that meet these criteria. Their meta-labels are the LLM’s failure patterns that could be taught to users, so they do exist. We next test whether prompting and embedding-based approaches can surface these known failures. Without this, users cannot be taught about them to reduce their overreliance. We find mixed results across methods, which could explain the negative result. Finally, we revisit the final metric that measures teaching effectiveness. We propose to assess a user’s ability to effectively use the given failure patterns to anticipate when an LLM is error-prone. A user study shows a positive effect from teaching with this metric, unlike the human-AI team accuracy. Our findings show that teaching failure patterns could be a viable approach to mitigating overreliance, but success depends on better automated failure-discovery methods and using metrics like ours. Subjects: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21422 [cs.CL] (or arXiv:2512.21422v1 [cs.CL] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21422 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite
zh
[NLP-38] Query Carefully: Detecting the Unanswerables in Text-to-SQL Tasks
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决文本到SQL(Text-to-SQL)系统在生物医学场景中因生成可执行但错误的SQL语句而带来的隐性风险,尤其是在面对模糊、超出模式范围或无法回答的问题时,模型可能输出看似合理但实际上不正确的SQL查询,从而误导用户。解决方案的关键在于提出一个名为Query Carefully的流水线,其核心包括:基于大语言模型(LLM)的SQL生成机制、显式的无答案检测规则(No-Answer Rules, NAR)、以及结合可回答与不可回答样本的少样本提示策略,同时设计了一个轻量级用户界面以透明展示中间SQL、执行结果及拒绝回答(abstentions),从而提升系统的可靠性与可解释性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21345
作者: Jasmin Saxer(1),Isabella Maria Aigner(2),Luise Linzmeier(3),Andreas Weiler(1),Kurt Stockinger(1) ((1) Institute of Computer Science, Zurich University of Applied Sciences, Winterthur, Switzerland, (2) Institute of Medical Virology, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland, (3) Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University Hospital Zurich, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland)
机构: 未知
类目: Databases (cs.DB); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computation and Language (cs.CL)
备注: Accepted to the HC@AIxIA + HYDRA 2025
Abstract:Text-to-SQL systems allow non-SQL experts to interact with relational databases using natural language. However, their tendency to generate executable SQL for ambiguous, out-of-scope, or unanswerable queries introduces a hidden risk, as outputs may be misinterpreted as correct. This risk is especially serious in biomedical contexts, where precision is critical. We therefore present Query Carefully, a pipeline that integrates LLM-based SQL generation with explicit detection and handling of unanswerable inputs. Building on the OncoMX component of ScienceBenchmark, we construct OncoMX-NAQ (No-Answer Questions), a set of 80 no-answer questions spanning 8 categories (non-SQL, out-of-schema/domain, and multiple ambiguity types). Our approach employs llama3.3:70b with schema-aware prompts, explicit No-Answer Rules (NAR), and few-shot examples drawn from both answerable and unanswerable questions. We evaluate SQL exact match, result accuracy, and unanswerable-detection accuracy. On the OncoMX dev split, few-shot prompting with answerable examples increases result accuracy, and adding unanswerable examples does not degrade performance. On OncoMX-NAQ, balanced prompting achieves the highest unanswerable-detection accuracy (0.8), with near-perfect results for structurally defined categories (non-SQL, missing columns, out-of-domain) but persistent challenges for missing-value queries (0.5) and column ambiguity (0.3). A lightweight user interface surfaces interim SQL, execution results, and abstentions, supporting transparent and reliable text-to-SQL in biomedical applications.
zh
[NLP-39] From Questions to Clinical Recommendations: Large Language Models Driving Evidence-Based Clinical Decision Making
【速读】: 该论文旨在解决临床实践中将循证医学证据高效整合到实时决策中的难题,主要挑战包括繁重的工作负荷、复杂的专业流程以及时间限制。其解决方案的关键在于开发了一个名为Quicker的基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的循证临床决策支持系统,能够自动化完成从问题分解、文献检索、筛选到证据评估与推荐生成的全流程,并模拟标准临床指南制定过程。该系统通过端到端自动化链条和交互式界面实现定制化决策支持,在多项指标上表现优异,显著提升决策效率与质量,例如单个审阅者与Quicker协作可将推荐制定时间缩短至20–40分钟。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2505.10282
作者: Dubai Li,Nan Jiang,Kangping Huang,Ruiqi Tu,Shuyu Ouyang,Huayu Yu,Lin Qiao,Chen Yu,Tianshu Zhou,Danyang Tong,Qian Wang,Mengtao Li,Xiaofeng Zeng,Yu Tian,Xinping Tian,Jingsong Li
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学)
类目: Computation and Language (cs.CL); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Clinical evidence, derived from rigorous research and data analysis, provides healthcare professionals with reliable scientific foundations for informed decision-making. Integrating clinical evidence into real-time practice is challenging due to the enormous workload, complex professional processes, and time constraints. This highlights the need for tools that automate evidence synthesis to support more efficient and accurate decision making in clinical settings. This study introduces Quicker, an evidence-based clinical decision support system powered by large language models (LLMs), designed to automate evidence synthesis and generate clinical recommendations modeled after standard clinical guideline development processes. Quicker implements a fully automated chain that covers all phases, from questions to clinical recommendations, and further enables customized decision-making through integrated tools and interactive user interfaces. To evaluate Quicker’s capabilities, we developed the Q2CRBench-3 benchmark dataset, based on clinical guideline development records for three different diseases. Experimental results highlighted Quicker’s strong performance, with fine-grained question decomposition tailored to user preferences, retrieval sensitivities comparable to human experts, and literature screening performance approaching comprehensive inclusion of relevant studies. In addition, Quicker-assisted evidence assessment effectively supported human reviewers, while Quicker’s recommendations were more comprehensive and logically coherent than those of clinicians. In system-level testing, collaboration between a single reviewer and Quicker reduced the time required for recommendation development to 20-40 minutes. In general, our findings affirm the potential of Quicker to help physicians make quicker and more reliable evidence-based clinical decisions.
zh
计算机视觉
[CV-0] See Less See Right: Bi-directional Perceptual Shaping For Multimodal Reasoning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型视觉语言模型(Large Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在推理过程中对细粒度视觉证据(如图表中的多段线)依赖不足、跨领域泛化能力差以及推理时计算开销高的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出双向感知塑造(Bi-directional Perceptual Shaping, BiPS),通过引入两种KL散度约束机制:一是保持原图与仅保留问题相关区域的“证据保留视图”之间的一致性,促使模型覆盖支持答案的像素;二是使原图与掩码关键像素的“证据移除视图”之间产生分离,强制模型依赖细粒度视觉信息而非仅从文本中推断,从而避免文本捷径(text-only shortcuts)。该方法在八个基准测试上平均提升Qwen2.5-VL-7B性能8.2%,并展现出优异的跨域泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22120
作者: Shuoshuo Zhang,Yizhen Zhang,Jingjing Fu,Lei Song,Jiang Bian,Yujiu Yang,Rui Wang
机构: Microsoft Research (微软研究院); Tsinghua University (清华大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Large vision-language models (VLMs) often benefit from intermediate visual cues, either injected via external tools or generated as latent visual tokens during reasoning, but these mechanisms still overlook fine-grained visual evidence (e.g., polylines in charts), generalize poorly across domains, and incur high inference-time cost. In this paper, we propose Bi-directional Perceptual Shaping (BiPS), which transforms question-conditioned masked views into bidirectional where-to-look signals that shape perception during training. BiPS first applies a KL-consistency constraint between the original image and an evidence-preserving view that keeps only question-relevant regions, encouraging coarse but complete coverage of supporting pixels. It then applies a KL-separation constraint between the original and an evidence-ablated view where critical pixels are masked so the image no longer supports the original answer, discouraging text-only shortcuts (i.e., answering from text alone) and enforcing fine-grained visual reliance. Across eight benchmarks, BiPS boosts Qwen2.5-VL-7B by 8.2% on average and shows strong out-of-domain generalization to unseen datasets and image types.
zh
[CV-1] ProEdit: Inversion-based Editing From Prompts Done Right
【速读】:该论文旨在解决基于反演(inversion-based)的视觉编辑方法在编辑过程中过度依赖源图像信息,导致目标图像中关键属性(如姿态、数量或颜色)无法按指令准确修改的问题。其核心解决方案在于从注意力机制和潜在空间两个维度进行优化:在注意力层面引入KV-mix策略,通过混合源图像与目标图像在编辑区域的键值(Key-Value, KV)特征,在保持背景一致性的同时削弱源图像对编辑区域的影响;在潜在空间层面提出Latents-Shift方法,通过对源图像潜在表示的编辑区域进行扰动,消除反演潜在变量对采样过程的干扰。该设计具有即插即用特性,可无缝集成至现有反演与编辑框架(如RF-Solver、FireFlow和UniEdit),并在多个图像和视频编辑基准上实现最优性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22118
作者: Zhi Ouyang,Dian Zheng,Xiao-Ming Wu,Jian-Jian Jiang,Kun-Yu Lin,Jingke Meng,Wei-Shi Zheng
机构: Sun Yat-sen University (中山大学); CUHK MMLab (香港中文大学多媒体实验室); College of Computing and Data Science, Nanyang Technological University (南洋理工大学计算机与数据科学学院); The University of Hong Kong (香港大学); Key Laboratory of Machine Intelligence and Advanced Computing, Ministry of Education, China (教育部机器智能与先进计算重点实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Equal contributions from first two authors. Project page: this https URL Code: this https URL
Abstract:Inversion-based visual editing provides an effective and training-free way to edit an image or a video based on user instructions. Existing methods typically inject source image information during the sampling process to maintain editing consistency. However, this sampling strategy overly relies on source information, which negatively affects the edits in the target image (e.g., failing to change the subject’s atributes like pose, number, or color as instructed). In this work, we propose ProEdit to address this issue both in the attention and the latent aspects. In the attention aspect, we introduce KV-mix, which mixes KV features of the source and the target in the edited region, mitigating the influence of the source image on the editing region while maintaining background consistency. In the latent aspect, we propose Latents-Shift, which perturbs the edited region of the source latent, eliminating the influence of the inverted latent on the sampling. Extensive experiments on several image and video editing benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves SOTA performance. In addition, our design is plug-and-play, which can be seamlessly integrated into existing inversion and editing methods, such as RF-Solver, FireFlow and UniEdit.
zh
[CV-2] Learning Association via Track-Detection Matching for Multi-Object Tracking
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多目标跟踪(Multi-object Tracking, MOT)中如何高效且准确地维持目标身份识别的问题,尤其针对传统“检测后跟踪”(tracking-by-detection)方法依赖人工设计关联启发式规则、而端到端方法计算复杂度高的局限性。其核心解决方案是提出一种基于轨迹-检测链接预测(Track-Detection Link Prediction, TDLP)的新方法,该方法通过在每帧中对轨迹与检测框之间的连接关系进行预测,实现对每个轨迹的正确延续判断,从而直接从数据中学习关联策略,无需手工规则;同时,TDLP以几何特征(如边界框)为主设计架构,并可选融合姿态和外观等附加信息,在保持模块化和计算效率的同时显著提升性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22105
作者: Momir Adžemović
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 14 pages (+4 for references), 8 tables, 4 figures
Abstract:Multi-object tracking aims to maintain object identities over time by associating detections across video frames. Two dominant paradigms exist in literature: tracking-by-detection methods, which are computationally efficient but rely on handcrafted association heuristics, and end-to-end approaches, which learn association from data at the cost of higher computational complexity. We propose Track-Detection Link Prediction (TDLP), a tracking-by-detection method that performs per-frame association via link prediction between tracks and detections, i.e., by predicting the correct continuation of each track at every frame. TDLP is architecturally designed primarily for geometric features such as bounding boxes, while optionally incorporating additional cues, including pose and appearance. Unlike heuristic-based methods, TDLP learns association directly from data without handcrafted rules, while remaining modular and computationally efficient compared to end-to-end trackers. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks demonstrate that TDLP consistently surpasses state-of-the-art performance across both tracking-by-detection and end-to-end methods. Finally, we provide a detailed analysis comparing link prediction with metric learning-based association and show that link prediction is more effective, particularly when handling heterogeneous features such as detection bounding boxes. Our code is available at \hrefthis https URLthis https URL.
zh
[CV-3] Yume-1.5: A Text-Controlled Interactive World Generation Model
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前基于扩散模型生成交互式、可探索世界时面临的三大关键挑战:模型参数量过大、推理步骤冗长以及历史上下文快速增长导致的实时性能受限,且缺乏文本控制生成能力。其解决方案的核心在于提出一种名为\method的新框架,通过三个关键技术组件实现突破:(1)集成统一上下文压缩与线性注意力机制的长视频生成框架,有效降低计算复杂度;(2)基于双向注意力蒸馏和增强文本嵌入策略的实时流式加速方法,提升生成效率;(3)支持文本控制的世界事件生成机制,实现对生成内容的语义引导。该框架可在单张图像或文本提示下生成真实感强、连续且可键盘交互的虚拟世界,显著改善了现有方法在实时性和可控性方面的不足。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22096
作者: Xiaofeng Mao,Zhen Li,Chuanhao Li,Xiaojie Xu,Kaining Ying,Tong He,Jiangmiao Pang,Yu Qiao,Kaipeng Zhang
机构: Shanghai AI Laboratory (上海人工智能实验室); Fudan University (复旦大学); Shanghai Innovation Institute (上海创新研究院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Recent approaches have demonstrated the promise of using diffusion models to generate interactive and explorable worlds. However, most of these methods face critical challenges such as excessively large parameter sizes, reliance on lengthy inference steps, and rapidly growing historical context, which severely limit real-time performance and lack text-controlled generation capabilities. To address these challenges, we propose \method, a novel framework designed to generate realistic, interactive, and continuous worlds from a single image or text prompt. \method achieves this through a carefully designed framework that supports keyboard-based exploration of the generated worlds. The framework comprises three core components: (1) a long-video generation framework integrating unified context compression with linear attention; (2) a real-time streaming acceleration strategy powered by bidirectional attention distillation and an enhanced text embedding scheme; (3) a text-controlled method for generating world events. We have provided the codebase in the supplementary material.
zh
[CV-4] StreamAvatar: Streaming Diffusion Models for Real-Time Interactive Human Avatars
【速读】:该论文旨在解决实时流式交互式数字人(digital human)生成中的两大核心挑战:一是基于扩散模型(diffusion-based)的人像生成方法因非因果架构和高计算成本难以满足实时性需求;二是现有交互方案通常局限于头部与肩部区域,无法生成连贯的手势与身体动作。解决方案的关键在于提出一个两阶段自回归适配与加速框架,通过自回归蒸馏(autoregressive distillation)和对抗精炼(adversarial refinement)将高保真视频扩散模型转化为适用于实时交互的生成机制,并引入三个关键组件以保障长期稳定性与一致性:参考锚定位置重编码(Reference-Anchored Positional Re-encoding, RAPR)、参考池(Reference Sink)以及一致性感知判别器(Consistency-Aware Discriminator),从而实现单次输入即可驱动具备自然说话与倾听行为及协调手势的交互式数字人模型。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22065
作者: Zhiyao Sun,Ziqiao Peng,Yifeng Ma,Yi Chen,Zhengguang Zhou,Zixiang Zhou,Guozhen Zhang,Youliang Zhang,Yuan Zhou,Qinglin Lu,Yong-Jin Liu
机构: Tsinghua University (清华大学); Renmin University of China (中国人民大学); Tencent Hunyuan (腾讯混元); Nanjing University (南京大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注: Project page: this https URL
Abstract:Real-time, streaming interactive avatars represent a critical yet challenging goal in digital human research. Although diffusion-based human avatar generation methods achieve remarkable success, their non-causal architecture and high computational costs make them unsuitable for streaming. Moreover, existing interactive approaches are typically limited to head-and-shoulder region, limiting their ability to produce gestures and body motions. To address these challenges, we propose a two-stage autoregressive adaptation and acceleration framework that applies autoregressive distillation and adversarial refinement to adapt a high-fidelity human video diffusion model for real-time, interactive streaming. To ensure long-term stability and consistency, we introduce three key components: a Reference Sink, a Reference-Anchored Positional Re-encoding (RAPR) strategy, and a Consistency-Aware Discriminator. Building on this framework, we develop a one-shot, interactive, human avatar model capable of generating both natural talking and listening behaviors with coherent gestures. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing approaches in generation quality, real-time efficiency, and interaction naturalness. Project page: this https URL .
zh
[CV-5] MAI-UI Technical Report: Real-World Centric Foundation GUI Agents
【速读】:该论文旨在解决GUI代理(GUI Agent)在真实场景中部署的四大核心挑战:缺乏原生的代理-用户交互能力、仅依赖UI操作的局限性、缺少实用的部署架构,以及在动态环境中的脆弱性。解决方案的关键在于提出了一套统一的方法论:首先,构建一个自进化数据流水线,将导航数据扩展至包含用户交互和MCP工具调用;其次,设计原生设备-云协同系统,根据任务状态路由执行路径;最后,引入在线强化学习(Online RL)框架,并通过高级优化技术实现并行环境规模与上下文长度的有效扩展。该方案显著提升了GUI定位和移动端导航性能,在多个基准测试中达到新SOTA水平,同时优化了资源利用效率与隐私保护。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22047
作者: Hanzhang Zhou,Xu Zhang,Panrong Tong,Jianan Zhang,Liangyu Chen,Quyu Kong,Chenglin Cai,Chen Liu,Yue Wang,Jingren Zhou,Steven Hoi
机构: Tongyi Lab (通义实验室); Alibaba Group (阿里巴巴集团)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:The development of GUI agents could revolutionize the next generation of human-computer interaction. Motivated by this vision, we present MAI-UI, a family of foundation GUI agents spanning the full spectrum of sizes, including 2B, 8B, 32B, and 235B-A22B variants. We identify four key challenges to realistic deployment: the lack of native agent-user interaction, the limits of UI-only operation, the absence of a practical deployment architecture, and brittleness in dynamic environments. MAI-UI addresses these issues with a unified methodology: a self-evolving data pipeline that expands the navigation data to include user interaction and MCP tool calls, a native device-cloud collaboration system routes execution by task state, and an online RL framework with advanced optimizations to scale parallel environments and context length. MAI-UI establishes new state-of-the-art across GUI grounding and mobile navigation. On grounding benchmarks, it reaches 73.5% on ScreenSpot-Pro, 91.3% on MMBench GUI L2, 70.9% on OSWorld-G, and 49.2% on UI-Vision, surpassing Gemini-3-Pro and Seed1.8 on ScreenSpot-Pro. On mobile GUI navigation, it sets a new SOTA of 76.7% on AndroidWorld, surpassing UI-Tars-2, Gemini-2.5-Pro and Seed1.8. On MobileWorld, MAI-UI obtains 41.7% success rate, significantly outperforming end-to-end GUI models and competitive with Gemini-3-Pro based agentic frameworks. Our online RL experiments show significant gains from scaling parallel environments from 32 to 512 (+5.2 points) and increasing environment step budget from 15 to 50 (+4.3 points). Finally, the native device-cloud collaboration system improves on-device performance by 33%, reduces cloud model calls by over 40%, and preserves user privacy.
zh
[CV-6] Backdoor Attacks on Prompt-Driven Video Segmentation Foundation Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式视频分割基础模型(Prompt-driven Video Segmentation Foundation Models, VSFMs)在部署应用中面临的后门攻击威胁问题。研究发现,传统后门攻击方法(如BadNet)在VSFMs上几乎无效(攻击成功率ASR低于5%),原因在于模型编码器的梯度对干净样本与触发样本保持高度一致,且注意力机制仍聚焦于真实目标区域,导致编码器难以学习到与触发器相关的特征表示。为此,作者提出首个专为prompt-driven VSFMs设计的后门攻击框架BadVSFM,其核心创新在于采用两阶段策略:第一阶段通过引导图像编码器使触发帧映射到指定目标嵌入空间,同时保持干净帧与参考编码器对齐;第二阶段训练掩码解码器,使得不同提示类型下的触发帧-提示对均输出共享的目标掩码,而干净输出则贴近参考解码器。实验表明,BadVSFM在多种触发条件和提示类型下均能实现强且可控的后门效果,同时维持良好的干净分割性能,并揭示了当前VSFMs存在尚未被充分探索的安全漏洞。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22046
作者: Zongmin Zhang,Zhen Sun,Yifan Liao,Wenhan Dong,Xinlei He,Xingshuo Han,Shengmin Xu,Xinyi Huang
机构: Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou); Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics; Fujian Normal University; Jinan University
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Cryptography and Security (cs.CR)
备注:
Abstract:Prompt-driven Video Segmentation Foundation Models (VSFMs) such as SAM2 are increasingly deployed in applications like autonomous driving and digital pathology, raising concerns about backdoor threats. Surprisingly, we find that directly transferring classic backdoor attacks (e.g., BadNet) to VSFMs is almost ineffective, with ASR below 5%. To understand this, we study encoder gradients and attention maps and observe that conventional training keeps gradients for clean and triggered samples largely aligned, while attention still focuses on the true object, preventing the encoder from learning a distinct trigger-related representation. To address this challenge, we propose BadVSFM, the first backdoor framework tailored to prompt-driven VSFMs. BadVSFM uses a two-stage strategy: (1) steer the image encoder so triggered frames map to a designated target embedding while clean frames remain aligned with a clean reference encoder; (2) train the mask decoder so that, across prompt types, triggered frame-prompt pairs produce a shared target mask, while clean outputs stay close to a reference decoder. Extensive experiments on two datasets and five VSFMs show that BadVSFM achieves strong, controllable backdoor effects under diverse triggers and prompts while preserving clean segmentation quality. Ablations over losses, stages, targets, trigger settings, and poisoning rates demonstrate robustness to reasonable hyperparameter changes and confirm the necessity of the two-stage design. Finally, gradient-conflict analysis and attention visualizations show that BadVSFM separates triggered and clean representations and shifts attention to trigger regions, while four representative defenses remain largely ineffective, revealing an underexplored vulnerability in current VSFMs.
zh
[CV-7] Patch-Discontinuity Mining for Generalized Deepfake Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决深度伪造(deepfake)检测方法在跨域和跨篡改场景下泛化能力不足的问题。现有方法通常依赖手工设计的取证特征和复杂网络结构,在单一域内表现良好,但面对未见过的伪造模式时性能显著下降。解决方案的关键在于提出GenDF框架,其核心创新包括:基于深度伪造特性的表示学习以捕捉真实与虚假人脸图像间的判别性模式、特征空间重分布以缓解分布偏移问题,以及分类不变的特征增强策略,在不引入额外可训练参数的前提下提升模型泛化能力。该方法仅需0.28M可训练参数即实现跨域和跨篡改场景下的最优性能,验证了其高效性与有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22027
作者: Huanhuan Yuan,Yang Ping,Zhengqin Xu,Junyi Cao,Shuai Jia,Chao Ma
机构: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); Chinese Academy of Military Science (军事科学院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Our paper was accepted by the IEEE Transactions on Multimedia
Abstract:The rapid advancement of generative artificial intelligence has enabled the creation of highly realistic fake facial images, posing serious threats to personal privacy and the integrity of online information. Existing deepfake detection methods often rely on handcrafted forensic cues and complex architectures, achieving strong performance in intra-domain settings but suffering significant degradation when confronted with unseen forgery patterns. In this paper, we propose GenDF, a simple yet effective framework that transfers a powerful large-scale vision model to the deepfake detection task with a compact and neat network design. GenDF incorporates deepfake-specific representation learning to capture discriminative patterns between real and fake facial images, feature space redistribution to mitigate distribution mismatch, and a classification-invariant feature augmentation strategy to enhance generalization without introducing additional trainable parameters. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GenDF achieves state-of-the-art generalization performance in cross-domain and cross-manipulation settings while requiring only 0.28M trainable parameters, validating the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed framework.
zh
[CV-8] SketchPlay: Intuitive Creation of Physically Realistic VR Content with Gesture-Driven Sketching
【速读】:该论文旨在解决非专业用户在虚拟现实(VR)环境中创建物理上真实感内容时面临的高门槛问题,传统方法依赖复杂的建模工具或预定义的3D模型、纹理和动画,限制了创作的普及性。其解决方案的关键在于提出SketchPlay框架,通过将用户空中绘制的草图(sketches)与手势(gestures)相结合:草图用于捕捉物体和场景的结构及空间布局,手势则提供速度、方向和力等物理线索以定义动态行为;这种结构与动力学信息的融合使系统能够生成包括刚体运动、弹性变形和布料模拟在内的多种复杂物理现象,从而实现直观且富有表现力的内容创作体验。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22016
作者: Xiangwen Zhang,Xiaowei Dai,Runnan Chen,Xiaoming Chen,Zeke Zexi Hu
机构: Beijing Technology and Business University (北京工商大学); The University of Sydney (悉尼大学)
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Creating physically realistic content in VR often requires complex modeling tools or predefined 3D models, textures, and animations, which present significant barriers for non-expert users. In this paper, we propose SketchPlay, a novel VR interaction framework that transforms humans’ air-drawn sketches and gestures into dynamic, physically realistic scenes, making content creation intuitive and playful like drawing. Specifically, sketches capture the structure and spatial arrangement of objects and scenes, while gestures convey physical cues such as velocity, direction, and force that define movement and behavior. By combining these complementary forms of input, SketchPlay captures both the structure and dynamics of user-created content, enabling the generation of a wide range of complex physical phenomena, such as rigid body motion, elastic deformation, and cloth dynamics. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared to traditional text-driven methods, SketchPlay offers significant advantages in expressiveness, and user experience. By providing an intuitive and engaging creation process, SketchPlay lowers the entry barrier for non-expert users and shows strong potential for applications in education, art, and immersive storytelling.
zh
[CV-9] LongFly: Long-Horizon UAV Vision-and-Language Navigation with Spatiotemporal Context Integration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决长时程无人机视觉与语言导航(UAV VLN)中因环境复杂性导致的时空上下文建模困难问题,具体表现为信息密度高、视角变化快及动态结构多变,进而引发语义对齐不准和路径规划不稳定。其解决方案的关键在于提出LongFly框架,通过三个核心模块实现:1)基于槽位的历史图像压缩模块,将多视角历史观测动态提炼为固定长度的紧凑表征;2)时空轨迹编码模块,捕捉无人机轨迹的时间动态性和空间结构;3)提示引导的多模态融合模块,实现现有时空上下文与当前观测的深度融合,支持时间推理与鲁棒航点预测。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22010
作者: Wen Jiang,Li Wang,Kangyao Huang,Wei Fan,Jinyuan Liu,Shaoyu Liu,Hongwei Duan,Bin Xu,Xiangyang Ji
机构: Beijing Institute of Technology (北京理工大学); Tsinghua University (清华大学); Dalian University of Technology (大连理工大学); Xidian University (西安电子科技大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are crucial tools for post-disaster search and rescue, facing challenges such as high information density, rapid changes in viewpoint, and dynamic structures, especially in long-horizon navigation. However, current UAV vision-and-language navigation(VLN) methods struggle to model long-horizon spatiotemporal context in complex environments, resulting in inaccurate semantic alignment and unstable path planning. To this end, we propose LongFly, a spatiotemporal context modeling framework for long-horizon UAV VLN. LongFly proposes a history-aware spatiotemporal modeling strategy that transforms fragmented and redundant historical data into structured, compact, and expressive representations. First, we propose the slot-based historical image compression module, which dynamically distills multi-view historical observations into fixed-length contextual representations. Then, the spatiotemporal trajectory encoding module is introduced to capture the temporal dynamics and spatial structure of UAV trajectories. Finally, to integrate existing spatiotemporal context with current observations, we design the prompt-guided multimodal integration module to support time-based reasoning and robust waypoint prediction. Experimental results demonstrate that LongFly outperforms state-of-the-art UAV VLN baselines by 7.89% in success rate and 6.33% in success weighted by path length, consistently across both seen and unseen environments.
zh
[CV-10] SHIFT: Lightweight Slow-Fast GUI Agent with Adaptive Perception
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在图形用户界面(Graphical User Interface, GUI)代理任务中难以兼顾高效性与精确性的难题,尤其是在需要细粒度视觉定位的交互场景下表现不足的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出iSHIFT:一种基于隐式慢-快混合推理机制的轻量级代理架构,其核心创新是通过引入感知控制模块和可灵活调整的提示token,使模型能够在高精度的“慢模式”(依赖详细视觉锚定)与高效率的“快模式”(利用全局线索)之间动态切换,并借助特殊感知token引导注意力至关键屏幕区域,从而实现推理深度与视觉关注区域的自适应调控。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22009
作者: Sarthak Mehrotra,Sairam V C Rebbapragada,Mani Hemanth Reddy Bonthu,Vineeth N Balasubramanian
机构: Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay (印度理工学院,孟买); Indian Institute of Technology, Hyderabad (印度理工学院,海得拉巴)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) show strong potential for interpreting and interacting with complex, pixel-rich Graphical User Interface (GUI) environments. However, building agents that are both efficient for high-level tasks and precise for fine-grained interactions remains challenging. GUI agents must perform routine actions efficiently while also handling tasks that demand exact visual grounding, yet existing approaches struggle when accuracy depends on identifying specific interface elements. These MLLMs also remain large and cannot adapt their reasoning depth to the task at hand. In this work, we introduce iSHIFT: Implicit Slow-fast Hybrid Inference with Flexible Tokens, a lightweight agent that integrates latent thinking (implicit chain-of-thought) with a perception control module. iSHIFT enables an MLLM to switch between a slow mode, which leverages detailed visual grounding for high precision and a fast mode that uses global cues for efficiency. Special perception tokens guide attention to relevant screen regions, allowing the model to decide both how to reason and where to focus. Despite its compact 2.5B size, iSHIFT matches state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmark datasets.
zh
[CV-11] Look Closer! An Adversarial Parametric Editing Framework for Hallucination Mitigation in VLMs
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)中存在的持续性幻觉问题,即模型生成与视觉输入不符的输出。现有研究认为幻觉源于VLM对语言先验的过度依赖以及视觉特征整合不足,并提出启发式解码校准策略进行缓解,但这些非可训练方法优化潜力有限。本文提出一种对抗性参数编辑框架ALEA-Hallu,其核心在于采用“激活-定位-对抗编辑”(Activate-Locate-Edit Adversarially)范式:首先构建包含锚定于视觉特征的正样本和反映语言模型先验偏倚的负样本的激活数据集;接着通过分析响应对之间的差异隐藏状态识别易产生幻觉的参数簇;最后利用注入对抗调优前缀的提示进行微调,该前缀被优化以最大化对视觉信息的忽视,从而迫使模型优先依赖视觉证据而非固有参数偏置。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21999
作者: Jiayu Hu,Beibei Li,Jiangwei Xia,Yanjun Qin,Bing Ji,Zhongshi He
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have garnered increasing attention in the AI community due to their promising practical applications, they exhibit persistent hallucination issues, generating outputs misaligned with visual inputs. Recent studies attribute these hallucinations to VLMs’ over-reliance on linguistic priors and insufficient visual feature integration, proposing heuristic decoding calibration strategies to mitigate them. However, the non-trainable nature of these strategies inherently limits their optimization potential. To this end, we propose an adversarial parametric editing framework for Hallucination mitigation in VLMs, which follows an \textbfActivate-\textbfLocate-\textbfEdit \textbfAdversarially paradigm. Specifically, we first construct an activation dataset that comprises grounded responses (positive samples attentively anchored in visual features) and hallucinatory responses (negative samples reflecting LLM prior bias and internal knowledge artifacts). Next, we identify critical hallucination-prone parameter clusters by analyzing differential hidden states of response pairs. Then, these clusters are fine-tuned using prompts injected with adversarial tuned prefixes that are optimized to maximize visual neglect, thereby forcing the model to prioritize visual evidence over inherent parametric biases. Evaluations on both generative and discriminative VLM tasks demonstrate the significant effectiveness of ALEAHallu in alleviating hallucinations. Our code is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-12] LVLM-Aided Alignment of Task-Specific Vision Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决小规模任务特定视觉模型在高风险领域中因依赖伪相关性(spurious correlations)而导致的鲁棒性差的问题,这类模型虽计算资源消耗低且具备可解释性,但其决策逻辑常与人类领域知识不一致。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于大型视觉语言模型(Large Vision Language Model, LVLM)的视觉对齐方法(LVLM-Aided Visual Alignment, LVLM-VA),通过构建双向接口将模型行为映射为自然语言,并将人类提供的类别级规范转化为图像级批评,从而实现领域专家与模型之间的高效交互,显著提升模型行为与人类先验知识的一致性,同时减少对伪特征和群体特异性偏见的依赖。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21985
作者: Alexander Koebler,Lukas Kuhn,Ingo Thon,Florian Buettner
机构: 1. University of Tübingen (图宾根大学); 2. Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems (马克斯·普朗克智能系统研究所); 3. German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (德国神经退行性疾病中心)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:In high-stakes domains, small task-specific vision models are crucial due to their low computational requirements and the availability of numerous methods to explain their results. However, these explanations often reveal that the models do not align well with human domain knowledge, relying instead on spurious correlations. This might result in brittle behavior once deployed in the real-world. To address this issue, we introduce a novel and efficient method for aligning small task-specific vision models with human domain knowledge by leveraging the generalization capabilities of a Large Vision Language Model (LVLM). Our LVLM-Aided Visual Alignment (LVLM-VA) method provides a bidirectional interface that translates model behavior into natural language and maps human class-level specifications to image-level critiques, enabling effective interaction between domain experts and the model. Our method demonstrates substantial improvement in aligning model behavior with human specifications, as validated on both synthetic and real-world datasets. We show that it effectively reduces the model’s dependence on spurious features and on group-specific biases, without requiring fine-grained feedback.
zh
[CV-13] A Lightweight Multi-Scale Attention Framework for Real-Time Spinal Endoscopic Instance Segmentation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决脊柱内镜手术中实时实例分割(Real-time instance segmentation)的难题,其核心挑战包括视野狭窄、镜面反光、烟雾/出血干扰、边界模糊以及尺度变化剧烈等问题,同时受限于手术设备算力,模型需在准确性和速度之间取得平衡,并能在小批量(甚至单样本)训练下保持稳定性。解决方案的关键在于提出轻量级多尺度注意力框架LMSF-A,该框架在主干网络(backbone)、颈部(neck)和头部(head)三部分协同设计:主干采用C2f-Pro模块融合Re-parameterized Convolution(RVB)与高效多尺度注意力(EMA),实现多分支训练与推理时单路径加速;颈部引入Scale-Sequence Feature Fusion(SSFF)与Triple Feature Encoding(TFE)增强跨尺度一致性与高分辨率特征细节;头部采用轻量多任务共享头(LMSH),通过共享卷积和GroupNorm减少参数量并提升单样本训练稳定性。整体模型仅需1.8M参数和8.8 GFLOPs,在多个指标上优于或媲美现有方法,且具备良好的泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21984
作者: Qi Lai,JunYan Li,Qiang Cai,Lei Wang,Tao Yan,XiaoKun Liang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Real-time instance segmentation for spinal endoscopy is important for identifying and protecting critical anatomy during surgery, but it is difficult because of the narrow field of view, specular highlights, smoke/bleeding, unclear boundaries, and large scale changes. Deployment is also constrained by limited surgical hardware, so the model must balance accuracy and speed and remain stable under small-batch (even batch-1) training. We propose LMSF-A, a lightweight multi-scale attention framework co-designed across backbone, neck, and head. The backbone uses a C2f-Pro module that combines RepViT-style re-parameterized convolution (RVB) with efficient multi-scale attention (EMA), enabling multi-branch training while collapsing into a single fast path for inference. The neck improves cross-scale consistency and boundary detail using Scale-Sequence Feature Fusion (SSFF) and Triple Feature Encoding (TFE), which strengthens high-resolution features. The head adopts a Lightweight Multi-task Shared Head (LMSH) with shared convolutions and GroupNorm to reduce parameters and support batch-1 stability. We also release the clinically reviewed PELD dataset (61 patients, 610 images) with instance masks for adipose tissue, bone, ligamentum flavum, and nerve. Experiments show that LMSF-A is highly competitive (or even better than) in all evaluation metrics and much lighter than most instance segmentation methods requiring only 1.8M parameters and 8.8 GFLOPs, and it generalizes well to a public teeth benchmark. Code and dataset: this https URL.
zh
[CV-14] Perceive and Calibrate: Analyzing and Enhancing Robustness of Medical Multi-Modal Large Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学多模态大语言模型(Medical Multi-modal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在真实临床场景中对输入扰动(如影像伪影和文本错误)敏感的问题,这一问题严重限制了其临床应用的安全性与可靠性。现有研究多集中于通用领域文本模态的鲁棒性提升,且依赖昂贵的微调策略,难以应对医疗领域复杂的噪声模式并满足严格的医疗安全标准。论文的关键解决方案是提出一种无需训练的内在增强型多模态校准框架(Inherent-enhanced Multi-modal Calibration, IMC),基于“感知-校准”原则,利用MLLMs自身的去噪能力实现跨模态鲁棒性增强:视觉模态上设计了扰动感知去噪校准(Perturbation-aware Denoising Calibration, PDC),通过模型自身视觉编码器识别噪声并进行原型引导特征校准;文本模态上构建自实例化多智能体系统(Self-instantiated Multi-agent System, SMS),利用模型自评估能力,通过协作式智能体层级对噪声文本进行精炼。实验表明该方法在多模态噪声下达到当前最优性能,具备提升MLLMs在真实临床环境中鲁棒性的潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21964
作者: Dunyuan XU,Xikai Yang,Yaoqian Li,Juzheng Miao,Jinpeng Li,Pheng-Ann Heng
机构: The Chinese University of Hong Kong (香港中文大学); The Chinese University of Hong Kong (香港中文大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Medical Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown promising clinical performance. However, their sensitivity to real-world input perturbations, such as imaging artifacts and textual errors, critically undermines their clinical applicability. Systematic analysis of such noise impact on medical MLLMs remains largely unexplored. Furthermore, while several works have investigated the MLLMs’ robustness in general domains, they primarily focus on text modality and rely on costly fine-tuning. They are inadequate to address the complex noise patterns and fulfill the strict safety standards in medicine. To bridge this gap, this work systematically analyzes the impact of various perturbations on medical MLLMs across both visual and textual modalities. Building on our findings, we introduce a training-free Inherent-enhanced Multi-modal Calibration (IMC) framework that leverages MLLMs’ inherent denoising capabilities following the perceive-and-calibrate principle for cross-modal robustness enhancement. For the visual modality, we propose a Perturbation-aware Denoising Calibration (PDC) which leverages MLLMs’ own vision encoder to identify noise patterns and perform prototype-guided feature calibration. For text denoising, we design a Self-instantiated Multi-agent System (SMS) that exploits the MLLMs’ self-assessment capabilities to refine noisy text through a cooperative hierarchy of agents. We construct a benchmark containing 11 types of noise across both image and text modalities on 2 datasets. Experimental results demonstrate our method achieves the state-of-the-art performance across multiple modalities, showing potential to enhance MLLMs’ robustness in real clinical scenarios.
zh
[CV-15] Automated Discovery of Parsimonious Spectral Indices via Normalized Difference Polynomials
【速读】:该论文旨在解决植被分类中特征选择效率与可解释性不足的问题,特别是如何从多光谱遥感数据中自动提取紧凑且具有判别力的光谱指数(spectral indices)。其关键解决方案是构建一个结构化的候选特征空间:首先计算所有波段对的归一化差异(normalized difference),再通过二阶多项式扩展生成高维特征集(如Sentinel-2的10波段配置下产生1,080个候选特征),随后利用ANOVA过滤、递归特征消除和L₁正则化支持向量机(L₁-regularized SVM)等方法筛选出少量高精度指数。实验表明,仅需两个红边波段的归一化差异乘积即可达到96.26%准确率,进一步增加至八个指数后提升至97.70%,且所选特征均为低阶交互项,揭示了光谱相互作用在分类中的主导作用,同时确保结果具备良好的可部署性和解释性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21948
作者: Ali Lotfi,Adam Carter,Thuan Ha,Mohammad Meysami,Kwabena Nketia,Steve Shirtliffe
机构: Nutrien Centre for Sustainable and Digital Agriculture, Department of Plant Sciences, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada; Crop Development Centre, Department of Plant Sciences, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada; Department of Economics, Applied Statistics, and International Business, New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, NM, USA
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 23 pages, 5 figures, 6 tables
Abstract:We introduce an automated way to find compact spectral indices for vegetation classification. The idea is to take all pairwise normalized differences from the spectral bands and then build polynomial combinations up to a fixed degree, which gives a structured search space that still keeps the illumination invariance needed in remote sensing. For a sensor with n bands this produces \binomn2 base normalized differences, and the degree-2 polynomial expansion gives 1,080 candidate features for the 10-band Sentinel-2 configuration we use here. Feature selection methods (ANOVA filtering, recursive elimination, and L_1 -regularized SVM) then pick out small sets of indices that reach the desired accuracy, so the final models stay simple and easy to interpret. We test the framework on Kochia (\textitBassia scoparia) detection using Sentinel-2 imagery from Saskatchewan, Canada ( N = 2,318 samples, 2022–2024). A single degree-2 index, the product of two normalized differences from the red-edge bands, already reaches 96.26% accuracy, and using eight indices only raises this to 97.70%. In every case the chosen features are degree-2 products built from bands b_4 through b_8 , which suggests that the discriminative signal comes from spectral \emphinteractions rather than individual band ratios. Because the indices involve only simple arithmetic, they can be deployed directly in platforms like Google Earth Engine. The same approach works for other sensors and classification tasks, and an open-source implementation (\textttndindex) is available.
zh
[CV-16] Data relativistic uncertainty framework for low-illumination anime scenery image enhancement
【速读】:该论文旨在解决动漫场景图像在低光照条件下质量退化的问题,以弥合自然图像与动漫图像在低光增强任务中的领域差距(domain gap)。针对这一尚未充分探索的任务,作者首先构建了一个未配对的动漫场景图像数据集,涵盖多样环境和光照条件,缓解数据稀缺问题;其核心解决方案是提出一种基于不确定性信息的数据相对不确定性框架(Data Relativistic Uncertainty, DRU),受相对生成对抗网络(Relativistic GAN)启发,通过类比光的波粒二象性,可解释地定义并量化明暗样本的光照不确定性,并据此动态调整目标函数,从而在数据不确定性下重新校准模型学习过程。实验表明,基于DRU训练的EnlightenGAN版本在感知质量和美学表现上优于现有方法,展现出数据驱动学习的新范式潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21944
作者: Yiquan Gao,John See
机构: Heriot-Watt University (赫瑞-瓦特大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Multimedia (cs.MM)
备注: Preprint, awaiting submission to the appropriate conference or journal
Abstract:By contrast with the prevailing works of low-light enhancement in natural images and videos, this study copes with the low-illumination quality degradation in anime scenery images to bridge the domain gap. For such an underexplored enhancement task, we first curate images from various sources and construct an unpaired anime scenery dataset with diverse environments and illumination conditions to address the data scarcity. To exploit the power of uncertainty information inherent with the diverse illumination conditions, we propose a Data Relativistic Uncertainty (DRU) framework, motivated by the idea from Relativistic GAN. By analogy with the wave-particle duality of light, our framework interpretably defines and quantifies the illumination uncertainty of dark/bright samples, which is leveraged to dynamically adjust the objective functions to recalibrate the model learning under data uncertainty. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of DRU framework by training several versions of EnlightenGANs, yielding superior perceptual and aesthetic qualities beyond the state-of-the-art methods that are incapable of learning from data uncertainty perspective. We hope our framework can expose a novel paradigm of data-centric learning for potential visual and language domains. Code is available.
zh
[CV-17] Unsupervised Anomaly Detection in Brain MRI via Disentangled Anatomy Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决脑部磁共振成像(MRI)中病变检测的两个关键挑战:一是现有无监督学习方法在多模态和多中心MRI数据上泛化能力受限,因其依赖正常样本中的特定成像信息;二是异常残差从输入图像传播至重建的伪健康图像(PHI)中,限制了模型性能。解决方案的核心在于提出两种新型模块构成的新PHI重建框架:首先,通过解耦表示模块将MRI分解为成像信息与不变于成像条件的解剖结构信息,引入脑部解剖先验和可微分独热编码操作符以增强解耦稳定性;其次,设计边缘到图像恢复模块,利用解剖图像的高频边缘信息重建高质量PHI,从而减少异常像素输入并保留结构细节,有效抑制异常残差传播。该方法在9个公共数据集(4,443例来自多个中心的MRI)上优于17种SOTA方法,在平均精度(AP)和Dice相似系数(DSC)上分别提升+18.32%和+13.64%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21924
作者: Tao Yang,Xiuying Wang,Hao Liu,Guanzhong Gong,Lian-Ming Wu,Yu-Ping Wang,Lisheng Wang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted by Medical Image Analysis (2025)
Abstract:Detection of various lesions in brain MRI is clinically critical, but challenging due to the diversity of lesions and variability in imaging conditions. Current unsupervised learning methods detect anomalies mainly through reconstructing abnormal images into pseudo-healthy images (PHIs) by normal samples learning and then analyzing differences between images. However, these unsupervised models face two significant limitations: restricted generalizability to multi-modality and multi-center MRIs due to their reliance on the specific imaging information in normal training data, and constrained performance due to abnormal residuals propagated from input images to reconstructed PHIs. To address these limitations, two novel modules are proposed, forming a new PHI reconstruction framework. Firstly, the disentangled representation module is proposed to improve generalizability by decoupling brain MRI into imaging information and essential imaging-invariant anatomical images, ensuring that the reconstruction focuses on the anatomy. Specifically, brain anatomical priors and a differentiable one-hot encoding operator are introduced to constrain the disentanglement results and enhance the disentanglement stability. Secondly, the edge-to-image restoration module is designed to reconstruct high-quality PHIs by restoring the anatomical representation from the high-frequency edge information of anatomical images, and then recoupling the disentangled imaging information. This module not only suppresses abnormal residuals in PHI by reducing abnormal pixels input through edge-only input, but also effectively reconstructs normal regions using the preserved structural details in the edges. Evaluated on nine public datasets (4,443 patients’ MRIs from multiple centers), our method outperforms 17 SOTA methods, achieving absolute improvements of +18.32% in AP and +13.64% in DSC.
zh
[CV-18] AutoPP: Towards Automated Product Poster Generation and Optimization AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决产品海报(Product Poster)生成与优化过程中人工干预成本高、效率低的问题。传统方法依赖设计师手动创作并根据线上点击率(Click-Through Rate, CTR)反馈进行迭代,耗时且难以规模化。解决方案的关键在于提出AutoPP自动化流水线:首先通过统一设计模块将背景、文本和布局三个核心元素整合为结构化输出;再利用元素渲染模块将这些元素编码为条件令牌(condition tokens),实现可控且高效的海报生成;最后引入基于在线反馈的优化器,通过系统性替换元素并采用隔离直接偏好优化(Isolated Direct Preference Optimization, IDPO)精准归因CTR提升,从而实现端到端的自动优化。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21921
作者: Jiahao Fan,Yuxin Qin,Wei Feng,Yanyin Chen,Yaoyu Li,Ao Ma,Yixiu Li,Li Zhuang,Haoyi Bian,Zheng Zhang,Jingjing Lv,Junjie Shen,Ching Law
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Accepted to AAAI 2026
Abstract:Product posters blend striking visuals with informative text to highlight the product and capture customer attention. However, crafting appealing posters and manually optimizing them based on online performance is laborious and resource-consuming. To address this, we introduce AutoPP, an automated pipeline for product poster generation and optimization that eliminates the need for human intervention. Specifically, the generator, relying solely on basic product information, first uses a unified design module to integrate the three key elements of a poster (background, text, and layout) into a cohesive output. Then, an element rendering module encodes these elements into condition tokens, efficiently and controllably generating the product poster. Based on the generated poster, the optimizer enhances its Click-Through Rate (CTR) by leveraging online feedback. It systematically replaces elements to gather fine-grained CTR comparisons and utilizes Isolated Direct Preference Optimization (IDPO) to attribute CTR gains to isolated elements. Our work is supported by AutoPP1M, the largest dataset specifically designed for product poster generation and optimization, which contains one million high-quality posters and feedback collected from over one million users. Experiments demonstrate that AutoPP achieves state-of-the-art results in both offline and online settings. Our code and dataset are publicly available at: this https URL
zh
[CV-19] Patch as Node: Human-Centric Graph Representation Learning for Multimodal Action Recognition
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态动作识别中RGB图像与骨骼数据(skeleton data)因固有异质性导致的特征融合不充分问题,从而未能有效挖掘两者间的互补潜力。其核心解决方案是提出PAN(Person-centric Attention Network),首次构建以人体为中心的图表示学习框架,将包含人体关节信息的RGB图像块(token embeddings)建模为时空图结构,通过人本图建模抑制RGB帧中的冗余信息,并与基于骨骼的方法对齐,实现更高效且语义一致的多模态特征融合。关键创新在于引入注意力驱动的后校准机制(attention-based post calibration),降低对高质量骨骼数据的依赖,同时保持模型性能;并设计两种变体——PAN-Ensemble(双路径图卷积网络+晚期融合)和PAN-Unified(单网络统一图表示学习),分别在分离式与统一式多模态建模场景下达到当前最优(SOTA)性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21916
作者: Zeyu Liang,Hailun Xia,Naichuan Zheng
机构: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (北京邮电大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:While human action recognition has witnessed notable achievements, multimodal methods fusing RGB and skeleton modalities still suffer from their inherent heterogeneity and fail to fully exploit the complementary potential between them. In this paper, we propose PAN, the first human-centric graph representation learning framework for multimodal action recognition, in which token embeddings of RGB patches containing human joints are represented as spatiotemporal graphs. The human-centric graph modeling paradigm suppresses the redundancy in RGB frames and aligns well with skeleton-based methods, thus enabling a more effective and semantically coherent fusion of multimodal features. Since the sampling of token embeddings heavily relies on 2D skeletal data, we further propose attention-based post calibration to reduce the dependency on high-quality skeletal data at a minimal cost interms of model performance. To explore the potential of PAN in integrating with skeleton-based methods, we present two variants: PAN-Ensemble, which employs dual-path graph convolution networks followed by late fusion, and PAN-Unified, which performs unified graph representation learning within a single network. On three widely used multimodal action recognition datasets, both PAN-Ensemble and PAN-Unified achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in their respective settings of multimodal fusion: separate and unified modeling, respectively.
zh
[CV-20] High-Fidelity and Long-Duration Human Image Animation with Diffusion Transformer
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前扩散模型在人类图像动画生成中面临的两大核心问题:一是难以生成长时间跨度的视频,二是对人脸和手部等细粒度特征的合成能力不足,限制了其在高保真应用场景中的实用性。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于扩散Transformer(Diffusion Transformer, DiT)的框架,通过引入混合隐式引导信号与锐度引导因子来增强面部和手部细节的控制;设计时间感知的位置偏移融合模块(Position Shift Adaptive Module),实现任意长度视频的生成;同时采用新颖的数据增强策略和骨骼对齐模型以降低不同个体间身体形态差异的影响,从而显著提升生成视频的保真度与时序一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21905
作者: Shen Zheng,Jiaran Cai,Yuansheng Guan,Shenneng Huang,Xingpei Ma,Junjie Cao,Hanfeng Zhao,Qiang Zhang,Shunsi Zhang,Xiao-Ping Zhang
机构: Guangzhou Quwan Network Technology (广州趣丸网络科技); Tsinghua University (清华大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Recent progress in diffusion models has significantly advanced the field of human image animation. While existing methods can generate temporally consistent results for short or regular motions, significant challenges remain, particularly in generating long-duration videos. Furthermore, the synthesis of fine-grained facial and hand details remains under-explored, limiting the applicability of current approaches in real-world, high-quality applications. To address these limitations, we propose a diffusion transformer (DiT)-based framework which focuses on generating high-fidelity and long-duration human animation videos. First, we design a set of hybrid implicit guidance signals and a sharpness guidance factor, enabling our framework to additionally incorporate detailed facial and hand features as guidance. Next, we incorporate the time-aware position shift fusion module, modify the input format within the DiT backbone, and refer to this mechanism as the Position Shift Adaptive Module, which enables video generation of arbitrary length. Finally, we introduce a novel data augmentation strategy and a skeleton alignment model to reduce the impact of human shape variations across different identities. Experimental results demonstrate that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches, achieving superior performance in both high-fidelity and long-duration human image animation.
zh
[CV-21] CrownGen: Patient-customized Crown Generation via Point Diffusion Model
【速读】:该论文旨在解决修复牙科中冠(crown)设计过程高度依赖人工、效率低下的问题。其核心解决方案是提出CrownGen框架,该框架基于一种新颖的牙齿级点云表示,结合去噪扩散模型实现患者定制化冠设计自动化;关键创新在于引入边界预测模块以建立空间先验,并通过扩散生成模块在单次推理中合成多颗牙齿的高保真形态,从而显著提升几何精度并大幅减少主动设计时间。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21890
作者: Juyoung Bae,Moo Hyun Son,Jiale Peng,Wanting Qu,Wener Chen,Zelin Qiu,Kaixin Li,Xiaojuan Chen,Yifan Lin,Hao Chen
机构: The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (香港科技大学); The University of Hong Kong (香港大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Digital crown design remains a labor-intensive bottleneck in restorative dentistry. We present \textbfCrownGen, a generative framework that automates patient-customized crown design using a denoising diffusion model on a novel tooth-level point cloud representation. The system employs two core components: a boundary prediction module to establish spatial priors and a diffusion-based generative module to synthesize high-fidelity morphology for multiple teeth in a single inference pass. We validated CrownGen through a quantitative benchmark on 496 external scans and a clinical study of 26 restoration cases. Results demonstrate that CrownGen surpasses state-of-the-art models in geometric fidelity and significantly reduces active design time. Clinical assessments by trained dentists confirmed that CrownGen-assisted crowns are statistically non-inferior in quality to those produced by expert technicians using manual workflows. By automating complex prosthetic modeling, CrownGen offers a scalable solution to lower costs, shorten turnaround times, and enhance patient access to high-quality dental care.
zh
[CV-22] Reloc-VGGT: Visual Re-localization with Geometry Grounded Transformer
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统视觉定位(Visual Localization)方法中因采用后融合(late-fusion)策略导致的空间信息整合不足、在复杂环境中精度下降的问题。现有方法多将定位建模为成对姿态回归任务,通过估计图像间的相对位姿再进行平均得到绝对位姿,但这种方式难以有效利用多视角空间关系。其解决方案的关键在于提出首个基于早期融合(early-fusion)机制的视觉定位框架——Reloc-VGGT,该框架以VGGT骨干网络为基础编码多视图3D几何信息,并引入姿态标记器(pose tokenizer)与投影模块,更有效地挖掘来自多个数据库视图的空间关联性;同时设计了一种稀疏掩码注意力(sparse mask attention)策略,避免全局注意力带来的二次计算复杂度,从而实现大规模场景下的实时性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21883
作者: Tianchen Deng,Wenhua Wu,Kunzhen Wu,Guangming Wang,Siting Zhu,Shenghai Yuan,Xun Chen,Guole Shen,Zhe Liu,Hesheng Wang
机构: Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); Nanyang Technological University (南洋理工大学); Cambridge University (剑桥大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Visual localization has traditionally been formulated as a pair-wise pose regression problem. Existing approaches mainly estimate relative poses between two images and employ a late-fusion strategy to obtain absolute pose estimates. However, the late motion average is often insufficient for effectively integrating spatial information, and its accuracy degrades in complex environments. In this paper, we present the first visual localization framework that performs multi-view spatial integration through an early-fusion mechanism, enabling robust operation in both structured and unstructured environments. Our framework is built upon the VGGT backbone, which encodes multi-view 3D geometry, and we introduce a pose tokenizer and projection module to more effectively exploit spatial relationships from multiple database views. Furthermore, we propose a novel sparse mask attention strategy that reduces computational cost by avoiding the quadratic complexity of global attention, thereby enabling real-time performance at scale. Trained on approximately eight million posed image pairs, Reloc-VGGT demonstrates strong accuracy and remarkable generalization ability. Extensive experiments across diverse public datasets consistently validate the effectiveness and efficiency of our approach, delivering high-quality camera pose estimates in real time while maintaining robustness to unseen environments. Our code and models will be publicly released upon this http URL://github.com/dtc111111/Reloc-VGGT.
zh
[CV-23] SLIM-Brain: A Data- and Training-Efficient Foundation Model for fMRI Data Analysis
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前基于功能磁共振成像(fMRI)分析的基座模型(foundation model)在数据效率和训练效率上的双重瓶颈问题。现有方法中,基于图谱(atlas-based)的方法虽能降低维度但丢失空间细节且需大规模队列训练;而无图谱(atlas-free)方法虽保留 voxel 级别空间精度,却因内存与计算开销过大难以进行大规模预训练。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种两阶段自适应设计的 SLIM-Brain 模型:首先通过轻量级时序提取器捕获全局上下文并按显著性排序数据窗口,随后采用 4D 分层编码器(Hiera-JEPA)仅对 top-k 选定窗口学习细粒度 voxel 表征,并删除约 70% 的掩码补丁,从而显著提升数据与训练效率,在仅需 4000 次预训练会话及约 30% GPU 内存的情况下实现优于传统 voxel 级方法的性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21881
作者: Mo Wang,Junfeng Xia,Wenhao Ye,Enyu Liu,Kaining Peng,Jianfeng Feng,Quanying Liu,Hongkai Wen
机构: Southern University of Science and Technology (南方科技大学); University of Warwick (华威大学); Fudan University (复旦大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC)
备注: The code will be released after review
Abstract:Foundation models are emerging as a powerful paradigm for fMRI analysis, but current approaches face a dual bottleneck of data- and training-efficiency. Atlas-based methods aggregate voxel signals into fixed regions of interest, reducing data dimensionality but discarding fine-grained spatial details, and requiring extremely large cohorts to train effectively as general-purpose foundation models. Atlas-free methods, on the other hand, operate directly on voxel-level information - preserving spatial fidelity but are prohibitively memory- and compute-intensive, making large-scale pre-training infeasible. We introduce SLIM-Brain (Sample-efficient, Low-memory fMRI Foundation Model for Human Brain), a new atlas-free foundation model that simultaneously improves both data- and training-efficiency. SLIM-Brain adopts a two-stage adaptive design: (i) a lightweight temporal extractor captures global context across full sequences and ranks data windows by saliency, and (ii) a 4D hierarchical encoder (Hiera-JEPA) learns fine-grained voxel-level representations only from the top- k selected windows, while deleting about 70% masked patches. Extensive experiments across seven public benchmarks show that SLIM-Brain establishes new state-of-the-art performance on diverse tasks, while requiring only 4 thousand pre-training sessions and approximately 30% of GPU memory comparing to traditional voxel-level methods.
zh
[CV-24] DPAR: Dynamic Patchification for Efficient Autoregressive Visual Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决Decoder-only自回归图像生成模型中因固定长度标记化方案导致的计算与内存开销随图像分辨率呈二次增长的问题。其核心解决方案是提出DPAR(Dynamic Patch Aggregation for Autoregressive image generation),通过利用轻量级无监督自回归模型预测的下一标记熵作为信息含量指标,动态地将图像标记聚合成不同数量的补丁(patch),从而减少标记总数并优化计算资源分配。该方法仅对标准解码器架构进行最小改动,确保与多模态生成框架兼容,并在训练时自动聚焦于高信息区域,同时使模型具备对补丁边界不敏感的鲁棒性,支持推理阶段使用更大补丁尺寸,最终实现高达40%的训练FLOPs降低及FID指标提升27.1%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21867
作者: Divyansh Srivastava,Akshay Mehra,Pranav Maneriker,Debopam Sanyal,Vishnu Raj,Vijay Kamarshi,Fan Du,Joshua Kimball
机构: University of California, San Diego (加州大学圣地亚哥分校); Dolby Laboratories (杜比实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Decoder-only autoregressive image generation typically relies on fixed-length tokenization schemes whose token counts grow quadratically with resolution, substantially increasing the computational and memory demands of attention. We present DPAR, a novel decoder-only autoregressive model that dynamically aggregates image tokens into a variable number of patches for efficient image generation. Our work is the first to demonstrate that next-token prediction entropy from a lightweight and unsupervised autoregressive model provides a reliable criterion for merging tokens into larger patches based on information content. DPAR makes minimal modifications to the standard decoder architecture, ensuring compatibility with multimodal generation frameworks and allocating more compute to generation of high-information image regions. Further, we demonstrate that training with dynamically sized patches yields representations that are robust to patch boundaries, allowing DPAR to scale to larger patch sizes at inference. DPAR reduces token count by 1.81x and 2.06x on Imagenet 256 and 384 generation resolution respectively, leading to a reduction of up to 40% FLOPs in training costs. Further, our method exhibits faster convergence and improves FID by up to 27.1% relative to baseline models.
zh
[CV-25] EasyOmnimatte: Taming Pretrained Inpainting Diffusion Models for End-to-End Video Layered Decomposition
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有视频全景遮罩(video omnimatte)方法依赖缓慢的多阶段或推理时优化流程、未能充分利用生成式先验而导致分解效果不佳的问题。其核心解决方案是提出一种统一的端到端视频全景遮罩方法 EasyOmnimatte,关键创新在于对预训练视频修复扩散模型进行双专家微调:一个仅在特定 DiT(Diffusion Transformer)块上应用 LoRA 的 Effect Expert,用于捕捉前景及其相关效应的粗略结构;另一个是全模型 LoRA 微调的 Quality Expert,用于精细化 alpha 遮罩。在采样过程中,Effect Expert 在高噪声早期步骤主导去噪,Quality Expert 则在低噪声后期接管,从而避免两次完整扩散过程,显著降低计算成本且不牺牲输出质量。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21865
作者: Yihan Hu,Xuelin Chen,Xiaodong Cun
机构: GVC Lab, Great Bay University (大湾大学); Adobe Research (Adobe 研究院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Existing video omnimatte methods typically rely on slow, multi-stage, or inference-time optimization pipelines that fail to fully exploit powerful generative priors, producing suboptimal decompositions. Our key insight is that, if a video inpainting model can be finetuned to remove the foreground-associated effects, then it must be inherently capable of perceiving these effects, and hence can also be finetuned for the complementary task: foreground layer decomposition with associated effects. However, although naïvely finetuning the inpainting model with LoRA applied to all blocks can produce high-quality alpha mattes, it fails to capture associated effects. Our systematic analysis reveals this arises because effect-related cues are primarily encoded in specific DiT blocks and become suppressed when LoRA is applied across all blocks. To address this, we introduce EasyOmnimatte, the first unified, end-to-end video omnimatte method. Concretely, we finetune a pretrained video inpainting diffusion model to learn dual complementary experts while keeping its original weights intact: an Effect Expert, where LoRA is applied only to effect-sensitive DiT blocks to capture the coarse structure of the foreground and associated effects, and a fully LoRA-finetuned Quality Expert learns to refine the alpha matte. During sampling, Effect Expert is used for denoising at early, high-noise steps, while Quality Expert takes over at later, low-noise steps. This design eliminates the need for two full diffusion passes, significantly reducing computational cost without compromising output quality. Ablation studies validate the effectiveness of this Dual-Expert strategy. Experiments demonstrate that EasyOmnimatte sets a new state-of-the-art for video omnimatte and enables various downstream tasks, significantly outperforming baselines in both quality and efficiency.
zh
[CV-26] Balancing Accuracy and Efficiency: CNN Fusion Models for Diabetic Retinopathy Screening
【速读】:该论文旨在解决糖尿病视网膜病变(Diabetic Retinopathy, DR)大规模筛查中因专科医生资源有限及设备与人群间图像质量差异导致的准确性与效率难题。其核心解决方案是采用特征级融合(feature-level fusion)策略,将多个预训练卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)骨干模型(ResNet50、EfficientNet-B0 和 DenseNet121)的特征表示进行整合,以提升在多源异构眼底图像数据集上的泛化能力。实验表明,EfficientNet-B0 + DenseNet121 的双模型融合方法在保持较高准确率(82.89%)的同时,实现了良好的推理延迟平衡,优于单一模型和三模型融合方案,验证了轻量级特征融合在提升DR二分类筛查性能方面的有效性与实用性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21861
作者: Md Rafid Islam,Rafsan Jany,Akib Ahmed,Mohammad Ashrafuzzaman Khan
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Diabetic retinopathy (DR) remains a leading cause of preventable blindness, yet large-scale screening is constrained by limited specialist availability and variable image quality across devices and populations. This work investigates whether feature-level fusion of complementary convolutional neural network (CNN) backbones can deliver accurate and efficient binary DR screening on globally sourced fundus images. Using 11,156 images pooled from five public datasets (APTOS, EyePACS, IDRiD, Messidor, and ODIR), we frame DR detection as a binary classification task and compare three pretrained models (ResNet50, EfficientNet-B0, and DenseNet121) against pairwise and tri-fusion variants. Across five independent runs, fusion consistently outperforms single backbones. The EfficientNet-B0 + DenseNet121 (Eff+Den) fusion model achieves the best overall mean performance (accuracy: 82.89%) with balanced class-wise F1-scores for normal (83.60%) and diabetic (82.60%) cases. While the tri-fusion is competitive, it incurs a substantially higher computational cost. Inference profiling highlights a practical trade-off: EfficientNet-B0 is the fastest (approximately 1.16 ms/image at batch size 1000), whereas the Eff+Den fusion offers a favorable accuracy–latency balance. These findings indicate that lightweight feature fusion can enhance generalization across heterogeneous datasets, supporting scalable binary DR screening workflows where both accuracy and throughput are critical.
zh
[CV-27] raining-free Conditional Image Embedding Framework Leverag ing Large Vision Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决如何生成聚焦于特定文本条件(如颜色、类别等)的图像嵌入表示问题,即在不依赖额外训练的情况下实现对图像中特定语义特征的精准捕捉。其解决方案的关键在于利用大视觉语言模型(Large Vision-Language Model, LVLM)生成与给定条件相关的单字描述,并提取LVLM最后一层token的隐藏状态向量作为条件图像嵌入(Conditional Image Embedding),从而实现无需训练即可适配任意图像和条件的通用性方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21860
作者: Masayuki Kawarada,Kosuke Yamada,Antonio Tejero-de-Pablos,Naoto Inoue
机构: CyberAgent( CyberAgent)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Conditional image embeddings are feature representations that focus on specific aspects of an image indicated by a given textual condition (e.g., color, genre), which has been a challenging problem. Although recent vision foundation models, such as CLIP, offer rich representations of images, they are not designed to focus on a specified condition. In this paper, we propose DIOR, a method that leverages a large vision-language model (LVLM) to generate conditional image embeddings. DIOR is a training-free approach that prompts the LVLM to describe an image with a single word related to a given condition. The hidden state vector of the LVLM’s last token is then extracted as the conditional image embedding. DIOR provides a versatile solution that can be applied to any image and condition without additional training or task-specific priors. Comprehensive experimental results on conditional image similarity tasks demonstrate that DIOR outperforms existing training-free baselines, including CLIP. Furthermore, DIOR achieves superior performance compared to methods that require additional training across multiple settings.
zh
[CV-28] Fast Inference of Visual Autoregressive Model with Adjacency-Adaptive Dynamical Draft Trees
【速读】:该论文旨在解决自回归(Autoregressive, AR)图像模型在推理过程中因序列化生成导致效率低下的问题,尤其是针对高分辨率图像(如576×576)需约2000步才能完成生成的瓶颈。现有基于草稿树(draft tree)的推测解码方法在文本大语言模型(LLM)中表现优异,但在视觉AR模型中效果不佳,其关键障碍在于不同图像区域的token预测难度存在空间差异,导致草稿树中接受率(acceptance rate)不一致,从而限制了加速潜力。论文提出的解决方案是设计一种邻接自适应动态草稿树(Adjacency-Adaptive Dynamical Draft Trees, ADT-Tree),其核心创新在于:通过利用相邻token状态和历史接受率动态调整草稿树的深度与宽度——初始阶段基于水平邻接关系构建草稿树,随后采用二分适应策略优化结构,在简单区域扩展深度以提升并行度,在复杂区域增加宽度以增强鲁棒性。实验表明,ADT-Tree在MS-COCO 2017和PartiPrompts数据集上分别实现3.13倍和3.05倍的加速比,并可与松弛采样方法(如LANTERN)无缝集成进一步提速。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21857
作者: Haodong Lei,Hongsong Wang,Xin Geng,Liang Wang,Pan Zhou
机构: Southeast University (东南大学); Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院); University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院大学); Singapore Management University (新加坡管理大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) image models achieve diffusion-level quality but suffer from sequential inference, requiring approximately 2,000 steps for a 576x576 image. Speculative decoding with draft trees accelerates LLMs yet underperforms on visual AR models due to spatially varying token prediction difficulty. We identify a key obstacle in applying speculative decoding to visual AR models: inconsistent acceptance rates across draft trees due to varying prediction difficulties in different image regions. We propose Adjacency-Adaptive Dynamical Draft Trees (ADT-Tree), an adjacency-adaptive dynamic draft tree that dynamically adjusts draft tree depth and width by leveraging adjacent token states and prior acceptance rates. ADT-Tree initializes via horizontal adjacency, then refines depth/width via bisectional adaptation, yielding deeper trees in simple regions and wider trees in complex ones. The empirical evaluations on MS-COCO 2017 and PartiPrompts demonstrate that ADT-Tree achieves speedups of 3.13xand 3.05x, respectively. Moreover, it integrates seamlessly with relaxed sampling methods such as LANTERN, enabling further acceleration. Code is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-29] Breaking Alignment Barriers: TPS-Driven Semantic Correlation Learning for Alignment-Free RGB-T Salient Object Detection AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有RGB-T显著目标检测(RGB-T SOD)方法在处理实际场景中原始、未对齐的RGB与热成像(Thermal, T)图像对时性能显著下降的问题。其核心挑战在于跨模态差异,如空间错位、尺度变化和视角偏移等,导致依赖人工对齐标注数据的方法难以适应真实环境。解决方案的关键在于提出一种轻量级网络架构TPS-SCL,通过引入薄板样条对齐模块(TPSAM)缓解模态间空间不一致性,并设计语义相关性约束模块(SCCM)以抑制冗余背景干扰;同时结合双流MobileViT编码器与高效Mamba扫描机制建模跨模态语义关联,以及交叉模态相关模块(CMCM)充分挖掘并融合多模态依赖关系,从而实现高精度且低计算开销的显著目标检测。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21856
作者: Lupiao Hu,Fasheng Wang,Fangmei Chen,Fuming Sun,Haojie Li
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted by AAAI2026
Abstract:Existing RGB-T salient object detection methods predominantly rely on manually aligned and annotated datasets, struggling to handle real-world scenarios with raw, unaligned RGB-T image pairs. In practical applications, due to significant cross-modal disparities such as spatial misalignment, scale variations, and viewpoint shifts, the performance of current methods drastically deteriorates on unaligned datasets. To address this issue, we propose an efficient RGB-T SOD method for real-world unaligned image pairs, termed Thin-Plate Spline-driven Semantic Correlation Learning Network (TPS-SCL). We employ a dual-stream MobileViT as the encoder, combined with efficient Mamba scanning mechanisms, to effectively model correlations between the two modalities while maintaining low parameter counts and computational overhead. To suppress interference from redundant background information during alignment, we design a Semantic Correlation Constraint Module (SCCM) to hierarchically constrain salient features. Furthermore, we introduce a Thin-Plate Spline Alignment Module (TPSAM) to mitigate spatial discrepancies between modalities. Additionally, a Cross-Modal Correlation Module (CMCM) is incorporated to fully explore and integrate inter-modal dependencies, enhancing detection performance. Extensive experiments on various datasets demonstrate that TPS-SCL attains state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance among existing lightweight SOD methods and outperforms mainstream RGB-T SOD approaches.
zh
[CV-30] Scalable Class-Incremental Learning Based on Parametric Neural Collapse
【速读】:该论文旨在解决类别增量学习(Class Incremental Learning, CIL)中面临的两大核心问题:一是由于模型结构扩展导致的特征模块间差异和类别分布演化引起的类错位(class misalignment),二是序列扩展模型中的特征漂移(feature drift)问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于参数化神经坍缩(Parametric Neural Collapse, PNC)的可扩展类别增量学习方法(SCL-PNC),其核心创新包括:1)引入可适配层(adapt-layer)实现按需、低成本的骨干网络扩展;2)将静态的等角紧框架(Equiangular Tight Frame, ETF)转化为动态参数化形式,以适应增量类别分布变化;3)设计并行扩展架构结合知识蒸馏算法,确保不同扩展模块间的特征一致性。通过结构化的可扩展骨干网络、适配层与参数化ETF分类器协同作用,SCL-PNC在保持模型效率的同时有效缓解灾难性遗忘和特征漂移问题。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21845
作者: Chuangxin Zhang,Guangfeng Lin,Enhui Zhao,Kaiyang Liao,Yajun Chen
机构: Xi’an University of Technology (西安理工大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 42 pages, 8 figures, submitted to Pattern Recognition (PR)
Abstract:Incremental learning often encounter challenges such as overfitting to new data and catastrophic forgetting of old data. Existing methods can effectively extend the model for new tasks while freezing the parameters of the old model, but ignore the necessity of structural efficiency to lead to the feature difference between modules and the class misalignment due to evolving class distributions. To address these issues, we propose scalable class-incremental learning based on parametric neural collapse (SCL-PNC) that enables demand-driven, minimal-cost backbone expansion by adapt-layer and refines the static into a dynamic parametric Equiangular Tight Frame (ETF) framework according to incremental class. This method can efficiently handle the model expansion question with the increasing number of categories in real-world scenarios. Additionally, to counteract feature drift in serial expansion models, the parallel expansion framework is presented with a knowledge distillation algorithm to align features across expansion modules. Therefore, SCL-PNC can not only design a dynamic and extensible ETF classifier to address class misalignment due to evolving class distributions, but also ensure feature consistency by an adapt-layer with knowledge distillation between extended modules. By leveraging neural collapse, SCL-PNC induces the convergence of the incremental expansion model through a structured combination of the expandable backbone, adapt-layer, and the parametric ETF classifier. Experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our proposed method. Our code is available at this https URL ETF2. Keywords: Class incremental learning; Catastrophic forgetting; Neural collapse;Knowledge distillation; Expanded model.
zh
[CV-31] End-to-End 3D Spatiotemporal Perception with Multimodal Fusion and V2X Collaboration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决车联网(V2X)场景下因遮挡、视角受限及通信延迟导致的3D时空感知可靠性下降问题,尤其关注多视角协同感知与多模态融合的挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出XET-V2X框架,该框架通过引入基于多尺度可变形注意力机制的双层空间交叉注意力模块,实现异构视角与模态间的高效对齐;首先聚合多视图图像特征以增强语义一致性,再由更新的空间查询引导点云融合,从而在保证跨模态交互有效性的同时降低计算开销,最终实现鲁棒且时序稳定的感知性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21831
作者: Zhenwei Yang,Yibo Ai,Weidong Zhang
机构: National Center for Materials Service Safety (国家材料服役安全研究中心); University of Science and Technology Beijing (北京科技大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 19 pages, 19 figures
Abstract:Multi-view cooperative perception and multimodal fusion are essential for reliable 3D spatiotemporal understanding in autonomous driving, especially under occlusions, limited viewpoints, and communication delays in V2X scenarios. This paper proposes XET-V2X, a multi-modal fused end-to-end tracking framework for v2x collaboration that unifies multi-view multimodal sensing within a shared spatiotemporal representation. To efficiently align heterogeneous viewpoints and modalities, XET-V2X introduces a dual-layer spatial cross-attention module based on multi-scale deformable attention. Multi-view image features are first aggregated to enhance semantic consistency, followed by point cloud fusion guided by the updated spatial queries, enabling effective cross-modal interaction while reducing computational overhead. Experiments on the real-world V2X-Seq-SPD dataset and the simulated V2X-Sim-V2V and V2X-Sim-V2I benchmarks demonstrate consistent improvements in detection and tracking performance under varying communication delays. Both quantitative results and qualitative visualizations indicate that XET-V2X achieves robust and temporally stable perception in complex traffic scenarios.
zh
[CV-32] Few Tokens Matter: Entropy Guided Attacks on Vision-Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在面对对抗攻击时的脆弱性问题,特别是如何更高效且更具破坏力地诱导模型生成有害内容。其解决方案的关键在于识别并利用生成过程中具有高熵的少数关键决策点(约占总token数的20%),这些位置对输出轨迹的稳定性起决定性作用。通过仅在这些高熵位置施加扰动,攻击者能够在显著降低攻击预算的同时实现与全局攻击相当甚至更优的语义退化效果,并大幅提高良性输出转为有害输出的比例(35–49%)。这一发现揭示了VLM安全机制中的新弱点,并提出了基于熵银行引导的对抗攻击方法(Entropy-bank Guided Adversarial attacks, EGA),实现了高成功率(93–95%)与强危害转化能力的协同优化。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21815
作者: Mengqi He,Xinyu Tian,Xin Shen,Jinhong Ni,Shu Zou,Zhaoyuan Yang,Jing Zhang
机构: Australia National University (澳大利亚国立大学); The University of Queensland (昆士兰大学); GE Research (GE 研究院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 19 Pages,11 figures,8 tables
Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) achieve remarkable performance but remain vulnerable to adversarial attacks. Entropy, a measure of model uncertainty, is strongly correlated with the reliability of VLM. Prior entropy-based attacks maximize uncertainty at all decoding steps, implicitly assuming that every token contributes equally to generation instability. We show instead that a small fraction (about 20%) of high-entropy tokens, i.e., critical decision points in autoregressive generation, disproportionately governs output trajectories. By concentrating adversarial perturbations on these positions, we achieve semantic degradation comparable to global methods while using substantially smaller budgets. More importantly, across multiple representative VLMs, such selective attacks convert 35-49% of benign outputs into harmful ones, exposing a more critical safety risk. Remarkably, these vulnerable high-entropy forks recur across architecturally diverse VLMs, enabling feasible transferability (17-26% harmful rates on unseen targets). Motivated by these findings, we propose Entropy-bank Guided Adversarial attacks (EGA), which achieves competitive attack success rates (93-95%) alongside high harmful conversion, thereby revealing new weaknesses in current VLM safety mechanisms.
zh
[CV-33] SP 500 Stocks Movement Prediction using CNN
【速读】:该论文旨在解决股票市场走势预测问题,特别是针对标普500指数(S&P 500 index)的运动趋势预测。传统方法多依赖于单一维度的金融工程数据,难以充分捕捉真实市场中复杂的多变量动态特征。其解决方案的关键在于使用未经处理的多变量原始市场数据(包括除权除息事件等真实市场信息),并将这些数据转化为历史数据矩阵(类比图像),进而应用卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network, CNN)进行建模与预测。该方法突破了传统单变量建模局限,实现了基于多维原始数据的端到端学习,在个股、行业或投资组合层面均展现出良好预测性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21804
作者: Rahul Gupta
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computational Engineering, Finance, and Science (cs.CE)
备注: 9 pages, 19 diagrams. Originally submitted as a part of my Stanford University program taught by Dr. Fei Fei Lee and Andrej Karpathy CS231N 2018
Abstract:This paper is about predicting the movement of stock consist of SP 500 index. Historically there are many approaches have been tried using various methods to predict the stock movement and being used in the market currently for algorithm trading and alpha generating systems using traditional mathematical approaches [1, 2]. The success of artificial neural network recently created a lot of interest and paved the way to enable prediction using cutting-edge research in the machine learning and deep learning. Some of these papers have done a great job in implementing and explaining benefits of these new technologies. Although most these papers do not go into the complexity of the financial data and mostly utilize single dimension data, still most of these papers were successful in creating the ground for future research in this comparatively new phenomenon. In this paper, I am trying to use multivariate raw data including stock split/dividend events (as-is) present in real-world market data instead of engineered financial data. Convolution Neural Network (CNN), the best-known tool so far for image classification, is used on the multi-dimensional stock numbers taken from the market mimicking them as a vector of historical data matrices (read images) and the model achieves promising results. The predictions can be made stock by stock, i.e., a single stock, sector-wise or for the portfolio of stocks. Comments: 9 pages, 19 diagrams. Originally submitted as a part of my Stanford University program taught by Dr. Fei Fei Lee and Andrej Karpathy CS231N 2018 Subjects: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computational Engineering, Finance, and Science (cs.CE) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21804 [cs.CV] (or arXiv:2512.21804v1 [cs.CV] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21804 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) Journalreference: ADaSci Lattice Journal, Vol. 1, January 10, 2021
zh
[CV-34] CellM amba: Adaptive Mamba for Accurate and Efficient Cell Detection BMVC2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决病理图像中细胞检测的挑战,包括细胞密集排列、类间差异细微以及背景干扰严重等问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种轻量且高精度的一阶段检测模型CellMamba,该模型基于VSSD骨干网络,引入CellMamba Block,其中结合NC-Mamba或Multi-Head Self-Attention(MSA)与创新的Triple-Mapping Adaptive Coupling(TMAC)模块;TMAC通过将通道拆分为两条并行分支,分别配备双独特注意力图和一个共识注意力图,并自适应融合以保留局部敏感性和全局一致性,从而增强空间判别能力;此外,设计了自适应Mamba Head,利用可学习权重融合多尺度特征,提升在不同目标尺寸下的鲁棒性检测性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21803
作者: Ruochen Liu,Yi Tian,Jiahao Wang,Hongbin Liu,Xianxu Hou,Jingxin Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 36th British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC 2025)
Abstract:Cell detection in pathological images presents unique challenges due to densely packed objects, subtle inter-class differences, and severe background clutter. In this paper, we propose CellMamba, a lightweight and accurate one-stage detector tailored for fine-grained biomedical instance detection. Built upon a VSSD backbone, CellMamba integrates CellMamba Blocks, which couple either NC-Mamba or Multi-Head Self-Attention (MSA) with a novel Triple-Mapping Adaptive Coupling (TMAC) module. TMAC enhances spatial discriminability by splitting channels into two parallel branches, equipped with dual idiosyncratic and one consensus attention map, adaptively fused to preserve local sensitivity and global consistency. Furthermore, we design an Adaptive Mamba Head that fuses multi-scale features via learnable weights for robust detection under varying object sizes. Extensive experiments on two public datasets-CoNSeP and CytoDArk0-demonstrate that CellMamba outperforms both CNN-based, Transformer-based, and Mamba-based baselines in accuracy, while significantly reducing model size and inference latency. Our results validate CellMamba as an efficient and effective solution for high-resolution cell detection.
zh
[CV-35] Diffusion Posterior Sampling for Super-Resolution under Gaussian Measurement Noise
【速读】:该论文旨在解决单图像超分辨率(Single-Image Super-Resolution, SISR)中如何在已知退化模型下实现高质量重建的问题,特别是在存在加性高斯噪声的4×放大场景中。解决方案的关键在于提出一种扩散后验采样(Diffusion Posterior Sampling, DPS)方法,通过结合无条件扩散先验与基于梯度的条件约束,实现测量一致性(measurement consistency)的优化。该方法利用似然引导的采样流程,在不重新训练扩散模型的前提下,通过调节指导尺度(guidance scale)和噪声标准差(noise standard deviation),平衡扩散先验与观测梯度强度,从而获得稳定且高质量的重建结果。实验表明,最优配置为指导尺度0.95、噪声标准差σ=0.01时,综合评分(PSNR/40 + SSIM)达到1.45231,显著提升了边缘清晰度与面部细节的一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21797
作者: Abu Hanif Muhammad Syarubany
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:This report studies diffusion posterior sampling (DPS) for single-image super-resolution (SISR) under a known degradation model. We implement a likelihood-guided sampling procedure that combines an unconditional diffusion prior with gradient-based conditioning to enforce measurement consistency for 4\times super-resolution with additive Gaussian noise. We evaluate posterior sampling (PS) conditioning across guidance scales and noise levels, using PSNR and SSIM as fidelity metrics and a combined selection score (\mathrmPSNR/40)+\mathrmSSIM . Our ablation shows that moderate guidance improves reconstruction quality, with the best configuration achieved at PS scale 0.95 and noise standard deviation \sigma=0.01 (score 1.45231 ). Qualitative results confirm that the selected PS setting restores sharper edges and more coherent facial details compared to the downsampled inputs, while alternative conditioning strategies (e.g., MCG and PS-annealed) exhibit different texture fidelity trade-offs. These findings highlight the importance of balancing diffusion priors and measurement-gradient strength to obtain stable, high-quality reconstructions without retraining the diffusion model for each operator.
zh
[CV-36] AI for Mycetoma Diagnosis in Histopathological Images: The MICCAI 2024 Challenge
【速读】:该论文旨在解决热带地区常见但被忽视的疾病——真菌性或细菌性麦藓病(mycetoma)在低资源环境下诊断困难的问题,尤其是在缺乏专业病理学家的情况下。其解决方案的关键在于利用人工智能(AI)技术,通过组织病理图像自动分割麦藓病颗粒并分类其类型,从而提升诊断效率与准确性。研究通过组织“麦藓病微图像检测与分类挑战赛”(mAIcetoma),征集全球团队开发深度学习模型,并提供标准化数据集(MyData)用于训练和评估。结果表明,所有参赛模型均实现了高精度的颗粒分割,且最优模型在类型分类任务中表现显著,验证了基于AI的自动化诊断方法在麦藓病管理中的可行性与有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21792
作者: Hyam Omar Ali,Sahar Alhesseen,Lamis Elkhair,Adrian Galdran,Ming Feng,Zhixiang Xiong,Zengming Lin,Kele Xu,Liang Hu,Benjamin Keel,Oliver Mills,James Battye,Akshay Kumar,Asra Aslam,Prasad Dutande,Ujjwal Baid,Bhakti Baheti,Suhas Gajre,Aravind Shrenivas Murali,Eung-Joo Lee,Ahmed Fahal,Rachid Jennane
机构: University of Orléans (奥尔良大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Mycetoma is a neglected tropical disease caused by fungi or bacteria leading to severe tissue damage and disabilities. It affects poor and rural communities and presents medical challenges and socioeconomic burdens on patients and healthcare systems in endemic regions worldwide. Mycetoma diagnosis is a major challenge in mycetoma management, particularly in low-resource settings where expert pathologists are limited. To address this challenge, this paper presents an overview of the Mycetoma MicroImage: Detect and Classify Challenge (mAIcetoma) which was organized to advance mycetoma diagnosis through AI solutions. mAIcetoma focused on developing automated models for segmenting mycetoma grains and classifying mycetoma types from histopathological images. The challenge attracted the attention of several teams worldwide to participate and five finalist teams fulfilled the challenge objectives. The teams proposed various deep learning architectures for the ultimate goal of this challenge. Mycetoma database (MyData) was provided to participants as a standardized dataset to run the proposed models. Those models were evaluated using evaluation metrics. Results showed that all the models achieved high segmentation accuracy, emphasizing the necessitate of grain detection as a critical step in mycetoma diagnosis. In addition, the top-performing models show a significant performance in classifying mycetoma types.
zh
[CV-37] InstructMoLE: Instruction-Guided Mixture of Low-rank Experts for Multi-Conditional Image Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决扩散Transformer(Diffusion Transformers, DiTs)在参数高效微调(Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning)过程中,因使用单体适配器(如LoRA)而导致的任务干扰问题,以及现有混合低秩专家(Mixture of Low-rank Experts, MoLE)架构中基于token级路由策略引发的全局语义不一致问题,例如空间碎片化和语义漂移。其解决方案的关键在于提出InstructMoLE框架,通过引入指令引导的全局路由机制(Instruction-Guided Routing, IGR),将用户完整指令作为全局路由信号,确保所有输入token共享同一组专家组合,从而保持生成过程的全局语义一致性与结构完整性;同时设计输出空间正交性损失(output-space orthogonality loss),增强专家功能多样性,防止表征坍缩,显著提升多条件图像生成任务中的控制精度与用户意图契合度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21788
作者: Jinqi Xiao,Qing Yan,Liming Jiang,Zichuan Liu,Hao Kang,Shen Sang,Tiancheng Zhi,Jing Liu,Cheng Yang,Xin Lu,Bo Yuan
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) for diverse, multi-conditional tasks often suffers from task interference when using monolithic adapters like LoRA. The Mixture of Low-rank Experts (MoLE) architecture offers a modular solution, but its potential is usually limited by routing policies that operate at a token level. Such local routing can conflict with the global nature of user instructions, leading to artifacts like spatial fragmentation and semantic drift in complex image generation tasks. To address these limitations, we introduce InstructMoLE, a novel framework that employs an Instruction-Guided Mixture of Low-Rank Experts. Instead of per-token routing, InstructMoLE utilizes a global routing signal, Instruction-Guided Routing (IGR), derived from the user’s comprehensive instruction. This ensures that a single, coherently chosen expert council is applied uniformly across all input tokens, preserving the global semantics and structural integrity of the generation process. To complement this, we introduce an output-space orthogonality loss, which promotes expert functional diversity and mitigates representational collapse. Extensive experiments demonstrate that InstructMoLE significantly outperforms existing LoRA adapters and MoLE variants across challenging multi-conditional generation benchmarks. Our work presents a robust and generalizable framework for instruction-driven fine-tuning of generative models, enabling superior compositional control and fidelity to user intent.
zh
[CV-38] Scene-VLM: Multimodal Video Scene Segmentation via Vision-Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决长视频场景分割(scene segmentation)任务中现有基于编码器的方法存在的局限性,包括视觉中心偏差、孤立分类每一段(shot)而忽视时序依赖关系,以及缺乏叙事理解能力和可解释性。其解决方案的关键在于提出首个经过微调的视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Model, VLM)框架——Scene-VLM,该框架通过联合处理图像帧、语音转录文本及可选元数据,实现跨连续片段的多模态推理;同时引入因果依赖的序列化预测机制与上下文聚焦窗口(context-focus window),确保每个片段决策获得充分的时间上下文支持,并利用VLM的token级logits提取置信度分数,从而实现可控的精确率-召回率权衡。此外,该方法还可通过少量目标监督生成连贯的自然语言理由(rationales)来解释边界判定,显著提升了模型的可解释性和性能,在MovieNet等基准上达到当前最优效果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21778
作者: Nimrod Berman,Adam Botach,Emanuel Ben-Baruch,Shunit Haviv Hakimi,Asaf Gendler,Ilan Naiman,Erez Yosef,Igor Kviatkovsky
机构: Ben-Gurion University (本古里安大学); Amazon Prime Video (亚马逊Prime视频); Tel-Aviv University (特拉维夫大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Segmenting long-form videos into semantically coherent scenes is a fundamental task in large-scale video understanding. Existing encoder-based methods are limited by visual-centric biases, classify each shot in isolation without leveraging sequential dependencies, and lack both narrative understanding and explainability. In this paper, we present Scene-VLM, the first fine-tuned vision-language model (VLM) framework for video scene segmentation. Scene-VLM jointly processes visual and textual cues including frames, transcriptions, and optional metadata to enable multimodal reasoning across consecutive shots. The model generates predictions sequentially with causal dependencies among shots and introduces a context-focus window mechanism to ensure sufficient temporal context for each shot-level decision. In addition, we propose a scheme to extract confidence scores from the token-level logits of the VLM, enabling controllable precision-recall trade-offs that were previously limited to encoder-based methods. Furthermore, we demonstrate that our model can be aligned to generate coherent natural-language rationales for its boundary decisions through minimal targeted supervision. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on standard scene segmentation benchmarks. On MovieNet, for example, Scene-VLM yields significant improvements of +6 AP and +13.7 F1 over the previous leading method.
zh
[CV-39] Inference-based GAN Video Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式视频模型在时间尺度扩展上的局限性问题,即现有方法(如GAN、VAE或扩散网络)在生成较长视频序列时,难以保持时空连续性与动态一致性,导致视频质量显著下降。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于马尔可夫链框架的新型记忆高效生成机制,其中每个状态对应一个短序列的VAE-GAN生成器,并通过引入回溯机制(recall mechanism)实现子视频片段的顺序连接,从而有效建模长时依赖关系,确保生成数百至数千帧的高质量、连贯且语义合理的长视频序列。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21776
作者: Jingbo Yang,Adrian G. Bors
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Video generation has seen remarkable progresses thanks to advancements in generative deep learning. Generated videos should not only display coherent and continuous movement but also meaningful movement in successions of scenes. Generating models such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) or Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) and more recently Diffusion Networks have been used for generating short video sequences, usually of up to 16 frames. In this paper, we first propose a new type of video generator by enabling adversarial-based unconditional video generators with a variational encoder, akin to a VAE-GAN hybrid structure, in order to enable the generation process with inference capabilities. The proposed model, as in other video deep learning-based processing frameworks, incorporates two processing branches, one for content and another for movement. However, existing models struggle with the temporal scaling of the generated videos. In classical approaches when aiming to increase the generated video length, the resulting video quality degrades, particularly when considering generating significantly long sequences. To overcome this limitation, our research study extends the initially proposed VAE-GAN video generation model by employing a novel, memory-efficient approach to generate long videos composed of hundreds or thousands of frames ensuring their temporal continuity, consistency and dynamics. Our approach leverages a Markov chain framework with a recall mechanism, with each state representing a VAE-GAN short-length video generator. This setup allows for the sequential connection of generated video sub-sequences, enabling temporal dependencies, resulting in meaningful long video sequences.
zh
[CV-40] BertsWin: Resolving Topological Sparsity in 3D Masked Autoencoders via Component-Balanced Structural Optimization
【速读】:该论文旨在解决自监督学习(Self-Supervised Learning, SSL)与视觉Transformer(Vision Transformer, ViT)在3D体素图像中应用时面临的挑战,尤其是标准掩码自动编码器(Masked Autoencoder, MAE)难以捕捉三维空间关系的问题,特别是在预训练阶段丢弃75%令牌的情况下。其解决方案的关键在于提出BertsWin架构——一种结合完整BERT式令牌掩码机制与Swin Transformer窗口的混合模型,通过构建完整的3D令牌网格(包含掩码和可见区域)来保留空间拓扑结构,并利用单层局部Swin窗口降低计算复杂度。该设计不仅维持了理论FLOP与稀疏ViT基线相当,还实现了5.8倍的语义收敛加速和15倍训练轮次减少(44 vs 660),且无额外计算开销,显著提升了3D医学图像重建的效率与精度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21769
作者: Evgeny Alves Limarenko,Anastasiia Studenikina
机构: Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (莫斯科物理技术研究所)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Image and Video Processing (eess.IV)
备注: Code available at this https URL and this https URL . Zenodo repository (DOI: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17916932 ) contains source images, training logs, trained models, and code
Abstract:The application of self-supervised learning (SSL) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) approaches demonstrates promising results in the field of 2D medical imaging, but the use of these methods on 3D volumetric images is fraught with difficulties. Standard Masked Autoencoders (MAE), which are state-of-the-art solution for 2D, have a hard time capturing three-dimensional spatial relationships, especially when 75% of tokens are discarded during pre-training. We propose BertsWin, a hybrid architecture combining full BERT-style token masking using Swin Transformer windows, to enhance spatial context learning in 3D during SSL pre-training. Unlike the classic MAE, which processes only visible areas, BertsWin introduces a complete 3D grid of tokens (masked and visible), preserving the spatial topology. And to smooth out the quadratic complexity of ViT, single-level local Swin windows are used. We introduce a structural priority loss function and evaluate the results of cone beam computed tomography of the temporomandibular joints. The subsequent assessment includes TMJ segmentation on 3D CT scans. We demonstrate that the BertsWin architecture, by maintaining a complete three-dimensional spatial topology, inherently accelerates semantic convergence by a factor of 5.8x compared to standard ViT-MAE baselines. Furthermore, when coupled with our proposed GradientConductor optimizer, the full BertsWin framework achieves a 15-fold reduction in training epochs (44 vs 660) required to reach state-of-the-art reconstruction fidelity. Analysis reveals that BertsWin achieves this acceleration without the computational penalty typically associated with dense volumetric processing. At canonical input resolutions, the architecture maintains theoretical FLOP parity with sparse ViT baselines, resulting in a significant net reduction in total computational resources due to faster convergence.
zh
[CV-41] A-QCF-Net: An Adaptive Quaternion Cross-Fusion Network for Multimodal Liver Tumor Segmentation from Unpaired Datasets
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态医学影像(如CT和MRI)在深度学习模型训练中因数据稀缺且缺乏配对与空间对齐而导致的建模难题。其核心解决方案是提出一种自适应四元数交叉融合网络(Adaptive Quaternion Cross-Fusion Network, A-QCF-Net),关键在于引入了自适应四元数交叉融合(A-QCF)模块——该模块作为数据驱动的注意力机制,实现了双流特征之间的双向知识迁移,通过动态调节信息流动,使CT提供的清晰解剖边界与MRI提供的细微软组织对比得以相互交换并增强各自特征表示,从而在未配对的LiTS(CT)和ATLAS(MRI)数据集上联合训练出一个统一分割模型,显著提升肿瘤分割性能(Dice分数分别提高5.4%和4.7%),并经Grad-CAM类可解释性分析验证其临床意义。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21760
作者: Arunkumar V,Firos V M,Senthilkumar S,Gangadharan G R
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Multimodal medical imaging provides complementary information that is crucial for accurate delineation of pathology, but the development of deep learning models is limited by the scarcity of large datasets in which different modalities are paired and spatially aligned. This paper addresses this fundamental limitation by proposing an Adaptive Quaternion Cross-Fusion Network (A-QCF-Net) that learns a single unified segmentation model from completely separate and unpaired CT and MRI cohorts. The architecture exploits the parameter efficiency and expressive power of Quaternion Neural Networks to construct a shared feature space. At its core is the Adaptive Quaternion Cross-Fusion (A-QCF) block, a data driven attention module that enables bidirectional knowledge transfer between the two streams. By learning to modulate the flow of information dynamically, the A-QCF block allows the network to exchange abstract modality specific expertise, such as the sharp anatomical boundary information available in CT and the subtle soft tissue contrast provided by MRI. This mutual exchange regularizes and enriches the feature representations of both streams. We validate the framework by jointly training a single model on the unpaired LiTS (CT) and ATLAS (MRI) datasets. The jointly trained model achieves Tumor Dice scores of 76.7% on CT and 78.3% on MRI, significantly exceeding the strong unimodal nnU-Net baseline by margins of 5.4% and 4.7% respectively. Furthermore, comprehensive explainability analysis using Grad-CAM and Grad-CAM++ confirms that the model correctly focuses on relevant pathological structures, ensuring the learned representations are clinically meaningful. This provides a robust and clinically viable paradigm for unlocking the large unpaired imaging archives that are common in healthcare.
zh
[CV-42] Modified TSception for Analyzing Driver Drowsiness and Mental Workload from EEG
【速读】:该论文旨在解决驾驶员疲劳(driver drowsiness)检测中实时性与可靠性的难题,以提升道路安全。其核心解决方案是提出一种改进的TSception架构(Modified TSception),关键创新在于引入五层时间细化策略以捕捉多尺度脑电(Electroencephalography, EEG)动态,并采用自适应平均池化(Adaptive Average Pooling)增强对不同输入维度EEG信号的结构灵活性,同时设计两级融合机制优化时空特征整合,从而显著提升模型性能的稳定性(置信区间从0.36降至0.24)和跨任务泛化能力(在SEED-VIG和STEW数据集上分别实现83.46%和95.93%的准确率)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21747
作者: Gourav Siddhad,Anurag Singh,Rajkumar Saini,Partha Pratim Roy
机构: Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee (印度理工学院,鲁尔基分校); Indian Institute of Technology, Dhanbad (印度理工学院,丹巴德分校)
类目: Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 8 Pages, 3 Figures, 1 Table
Abstract:Driver drowsiness remains a primary cause of traffic accidents, necessitating the development of real-time, reliable detection systems to ensure road safety. This study presents a Modified TSception architecture designed for the robust assessment of driver fatigue using Electroencephalography (EEG). The model introduces a novel hierarchical architecture that surpasses the original TSception by implementing a five-layer temporal refinement strategy to capture multi-scale brain dynamics. A key innovation is the use of Adaptive Average Pooling, which provides the structural flexibility to handle varying EEG input dimensions, and a two - stage fusion mechanism that optimizes the integration of spatiotemporal features for improved stability. When evaluated on the SEED-VIG dataset and compared against established methods - including SVM, Transformer, EEGNet, ConvNeXt, LMDA-Net, and the original TSception - the Modified TSception achieves a comparable accuracy of 83.46% (vs. 83.15% for the original). Critically, the proposed model exhibits a substantially reduced confidence interval (0.24 vs. 0.36), signifying a marked improvement in performance stability. Furthermore, the architecture’s generalizability is validated on the STEW mental workload dataset, where it achieves state-of-the-art results with 95.93% and 95.35% accuracy for 2-class and 3-class classification, respectively. These improvements in consistency and cross-task generalizability underscore the effectiveness of the proposed modifications for reliable EEG-based monitoring of drowsiness and mental workload.
zh
[CV-43] Dynamic Feedback Engines: Layer-Wise Control for Self-Regulating Continual Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决持续学习(Continual Learning)中普遍存在的灾难性遗忘问题,即模型在学习新任务时会严重损害对先前任务的性能。现有方法通常对网络各层采取统一处理策略,难以平衡稳定性(stability)与可塑性(plasticity)之间的权衡。其核心创新在于提出一种基于熵感知(entropy-aware)的动态反馈机制:通过监测每一层输出的不确定性(熵),智能调节不同层的学习行为——对高熵层降低熵以缓解欠拟合,对低熵层增加熵以抑制过拟合。这种自适应调控促使模型收敛至更宽的局部极小值区域,从而提升泛化能力。该方法具有通用性,可无缝集成于基于回放(replay)或正则化(regularization)的持续学习框架中,并在多个数据集上显著优于当前最优基线。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21743
作者: Hengyi Wu,Zhenyi Wang,Heng Huang
机构: University of Maryland, College Park (马里兰大学学院公园分校); University of Central Florida (中佛罗里达大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 14 pages
Abstract:Continual learning aims to acquire new tasks while preserving performance on previously learned ones, but most methods struggle with catastrophic forgetting. Existing approaches typically treat all layers uniformly, often trading stability for plasticity or vice versa. However, different layers naturally exhibit varying levels of uncertainty (entropy) when classifying tasks. High-entropy layers tend to underfit by failing to capture task-specific patterns, while low-entropy layers risk overfitting by becoming overly confident and specialized. To address this imbalance, we propose an entropy-aware continual learning method that employs a dynamic feedback mechanism to regulate each layer based on its entropy. Specifically, our approach reduces entropy in high-entropy layers to mitigate underfitting and increases entropy in overly confident layers to alleviate overfitting. This adaptive regulation encourages the model to converge to wider local minima, which have been shown to improve generalization. Our method is general and can be seamlessly integrated with both replay- and regularization-based approaches. Experiments on various datasets demonstrate substantial performance gains over state-of-the-art continual learning baselines.
zh
[CV-44] SyncAnyone: Implicit Disentanglement via Progressive Self-Correction for Lip-Syncing in the wild
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有生成式 AI(Generative AI)视频配音方法中因掩码训练策略导致的时空上下文破坏问题,具体表现为面部动态运动建模不准确、面部结构与背景一致性差。其核心解决方案是提出一种两阶段学习框架 SyncAnyone:第一阶段利用基于扩散模型的视频 Transformer 进行掩码嘴巴修复,以实现高精度的音频驱动唇动生成;第二阶段则通过无掩码微调管道,借助合成伪配对数据(源视频与随机采样音频生成的同步视频)进一步优化模型,从而消除掩码引入的伪影,提升唇部编辑精度和背景一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21736
作者: Xindi Zhang,Dechao Meng,Steven Xiao,Qi Wang,Peng Zhang,Bang Zhang
机构: Tongyi Lab, Alibaba Group (通义实验室,阿里巴巴集团)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:High-quality AI-powered video dubbing demands precise audio-lip synchronization, high-fidelity visual generation, and faithful preservation of identity and background. Most existing methods rely on a mask-based training strategy, where the mouth region is masked in talking-head videos, and the model learns to synthesize lip movements from corrupted inputs and target audios. While this facilitates lip-sync accuracy, it disrupts spatiotemporal context, impairing performance on dynamic facial motions and causing instability in facial structure and background consistency. To overcome this limitation, we propose SyncAnyone, a novel two-stage learning framework that achieves accurate motion modeling and high visual fidelity simultaneously. In Stage 1, we train a diffusion-based video transformer for masked mouth inpainting, leveraging its strong spatiotemporal modeling to generate accurate, audio-driven lip movements. However, due to input corruption, minor artifacts may arise in the surrounding facial regions and the background. In Stage 2, we develop a mask-free tuning pipeline to address mask-induced artifacts. Specifically, on the basis of the Stage 1 model, we develop a data generation pipeline that creates pseudo-paired training samples by synthesizing lip-synced videos from the source video and random sampled audio. We further tune the stage 2 model on this synthetic data, achieving precise lip editing and better background consistency. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art results in visual quality, temporal coherence, and identity preservation under in-the wild lip-syncing scenarios.
zh
[CV-45] Knot Forcing: Taming Autoregressive Video Diffusion Models for Real-time Infinite Interactive Portrait Animation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决实时人像动画(real-time portrait animation)中的关键挑战,包括高视觉保真度、时间一致性、超低延迟以及对动态输入(如参考图像和驱动信号)的响应能力。现有方法中,基于扩散模型的方法虽能实现高质量输出,但因其非因果特性难以支持流式部署;而因果自回归视频生成方法则存在误差累积、块边界运动不连续及长期一致性下降等问题。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为Knot Forcing的新颖流式框架,其核心设计包括:(1)基于缓存参考图像的键值(KV)状态进行全局身份保持,并结合滑动窗口注意力实现局部时序建模的分块生成策略;(2)引入时序结点(temporal knot)模块,通过相邻块重叠与图像到视频条件引导传播时空线索,平滑跨块运动过渡;(3)采用“提前运行”机制,在推理过程中动态更新参考帧的时间坐标,使其语义上下文始终领先于当前生成帧,从而保障长时间的一致性。该方案实现了无限序列上的高保真、时序一致且交互式的实时人像动画,在消费级GPU上具备强视觉稳定性与实时性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21734
作者: Steven Xiao,XIndi Zhang,Dechao Meng,Qi Wang,Peng Zhang,Bang Zhang
机构: Tongyi Lab, Alibaba Group (通义实验室,阿里巴巴集团)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Real-time portrait animation is essential for interactive applications such as virtual assistants and live avatars, requiring high visual fidelity, temporal coherence, ultra-low latency, and responsive control from dynamic inputs like reference images and driving signals. While diffusion-based models achieve strong quality, their non-causal nature hinders streaming deployment. Causal autoregressive video generation approaches enable efficient frame-by-frame generation but suffer from error accumulation, motion discontinuities at chunk boundaries, and degraded long-term consistency. In this work, we present a novel streaming framework named Knot Forcing for real-time portrait animation that addresses these challenges through three key designs: (1) a chunk-wise generation strategy with global identity preservation via cached KV states of the reference image and local temporal modeling using sliding window attention; (2) a temporal knot module that overlaps adjacent chunks and propagates spatio-temporal cues via image-to-video conditioning to smooth inter-chunk motion transitions; and (3) A “running ahead” mechanism that dynamically updates the reference frame’s temporal coordinate during inference, keeping its semantic context ahead of the current rollout frame to support long-term coherence. Knot Forcing enables high-fidelity, temporally consistent, and interactive portrait animation over infinite sequences, achieving real-time performance with strong visual stability on consumer-grade GPUs.
zh
[CV-46] AstraNav-World: World Model for Foresight Control and Consistency
【速读】:该论文旨在解决开放动态环境中具身导航(embodied navigation)对准确未来预测与行动序列规划的联合推理问题,尤其针对传统“先设想后规划”(envision-then-plan)解耦架构中累积误差严重、物理一致性不足的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出AstraNav-World——一个端到端的世界模型,通过统一的概率框架同步建模未来视觉状态与动作序列:利用基于扩散的视频生成器与视觉语言策略(vision-language policy)实现视觉与动作的协同演化(synchronized rollouts),并采用双向约束训练目标——既生成动作条件下的多步视觉预测,又从预测视觉中推导出任务相关的轨迹,从而确保预测可执行且决策扎根于物理一致的未来场景。这种紧密耦合的视觉-动作联合学习机制显著提升了轨迹准确性与成功率,并在真实世界零样本迁移测试中展现出强泛化能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21714
作者: Junjun Hu,Jintao Chen,Haochen Bai,Minghua Luo,Shichao Xie,Ziyi Chen,Fei Liu,Zedong Chu,Xinda Xue,Botao Ren,Xiaolong Wu,Mu Xu,Shanghang Zhang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Embodied navigation in open, dynamic environments demands accurate foresight of how the world will evolve and how actions will unfold over time. We propose AstraNav-World, an end-to-end world model that jointly reasons about future visual states and action sequences within a unified probabilistic framework. Our framework integrates a diffusion-based video generator with a vision-language policy, enabling synchronized rollouts where predicted scenes and planned actions are updated simultaneously. Training optimizes two complementary objectives: generating action-conditioned multi-step visual predictions and deriving trajectories conditioned on those predicted visuals. This bidirectional constraint makes visual predictions executable and keeps decisions grounded in physically consistent, task-relevant futures, mitigating cumulative errors common in decoupled “envision-then-plan” pipelines. Experiments across diverse embodied navigation benchmarks show improved trajectory accuracy and higher success rates. Ablations confirm the necessity of tight vision-action coupling and unified training, with either branch removal degrading both prediction quality and policy reliability. In real-world testing, AstraNav-World demonstrated exceptional zero-shot capabilities, adapting to previously unseen scenarios without any real-world fine-tuning. These results suggest that AstraNav-World captures transferable spatial understanding and planning-relevant navigation dynamics, rather than merely overfitting to simulation-specific data distribution. Overall, by unifying foresight vision and control within a single generative model, we move closer to reliable, interpretable, and general-purpose embodied agents that operate robustly in open-ended real-world settings.
zh
[CV-47] RAPTOR: Real-Time High-Resolution UAV Video Prediction with Efficient Video Attention
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视频预测领域长期存在的三难困境:高分辨率与感知质量的提升通常以牺牲实时性为代价,这限制了其在低延迟关键场景(如密集城市环境中自主无人机)中的应用。现有方法依赖迭代生成(如扩散模型、自回归模型)或二次复杂度注意力机制,在边缘硬件上难以满足性能需求。解决方案的关键在于提出RAPTOR架构,其核心创新是高效视频注意力(Efficient Video Attention, EVA)模块,该模块通过因子分解时空建模,将原本O((ST)²)或O(ST)的时间复杂度降至O(S + T),内存复杂度降至O(max(S, T)),从而实现512²及以上分辨率下的全局上下文建模,并支持单次前向传播避免误差累积;同时配合三阶段训练课程,逐步从粗粒度结构到精细时序一致性细节优化预测结果,最终在Jetson AGX Orin上实现超过30 FPS的推理速度,显著优于现有方法并提升真实无人机导航任务的成功率18%。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21710
作者: Zhan Chen,Zile Guo,Enze Zhu,Peirong Zhang,Xiaoxuan Liu,Lei Wang,Yidan Zhang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Video prediction is plagued by a fundamental trilemma: achieving high-resolution and perceptual quality typically comes at the cost of real-time speed, hindering its use in latency-critical applications. This challenge is most acute for autonomous UAVs in dense urban environments, where foreseeing events from high-resolution imagery is non-negotiable for safety. Existing methods, reliant on iterative generation (diffusion, autoregressive models) or quadratic-complexity attention, fail to meet these stringent demands on edge hardware. To break this long-standing trade-off, we introduce RAPTOR, a video prediction architecture that achieves real-time, high-resolution performance. RAPTOR’s single-pass design avoids the error accumulation and latency of iterative approaches. Its core innovation is Efficient Video Attention (EVA), a novel translator module that factorizes spatiotemporal modeling. Instead of processing flattened spacetime tokens with O((ST)^2) or O(ST) complexity, EVA alternates operations along the spatial (S) and temporal (T) axes. This factorization reduces the time complexity to O(S + T) and memory complexity to O(max(S, T)) , enabling global context modeling at 512^2 resolution and beyond, operating directly on dense feature maps with a patch-free design. Complementing this architecture is a 3-stage training curriculum that progressively refines predictions from coarse structure to sharp, temporally coherent details. Experiments show RAPTOR is the first predictor to exceed 30 FPS on a Jetson AGX Orin for 512^2 video, setting a new state-of-the-art on UAVid, KTH, and a custom high-resolution dataset in PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS. Critically, RAPTOR boosts the mission success rate in a real-world UAV navigation task by 18/%, paving the way for safer and more anticipatory embodied agents.
zh
[CV-48] Spatiotemporal-Untrammelled Mixture of Experts for Multi-Person Motion Prediction AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多人群体运动预测中两个核心问题:一是现有方法依赖位置编码导致时空表示僵化,难以灵活捕捉复杂的时空依赖关系;二是传统注意力机制存在二次时间复杂度,造成计算成本过高。解决方案的关键在于提出时空无束缚的专家混合模型(Spatiotemporal-Untrammelled Mixture of Experts, ST-MoE),通过引入四类专精于不同空间或时间依赖模式的时空专家来自适应挖掘复杂运动模式,并采用双向时空Mamba作为专家结构,在共享双向时序与空间Mamba的基础上以差异化组合实现高效建模与参数节约。该设计在保持高精度的同时显著降低计算开销,实验表明其在多个基准数据集上优于当前最优方法,且模型参数减少41.38%,训练速度提升3.6倍。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21707
作者: Zheng Yin,Chengjian Li,Xiangbo Shu,Meiqi Cao,Rui Yan,Jinhui Tang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 12 pages, 7 figures, Accepted by AAAI 2026 (oral)
Abstract:Comprehensively and flexibly capturing the complex spatio-temporal dependencies of human motion is critical for multi-person motion prediction. Existing methods grapple with two primary limitations: i) Inflexible spatiotemporal representation due to reliance on positional encodings for capturing spatiotemporal information. ii) High computational costs stemming from the quadratic time complexity of conventional attention mechanisms. To overcome these limitations, we propose the Spatiotemporal-Untrammelled Mixture of Experts (ST-MoE), which flexibly explores complex spatio-temporal dependencies in human motion and significantly reduces computational cost. To adaptively mine complex spatio-temporal patterns from human motion, our model incorporates four distinct types of spatiotemporal experts, each specializing in capturing different spatial or temporal dependencies. To reduce the potential computational overhead while integrating multiple experts, we introduce bidirectional spatiotemporal Mamba as experts, each sharing bidirectional temporal and spatial Mamba in distinct combinations to achieve model efficiency and parameter economy. Extensive experiments on four multi-person benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach not only outperforms state-of-art in accuracy but also reduces model parameter by 41.38% and achieves a 3.6x speedup in training. The code is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-49] FUSE: Unifying Spectral and Semantic Cues for Robust AI-Generated Image Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决AI生成图像(AI-generated images)的可靠检测问题,尤其是在面对多种生成模型(如Diffusion、GAN等)时,现有方法普遍存在泛化能力不足、对高保真图像检测效果差等挑战。解决方案的关键在于提出一种混合系统FUSE,通过融合频域特征(由快速傅里叶变换提取的谱特征)与语义特征(来自CLIP视觉编码器),构建联合表示,并采用两阶段渐进式训练策略,从而实现跨生成器的强泛化性能。实验表明,该方法在多个基准数据集上均达到先进水平,尤其在Chameleon数据集上显著优于现有方法,验证了多模态特征融合在通用检测任务中的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21695
作者: Md. Zahid Hossain,Most. Sharmin Sultana Samu,Md. Kamrozzaman Bhuiyan,Farhad Uz Zaman,Md. Rakibul Islam
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: accepted for publication in 2025 28th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT)
Abstract:The fast evolution of generative models has heightened the demand for reliable detection of AI-generated images. To tackle this challenge, we introduce FUSE, a hybrid system that combines spectral features extracted through Fast Fourier Transform with semantic features obtained from the CLIP’s Vision encoder. The features are fused into a joint representation and trained progressively in two stages. Evaluations on GenImage, WildFake, DiTFake, GPT-ImgEval and Chameleon datasets demonstrate strong generalization across multiple generators. Our FUSE (Stage 1) model demonstrates state-of-the-art results on the Chameleon benchmark. It also attains 91.36% mean accuracy on the GenImage dataset, 88.71% accuracy across all tested generators, and a mean Average Precision of 94.96%. Stage 2 training further improves performance for most generators. Unlike existing methods, which often perform poorly on high-fidelity images in Chameleon, our approach maintains robustness across diverse generators. These findings highlight the benefits of integrating spectral and semantic features for generalized detection of images generated by AI.
zh
[CV-50] BeHGAN: Bengali Handwritten Word Generation from Plain Text Using Generative Adversarial Networks
【速读】:该论文旨在解决 Bengali 语言 handwritten text generation (HTG) 数据集稀缺且生成效果受限的问题。当前 HTG 领域因个体书写风格差异大而面临挑战,尤其对于像孟加拉语这样研究较少的语言,缺乏高质量、多样化的手写数据成为主要瓶颈。解决方案的关键在于构建并使用一个自收集的孟加拉语手写样本数据集,涵盖约五百名不同年龄和性别个体的书写样本,并通过预处理确保图像的一致性与质量。基于此数据集,作者提出了一种能够从输入纯文本生成多样化手写文本的方法,从而推动孟加拉语手写生成技术的发展。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21694
作者: Md. Rakibul Islam,Md. Kamrozzaman Bhuiyan,Safwan Muntasir,Arifur Rahman Jawad,Most. Sharmin Sultana Samu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted for publication in 2025 28th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT)
Abstract:Handwritten Text Recognition (HTR) is a well-established research area. In contrast, Handwritten Text Generation (HTG) is an emerging field with significant potential. This task is challenging due to the variation in individual handwriting styles. A large and diverse dataset is required to generate realistic handwritten text. However, such datasets are difficult to collect and are not readily available. Bengali is the fifth most spoken language in the world. While several studies exist for languages such as English and Arabic, Bengali handwritten text generation has received little attention. To address this gap, we propose a method for generating Bengali handwritten words. We developed and used a self-collected dataset of Bengali handwriting samples. The dataset includes contributions from approximately five hundred individuals across different ages and genders. All images were pre-processed to ensure consistency and quality. Our approach demonstrates the ability to produce diverse handwritten outputs from input plain text. We believe this work contributes to the advancement of Bengali handwriting generation and can support further research in this area.
zh
[CV-51] Prior-AttUNet: Retinal OCT Fluid Segmentation Based on Normal Anatomical Priors and Attention Gating
【速读】:该论文旨在解决光学相干断层扫描(Optical Coherence Tomography, OCT)图像中黄斑水肿(macular edema)区域分割的难题,尤其是由边界模糊和跨设备异质性带来的挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出Prior-AttUNet模型,该模型采用混合双路径架构:一方面通过变分自编码器(Variational Autoencoder)提供多尺度正常解剖先验信息,另一方面在分割主干网络中引入密集连接块与空间金字塔池化模块以增强上下文特征提取能力;此外,设计了一种由解剖先验引导的三重注意力机制,在解码阶段动态调节特征重要性,显著提升边界识别精度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21693
作者: Li Yang,Yuting Liu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Accurate segmentation of macular edema, a hallmark pathological feature in vision-threatening conditions such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic macular edema, is essential for clinical diagnosis and management. To overcome the challenges of segmenting fluid regions in optical coherence tomography (OCT) images-notably ambiguous boundaries and cross-device heterogeneity-this study introduces Prior-AttUNet, a segmentation model augmented with generative anatomical priors. The framework adopts a hybrid dual-path architecture that integrates a generative prior pathway with a segmentation network. A variational autoencoder supplies multi-scale normative anatomical priors, while the segmentation backbone incorporates densely connected blocks and spatial pyramid pooling modules to capture richer contextual information. Additionally, a novel triple-attention mechanism, guided by anatomical priors, dynamically modulates feature importance across decoding stages, substantially enhancing boundary delineation. Evaluated on the public RETOUCH benchmark, Prior-AttUNet achieves excellent performance across three OCT imaging devices (Cirrus, Spectralis, and Topcon), with mean Dice similarity coefficients of 93.93%, 95.18%, and 93.47%, respectively. The model maintains a low computational cost of 0.37 TFLOPs, striking an effective balance between segmentation precision and inference efficiency. These results demonstrate its potential as a reliable tool for automated clinical analysis.
zh
[CV-52] ShinyNeRF: Digitizing Anisotropic Appearance in Neural Radiance Fields
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有神经辐射场(Neural Radiance Fields, NeRF)方法在重建各向异性镜面反射表面(如拉丝金属)时精度不足的问题。其关键解决方案在于提出ShinyNeRF框架,通过学习出射辐射的编码混合分布,将各向同性von Mises-Fisher(vMF)分布近似为各向异性球面高斯(Anisotropic Spherical Gaussian, ASG)分布,从而联合估计表面法向量、切向量、镜面集中度及各向异性幅度等物理属性,实现对复杂材质的高保真建模与可解释编辑。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21692
作者: Albert Barreiro,Roger Marí,Rafael Redondo,Gloria Haro,Carles Bosch
机构: Eurecat, Centre Tecnològic de Catalunya; Universitat Pompeu Fabra; Universitat de Vic - UCC
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Graphics (cs.GR)
备注:
Abstract:Recent advances in digitization technologies have transformed the preservation and dissemination of cultural heritage. In this vein, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have emerged as a leading technology for 3D digitization, delivering representations with exceptional realism. However, existing methods struggle to accurately model anisotropic specular surfaces, typically observed, for example, on brushed metals. In this work, we introduce ShinyNeRF, a novel framework capable of handling both isotropic and anisotropic reflections. Our method is capable of jointly estimating surface normals, tangents, specular concentration, and anisotropy magnitudes of an Anisotropic Spherical Gaussian (ASG) distribution, by learning an approximation of the outgoing radiance as an encoded mixture of isotropic von Mises-Fisher (vMF) distributions. Experimental results show that ShinyNeRF not only achieves state-of-the-art performance on digitizing anisotropic specular reflections, but also offers plausible physical interpretations and editing of material properties compared to existing methods.
zh
[CV-53] Analyzing the Mechanism of Attention Collapse in VGGT from a Dynamics Perspective
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉几何接地变换器(Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer, VGGT)在处理长序列输入时出现的全局自注意力层崩溃问题:当输入序列超过数百帧时,注意力矩阵迅速退化为近似秩一矩阵,导致token特征空间退化至几乎一维,进而引发重建误差累积。解决方案的关键在于将全局注意力迭代过程建模为一种退化的扩散过程,并通过严格的数学分析证明,token特征流以 $ O(1/L) $ 的速率收敛到狄拉克型测度,从而推导出一个闭式均场偏微分方程,精确预测了实验中观察到的秩坍缩现象。该理论不仅定量匹配注意力热图演化和已有实验结果,还解释了token合并修复策略(周期性移除冗余token)为何能减缓有效扩散系数、延迟崩溃但不增加额外参数。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21691
作者: Huan Li,Longjun Luo,Yuling Shi,Xiaodong Gu
机构: Huazhong University of Science and Technology (华中科技大学); Guangdong University of Technology (广东工业大学); Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 8 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:Visual Geometry Grounded Transformer (VGGT) delivers state-of-the-art feed-forward 3D reconstruction, yet its global self-attention layer suffers from a drastic collapse phenomenon when the input sequence exceeds a few hundred frames: attention matrices rapidly become near rank-one, token geometry degenerates to an almost one-dimensional subspace, and reconstruction error accumulates this http URL this report,we establish a rigorous mathematical explanation of the collapse by viewing the global-attention iteration as a degenerate diffusion this http URL prove that,in VGGT, the token-feature flow converges toward a Dirac-type measure at a O(1/L) rate, where L is the layer index, yielding a closed-form mean-field partial differential equation that precisely predicts the empirically observed rank this http URL theory quantitatively matches the attention-heat-map evolution and a series of experiments outcomes reported in relevant works and explains why its token-merging remedy – which periodically removes redundant tokens – slows the effective diffusion coefficient and thereby delays collapse without additional this http URL believe the analysis provides a principled lens for interpreting future scalable 3D-vision transformers,and we highlight its potential for multi-modal generalization.
zh
[CV-54] SlideChain: Semantic Provenance for Lecture Understanding via Blockchain Registration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现代视觉-语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在教育内容生成与解释中面临的语义输出不可验证、不可复现和难以审计的问题,尤其是在高风险的定量STEM领域。其核心挑战在于不同模型家族、推理设置和计算环境导致的语义不一致性,削弱了AI生成教学材料的可靠性。解决方案的关键是提出SlideChain——一个基于区块链的溯源框架,通过为每张幻灯片的多模态语义提取结果构建结构化溯源记录,并将这些记录的加密哈希锚定于本地EVM兼容区块链上,从而实现防篡改的可审计性和持久的语义基线。该方法首次系统性地分析了跨模型语义分歧、相似性及课程级变异性,验证了其在保证完整性、可复现性和扩展性方面的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21684
作者: Md Motaleb Hossen Manik,Md Zabirul Islam,Ge Wang
机构: Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (伦斯勒理工学院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Modern vision–language models (VLMs) are increasingly used to interpret and generate educational content, yet their semantic outputs remain challenging to verify, reproduce, and audit over time. Inconsistencies across model families, inference settings, and computing environments undermine the reliability of AI-generated instructional material, particularly in high-stakes and quantitative STEM domains. This work introduces SlideChain, a blockchain-backed provenance framework designed to provide verifiable integrity for multimodal semantic extraction at scale. Using the SlideChain Slides Dataset-a curated corpus of 1,117 medical imaging lecture slides from a university course-we extract concepts and relational triples from four state-of-the-art VLMs and construct structured provenance records for every slide. SlideChain anchors cryptographic hashes of these records on a local EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine)-compatible blockchain, providing tamper-evident auditability and persistent semantic baselines. Through the first systematic analysis of semantic disagreement, cross-model similarity, and lecture-level variability in multimodal educational content, we reveal pronounced cross-model discrepancies, including low concept overlap and near-zero agreement in relational triples on many slides. We further evaluate gas usage, throughput, and scalability under simulated deployment conditions, and demonstrate perfect tamper detection along with deterministic reproducibility across independent extraction runs. Together, these results show that SlideChain provides a practical and scalable step toward trustworthy, verifiable multimodal educational pipelines, supporting long-term auditability, reproducibility, and integrity for AI-assisted instructional systems.
zh
[CV-55] Contrastive Graph Modeling for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决跨域少样本医学图像分割(Cross-domain few-shot medical image segmentation, CD-FSMIS)中因域特定信息被过滤而导致的跨域性能受限与源域精度下降的问题。现有方法为提升泛化能力常忽略域特异性特征,从而削弱了模型在目标域的适应性和源域上的分割准确性。其解决方案的关键在于提出对比图建模(Contrastive Graph Modeling, C-Graph)框架,通过将图像特征表示为图结构(像素为节点、语义亲和性为边),引入结构先验图(Structural Prior Graph, SPG)层以显式建模节点间依赖关系并传递目标类别结构信息;在此基础上设计子图匹配解码(Subgraph Matching Decoding, SMD)机制,利用节点间的语义关联引导预测,并结合混淆最小化节点对比(Confusion-minimizing Node Contrast, CNC)损失函数,在图空间中增强节点可区分性,从而缓解节点歧义与子图异质性问题。该方法在多个跨域基准上显著优于现有方法,同时保持对源域的良好分割性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21683
作者: Yuntian Bo,Tao Zhou,Zechao Li,Haofeng Zhang,Ling Shao
机构: Nanjing University of Science and Technology (南京理工大学); University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (中国科学院大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted to IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging (T-MI), 2026
Abstract:Cross-domain few-shot medical image segmentation (CD-FSMIS) offers a promising and data-efficient solution for medical applications where annotations are severely scarce and multimodal analysis is required. However, existing methods typically filter out domain-specific information to improve generalization, which inadvertently limits cross-domain performance and degrades source-domain accuracy. To address this, we present Contrastive Graph Modeling (C-Graph), a framework that leverages the structural consistency of medical images as a reliable domain-transferable prior. We represent image features as graphs, with pixels as nodes and semantic affinities as edges. A Structural Prior Graph (SPG) layer is proposed to capture and transfer target-category node dependencies and enable global structure modeling through explicit node interactions. Building upon SPG layers, we introduce a Subgraph Matching Decoding (SMD) mechanism that exploits semantic relations among nodes to guide prediction. Furthermore, we design a Confusion-minimizing Node Contrast (CNC) loss to mitigate node ambiguity and subgraph heterogeneity by contrastively enhancing node discriminability in the graph space. Our method significantly outperforms prior CD-FSMIS approaches across multiple cross-domain benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art performance while simultaneously preserving strong segmentation accuracy on the source domain.
zh
[CV-56] UniPercept: Towards Unified Perceptual-Level Image Understanding across Aesthetics Quality Structure and Texture
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Models, MLLMs)在感知层图像理解能力上的局限性,尤其在美学(Aesthetics)、质量(Quality)、结构与纹理(Structure and Texture)等感知维度上的表现不足。解决方案的关键在于提出UniPercept-Bench——一个统一的感知层图像理解基准框架,构建了分层定义体系与大规模数据集,并设计了基于领域自适应预训练(Domain-Adaptive Pre-Training)和任务对齐强化学习(Task-Aligned Reinforcement Learning)的强基线模型UniPercept,从而实现跨视觉评分(Visual Rating, VR)与视觉问答(Visual Question Answering, VQA)任务的鲁棒泛化能力。该方案不仅提升了MLLMs在感知层面的理解性能,还可作为文本到图像生成中的即插即用奖励模型(plug-and-play reward model),为后续研究奠定了坚实基础。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21675
作者: Shuo Cao,Jiayang Li,Xiaohui Li,Yuandong Pu,Kaiwen Zhu,Yuanting Gao,Siqi Luo,Yi Xin,Qi Qin,Yu Zhou,Xiangyu Chen,Wenlong Zhang,Bin Fu,Yu Qiao,Yihao Liu
机构: University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学); Shanghai AI Laboratory (上海人工智能实验室); Peking University (北京大学); Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); Tsinghua University (清华大学); Nanjing University (南京大学); Sun Yat-sen University (中山大学); Tele-AI (Tele-AI)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 27 pages, 14 figures, 17 tables
Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in visual understanding tasks such as visual grounding, segmentation, and captioning. However, their ability to perceive perceptual-level image features remains limited. In this work, we present UniPercept-Bench, a unified framework for perceptual-level image understanding across three key domains: Aesthetics, Quality, Structure and Texture. We establish a hierarchical definition system and construct large-scale datasets to evaluate perceptual-level image understanding. Based on this foundation, we develop a strong baseline UniPercept trained via Domain-Adaptive Pre-Training and Task-Aligned RL, enabling robust generalization across both Visual Rating (VR) and Visual Question Answering (VQA) tasks. UniPercept outperforms existing MLLMs on perceptual-level image understanding and can serve as a plug-and-play reward model for text-to-image generation. This work defines Perceptual-Level Image Understanding in the era of MLLMs and, through the introduction of a comprehensive benchmark together with a strong baseline, provides a solid foundation for advancing perceptual-level multimodal image understanding.
zh
[CV-57] Comparative Analysis of Deep Learning Models for Perception in Autonomous Vehicles
【速读】:该论文旨在解决自动驾驶车辆(AV)感知系统中目标检测模型的效率与精度平衡问题,即如何在保证高检测准确率的同时提升训练效率。其解决方案的关键在于对两种新兴深度学习(DL)模型——YOLO-NAS和YOLOv8s进行对比实验,基于自建数据集评估二者在训练时间与检测准确率上的表现差异;结果表明,YOLOv8s模型在保持83%检测准确率的同时,相较YOLO-NAS模型节省了75%的训练时间,从而为实际应用中选择更高效的感知模型提供了实证依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21673
作者: Jalal Khan
机构: United Arab Emirates University (阿联酋大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 6 pages, 3 figures
Abstract:Recently, a plethora of machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) algorithms have been proposed to achieve the efficiency, safety, and reliability of autonomous vehicles (AVs). The AVs use a perception system to detect, localize, and identify other vehicles, pedestrians, and road signs to perform safe navigation and decision-making. In this paper, we compare the performance of DL models, including YOLO-NAS and YOLOv8, for a detection-based perception task. We capture a custom dataset and experiment with both DL models using our custom dataset. Our analysis reveals that the YOLOv8s model saves 75% of training time compared to the YOLO-NAS model. In addition, the YOLOv8s model (83%) outperforms the YOLO-NAS model (81%) when the target is to achieve the highest object detection accuracy. These comparative analyses of these new emerging DL models will allow the relevant research community to understand the models’ performance under real-world use case scenarios.
zh
[CV-58] he Deepfake Detective: Interpreting Neural Forensics Through Sparse Features and Manifolds
【速读】:该论文旨在解决深度伪造检测模型(deepfake detection models)决策过程不透明的问题,即如何揭示其内部工作机制以增强模型的可解释性。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种机制可解释性框架,结合稀疏自编码器(sparse autoencoder, SAE)对网络内部表征的分析与一种新颖的取证流形分析方法,该方法通过控制性地操纵伪造痕迹(forensic artifacts)来探测模型特征的响应。研究表明,仅有少量潜在特征在每层中被激活,且模型特征流形的几何特性(如内在维度、曲率和特征选择性)随不同类型的伪造痕迹系统性变化,从而首次实现了对深度伪造检测模型“黑箱”内部机制的初步解析,并为开发更具可解释性和鲁棒性的模型提供了依据。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21670
作者: Subramanyam Sahoo,Jared Junkin
机构: Berkeley AI Safety Initiative (BASIS); University of California, Berkeley; Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering; Johns Hopkins University
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 10 pages, 5 figures, Initial Work
Abstract:Deepfake detection models have achieved high accuracy in identifying synthetic media, but their decision processes remain largely opaque. In this paper we present a mechanistic interpretability framework for deepfake detection applied to a vision-language model. Our approach combines a sparse autoencoder (SAE) analysis of internal network representations with a novel forensic manifold analysis that probes how the model’s features respond to controlled forensic artifact manipulations. We demonstrate that only a small fraction of latent features are actively used in each layer, and that the geometric properties of the model’s feature manifold, including intrinsic dimensionality, curvature, and feature selectivity, vary systematically with different types of deepfake artifacts. These insights provide a first step toward opening the “black box” of deepfake detectors, allowing us to identify which learned features correspond to specific forensic artifacts and to guide the development of more interpretable and robust models.
zh
[CV-59] Omni-Weather: Unified Multimodal Foundation Model for Weather Generation and Understanding ICLR2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决天气建模中生成与理解任务长期分离的问题,即现有方法通常将天气预测(generation)与机制解释(understanding)视为独立目标,缺乏统一框架。解决方案的关键在于提出Omni-Weather——首个将天气生成与理解统一于单一架构中的多模态基础模型。其核心创新包括:1)引入雷达编码器用于天气生成任务,并通过共享的自注意力机制实现生成与理解的联合处理;2)构建Chain-of-Thought数据集以支持因果推理,提升输出的可解释性与感知质量。实验表明,该模型在生成和理解两个维度均达到最先进性能,且二者相互促进,验证了统一建模的有效性与价值。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21643
作者: Zhiwang Zhou,Yuandong Pu,Xuming He,Yidi Liu,Yixin Chen,Junchao Gong,Xiang Zhuang,Wanghan Xu,Qinglong Cao,Shixiang Tang,Yihao Liu,Wenlong Zhang,Lei Bai
机构: Tongji University (同济大学); Shanghai AI Laboratory; Shanghai Jiao Tong University (上海交通大学); Zhejiang University (浙江大学); University of Science and Technology of China (中国科学技术大学); UCLA (加州大学洛杉矶分校)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 25 pages, 12 figures. ICLR 2026 submission
Abstract:Weather modeling requires both accurate prediction and mechanistic interpretation, yet existing methods treat these goals in isolation, separating generation from understanding. To address this gap, we present Omni-Weather, the first multimodal foundation model that unifies weather generation and understanding within a single architecture. Omni-Weather integrates a radar encoder for weather generation tasks, followed by unified processing using a shared self-attention mechanism. Moreover, we construct a Chain-of-Thought dataset for causal reasoning in weather generation, enabling interpretable outputs and improved perceptual quality. Extensive experiments show Omni-Weather achieves state-of-the-art performance in both weather generation and understanding. Our findings further indicate that generative and understanding tasks in the weather domain can mutually enhance each other. Omni-Weather also demonstrates the feasibility and value of unifying weather generation and understanding.
zh
[CV-60] rackTeller: Temporal Multimodal 3D Grounding for Behavior-Dependent Object References
【速读】:该论文旨在解决动态3D驾驶场景中基于自然语言的物体定位(language-based 3D grounding)问题,尤其针对通过近期运动或短时交互描述目标的参照表达(referring expressions),这类表达无法仅依赖静态外观或几何特征进行准确识别。解决方案的关键在于提出TrackTeller框架,其核心创新包括:1)融合LiDAR与图像信息构建统一的UniScene表示以对齐文本语义;2)采用语言条件解码生成语义感知的3D候选区域;3)利用运动历史和短期动态信息进行时序推理,从而实现更鲁棒的多帧联合接地决策。实验表明,该方法在NuPrompt基准上显著优于现有基线,实现了平均多目标跟踪准确率提升70%,误报频率降低3.15–3.4倍。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21641
作者: Jiahong Yu,Ziqi Wang,Hailiang Zhao,Wei Zhai,Xueqiang Yan,Shuiguang Deng
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); Fudan University (复旦大学); Huawei Technologies Ltd. (华为技术有限公司)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Understanding natural-language references to objects in dynamic 3D driving scenes is essential for interactive autonomous systems. In practice, many referring expressions describe targets through recent motion or short-term interactions, which cannot be resolved from static appearance or geometry alone. We study temporal language-based 3D grounding, where the objective is to identify the referred object in the current frame by leveraging multi-frame observations. We propose TrackTeller, a temporal multimodal grounding framework that integrates LiDAR-image fusion, language-conditioned decoding, and temporal reasoning in a unified architecture. TrackTeller constructs a shared UniScene representation aligned with textual semantics, generates language-aware 3D proposals, and refines grounding decisions using motion history and short-term dynamics. Experiments on the NuPrompt benchmark demonstrate that TrackTeller consistently improves language-grounded tracking performance, outperforming strong baselines with a 70% relative improvement in Average Multi-Object Tracking Accuracy and a 3.15-3.4 times reduction in False Alarm Frequency.
zh
[CV-61] raining-Free Disentangled Text-Guided Image Editing via Sparse Latent Constraints
【速读】:该论文旨在解决文本驱动图像编辑中属性纠缠(attribute entanglement)的问题,即在修改目标属性(如添加刘海)时,会无意间改变其他语义属性(如身份或外观)。其解决方案的关键在于改进原始的Predict, Prevent, and Evaluate (PPE) 框架中的正则化策略:通过引入基于L1范数的稀疏性约束,对潜在空间(latent space)操作施加稀疏性限制,从而促使编辑更加聚焦和可控,有效减少非目标属性的意外变化,同时保持面部身份的一致性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21637
作者: Mutiara Shabrina,Nova Kurnia Putri,Jefri Satria Ferdiansyah,Sabita Khansa Dewi,Novanto Yudistira
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Text-driven image manipulation often suffers from attribute entanglement, where modifying a target attribute (e.g., adding bangs) unintentionally alters other semantic properties such as identity or appearance. The Predict, Prevent, and Evaluate (PPE) framework addresses this issue by leveraging pre-trained vision-language models for disentangled editing. In this work, we analyze the PPE framework, focusing on its architectural components, including BERT-based attribute prediction and StyleGAN2-based image generation on the CelebA-HQ dataset. Through empirical analysis, we identify a limitation in the original regularization strategy, where latent updates remain dense and prone to semantic leakage. To mitigate this issue, we introduce a sparsity-based constraint using L1 regularization on latent space manipulation. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach enforces more focused and controlled edits, effectively reducing unintended changes in non-target attributes while preserving facial identity.
zh
[CV-62] SymDrive: Realistic and Controllable Driving Simulator via Symmetric Auto-regressive Online Restoration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决自动驾驶(Autonomous Driving, AD)中因长尾数据稀缺导致的高保真、可交互3D仿真难题,现有方法难以同时实现逼真的渲染与交通要素的精准编辑,尤其在大视角新视图合成时易出现几何或光照伪影。解决方案的关键在于提出SymDrive——一个基于扩散模型的统一框架,其核心创新为引入对称自回归在线修复(Symmetric Auto-regressive Online Restoration)范式:通过构建成对对称视图,利用真实场景引导的双视图公式恢复细节,并采用自回归策略保证横向视图的一致性生成;此外,借助该修复能力实现无需训练的融合机制,将车辆插入视为上下文感知的图像修复(context-aware inpainting),从而确保光照与阴影一致性,显著提升新视图增强和3D车辆插入的真实性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21618
作者: Zhiyuan Liu,Daocheng Fu,Pinlong Cai,Lening Wang,Ying Liu,Yilong Ren,Botian Shi,Jianqiang Wang
机构: Tsinghua University (清华大学); Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory; Beihang University (北京航空航天大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Robotics (cs.RO)
备注:
Abstract:High-fidelity and controllable 3D simulation is essential for addressing the long-tail data scarcity in Autonomous Driving (AD), yet existing methods struggle to simultaneously achieve photorealistic rendering and interactive traffic editing. Current approaches often falter in large-angle novel view synthesis and suffer from geometric or lighting artifacts during asset manipulation. To address these challenges, we propose SymDrive, a unified diffusion-based framework capable of joint high-quality rendering and scene editing. We introduce a Symmetric Auto-regressive Online Restoration paradigm, which constructs paired symmetric views to recover fine-grained details via a ground-truth-guided dual-view formulation and utilizes an auto-regressive strategy for consistent lateral view generation. Furthermore, we leverage this restoration capability to enable a training-free harmonization mechanism, treating vehicle insertion as context-aware inpainting to ensure seamless lighting and shadow consistency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SymDrive achieves state-of-the-art performance in both novel-view enhancement and realistic 3D vehicle insertion.
zh
[CV-63] CausalFSFG: Rethinking Few-Shot Fine-Grained Visual Categorization from Causal Perspective
【速读】:该论文旨在解决少样本细粒度视觉分类(Few-shot Fine-grained Visual Categorization, FS-FGVC)中因支持样本集作为混杂变量(confounding variable)而导致的偏差数据分布问题,这种偏差会误导判别性特征的提取,从而降低分类性能。解决方案的关键在于引入因果推断思想,构建结构因果模型(Structural Causal Model, SCM),通过两个核心组件消除虚假相关性:(1) 样本级干预的多尺度编码器(Interventional Multi-scale Encoder, IMSE),用于干预支持样本分布;(2) 特征级干预的掩码特征重建模块(Interventional Masked Feature Reconstruction, IMFR),用于干预特征空间中的伪关联,从而揭示输入到子类别之间的真实因果关系,显著提升FS-FGVC的性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21617
作者: Zhiwen Yang,Jinglin Xu,Yuxin Pen
机构: Peking University (北京大学); University of Science and Technology Beijing (北京科技大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 12 pages, 5 figures, accepted by IEEE TMM
Abstract:Few-shot fine-grained visual categorization (FS-FGVC) focuses on identifying various subcategories within a common superclass given just one or few support examples. Most existing methods aim to boost classification accuracy by enriching the extracted features with discriminative part-level details. However, they often overlook the fact that the set of support samples acts as a confounding variable, which hampers the FS-FGVC performance by introducing biased data distribution and misguiding the extraction of discriminative features. To address this issue, we propose a new causal FS-FGVC (CausalFSFG) approach inspired by causal inference for addressing biased data distributions through causal intervention. Specifically, based on the structural causal model (SCM), we argue that FS-FGVC infers the subcategories (i.e., effect) from the inputs (i.e., cause), whereas both the few-shot condition disturbance and the inherent fine-grained nature (i.e., large intra-class variance and small inter-class variance) lead to unobservable variables that bring spurious correlations, compromising the final classification performance. To further eliminate the spurious correlations, our CausalFSFG approach incorporates two key components: (1) Interventional multi-scale encoder (IMSE) conducts sample-level interventions, (2) Interventional masked feature reconstruction (IMFR) conducts feature-level interventions, which together reveal real causalities from inputs to subcategories. Extensive experiments and thorough analyses on the widely-used public datasets, including CUB-200-2011, Stanford Dogs, and Stanford Cars, demonstrate that our CausalFSFG achieves new state-of-the-art performance. The code is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-64] AMEing Long Contexts in Personalization: Towards Training-Free and State-Aware MLLM Personalized Assistant KDD2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Model, MLLM)个性化任务中长期上下文对话能力不足的问题。现有方法通常仅关注静态的视觉识别与文本替换,忽略了在持续对话中对个性化概念(personalized concept)随时间演变的感知与响应能力,从而限制了模型在真实场景下的交互质量。解决方案的关键在于提出首个面向长上下文MLLM个性化的评估基准LCMP,并设计了一种无需训练的状态感知框架TAME。TAME通过引入双记忆机制分别管理个性化概念的时间变化和持久特征,并结合一种新颖的“检索-对齐增强生成”(Retrieve-then-Align Augmented Generation, RA2G)范式,在不依赖额外训练的前提下,从多记忆知识库中提取语境适配信息以提升复杂查询下的交互表现,显著增强了模型在长期对话中的适应性与个性化水平。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21616
作者: Rongpei Hong,Jian Lang,Ting Zhong,Yong Wang,Fan Zhou
机构: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (电子科技大学); Aiwen Technology Co., Ltd. (艾文科技有限公司); Intelligent Digital Media Technology Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (四川省智能数字媒体技术重点实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted by KDD 2026 research track. Code and data are available at this https URL
Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) Personalization is a critical research problem that facilitates personalized dialogues with MLLMs targeting specific entities (known as personalized concepts). However, existing methods and benchmarks focus on the simple, context-agnostic visual identification and textual replacement of the personalized concept (e.g., “A yellow puppy” - “Your puppy Mochi”), overlooking the ability to support long-context conversations. An ideal personalized MLLM assistant is capable of engaging in long-context dialogues with humans and continually improving its experience quality by learning from past dialogue histories. To bridge this gap, we propose LCMP, the first Long-Context MLLM Personalization evaluation benchmark. LCMP assesses the capability of MLLMs in perceiving variations of personalized concepts and generating contextually appropriate personalized responses that reflect these variations. As a strong baseline for LCMP, we introduce a novel training-free and state-aware framework TAME. TAME endows MLLMs with double memories to manage the temporal and persistent variations of each personalized concept in a differentiated manner. In addition, TAME incorporates a new training-free Retrieve-then-Align Augmented Generation (RA2G) paradigm. RA2G introduces an alignment step to extract the contextually fitted information from the multi-memory retrieved knowledge to the current questions, enabling better interactions for complex real-world user queries. Experiments on LCMP demonstrate that TAME achieves the best performance, showcasing remarkable and evolving interaction experiences in long-context scenarios.
zh
[CV-65] Robustness and Scalability Of Machine Learning for Imbalanced Clinical Data in Emergency and Critical Care
【速读】:该论文旨在解决急诊和重症监护环境中预测模型在严重数据不平衡情况下的可靠性与计算效率问题。临床数据的偏斜会削弱模型对罕见但关键结局的预测能力,从而影响其在真实世界中的应用效果。解决方案的关键在于系统评估经典机器学习模型(如XGBoost)、先进深度学习模型(如TabNet)及其轻量化变体TabResNet在MIMIC-IV-ED和eICU数据集上的表现,发现树基集成方法(特别是XGBoost)在不同不平衡水平下表现出最稳定的性能,并且具有良好的可扩展性;而深度学习模型虽具备强大表征能力,但在不平衡数据下性能下降显著且计算成本较高,TabResNet虽降低了复杂度但仍未能超越树基模型。因此,研究指出,在高风险、时效性强的临床场景中,模型的鲁棒性和计算效率应优先于架构复杂度,树基集成方法是当前最实用的选择。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21602
作者: Yusuf Brima,Marcellin Atemkeng
机构: Osnabrück University (奥斯纳布吕克大学); Rhodes University (罗德斯大学); National Institute for Theoretical and Computational Sciences (国家理论与计算科学研究所)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Emergency and intensive care environments require predictive models that are both accurate and computationally efficient, yet clinical data in these settings are often severely imbalanced. Such skewness undermines model reliability, particularly for rare but clinically crucial outcomes, making robustness and scalability essential for real-world usage. In this paper, we systematically evaluate the robustness and scalability of classical machine learning models on imbalanced tabular data from MIMIC-IV-ED and eICU. Class imbalance was quantified using complementary metrics, and we compared the performance of tree-based methods, the state-of-the-art TabNet deep learning model, and a custom lightweight residual network. TabResNet was designed as a computationally efficient alternative to TabNet, replacing its complex attention mechanisms with a streamlined residual architecture to maintain representational capacity for real-time clinical use. All models were optimized via a Bayesian hyperparameter search and assessed on predictive performance, robustness to increasing imbalance, and computational scalability. Our results, on seven clinically vital predictive tasks, show that tree-based methods, particularly XGBoost, consistently achieved the most stable performance across imbalance levels and scaled efficiently with sample size. Deep tabular models degraded more sharply under imbalance and incurred higher computational costs, while TabResNet provided a lighter alternative to TabNet but did not surpass ensemble benchmarks. These findings indicate that in emergency and critical care, robustness to imbalance and computational scalability could outweigh architectural complexity. Tree-based ensemble methods currently offer the most practical and clinically feasible choice, equipping practitioners with a framework for selecting models suited to high-stakes, time-sensitive environments.
zh
[CV-66] GaussianEM: Model compositional and conformational heterogeneity using 3D Gaussians
【速读】:该论文旨在解决冷冻电镜(cryo-EM)数据中同时存在连续运动与离散构象状态时,如何准确建模蛋白质构象异质性的问题。其关键解决方案是提出GaussianEM框架,该框架基于高斯伪原子表示,采用双编码器-单解码器架构,将实验cryo-EM图像映射为独立的高斯成分,并通过高斯参数的变化来刻画结构变异性,从而在保持局部结构一致性的同时,直观且可解释地描述构象变化,并自然衔接密度模型与原子模型之间的鸿沟。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21599
作者: Bintao He,Yiran Cheng,Hongjia Li,Xiang Gao,Xin Gao,Fa Zhang,Renmin Han
机构: King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST); Beijing Institute of Technology (北京理工大学); Shandong University (山东大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Understanding protein flexibility and its dynamic interactions with other molecules is essential for protein function study. Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) provides an opportunity to directly observe macromolecular dynamics. However, analyzing datasets that contain both continuous motions and discrete states remains highly challenging. Here we present GaussianEM, a Gaussian pseudo-atomic framework that simultaneously models compositional and conformational heterogeneity from experimental cryo-EM images. GaussianEM employs a two-encoder-one-decoder architecture to map an image to its individual Gaussian components, and represent structural variability through changes in Gaussian parameters. This approach provides an intuitive and interpretable description of conformational changes, preserves local structural consistency along the transition trajectories, and naturally bridges the gap between density-based models and corresponding atomic models. We demonstrate the effectiveness of GaussianEM on both simulated and experimental datasets.
zh
[CV-67] From Shallow Humor to Metaphor: Towards Label-Free Harmful Meme Detection via LMM Agent Self-Improvement KDD2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决在线媒体中有害模因(harmful memes)检测面临的两大挑战:一是现有方法严重依赖大规模标注数据进行训练,导致人工标注成本高且难以适应有害内容的持续演化;二是缺乏对复杂、隐蔽型模因的有效识别能力。解决方案的关键在于提出ALARM框架,其核心创新是利用“浅层”模因(shallow memes)中的表达信息,通过自监督机制迭代提升模型对复杂模因的检测能力。具体而言,ALARM引入基于置信度的显式模因识别机制以自动标注显式模因,并设计了一种成对学习引导的LMM代理自我改进范式,将显式模因重构为对比对(正例与负例),使大型多模态模型(Large Multimodal Model, LMM)代理能够自主提取高层检测线索,从而实现无需标签的高效、自适应检测性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21598
作者: Jian Lang,Rongpei Hong,Ting Zhong,Leiting Chen,Qiang Gao,Fan Zhou
机构: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (电子科技大学); Southwestern University of Finance and Economics (西南财经大学); Intelligent Digital Media Technology Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (四川省智能数字媒体技术重点实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 12 pages. Accepted by KDD 2026 research track. Codes are released at this https URL
Abstract:The proliferation of harmful memes on online media poses significant risks to public health and stability. Existing detection methods heavily rely on large-scale labeled data for training, which necessitates substantial manual annotation efforts and limits their adaptability to the continually evolving nature of harmful content. To address these challenges, we present ALARM, the first lAbeL-free hARmful Meme detection framework powered by Large Multimodal Model (LMM) agent self-improvement. The core innovation of ALARM lies in exploiting the expressive information from “shallow” memes to iteratively enhance its ability to tackle more complex and subtle ones. ALARM consists of a novel Confidence-based Explicit Meme Identification mechanism that isolates the explicit memes from the original dataset and assigns them pseudo-labels. Besides, a new Pairwise Learning Guided Agent Self-Improvement paradigm is introduced, where the explicit memes are reorganized into contrastive pairs (positive vs. negative) to refine a learner LMM agent. This agent autonomously derives high-level detection cues from these pairs, which in turn empower the agent itself to handle complex and challenging memes effectively. Experiments on three diverse datasets demonstrate the superior performance and strong adaptability of ALARM to newly evolved memes. Notably, our method even outperforms label-driven methods. These results highlight the potential of label-free frameworks as a scalable and promising solution for adapting to novel forms and topics of harmful memes in dynamic online environments.
zh
[CV-68] UltraLBM-UNet: Ultralight Bidirectional Mamba-based Model for Skin Lesion Segmentation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决皮肤病变分割任务中现有方法在准确性、鲁棒性和资源效率方面存在的局限性,尤其是低性能与高计算复杂度的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种轻量级U-Net变体UltraLBM-UNet,该模型融合了基于双向Mamba的全局建模机制与多分支局部特征感知结构,通过高效局部特征注入和双向状态空间建模,在保持计算紧凑性的同时增强跨空间维度的上下文交互能力,从而实现高精度且适合即时诊疗部署的病变分割效果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21584
作者: Linxuan Fan(1),Juntao Jiang(2),Weixuan Liu(3),Zhucun Xue(2),Jiajun Lv(2),Jiangning Zhang(2),Yong Liu(2) ((1) Data Science Institute, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, USA (2) College of Control Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China (3) School of Computer Science and Technology, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China)
机构: Vanderbilt University (范德比尔特大学); Zhejiang University (浙江大学); East China Normal University (华东师范大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 12 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:Skin lesion segmentation is a crucial step in dermatology for guiding clinical decision-making. However, existing methods for accurate, robust, and resource-efficient lesion analysis have limitations, including low performance and high computational complexity. To address these limitations, we propose UltraLBM-UNet, a lightweight U-Net variant that integrates a bidirectional Mamba-based global modeling mechanism with multi-branch local feature perception. The proposed architecture integrates efficient local feature injection with bidirectional state-space modeling, enabling richer contextual interaction across spatial dimensions while maintaining computational compactness suitable for point-of-care deployment. Extensive experiments on the ISIC 2017, ISIC 2018, and PH2 datasets demonstrate that our model consistently achieves state-of-the-art segmentation accuracy, outperforming existing lightweight and Mamba counterparts with only 0.034M parameters and 0.060 GFLOPs. In addition, we introduce a hybrid knowledge distillation strategy to train an ultra-compact student model, where the distilled variant UltraLBM-UNet-T, with only 0.011M parameters and 0.019 GFLOPs, achieves competitive segmentation performance. These results highlight the suitability of UltraLBM-UNet for point-of-care deployment, where accurate and robust lesion analyses are essential. The source code is publicly available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-69] LLM -Free Image Captioning Evaluation in Reference-Flexible Settings AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决图像描述(image captioning)自动评估中现有指标存在的两个核心问题:一是基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的评估指标存在偏倚,倾向于高估自身生成的caption;二是无LLM的评估指标虽具中立性,但性能往往不稳定或不够优异。其解决方案的关键在于提出Pearl——一种无需依赖LLM的监督式评估指标,通过引入新颖的机制学习图像-描述和描述-描述之间的相似性表示,并在大规模人工标注数据集(约33.3万条人类判断,来自2360名标注者对7.5万余张图像的评估)上进行训练与验证,从而在参考文本存在与不存在两种场景下均实现了优于现有无LLM指标的性能表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21582
作者: Shinnosuke Hirano,Yuiga Wada,Kazuki Matsuda,Seitaro Otsuki,Komei Sugiura
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted for presentation at AAAI2026
Abstract:We focus on the automatic evaluation of image captions in both reference-based and reference-free settings. Existing metrics based on large language models (LLMs) favor their own generations; therefore, the neutrality is in question. Most LLM-free metrics do not suffer from such an issue, whereas they do not always demonstrate high performance. To address these issues, we propose Pearl, an LLM-free supervised metric for image captioning, which is applicable to both reference-based and reference-free settings. We introduce a novel mechanism that learns the representations of image–caption and caption–caption similarities. Furthermore, we construct a human-annotated dataset for image captioning metrics, that comprises approximately 333k human judgments collected from 2,360 annotators across over 75k images. Pearl outperformed other existing LLM-free metrics on the Composite, Flickr8K-Expert, Flickr8K-CF, Nebula, and FOIL datasets in both reference-based and reference-free settings. Our project page is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-70] owards Long-window Anchoring in Vision-Language Model Distillation AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决小规模视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在长上下文理解中因窗口尺寸受限而导致的语言-图像对齐能力不足的问题。现有方法在小模型上难以有效迁移大型模型所具备的长距离注意力机制,从而限制了其在复杂多模态任务中的表现。解决方案的关键在于提出LAid方法,通过两个互补组件实现长程注意力机制的有效迁移:(1) 渐进式距离加权注意力匹配机制,在训练过程中动态增强对较长位置差异的关注;(2) 可学习的RoPE响应增益调制模块,选择性放大关键位置敏感区域的响应强度。这一设计显著提升了小模型的有效上下文窗口长度(最高达基线的3.2倍),同时保持或改善了标准多模态基准性能,并通过频谱分析验证了低频重要注意力成分的成功保留。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21576
作者: Haoyi Zhou,Shuo Li,Tianyu Chen,Qi Song,Chonghan Gao,Jianxin Li
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted by AAAI 2026
Abstract:While large vision-language models (VLMs) demonstrate strong long-context understanding, their prevalent small branches fail on linguistics-photography alignment for a limited window size. We discover that knowledge distillation improves students’ capability as a complement to Rotary Position Embeddings (RoPE) on window sizes (anchored from large models). Building on this insight, we propose LAid, which directly aims at the transfer of long-range attention mechanisms through two complementary components: (1) a progressive distance-weighted attention matching that dynamically emphasizes longer position differences during training, and (2) a learnable RoPE response gain modulation that selectively amplifies position sensitivity where needed. Extensive experiments across multiple model families demonstrate that LAid-distilled models achieve up to 3.2 times longer effective context windows compared to baseline small models, while maintaining or improving performance on standard VL benchmarks. Spectral analysis also suggests that LAid successfully preserves crucial low-frequency attention components that conventional methods fail to transfer. Our work not only provides practical techniques for building more efficient long-context VLMs but also offers theoretical insights into how positional understanding emerges and transfers during distillation.
zh
[CV-71] Exploration of Reproducible Generated Image Detection AAAI
【速读】:该论文旨在解决AI生成内容(AIGC)图像检测技术中存在的可复现性差和泛化能力不足的核心问题,这些问题严重限制了该类技术的实际应用。其解决方案的关键在于通过系统回顾7篇代表性文献、构建轻量级测试数据集并复现一种典型检测方法,识别出导致可复现性困境的根本原因:一是论文常省略预处理步骤和参数设置等隐含细节;二是多数检测方法过度依赖特定生成器的专属特征,而非学习AIGC图像的通用内在特征。研究结果表明,严格遵循原始论文的核心流程可实现基础性能复现,但一旦预处理破坏关键特征或跨生成器测试,检测性能显著下降,从而为提升AIGC检测技术的可复现性和泛化能力提供了实证依据与改进方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21562
作者: Yihang Duan
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: AAAI workshop RAI accepted
Abstract:While the technology for detecting AI-Generated Content (AIGC) images has advanced rapidly, the field still faces two core issues: poor reproducibility and insufficient gen eralizability, which hinder the practical application of such technologies. This study addresses these challenges by re viewing 7 key papers on AIGC detection, constructing a lightweight test dataset, and reproducing a representative detection method. Through this process, we identify the root causes of the reproducibility dilemma in the field: firstly, papers often omit implicit details such as prepro cessing steps and parameter settings; secondly, most detec tion methods overfit to exclusive features of specific gener ators rather than learning universal intrinsic features of AIGC images. Experimental results show that basic perfor mance can be reproduced when strictly following the core procedures described in the original papers. However, de tection performance drops sharply when preprocessing dis rupts key features or when testing across different genera tors. This research provides empirical evidence for improv ing the reproducibility of AIGC detection technologies and offers reference directions for researchers to disclose ex perimental details more comprehensively and verify the generalizability of their proposed methods.
zh
[CV-72] oward Intelligent Scene Augmentation for Context-Aware Object Placement and Sponsor-Logo Integration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前智能图像编辑中插入对象缺乏上下文合理性的问题,即现有方法虽能借助视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)和扩散模型实现引导式视觉操作,但难以确保所插入对象在语义与场景布局上符合实际情境。其解决方案的关键在于提出两个新任务:一是“上下文感知的对象插入”(context-aware object insertion),要求预测合适对象类别、生成该对象并将其合理放置于场景中;二是“赞助产品标志增强”(sponsor-product logo augmentation),用于检测商品并插入正确的品牌标识,即使物品原本无标或标错。为支撑这两个任务,作者构建了两个包含类别标注、放置区域及赞助-产品标签的新数据集,从而推动更符合现实逻辑的图像编辑研究与应用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21560
作者: Unnati Saraswat,Tarun Rao,Namah Gupta,Shweta Swami,Shikhar Sharma,Prateek Narang,Dhruv Kumar
机构: Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani, India (比尔拉理工大学与科学学院,皮拉尼,印度)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Intelligent image editing increasingly relies on advances in computer vision, multimodal reasoning, and generative modeling. While vision-language models (VLMs) and diffusion models enable guided visual manipulation, existing work rarely ensures that inserted objects are \emphcontextually appropriate. We introduce two new tasks for advertising and digital media: (1) \emphcontext-aware object insertion, which requires predicting suitable object categories, generating them, and placing them plausibly within the scene; and (2) \emphsponsor-product logo augmentation, which involves detecting products and inserting correct brand logos, even when items are unbranded or incorrectly branded. To support these tasks, we build two new datasets with category annotations, placement regions, and sponsor-product labels.
zh
[CV-73] EraseLoRA: MLLM -Driven Foreground Exclusion and Background Subtype Aggregation for Dataset-Free Object Removal
【速读】:该论文旨在解决图像中目标移除(object removal)任务中的核心挑战:如何在不依赖训练数据集的情况下,避免被遮挡目标的重现,并高质量重建被遮挡区域的背景结构与上下文一致性。传统基于自注意力机制干预的方法存在两个缺陷:一是非目标前景常被误判为背景导致无关物体再生;二是直接操作注意力机制破坏细节并阻碍背景线索的协同整合。其解决方案的关键在于提出EraseLoRA框架,通过两个创新模块实现无监督背景感知推理与测试时适应:首先,背景感知前景排除(Background-aware Foreground Exclusion, BFE)利用多模态大语言模型从单张图像-掩码对中分离出目标前景、非目标前景和干净背景,从而生成可靠背景线索并剔除干扰项;其次,背景感知重建与子类型聚合(Background-aware Reconstruction with Subtype Aggregation, BRSA)在测试阶段进行优化,将推断出的背景子类型视为互补组件,通过重建与对齐目标强制其一致融合,无需显式干预注意力机制即可保留局部细节与全局结构。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21545
作者: Sanghyun Jo,Donghwan Lee,Eunji Jung,Seong Je Oh,Kyungsu Kim
机构: Seoul National University (首尔国立大学); Seoul National University Medical Research Center (首尔国立大学医学研究中心)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Object removal differs from common inpainting, since it must prevent the masked target from reappearing and reconstruct the occluded background with structural and contextual fidelity, rather than merely filling a hole plausibly. Recent dataset-free approaches that redirect self-attention inside the mask fail in two ways: non-target foregrounds are often misinterpreted as background, which regenerates unwanted objects, and direct attention manipulation disrupts fine details and hinders coherent integration of background cues. We propose EraseLoRA, a novel dataset-free framework that replaces attention surgery with background-aware reasoning and test-time adaptation. First, Background-aware Foreground Exclusion (BFE), uses a multimodal large-language models to separate target foreground, non-target foregrounds, and clean background from a single image-mask pair without paired supervision, producing reliable background cues while excluding distractors. Second, Background-aware Reconstruction with Subtype Aggregation (BRSA), performs test-time optimization that treats inferred background subtypes as complementary pieces and enforces their consistent integration through reconstruction and alignment objectives, preserving local detail and global structure without explicit attention intervention. We validate EraseLoRA as a plug-in to pretrained diffusion models and across benchmarks for object removal, demonstrating consistent improvements over dataset-free baselines and competitive results against dataset-driven methods. The code will be made available upon publication.
zh
[CV-74] Vision Transformers are Circulant Attention Learners AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉 Transformer 中自注意力机制(self-attention mechanism)因二次计算复杂度(quadratic complexity)在高分辨率场景下带来的沉重计算负担问题。传统方法通过引入手工设计的稀疏或局部模式来缓解此问题,但不可避免地削弱了模型容量。其解决方案的关键在于发现并利用自注意力矩阵常近似为具有快速乘法特性的结构化矩阵——块循环矩阵(Block Circulant matrix with Circulant Blocks, BCCB),并据此提出一种基于最近 BCCB 矩阵显式建模的高效计算算法,使得整体计算复杂度降至 O(NlogN),同时保持与标准自注意力相近的表达能力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21542
作者: Dongchen Han,Tianyu Li,Ziyi Wang,Gao Huang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: AAAI 2026
Abstract:The self-attention mechanism has been a key factor in the advancement of vision Transformers. However, its quadratic complexity imposes a heavy computational burden in high-resolution scenarios, restricting the practical application. Previous methods attempt to mitigate this issue by introducing handcrafted patterns such as locality or sparsity, which inevitably compromise model capacity. In this paper, we present a novel attention paradigm termed \textbfCirculant Attention by exploiting the inherent efficient pattern of self-attention. Specifically, we first identify that the self-attention matrix in vision Transformers often approximates the Block Circulant matrix with Circulant Blocks (BCCB), a kind of structured matrix whose multiplication with other matrices can be performed in \mathcalO(N\log N) time. Leveraging this interesting pattern, we explicitly model the attention map as its nearest BCCB matrix and propose an efficient computation algorithm for fast calculation. The resulting approach closely mirrors vanilla self-attention, differing only in its use of BCCB matrices. Since our design is inspired by the inherent efficient paradigm, it not only delivers \mathcalO(N\log N) computation complexity, but also largely maintains the capacity of standard self-attention. Extensive experiments on diverse visual tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, establishing circulant attention as a promising alternative to self-attention for vision Transformer architectures. Code is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-75] Hierarchy-Aware Fine-Tuning of Vision-Language Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决视觉-语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)在层次分类任务中适应结构化标签体系的问题。现有方法通常将标签视为扁平类别,需对模型进行全量微调,不仅计算成本高,还导致不同层级间预测不一致。解决方案的关键在于提出一种轻量级、层次感知的微调框架,通过两个核心损失函数实现:Tree-Path KL Divergence(TP-KL)确保预测沿真实标签路径的垂直一致性,Hierarchy-Sibling Smoothed Cross-Entropy(HiSCE)促使同级子类之间预测一致;二者均在VLM共享嵌入空间中优化,并与LoRA(Low-Rank Adaptation)高效集成,在仅更新少量参数的前提下显著提升全路径准确率并降低树状不一致性误差。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21529
作者: Jiayu Li,Rajesh Gangireddy,Samet Akcay,Wei Cheng,Juhua Hu
机构: University of Washington (华盛顿大学); Intel; Google (谷歌)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) learn powerful multimodal representations through large-scale image-text pretraining, but adapting them to hierarchical classification is underexplored. Standard approaches treat labels as flat categories and require full fine-tuning, which is expensive and produces inconsistent predictions across taxonomy levels. We propose an efficient hierarchy-aware fine-tuning framework that updates a few parameters while enforcing structural consistency. We combine two objectives: Tree-Path KL Divergence (TP-KL) aligns predictions along the ground-truth label path for vertical coherence, while Hierarchy-Sibling Smoothed Cross-Entropy (HiSCE) encourages consistent predictions among sibling classes. Both losses work in the VLM’s shared embedding space and integrate with lightweight LoRA adaptation. Experiments across multiple benchmarks show consistent improvements in Full-Path Accuracy and Tree-based Inconsistency Error with minimal parameter overhead. Our approach provides an efficient strategy for adapting VLMs to structured taxonomies.
zh
[CV-76] Global-Graph Guided and Local-Graph Weighted Contrastive Learning for Unified Clustering on Incomplete and Noise Multi-View Data
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多视图聚类(Multi-view Clustering, MVC)中因数据不完整或噪声导致的稀疏配对样本(rare-paired samples)和错误配对样本(mis-paired samples)问题,这些问题会显著削弱基于对比学习(Contrastive Learning, CL)方法的有效性。解决方案的关键在于提出一个统一的、无需数据插补(imputation-free)的全局-局部图引导对比学习框架:首先设计全局图引导对比学习,通过构建全视图亲和图生成新的样本对以充分挖掘多视图互补信息;其次引入局部图加权对比学习,利用局部邻域信息为每对样本分配权重,自适应地增强或抑制对比学习信号,从而缓解错误配对带来的优化偏差。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21516
作者: Hongqing He,Jie Xu,Wenyuan Yang,Yonghua Zhu,Guoqiu Wen,Xiaofeng Zhu
机构: Guangxi Normal University (广西师范大学); University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (电子科技大学); Singapore University of Technology and Design (新加坡科技设计大学); Hainan University (海南大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Recently, contrastive learning (CL) plays an important role in exploring complementary information for multi-view clustering (MVC) and has attracted increasing attention. Nevertheless, real-world multi-view data suffer from data incompleteness or noise, resulting in rare-paired samples or mis-paired samples which significantly challenges the effectiveness of CL-based MVC. That is, rare-paired issue prevents MVC from extracting sufficient multi-view complementary information, and mis-paired issue causes contrastive learning to optimize the model in the wrong direction. To address these issues, we propose a unified CL-based MVC framework for enhancing clustering effectiveness on incomplete and noise multi-view data. First, to overcome the rare-paired issue, we design a global-graph guided contrastive learning, where all view samples construct a global-view affinity graph to form new sample pairs for fully exploring complementary information. Second, to mitigate the mis-paired issue, we propose a local-graph weighted contrastive learning, which leverages local neighbors to generate pair-wise weights to adaptively strength or weaken the pair-wise contrastive learning. Our method is imputation-free and can be integrated into a unified global-local graph-guided contrastive learning framework. Extensive experiments on both incomplete and noise settings of multi-view data demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance compared with state-of-the-art approaches.
zh
[CV-77] DiverseGRPO: Mitigating Mode Collapse in Image Generation via Diversity-Aware GRPO
【速读】:该论文旨在解决基于GRPO(Group Relative Policy Optimization)的图像生成模型在训练后期出现的输出同质化问题,即模型虽能提升图像质量,但缺乏视觉多样性与创造性,限制了其应用场景。问题根源在于传统GRPO仅以单样本质量作为奖励信号,忽视分布层面的多样性;同时,常规正则化策略未能充分考虑早期去噪阶段对多样性保持的关键作用,导致正则化预算分配失衡。解决方案的关键在于从奖励建模和生成动态两个维度重构优化机制:首先提出基于语义分组的分布级创意奖励(distributional creativity bonus),通过谱聚类构建样本分布表示,并根据群体规模自适应分配探索性奖励以激励发现新视觉模式;其次引入结构感知正则化(structure-aware regularization),强化早期去噪阶段的约束以保留多样性,同时不损害奖励优化效率。实验表明,该方法在保持相同图像质量的前提下,显著提升了13%–18%的语义多样性,确立了GRPO图像生成的新帕累托前沿。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21514
作者: Henglin Liu,Huijuan Huang,Jing Wang,Chang Liu,Xiu Li,Xiangyang Ji
机构: Tsinghua University (清华大学); Kling Team, Kuaishou Technology (快手科技); Shenzhen Campus of Sun Yat-sen University (中山大学深圳校区)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Project Page: this https URL
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL), particularly GRPO, improves image generation quality significantly by comparing the relative performance of images generated within the same group. However, in the later stages of training, the model tends to produce homogenized outputs, lacking creativity and visual diversity, which restricts its application scenarios. This issue can be analyzed from both reward modeling and generation dynamics perspectives. First, traditional GRPO relies on single-sample quality as the reward signal, driving the model to converge toward a few high-reward generation modes while neglecting distribution-level diversity. Second, conventional GRPO regularization neglects the dominant role of early-stage denoising in preserving diversity, causing a misaligned regularization budget that limits the achievable quality–diversity trade-off. Motivated by these insights, we revisit the diversity degradation problem from both reward modeling and generation dynamics. At the reward level, we propose a distributional creativity bonus based on semantic grouping. Specifically, we construct a distribution-level representation via spectral clustering over samples generated from the same caption, and adaptively allocate exploratory rewards according to group sizes to encourage the discovery of novel visual modes. At the generation level, we introduce a structure-aware regularization, which enforces stronger early-stage constraints to preserve diversity without compromising reward optimization efficiency. Experiments demonstrate that our method achieves a 13%–18% improvement in semantic diversity under matched quality scores, establishing a new Pareto frontier between image quality and diversity for GRPO-based image generation.
zh
[CV-78] MuS-Polar3D: A Benchmark Dataset for Computational Polarimetric 3D Imaging under Multi-Scattering Conditions
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前基于偏振的水下三维(3D)成像方法在复杂散射条件下缺乏高质量、多样化且可量化评估的数据集问题,从而阻碍了不同单视角与多视角偏振成像算法之间的公平比较。其解决方案的关键在于构建首个公开可用的基准数据集MuS-Polar3D,该数据集包含42个物体在7种定量控制的散射条件和5个观测视角下采集的偏振图像,并配有高精度3D模型(误差±0.05 mm)、法向量图和前景掩码,支持包括法向估计、目标分割、去散射和3D重建在内的多种视觉任务;同时,从成像链角度出发,提出将水下散射环境下的3D重建解耦为“去散射—3D重建”两阶段流程,显著提升了复杂散射条件下重建性能,实验证明该方案在多个基线方法中实现了最低平均角度误差(15.49°)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21513
作者: Puyun Wang,Kaimin Yu,Huayang He,Xianyu Wu
机构: Fuzhou University (福州大学); Research Institute of Highway, Ministry of Transport (交通运输部公路科学研究院)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Polarization-based underwater 3D imaging exploits polarization cues to suppress background scattering, exhibiting distinct advantages in turbid water. Although data-driven polarization-based underwater 3D reconstruction methods show great potential, existing public datasets lack sufficient diversity in scattering and observation conditions, hindering fair comparisons among different approaches, including single-view and multi-view polarization imaging methods. To address this limitation, we construct MuS-Polar3D, a benchmark dataset comprising polarization images of 42 objects captured under seven quantitatively controlled scattering conditions and five viewpoints, together with high-precision 3D models (+/- 0.05 mm accuracy), normal maps, and foreground masks. The dataset supports multiple vision tasks, including normal estimation, object segmentation, descattering, and 3D reconstruction. Inspired by computational imaging, we further decouple underwater 3D reconstruction under scattering into a two-stage pipeline, namely descattering followed by 3D reconstruction, from an imaging-chain perspective. Extensive evaluations using multiple baseline methods under complex scattering conditions demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed benchmark, achieving a best mean angular error of 15.49 degrees. To the best of our knowledge, MuS-Polar3D is the first publicly available benchmark dataset for quantitative turbidity underwater polarization-based 3D imaging, enabling accurate reconstruction and fair algorithm evaluation under controllable scattering conditions. The dataset and code are publicly available at this https URL. Subjects: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21513 [cs.CV] (or arXiv:2512.21513v1 [cs.CV] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21513 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[CV-79] Fixed-Threshold Evaluation of a Hybrid CNN-ViT for AI-Generated Image Detection Across Photos and Art
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式 AI (Generative AI) 图像检测器在实际部署中因后处理变换(如JPEG压缩、模糊、下采样)导致性能下降的问题,以及现有方法因对每种变换重新调整决策阈值而产生误导性鲁棒性评估的问题。其解决方案的关键在于引入一种固定阈值评估协议(fixed-threshold evaluation protocol),即在干净验证数据上一次性选定决策阈值并保持不变于所有后处理条件下,从而消除因动态调参造成的鲁棒性高估,真实揭示模型在不同场景下的性能差距,并提供可操作的部署建议:对于干净照片验证优先使用CNN,压缩内容检测推荐ViT,艺术/图形类内容筛查则采用混合架构以实现跨域平衡性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21512
作者: Md Ashik Khan,Arafat Alam Jion
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted at the 2025 28th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT). 6 pages, 5 figures
Abstract:AI image generators create both photorealistic images and stylized art, necessitating robust detectors that maintain performance under common post-processing transformations (JPEG compression, blur, downscaling). Existing methods optimize single metrics without addressing deployment-critical factors such as operating point selection and fixed-threshold robustness. This work addresses misleading robustness estimates by introducing a fixed-threshold evaluation protocol that holds decision thresholds, selected once on clean validation data, fixed across all post-processing transformations. Traditional methods retune thresholds per condition, artificially inflating robustness estimates and masking deployment failures. We report deployment-relevant performance at three operating points (Low-FPR, ROC-optimal, Best-F1) under systematic degradation testing using a lightweight CNN-ViT hybrid with gated fusion and optional frequency enhancement. Our evaluation exposes a statistically validated forensic-semantic spectrum: frequency-aided CNNs excel on pristine photos but collapse under compression (93.33% to 61.49%), whereas ViTs degrade minimally (92.86% to 88.36%) through robust semantic pattern recognition. Multi-seed experiments demonstrate that all architectures achieve 15% higher AUROC on artistic content (0.901-0.907) versus photorealistic images (0.747-0.759), confirming that semantic patterns provide fundamentally more reliable detection cues than forensic artifacts. Our hybrid approach achieves balanced cross-domain performance: 91.4% accuracy on tiny-genimage photos, 89.7% on AiArtData art/graphics, and 98.3% (competitive) on CIFAKE. Fixed-threshold evaluation eliminates retuning inflation, reveals genuine robustness gaps, and yields actionable deployment guidance: prefer CNNs for clean photo verification, ViTs for compressed content, and hybrids for art/graphics screening.
zh
[CV-80] Missing Pattern Tree based Decision Grouping and Ensemble for Deep Incomplete Multi-View Clustering
【速读】:该论文旨在解决不完整多视图聚类(Incomplete Multi-View Clustering, IMVC)中因高度不一致的缺失模式导致可用多视图对未能被充分利用的问题,即“配对利用不足”(pair under-utilization)问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于缺失模式树(missing-pattern tree)的IMVC框架TreeEIC:首先通过构建缺失模式树将数据划分为多个决策集(decision set),并在每个决策集中进行多视图聚类;其次设计多视图决策集成模块,利用不确定性加权机制抑制不可靠聚类决策并生成鲁棒结果;最后引入从集成到个体的知识蒸馏模块,使整体集成与各视图特定模型之间通过优化跨视图一致性损失和簇间判别损失相互促进,从而实现更高效且稳定的聚类性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21510
作者: Wenyuan Yang,Jie Xu,Hongqing He,Jiangzhang Gan,Xiaofeng Zhu
机构: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (电子科技大学); Hainan University (海南大学); Singapore University of Technology and Design (新加坡科技设计大学); Guangxi Normal University (广西师范大学)
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Real-world multi-view data usually exhibits highly inconsistent missing patterns which challenges the effectiveness of incomplete multi-view clustering (IMVC). Although existing IMVC methods have made progress from both imputation-based and imputation-free routes, they have overlooked the pair under-utilization issue, i.e., inconsistent missing patterns make the incomplete but available multi-view pairs unable to be fully utilized, thereby limiting the model performance. To address this, we propose a novel missing-pattern tree based IMVC framework entitled TreeEIC. Specifically, to achieve full exploitation of available multi-view pairs, TreeEIC first defines the missing-pattern tree model to group data into multiple decision sets according to different missing patterns, and then performs multi-view clustering within each set. Furthermore, a multi-view decision ensemble module is proposed to aggregate clustering results from all decision sets, which infers uncertainty-based weights to suppress unreliable clustering decisions and produce robust decisions. Finally, an ensemble-to-individual knowledge distillation module transfers the ensemble knowledge to view-specific clustering models, which enables ensemble and individual modules to promote each other by optimizing cross-view consistency and inter-cluster discrimination losses. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that our TreeEIC achieves state-of-the-art IMVC performance and exhibits superior robustness under highly inconsistent missing patterns.
zh
[CV-81] Fixed-Budget Parameter-Efficient Training with Frozen Encoders Improves Multimodal Chest X-Ray Classification
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多模态胸部X光图像分析中大规模视觉-语言模型微调带来的高计算成本问题。其关键解决方案是采用参数高效训练(Parameter-Efficient Training, PET)策略,包括冻结编码器、BitFit、LoRA和适配器(Adapter)等方法,在保持高性能的同时显著减少可训练参数量。实验表明,在固定参数预算下(2.37M参数,占总参数的2.51%),所有PET方法均实现AUROC在0.892–0.908之间,优于全参数微调(0.770 AUROC,使用94.3M参数,为PET方案的40倍),且在更大规模数据集CheXpert上仍具可扩展性,验证了PET策略在资源受限场景下的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21508
作者: Md Ashik Khan,Md Nahid Siddique
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Accepted at the 2025 28th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT). 6 pages, 6 figures
Abstract:Multimodal chest X-Ray analysis often fine-tunes large vision-language models, which is computationally costly. We study parameter-efficient training (PET) strategies, including frozen encoders, BitFit, LoRA, and adapters for multi-label classification on the Indiana University Chest X-Ray dataset (3,851 image-report pairs; 579 test samples). To mitigate data leakage, we redact pathology terms from reports used as text inputs while retaining clinical context. Under a fixed parameter budget (2.37M parameters, 2.51% of total), all PET variants achieve AUROC between 0.892 and 0.908, outperforming full fine-tuning (0.770 AUROC), which uses 94.3M trainable parameters, a 40x reduction. External validation on CheXpert (224,316 images, 58x larger) confirms scalability: all PET methods achieve 0.69 AUROC with 9% trainable parameters, with Adapter achieving best performance (0.7214 AUROC). Budget-matched comparisons reveal that vision-only models (0.653 AUROC, 1.06M parameters) outperform budget-matched multimodal models (0.641 AUROC, 1.06M parameters), indicating improvements arise primarily from parameter allocation rather than cross-modal synergy. While PET methods show degraded calibration (ECE: 0.29-0.34) compared to simpler models (ECE: 0.049), this represents a tractable limitation addressable through post-hoc calibration methods. These findings demonstrate that frozen encoder strategies provide superior discrimination at substantially reduced computational cost, though calibration correction is essential for clinical deployment.
zh
[CV-82] SVBench: Evaluation of Video Generation Models on Social Reasoning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前生成式 AI (Generative AI) 在视频生成中缺乏社会推理能力的问题,即模型难以理解并生成符合人类社会认知逻辑的行为,如意图推断、信念推理、共同注意和亲社会行为等。解决方案的关键在于提出首个用于评估视频生成中社会推理能力的基准测试(benchmark),该基准基于发展心理学与社会心理学的经典实验范式,构建了包含七类核心维度的社会认知框架,并设计了一种无需训练的基于代理(agent-based)的流水线方法:通过提取实验中的推理机制、合成多样化视频场景、利用线索驱动的批判机制控制概念中立性和难度,以及采用高容量视觉语言模型(VLM)作为判别器,在五个可解释维度上对生成视频进行量化评估。此框架首次系统性揭示了主流视频生成模型在深层社会推理上的显著缺陷。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21507
作者: Wenshuo Peng,Gongxuan Wang,Tianmeng Yang,Chuanhao Li,Xiaojie Xu,Hui He,Kaipeng Zhang
机构: Tsinghua University (清华大学); Shanghai AI Laboratory (上海人工智能实验室); Peking University (北京大学); Harbin Institute of Technology (哈尔滨工业大学); The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (香港科技大学)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 10pages
Abstract:Recent text-to-video generation models exhibit remarkable progress in visual realism, motion fidelity, and text-video alignment, yet they remain fundamentally limited in their ability to generate socially coherent behavior. Unlike humans, who effortlessly infer intentions, beliefs, emotions, and social norms from brief visual cues, current models tend to render literal scenes without capturing the underlying causal or psychological logic. To systematically evaluate this gap, we introduce the first benchmark for social reasoning in video generation. Grounded in findings from developmental and social psychology, our benchmark organizes thirty classic social cognition paradigms into seven core dimensions, including mental-state inference, goal-directed action, joint attention, social coordination, prosocial behavior, social norms, and multi-agent strategy. To operationalize these paradigms, we develop a fully training-free agent-based pipeline that (i) distills the reasoning mechanism of each experiment, (ii) synthesizes diverse video-ready scenarios, (iii) enforces conceptual neutrality and difficulty control through cue-based critique, and (iv) evaluates generated videos using a high-capacity VLM judge across five interpretable dimensions of social reasoning. Using this framework, we conduct the first large-scale study across seven state-of-the-art video generation systems. Our results reveal substantial performance gaps: while modern models excel in surface-level plausibility, they systematically fail in intention recognition, belief reasoning, joint attention, and prosocial inference.
zh
[CV-83] Generative Multi-Focus Image Fusion
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多聚焦图像融合(Multi-focus Image Fusion)中两个关键问题:一是现有算法通常假设场景中每个空间位置至少在一个输入图像中处于清晰状态,这在实际复杂场景中难以满足;二是当前融合模型因焦点估计不确定性或硬性选择操作,在复杂现实场景中易产生边缘伪影。解决方案的关键在于提出一种两级级联的生成式融合框架GMFF(Generative Multi-focus Image Fusion Framework):第一阶段采用确定性融合方法StackMFF V4,整合可用的焦点平面信息生成初始融合图像;第二阶段引入基于潜在扩散模型的生成式修复机制IFControlNet,利用生成式AI能力重建缺失焦点平面内容、恢复细节并消除边缘伪影,从而实现高质量且鲁棒的融合效果。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21495
作者: Xinzhe Xie,Buyu Guo,Bolin Li,Shuangyan He,Yanzhen Gu,Qingyan Jiang,Peiliang Li
机构: Zhejiang University (浙江大学); Donghai Laboratory (东海实验室); Hainan Institute, Zhejiang University (海南研究院); Hainan Provincial Observatory of Ecological Environment and Fishery Resource in Yazhou Bay (三亚湾生态环境与渔业资源海南省观测站)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:Multi-focus image fusion aims to generate an all-in-focus image from a sequence of partially focused input images. Existing fusion algorithms generally assume that, for every spatial location in the scene, there is at least one input image in which that location is in focus. Furthermore, current fusion models often suffer from edge artifacts caused by uncertain focus estimation or hard-selection operations in complex real-world scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose a generative multi-focus image fusion framework, termed GMFF, which operates in two sequential stages. In the first stage, deterministic fusion is implemented using StackMFF V4, the latest version of the StackMFF series, and integrates the available focal plane information to produce an initial fused image. The second stage, generative restoration, is realized through IFControlNet, which leverages the generative capabilities of latent diffusion models to reconstruct content from missing focal planes, restore fine details, and eliminate edge artifacts. Each stage is independently developed and functions seamlessly in a cascaded manner. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GMFF achieves state-of-the-art fusion performance and exhibits significant potential for practical applications, particularly in scenarios involving complex multi-focal content. The implementation is publicly available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-84] GPF-Net: Gated Progressive Fusion Learning for Polyp Re-Identification
【速读】:该论文旨在解决结肠镜下息肉重识别(Colonoscopic Polyp Re-Identification)任务中因高阶特征分辨率较低而导致的小目标匹配性能下降问题,尤其是在不同视角和相机拍摄条件下保持息肉一致性识别的挑战。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为“门控渐进融合网络”(Gated Progressive Fusion network)的新架构,其核心创新是通过全连接方式引入门控机制,实现多层级特征的逐层选择性融合,从而在多尺度特征交互中逐步优化语义信息,显著提升小目标息肉的匹配准确率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21476
作者: Suncheng Xiang,Xiaoyang Wang,Junjie Jiang,Hejia Wang,Dahong Qian
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Work in progress
Abstract:Colonoscopic Polyp Re-Identification aims to match the same polyp from a large gallery with images from different views taken using different cameras, which plays an important role in the prevention and treatment of colorectal cancer in computer-aided diagnosis. However, the coarse resolution of high-level features of a specific polyp often leads to inferior results for small objects where detailed information is important. To address this challenge, we propose a novel architecture, named Gated Progressive Fusion network, to selectively fuse features from multiple levels using gates in a fully connected way for polyp ReID. On the basis of it, a gated progressive fusion strategy is introduced to achieve layer-wise refinement of semantic information through multi-level feature interactions. Experiments on standard benchmarks show the benefits of the multimodal setting over state-of-the-art unimodal ReID models, especially when combined with the specialized multimodal fusion strategy.
zh
[CV-85] IMA: ISIC Archive Multi-Annotator Dermoscopic Skin Lesion Segmentation Dataset
【速读】:该论文旨在解决医学图像分割领域中多标注者(multi-annotator)数据集稀缺的问题,尤其针对皮肤病变的 dermoscopic 图像分割任务。当前缺乏大规模、公开可用且带有标注者元信息的皮肤病变分割(Skin Lesion Segmentation, SLS)数据集,限制了对标注者间差异和偏好建模的研究。解决方案的关键在于构建并发布 ISIC MultiAnnot++ 数据集,该数据集包含 17,684 个分割掩膜覆盖 14,967 张 dermoscopic 图像,其中 2,394 张图像拥有 2–5 个不同标注者的分割结果,并附带标注者技能水平和工具等元数据,从而支持标注者特定偏好建模与标注一致性分析等前沿研究方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21472
作者: Kumar Abhishek,Jeremy Kawahara,Ghassan Hamarneh
机构: Simon Fraser University (西蒙菲莎大学); AIP Labs (匈牙利科学院实验室)
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 11 pages, 7 figures
Abstract:Multi-annotator medical image segmentation is an important research problem, but requires annotated datasets that are expensive to collect. Dermoscopic skin lesion imaging allows human experts and AI systems to observe morphological structures otherwise not discernable from regular clinical photographs. However, currently there are no large-scale publicly available multi-annotator skin lesion segmentation (SLS) datasets with annotator-labels for dermoscopic skin lesion imaging. We introduce ISIC MultiAnnot++, a large public multi-annotator skin lesion segmentation dataset for images from the ISIC Archive. The final dataset contains 17,684 segmentation masks spanning 14,967 dermoscopic images, where 2,394 dermoscopic images have 2-5 segmentations per image, making it the largest publicly available SLS dataset. Further, metadata about the segmentation, including the annotators’ skill level and segmentation tool, is included, enabling research on topics such as annotator-specific preference modeling for segmentation and annotator metadata analysis. We provide an analysis on the characteristics of this dataset, curated data partitions, and consensus segmentation masks.
zh
[CV-86] CCAD: Compressed Global Feature Conditioned Anomaly Detection
【速读】:该论文旨在解决工业场景中异常检测(anomaly detection)面临的两大挑战:一是无监督表示学习方法在域偏移(domain shift)下难以提取鲁棒特征;二是基于重建的方法因约束不足导致训练效率低且性能下降。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为压缩全局特征条件异常检测(Compressed Global Feature Conditioned Anomaly Detection, CCAD)的新方法,其核心创新是将全局特征作为新的模态条件引入重建模型,从而融合重建与无监督表示学习的优势;同时设计自适应压缩机制,在提升模型泛化能力的同时优化训练效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21459
作者: Xiao Jin,Liang Diao,Qixin Xiao,Yifan Hu,Ziqi Zhang,Yuchen Liu,Haisong Gu
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 18 pages, 9 figures
Abstract:Anomaly detection holds considerable industrial significance, especially in scenarios with limited anomalous data. Currently, reconstruction-based and unsupervised representation-based approaches are the primary focus. However, unsupervised representation-based methods struggle to extract robust features under domain shift, whereas reconstruction-based methods often suffer from low training efficiency and performance degradation due to insufficient constraints. To address these challenges, we propose a novel method named Compressed Global Feature Conditioned Anomaly Detection (CCAD). CCAD synergizes the strengths of both paradigms by adapting global features as a new modality condition for the reconstruction model. Furthermore, we design an adaptive compression mechanism to enhance both generalization and training efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CCAD consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of AUC while achieving faster convergence. In addition, we contribute a reorganized and re-annotated version of the DAGM 2007 dataset with new annotations to further validate our method’s effectiveness. The code for reproducing main results is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-87] Intelligent recognition of GPR road hidden defect images based on feature fusion and attention mechanism
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统地面穿透雷达(Ground Penetrating Radar, GPR)图像解释高度依赖主观经验、效率低且准确性差的问题。其核心解决方案在于提出一个综合框架:首先,采用深度卷积生成对抗网络(DCGAN)进行数据增强,以合成高保真GPR图像,在复杂背景中保持缺陷形态不变,缓解数据稀缺问题;其次,设计多模态链与全局注意力网络(Multi-modal Chain and Global Attention Network, MCGA-Net),通过多模态链特征融合(MCFF)实现分层多尺度缺陷表征,并引入全局注意力机制(GAM)增强上下文感知能力;最后,利用MS COCO预训练模型迁移学习微调主干网络,加速收敛并提升泛化性能。该框架在小目标、弱信号及高斯噪声等挑战场景下仍具鲁棒性,显著优于现有方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21452
作者: Haotian Lv,Yuhui Zhang,Jiangbo Dai,Hanli Wu,Jiaji Wang,Dawei Wang
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing
Abstract:Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) has emerged as a pivotal tool for non-destructive evaluation of subsurface road defects. However, conventional GPR image interpretation remains heavily reliant on subjective expertise, introducing inefficiencies and inaccuracies. This study introduces a comprehensive framework to address these limitations: (1) A DCGAN-based data augmentation strategy synthesizes high-fidelity GPR images to mitigate data scarcity while preserving defect morphology under complex backgrounds; (2) A novel Multi-modal Chain and Global Attention Network (MCGA-Net) is proposed, integrating Multi-modal Chain Feature Fusion (MCFF) for hierarchical multi-scale defect representation and Global Attention Mechanism (GAM) for context-aware feature enhancement; (3) MS COCO transfer learning fine-tunes the backbone network, accelerating convergence and improving generalization. Ablation and comparison experiments validate the framework’s efficacy. MCGA-Net achieves Precision (92.8%), Recall (92.5%), and mAP@50 (95.9%). In the detection of Gaussian noise, weak signals and small targets, MCGA-Net maintains robustness and outperforms other models. This work establishes a new paradigm for automated GPR-based defect detection, balancing computational efficiency with high accuracy in complex subsurface environments.
zh
[CV-88] Scalable Deep Subspace Clustering Network
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统子空间聚类方法在大规模数据场景下面临的计算复杂度瓶颈问题,即由于构建全量 n×n 相似性矩阵和进行谱分解带来的 O(n3) 时间复杂度限制。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为 SDSNet(Scalable Deep Subspace Network)的深度子空间聚类框架,通过三项核心设计实现 O(n) 复杂度:(1) 基于地标点(landmark-based)的近似策略避免显式构造完整相似性矩阵;(2) 联合优化自编码器重构损失与自表达(self-expression)目标,提升特征学习与聚类一致性;(3) 在因子分解表示上直接执行谱聚类,从而显著降低计算开销。实验表明,该方法在保持与前沿方法相当聚类性能的同时,大幅提升了计算效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21434
作者: Nairouz Mrabah,Mohamed Bouguessa,Sihem Sami
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: Published at the 2025 IEEE 12th International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA)
Abstract:Subspace clustering methods face inherent scalability limits due to the O(n^3) cost (with n denoting the number of data samples) of constructing full n\times n affinities and performing spectral decomposition. While deep learning-based approaches improve feature extraction, they maintain this computational bottleneck through exhaustive pairwise similarity computations. We propose SDSNet (Scalable Deep Subspace Network), a deep subspace clustering framework that achieves \mathcalO(n) complexity through (1) landmark-based approximation, avoiding full affinity matrices, (2) joint optimization of auto-encoder reconstruction with self-expression objectives, and (3) direct spectral clustering on factorized representations. The framework combines convolutional auto-encoders with subspace-preserving constraints. Experimental results demonstrate that SDSNet achieves comparable clustering quality to state-of-the-art methods with significantly improved computational efficiency.
zh
[CV-89] A Tool Bottleneck Framework for Clinically-Informed and Interpretable Medical Image Understanding
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前基于视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)的工具使用框架在医学图像理解任务中表现不佳的问题,尤其针对医学影像中关键信息以空间局部特征形式存在、难以通过纯文本方式有效组合或融合的挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出了一种名为“工具瓶颈框架”(Tool Bottleneck Framework, TBF)的新方法,该框架利用一个预训练的医学VLM从工具箱中选择提取临床相关特征的专用工具,并通过一个可学习的“工具瓶颈模型”(Tool Bottleneck Model, TBM)以神经网络方式直接融合这些工具输出,而非依赖传统文本驱动的函数调用或自然语言编排。TBM的设计使得无论VLM如何选择工具,都能高效地进行特征融合并生成最终预测,从而显著提升模型在医学图像分析中的性能与可解释性,尤其在数据有限场景下优势明显。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21414
作者: Christina Liu,Alan Q. Wang,Joy Hsu,Jiajun Wu,Ehsan Adeli
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Recent tool-use frameworks powered by vision-language models (VLMs) improve image understanding by grounding model predictions with specialized tools. Broadly, these frameworks leverage VLMs and a pre-specified toolbox to decompose the prediction task into multiple tool calls (often deep learning models) which are composed to make a prediction. The dominant approach to composing tools is using text, via function calls embedded in VLM-generated code or natural language. However, these methods often perform poorly on medical image understanding, where salient information is encoded as spatially-localized features that are difficult to compose or fuse via text alone. To address this, we propose a tool-use framework for medical image understanding called the Tool Bottleneck Framework (TBF), which composes VLM-selected tools using a learned Tool Bottleneck Model (TBM). For a given image and task, TBF leverages an off-the-shelf medical VLM to select tools from a toolbox that each extract clinically-relevant features. Instead of text-based composition, these tools are composed by the TBM, which computes and fuses the tool outputs using a neural network before outputting the final prediction. We propose a simple and effective strategy for TBMs to make predictions with any arbitrary VLM tool selection. Overall, our framework not only improves tool-use in medical imaging contexts, but also yields more interpretable, clinically-grounded predictors. We evaluate TBF on tasks in histopathology and dermatology and find that these advantages enable our framework to perform on par with or better than deep learning-based classifiers, VLMs, and state-of-the-art tool-use frameworks, with particular gains in data-limited regimes. Our code is available at this https URL.
zh
[CV-90] Understanding Virality: A Rubric based Vision-Language Model Framework for Short-Form Edutainment Evaluation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决短视频内容评估中仅依赖表面质量指标(如SSIM、FID)而难以捕捉真实用户参与度的问题,尤其关注音频视觉特征如何驱动观众行为。其解决方案的关键在于构建一个基于视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)的数据驱动评估框架:首先利用VLM无监督提取多模态特征,继而通过聚类生成可解释的因子,并训练回归模型预测观众参与度。该方法在YouTube Shorts数据集上验证了预测参与度与实际行为高度相关,相比传统指标更具可解释性和扩展性,从而推动了面向人类对齐的视频理解发展。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21402
作者: Arnav Gupta,Gurekas Singh Sahney,Hardik Rathi,Abhishek Chandwani,Ishaan Gupta,Pratik Narang,Dhruv Kumar
机构: Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani (比尔拉理工大学,皮拉尼校区); GenimeLabs
类目: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: Under Review
Abstract:Evaluating short-form video content requires moving beyond surface-level quality metrics toward human-aligned, multimodal reasoning. While existing frameworks like VideoScore-2 assess visual and semantic fidelity, they do not capture how specific audiovisual attributes drive real audience engagement. In this work, we propose a data-driven evaluation framework that uses Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to extract unsupervised audiovisual features, clusters them into interpretable factors, and trains a regression-based evaluator to predict engagement on short-form edutainment videos. Our curated YouTube Shorts dataset enables systematic analysis of how VLM-derived features relate to human engagement behavior. Experiments show strong correlations between predicted and actual engagement, demonstrating that our lightweight, feature-based evaluator provides interpretable and scalable assessments compared to traditional metrics (e.g., SSIM, FID). By grounding evaluation in both multimodal feature importance and human-centered engagement signals, our approach advances toward robust and explainable video understanding.
zh
[CV-91] he Color-Clinical Decoupling: Why Perceptual Calibration Fails Clinical Biomarkers in Smartphone Dermatology
【速读】:该论文旨在解决智能手机远程皮肤科(smartphone-based tele-dermatology)中颜色校准是否能确保临床级生物标志物可靠提取的问题,尤其针对肤色较深的皮肤光型(Fitzpatrick III-IV)人群。研究表明,尽管线性色彩校正矩阵(Linear Color Correction Matrix, CCM)可显著降低颜色误差(达67–77%),实现接近临床精度(ΔE < 2.3),但这种感知准确性并未转化为生物标志物的一致性——即出现“颜色-临床解耦”(color-clinical decoupling)现象:个体肤质角度(Individual Typology Angle, ITA)在不同设备间一致性差(ICC = 0.40),而黑色素指数(Melanin Index)则表现良好(ICC = 0.77)。其关键原因在于ITA对b*色度通道噪声敏感,并受面部区域差异影响显著(占颜色方差25.2%,远高于设备效应7.0%)。因此,解决方案的核心是摒弃传统的单点校准策略,转而采用区域感知(region-aware)的协议以提升移动皮肤科中生物标志物的可靠性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21988
作者: Sungwoo Kang
机构: Korea University (韩国科学技术院)
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Quantitative Methods (q-bio.QM)
备注:
Abstract:Smartphone-based tele-dermatology assumes that colorimetric calibration ensures clinical reliability, yet this remains untested for underrepresented skin phototypes. We investigated whether standard calibration translates to reliable clinical biomarkers using 43,425 images from 965 Korean subjects (Fitzpatrick III-IV) across DSLR, tablet, and smartphone devices. While Linear Color Correction Matrix (CCM) normalization reduced color error by 67-77% – achieving near-clinical accuracy (Delta E 2.3) – this success did not translate to biomarker reliability. We identify a phenomenon termed “color-clinical decoupling”: despite perceptual accuracy, the Individual Typology Angle (ITA) showed poor inter-device agreement (ICC = 0.40), while the Melanin Index achieved good agreement (ICC = 0.77). This decoupling is driven by the ITA formula’s sensitivity to b* channel noise and is further compounded by anatomical variance. Facial region accounts for 25.2% of color variance – 3.6x greater than device effects (7.0%) – challenging the efficacy of single-patch calibration. Our results demonstrate that current colorimetric standards are insufficient for clinical-grade biomarker extraction, necessitating region-aware protocols for mobile dermatology. Subjects: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Quantitative Methods (q-bio.QM) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21988 [eess.IV] (or arXiv:2512.21988v1 [eess.IV] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21988 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[CV-92] RT-Focuser: A Real-Time Lightweight Model for Edge-side Image Deblurring
【速读】:该论文旨在解决由相机或物体运动引起的运动模糊(motion blur)问题,此类模糊现象严重降低图像质量,并对自动驾驶、无人机感知和医学成像等实时应用构成挑战。解决方案的关键在于提出一种轻量级U型网络RT-Focuser,其核心创新包括:轻量化去模糊模块(Lightweight Deblurring Block, LD)用于边缘感知特征提取,多层级集成聚合模块(Multi-Level Integrated Aggregation, MLIA)实现编码器特征融合,以及跨源融合模块(Cross-source Fusion Block, X-Fuse)支持解码器的渐进式优化。该模型在仅使用单张模糊输入的情况下, achieves 30.67 dB PSNR,参数量仅为5.85M,计算复杂度为15.76 GMACs,在GPU与移动端均能实现6ms/帧的推理速度,超过140 FPS,具备良好的边缘部署潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21975
作者: Zhuoyu Wu,Wenhui Ou,Qiawei Zheng,Jiayan Yang,Quanjun Wang,Wenqi Fang,Zheng Wang,Yongkui Yang,Heshan Li
机构: 未知
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注: 2 pages, 2 figures, this paper already accepted by IEEE ICTA 2025
Abstract:Motion blur caused by camera or object movement severely degrades image quality and poses challenges for real-time applications such as autonomous driving, UAV perception, and medical imaging. In this paper, a lightweight U-shaped network tailored for real-time deblurring is presented and named RT-Focuser. To balance speed and accuracy, we design three key components: Lightweight Deblurring Block (LD) for edge-aware feature extraction, Multi-Level Integrated Aggregation module (MLIA) for encoder integration, and Cross-source Fusion Block (X-Fuse) for progressive decoder refinement. Trained on a single blurred input, RT-Focuser achieves 30.67 dB PSNR with only 5.85M parameters and 15.76 GMACs. It runs 6ms per frame on GPU and mobile, exceeds 140 FPS on both, showing strong potential for deployment on the edge. The official code and usage are available on: this https URL.
zh
[CV-93] Residual Prior Diffusion: A Probabilistic Framework Integrating Coarse Latent Priors with Diffusion Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决标准扩散模型在处理多尺度数据时面临的挑战,即模型需同时捕捉数据分布的全局结构与细粒度局部特征,而这两者在尺度上存在显著差异时会导致建模困难。解决方案的关键在于提出残差先验扩散(Residual Prior Diffusion, RPD),其核心思想是将生成过程分为两个阶段:首先训练一个粗粒度先验模型以学习数据分布的大尺度结构,随后利用扩散模型学习该先验与真实数据分布之间的残差,从而降低目标预测难度。RPD被形式化为具有可计算证据下界(evidence lower bound)的显式概率模型,优化目标等价于常见的噪声预测或速度预测任务,并通过引入辅助变量进一步利用先验信息,理论上证明了其对预测问题复杂度的缓解作用。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21593
作者: Takuro Kutsuna
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 40 pages
Abstract:Diffusion models have become a central tool in deep generative modeling, but standard formulations rely on a single network and a single diffusion schedule to transform a simple prior, typically a standard normal distribution, into the target data distribution. As a result, the model must simultaneously represent the global structure of the distribution and its fine-scale local variations, which becomes difficult when these scales are strongly mismatched. This issue arises both in natural images, where coarse manifold-level structure and fine textures coexist, and in low-dimensional distributions with highly concentrated local structure. To address this issue, we propose Residual Prior Diffusion (RPD), a two-stage framework in which a coarse prior model first captures the large-scale structure of the data distribution, and a diffusion model is then trained to represent the residual between the prior and the target data distribution. We formulate RPD as an explicit probabilistic model with a tractable evidence lower bound, whose optimization reduces to the familiar objectives of noise prediction or velocity prediction. We further introduce auxiliary variables that leverage information from the prior model and theoretically analyze how they reduce the difficulty of the prediction problem in RPD. Experiments on synthetic datasets with fine-grained local structure show that standard diffusion models fail to capture local details, whereas RPD accurately captures fine-scale detail while preserving the large-scale structure of the distribution. On natural image generation tasks, RPD achieved generation quality that matched or exceeded that of representative diffusion-based baselines and it maintained strong performance even with a small number of inference steps.
zh
[CV-94] A Graph-Augmented knowledge Distillation based Dual-Stream Vision Transformer with Region-Aware Attention for Gastrointestinal Disease Classification with Explainable AI
【速读】:该论文旨在解决胃肠疾病(Gastrointestinal Diseases)在内镜和组织病理图像中准确分类的难题,其核心挑战在于数据量庞大以及不同类别间视觉特征的细微差异。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种基于教师-学生知识蒸馏(Teacher-Student Knowledge Distillation)的混合双流深度学习框架:教师模型融合了Swin Transformer的全局上下文推理能力与Vision Transformer的局部细粒度特征提取能力,而学生网络采用轻量级Tiny-ViT结构,通过软标签蒸馏继承教师模型的语义与形态学知识,在保证诊断准确性的同时显著降低计算复杂度,从而实现高效且可解释的智能诊断。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21372
作者: Md Assaduzzaman,Nushrat Jahan Oyshi,Eram Mahamud
机构: 未知
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (cs.CV)
备注:
Abstract:The accurate classification of gastrointestinal diseases from endoscopic and histopathological imagery remains a significant challenge in medical diagnostics, mainly due to the vast data volume and subtle variation in inter-class visuals. This study presents a hybrid dual-stream deep learning framework built on teacher-student knowledge distillation, where a high-capacity teacher model integrates the global contextual reasoning of a Swin Transformer with the local fine-grained feature extraction of a Vision Transformer. The student network was implemented as a compact Tiny-ViT structure that inherits the teacher’s semantic and morphological knowledge via soft-label distillation, achieving a balance between efficiency and diagnostic accuracy. Two carefully curated Wireless Capsule Endoscopy datasets, encompassing major GI disease classes, were employed to ensure balanced representation and prevent inter-sample bias. The proposed framework achieved remarkable performance with accuracies of 0.9978 and 0.9928 on Dataset 1 and Dataset 2 respectively, and an average AUC of 1.0000, signifying near-perfect discriminative capability. Interpretability analyses using Grad-CAM, LIME, and Score-CAM confirmed that the model’s predictions were grounded in clinically significant tissue regions and pathologically relevant morphological cues, validating the framework’s transparency and reliability. The Tiny-ViT demonstrated diagnostic performance with reduced computational complexity comparable to its transformer-based teacher while delivering faster inference, making it suitable for resource-constrained clinical environments. Overall, the proposed framework provides a robust, interpretable, and scalable solution for AI-assisted GI disease diagnosis, paving the way toward future intelligent endoscopic screening that is compatible with clinical practicality.
zh
人工智能
[AI-0] Agent ic Structured Graph Traversal for Root Cause Analysis of Code-related Incidents in Cloud Applications
【速读】:该论文旨在解决云环境(cloud)中由代码(code)和配置(configuration)引发的生产事故(production cloud incidents)的根因定位(Root Cause Analysis, RCA)难题,此类事故平均每小时造成的损失超过200万美元。解决方案的关键在于提出PRAXIS——一个基于大语言模型(LLM)的代理工作流(agentic workflow)编排器,其核心创新是通过结构化遍历两种图结构来实现跨层级依赖分析:一是服务依赖图(Service Dependency Graph, SDG),用于刻画微服务间的调用关系;二是 hammock-block 程序依赖图(Program Dependence Graph, PDG),用于捕捉每个微服务内部的代码级依赖。LLM作为遍历策略,在这两种图之间动态移动,从而精准定位并解释故障根源。实验表明,PRAXIS相较当前最优的ReAct基线方法,在RCA准确率上提升达3.1倍,同时token消耗降低3.8倍。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22113
作者: Shengkun Cui,Rahul Krishna,Saurabh Jha,Ravishankar K. Iyer
机构: 未知
类目: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Software Engineering (cs.SE)
备注:
Abstract:Cloud incidents pose major operational challenges in production, with unresolved production cloud incidents cost on average over 2M per hour. Prior research identifies code- and configuration-related issues as the predominant category of root causes in cloud incidents. This paper introduces PRAXIS, an orchestrator that manages and deploys an agentic workflow for diagnosing code- and configuration-caused cloud incidents. PRAXIS employs an LLM-driven structured traversal over two types of graph: (1) a service dependency graph (SDG) that captures microservice-level dependencies; and (2) a hammock-block program dependence graph (PDG) that captures code-level dependencies for each microservice. Together, these graphs encode microservice- and code-level dependencies and the LLM acts as a traversal policy over these graphs, moving between services and code dependencies to localize and explain failures. Compared to state-of-the-art ReAct baselines, PRAXIS improves RCA accuracy by up to 3.1x while reducing token consumption by 3.8x. PRAXIS is demonstrated on a set of 30 comprehensive real-world incidents that is being compiled into an RCA benchmark.
zh
[AI-1] Pruning as a Game: Equilibrium-Driven Sparsification of Neural Networks
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统神经网络剪枝方法中将稀疏性(sparsity)视为外部约束的问题,这类方法通常依赖启发式重要性评分或训练过程中的正则化来实现剪枝,缺乏理论依据且难以解释。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种全新的视角:将剪枝建模为模型组件之间战略互动的均衡结果。具体而言,作者将权重、神经元或滤波器等参数组视为连续非合作博弈中的参与者,每个参与者通过调整自身在网络中的参与度来权衡贡献与冗余及竞争关系;当持续参与成为劣势策略时,稀疏性自然涌现于均衡状态。基于此理论框架,作者设计了一种基于均衡驱动的剪枝算法,在无需显式重要性评分的情况下联合更新网络参数和参与变量,从而实现了可解释、理论支撑的剪枝机制。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22106
作者: Zubair Shah,Noaman Khan
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Preprint. Under review / to be submitted to a conference
Abstract:Neural network pruning is widely used to reduce model size and computational cost. Yet, most existing methods treat sparsity as an externally imposed constraint, enforced through heuristic importance scores or training-time regularization. In this work, we propose a fundamentally different perspective: pruning as an equilibrium outcome of strategic interaction among model components. We model parameter groups such as weights, neurons, or filters as players in a continuous non-cooperative game, where each player selects its level of participation in the network to balance contribution against redundancy and competition. Within this formulation, sparsity emerges naturally when continued participation becomes a dominated strategy at equilibrium. We analyze the resulting game and show that dominated players collapse to zero participation under mild conditions, providing a principled explanation for pruning behavior. Building on this insight, we derive a simple equilibrium-driven pruning algorithm that jointly updates network parameters and participation variables without relying on explicit importance scores. This work focuses on establishing a principled formulation and empirical validation of pruning as an equilibrium phenomenon, rather than exhaustive architectural or large-scale benchmarking. Experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves competitive sparsity-accuracy trade-offs while offering an interpretable, theory-grounded alternative to existing pruning methods.
zh
[AI-2] From In Silico to In Vitro: Evaluating Molecule Generative Models for Hit Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决药物发现流程中“hit识别”这一关键但资源密集的步骤,传统方法依赖于大规模化合物库的高通量筛选(High-Throughput Screening, HTS),存在耗时和成本高的问题。为应对这一挑战,研究提出将生成式AI(Generative AI)模型应用于hit-like分子的直接生成,从而替代或整合进现有hit识别工作流。解决方案的关键在于:首次将hit-like分子生成明确建模为一个独立任务,并构建了一个多阶段过滤评估框架,融合理化性质、结构特征及生物活性相关标准以定义hit-like化学空间;在此基础上,对比了两种自回归模型与一种扩散模型在不同数据集和训练设置下的表现,验证了生成模型可产出有效、多样且具有生物学相关性的化合物,部分GSK-3β hits已合成并体外验证活性,揭示了当前评价指标与训练数据的局限性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22031
作者: Nagham Osman,Vittorio Lembo,Giovanni Bottegoni,Laura Toni
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Hit identification is a critical yet resource-intensive step in the drug discovery pipeline, traditionally relying on high-throughput screening of large compound libraries. Despite advancements in virtual screening, these methods remain time-consuming and costly. Recent progress in deep learning has enabled the development of generative models capable of learning complex molecular representations and generating novel compounds de novo. However, using ML to replace the entire drug-discovery pipeline is highly challenging. In this work, we rather investigate whether generative models can replace one step of the pipeline: hit-like molecule generation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to explicitly frame hit-like molecule generation as a standalone task and empirically test whether generative models can directly support this stage of the drug discovery pipeline. Specifically, we investigate if such models can be trained to generate hit-like molecules, enabling direct incorporation into, or even substitution of, traditional hit identification workflows. We propose an evaluation framework tailored to this task, integrating physicochemical, structural, and bioactivity-related criteria within a multi-stage filtering pipeline that defines the hit-like chemical space. Two autoregressive and one diffusion-based generative models were benchmarked across various datasets and training settings, with outputs assessed using standard metrics and target-specific docking scores. Our results show that these models can generate valid, diverse, and biologically relevant compounds across multiple targets, with a few selected GSK-3 \beta hits synthesized and confirmed active in vitro. We also identify key limitations in current evaluation metrics and available training data.
zh
[AI-3] LibContinual: A Comprehensive Library towards Realistic Continual Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决持续学习(Continual Learning, CL)领域中因灾难性遗忘(catastrophic forgetting)导致的旧任务性能下降问题,以及由此引发的研究方法碎片化、评估标准不统一和可复现性差等挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个名为LibContinual的综合性、可复现的开源库,该库采用高内聚、低耦合的模块化架构,集成19种代表性算法并覆盖五类主流方法,构建了标准化的执行环境;同时,基于此统一框架,作者系统性地识别出三大隐含假设——离线数据可用性、无约束内存资源和任务内语义同质性,并通过严格的在线CL设置、统一内存预算协议及类别随机化场景进行验证,揭示了多数现有方法在真实世界约束下的性能显著下降,从而强调了资源感知与语义鲁棒性持续学习策略的必要性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22029
作者: Wenbin Li,Shangge Liu,Borui Kang,Yiyang Chen,KaXuan Lew,Yang Chen,Yinghuan Shi,Lei Wang,Yang Gao,Jiebo Luo
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:A fundamental challenge in Continual Learning (CL) is catastrophic forgetting, where adapting to new tasks degrades the performance on previous ones. While the field has evolved with diverse methods, this rapid surge in diverse methodologies has culminated in a fragmented research landscape. The lack of a unified framework, including inconsistent implementations, conflicting dependencies, and varying evaluation protocols, makes fair comparison and reproducible research increasingly difficult. To address this challenge, we propose LibContinual, a comprehensive and reproducible library designed to serve as a foundational platform for realistic CL. Built upon a high-cohesion, low-coupling modular architecture, LibContinual integrates 19 representative algorithms across five major methodological categories, providing a standardized execution environment. Meanwhile, leveraging this unified framework, we systematically identify and investigate three implicit assumptions prevalent in mainstream evaluation: (1) offline data accessibility, (2) unregulated memory resources, and (3) intra-task semantic homogeneity. We argue that these assumptions often overestimate the real-world applicability of CL methods. Through our comprehensive analysis using strict online CL settings, a novel unified memory budget protocol, and a proposed category-randomized setting, we reveal significant performance drops in many representative CL methods when subjected to these real-world constraints. Our study underscores the necessity of resource-aware and semantically robust CL strategies, and offers LibContinual as a foundational toolkit for future research in realistic continual learning. The source code is available from \hrefthis https URLthis https URL.
zh
[AI-4] Meta-Learning-Based Handover Management in NextG O-RAN
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统切换(Traditional Handover, THO)和条件切换(Conditional Handover, CHO)在密集部署和高频段场景下存在的性能瓶颈问题,包括切换失败率高、延迟大以及信令开销与资源利用之间的复杂权衡。其核心解决方案是提出 CONTRA 框架,首次在 O-RAN 架构中联合优化 THO 与 CHO 策略,通过两种变体实现灵活控制:一是预先为用户分配切换类型以满足差异化服务需求,二是基于实时系统状态动态决策切换方式;关键创新在于引入一种实用的元学习算法,在无需未来信息的情况下实现近似最优的运行时适应能力(即“通用无悔”性能保障),从而显著提升用户吞吐量并降低切换成本,优于现有 3GPP 兼容方案及强化学习基线方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22022
作者: Michail Kalntis,George Iosifidis,José Suárez-Varela,Andra Lutu,Fernando A. Kuipers
机构: 未知
类目: Networking and Internet Architecture (cs.NI); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:While traditional handovers (THOs) have served as a backbone for mobile connectivity, they increasingly suffer from failures and delays, especially in dense deployments and high-frequency bands. To address these limitations, 3GPP introduced Conditional Handovers (CHOs) that enable proactive cell reservations and user-driven execution. However, both handover (HO) types present intricate trade-offs in signaling, resource usage, and reliability. This paper presents unique, countrywide mobility management datasets from a top-tier mobile network operator (MNO) that offer fresh insights into these issues and call for adaptive and robust HO control in next-generation networks. Motivated by these findings, we propose CONTRA, a framework that, for the first time, jointly optimizes THOs and CHOs within the O-RAN architecture. We study two variants of CONTRA: one where users are a priori assigned to one of the HO types, reflecting distinct service or user-specific requirements, as well as a more dynamic formulation where the controller decides on-the-fly the HO type, based on system conditions and needs. To this end, it relies on a practical meta-learning algorithm that adapts to runtime observations and guarantees performance comparable to an oracle with perfect future information (universal no-regret). CONTRA is specifically designed for near-real-time deployment as an O-RAN xApp and aligns with the 6G goals of flexible and intelligent control. Extensive evaluations leveraging crowdsourced datasets show that CONTRA improves user throughput and reduces both THO and CHO switching costs, outperforming 3GPP-compliant and Reinforcement Learning (RL) baselines in dynamic and real-world scenarios.
zh
[AI-5] Semiparametric Preference Optimization: Your Language Model is Secretly a Single-Index Model
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)在偏好对齐过程中因假设已知链接函数(link function)而导致的奖励估计偏差与策略错位问题。传统方法通常假设偏好分布与隐含奖励之间存在特定形式的链接函数(如Bradley-Terry模型中的逻辑斯蒂链接),但若该假设错误,将导致推理出的奖励有偏,进而使策略偏离最优。为应对这一挑战,作者提出在未知且无限制链接函数条件下进行策略对齐,其核心创新在于构建一个基于f-散度约束的奖励最大化问题,并证明:若解在策略类中可实现,则等价于一个半参数单指标二元选择模型(semiparametric single-index binary choice model),其中标量指数由策略决定,其余偏好分布则作为该指数的任意函数。解决方案的关键在于放弃对可识别有限维结构参数的估计(区别于计量经济学方法),转而聚焦于策略学习本身,允许不可识别和非参数化的指数结构,并通过三种机制——链接函数剖面化(profiling)、正交化(orthogonalization)以及无链接的二分排名目标(link-agnostic bipartite ranking objectives)——设计策略学习器,同时提供依赖于指数类泛函复杂度的有限样本策略误差界。最终方法对偏好噪声分布和尺度具有鲁棒性,且直接优化策略而不显式拟合奖励函数。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21917
作者: Nathan Kallus
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Econometrics (econ.EM); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
备注:
Abstract:Aligning large language models to preference data is commonly implemented by assuming a known link function between the distribution of observed preferences and the unobserved rewards (e.g., a logistic link as in Bradley-Terry). If the link is wrong, however, inferred rewards can be biased and policies be misaligned. We study policy alignment to preferences under an unknown and unrestricted link. We consider an f -divergence-constrained reward maximization problem and show that realizability of the solution in a policy class implies a semiparametric single-index binary choice model, where a scalar-valued index determined by a policy captures the dependence on demonstrations and the rest of the preference distribution is an unrestricted function thereof. Rather than focus on estimation of identifiable finite-dimensional structural parameters in the index as in econometrics, we focus on policy learning, focusing on error to the optimal policy and allowing unidentifiable and nonparametric indices. We develop a variety of policy learners based on profiling the link function, orthogonalizing the link function, and using link-agnostic bipartite ranking objectives. We analyze these and provide finite-sample policy error bounds that depend on generic functional complexity measures of the index class. We further consider practical implementations using first-order optimization suited to neural networks and batched data. The resulting methods are robust to unknown preference noise distribution and scale, while preserving the direct optimization of policies without explicitly fitting rewards.
zh
[AI-6] SpatialBench: Can Agents Analyze Real-World Spatial Biology Data? NEURIPS2024
【速读】:该论文旨在解决空间转录组学(spatial transcriptomics)数据规模与复杂性迅速增长背景下,计算分析成为生物发现瓶颈的问题,特别是当前前沿生成式 AI (Generative AI) 模型在处理真实世界混乱的空间组学数据时是否具备提取生物学洞察能力尚不明确。解决方案的关键在于提出 SpatialBench——一个包含 146 个可验证问题的基准测试集,这些问题源自五种空间技术及七个任务类别的真实分析流程,每个问题提供分析步骤前的数据快照和确定性评分器以评估关键生物学结果的恢复情况。通过该基准测试,研究揭示了基础模型准确率较低(20–38%),且存在显著的模型-任务和模型-平台交互效应,强调工具设计、提示工程、控制流和执行环境应作为首要对象进行评估与优化,从而为开发能忠实、透明、可重现地交互真实空间数据的智能代理提供测量工具与诊断视角。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21907
作者: Kenny Workman,Zhen Yang,Harihara Muralidharan,Hannah Le
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 10 pages, 9 figures, 4 tables; NeurIPS 2024 format
Abstract:Spatial transcriptomics assays are rapidly increasing in scale and complexity, making computational analysis a major bottleneck in biological discovery. Although frontier AI agents have improved dramatically at software engineering and general data analysis, it remains unclear whether they can extract biological insight from messy, real-world spatial datasets. We introduce SpatialBench, a benchmark of 146 verifiable problems derived from practical spatial analysis workflows spanning five spatial technologies and seven task categories. Each problem provides a snapshot of experimental data immediately prior to an analysis step and a deterministic grader that evaluates recovery of a key biological result. Benchmark data on frontier models shows that base model accuracy remains low (20-38% across model families), with strong model-task and model-platform interactions. Harness design has a large empirical effect on performance, indicating that tools, prompts, control flow, and execution environment should be evaluated and improved as first-class objects. SpatialBench serves both as a measurement tool and a diagnostic lens for developing agents that can interact with real spatial datasets faithfully, transparently, and reproducibly.
zh
[AI-7] Flexible Multitask Learning with Factorized Diffusion Policy
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多任务学习中机器人动作分布高度多元且复杂导致的策略拟合困难问题,现有单一模型常因欠拟合和缺乏灵活性而难以高效适应新任务。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种模块化扩散策略框架(modular diffusion policy framework),通过将复杂的动作分布分解为多个专用扩散模型的组合,每个模型捕捉行为空间中的特定子模式,从而实现更有效的整体策略;同时,该模块化结构支持通过添加或微调组件灵活适配新任务,天然缓解灾难性遗忘问题。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21898
作者: Chaoqi Liu,Haonan Chen,Sigmund H. Høeg,Shaoxiong Yao,Yunzhu Li,Kris Hauser,Yilun Du
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Multitask learning poses significant challenges due to the highly multimodal and diverse nature of robot action distributions. However, effectively fitting policies to these complex task distributions is often difficult, and existing monolithic models often underfit the action distribution and lack the flexibility required for efficient adaptation. We introduce a novel modular diffusion policy framework that factorizes complex action distributions into a composition of specialized diffusion models, each capturing a distinct sub-mode of the behavior space for a more effective overall policy. In addition, this modular structure enables flexible policy adaptation to new tasks by adding or fine-tuning components, which inherently mitigates catastrophic forgetting. Empirically, across both simulation and real-world robotic manipulation settings, we illustrate how our method consistently outperforms strong modular and monolithic baselines.
zh
[AI-8] MMCTOP: A Multimodal Textualization and Mixture-of-Experts Framework for Clinical Trial Outcome Prediction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决高维生物医学信息学中多模态数据融合的挑战,即如何有效整合来自分子结构表征、临床试验协议元数据与长篇入选标准叙述文本、以及疾病本体等异构生物医学信号,以提升临床试验结果预测的准确性。其解决方案的关键在于提出MMCTOP框架,该框架通过模式感知表示学习(modality-aware representation learning)实现跨模态对齐嵌入,并采用药物-疾病条件稀疏专家混合模型(drug-disease-conditioned sparse Mixture-of-Experts, SMoE)进行选择性专家路由和上下文感知的专家融合;同时引入基于schema的文本规范化(schema-guided textualization)和输入保真度验证机制,确保特征提取的可靠性和可解释性,从而在保持计算效率的同时显著提升预测性能与稳定性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21897
作者: Carolina Aparício,Qi Shi,Bo Wen,Tesfaye Yadete,Qiwei Han
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 15 pages, 3 figures, 5 tables
Abstract:Addressing the challenge of multimodal data fusion in high-dimensional biomedical informatics, we propose MMCTOP, a MultiModal Clinical-Trial Outcome Prediction framework that integrates heterogeneous biomedical signals spanning (i) molecular structure representations, (ii) protocol metadata and long-form eligibility narratives, and (iii) disease ontologies. MMCTOP couples schema-guided textualization and input-fidelity validation with modality-aware representation learning, in which domain-specific encoders generate aligned embeddings that are fused by a transformer backbone augmented with a drug-disease-conditioned sparse Mixture-of-Experts (SMoE). This design explicitly supports specialization across therapeutic and design subspaces while maintaining scalable computation through top-k routing. MMCTOP achieves consistent improvements in precision, F1, and AUC over unimodal and multimodal baselines on benchmark datasets, and ablations show that schema-guided textualization and selective expert routing contribute materially to performance and stability. We additionally apply temperature scaling to obtain calibrated probabilities, ensuring reliable risk estimation for downstream decision support. Overall, MMCTOP advances multimodal trial modeling by combining controlled narrative normalization, context-conditioned expert fusion, and operational safeguards aimed at auditability and reproducibility in biomedical informatics.
zh
[AI-9] Aerial World Model for Long-horizon Visual Generation and Navigation in 3D Space
【速读】:该论文旨在解决无人机(UAV)在大规模三维环境中自主导航时缺乏高阶语义信息整合能力的问题,现有导航策略多聚焦于低层次目标如避障和轨迹平滑性,难以有效利用场景语义进行规划。解决方案的关键在于提出一种空中导航世界模型(Aerial Navigation World Model, ANWM),该模型通过条件预测未来视觉观测来评估候选轨迹的语义合理性与导航效用;其核心创新是引入物理启发的“未来帧投影”(Future Frame Projection, FFP)模块,将历史帧投影至未来视角以提供粗粒度几何先验,从而降低远距离视觉生成中的表征不确定性,并捕捉三维轨迹与第一人称观测之间的映射关系。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21887
作者: Weichen Zhang,Peizhi Tang,Xin Zeng,Fanhang Man,Shiquan Yu,Zichao Dai,Baining Zhao,Hongjin Chen,Yu Shang,Wei Wu,Chen Gao,Xinlei Chen,Xin Wang,Yong Li,Wenwu Zhu
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have emerged as powerful embodied agents. One of the core abilities is autonomous navigation in large-scale three-dimensional environments. Existing navigation policies, however, are typically optimized for low-level objectives such as obstacle avoidance and trajectory smoothness, lacking the ability to incorporate high-level semantics into planning. To bridge this gap, we propose ANWM, an aerial navigation world model that predicts future visual observations conditioned on past frames and actions, thereby enabling agents to rank candidate trajectories by their semantic plausibility and navigational utility. ANWM is trained on 4-DoF UAV trajectories and introduces a physics-inspired module: Future Frame Projection (FFP), which projects past frames into future viewpoints to provide coarse geometric priors. This module mitigates representational uncertainty in long-distance visual generation and captures the mapping between 3D trajectories and egocentric observations. Empirical results demonstrate that ANWM significantly outperforms existing world models in long-distance visual forecasting and improves UAV navigation success rates in large-scale environments.
zh
[AI-10] Optimizing Resource Allocation for Geographically-Distributed Inference by Large Language Models
【速读】:该论文致力于解决分布式大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)推理中的资源分配优化问题,核心在于如何高效地进行模型块(block)放置和请求路由决策,以最小化推理延迟。其关键解决方案包括:首先构建了实验验证的性能模型,能够准确预测不同块放置与请求路由策略下的推理性能;其次将离线优化问题形式化为混合整数线性规划(Mixed Integer Linear Programming, MILP)问题,并证明其NP-hard性质,同时提出一种具有性能保证的多项式复杂度算法;最后将该算法扩展至在线场景,在负载受限条件下仍保持相同的性能保障。通过大量实验与仿真验证,该方案显著优于现有最优方法,尤其在地理分布式的服务器环境中表现突出。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21884
作者: Tingyang Sun,Ting He,Bo Ji,Parimal Parag
机构: 未知
类目: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Networking and Internet Architecture (cs.NI)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models have demonstrated extraordinary performance in many AI tasks but are expensive to use, even after training, due to their requirement of high-end GPUs. Recently, a distributed system called PETALS was developed to lower the barrier for deploying LLMs by splitting the model blocks across multiple servers with low-end GPUs distributed over the Internet, which was much faster than swapping the model parameters between the GPU memory and other cheaper but slower local storage media. However, the performance of such a distributed system critically depends on the resource allocation, and how to do so optimally remains unknown. In this work, we present the first systematic study of the resource allocation problem in distributed LLM inference, with focus on two important decisions: block placement and request routing. Our main results include: experimentally validated performance models that can predict the inference performance under given block placement and request routing decisions, a formulation of the offline optimization of block placement and request routing as a mixed integer linear programming problem together with the NP-hardness proof and a polynomial-complexity algorithm with guaranteed performance, and an adaptation of the offline algorithm for the online setting with the same performance guarantee under bounded load. Through both experiments and experimentally-validated simulations, we have verified that the proposed solution can substantially reduce the inference time compared to the state-of-the-art solution in diverse settings with geographically-distributed servers. As a byproduct, we have also developed a light-weighted CPU-only simulator capable of predicting the performance of distributed LLM inference on GPU servers, which can evaluate large deployments and facilitate future research for researchers with limited GPU access.
zh
[AI-11] MASFIN: A Multi-Agent System for Decomposed Financial Reasoning and Forecasting NEURIPS2025
【速读】:该论文旨在解决量化金融领域中传统方法易受幸存者偏差(survivorship bias)影响,以及现有AI驱动方法在信号整合、可复现性和计算效率方面的不足。其解决方案的关键在于提出MASFIN——一个模块化多智能体框架,通过将大语言模型(LLMs)与结构化财务指标和非结构化新闻数据融合,并嵌入显式的偏见缓解协议,实现对异构信息的透明、可复现分析。该框架采用GPT-4.1-nano以保障推理的可复现性与成本效益,并生成每周包含15–30只股票的组合,权重经优化以提升短期表现,在八周评估期内累计收益达7.33%,优于多个基准指数,验证了偏见感知型生成式AI在金融预测中的潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21878
作者: Marc S. Montalvo,Hamed Yaghoobian
机构: 未知
类目: Multiagent Systems (cs.MA); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted to the NeurIPS 2025 Workshop on Generative AI in Finance
Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) are transforming data-intensive domains, with finance representing a high-stakes environment where transparent and reproducible analysis of heterogeneous signals is essential. Traditional quantitative methods remain vulnerable to survivorship bias, while many AI-driven approaches struggle with signal integration, reproducibility, and computational efficiency. We introduce MASFIN, a modular multi-agent framework that integrates LLMs with structured financial metrics and unstructured news, while embedding explicit bias-mitigation protocols. The system leverages GPT-4.1-nano for reproducability and cost-efficient inference and generates weekly portfolios of 15-30 equities with allocation weights optimized for short-term performance. In an eight-week evaluation, MASFIN delivered a 7.33% cumulative return, outperforming the SP 500, NASDAQ-100, and Dow Jones benchmarks in six of eight weeks, albeit with higher volatility. These findings demonstrate the promise of bias-aware, generative AI frameworks for financial forecasting and highlight opportunities for modular multi-agent design to advance practical, transparent, and reproducible approaches in quantitative finance.
zh
[AI-12] Secure and Explainable Fraud Detection in Finance via Hierarchical Multi-source Dataset Distillation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多机构协作下金融欺诈检测中的隐私保护与模型可解释性难题,尤其是在数据共享受限的场景中如何兼顾性能、透明度与安全性。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种可解释且隐私保护的数据蒸馏框架:将训练好的随机森林(Random Forest)转化为透明的轴对齐规则区域(leaf hyperrectangles),并在每个规则区域内均匀采样生成合成交易数据,从而构建一个紧凑、可审计的替代数据集;该方法在保留局部特征交互关系的同时不暴露原始敏感记录,同时利用规则区域实现双重解释性——全局层面通过规则统计量(如支持度和支持提升度)描述模式,局部层面则通过分配每条记录至生成它的规则区域提供人类可读的推理依据及基于树投票分歧的校准不确定性估计。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21866
作者: Yiming Qian,Thorsten Neumann,Xueyining Huang,David Hardoon,Fei Gao,Yong Liu,Siow Mong Rick Goh
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:We propose an explainable, privacy-preserving dataset distillation framework for collaborative financial fraud detection. A trained random forest is converted into transparent, axis-aligned rule regions (leaf hyperrectangles), and synthetic transactions are generated by uniformly sampling within each region. This produces a compact, auditable surrogate dataset that preserves local feature interactions without exposing sensitive original records. The rule regions also support explainability: aggregated rule statistics (for example, support and lift) describe global patterns, while assigning each case to its generating region gives concise human-readable rationales and calibrated uncertainty based on tree-vote disagreement. On the IEEE-CIS fraud dataset (590k transactions across three institution-like clusters), distilled datasets reduce data volume by 85% to 93% (often under 15% of the original) while maintaining competitive precision and micro-F1, with only a modest AUC drop. Sharing and augmenting with synthesized data across institutions improves cross-cluster precision, recall, and AUC. Real vs. synthesized structure remains highly similar (over 93% by nearest-neighbor cosine analysis). Membership-inference attacks perform at chance level (about 0.50) when distinguishing training from hold-out records, suggesting low memorization risk. Removing high-uncertainty synthetic points using disagreement scores further boosts AUC (up to 0.687) and improves calibration. Sensitivity tests show weak dependence on the distillation ratio (AUC about 0.641 to 0.645 from 6% to 60%). Overall, tree-region distillation enables trustworthy, deployable fraud analytics with interpretable global rules, per-case rationales with quantified uncertainty, and strong privacy properties suitable for multi-institution settings and regulatory audit. Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21866 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2512.21866v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21866 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) Journalreference: The ACM International Conference on AI in Finance (ICAIF) Workshop, 2025
zh
[AI-13] MoonBot: Modular and On-Demand Reconfigurable Robot Toward Moon Base Construction
【速读】:该论文旨在解决月球表面探索与开发中对多功能、高适应性机器人系统的需求,尤其是在严苛的月球载荷质量限制下如何实现任务灵活性与环境适应性的平衡。其解决方案的关键在于提出并设计了一种模块化、按需重构的机器人系统(MoonBot),通过可重构结构在有限质量约束内最大化功能扩展能力,并支持多样化的月面任务,如土木工程作业、基础设施组件运输部署及充气模块辅助操作,从而验证了模块化设计在实际场景中的可行性与有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21853
作者: Kentaro Uno,Elian Neppel,Gustavo H. Diaz,Ashutosh Mishra,Shamistan Karimov,A. Sejal Jain,Ayesha Habib,Pascal Pama,Hazal Gozbasi,Shreya Santra,Kazuya Yoshida
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: This is the authors’ version of a paper accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Field Robotics, © IEEE. The final published version is available at this https URL
Abstract:The allure of lunar surface exploration and development has recently captured widespread global attention. Robots have proved to be indispensable for exploring uncharted terrains, uncovering and leveraging local resources, and facilitating the construction of future human habitats. In this article, we introduce the modular and on-demand reconfigurable robot (MoonBot), a modular and reconfigurable robotic system engineered to maximize functionality while operating within the stringent mass constraints of lunar payloads and adapting to varying environmental conditions and task requirements. This article details the design and development of MoonBot and presents a preliminary field demonstration that validates the proof of concept through the execution of milestone tasks simulating the establishment of lunar infrastructure. These tasks include essential civil engineering operations, infrastructural component transportation and deployment, and assistive operations with inflatable modules. Furthermore, we systematically summarize the lessons learned during testing, focusing on the connector design and providing valuable insights for the advancement of modular robotic systems in future lunar missions.
zh
[AI-14] A Comedy of Estimators: On KL Regularization in RL Training of LLM s
【速读】:该论文旨在解决强化学习(Reinforcement Learning, RL)训练大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)时,KL正则化项估计方法不当导致的梯度偏差问题。现有实践中广泛采用的KL估计器配置并未提供对目标函数的正确梯度,从而造成理论目标与实际实现之间的不一致,影响模型性能。论文的关键解决方案在于系统性地分析多种KL估计器配置的梯度性质,揭示设计选择如何引入偏差,并通过在Qwen2.5-7B、Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct和Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507上的实证研究证明:在on-policy设置中,使用无偏梯度估计器可显著提升模型在分布内与分布外任务上的稳定性与性能;而在off-policy设置中,KL正则化有助于缓解异步训练带来的不稳定性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21852
作者: Vedant Shah,Johan Obando-Ceron,Vineet Jain,Brian Bartoldson,Bhavya Kailkhura,Sarthak Mittal,Glen Berseth,Pablo Samuel Castro,Yoshua Bengio,Nikolay Malkin,Moksh Jain,Siddarth Venkatraman,Aaron Courville
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The reasoning performance of large language models (LLMs) can be substantially improved by training them with reinforcement learning (RL). The RL objective for LLM training involves a regularization term, which is the reverse Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence between the trained policy and the reference policy. Since computing the KL divergence exactly is intractable, various estimators are used in practice to estimate it from on-policy samples. Despite its wide adoption, including in several open-source libraries, there is no systematic study analyzing the numerous ways of incorporating KL estimators in the objective and their effect on the downstream performance of RL-trained models. Recent works show that prevailing practices for incorporating KL regularization do not provide correct gradients for stated objectives, creating a discrepancy between the objective and its implementation. In this paper, we further analyze these practices and study the gradients of several estimators configurations, revealing how design choices shape gradient bias. We substantiate these findings with empirical observations by RL fine-tuning \textttQwen2.5-7B, \textttLlama-3.1-8B-Instruct and \textttQwen3-4B-Instruct-2507 with different configurations and evaluating their performance on both in- and out-of-distribution tasks. Through our analysis, we observe that, in on-policy settings: (1) estimator configurations with biased gradients can result in training instabilities; and (2) using estimator configurations resulting in unbiased gradients leads to better performance on in-domain as well as out-of-domain tasks. We also investigate the performance resulting from different KL configurations in off-policy settings and observe that KL regularization can help stabilize off-policy RL training resulting from asynchronous setups.
zh
[AI-15] Multi-agent Adaptive Mechanism Design
【速读】:该论文致力于解决在缺乏代理人先验信念知识的情况下,如何设计一种能够激励多个理性代理人在序贯机制中诚实报告的机制问题。其核心挑战在于同时保障机制的激励相容性(incentive compatibility)与成本最优性(cost-optimality)。解决方案的关键是提出了一种分布鲁棒自适应机制(Distributionally Robust Adaptive Mechanism, DRAM),该框架融合了机制设计与在线学习的思想:通过迭代估计代理人的信念,并在每个阶段使用一个模糊集不断缩小的分布鲁棒线性规划来更新机制参数,从而在保持高概率诚实报告的同时实现 O~(T) 的累积遗憾(cumulative regret)。此外,作者建立了匹配的下界,表明在激励约束未知且需被学习的情形下,任何诚实的自适应机制都无法在渐近意义上超越此性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21794
作者: Qiushi Han,David Simchi-Levi,Renfei Tan,Zishuo Zhao
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Science and Game Theory (cs.GT); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA); Theoretical Economics (econ.TH)
备注:
Abstract:We study a sequential mechanism design problem in which a principal seeks to elicit truthful reports from multiple rational agents while starting with no prior knowledge of agents’ beliefs. We introduce Distributionally Robust Adaptive Mechanism (DRAM), a general framework combining insights from both mechanism design and online learning to jointly address truthfulness and cost-optimality. Throughout the sequential game, the mechanism estimates agents’ beliefs and iteratively updates a distributionally robust linear program with shrinking ambiguity sets to reduce payments while preserving truthfulness. Our mechanism guarantees truthful reporting with high probability while achieving \tildeO(\sqrtT) cumulative regret, and we establish a matching lower bound showing that no truthful adaptive mechanism can asymptotically do better. The framework generalizes to plug-in estimators, supporting structured priors and delayed feedback. To our knowledge, this is the first adaptive mechanism under general settings that maintains truthfulness and achieves optimal regret when incentive constraints are unknown and must be learned.
zh
[AI-16] Accelerating Scientific Discovery with Autonomous Goal-evolving Agents
【速读】:该论文旨在解决科学发现代理(Scientific Discovery Agents)在面对重大科学挑战时,因依赖科学家预先设定的定量目标函数而受限的问题。这些目标函数往往只是对真实科学目标的不完美代理(imperfect proxies),导致代理性能受限。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为SAGA(Scientific Autonomous Goal-evolving Agent)的框架,其核心是采用双层架构:外层由大语言模型(LLM)代理负责分析优化结果、提出新目标并将其转化为可计算的评分函数;内层则基于当前目标进行解空间优化。这种设计使目标函数不再是固定输入,而是通过系统性探索目标空间及其权衡关系来动态演化,从而显著提升科学发现代理的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21782
作者: Yuanqi Du,Botao Yu,Tianyu Liu,Tony Shen,Junwu Chen,Jan G. Rittig,Kunyang Sun,Yikun Zhang,Zhangde Song,Bo Zhou,Cassandra Masschelein,Yingze Wang,Haorui Wang,Haojun Jia,Chao Zhang,Hongyu Zhao,Martin Ester,Teresa Head-Gordon,Carla P. Gomes,Huan Sun,Chenru Duan,Philippe Schwaller,Wengong Jin
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Materials Science (cond-mat.mtrl-sci); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Chemical Physics (physics.chem-ph)
备注:
Abstract:There has been unprecedented interest in developing agents that expand the boundary of scientific discovery, primarily by optimizing quantitative objective functions specified by scientists. However, for grand challenges in science , these objectives are only imperfect proxies. We argue that automating objective function design is a central, yet unmet requirement for scientific discovery agents. In this work, we introduce the Scientific Autonomous Goal-evolving Agent (SAGA) to amend this challenge. SAGA employs a bi-level architecture in which an outer loop of LLM agents analyzes optimization outcomes, proposes new objectives, and converts them into computable scoring functions, while an inner loop performs solution optimization under the current objectives. This bi-level design enables systematic exploration of the space of objectives and their trade-offs, rather than treating them as fixed inputs. We demonstrate the framework through a broad spectrum of applications, including antibiotic design, inorganic materials design, functional DNA sequence design, and chemical process design, showing that automating objective formulation can substantially improve the effectiveness of scientific discovery agents.
zh
[AI-17] Compliance Rating Scheme: A Data Provenance Framework for Generative AI Datasets
【速读】:该论文旨在解决生成式人工智能(Generative AI)发展中数据集构建过程中存在的伦理与法律合规性缺失问题,特别是由于数据收集方式不透明、缺乏溯源机制,导致数据集在共享和再利用过程中其来源、合法性及安全性信息易被丢失。解决方案的关键在于提出一种合规评分体系(Compliance Rating Scheme, CRS),用于评估数据集在透明度、责任归属和安全性方面的合规程度,并开发了一个基于数据溯源技术的开源Python库,实现对现有数据集的合规性评估以及在新数据集构建阶段的主动引导,从而推动负责任的数据采集与AI模型训练流程。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21775
作者: Matyas Bohacek,Ignacio Vilanova Echavarri
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computers and Society (cs.CY); Databases (cs.DB)
备注:
Abstract:Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) has experienced exponential growth in recent years, partly facilitated by the abundance of large-scale open-source datasets. These datasets are often built using unrestricted and opaque data collection practices. While most literature focuses on the development and applications of GAI models, the ethical and legal considerations surrounding the creation of these datasets are often neglected. In addition, as datasets are shared, edited, and further reproduced online, information about their origin, legitimacy, and safety often gets lost. To address this gap, we introduce the Compliance Rating Scheme (CRS), a framework designed to evaluate dataset compliance with critical transparency, accountability, and security principles. We also release an open-source Python library built around data provenance technology to implement this framework, allowing for seamless integration into existing dataset-processing and AI training pipelines. The library is simultaneously reactive and proactive, as in addition to evaluating the CRS of existing datasets, it equally informs responsible scraping and construction of new datasets.
zh
[AI-18] How Do Agents Perform Code Optimization? An Empirical Study
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前生成式 AI (Generative AI) 在真实世界性能优化任务中的表现尚不明确的问题,特别是对比AI生成与人类编写的性能优化代码提交(PRs)在采纳率、可维护性、优化模式及验证实践等方面的差异。其解决方案的关键在于通过实证研究方法,系统分析来自AIDev数据集的324个AI生成和83个人类编写的性能优化PRs,发现AI生成的PR在显式性能验证方面显著低于人类(45.7% vs. 63.6%,p=0.007),但两者在优化模式上具有高度一致性,从而揭示了AI在性能优化任务中的优势与局限,并为未来提升智能体代码优化能力提供了方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21757
作者: Huiyun Peng,Antonio Zhong,Ricardo Andrés Calvo Méndez,Kelechi G. Kalu,James C. Davis
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Performance optimization is a critical yet challenging aspect of software development, often requiring a deep understanding of system behavior, algorithmic tradeoffs, and careful code modifications. Although recent advances in AI coding agents have accelerated code generation and bug fixing, little is known about how these agents perform on real-world performance optimization tasks. We present the first empirical study comparing agent- and human-authored performance optimization commits, analyzing 324 agent-generated and 83 human-authored PRs from the AIDev dataset across adoption, maintainability, optimization patterns, and validation practices. We find that AI-authored performance PRs are less likely to include explicit performance validation than human-authored PRs (45.7% vs. 63.6%, p=0.007 ). In addition, AI-authored PRs largely use the same optimization patterns as humans. We further discuss limitations and opportunities for advancing agentic code optimization.
zh
[AI-19] A Model of Causal Explanation on Neural Networks for Tabular Data
【速读】:该论文旨在解决神经网络(Neural Network, NN)模型在表格数据上预测结果的可解释性问题,特别是针对伪相关性(pseudo-correlation)、因果关系(causality)以及组合性原因(combinatorial reasons)等挑战。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为CENNET的因果解释方法,该方法通过将结构因果模型(Structural Causal Models, SCMs)与神经网络有效结合,在不牺牲预测准确性的前提下,提供对NN预测结果的因果层面解释,并引入基于熵的解释能力指数以量化解释质量。实验表明,CENNET在合成数据和准真实数据上的分类任务中优于现有解释方法。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21746
作者: Takashi Isozaki,Masahiro Yamamoto,Atsushi Noda
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: \c{opyright}2025. This manuscript version is made available under the CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 license this https URL
Abstract:The problem of explaining the results produced by machine learning methods continues to attract attention. Neural network (NN) models, along with gradient boosting machines, are expected to be utilized even in tabular data with high prediction accuracy. This study addresses the related issues of pseudo-correlation, causality, and combinatorial reasons for tabular data in NN predictors. We propose a causal explanation method, CENNET, and a new explanation power index using entropy for the method. CENNET provides causal explanations for predictions by NNs and uses structural causal models (SCMs) effectively combined with the NNs although SCMs are usually not used as predictive models on their own in terms of predictive accuracy. We show that CEN-NET provides such explanations through comparative experiments with existing methods on both synthetic and quasi-real data in classification tasks.
zh
[AI-20] HELP: Hierarchical Embodied Language Planner for Household Tasks
【速读】:该论文旨在解决复杂场景中具身智能体(embodied agent)在自然语言指令下进行有效规划的问题,尤其是在真实或模拟环境中如何利用大语言模型(LLM)处理语言歧义、环境信息检索及可用技能整合的能力。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种分层式具身语言规划架构——HELP(Hierarchical Embodied Language Planner),该架构由多个基于LLM的智能体组成,每个智能体专门负责解决不同的子任务,从而实现对复杂任务的模块化分解与协同执行。同时,研究强调使用参数量较小的开源LLM以支持自主部署,提升了系统的实用性与可扩展性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21723
作者: Alexandr V. Korchemnyi,Anatoly O. Onishchenko,Eva A. Bakaeva,Alexey K. Kovalev,Aleksandr I. Panov
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注:
Abstract:Embodied agents tasked with complex scenarios, whether in real or simulated environments, rely heavily on robust planning capabilities. When instructions are formulated in natural language, large language models (LLMs) equipped with extensive linguistic knowledge can play this role. However, to effectively exploit the ability of such models to handle linguistic ambiguity, to retrieve information from the environment, and to be based on the available skills of an agent, an appropriate architecture must be designed. We propose a Hierarchical Embodied Language Planner, called HELP, consisting of a set of LLM-based agents, each dedicated to solving a different subtask. We evaluate the proposed approach on a household task and perform real-world experiments with an embodied agent. We also focus on the use of open source LLMs with a relatively small number of parameters, to enable autonomous deployment.
zh
[AI-21] Multiconnectivity for SAGIN: Current Trends Challenges AI-driven Solutions and Opportunities
【速读】:该论文旨在解决空间-空中-地面一体化网络(Space-air-ground-integrated network, SAGIN)环境下多连接(Multiconnectivity, MC)技术实施所面临的复杂资源分配问题。由于SAGIN中存在多种链路类型(如空对空、空对地、地对地等)以及非地面网络(Non-Terrestrial Network, NTN)与地面网络(Terrestrial Network, TN)之间的异构性,传统静态或基于规则的资源调度方法难以适应动态变化的网络环境,导致性能瓶颈。解决方案的关键在于引入基于智能体的强化学习(Agentic Reinforcement Learning, Agentic RL)方法,通过学习复杂环境中多接入技术(Radio Access Technology, RAT)间的协同决策机制,实现对时延、容量等关键指标的优化,并在可接受的功耗代价下显著提升网络整体性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21717
作者: Abd Ullah Khan,Adnan Shahid,Haejoon Jung,Hyundong Shin
机构: 未知
类目: Networking and Internet Architecture (cs.NI); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Social and Information Networks (cs.SI)
备注:
Abstract:Space-air-ground-integrated network (SAGIN)-enabled multiconnectivity (MC) is emerging as a key enabler for next-generation networks, enabling users to simultaneously utilize multiple links across multi-layer non-terrestrial networks (NTN) and multi-radio access technology (multi-RAT) terrestrial networks (TN). However, the heterogeneity of TN and NTN introduces complex architectural challenges that complicate MC implementation. Specifically, the diversity of link types, spanning air-to-air, air-to-space, space-to-space, space-to-ground, and ground-to-ground communications, renders optimal resource allocation highly complex. Recent advancements in reinforcement learning (RL) and agentic artificial intelligence (AI) have shown remarkable effectiveness in optimal decision-making in complex and dynamic environments. In this paper, we review the current developments in SAGIN-enabled MC and outline the key challenges associated with its implementation. We further highlight the transformative potential of AI-driven approaches for resource optimization in a heterogeneous SAGIN environment. To this end, we present a case study on resource allocation optimization enabled by agentic RL for SAGIN-enabled MC involving diverse radio access technologies (RATs). Results show that learning-based methods can effectively handle complex scenarios and substantially enhance network performance in terms of latency and capacity while incurring a moderate increase in power consumption as an acceptable tradeoff. Finally, open research problems and future directions are presented to realize efficient SAGIN-enabled MC.
zh
[AI-22] Zero-Shot to Zero-Lies: Detecting Bengali Deepfake Audio through Transfer Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决 Bengali 语言环境下深度伪造音频(deepfake audio)检测问题,这一领域在以往研究中几乎处于空白状态。针对低资源语言场景下检测性能不足的挑战,研究提出通过预训练模型零样本(zero-shot)推理与微调(fine-tuning)相结合的方法进行系统性评估。关键解决方案在于:首先利用多个主流预训练模型(如 Wav2Vec2-XLSR-53、Whisper 等)进行零样本检测,发现其性能有限;随后对多种架构(包括 ResNet18、LCNN-Attention、ViT-B16 等)进行针对性微调,显著提升检测性能,其中 ResNet18 在准确率(79.17%)、F1 分数(79.12%)、AUC(84.37%)和等错误率(EER,24.35%)上均表现最优,验证了微调策略在低资源语言语音伪造检测中的有效性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21702
作者: Most. Sharmin Sultana Samu,Md. Rakibul Islam,Md. Zahid Hossain,Md. Kamrozzaman Bhuiyan,Farhad Uz Zaman
机构: 未知
类目: ound (cs.SD); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted for publication in 2025 28th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology (ICCIT)
Abstract:The rapid growth of speech synthesis and voice conversion systems has made deepfake audio a major security concern. Bengali deepfake detection remains largely unexplored. In this work, we study automatic detection of Bengali audio deepfakes using the BanglaFake dataset. We evaluate zeroshot inference with several pretrained models. These include Wav2Vec2-XLSR-53, Whisper, PANNsCNN14, WavLM and Audio Spectrogram Transformer. Zero-shot results show limited detection ability. The best model, Wav2Vec2-XLSR-53, achieves 53.80% accuracy, 56.60% AUC and 46.20% EER. We then f ine-tune multiple architectures for Bengali deepfake detection. These include Wav2Vec2-Base, LCNN, LCNN-Attention, ResNet18, ViT-B16 and CNN-BiLSTM. Fine-tuned models show strong performance gains. ResNet18 achieves the highest accuracy of 79.17%, F1 score of 79.12%, AUC of 84.37% and EER of 24.35%. Experimental results confirm that fine-tuning significantly improves performance over zero-shot inference. This study provides the first systematic benchmark of Bengali deepfake audio detection. It highlights the effectiveness of f ine-tuned deep learning models for this low-resource language.
zh
[AI-23] owards Responsible and Explainable AI Agents with Consensus-Driven Reasoning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前自主代理型人工智能(Agentic AI)系统在追求功能性和可扩展性的同时,普遍缺乏可解释性(Explainability)与责任机制(Responsibility)的问题,尤其是在代理输出直接影响下游决策或行动时,其透明度、安全性与治理能力不足。解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于多模型共识与推理层治理的负责任(Responsible AI, RAI)和可解释(Explainable AI, XAI)代理架构:通过异构大语言模型(LLM)与视觉语言模型(VLM)组成的联盟独立生成候选输出,并显式暴露不确定性、分歧与替代解释;再由专用推理代理对这些输出进行结构化整合,强制执行安全与政策约束,缓解幻觉与偏见,最终生成可审计、有证据支撑的决策。该设计实现了决策过程的可追溯性与责任归属,从而在保障自主性与规模化的同时,构建了内置的责任制与透明性机制。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21699
作者: Eranga Bandara,Tharaka Hewa,Ross Gore,Sachin Shetty,Ravi Mukkamala,Peter Foytik,Abdul Rahman,Safdar H. Bouk,Xueping Liang,Amin Hass,Sachini Rajapakse,Ng Wee Keong,Kasun De Zoysa,Aruna Withanage,Nilaan Loganathan
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Agentic AI represents a major shift in how autonomous systems reason, plan, and execute multi-step tasks through the coordination of Large Language Models (LLMs), Vision Language Models (VLMs), tools, and external services. While these systems enable powerful new capabilities, increasing autonomy introduces critical challenges related to explainability, accountability, robustness, and governance, especially when agent outputs influence downstream actions or decisions. Existing agentic AI implementations often emphasize functionality and scalability, yet provide limited mechanisms for understanding decision rationale or enforcing responsibility across agent interactions. This paper presents a Responsible(RAI) and Explainable(XAI) AI Agent Architecture for production-grade agentic workflows based on multi-model consensus and reasoning-layer governance. In the proposed design, a consortium of heterogeneous LLM and VLM agents independently generates candidate outputs from a shared input context, explicitly exposing uncertainty, disagreement, and alternative interpretations. A dedicated reasoning agent then performs structured consolidation across these outputs, enforcing safety and policy constraints, mitigating hallucinations and bias, and producing auditable, evidence-backed decisions. Explainability is achieved through explicit cross-model comparison and preserved intermediate outputs, while responsibility is enforced through centralized reasoning-layer control and agent-level constraints. We evaluate the architecture across multiple real-world agentic AI workflows, demonstrating that consensus-driven reasoning improves robustness, transparency, and operational trust across diverse application domains. This work provides practical guidance for designing agentic AI systems that are autonomous and scalable, yet responsible and explainable by construction.
zh
[AI-24] RIPCN: A Road Impedance Principal Component Network for Probabilistic Traffic Flow Forecasting KDD2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决概率交通流预测(Probabilistic Traffic Flow Forecasting, PTFF)中的两个关键挑战:一是如何揭示并建模交通流不确定性的成因以提升预测可靠性,二是如何捕捉不确定性在时空维度上的相关性以实现更精准的预测。其解决方案的核心在于提出RIPCN(Road Impedance Principal Component Network),该模型融合了领域特定的交通理论与时空主成分学习机制:首先设计了一个动态阻抗演化网络(Dynamic Impedance Evolution Network),通过刻画由道路拥堵水平和流量变异驱动的方向性交通转移模式,明确识别不确定性的直接来源,从而增强预测的可靠性和可解释性;其次引入主成分网络(Principal Component Network),用于预测未来流量协方差矩阵的主要特征向量,有效捕获时空维度上的不确定性相关结构,在保证高精度不确定性估计的同时也提升了点预测性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21685
作者: Haochen Lv,Yan Lin,Shengnan Guo,Xiaowei Mao,Hong Nie,Letian Gong,Youfang Lin,Huaiyu Wan
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted at KDD 2026. 12 pages, 10 figures
Abstract:Accurate traffic flow forecasting is crucial for intelligent transportation services such as navigation and ride-hailing. In such applications, uncertainty estimation in forecasting is important because it helps evaluate traffic risk levels, assess forecast reliability, and provide timely warnings. As a result, probabilistic traffic flow forecasting (PTFF) has gained significant attention, as it produces both point forecasts and uncertainty estimates. However, existing PTFF approaches still face two key challenges: (1) how to uncover and model the causes of traffic flow uncertainty for reliable forecasting, and (2) how to capture the spatiotemporal correlations of uncertainty for accurate prediction. To address these challenges, we propose RIPCN, a Road Impedance Principal Component Network that integrates domain-specific transportation theory with spatiotemporal principal component learning for PTFF. RIPCN introduces a dynamic impedance evolution network that captures directional traffic transfer patterns driven by road congestion level and flow variability, revealing the direct causes of uncertainty and enhancing both reliability and interpretability. In addition, a principal component network is designed to forecast the dominant eigenvectors of future flow covariance, enabling the model to capture spatiotemporal uncertainty correlations. This design allows for accurate and efficient uncertainty estimation while also improving point prediction performance. Experimental results on real-world datasets show that our approach outperforms existing probabilistic forecasting methods. Comments: Accepted at KDD 2026. 12 pages, 10 figures Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) ACMclasses: I.2.6; I.5.1; G.3 Cite as: arXiv:2512.21685 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2512.21685v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21685 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-25] Near-Optimal Coalition Structures in Polynomial Time
【速读】:该论文旨在解决经典的联盟结构生成(Coalition Structure Generation, CSG)问题,即在给定联盟价值函数的情况下,寻找一种将参与者划分为互不相交联盟的划分方式,以最大化总福利。研究通过对比三种算法范式——动态规划(Dynamic Programming, DP)、混合整数线性规划(Mixed-Integer Linear Programming, MILP)分支定界法以及基于贪心或 l₁ 型稀疏松弛的方法——的 anytime 行为,发现:在一种简单的随机“稀疏协同效应”模型下,稀疏松弛方法能够在多项式时间内以高概率恢复出接近最优福利的联盟结构;而广义的 DP 和 MILP 算法则需指数时间才能达到类似解质量。该研究的关键在于证明了稀疏松弛方法在概率意义上具有优越的 anytime 性能,从而建立了相对于传统精确方法的严格概率性优势,即使后者最终仍能保证最优解。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21657
作者: Angshul Majumdar
机构: 未知
类目: Computer Science and Game Theory (cs.GT); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 13 pages
Abstract:We study the classical coalition structure generation (CSG) problem and compare the anytime behavior of three algorithmic paradigms: dynamic programming (DP), MILP branch-and-bound, and sparse relaxations based on greedy or l_1 -type methods. Under a simple random “sparse synergy” model for coalition values, we prove that sparse relaxations recover coalition structures whose welfare is arbitrarily close to optimal in polynomial time with high probability. In contrast, broad classes of DP and MILP algorithms require exponential time before attaining comparable solution quality. This establishes a rigorous probabilistic anytime separation in favor of sparse relaxations, even though exact methods remain ultimately optimal.
zh
[AI-26] Structural Induced Exploration for Balanced and Scalable Multi-Robot Path Planning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决多机器人路径规划(Multi-robot path planning)中因组合复杂性导致的全局效率与机器人间任务分配公平性难以平衡的问题。传统群体智能方法在小规模实例上有效,但在复杂环境中易早熟收敛且难以扩展。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种结构诱导探索框架(structure-induced exploration framework),通过在蚁群优化(Ant Colony Optimization, ACO)搜索过程中引入结构先验(structural prior),利用任务的空间分布约束搜索空间;同时设计基于负载感知的目标函数以优化总行程距离与单个机器人工作负载之间的权衡,并采用显式重叠抑制策略确保任务在团队间的均衡分配。该方法显著提升了路径紧凑性、稳定性及负载均衡性,在多种基准场景下优于主流元启发式算法,具备良好的可扩展性和可解释性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21654
作者: Zikun Guo,Adeyinka P. Adedigba,Rammohan Mallipeddi,Heoncheol Lee
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 20pages, 6Figues
Abstract:Multi-robot path planning is a fundamental yet challenging problem due to its combinatorial complexity and the need to balance global efficiency with fair task allocation among robots. Traditional swarm intelligence methods, although effective on small instances, often converge prematurely and struggle to scale to complex environments. In this work, we present a structure-induced exploration framework that integrates structural priors into the search process of the ant colony optimization (ACO). The approach leverages the spatial distribution of the task to induce a structural prior at initialization, thereby constraining the search space. The pheromone update rule is then designed to emphasize structurally meaningful connections and incorporates a load-aware objective to reconcile the total travel distance with individual robot workload. An explicit overlap suppression strategy further ensures that tasks remain distinct and balanced across the team. The proposed framework was validated on diverse benchmark scenarios covering a wide range of instance sizes and robot team configurations. The results demonstrate consistent improvements in route compactness, stability, and workload distribution compared to representative metaheuristic baselines. Beyond performance gains, the method also provides a scalable and interpretable framework that can be readily applied to logistics, surveillance, and search-and-rescue applications where reliable large-scale coordination is essential.
zh
[AI-27] Variance-Aware Prior-Based Tree Policies for Monte Carlo Tree Search
【速读】:该论文旨在解决如何在蒙特卡洛树搜索(Monte Carlo Tree Search, MCTS)中系统性地设计包含先验信息的树策略(tree policy),以提升探索效率并加速强化学习训练的问题。现有方法如PUCT虽通过引入先验项显著改善了AlphaZero类算法的性能,但其推导缺乏理论基础,且难以扩展至其他具有更强理论保障的UCB变体(如UCB-V)。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为Inverse-RPO的新方法,该方法将MCTS建模为正则化策略优化(Regularized Policy Optimization, RPO)问题,并基于此框架从任意无先验的UCB出发,系统推导出对应的含先验UCT形式。作者以此方法应用于方差感知的UCB-V,得到了两种新的含先验树策略,能有效利用动作值估计的方差信息进行更优探索,实验表明其性能优于PUCT且无需额外计算开销。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21648
作者: Maximilian Weichart
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) has profoundly influenced reinforcement learning (RL) by integrating planning and learning in tasks requiring long-horizon reasoning, exemplified by the AlphaZero family of algorithms. Central to MCTS is the search strategy, governed by a tree policy based on an upper confidence bound (UCB) applied to trees (UCT). A key factor in the success of AlphaZero is the introduction of a prior term in the UCB1-based tree policy PUCT, which improves exploration efficiency and thus accelerates training. While many alternative UCBs with stronger theoretical guarantees than UCB1 exist, extending them to prior-based UCTs has been challenging, since PUCT was derived empirically rather than from first principles. Recent work retrospectively justified PUCT by framing MCTS as a regularized policy optimization (RPO) problem. Building on this perspective, we introduce Inverse-RPO, a general methodology that systematically derives prior-based UCTs from any prior-free UCB. Applying this method to the variance-aware UCB-V, we obtain two new prior-based tree policies that incorporate variance estimates into the search. Experiments indicate that these variance-aware prior-based UCTs outperform PUCT across multiple benchmarks without incurring additional computational cost. We also provide an extension of the mctx library supporting variance-aware UCTs, showing that the required code changes are minimal and intended to facilitate further research on principled prior-based UCTs. Code: this http URL.
zh
[AI-28] Multiple-play Stochastic Bandits with Prioritized Arm Capacity Sharing
【速读】:该论文旨在解决由大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)应用、边缘智能等场景引发的资源分配问题,其核心是设计一种适用于多选择(multiple-play)随机老虎机(stochastic bandits)的变体模型,其中每个臂(arm)具有随机容量,且单位容量关联奖励函数,每次选择(play)具有优先级权重,资源按优先级高低分配。解决方案的关键在于:首先提出一个最优离线算法 MSB-PRS-OffOpt,可在给定参数下以 O(MK3) 的计算复杂度找到最优分配策略;进而利用该算法作为子程序构建基于近似上置信界(UCB)的在线学习算法,实现了实例无关和实例相关的遗憾上界分别与理论下界匹配,仅相差 KlnKT 和 α1K2 因子,从而有效应对由优先级资源共享机制诱导的非线性组合效用函数所带来的优化与学习挑战。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21626
作者: Hong Xie,Haoran Gu,Yanying Huang,Tao Tan,Defu Lian
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 17 pages
Abstract:This paper proposes a variant of multiple-play stochastic bandits tailored to resource allocation problems arising from LLM applications, edge intelligence, etc. The model is composed of M arms and K plays. Each arm has a stochastic number of capacities, and each unit of capacity is associated with a reward function. Each play is associated with a priority weight. When multiple plays compete for the arm capacity, the arm capacity is allocated in a larger priority weight first manner. Instance independent and instance dependent regret lower bounds of \Omega( \alpha_1 \sigma \sqrtKM T ) and \Omega(\alpha_1 \sigma^2 \fracM\Delta \ln T) are proved, where \alpha_1 is the largest priority weight and \sigma characterizes the reward tail. When model parameters are given, we design an algorithm named \textttMSB-PRS-OffOpt to locate the optimal play allocation policy with a computational complexity of O(MK^3) . Utilizing \textttMSB-PRS-OffOpt as a subroutine, an approximate upper confidence bound (UCB) based algorithm is designed, which has instance independent and instance dependent regret upper bounds matching the corresponding lower bound up to factors of \sqrtK \ln KT and \alpha_1 K^2 respectively. To this end, we address nontrivial technical challenges arising from optimizing and learning under a special nonlinear combinatorial utility function induced by the prioritized resource sharing mechanism.
zh
[AI-29] Democratizing Drug Discovery with an Orchestrated Knowledge-Driven Multi-Agent Team for User-Guided Therapeutic Design
【速读】:该论文旨在解决药物发现过程中因学科碎片化和计算设计与生理验证之间存在执行鸿沟而导致的效率低下问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一个名为OrchestRA的人机协同多智能体平台,该平台将生物学、化学与药理学深度融合为一个自主驱动的发现引擎;其中,生物学家智能体基于包含1000万条关联的知识图谱进行深度推理以识别高置信度靶点,化学家智能体自主探测结构口袋用于从头设计或药物重定位,药理学家智能体则通过严格的生理基础药代动力学(PBPK)模拟评估候选分子,三者在协调器(Orchestrator)控制下形成动态反馈回路,使药代动力学和毒性特征直接触发结构再优化,从而实现从随机搜索到可编程证据驱动工程范式的转变。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21623
作者: Takahide Suzuki,Kazuki Nakanishi,Takashi Fujiwara,Hideyuki Shimizu
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA); Quantitative Methods (q-bio.QM)
备注: 51 pages, 4 figures (with supplementary information)
Abstract:Therapeutic discovery remains a formidable challenge, impeded by the fragmentation of specialized domains and the execution gap between computational design and physiological validation. Although generative AI offers promise, current models often function as passive assistants rather than as autonomous executors. Here, we introduce OrchestRA, a human-in-the-loop multi-agent platform that unifies biology, chemistry, and pharmacology into an autonomous discovery engine. Unlike static code generators, our agents actively execute simulations and reason the results to drive iterative optimization. Governed by an Orchestrator, a Biologist Agent leverages deep reasoning over a massive knowledge graph (10 million associations) to pinpoint high-confidence targets; a Chemist Agent autonomously detects structural pockets for de novo design or drug repositioning; and a Pharmacologist Agent evaluates candidates via rigorous physiologically based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) simulations. This architecture establishes a dynamic feedback loop where pharmacokinetic and toxicity profiles directly trigger structural reoptimization. By seamlessly integrating autonomous execution with human guidance, OrchestRA democratizes therapeutic design, transforming drug discovery from a stochastic search to a programmable evidence-based engineering discipline.
zh
[AI-30] AMS-IO-Bench and AMS-IO-Agent : Benchmarking and Structured Reasoning for Analog and Mixed-Signal Integrated Circuit Input/Output Design AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决模拟与混合信号(Analog and Mixed-Signal, AMS)集成电路(IC)设计中输入/输出(I/O)子系统自动化生成效率低、依赖人工经验且易出错的问题。解决方案的关键在于提出AMS-IO-Agent,一个基于大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)的领域专用智能代理,其核心创新是构建了一个结构化的领域知识库以捕获可重用的设计约束与规范,并通过设计意图结构化模块将模糊的自然语言需求转化为可验证的逻辑步骤(采用JSON和Python作为中间表示格式),从而实现从设计意图到工业级I/O环自动布局的端到端映射。该方法在AMS-IO-Bench基准测试中实现了超过70%的DRC+LVS通过率,并将设计周期从数小时缩短至分钟级,且生成的I/O环已在28 nm CMOS工艺中流片验证,标志着首个由LLM代理完成并直接用于硅片实现的非平凡AMS IC子任务。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21613
作者: Zhishuai Zhang,Xintian Li,Shilong Liu,Aodong Zhang,Lu Jie,Nan Sun
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 8 pages, 5 figures. Accepted to AAAI 2026
Abstract:In this paper, we propose AMS-IO-Agent, a domain-specialized LLM-based agent for structure-aware input/output (I/O) subsystem generation in analog and mixed-signal (AMS) integrated circuits (ICs). The central contribution of this work is a framework that connects natural language design intent with industrial-level AMS IC design deliverables. AMS-IO-Agent integrates two key capabilities: (1) a structured domain knowledge base that captures reusable constraints and design conventions; (2) design intent structuring, which converts ambiguous user intent into verifiable logic steps using JSON and Python as intermediate formats. We further introduce AMS-IO-Bench, a benchmark for wirebond-packaged AMS I/O ring automation. On this benchmark, AMS-IO-Agent achieves over 70% DRC+LVS pass rate and reduces design turnaround time from hours to minutes, outperforming the baseline LLM. Furthermore, an agent-generated I/O ring was fabricated and validated in a 28 nm CMOS tape-out, demonstrating the practical effectiveness of the approach in real AMS IC design flows. To our knowledge, this is the first reported human-agent collaborative AMS IC design in which an LLM-based agent completes a nontrivial subtask with outputs directly used in silicon.
zh
[AI-31] LLM -I2I: Boost Your Small Item2Item Recommendation Model with Large Language Model
【速读】:该论文旨在解决Item-to-Item (I2I)推荐模型在实际应用中面临的两个核心挑战:一是模型中心方法(model-centric approaches)虽能提升性能但增加计算开销和部署复杂度;二是数据中心方法(data-centric methods)虽具成本优势,却受限于数据稀疏性和噪声问题。解决方案的关键在于提出LLM-I2I框架,该框架利用大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)进行数据增强与净化:首先通过LLM生成器合成长尾物品的用户-物品交互数据以缓解稀疏性问题,其次通过LLM判别器过滤真实与合成数据中的噪声交互,最终融合高质量数据训练I2I模型,从而在不修改模型架构的前提下显著提升推荐效果,尤其在长尾物品上的表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21595
作者: Yinfu Feng,Yanjing Wu,Rong Xiao,Xiaoyi Zen
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Item-to-Item (I2I) recommendation models are widely used in real-world systems due to their scalability, real-time capabilities, and high recommendation quality. Research to enhance I2I performance focuses on two directions: 1) model-centric approaches, which adopt deeper architectures but risk increased computational costs and deployment complexity, and 2) data-centric methods, which refine training data without altering models, offering cost-effectiveness but struggling with data sparsity and noise. To address these challenges, we propose LLM-I2I, a data-centric framework leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) to mitigate data quality issues. LLM-I2I includes (1) an LLM-based generator that synthesizes user-item interactions for long-tail items, alleviating data sparsity, and (2) an LLM-based discriminator that filters noisy interactions from real and synthetic data. The refined data is then fused to train I2I models. Evaluated on industry (AEDS) and academic (ARD) datasets, LLM-I2I consistently improves recommendation accuracy, particularly for long-tail items. Deployed on a large-scale cross-border e-commerce platform, it boosts recall number (RN) by 6.02% and gross merchandise value (GMV) by 1.22% over existing I2I models. This work highlights the potential of LLMs in enhancing data-centric recommendation systems without modifying model architectures.
zh
[AI-32] A Medical Multimodal Diagnostic Framework Integrating Vision-Language Models and Logic Tree Reasoning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前多模态医学人工智能模型在临床应用中因幻觉(hallucination)或推理链不一致而导致可信度不足的问题。现有模型虽能整合临床文本与医学影像,但缺乏逻辑严谨性与可解释性,难以获得医生信任。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于LLaVA架构的诊断框架,通过引入逻辑正则化推理机制,将诊断任务分解为可验证的步骤,并利用逻辑树生成器构建结构化的前提与结论链条,从而实现跨模态对齐与可追溯的推理过程,显著提升诊断准确性和推理透明度。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21583
作者: Zelin Zang,Wenyi Gu,Siqi Ma,Dan Yang,Yue Shen,Zhu Zhang,Guohui Fan,Wing-Kuen Ling,Fuji Yang
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:With the rapid growth of large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs) in medicine, simply integrating clinical text and medical imaging does not guarantee reliable reasoning. Existing multimodal models often produce hallucinations or inconsistent chains of thought, limiting clinical trust. We propose a diagnostic framework built upon LLaVA that combines vision-language alignment with logic-regularized reasoning. The system includes an input encoder for text and images, a projection module for cross-modal alignment, a reasoning controller that decomposes diagnostic tasks into steps, and a logic tree generator that assembles stepwise premises into verifiable conclusions. Evaluations on MedXpertQA and other benchmarks show that our method improves diagnostic accuracy and yields more interpretable reasoning traces on multimodal tasks, while remaining competitive on text-only settings. These results suggest a promising step toward trustworthy multimodal medical AI.
zh
[AI-33] NEMO-4-PAYPAL: Leverag ing NVIDIAs Nemo Framework for empowering PayPals Commerce Agent
【速读】:该论文旨在解决电商场景中多智能体系统(multi-agent system)在检索组件上的性能瓶颈问题,尤其是检索环节占总响应时间超过50%的延迟问题。解决方案的关键在于基于NVIDIA NeMo框架对小语言模型(small language model, SLM)进行生成式AI(Generative AI)驱动的微调优化,采用LoRA(Low-Rank Adaptation)方法,在学习率、优化器(Adam/AdamW)、余弦退火调度和LoRA秩等超参数空间内进行系统性搜索,最终实现显著降低延迟与成本的同时保持或提升代理质量。这一策略首次将NeMo框架应用于电商专用智能体优化,并构建了可扩展的生产级多智能体系统优化框架。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21578
作者: Ali Sahami,Sudhanshu Garg,Andrew Wang,Chaitanya Kulkarni,Farhad Farahani,Sean Yun-Shiuan Chuang,Jian Wan,Srinivasan Manoharan,Uma Kona,Nitin Sharma,Linsey Pang,Prakhar Mehrotra,Jessica Clark,Mark Moyou
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:We present the development and optimization of PayPal’s Commerce Agent, powered by NEMO-4-PAYPAL, a multi-agent system designed to revolutionize agentic commerce on the PayPal platform. Through our strategic partnership with NVIDIA, we leveraged the NeMo Framework for LLM model fine-tuning to enhance agent performance. Specifically, we optimized the Search and Discovery agent by replacing our base model with a fine-tuned Nemotron small language model (SLM). We conducted comprehensive experiments using the llama3.1-nemotron-nano-8B-v1 architecture, training LoRA-based models through systematic hyperparameter sweeps across learning rates, optimizers (Adam, AdamW), cosine annealing schedules, and LoRA ranks. Our contributions include: (1) the first application of NVIDIA’s NeMo Framework to commerce-specific agent optimization, (2) LLM powered fine-tuning strategy for retrieval-focused commerce tasks, (3) demonstration of significant improvements in latency and cost while maintaining agent quality, and (4) a scalable framework for multi-agent system optimization in production e-commerce environments. Our results demonstrate that the fine-tuned Nemotron SLM effectively resolves the key performance issue in the retrieval component, which represents over 50% of total agent response time, while maintaining or enhancing overall system performance. Subjects: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21578 [cs.AI] (or arXiv:2512.21578v1 [cs.AI] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21578 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
zh
[AI-34] Bidirectional Human-AI Alignment in Education for Trustworthy Learning Environments
【速读】:该论文旨在解决人工智能(Artificial Intelligence, AI)在教育领域应用中面临的伦理与实践挑战,特别是如何在提升个性化学习、评估效率和教师支持能力的同时,保障教育公平、学生隐私与自主性。其解决方案的关键在于提出“双向人机对齐”(bidirectional human-AI alignment)的概念,强调不仅需将人类价值观嵌入AI系统设计中,还需赋予教师、学生及教育机构解读、批判并引导AI技术的能力,从而构建可信的学习环境。通过这一机制,实现AI与人类在教育场景中的协同进化与共同成长。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21552
作者: Hua Shen
机构: 未知
类目: Computers and Society (cs.CY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC)
备注: Book Chapter
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming education, offering unprecedented opportunities to personalize learning, enhance assessment, and support educators. Yet these opportunities also introduce risks related to equity, privacy, and student autonomy. This chapter develops the concept of bidirectional human-AI alignment in education, emphasizing that trustworthy learning environments arise not only from embedding human values into AI systems but also from equipping teachers, students, and institutions with the skills to interpret, critique, and guide these technologies. Drawing on emerging research and practical case examples, we explore AI’s evolution from support tool to collaborative partner, highlighting its impacts on teacher roles, student agency, and institutional governance. We propose actionable strategies for policymakers, developers, and educators to ensure that AI advances equity, transparency, and human flourishing rather than eroding them. By reframing AI adoption as an ongoing process of mutual adaptation, the chapter envisions a future in which humans and intelligent systems learn, innovate, and grow together.
zh
[AI-35] Leash: Adaptive Length Penalty and Reward Shaping for Efficient Large Reasoning Model
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有方法依赖固定长度惩罚(fixed length penalties)所带来的适应性不足问题,这类方法难以根据大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)推理能力的动态演化进行调整,从而导致准确率与简洁性之间的权衡不优。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种基于强化学习的自适应长度惩罚与奖励塑形框架——Leash(adaptive LEngth penAlty and reward SHaping),将长度控制建模为约束优化问题,并采用拉格朗日对偶法动态调节惩罚系数:当生成内容超过目标长度时增强惩罚,反之则放松惩罚,以此引导模型在不牺牲任务性能的前提下生成更简洁的推理过程。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21540
作者: Yanhao Li,Lu Ma,Jiaran Zhang,Lexiang Tang,Wentao Zhang,Guibo Luo
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Existing approaches typically rely on fixed length penalties, but such penalties are hard to tune and fail to adapt to the evolving reasoning abilities of LLMs, leading to suboptimal trade-offs between accuracy and conciseness. To address this challenge, we propose Leash (adaptive LEngth penAlty and reward SHaping), a reinforcement learning framework for efficient reasoning in LLMs. We formulate length control as a constrained optimization problem and employ a Lagrangian primal-dual method to dynamically adjust the penalty coefficient. When generations exceed the target length, the penalty is intensified; when they are shorter, it is relaxed. This adaptive mechanism guides models toward producing concise reasoning without sacrificing task performance. Experiments on Deepseek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B and Qwen3-4B-Thinking-2507 show that Leash reduces the average reasoning length by 60% across diverse tasks - including in-distribution mathematical reasoning and out-of-distribution domains such as coding and instruction following - while maintaining competitive performance. Our work thus presents a practical and effective paradigm for developing controllable and efficient LLMs that balance reasoning capabilities with computational budgets.
zh
[AI-36] Selective LLM -Guided Regularization for Enhancing Recommendation Models
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前基于大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的推荐系统中存在的两个核心问题:一是将LLM作为独立推荐器时存在计算成本高、用户-物品空间中部分区域预测不可靠的问题;二是采用全局知识蒸馏策略时,强制下游模型无差别地模仿LLM输出,即使在LLM预测不准确的情况下也会引入噪声。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种选择性LLM引导正则化(Selective LLM Guided Regularization)框架,该方法通过一个可训练的门控机制(gating mechanism),结合用户历史长度、物品流行度和模型不确定性等信号,动态判断何时激活LLM提供的成对排序监督信号,从而实现“按需”使用LLM知识。所有LLM评分均离线完成,不增加在线推理开销,且实验证明该策略在整体准确率及冷启动和长尾场景下均显著优于全局蒸馏基线。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21526
作者: Shanglin Yang,Zhan Shi
机构: 未知
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Large language models provide rich semantic priors and strong reasoning capabilities, making them promising auxiliary signals for recommendation. However, prevailing approaches either deploy LLMs as standalone recommender or apply global knowledge distillation, both of which suffer from inherent drawbacks. Standalone LLM recommender are costly, biased, and unreliable across large regions of the user item space, while global distillation forces the downstream model to imitate LLM predictions even when such guidance is inaccurate. Meanwhile, recent studies show that LLMs excel particularly in re-ranking and challenging scenarios, rather than uniformly across all this http URL introduce Selective LLM Guided Regularization, a model-agnostic and computation efficient framework that activates LLM based pairwise ranking supervision only when a trainable gating mechanism informing by user history length, item popularity, and model uncertainty predicts the LLM to be reliable. All LLM scoring is performed offline, transferring knowledge without increasing inference cost. Experiments across multiple datasets show that this selective strategy consistently improves overall accuracy and yields substantial gains in cold start and long tail regimes, outperforming global distillation baselines.
zh
[AI-37] Efficient MoE Inference with Fine-Grained Scheduling of Disaggregated Expert Parallelism
【速读】:该论文旨在解决混合专家(Mixture-of-Experts, MoE)架构在推理阶段因KV缓存占用内存和稀疏专家激活导致的计算效率低下问题,尤其是在分布式环境中缺乏对共享专家支持与高效任务调度机制时性能受限的问题。其解决方案的核心是提出FinDEP——一种面向解耦专家并行(Disaggregated Expert Parallelism, DEP)的细粒度任务调度算法,通过将计算与通信拆分为更小的任务以实现精细化流水线化、构建支持可变粒度和顺序的调度优化模型,并设计高效的求解器来应对大规模搜索空间,从而显著提升MoE推理吞吐量,在多个GPU系统上实验表明最高可实现1.61倍的吞吐提升。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21487
作者: Xinglin Pan,Shaohuai Shi,Wenxiang Lin,Yuxin Wang,Zhenheng Tang,Wei Wang,Xiaowen Chu
机构: 未知
类目: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture scales model size with sublinear computational increase but suffers from memory-intensive inference due to KV caches and sparse expert activation. Recent disaggregated expert parallelism (DEP) distributes attention and experts to dedicated GPU groups but lacks support for shared experts and efficient task scheduling, limiting performance. We propose FinDEP, a fine-grained task scheduling algorithm for DEP that maximizes task overlap to improve MoE inference throughput. FinDEP introduces three innovations: 1) partitioning computation/communication into smaller tasks for fine-grained pipelining, 2) formulating a scheduling optimization supporting variable granularity and ordering, and 3) developing an efficient solver for this large search space. Experiments on four GPU systems with DeepSeek-V2 and Qwen3-MoE show FinDEP improves throughput by up to 1.61x over prior methods, achieving up to 1.24x speedup on a 32-GPU system. Subjects: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21487 [cs.DC] (or arXiv:2512.21487v1 [cs.DC] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21487 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite
zh
[AI-38] LogicLens: Visual-Logical Co-Reasoning for Text-Centric Forgery Analysis
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前文本中心伪造内容(text-centric forgery)检测中存在的一系列问题:现有方法多依赖粗粒度视觉分析,缺乏深度推理能力;同时将检测、定位与解释视为独立子任务,忽视了三者之间的内在关联,难以实现整体性能提升。其解决方案的核心在于提出一个统一的视觉-文本协同推理框架 LogicLens,该框架通过创新的跨线索链式思维(Cross-Cues-aware Chain of Thought, CCT)机制,迭代地交叉验证视觉线索与文本逻辑,从而实现深层次的联合推理;此外,引入基于GRPO优化的加权多任务奖励函数以确保各子任务间的鲁棒对齐,显著提升了模型在检测精度、定位准确性和可解释性方面的综合表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21482
作者: Fanwei Zeng,Changtao Miao,Jing Huang,Zhiya Tan,Shutao Gong,Xiaoming Yu,Yang Wang,Huazhe Tan,Weibin Yao,Jianshu Li
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 11 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables
Abstract:Sophisticated text-centric forgeries, fueled by rapid AIGC advancements, pose a significant threat to societal security and information authenticity. Current methods for text-centric forgery analysis are often limited to coarse-grained visual analysis and lack the capacity for sophisticated reasoning. Moreover, they typically treat detection, grounding, and explanation as discrete sub-tasks, overlooking their intrinsic relationships for holistic performance enhancement. To address these challenges, we introduce LogicLens, a unified framework for Visual-Textual Co-reasoning that reformulates these objectives into a joint task. The deep reasoning of LogicLens is powered by our novel Cross-Cues-aware Chain of Thought (CCT) mechanism, which iteratively cross-validates visual cues against textual logic. To ensure robust alignment across all tasks, we further propose a weighted multi-task reward function for GRPO-based optimization. Complementing this framework, we first designed the PR ^2 (Perceiver, Reasoner, Reviewer) pipeline, a hierarchical and iterative multi-agent system that generates high-quality, cognitively-aligned annotations. Then, we constructed RealText, a diverse dataset comprising 5,397 images with fine-grained annotations, including textual explanations, pixel-level segmentation, and authenticity labels for model training. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of LogicLens across multiple benchmarks. In a zero-shot evaluation on T-IC13, it surpasses the specialized framework by 41.4% and GPT-4o by 23.4% in macro-average F1 score. Moreover, on the challenging dense-text T-SROIE dataset, it establishes a significant lead over other MLLM-based methods in mF1, CSS, and the macro-average F1. Our dataset, model, and code will be made publicly available.
zh
[AI-39] dUltra: Ultra-Fast Diffusion Language Models via Reinforcement Learning
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前掩码扩散语言模型(Masked Diffusion Language Models, MDLMs)在并行生成Token时效率低下的问题,即尽管MDLM具备并行生成潜力,但现有开源模型每轮前向传播仅能解码少于5个Token,导致其采样速度与自回归(Autoregressive, AR)模型结合推测解码(Speculative Decoding)方案相当,难以体现对主流AR方法的优势。解决方案的关键在于提出dUltra框架,这是一个基于组相对策略优化(Group Relative Policy Optimization, GRPO)的在线策略强化学习方法,通过引入一个可学习的“去掩码规划器头”(unmasking planner head),预测每个Token在独立伯努利分布下的去掩码概率,并联合优化扩散语言模型与去掩码顺序规划器,利用包含可验证奖励、蒸馏奖励及去掩码步数的复合奖励信号进行训练,从而实现更高效且准确的并行解码策略。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21446
作者: Shirui Chen,Jiantao Jiao,Lillian J. Ratliff,Banghua Zhu
机构: 未知
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Masked diffusion language models (MDLMs) offer the potential for parallel token generation, but most open-source MDLMs decode fewer than 5 tokens per model forward pass even with sophisticated sampling strategies. As a result, their sampling speeds are often comparable to AR + speculative decoding schemes, limiting their advantage over mainstream autoregressive approaches. Existing distillation-based accelerators (dParallel, d3LLM) finetune MDLMs on trajectories generated by a base model, which can become off-policy during finetuning and restrict performance to the quality of the base model’s samples. We propose \textttdUltra, an on-policy reinforcement learning framework based on Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) that learns unmasking strategies for efficient parallel decoding. dUltra introduces an unmasking planner head that predicts per-token unmasking likelihoods under independent Bernoulli distributions. We jointly optimize the base diffusion LLM and the unmasking order planner using reward signals combining verifiable reward, distillation reward, and the number of unmasking steps. Across mathematical reasoning and code generation tasks, dUltra improves the accuracy–efficiency trade-off over state-of-the-art heuristic and distillation baselines, moving towards achieving ``diffusion supremacy’’ over autoregressive models.
zh
[AI-40] hree-way decision with incomplete information based on similarity and satisfiability
【速读】:该论文旨在解决三支决策(Three-way decision)在不完整信息条件下的扩展问题,以提升其在现实世界应用中的实用性。传统方法主要基于完备信息,采用等价关系或逻辑公式的可满足性进行建模,但在实际场景中,数据常存在缺失或不确定性。论文的关键解决方案在于:一方面,提出一种新的对象相似度度量作为等价关系的推广,从而构建α-相似类和对象可逼近性两种三支决策方法;另一方面,引入公式可满足度的量化指标,实现对逻辑公式的定量化处理,并据此发展出α-意义集与公式置信度两种新方法。这些创新不仅延续了计算与概念双视角的框架,还通过引入“可逼近性”和“可满足度”等新概念,为不完整信息环境下的三支决策提供了更具适应性和理论深度的新路径。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21421
作者: Junfang Luo,Mengjun Hu,Keyun Qin
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Three-way decision is widely applied with rough set theory to learn classification or decision rules. The approaches dealing with complete information are well established in the literature, including the two complementary computational and conceptual formulations. The computational formulation uses equivalence relations, and the conceptual formulation uses satisfiability of logic formulas. In this paper, based on a briefly review of these two formulations, we generalize both formulations into three-way decision with incomplete information that is more practical in real-world applications. For the computational formulation, we propose a new measure of similarity degree of objects as a generalization of equivalence relations. Based on it, we discuss two approaches to three-way decision using alpha-similarity classes and approximability of objects, respectively. For the conceptual formulation, we propose a measure of satisfiability degree of formulas as a quantitative generalization of satisfiability with complete information. Based on it, we study two approaches to three-way decision using alpha-meaning sets of formulas and confidence of formulas, respectively. While using similarity classes is a common method of analyzing incomplete information in the literature, the proposed concept of approximability and the two approaches in conceptual formulation point out new promising directions.
zh
[AI-41] Feasible strategies in three-way conflict analysis with three-valued ratings
【速读】:该论文旨在解决现有三支冲突分析(three-way conflict analysis)研究中对可行策略(feasible strategies)识别不足的问题,尤其在冲突化解与调和过程中缺乏系统性的策略生成机制。其关键解决方案在于:首先基于正负相似度计算代理群体(clique of agents)的整体评分,进而引入加权一致性(weighted consistency)与非一致性(weighted non-consistency)测度,综合考虑代理与议题的权重,从而精准识别出可行策略及其最优解。该方法通过将加权代理-议题评估与一致性/非一致性分析相融合,实现了从可行策略到最优策略的系统性识别,显著提升了冲突解决模型的有效性与实用性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21420
作者: Jing Liu,Mengjun Hu,Guangming Lang
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Most existing work on three-way conflict analysis has focused on trisecting agent pairs, agents, or issues, which contributes to understanding the nature of conflicts but falls short in addressing their resolution. Specifically, the formulation of feasible strategies, as an essential component of conflict resolution and mitigation, has received insufficient scholarly attention. Therefore, this paper aims to investigate feasible strategies from two perspectives of consistency and non-consistency. Particularly, we begin with computing the overall rating of a clique of agents based on positive and negative similarity degrees. Afterwards, considering the weights of both agents and issues, we propose weighted consistency and non-consistency measures, which are respectively used to identify the feasible strategies for a clique of agents. Algorithms are developed to identify feasible strategies, L -order feasible strategies, and the corresponding optimal ones. Finally, to demonstrate the practicality, effectiveness, and superiority of the proposed models, we apply them to two commonly used case studies on NBA labor negotiations and development plans for Gansu Province and conduct a sensitivity analysis on parameters and a comparative analysis with existing state-of-the-art conflict analysis approaches. The comparison results demonstrate that our conflict resolution models outperform the conventional approaches by unifying weighted agent-issue evaluation with consistency and non-consistency measures to enable the systematic identification of not only feasible strategies but also optimal solutions.
zh
[AI-42] hree-way conflict analysis based on alliance and conflict functions
【速读】:该论文旨在解决三支冲突分析中代理(agent)、议题(issue)及代理对(agent pair)的划分问题,传统方法依赖单一函数(如评分函数或辅助函数)同时刻画正向与负向关系,导致在群体层面聚合时语义模糊。例如,联盟+1与冲突-1的关系平均后与中立0关系结果相同,但实际态度差异显著。解决方案的关键在于将辅助函数中的对立维度分离为独立的联盟函数与冲突函数,从而实现对代理、议题及其对的三支划分,并进一步引入联盟集(alliance set)与策略概念以支持冲突分析中的关键决策问题,提升了语义清晰度和模型实用性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21419
作者: Junfang Luo,Mengjun Hu,Guangming Lang,Xin Yang,Keyun Qin
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:Trisecting agents, issues, and agent pairs are essential topics of three-way conflict analysis. They have been commonly studied based on either a rating or an auxiliary function. A rating function defines the positive, negative, or neutral ratings of agents on issues. An auxiliary function defines the alliance, conflict, and neutrality relations between agents. These functions measure two opposite aspects in a single function, leading to challenges in interpreting their aggregations over a group of issues or agents. For example, when studying agent relations regarding a set of issues, a standard aggregation takes the average of an auxiliary function concerning single issues. Therefore, a pair of alliance +1 and conflict -1 relations will produce the same result as a pair of neutrality 0 relations, although the attitudes represented by the two pairs are very different. To clarify semantics, we separate the two opposite aspects in an auxiliary function into a pair of alliance and conflict functions. Accordingly, we trisect the agents, issues, and agent pairs and investigate their applications in solving a few crucial questions in conflict analysis. Particularly, we explore the concepts of alliance sets and strategies. A real-world application is given to illustrate the proposed models.
zh
[AI-43] LLM -Driven Feature-Level Adversarial Attacks on Android Malware Detectors
【速读】:该论文旨在解决机器学习(Machine Learning, ML)驱动的Android恶意软件检测系统面临的对抗攻击问题,即攻击者通过精心设计的特征级扰动来规避检测,同时保持恶意功能不变。解决方案的关键在于提出了一种名为LAMLAD的新颖对抗攻击框架,其核心创新是利用大语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)的生成与推理能力,构建一个双代理架构:其中LLM操纵器生成具备真实性和功能保留性的特征扰动,而LLM分析器则引导扰动过程以实现成功绕过;此外,通过引入检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)提升效率和上下文感知能力,使攻击在Drebin风格特征表示下具有高隐蔽性和成功率,实验表明其平均仅需三次尝试即可达到97%的攻击成功率(Attack Success Rate, ASR)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21404
作者: Tianwei Lan,Farid Naït-Abdesselam
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注:
Abstract:The rapid growth in both the scale and complexity of Android malware has driven the widespread adoption of machine learning (ML) techniques for scalable and accurate malware detection. Despite their effectiveness, these models remain vulnerable to adversarial attacks that introduce carefully crafted feature-level perturbations to evade detection while preserving malicious functionality. In this paper, we present LAMLAD, a novel adversarial attack framework that exploits the generative and reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to bypass ML-based Android malware classifiers. LAMLAD employs a dual-agent architecture composed of an LLM manipulator, which generates realistic and functionality-preserving feature perturbations, and an LLM analyzer, which guides the perturbation process toward successful evasion. To improve efficiency and contextual awareness, LAMLAD integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) into the LLM pipeline. Focusing on Drebin-style feature representations, LAMLAD enables stealthy and high-confidence attacks against widely deployed Android malware detection systems. We evaluate LAMLAD against three representative ML-based Android malware detectors and compare its performance with two state-of-the-art adversarial attack methods. Experimental results demonstrate that LAMLAD achieves an attack success rate (ASR) of up to 97%, requiring on average only three attempts per adversarial sample, highlighting its effectiveness, efficiency, and adaptability in practical adversarial settings. Furthermore, we propose an adversarial training-based defense strategy that reduces the ASR by more than 30% on average, significantly enhancing model robustness against LAMLAD-style attacks.
zh
[AI-44] Safe Path Planning and Observation Quality Enhancement Strategy for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Water Quality Monitoring Tasks
【速读】:该论文旨在解决无人机(UAV)在动态光照环境下进行水质监测时,因阴影和镜面反射(sun glint)导致的光谱畸变问题,从而提升数据可用性和监测精度。解决方案的关键在于提出一种主动路径规划方法:首先构建动态光照扰动预测模型,将时变的光暗干扰区域转化为三维虚拟障碍物;其次引入改进的受干扰流体动力学系统(Interfered Fluid Dynamical System, IFDS)算法生成平滑初始避障路径,并结合模型预测控制(Model Predictive Control, MPC)框架实现滚动时域优化与飞行动力学约束下的实时轨迹跟踪;此外设计动态飞行高度调整机制(Dynamic Flight Altitude Adjustment, DFAA),在可视范围受限时主动降低飞行高度以提高空间分辨率。该方案显著提升了避障成功率(98%)、路径平滑性及有效观测数据量(约27%)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21375
作者: Yuanshuang Fu(1),Qianyao Wang(2),Qihao Wang(2),Bonan Zhang(1),Jiaxin Zhao(2),Yiming Cao(2),Zhijun Li(2) ((1) University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, (2) North China University of Technology)
机构: 未知
类目: Robotics (cs.RO); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Systems and Control (eess.SY)
备注:
Abstract:Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) spectral remote sensing technology is widely used in water quality monitoring. However, in dynamic environments, varying illumination conditions, such as shadows and specular reflection (sun glint), can cause severe spectral distortion, thereby reducing data availability. To maximize the acquisition of high-quality data while ensuring flight safety, this paper proposes an active path planning method for dynamic light and shadow disturbance avoidance. First, a dynamic prediction model is constructed to transform the time-varying light and shadow disturbance areas into three-dimensional virtual obstacles. Second, an improved Interfered Fluid Dynamical System (IFDS) algorithm is introduced, which generates a smooth initial obstacle avoidance path by building a repulsive force field. Subsequently, a Model Predictive Control (MPC) framework is employed for rolling-horizon path optimization to handle flight dynamics constraints and achieve real-time trajectory tracking. Furthermore, a Dynamic Flight Altitude Adjustment (DFAA) mechanism is designed to actively reduce the flight altitude when the observable area is narrow, thereby enhancing spatial resolution. Simulation results show that, compared with traditional PID and single obstacle avoidance algorithms, the proposed method achieves an obstacle avoidance success rate of 98% in densely disturbed scenarios, significantly improves path smoothness, and increases the volume of effective observation data by approximately 27%. This research provides an effective engineering solution for precise UAV water quality monitoring in complex illumination environments.
zh
[AI-45] AInsteinBench: Benchmarking Coding Agents on Scientific Repositories
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前大型语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)在真实科研软件生态系统中作为科学计算开发代理(scientific computing development agent)的能力评估问题。现有基准主要聚焦于概念性科学推理或通用软件工程任务,缺乏对端到端科研开发流程的实证测试。解决方案的关键在于构建AInsteinBench——一个基于六类广泛应用的科学计算代码库(涵盖量子化学、量子计算、分子动力学等)的真实维护者提交的拉取请求(pull requests)所衍生的大规模基准,通过多阶段筛选与专家评审确保任务的科学挑战性、测试覆盖率和难度校准,并结合可执行环境、科学失效模式分析及测试驱动验证,系统评估LLM是否具备从表面代码生成迈向计算科学研究核心能力的潜力。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21373
作者: Titouan Duston,Shuo Xin,Yang Sun,Daoguang Zan,Aoyan Li,Shulin Xin,Kai Shen,Yixiao Chen,Qiming Sun,Ge Zhang,Jiashuo Liu,Huan Zhou,Jingkai Liu,Zhichen Pu,Yuanheng Wang,Bo-Xuan Ge,Xin Tong,Fei Ye,Zhi-Chao Zhao,Wen-Biao Han,Zhoujian Cao,Yueran Zhao,Weiluo Ren,Qingshen Long,Yuxiao Liu,Anni Huang,Yidi Du,Yuanyuan Rong,Jiahao Peng
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Programming Languages (cs.PL)
备注:
Abstract:We introduce AInsteinBench, a large-scale benchmark for evaluating whether large language model (LLM) agents can operate as scientific computing development agents within real research software ecosystems. Unlike existing scientific reasoning benchmarks which focus on conceptual knowledge, or software engineering benchmarks that emphasize generic feature implementation and issue resolving, AInsteinBench evaluates models in end-to-end scientific development settings grounded in production-grade scientific repositories. The benchmark consists of tasks derived from maintainer-authored pull requests across six widely used scientific codebases, spanning quantum chemistry, quantum computing, molecular dynamics, numerical relativity, fluid dynamics, and cheminformatics. All benchmark tasks are carefully curated through multi-stage filtering and expert review to ensure scientific challenge, adequate test coverage, and well-calibrated difficulty. By leveraging evaluation in executable environments, scientifically meaningful failure modes, and test-driven verification, AInsteinBench measures a model’s ability to move beyond surface-level code generation toward the core competencies required for computational scientific research.
zh
[AI-46] A Study of Solving Life-and-Death Problems in Go Using Relevance-Zone Based Solvers
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前先进计算机围棋求解器在处理死活(Life-and-Death, LD)问题时的局限性,特别是其在识别关键区域、模式匹配及决策逻辑上与人类专业棋手行为的差异。解决方案的关键在于采用基于相关区域搜索(Relevance-Zone Based Search, RZS)和相关区域模式表的技术,通过自动定位死活问题中的核心局部区域并提取一系列模式(包括罕见模式),从而提升求解准确性和可解释性。实验表明,该方法不仅能有效识别关键区域并发现新奇模式,还能在部分问题中得出与权威参考答案不同的解法,揭示了现有求解器在稀有模式估值和战略优先级(如直接求活 vs. 最大化地盘)上的偏差,为未来改进提供了明确方向。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21365
作者: Chung-Chin Shih,Ti-Rong Wu,Ting Han Wei,Yu-Shan Hsu,Hung Guei,I-Chen Wu
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted by IEEE Transactions on Games
Abstract:This paper analyzes the behavior of solving Life-and-Death (LD) problems in the game of Go using current state-of-the-art computer Go solvers with two techniques: the Relevance-Zone Based Search (RZS) and the relevance-zone pattern table. We examined the solutions derived by relevance-zone based solvers on seven LD problems from the renowned book “Life and Death Dictionary” written by Cho Chikun, a Go grandmaster, and found several interesting results. First, for each problem, the solvers identify a relevance-zone that highlights the critical areas for solving. Second, the solvers discover a series of patterns, including some that are rare. Finally, the solvers even find different answers compared to the given solutions for two problems. We also identified two issues with the solver: (a) it misjudges values of rare patterns, and (b) it tends to prioritize living directly rather than maximizing territory, which differs from the behavior of human Go players. We suggest possible approaches to address these issues in future work. Our code and data are available at this https URL.
zh
[AI-47] From Visual Perception to Deep Empathy: An Automated Assessment Framework for House-Tree-Person Drawings Using Multimodal LLM s and Multi-Agent Collaboration
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统House-Tree-Person (HTP) 绘画测验在临床心理学应用中长期存在的问题,包括评分标准不统一、依赖评估者主观经验以及缺乏标准化的量化编码体系。其解决方案的关键在于引入多智能体协作框架(multi-agent collaboration),通过角色分工实现特征识别与心理推断的解耦,并结合多模态大语言模型(Multimodal Large Language Model, MLLM)对绘画图像进行语义理解,从而生成具有高生态效度和内部一致性的心理报告。实验表明,MLLM 的解释与人类专家解释之间的平均余弦相似度达 0.75(标准差约 0.05),在结构导向型专家数据集中提升至 0.85,验证了该方法具备专家级认知水平,为数字心理健康服务提供了可标准化、可扩展的新范式。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21360
作者: Shuide Wen,Yu Sun,Beier Ku,Zhi Gao,Lijun Ma,Yang Yang,Can Jiao
机构: 未知
类目: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Systems and Control (eess.SY)
备注: 16 pages, 8 figures
Abstract:Background: The House-Tree-Person (HTP) drawing test, introduced by John Buck in 1948, remains a widely used projective technique in clinical psychology. However, it has long faced challenges such as heterogeneous scoring standards, reliance on examiners subjective experience, and a lack of a unified quantitative coding system. Results: Quantitative experiments showed that the mean semantic similarity between Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) interpretations and human expert interpretations was approximately 0.75 (standard deviation about 0.05). In structurally oriented expert data sets, this similarity rose to 0.85, indicating expert-level baseline comprehension. Qualitative analyses demonstrated that the multi-agent system, by integrating social-psychological perspectives and destigmatizing narratives, effectively corrected visual hallucinations and produced psychological reports with high ecological validity and internal coherence. Conclusions: The findings confirm the potential of multimodal large models as standardized tools for projective assessment. The proposed multi-agent framework, by dividing roles, decouples feature recognition from psychological inference and offers a new paradigm for digital mental-health services. Keywords: House-Tree-Person test; multimodal large language model; multi-agent collaboration; cosine similarity; computational psychology; artificial intelligence Comments: 16 pages, 8 figures Subjects: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Systems and Control (eess.SY) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21360 [cs.AI] (or arXiv:2512.21360v1 [cs.AI] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21360 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite Submission history From: Shuide Wen [view email] [v1] Tue, 23 Dec 2025 09:26:23 UTC (613 KB)
zh
[AI-48] Reflection-Driven Control for Trustworthy Code Agents AAAI2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决当前大型语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)代理在生成内容时缺乏可靠安全控制的问题,其输出可能不受约束、不可预测,甚至具有主动危害性。解决方案的关键在于提出一种名为“反射驱动控制”(Reflection-Driven Control)的标准化、可插拔的控制模块,该模块将“自我反思”从事后修补提升为代理推理过程中的显式步骤:在生成过程中,代理持续运行内部反思循环以监控和评估自身决策路径;一旦检测到潜在风险,系统会从动态演化的反思记忆中检索相关修复示例和安全编码规范,并将这些基于证据的约束直接注入后续推理步骤,从而在保障功能正确性的前提下显著提升代码生成的安全性和合规性。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21354
作者: Bin Wang,Jiazheng Quan,Xingrui Yu,Hansen Hu,Yuhao,Ivor Tsang
机构: 未知
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Software Engineering (cs.SE)
备注: Accepted to AAAI 2026 Workshop on Trust and Control in Agentic AI (TrustAgent)
Abstract:Contemporary large language model (LLM) agents are remarkably capable, but they still lack reliable safety controls and can produce unconstrained, unpredictable, and even actively harmful outputs. To address this, we introduce Reflection-Driven Control, a standardized and pluggable control module that can be seamlessly integrated into general agent architectures. Reflection-Driven Control elevates “self-reflection” from a post hoc patch into an explicit step in the agent’s own reasoning process: during generation, the agent continuously runs an internal reflection loop that monitors and evaluates its own decision path. When potential risks are detected, the system retrieves relevant repair examples and secure coding guidelines from an evolving reflective memory, injecting these evidence-based constraints directly into subsequent reasoning steps. We instantiate Reflection-Driven Control in the setting of secure code generation and systematically evaluate it across eight classes of security-critical programming tasks. Empirical results show that Reflection-Driven Control substantially improves the security and policy compliance of generated code while largely preserving functional correctness, with minimal runtime and token overhead. Taken together, these findings indicate that Reflection-Driven Control is a practical path toward trustworthy AI coding agents: it enables designs that are simultaneously autonomous, safer by construction, and auditable.
zh
[AI-49] Multi-Agent LLM Committees for Autonomous Software Beta Testing
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统手动软件beta测试成本高、耗时长的问题,以及单智能体大语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)在自动化测试中因幻觉(hallucination)和行为不一致导致的可靠性不足问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种多智能体委员会框架(multi-agent committee framework),通过引入多样化的视觉感知LLM、基于角色(persona-driven)的行为变异机制,并结合三轮投票协议实现协同决策,从而系统性地探索Web应用界面并提升测试准确性与鲁棒性。该框架在多个基准测试中显著优于单智能体基线,在任务成功率、动作执行效率、漏洞覆盖和缺陷检测F1分数等方面均表现出优越性能。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21352
作者: Sumanth Bharadwaj Hachalli Karanam,Dhiwahar Adhithya Kennady
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注:
Abstract:Manual software beta testing is costly and time-consuming, while single-agent large language model (LLM) approaches suffer from hallucinations and inconsistent behavior. We propose a multi-agent committee framework in which diverse vision-enabled LLMs collaborate through a three-round voting protocol to reach consensus on testing actions. The framework combines model diversity, persona-driven behavioral variation, and visual user interface understanding to systematically explore web applications. Across 84 experimental runs with 9 testing personas and 4 scenarios, multi-agent committees achieve an 89.5 percent overall task success rate. Configurations with 2 to 4 agents reach 91.7 to 100 percent success, compared to 78.0 percent for single-agent baselines, yielding improvements of 13.7 to 22.0 percentage points. At the action level, the system attains a 93.1 percent success rate with a median per-action latency of 0.71 seconds, enabling real-time and continuous integration testing. Vision-enabled agents successfully identify user interface elements, with navigation and reporting achieving 100 percent success and form filling achieving 99.2 percent success. We evaluate the framework on WebShop and OWASP benchmarks, achieving 74.7 percent success on WebShop compared to a 50.1 percent published GPT-3 baseline, and 82.0 percent success on OWASP Juice Shop security testing with coverage of 8 of the 10 OWASP Top 10 vulnerability categories. Across 20 injected regressions, the committee achieves an F1 score of 0.91 for bug detection, compared to 0.78 for single-agent baselines. The open-source implementation enables reproducible research and practical deployment of LLM-based software testing in CI/CD pipelines.
zh
[AI-50] CosmoCore-Evo: Evolutionary Dream-Replay Reinforcement Learning for Adaptive Code Generation
【速读】:该论文旨在解决大型语言模型(Large Language Models, LLMs)代理在面对分布偏移环境(如API变更或新库引入)时适应能力不足、生成代码缺乏新颖性的问题。其解决方案的关键在于提出CosmoCore-Evo,该框架在原有情感梦境重放强化学习(affective dream-replay reinforcement learning)基础上引入进化算法(evolutionary algorithms),将强化学习轨迹视为“基因组”,在梦境重放阶段执行突变与选择操作,从而打破训练模式的束缚,促进涌现行为并提升适应速度。通过在梦境队列(Dream Queue)中嵌入高适应度轨迹的变异及企业级优化的适应度函数(包含效率、合规性和可扩展性指标),CosmoCore-Evo实现了比原始CosmoCore和PPO、REAMER等基线方法更高的新颖性(最高提升35%)和更快的适应速度(提升25%)。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21351
作者: Santhosh Kumar Ravindran
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Neural and Evolutionary Computing (cs.NE)
备注: 10 pages, 2 figures; Code for Simulation
Abstract:Building on the affective dream-replay reinforcement learning framework of CosmoCore, we introduce CosmoCore-Evo, an extension that incorporates evolutionary algorithms to enhance adaptability and novelty in code generation tasks. Inspired by anthropological aspects of human evolution, such as natural selection and adaptation in early hominids, CosmoCore-Evo treats RL trajectories as ``genomes’’ that undergo mutation and selection during the nocturnal replay phase. This mechanism allows agents to break free from trained patterns, fostering emergent behaviors and improved performance in distribution-shifted environments, such as changing APIs or novel libraries. We augment the Dream Queue with evolutionary operations, including mutation of high-fitness trajectories and enterprise-tuned fitness functions that incorporate efficiency, compliance, and scalability metrics. Evaluated on extended benchmarks including HumanEval variants with shifts, BigCodeBench, and a custom PySpark pipeline simulation, CosmoCore-Evo achieves up to 35% higher novelty in solutions and 25% faster adaptation compared to the original CosmoCore and baselines like PPO and REAMER. Ablations confirm the role of evolutionary components in bridging the sentient gap for LLM agents. Code for replication, including a toy simulation, is provided.
zh
[AI-51] Fairness Is Not Just Ethical: Performance Trade-Off via Data Correlation Tuning to Mitigate Bias in ML Software ICSE2026
【速读】:该论文旨在解决传统软件公平性研究中忽视公平性作为核心软件质量属性的问题,即公平性本质上源于不同敏感用户群体间性能差异,而现有方法在提升未受惠群体预测性能、增强分布外泛化能力及地理迁移性方面存在不足。其解决方案的关键在于提出一种新颖的预处理方法——相关性调优(Correlation Tuning, CoT),通过引入Phi系数系统量化敏感属性与标签间的相关性,并采用多目标优化策略缓解代理偏差,从而在不依赖具体模型类型的前提下显著提升公平性指标表现。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21348
作者: Ying Xiao,Shangwen Wang,Sicen Liu,Dingyuan Xue,Xian Zhan,Yepang Liu,Jie M. Zhang
机构: 未知
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: Accepted to the 48th International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE 2026) Research Track
Abstract:Traditional software fairness research typically emphasizes ethical and social imperatives, neglecting that fairness fundamentally represents a core software quality issue arising directly from performance disparities across sensitive user groups. Recognizing fairness explicitly as a software quality dimension yields practical benefits beyond ethical considerations, notably improved predictive performance for unprivileged groups, enhanced out-of-distribution generalization, and increased geographic transferability in real-world deployments. Nevertheless, existing bias mitigation methods face a critical dilemma: while pre-processing methods offer broad applicability across model types, they generally fall short in effectiveness compared to post-processing techniques. To overcome this challenge, we propose Correlation Tuning (CoT), a novel pre-processing approach designed to mitigate bias by adjusting data correlations. Specifically, CoT introduces the Phi-coefficient, an intuitive correlation measure, to systematically quantify correlation between sensitive attributes and labels, and employs multi-objective optimization to address the proxy biases. Extensive evaluations demonstrate that CoT increases the true positive rate of unprivileged groups by an average of 17.5% and reduces three key bias metrics, including statistical parity difference (SPD), average odds difference (AOD), and equal opportunity difference (EOD), by more than 50% on average. CoT outperforms state-of-the-art methods by three and ten percentage points in single attribute and multiple attributes scenarios, respectively. We will publicly release our experimental results and source code to facilitate future research.
zh
[AI-52] EcoNet: Multiagent Planning and Control Of Household Energy Resources Using Active Inference
【速读】:该论文旨在解决家庭及社区层面能源管理中面临的复杂目标冲突与不确定性问题,例如在降低能源成本和减少温室气体排放的同时维持室内舒适温度,以及在天气和太阳能发电预测存在不确定性的情况下进行有效决策。解决方案的关键在于提出EcoNet,这是一种基于主动推理(active inference)的贝叶斯方法,能够通过概率建模协调多目标偏好并处理未来状态的不确定性,从而提升能源管理的智能化水平与协同效率。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21343
作者: John C. Boik,Kobus Esterhuysen,Jacqueline B. Hynes,Axel Constant,Ines Hipolito,Mahault Albarracin,Alex B. Kiefer,Karl Friston
机构: 未知
类目: ystems and Control (eess.SY); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Multiagent Systems (cs.MA)
备注: 17 pages, 9 figures
Abstract:Advances in automated systems afford new opportunities for intelligent management of energy at household, local area, and utility scales. Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) can play a role by optimizing the schedule and use of household energy devices and resources. One challenge is that the goals of a household can be complex and conflicting. For example, a household might wish to reduce energy costs and grid-associated greenhouse gas emissions, yet keep room temperatures comfortable. Another challenge is that an intelligent HEMS agent must make decisions under uncertainty. An agent must plan actions into the future, but weather and solar generation forecasts, for example, provide inherently uncertain estimates of future conditions. This paper introduces EcoNet, a Bayesian approach to household and neighborhood energy management that is based on active inference. The aim is to improve energy management and coordination, while accommodating uncertainties and taking into account potentially conditional and conflicting goals and preferences. Simulation results are presented and discussed.
zh
[AI-53] Applications of synthetic financial data in portfolio and risk modeling
【速读】:该论文旨在解决量化金融研究中因数据隐私和可获取性限制所带来的挑战,提出利用生成式模型(Generative Models)构建合成金融数据以支持投资组合构建、交易分析与风险建模等任务。其解决方案的关键在于采用TimeGAN与变分自编码器(Variational Autoencoders, VAEs)两类生成模型,其中TimeGAN在捕捉真实收益序列的分布形态、波动模式及自相关特性方面表现优异,尤其在均值-方差投资组合优化中能生成接近真实数据的权重配置、夏普比率与风险水平;而VAE虽训练更稳定但倾向于平滑极端市场波动,影响风险估计精度。研究表明,若生成模型能够有效建模时间动态结构,合成数据可作为真实金融数据的可靠替代品,实现隐私保护、成本降低与实验可复现性的目标。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21798
作者: Christophe D. Hounwanou,Yae Ulrich Gaba
机构: 未知
类目: atistical Finance (q-fin.ST); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI)
备注: 14 pages, submitted as a preprint. This study examines generative models (TimeGAN and VAE) for creating synthetic financial data to support portfolio construction, trading analysis, and risk modeling
Abstract:Synthetic financial data offers a practical way to address the privacy and accessibility challenges that limit research in quantitative finance. This paper examines the use of generative models, in particular TimeGAN and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), for creating synthetic return series that support portfolio construction, trading analysis, and risk modeling. Using historical daily returns from the S and P 500 as a benchmark, we generate synthetic datasets under comparable market conditions and evaluate them using statistical similarity metrics, temporal structure tests, and downstream financial tasks. The study shows that TimeGAN produces synthetic data with distributional shapes, volatility patterns, and autocorrelation behaviour that are close to those observed in real returns. When applied to mean-variance portfolio optimization, the resulting synthetic datasets lead to portfolio weights, Sharpe ratios, and risk levels that remain close to those obtained from real data. The VAE provides more stable training but tends to smooth extreme market movements, which affects risk estimation. Finally, the analysis supports the use of synthetic datasets as substitutes for real financial data in portfolio analysis and risk simulation, particularly when models are able to capture temporal dynamics. Synthetic data therefore provides a privacy-preserving, cost-effective, and reproducible tool for financial experimentation and model development.
zh
[AI-54] Enabling Ultra-Fast Cardiovascular Imaging Across Heterogeneous Clinical Environments with a Generalist Foundation Model and Multimodal Database
【速读】:该论文旨在解决心血管磁共振成像(Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, CMR)在临床广泛应用中面临的两大核心问题:一是扫描时间过长,限制了其效率;二是不同医疗环境下的设备、协议和患者群体存在显著异质性,导致重建模型难以通用。为应对这些挑战,研究提出了一种通用的重建基础模型——CardioMM,其关键在于将语义上下文理解与物理信息数据一致性相结合,从而实现对多种快速CMR成像场景的动态适应能力。该方案依托于迄今为止最大规模的多模态CMR k空间数据库MMCMR-427K(含427,465组多线圈k空间数据及结构化元数据),并通过在13个国际中心、12种CMR模态、15台扫描仪和17类心血管疾病中的广泛验证,证明CardioMM不仅在内部中心达到最先进性能,还能在未见外部环境中实现零样本泛化,即使在高达24倍加速比下仍能可靠保留关键心脏表型、定量心肌生物标志物和诊断级图像质量,从而为高通量、高质量且临床可用的心血管影像提供了可扩展的解决方案。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21652
作者: Zi Wang,Mingkai Huang,Zhang Shi,Hongjie Hu,Lan Lan,Hui Zhang,Yan Li,Xi Hu,Qing Lu,Zongming Zhu,Qiong Yao,Yuxiang Dai,Fanwen Wang,Yinzhe Wu,Jun Lyu,Qianqian Gao,Guangming Xu,Zhenxuan Zhang,Haosen Zhang,Qing Li,Guangming Wang,Tianxing He,Lizhen Lan,Siyue Li,Le Xue,Mengting Sun,Yuntong Lyu,Junpu Hu,Jiayu Zhu,Rizwan Ahmad,Zhengyu Bu,Xianling Qian,Guanke Cai,Ruiyu Cao,Weirui Cai,Chang Xu,Yuyang Ren,Feidan Yu,Siying Ma,Ziqiang Xu,Xinran Chen,Sha Hua,Daniel Kim,Yajing Zhang,Chen Ouyang,Wenjia Bai,Jing Qin,Yucheng Yang,Daniel Rueckert,He Wang,Qian Tao,Claudia Prieto,Michael Markl,Alistair Young,Lianming Wu,Shuo Wang,Chen Qin,Mengsu Zeng,Xihong Hu,Haibo Xu,Xiaobo Qu,Hao Li,Guang Yang,Chengyan Wang
机构: 未知
类目: Image and Video Processing (eess.IV); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Medical Physics (physics.med-ph)
备注: Github: this https URL
Abstract:Multimodal cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging provides comprehensive and non-invasive insights into cardiovascular disease (CVD) diagnosis and underlying mechanisms. Despite decades of advancements, its widespread clinical adoption remains constrained by prolonged scan times and heterogeneity across medical environments. This underscores the urgent need for a generalist reconstruction foundation model for ultra-fast CMR imaging, one capable of adapting across diverse imaging scenarios and serving as the essential substrate for all downstream analyses. To enable this goal, we curate MMCMR-427K, the largest and most comprehensive multimodal CMR k-space database to date, comprising 427,465 multi-coil k-space data paired with structured metadata across 13 international centers, 12 CMR modalities, 15 scanners, and 17 CVD categories in populations across three continents. Building on this unprecedented resource, we introduce CardioMM, a generalist reconstruction foundation model capable of dynamically adapting to heterogeneous fast CMR imaging scenarios. CardioMM unifies semantic contextual understanding with physics-informed data consistency to deliver robust reconstructions across varied scanners, protocols, and patient presentations. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that CardioMM achieves state-of-the-art performance in the internal centers and exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to unseen external settings. Even at imaging acceleration up to 24x, CardioMM reliably preserves key cardiac phenotypes, quantitative myocardial biomarkers, and diagnostic image quality, enabling a substantial increase in CMR examination throughput without compromising clinical integrity. Together, our open-access MMCMR-427K database and CardioMM framework establish a scalable pathway toward high-throughput, high-quality, and clinically accessible cardiovascular imaging.
zh
[AI-55] Atomistic Simulation Guided Convolutional Neural Networks for Thermal Modeling of Friction Stir Welding
【速读】:该论文旨在解决摩擦搅拌焊接(Friction Stir Welding, FSW)过程中温度演化预测的准确性问题,这对于理解热力耦合行为至关重要。解决方案的关键在于利用分子动力学模拟(Molecular Dynamics Simulation)获取原子尺度上的材料流动、塑性变形和产热过程,并将原子轨迹数据转化为包含局部高度变化、速度分量、速度幅值和原子密度的空间分辨二维网格;进而构建一个二维卷积神经网络模型,直接从这些物理信息驱动的特征中学习并预测温度分布。通过超参数优化与测试验证,模型在未见数据上表现出优异性能(R²=0.9439,RMSE=14.94 K,MAE=11.58 K),且类激活图分析表明其重点关注工具-材料界面区域,这与分子动力学模拟中高变形与产热区域一致,从而实现了原子尺度物理机制与温度预测之间的强关联。
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21344
作者: Akshansh Mishra
机构: 未知
类目: Materials Science (cond-mat.mtrl-sci); Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Computational Engineering, Finance, and Science (cs.CE); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
备注: 25 pages, 11 figures, 2 tables
Abstract:Accurate prediction of temperature evolution is essential for understanding thermomechanical behavior in friction stir welding. In this study, molecular dynamics simulations were performed using LAMMPS to model aluminum friction stir welding at the atomic scale, capturing material flow, plastic deformation, and heat generation during tool plunge, traverse, and retraction. Atomic positions and velocities were extracted from simulation trajectories and transformed into physics based two dimensional spatial grids. These grids represent local height variation, velocity components, velocity magnitude, and atomic density, preserving spatial correlations within the weld zone. A two-dimensional convolutional neural network was developed to predict temperature directly from the spatially resolved atomistic data. Hyperparameter optimization was carried out to determine an appropriate network configuration. The trained model demonstrates strong predictive capability, achieving a coefficient of determination R square of 0.9439, a root mean square error of 14.94 K, and a mean absolute error of 11.58 K on unseen test data. Class Activation Map analysis indicates that the model assigns higher importance to regions near the tool material interface, which are associated with intense deformation and heat generation in the molecular dynamics simulations. The results show that spatial learning from atomistic simulation data can accurately reproduce temperature trends in friction stir welding while remaining consistent with physical deformation and flow mechanisms observed at the atomic scale.
zh
机器学习
[LG-0] Explainable Multimodal Regression via Information Decomposition
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22102
作者: Zhaozhao Ma,Shujian Yu
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Project Page: this https URL
Abstract:Multimodal regression aims to predict a continuous target from heterogeneous input sources and typically relies on fusion strategies such as early or late fusion. However, existing methods lack principled tools to disentangle and quantify the individual contributions of each modality and their interactions, limiting the interpretability of multimodal fusion. We propose a novel multimodal regression framework grounded in Partial Information Decomposition (PID), which decomposes modality-specific representations into unique, redundant, and synergistic components. The basic PID framework is inherently underdetermined. To resolve this, we introduce inductive bias by enforcing Gaussianity in the joint distribution of latent representations and the transformed response variable (after inverse normal transformation), thereby enabling analytical computation of the PID terms. Additionally, we derive a closed-form conditional independence regularizer to promote the isolation of unique information within each modality. Experiments on six real-world datasets, including a case study on large-scale brain age prediction from multimodal neuroimaging data, demonstrate that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both predictive accuracy and interpretability, while also enabling informed modality selection for efficient inference. Implementation is available at this https URL.
[LG-1] Scaling Adversarial Training via Data Selection
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22069
作者: Youran Ye,Dejin Wang,Ajinkya Bhandare
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 6 pages. Conference workshop paper
Abstract:Projected Gradient Descent (PGD) is a strong and widely used first-order adversarial attack, yet its computational cost scales poorly, as all training samples undergo identical iterative inner-loop optimization despite contributing unequally to robustness. Motivated by this inefficiency, we propose \emphSelective Adversarial Training, which perturbs only a subset of critical samples in each minibatch. Specifically, we introduce two principled selection criteria: (1) margin-based sampling, which prioritizes samples near the decision boundary, and (2) gradient-matching sampling, which selects samples whose gradients align with the dominant batch optimization direction. Adversarial examples are generated only for the selected subset, while the remaining samples are trained cleanly using a mixed objective. Experiments on MNIST and CIFAR-10 show that the proposed methods achieve robustness comparable to, or even exceeding, full PGD adversarial training, while reducing adversarial computation by up to 50% , demonstrating that informed sample selection is sufficient for scalable adversarial robustness.
[LG-2] Prefill vs. Decode Bottlenecks: SRAM-Frequency Tradeoffs and the Memory-Bandwidth Ceiling
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22066
作者: Hannah Atmer,Yuan Yao,Thiemo Voigt,Stefanos Kaxiras
类目: Hardware Architecture (cs.AR); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Performance (cs.PF)
*备注:
Abstract:Energy consumption dictates the cost and environmental impact of deploying Large Language Models. This paper investigates the impact of on-chip SRAM size and operating frequency on the energy efficiency and performance of LLM inference, focusing on the distinct behaviors of the compute-bound prefill and memory-bound decode phases. Our simulation methodology combines OpenRAM for energy modeling, LLMCompass for latency simulation, and ScaleSIM for systolic array operational intensity. Our findings show that total energy use is predominantly determined by SRAM size in both phases, with larger buffers significantly increasing static energy due to leakage, which is not offset by corresponding latency benefits. We quantitatively explore the memory-bandwidth bottleneck, demonstrating that while high operating frequencies reduce prefill latency, their positive impact on memory-bound decode latency is capped by the external memory bandwidth. Counter-intuitively, high compute frequency can reduce total energy by reducing execution time and consequently decreasing static energy consumption more than the resulting dynamic power increase. We identify an optimal hardware configuration for the simulated workload: high operating frequencies (1200MHz-1400MHz) and a small local buffer size of 32KB to 64KB. This combination achieves the best energy-delay product, balancing low latency with high energy efficiency. Furthermore, we demonstrate how memory bandwidth acts as a performance ceiling, and that increasing compute frequency only yields performance gains up to the point where the workload becomes memory-bound. This analysis provides concrete architectural insights for designing energy-efficient LLM accelerators, especially for datacenters aiming to minimize their energy overhead.
[LG-3] Why Smooth Stability Assumptions Fail for ReLU Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22055
作者: Ronald Katende
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Optimization and Control (math.OC)
*备注:
Abstract:Stability analyses of modern learning systems are frequently derived under smoothness assumptions that are violated by ReLU-type nonlinearities. In this note, we isolate a minimal obstruction by showing that no uniform smoothness-based stability proxy such as gradient Lipschitzness or Hessian control can hold globally for ReLU networks, even in simple settings where training trajectories appear empirically stable. We give a concrete counterexample demonstrating the failure of classical stability bounds and identify a minimal generalized derivative condition under which stability statements can be meaningfully restored. The result clarifies why smooth approximations of ReLU can be misleading and motivates nonsmooth-aware stability frameworks.
[LG-4] Direction Finding with Sparse Arrays Based on Variable Window Size Spatial Smoothing
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22024
作者: Wesley S. Leite,Rodrigo C. de Lamare,Yuriy Zakharov,Wei Liu,Martin Haardt
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 2 figures, 5 pages
Abstract:In this work, we introduce a variable window size (VWS) spatial smoothing framework that enhances coarray-based direction of arrival (DOA) estimation for sparse linear arrays. By compressing the smoothing aperture, the proposed VWS Coarray MUSIC (VWS-CA-MUSIC) and VWS Coarray root-MUSIC (VWS-CA-rMUSIC) algorithms replace part of the perturbed rank-one outer products in the smoothed coarray data with unperturbed low-rank additional terms, increasing the separation between signal and noise subspaces, while preserving the signal subspace span. We also derive the bounds that guarantees identifiability, by limiting the values that can be assumed by the compression parameter. Simulations with sparse geometries reveal significant performance improvements and complexity savings relative to the fixed-window coarray MUSIC method.
[LG-5] HWL-HIN: A Hypergraph-Level Hypergraph Isomorphism Network as Powerful as the Hypergraph Weisfeiler-Lehman Test with Application to Higher-Order Network Robustness
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22014
作者: Chengyu Tian,Wenbin Pei
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Robustness in complex systems is of significant engineering and economic importance. However, conventional attack-based a posteriori robustness assessments incur prohibitive computational overhead. Recently, deep learning methods, such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), have been widely employed as surrogates for rapid robustness prediction. Nevertheless, these methods neglect the complex higher-order correlations prevalent in real-world systems, which are naturally modeled as hypergraphs. Although Hypergraph Neural Networks (HGNNs) have been widely adopted for hypergraph learning, their topological expressive power has not yet reached the theoretical upper bound. To address this limitation, inspired by Graph Isomorphism Networks, this paper proposes a hypergraph-level Hypergraph Isomorphism Network framework. Theoretically, this approach is proven to possess an expressive power strictly equivalent to the Hypergraph Weisfeiler-Lehman test and is applied to predict hypergraph robustness. Experimental results demonstrate that while maintaining superior efficiency in training and prediction, the proposed method not only outperforms existing graph-based models but also significantly surpasses conventional HGNNs in tasks that prioritize topological structure representation.
[LG-6] DuaDeep-SeqAffinity: Dual-Stream Deep Learning Framework for Sequence-Only Antigen-Antibody Affinity Prediction
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22007
作者: Aicha Boutorh,Soumia Bouyahiaoui,Sara Belhadj,Nour El Yakine Guendouz,Manel Kara Laouar
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Predicting the binding affinity between antigens and antibodies is fundamental to drug discovery and vaccine development. Traditional computational approaches often rely on experimentally determined 3D structures, which are scarce and computationally expensive to obtain. This paper introduces DuaDeep-SeqAffinity, a novel sequence-only deep learning framework that predicts affinity scores solely from their amino acid sequences using a dual-stream hybrid architecture. Our approach leverages pre-trained ESM-2 protein language model embeddings, combining 1D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for local motif detection with Transformer encoders for global contextual representation. A subsequent fusion module integrates these multi-faceted features, which are then passed to a fully connected network for final score regression. Experimental results demonstrate that DuaDeep-SeqAffinity significantly outperforms individual architectural components and existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. DuaDeep achieved a superior Pearson correlation of 0.688, an R^2 of 0.460, and a Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 0.737, surpassing single-branch variants ESM-CNN and ESM-Transformer. Notably, the model achieved an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.890, outperforming sequence-only benchmarks and even surpassing structure-sequence hybrid models. These findings prove that high-fidelity sequence embeddings can capture essential binding patterns typically reserved for structural modeling. By eliminating the reliance on 3D structures, DuaDeep-SeqAffinity provides a highly scalable and efficient solution for high-throughput screening of vast sequence libraries, significantly accelerating the therapeutic discovery pipeline.
[LG-7] Hybrid Combinatorial Multi-armed Bandits with Probabilistically Triggered Arms
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21925
作者: Kongchang Zhou,Tingyu Zhang,Wei Chen,Fang Kong
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:The problem of combinatorial multi-armed bandits with probabilistically triggered arms (CMAB-T) has been extensively studied. Prior work primarily focuses on either the online setting where an agent learns about the unknown environment through iterative interactions, or the offline setting where a policy is learned solely from logged data. However, each of these paradigms has inherent limitations: online algorithms suffer from high interaction costs and slow adaptation, while offline methods are constrained by dataset quality and lack of exploration capabilities. To address these complementary weaknesses, we propose hybrid CMAB-T, a new framework that integrates offline data with online interaction in a principled manner. Our proposed hybrid CUCB algorithm leverages offline data to guide exploration and accelerate convergence, while strategically incorporating online interactions to mitigate the insufficient coverage or distributional bias of the offline dataset. We provide theoretical guarantees on the algorithm’s regret, demonstrating that hybrid CUCB significantly outperforms purely online approaches when high-quality offline data is available, and effectively corrects the bias inherent in offline-only methods when the data is limited or misaligned. Empirical results further demonstrate the consistent advantage of our algorithm.
[LG-8] Exploring the Heterogeneity of Tabular Data: A Diversity-aware Data Generator via LLM s
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21915
作者: Yafeng Tang,Xiaoou Ding,Jianzhuo Du,Zishuo Yan,Zhuang Ma,Zheng Liang,Zekai Qian,Hongzhi Wang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Databases (cs.DB)
*备注: This manuscript has been submitted to IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering (TKDE) for peer review
Abstract:Tabular data generation has become increasingly essential for enabling robust machine learning applications, which require large-scale, high-quality data. Existing solutions leverage generative models to learn original data distributions. However, real-world data are naturally heterogeneous with diverse distributions, making it challenging to obtain a universally good model for diverse data generation. To address this limitation, we introduce Diversity-Aware Tabular data gEnerator (DATE), a framework that (i) prepares high-quality and distributionally distinct examples for in-context learning by effectively partitioning the original heterogeneous data into multiple diverse subsets; (ii) harnesses Large Language Models (LLMs) to explore the diversity of the partitioned distribution with decision tree reasoning as feedback, generating high-quality labeled data for each subset. However, the massive generated data inherently involves a trade-off between diversity and quality. To integrate this issue, existing solutions greedily select the validation-best data. However, we prove that the selection in heterogeneous settings does not possess the greedy-choice property, and design a Multi-Arm Bandit-based sampling algorithm that balances the diversity and quality of generated data. Extensive experiments on tabular classification and regression benchmarks demonstrate that DATE consistently outperforms state-of-the-art GAN-based and LLM-based methods. On average, DATE achieves a 23.75% reduction in error rate with just 100 generated data. Empirically, we demonstrate that data generated by DATE can improve the accuracy of Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and enhance the reasoning capability of LLMs on the target data. Code is available at this https URL.
[LG-9] GQ-VAE: A gated quantized VAE for learning variable length tokens
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21913
作者: Theo Datta,Kayla Huang,Sham Kakade,David Brandfonbrener
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:While most frontier models still use deterministic frequency-based tokenization algorithms such as byte-pair encoding (BPE), there has been significant recent work to design learned neural tokenizers. However, these schemes generally add to underlying language model complexity and force large changes to architecture, making them hard to implement at large scales. To overcome these challenges, we propose the gated quantized variational autoencoder (GQ-VAE), a novel architecture that can be independently pre-trained to serve as a drop-in replacement for existing tokenizers. The key innovation of the architecture is to learn to encode variable-length discrete tokens. GQ-VAE improves compression and language modeling performance over a standard VQ-VAE tokenizer, and approaches the compression rate and language modeling performance of BPE. Interestingly, if we use BPE with a smaller vocabulary, such that the compression is equivalent between GQ-VAE and BPE, we find that GQ-VAE improves downstream language model learning. We conclude with a discussion of several exciting avenues for future work. Code can be found at this https URL.
[LG-10] Smart IoT-Based Leak Forecasting and Detection for Energy-Efficient Liquid Cooling in AI Data Centers
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21801
作者: Krishna Chaitanya Sunkara,Rambabu Konakanchi
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Networking and Internet Architecture (cs.NI); Systems and Control (eess.SY)
*备注: 7 pages, 6 figures, IEEE conference format
Abstract:AI data centers which are GPU centric, have adopted liquid cooling to handle extreme heat loads, but coolant leaks result in substantial energy loss through unplanned shutdowns and extended repair periods. We present a proof-of-concept smart IoT monitoring system combining LSTM neural networks for probabilistic leak forecasting with Random Forest classifiers for instant detection. Testing on synthetic data aligned with ASHRAE 2021 standards, our approach achieves 96.5% detection accuracy and 87% forecasting accuracy at 90% probability within plus or minus 30-minute windows. Analysis demonstrates that humidity, pressure, and flow rate deliver strong predictive signals, while temperature exhibits minimal immediate response due to thermal inertia in server hardware. The system employs MQTT streaming, InfluxDB storage, and Streamlit dashboards, forecasting leaks 2-4 hours ahead while identifying sudden events within 1 minute. For a typical 47-rack facility, this approach could prevent roughly 1,500 kWh annual energy waste through proactive maintenance rather than reactive emergency procedures. While validation remains synthetic-only, results establish feasibility for future operational deployment in sustainable data center operations.
[LG-11] Synthetic Financial Data Generation for Enhanced Financial Modelling
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21791
作者: Christophe D. Hounwanou,Yae Ulrich Gaba,Pierre Ntakirutimana
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computational Finance (q-fin.CP)
*备注: 23 pages, 7 figures, 6 tables. Submitted as a preprint. This work presents a unified multi-criteria evaluation framework for synthetic financial data, applied to ARIMA-GARCH, VAEs, and TimeGAN models
Abstract:Data scarcity and confidentiality in finance often impede model development and robust testing. This paper presents a unified multi-criteria evaluation framework for synthetic financial data and applies it to three representative generative paradigms: the statistical ARIMA-GARCH baseline, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and Time-series Generative Adversarial Networks (TimeGAN). Using historical S and P 500 daily data, we evaluate fidelity (Maximum Mean Discrepancy, MMD), temporal structure (autocorrelation and volatility clustering), and practical utility in downstream tasks, specifically mean-variance portfolio optimization and volatility forecasting. Empirical results indicate that ARIMA-GARCH captures linear trends and conditional volatility but fails to reproduce nonlinear dynamics; VAEs produce smooth trajectories that underestimate extreme events; and TimeGAN achieves the best trade-off between realism and temporal coherence (e.g., TimeGAN attained the lowest MMD: 1.84e-3, average over 5 seeds). Finally, we articulate practical guidelines for selecting generative models according to application needs and computational constraints. Our unified evaluation protocol and reproducible codebase aim to standardize benchmarking in synthetic financial data research.
[LG-12] VAMP-Net: An Interpretable Multi-Path Framework of Genomic Permutation-Invariant Set Attention and Quality-Aware 1D-CNN for MTB Drug Resistance
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21786
作者: Aicha Boutorh,Kamar Hibatallah Baghdadi,Anais Daoud
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Genomic prediction of drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis remains challenging due to complex epistatic interactions and highly variable sequencing data quality. We present a novel Interpretable Variant-Aware Multi-Path Network (VAMP-Net) that addresses both challenges through complementary machine learning pathways. Path-1 employs a Set Attention Transformer processing permutation-invariant variant sets to capture epistatic interactions between genomic loci. Path-2 utilizes a 1D Convolutional Neural Network that analyzes Variant Call Format quality metrics to learn adaptive confidence scores. A fusion module combines both pathways for final resistance classification. We conduct comparative evaluations of unmasked versus padding-masked Set Attention Blocks, and demonstrate that our multi-path architecture achieves superior performance over baseline CNN and MLP models, with accuracy exceeding 95% and AUC around 97% for Rifampicin (RIF) and Rifabutin (RFB) resistance prediction. The framework provides dual-layer interpretability: Attention Weight Analysis reveals Epistatic networks, and Integrated Gradients (IG) was applied for critical resistance loci (notably rpoB), while gradient-based feature importance from the CNN pathway uncovers drug-specific dependencies on data quality metrics. This architecture advances clinical genomics by delivering state-of-the-art predictive performance alongside auditable interpretability at two distinct levels, genetic causality of mutation sets and technical confidence of sequencing evidence, establishing a new paradigm for robust, clinically-actionable resistance prediction.
[LG-13] Assessing the Effectiveness of Membership Inference on Generative Music
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21762
作者: Kurtis Chow,Omar Samiullah,Vinesh Sridhar,Hewen Zhang
类目: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 10 pages, 3 figures, 3 tables
Abstract:Generative AI systems are quickly improving, now able to produce believable output in several modalities including images, text, and audio. However, this fast development has prompted increased scrutiny concerning user privacy and the use of copyrighted works in training. A recent attack on machine-learning models called membership inference lies at the crossroads of these two concerns. The attack is given as input a set of records and a trained model and seeks to identify which of those records may have been used to train the model. On one hand, this attack can be used to identify user data used to train a model, which may violate their privacy especially in sensitive applications such as models trained on medical data. On the other hand, this attack can be used by rights-holders as evidence that a company used their works without permission to train a model. Remarkably, it appears that no work has studied the effect of membership inference attacks (MIA) on generative music. Given that the music industry is worth billions of dollars and artists would stand to gain from being able to determine if their works were being used without permission, we believe this is a pressing issue to study. As such, in this work we begin a preliminary study into whether MIAs are effective on generative music. We study the effect of several existing attacks on MuseGAN, a popular and influential generative music model. Similar to prior work on generative audio MIAs, our findings suggest that music data is fairly resilient to known membership inference techniques. Comments: 10 pages, 3 figures, 3 tables Subjects: Cryptography and Security (cs.CR); Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21762 [cs.CR] (or arXiv:2512.21762v1 [cs.CR] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21762 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-14] Approximation Capabilities of Feedforward Neural Networks with GELU Activations
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21749
作者: Konstantin Yakovlev,Nikita Puchkin
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 42 pages
Abstract:We derive an approximation error bound that holds simultaneously for a function and all its derivatives up to any prescribed order. The bounds apply to elementary functions, including multivariate polynomials, the exponential function, and the reciprocal function, and are obtained using feedforward neural networks with the Gaussian Error Linear Unit (GELU) activation. In addition, we report the network size, weight magnitudes, and behavior at infinity. Our analysis begins with a constructive approximation of multiplication, where we prove the simultaneous validity of error bounds over domains of increasing size for a given approximator. Leveraging this result, we obtain approximation guarantees for division and the exponential function, ensuring that all higher-order derivatives of the resulting approximators remain globally bounded.
[LG-15] Dictionary-Transform Generative Adversarial Networks
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21677
作者: Angshul Majumdar
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are widely used for distribution learning, yet their classical formulations remain theoretically fragile, with ill-posed objectives, unstable training dynamics, and limited interpretability. In this work, we introduce \emphDictionary-Transform Generative Adversarial Networks (DT-GAN), a fully model-based adversarial framework in which the generator is a sparse synthesis dictionary and the discriminator is an analysis transform acting as an energy model. By restricting both players to linear operators with explicit constraints, DT-GAN departs fundamentally from neural GAN architectures and admits rigorous theoretical analysis. We show that the DT-GAN adversarial game is well posed and admits at least one Nash equilibrium. Under a sparse generative model, equilibrium solutions are provably identifiable up to standard permutation and sign ambiguities and exhibit a precise geometric alignment between synthesis and analysis operators. We further establish finite-sample stability and consistency of empirical equilibria, demonstrating that DT-GAN training converges reliably under standard sampling assumptions and remains robust in heavy-tailed regimes. Experiments on mixture-structured synthetic data validate the theoretical predictions, showing that DT-GAN consistently recovers underlying structure and exhibits stable behavior under identical optimization budgets where a standard GAN degrades. DT-GAN is not proposed as a universal replacement for neural GANs, but as a principled adversarial alternative for data distributions that admit sparse synthesis structure. The results demonstrate that adversarial learning can be made interpretable, stable, and provably correct when grounded in classical sparse modeling. Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21677 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2512.21677v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21677 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-16] Rethinking Output Alignment For 1-bit Post-Training Quantization of Large Language Models
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21651
作者: Dung Anh Hoang,Cuong Pham,Cuong Nguyen,Trung le,Jianfei Cai,Thanh-Toan Do
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) deliver strong performance across a wide range of NLP tasks, but their massive sizes hinder deployment on resource-constrained devices. To reduce their computational and memory burden, various compression techniques have been proposed, including quantization, pruning, and knowledge distillation. Among these, post-training quantization (PTQ) is widely adopted for its efficiency, as it requires no retraining and only a small dataset for calibration, enabling low-cost deployment. Recent advances for post-training quantization have demonstrated that even sub-4-bit methods can maintain most of the original model performance. However, 1-bit quantization that converts floating-point weights to (\pm)1, remains particularly challenging, as existing 1-bit PTQ methods often suffer from significant performance degradation compared to the full-precision models. Specifically, most of existing 1-bit PTQ approaches focus on weight alignment, aligning the full-precision model weights with those of the quantized models, rather than directly aligning their outputs. Although the output-matching approach objective is more intuitive and aligns with the quantization goal, naively applying it in 1-bit LLMs often leads to notable performance degradation. In this paper, we investigate why and under what conditions output-matching fails, in the context of 1-bit LLM quantization. Based on our findings, we propose a novel data-aware PTQ approach for 1-bit LLMs that explicitly accounts for activation error accumulation while keeping optimization efficient. Empirical experiments demonstrate that our solution consistently outperforms existing 1-bit PTQ methods with minimal overhead.
[LG-17] Causal-HM: Restoring Physical Generative Logic in Multimodal Anomaly Detection via Hierarchical Modulation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21650
作者: Xiao Liu,Junchen Jin,Yanjie Zhao,Zhixuan Xing
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 10 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:Multimodal Unsupervised Anomaly Detection (UAD) is critical for quality assurance in smart manufacturing, particularly in complex processes like robotic welding. However, existing methods often suffer from causal blindness, treating process modalities (e.g., real-time video, audio, and sensors) and result modalities (e.g., post-weld images) as equal feature sources, thereby ignoring the inherent physical generative logic. Furthermore, the heterogeneity gap between high-dimensional visual data and low-dimensional sensor signals frequently leads to critical process context being drowned out. In this paper, we propose Causal-HM, a unified multimodal UAD framework that explicitly models the physical Process to Result dependency. Specifically, our framework incorporates two key innovations: a Sensor-Guided CHM Modulation mechanism that utilizes low-dimensional sensor signals as context to guide high-dimensional audio-visual feature extraction , and a Causal-Hierarchical Architecture that enforces a unidirectional generative mapping to identify anomalies that violate physical consistency. Extensive experiments on our newly constructed Weld-4M benchmark across four modalities demonstrate that Causal-HM achieves a state-of-the-art (SOTA) I-AUROC of 90.7%. Code will be released after the paper is accepted.
[LG-18] Mechanical Strength Prediction of Steel-Polypropylene Fiber-based High-Performance Concrete Using Hybrid Machine Learning Algorithms
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21638
作者: Jagaran Chakma,Zhiguang Zhou,Badhan Chakma
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 28 pages
Abstract:This research develops and evaluates machine learning models to predict the mechanical properties of steel-polypropylene fiber-reinforced high-performance concrete (HPC). Three model families were investigated: Extra Trees with XGBoost (ET-XGB), Random Forest with LightGBM (RF-LGBM), and Transformer with XGBoost (Transformer-XGB). The target properties included compressive strength (CS), flexural strength (FS), and tensile strength (TS), based on an extensive dataset compiled from published experimental studies. Model training involved k-fold cross-validation, hyperparameter optimization, Shapley additive explanations (SHAP), and uncertainty analysis to ensure both robustness and interpretability. Among the tested approaches, the ET-XGB model achieved the highest overall accuracy, with testing R^2 values of 0.994 for CS, 0.944 for FS, and 0.978 for TS and exhibited lowest uncertainty for CS and TS (approximately 13-16% and 30.4%, respectively). The RF-LGBM model provided the most stable and reliable predictions for FS (R^2 0.977), yielding the lowest uncertainty for FS (approximately 5-33%). The Transformer-XGB model demonstrated strong predictive capability (R^2 0.978 for TS and 0.967 for FS) but consistently showed the highest uncertainty, indicating reduced generalization reliability. SHAP analysis further indicated that fiber aspect ratios (AR1 and AR2), silica fume (Sfu), and steel fiber content (SF) were the most influential predictors of strength, whereas water content (W) and the water-binder ratio (w/b) consistently had negative effects. The findings confirm that machine learning models can provide accurate, interpretable, and generalizable predictions of HPC mechanical properties. These models offer valuable tools for optimizing concrete mix design and enhancing structural performance evaluation in engineering applications.
[LG-19] MAD-NG: Meta-Auto-Decoder Neural Galerkin Method for Solving Parametric Partial Differential Equations
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21633
作者: Qiuqi Li,Yiting Liu,Jin Zhao,Wencan Zhu
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Parametric partial differential equations (PDEs) are fundamental for modeling a wide range of physical and engineering systems influenced by uncertain or varying parameters. Traditional neural network-based solvers, such as Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs) and Deep Galerkin Methods, often face challenges in generalization and long-time prediction efficiency due to their dependence on full space-time approximations. To address these issues, we propose a novel and scalable framework that significantly enhances the Neural Galerkin Method (NGM) by incorporating the Meta-Auto-Decoder (MAD) paradigm. Our approach leverages space-time decoupling to enable more stable and efficient time integration, while meta-learning-driven adaptation allows rapid generalization to unseen parameter configurations with minimal retraining. Furthermore, randomized sparse updates effectively reduce computational costs without compromising accuracy. Together, these advancements enable our method to achieve physically consistent, long-horizon predictions for complex parameterized evolution equations with significantly lower computational overhead. Numerical experiments on benchmark problems demonstrate that our methods performs comparatively well in terms of accuracy, robustness, and adaptability.
[LG-20] A Data-Driven Multi-Objective Approach for Predicting Mechanical Performance Flowability and Porosity in Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC)
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21610
作者: Jagaran Chakma,Zhiguang Zhou,Jyoti Chakma,Cao YuSen
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: 20 pages
Abstract:This study presents a data-driven, multi-objective approach to predict the mechanical performance, flow ability, and porosity of Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC). Out of 21 machine learning algorithms tested, five high-performing models are selected, with XGBoost showing the best accuracy after hyperparameter tuning using Random Search and K-Fold Cross-Validation. The framework follows a two-stage process: the initial XGBoost model is built using raw data, and once selected as the final model, the dataset is cleaned by (1) removing multicollinear features, (2) identifying outliers with Isolation Forest, and (3) selecting important features using SHAP analysis. The refined dataset as model 2 is then used to retrain XGBoost, which achieves high prediction accuracy across all outputs. A graphical user interface (GUI) is also developed to support material designers. Overall, the proposed framework significantly improves the prediction accuracy and minimizes the need for extensive experimental testing in UHPC mix design.
[LG-21] Quantitative Verification of Omega-regular Properties in Probabilistic Programming
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21596
作者: Peixin Wang,Jianhao Bai,Min Zhang,C.-H. Luke Ong
类目: Programming Languages (cs.PL); Formal Languages and Automata Theory (cs.FL); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Logic in Computer Science (cs.LO); Symbolic Computation (cs.SC)
*备注:
Abstract:Probabilistic programming provides a high-level framework for specifying statistical models as executable programs with built-in randomness and conditioning. Existing inference techniques, however, typically compute posterior distributions over program states at fixed time points, most often at termination, thereby failing to capture the temporal evolution of probabilistic behaviors. We introduce temporal posterior inference (TPI), a new framework that unifies probabilistic programming with temporal logic by computing posterior distributions over execution traces that satisfy omega-regular specifications, conditioned on possibly temporal observations. To obtain rigorous quantitative guarantees, we develop a new method for computing upper and lower bounds on the satisfaction probabilities of omega-regular properties. Our approach decomposes Rabin acceptance conditions into persistence and recurrence components and constructs stochastic barrier certificates that soundly bound each component. We implement our approach in a prototype tool, TPInfer, and evaluate it on a suite of benchmarks, demonstrating effective and efficient inference over rich temporal properties in probabilistic models.
[LG-22] Videos are Sample-Efficient Supervisions: Behavior Cloning from Videos via Latent Representations
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21586
作者: Xin Liu,Haoran Li,Dongbin Zhao
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Humans can efficiently extract knowledge and learn skills from the videos within only a few trials and errors. However, it poses a big challenge to replicate this learning process for autonomous agents, due to the complexity of visual input, the absence of action or reward signals, and the limitations of interaction steps. In this paper, we propose a novel, unsupervised, and sample-efficient framework to achieve imitation learning from videos (ILV), named Behavior Cloning from Videos via Latent Representations (BCV-LR). BCV-LR extracts action-related latent features from high-dimensional video inputs through self-supervised tasks, and then leverages a dynamics-based unsupervised objective to predict latent actions between consecutive frames. The pre-trained latent actions are fine-tuned and efficiently aligned to the real action space online (with collected interactions) for policy behavior cloning. The cloned policy in turn enriches the agent experience for further latent action finetuning, resulting in an iterative policy improvement that is highly sample-efficient. We conduct extensive experiments on a set of challenging visual tasks, including both discrete control and continuous control. BCV-LR enables effective (even expert-level on some tasks) policy performance with only a few interactions, surpassing state-of-the-art ILV baselines and reinforcement learning methods (provided with environmental rewards) in terms of sample efficiency across 24/28 tasks. To the best of our knowledge, this work for the first time demonstrates that videos can support extremely sample-efficient visual policy learning, without the need to access any other expert supervision. Subjects: Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21586 [cs.LG] (or arXiv:2512.21586v1 [cs.LG] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21586 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration) Journalreference: NeurIPS 2025
[LG-23] RefineBridge: Generative Bridge Models Improve Financial Forecasting by Foundation Models
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21572
作者: Anthony Bolton,Wuyang Zhou,Zehua Chen,Giorgos Iacovides,Danilo Mandic
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Signal Processing (eess.SP)
*备注:
Abstract:Financial time series forecasting is particularly challenging for transformer-based time series foundation models (TSFMs) due to non-stationarity, heavy-tailed distributions, and high-frequency noise present in data. Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) has become a popular parameter-efficient method for adapting pre-trained TSFMs to downstream data domains. However, it still underperforms in financial data, as it preserves the network architecture and training objective of TSFMs rather than complementing the foundation model. To further enhance TSFMs, we propose a novel refinement module, RefineBridge, built upon a tractable Schrödinger Bridge (SB) generative framework. Given the forecasts of TSFM as generative prior and the observed ground truths as targets, RefineBridge learns context-conditioned stochastic transport maps to improve TSFM predictions, iteratively approaching the ground-truth target from even a low-quality prior. Simulations on multiple financial benchmarks demonstrate that RefineBridge consistently improves the performance of state-of-the-art TSFMs across different prediction horizons.
[LG-24] nncase: An End-to-End Compiler for Efficient LLM Deployment on Heterogeneous Storag e Architectures
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21571
作者: Hui Guo,Qihang Zheng,Chenghai Huo,Dongliang Guo,Haoqi Yang,Yang Zhang
类目: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:The efficient deployment of large language models (LLMs) is hindered by memory architecture heterogeneity, where traditional compilers suffer from fragmented workflows and high adaptation costs. We present nncase, an open-source, end-to-end compilation framework designed to unify optimization across diverse targets. Central to nncase is an e-graph-based term rewriting engine that mitigates the phase ordering problem, enabling global exploration of computation and data movement strategies. The framework integrates three key modules: Auto Vectorize for adapting to heterogeneous computing units, Auto Distribution for searching parallel strategies with cost-aware communication optimization, and Auto Schedule for maximizing on-chip cache locality. Furthermore, a buffer-aware Codegen phase ensures efficient kernel instantiation. Evaluations show that nncase outperforms mainstream frameworks like MLC LLM and Intel IPEX on Qwen3 series models and achieves performance comparable to the hand-optimized this http URL on CPUs, demonstrating the viability of automated compilation for high-performance LLM deployment. The source code is available at this https URL.
[LG-25] AnchorGK: Anchor-based Incremental and Stratified Graph Learning Framework for Inductive Spatio-Temporal Kriging
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21569
作者: Xiaobin Ren,Kaiqi Zhao,Katerina Taškova,Patricia Riddle
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Spatio-temporal kriging is a fundamental problem in sensor networks, driven by the sparsity of deployed sensors and the resulting missing observations. Although recent approaches model spatial and temporal correlations, they often under-exploit two practical characteristics of real deployments: the sparse spatial distribution of locations and the heterogeneous availability of auxiliary features across locations. To address these challenges, we propose AnchorGK, an Anchor-based Incremental and Stratified Graph Learning framework for inductive spatio-temporal kriging. AnchorGK introduces anchor locations to stratify the data in a principled manner. Anchors are constructed according to feature availability, and strata are then formed around these anchors. This stratification serves two complementary roles. First, it explicitly represents and continuously updates correlations between unobserved regions and surrounding observed locations within a graph learning framework. Second, it enables the systematic use of all available features across strata via an incremental representation mechanism, mitigating feature incompleteness without discarding informative signals. Building on the stratified structure, we design a dual-view graph learning layer that jointly aggregates feature-relevant and location-relevant information, learning stratum-specific representations that support accurate inference under inductive settings. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that AnchorGK consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines for spatio-temporal kriging.
[LG-26] Discovering Sparse Recovery Algorithms Using Neural Architecture Search
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21563
作者: Patrick Yubeaton,Sarthak Gupta,M. Salman Asif,Chinmay Hegde
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Presented at the 59th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers
Abstract:The design of novel algorithms for solving inverse problems in signal processing is an incredibly difficult, heuristic-driven, and time-consuming task. In this short paper, we the idea of automated algorithm discovery in the signal processing context through meta-learning tools such as Neural Architecture Search (NAS). Specifically, we examine the Iterative Shrinkage Thresholding Algorithm (ISTA) and its accelerated Fast ISTA (FISTA) variant as candidates for algorithm rediscovery. We develop a meta-learning framework which is capable of rediscovering (several key elements of) the two aforementioned algorithms when given a search space of over 50,000 variables. We then show how our framework can apply to various data distributions and algorithms besides ISTA/FISTA.
[LG-27] AVP-Fusion: Adaptive Multi-Modal Fusion and Contrastive Learning for Two-Stage Antiviral Peptide Identification
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21544
作者: Xinru Wen,Weizhong Lin,Xuan Xiao
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Accurate identification of antiviral peptides (AVPs) is critical for accelerating novel drug development. However, current computational methods struggle to capture intricate sequence dependencies and effectively handle ambiguous, hard-to-classify samples. To address these challenges, we propose AVP-Fusion, a novel two-stage deep learning framework integrating adaptive feature fusion and contrastive learning. Unlike traditional static feature concatenation, we construct a panoramic feature space using 10 distinct descriptors and introduce an Adaptive Gating this http URL mechanism dynamically regulates the weights of local motifs extracted by CNNs and global dependencies captured by BiLSTMs based on sequence context. Furthermore, to address data distribution challenges, we employ a contrastive learning strategy driven by Online Hard Example Mining (OHEM) and BLOSUM62-based data augmentation, which significantly sharpens the model’s decision boundaries. Experimental results on the benchmark Set 1 dataset demonstrate that AVP-Fusion achieves an accuracy of 0.9531 and an MCC of 0.9064, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art methods. In the second stage, leveraging transfer learning, the model enables precise subclass prediction for six viral families and eight specific viruses, even under limited sample sizes. In summary, AVP-Fusion serves as a robust and interpretable tool for high-throughput antiviral drug screening.
[LG-28] Generative Actor Critic
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21527
作者: Aoyang Qin,Deqian Kong,Wei Wang,Ying Nian Wu,Song-Chun Zhu,Sirui Xie
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Conventional Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms, typically focused on estimating or maximizing expected returns, face challenges when refining offline pretrained models with online experiences. This paper introduces Generative Actor Critic (GAC), a novel framework that decouples sequential decision-making by reframing \textitpolicy evaluation as learning a generative model of the joint distribution over trajectories and returns, p(\tau, y) , and \textitpolicy improvement as performing versatile inference on this learned model. To operationalize GAC, we introduce a specific instantiation based on a latent variable model that features continuous latent plan vectors. We develop novel inference strategies for both \textitexploitation, by optimizing latent plans to maximize expected returns, and \textitexploration, by sampling latent plans conditioned on dynamically adjusted target returns. Experiments on Gym-MuJoCo and Maze2D benchmarks demonstrate GAC’s strong offline performance and significantly enhanced offline-to-online improvement compared to state-of-the-art methods, even in absence of step-wise rewards.
[LG-29] First Provable Guarantees for Practical Private FL: Beyond Restrictive Assumptions
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21521
作者: Egor Shulgin,Grigory Malinovsky,Sarit Khirirat,Peter Richtárik
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Optimization and Control (math.OC); Machine Learning (stat.ML)
*备注:
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative training on decentralized data. Differential privacy (DP) is crucial for FL, but current private methods often rely on unrealistic assumptions (e.g., bounded gradients or heterogeneity), hindering practical application. Existing works that relax these assumptions typically neglect practical FL features, including multiple local updates and partial client participation. We introduce Fed- \alpha -NormEC, the first differentially private FL framework providing provable convergence and DP guarantees under standard assumptions while fully supporting these practical features. Fed- \alpha -NormE integrates local updates (full and incremental gradient steps), separate server and client stepsizes, and, crucially, partial client participation, which is essential for real-world deployment and vital for privacy amplification. Our theoretical guarantees are corroborated by experiments on private deep learning tasks.
[LG-30] When Bayesian Tensor Completion Meets Multioutput Gaussian Processes: Functional Universality and Rank Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21486
作者: Siyuan Li,Shikai Fang,Lei Cheng,Feng Yin,Yik-Chung Wu,Peter Gerstoft,Sergios Theodoridis
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Signal Processing (eess.SP)
*备注:
Abstract:Functional tensor decomposition can analyze multi-dimensional data with real-valued indices, paving the path for applications in machine learning and signal processing. A limitation of existing approaches is the assumption that the tensor rank-a critical parameter governing model complexity-is known. However, determining the optimal rank is a non-deterministic polynomial-time hard (NP-hard) task and there is a limited understanding regarding the expressive power of functional low-rank tensor models for continuous signals. We propose a rank-revealing functional Bayesian tensor completion (RR-FBTC) method. Modeling the latent functions through carefully designed multioutput Gaussian processes, RR-FBTC handles tensors with real-valued indices while enabling automatic tensor rank determination during the inference process. We establish the universal approximation property of the model for continuous multi-dimensional signals, demonstrating its expressive power in a concise format. To learn this model, we employ the variational inference framework and derive an efficient algorithm with closed-form updates. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the RR-FBTC over state-of-the-art approaches. The code is available at this https URL.
[LG-31] Statistical vs. Deep Learning Models for Estimating Substance Overdose Excess Mortality in the US
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21456
作者: Sukanya Krishna,Marie-Laure Charpignon,Maimuna Majumder
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Substance overdose mortality in the United States claimed over 80,000 lives in 2023, with the COVID-19 pandemic exacerbating existing trends through healthcare disruptions and behavioral changes. Estimating excess mortality, defined as deaths beyond expected levels based on pre-pandemic patterns, is essential for understanding pandemic impacts and informing intervention strategies. However, traditional statistical methods like SARIMA assume linearity, stationarity, and fixed seasonality, which may not hold under structural disruptions. We present a systematic comparison of SARIMA against three deep learning (DL) architectures (LSTM, Seq2Seq, and Transformer) for counterfactual mortality estimation using national CDC data (2015-2019 for training/validation, 2020-2023 for projection). We contribute empirical evidence that LSTM achieves superior point estimation (17.08% MAPE vs. 23.88% for SARIMA) and better-calibrated uncertainty (68.8% vs. 47.9% prediction interval coverage) when projecting under regime change. We also demonstrate that attention-based models (Seq2Seq, Transformer) underperform due to overfitting to historical means rather than capturing emergent trends. Ourreproducible pipeline incorporates conformal prediction intervals and convergence analysis across 60+ trials per configuration, and we provide an open-source framework deployable with 15 state health departments. Our findings establish that carefully validated DL models can provide more reliable counterfactual estimates than traditional methods for public health planning, while highlighting the need for calibration techniques when deploying neural forecasting in high-stakes domains.
[LG-32] RLLaVA: An RL-central Framework for Language and Vision Assistants
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21450
作者: Lei Zhao,Zihao Ma,Boyu Lin,Yuhe Liu,Wenjun Wu,Lei Huang
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: The code is available at this https URL
Abstract:We present an RL-central framework for Language and Vision Assistants (RLLaVA) with its formulation of Markov decision process (MDP). RLLaVA decouples RL algorithmic logic from model architecture and distributed execution, supporting researchers in implementing new RL algorithms with minimal code, and to plug in a broad family of RL methods and vision-language models (VLMs) while remaining agnostic to specific training and inference engines. RLLaVA makes resource-efficient training of 1B–7B models feasible on common GPUs; notably, 4B-scale models can be trained end-to-end with full-parameter updates on a single 24GB GPU. Experiments on multi-modal and agentic tasks demonstrate that RLLaVA has task extensibility, and the models trained with it consistently improve performance over base models, competitive with other specially engineered RL frameworks. The code is available at this https URL.
[LG-33] An Equivariance Toolbox for Learning Dynamics
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21447
作者: Yongyi Yang,Liu Ziyin
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Many theoretical results in deep learning can be traced to symmetry or equivariance of neural networks under parameter transformations. However, existing analyses are typically problem-specific and focus on first-order consequences such as conservation laws, while the implications for second-order structure remain less understood. We develop a general equivariance toolbox that yields coupled first- and second-order constraints on learning dynamics. The framework extends classical Noether-type analyses in three directions: from gradient constraints to Hessian constraints, from symmetry to general equivariance, and from continuous to discrete transformations. At the first order, our framework unifies conservation laws and implicit-bias relations as special cases of a single identity. At the second order, it provides structural predictions about curvature: which directions are flat or sharp, how the gradient aligns with Hessian eigenspaces, and how the loss landscape geometry reflects the underlying transformation structure. We illustrate the framework through several applications, recovering known results while also deriving new characterizations that connect transformation structure to modern empirical observations about optimization geometry.
[LG-34] Fuzzwise: Intelligent Initial Corpus Generation for Fuzzing
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21440
作者: Hridya Dhulipala,Xiaokai Rong,Aashish Yadavally,Tien N. Nguyen
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:In mutation-based greybox fuzzing, generating high-quality input seeds for the initial corpus is essential for effective fuzzing. Rather than conducting separate phases for generating a large corpus and subsequently minimizing it, we propose FuzzWise which integrates them into one process to generate the optimal initial corpus of seeds (ICS). FuzzWise leverages a multi-agent framework based on Large Language Models (LLMs). The first LLM agent generates test cases for the target program. The second LLM agent, which functions as a predictive code coverage module, assesses whether each generated test case will enhance the overall coverage of the current corpus. The streamlined process allows each newly generated test seed to be immediately evaluated for its contribution to the overall coverage. FuzzWise employs a predictive approach using an LLM and eliminates the need for actual execution, saving computational resources and time, particularly in scenarios where the execution is not desirable or even impossible. Our empirical evaluation demonstrates that FuzzWise generates significantly fewer test cases than baseline methods. Despite the lower number of test cases, FuzzWise achieves high code coverage and triggers more runtime errors compared to the baselines. Moreover, it is more time-efficient and coverage-efficient in producing an initial corpus catching more errors.
[LG-35] DeepCQ: General-Purpose Deep-Surrogate Framework for Lossy Compression Quality Prediction
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21433
作者: Khondoker Mirazul Mumenin,Robert Underwood,Dong Dai,Jinzhen Wang,Sheng Di,Zarija Lukić,Franck Cappello
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Performance (cs.PF)
*备注:
Abstract:Error-bounded lossy compression techniques have become vital for scientific data management and analytics, given the ever-increasing volume of data generated by modern scientific simulations and instruments. Nevertheless, assessing data quality post-compression remains computationally expensive due to the intensive nature of metric calculations. In this work, we present a general-purpose deep-surrogate framework for lossy compression quality prediction (DeepCQ), with the following key contributions: 1) We develop a surrogate model for compression quality prediction that is generalizable to different error-bounded lossy compressors, quality metrics, and input datasets; 2) We adopt a novel two-stage design that decouples the computationally expensive feature-extraction stage from the light-weight metrics prediction, enabling efficient training and modular inference; 3) We optimize the model performance on time-evolving data using a mixture-of-experts design. Such a design enhances the robustness when predicting across simulation timesteps, especially when the training and test data exhibit significant variation. We validate the effectiveness of DeepCQ on four real-world scientific applications. Our results highlight the framework’s exceptional predictive accuracy, with prediction errors generally under 10% across most settings, significantly outperforming existing methods. Our framework empowers scientific users to make informed decisions about data compression based on their preferred data quality, thereby significantly reducing I/O and computational overhead in scientific data analysis.
[LG-36] Cerberus: Multi-Agent Reasoning and Coverag e-Guided Exploration for Static Detection of Runtime Errors
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21431
作者: Hridya Dhulipala,Xiaokai Rong,Tien N. Nguyen
类目: oftware Engineering (cs.SE); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:In several software development scenarios, it is desirable to detect runtime errors and exceptions in code snippets without actual execution. A typical example is to detect runtime exceptions in online code snippets before integrating them into a codebase. In this paper, we propose Cerberus, a novel predictive, execution-free coverage-guided testing framework. Cerberus uses LLMs to generate the inputs that trigger runtime errors and to perform code coverage prediction and error detection without code execution. With a two-phase feedback loop, Cerberus first aims to both increasing code coverage and detecting runtime errors, then shifts to focus only detecting runtime errors when the coverage reaches 100% or its maximum, enabling it to perform better than prompting the LLMs for both purposes. Our empirical evaluation demonstrates that Cerberus performs better than conventional and learning-based testing frameworks for (in)complete code snippets by generating high-coverage test cases more efficiently, leading to the discovery of more runtime errors.
[LG-37] A Survey of Freshness-Aware Wireless Networking with Reinforcement Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21412
作者: Alimu Alibotaiken,Suyang Wang,Oluwaseun T. Ajayi,Yu Cheng
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Systems and Control (eess.SY)
*备注:
Abstract:The age of information (AoI) has become a central measure of data freshness in modern wireless systems, yet existing surveys either focus on classical AoI formulations or provide broad discussions of reinforcement learning (RL) in wireless networks without addressing freshness as a unified learning problem. Motivated by this gap, this survey examines RL specifically through the lens of AoI and generalized freshness optimization. We organize AoI and its variants into native, function-based, and application-oriented families, providing a clearer view of how freshness should be modeled in B5G and 6G systems. Building on this foundation, we introduce a policy-centric taxonomy that reflects the decisions most relevant to freshness, consisting of update-control RL, medium-access RL, risk-sensitive RL, and multi-agent RL. This structure provides a coherent framework for understanding how learning can support sampling, scheduling, trajectory planning, medium access, and distributed coordination. We further synthesize recent progress in RL-driven freshness control and highlight open challenges related to delayed decision processes, stochastic variability, and cross-layer design. The goal is to establish a unified foundation for learning-based freshness optimization in next-generation wireless networks.
[LG-38] kooplearn: A Scikit-Learn Compatible Library of Algorithms for Evolution Operator Learning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21409
作者: Giacomo Turri,Grégoire Pacreau,Giacomo Meanti,Timothée Devergne,Daniel Ordonez,Erfan Mirzaei,Bruno Belucci,Karim Lounici,Vladimir Kostic,Massimiliano Pontil,Pietro Novelli
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:kooplearn is a machine-learning library that implements linear, kernel, and deep-learning estimators of dynamical operators and their spectral decompositions. kooplearn can model both discrete-time evolution operators (Koopman/Transfer) and continuous-time infinitesimal generators. By learning these operators, users can analyze dynamical systems via spectral methods, derive data-driven reduced-order models, and forecast future states and observables. kooplearn’s interface is compliant with the scikit-learn API, facilitating its integration into existing machine learning and data science workflows. Additionally, kooplearn includes curated benchmark datasets to support experimentation, reproducibility, and the fair comparison of learning algorithms. The software is available at this https URL.
[LG-39] Learning to Reconfigure: Using Device Status to Select the Right Constrained Coding Scheme
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21396
作者: Doğukan Özbayrak,Ahmed Hareedy
类目: Information Theory (cs.IT); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Signal Processing (eess.SP)
*备注: 13 pages (double column), 4 figures, submitted to the IEEE Transactions on Communications (TCOM)
Abstract:In the age of data revolution, a modern storage~or transmission system typically requires different levels of protection. For example, the coding technique used to fortify data in a modern storage system when the device is fresh cannot be the same as that used when the device ages. Therefore, providing reconfigurable coding schemes and devising an effective way to perform this reconfiguration are key to extending the device lifetime. We focus on constrained coding schemes for the emerging two-dimensional magnetic recording (TDMR) technology. Recently, we have designed efficient lexicographically-ordered constrained (LOCO) coding schemes for various stages of the TDMR device lifetime, focusing on the elimination of isolation patterns, and demonstrated remarkable gains by using them. LOCO codes are naturally reconfigurable, and we exploit this feature in our work. Reconfiguration based on predetermined time stamps, which is what the industry adopts, neglects the actual device status. Instead, we propose offline and online learning methods to perform this task based on the device status. In offline learning, training data is assumed to be available throughout the time span of interest, while in online learning, we only use training data at specific time intervals to make consequential decisions. We fit the training data to polynomial equations that give the bit error rate in terms of TD density, then design an optimization problem in order to reach the optimal reconfiguration decisions to switch from a coding scheme to another. The objective is to maximize the storage capacity and/or minimize the decoding complexity. The problem reduces to a linear programming problem. We show that our solution is the global optimal based on problem characteristics, and we offer various experimental results that demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in TDMR systems.
[LG-40] A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Synthetic Data Generation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21395
作者: Natalia Espinosa-Dice,Nicholas J. Jackson,Chao Yan,Aaron Lee,Bradley A. Malin
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Synthetic data generation (SDG) is a promising approach for enabling data sharing in biomedical studies while preserving patient privacy. Yet, state-of-the-art generative models often require large datasets and complex training procedures, limiting their applicability in small-sample settings. In this work, we reframe SDG as a reinforcement learning (RL) problem and introduce RLSyn, a novel framework that models the data generator as a stochastic policy over patient records and optimizes it using Proximal Policy Optimization with discriminator-derived rewards, yielding more stable and data-efficient training. We evaluate RLSyn on two biomedical datasets - AI-READI and MIMIC-IV- and benchmark it against state-of-the-art generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion-based methods across extensive privacy, utility, and fidelity evaluations. RL-Syn performs comparably to diffusion models and outperforms GANs on MIMIC-IV, while outperforming both diffusion models and GANs on the smaller AI-READI dataset. These results demonstrate that reinforcement learning provides a principled and effective alternative for synthetic biomedical data generation, particularly in data-scarce regimes.
[LG-41] Physics-Informed Neural Solvers for Periodic Quantum Eigenproblems
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21349
作者: Haaris Mian
类目: Machine Learning (cs.LG); Computational Physics (physics.comp-ph)
*备注: Master’s thesis
Abstract:This thesis presents a physics-informed machine learning framework for solving the Floquet-Bloch eigenvalue problem associated with particles in two-dimensional periodic potentials, with a focus on honeycomb lattice geometry, due to its distinctive band topology featuring Dirac points and its relevance to materials such as graphene. By leveraging neural networks to learn complex Bloch functions and their associated eigenvalues (energies) simultaneously, we develop a mesh-free solver enforcing the governing Schrödinger equation, Bloch periodicity, and normalization constraints through a composite loss function without supervision. The model is trained over the Brillouin zone to recover band structures and Bloch modes, with numerical validation against traditional plane-wave expansion methods. We further explore transfer learning techniques to adapt the solver from nearly-free electron potentials to strongly varying potentials, demonstrating its ability to capture changes in band structure topology. This work contributes to the growing field of physics-informed machine learning for quantum eigenproblems, providing insights into the interplay between symmetry, band structure, and neural architectures.
[LG-42] Harnessing Data Spaces to Build Intelligent Smart City Infrastructures Across the Cloud-Edge Continuum
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21340
作者: Dimitrios Amaxilatis,Themistoklis Sarantakos,Nikolaos Tsironis,Souvik Sengupta,Kostas Ramantas,Jhofre Ojeda
类目: Distributed, Parallel, and Cluster Computing (cs.DC); Databases (cs.DB); Emerging Technologies (cs.ET); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Smart cities are increasingly adopting data-centric architectures to enhance the efficiency, sustainability, and resilience of urban services.
[LG-43] A Frobenius-Optimal Projection for Enforcing Linear Conservation in Learned Dynamical Models
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.22084
作者: John M. Mango,Ronald Katende
类目: Dynamical Systems (math.DS); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Numerical Analysis (math.NA)
*备注:
Abstract:We consider the problem of restoring linear conservation laws in data-driven linear dynamical models. Given a learned operator \widehatA and a full-rank constraint matrix C encoding one or more invariants, we show that the matrix closest to \widehatA in the Frobenius norm and satisfying C^\top A = 0 is the orthogonal projection A^\star = \widehatA - C(C^\top C)^-1C^\top \widehatA . This correction is uniquely defined, low rank and fully determined by the violation C^\top \widehatA . In the single-invariant case it reduces to a rank-one update. We prove that A^\star enforces exact conservation while minimally perturbing the dynamics, and we verify these properties numerically on a Markov-type example. The projection provides an elementary and general mechanism for embedding exact invariants into any learned linear model.
[LG-44] Modeling high dimensional point clouds with the spherical cluster model
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21960
作者: Frédéric Cazals,Antoine Commaret,Louis Goldenberg
类目: Methodology (stat.ME); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注: Main text: 4 figures, 15 pages
Abstract:A parametric cluster model is a statistical model providing geometric insights onto the points defining a cluster. The \em spherical cluster model (SC) approximates a finite point set P\subset \mathbbR^d by a sphere S(c,r) as follows. Taking r as a fraction \eta\in(0,1) (hyper-parameter) of the std deviation of distances between the center c and the data points, the cost of the SC model is the sum over all data points lying outside the sphere S of their power distance with respect to S . The center c of the SC model is the point minimizing this cost. Note that \eta=0 yields the celebrated center of mass used in KMeans clustering. We make three contributions. First, we show fitting a spherical cluster yields a strictly convex but not smooth combinatorial optimization problem. Second, we present an exact solver using the Clarke gradient on a suitable stratified cell complex defined from an arrangement of hyper-spheres. Finally, we present experiments on a variety of datasets ranging in dimension from d=9 to d=10,000 , with two main observations. First, the exact algorithm is orders of magnitude faster than BFGS based heuristics for datasets of small/intermediate dimension and small values of \eta , and for high dimensional datasets (say d100 ) whatever the value of \eta . Second, the center of the SC model behave as a parameterized high-dimensional median. The SC model is of direct interest for high dimensional multivariate data analysis, and the application to the design of mixtures of SC will be reported in a companion paper. Comments: Main text: 4 figures, 15 pages Subjects: Methodology (stat.ME); Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21960 [stat.ME] (or arXiv:2512.21960v1 [stat.ME] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21960 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-45] Matching for Scalable Sampling and Fine-Tuning
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21829
作者: Peter Potaptchik,Cheuk-Kit Lee,Michael S. Albergo
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:We propose a simple, scalable algorithm for using stochastic interpolants to sample from unnormalized densities and for fine-tuning generative models. The approach, Tilt Matching, arises from a dynamical equation relating the flow matching velocity to one targeting the same distribution tilted by a reward, implicitly solving a stochastic optimal control problem. The new velocity inherits the regularity of stochastic interpolant transports while also being the minimizer of an objective with strictly lower variance than flow matching itself. The update to the velocity field can be interpreted as the sum of all joint cumulants of the stochastic interpolant and copies of the reward, and to first order is their covariance. The algorithms do not require any access to gradients of the reward or backpropagating through trajectories of the flow or diffusion. We empirically verify that the approach is efficient and highly scalable, providing state-of-the-art results on sampling under Lennard-Jones potentials and is competitive on fine-tuning Stable Diffusion, without requiring reward multipliers. It can also be straightforwardly applied to tilting few-step flow map models.
[LG-46] Incorporating rank-free coupling and external field via an amplitude-only modulated spatial photonic Ising machine
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21587
作者: Ze Zheng,Yuegang Li,Hang Xu,Jingzheng Huang,Tailong Xiao,Guihua Zeng
类目: Optics (physics.optics); Disordered Systems and Neural Networks (cond-mat.dis-nn); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Mathematical Physics (math-ph); Applied Physics (physics.app-ph)
*备注: 4 pages, 3 figures
Abstract:Ising machines have emerged as effective solvers for combinatorial optimization problems, such as NP-hard problems, machine learning, and financial modeling. Recent spatial photonic Ising machines (SPIMs) excel in multi-node optimization and spin glass simulations, leveraging their large-scale and fully connected characteristics. However, existing laser diffraction-based SPIMs usually sacrifice time efficiency or spin count to encode high-rank spin-spin coupling and external fields, limiting their scalability for real-world applications. Here, we demonstrate an amplitude-only modulated rank-free spatial photonic Ising machine (AR-SPIM) with 200 iterations per second. By re-formulating an arbitrary Ising Hamiltonian as the sum of Hadamard products, followed by loading the corresponding matrices/vectors onto an aligned amplitude spatial light modulator and digital micro-mirrors device, we directly map a 797-spin Ising model with external fields (nearly 9-bit precision, -255 to 255) into an incoherent light field, eliminating the need for repeated and auxiliary operations. Serving as encoding accuracy metrics, the linear coefficient of determination and Pearson correlation coefficient between measured light intensities and Ising Hamiltonians exceed 0.9800, with values exceed 0.9997 globally. The AR-SPIM achieves less than 0.3% error rate for ground-state search of biased Max-cut problems with arbitrary ranks and weights, enables complex phase transition observations, and facilitates scalable spin counts for sparse Ising problems via removing zero-valued Hadamard product terms. This reconfigurable AR-SPIM can be further developed to support large-scale machine-learning training and deployed for practical applications in discrete optimization and quantum many-body simulations.
[LG-47] Quantum Nondecimated Wavelet Transform: Theory Circuits and Applications
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21478
作者: Brani Vidakovic
类目: Quantum Physics (quant-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Data Analysis, Statistics and Probability (physics.data-an); Computation (stat.CO)
*备注:
Abstract:The nondecimated or translation-invariant wavelet transform (NDWT) is a central tool in classical multiscale signal analysis, valued for its stability, redundancy, and shift invariance. This paper develops two complementary quantum formulations of the NDWT that embed these classical properties coherently into quantum computation. The first formulation is based on the epsilon-decimated interpretation of the NDWT and realizes all circularly shifted wavelet transforms simultaneously by promoting the shift index to a quantum register and applying controlled circular shifts followed by a wavelet analysis unitary. The resulting construction yields an explicit, fully unitary quantum representation of redundant wavelet coefficients and supports coherent postprocessing, including quantum shrinkage via ancilla-driven completely positive trace preserving maps. The second formulation is based on the Hadamard test and uses diagonal phase operators to probe scale-shift wavelet structure through interference, providing direct access to shift-invariant energy scalograms and multiscale spectra without explicit coefficient reconstruction. Together, these two approaches demonstrate that redundancy and translation invariance can be exploited rather than avoided in the quantum setting. Applications to denoising, feature extraction, and spectral scaling illustrate how quantum NDWTs provide a flexible and physically meaningful foundation for multiscale quantum signal processing.
[LG-48] An approach to Fisher-Rao metric for infinite dimensional non-parametric information geometry
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21451
作者: Bing Cheng,Howell Tong
类目: Machine Learning (stat.ML); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Being infinite dimensional, non-parametric information geometry has long faced an “intractability barrier” due to the fact that the Fisher-Rao metric is now a functional incurring difficulties in defining its inverse. This paper introduces a novel framework to resolve the intractability with an Orthogonal Decomposition of the Tangent Space ( T_fM=S \oplus S^\perp ), where S represents an observable covariate subspace. Through the decomposition, we derive the Covariate Fisher Information Matrix (cFIM), denoted as G_f , which is a finite-dimensional and computable representative of information extractable from the manifold’s geometry. Indeed, by proving the Trace Theorem: H_G(f)=\textTr(G_f) , we establish a rigorous foundation for the G-entropy previously introduced by us, thereby identifying it not merely as a gradient-based regularizer, but also as a fundamental geometric invariant representing the total explainable statistical information captured by the probability distribution associated with the model. Furthermore, we establish a link between G_f and the second-order derivative (i.e. the curvature) of the KL-divergence, leading to the notion of Covariate Cramér-Rao Lower Bound(CRLB). We demonstrate that G_f is congruent to the Efficient Fisher Information Matrix, thereby providing fundamental limits of variance for semi-parametric estimators. Finally, we apply our geometric framework to the Manifold Hypothesis, lifting the latter from a heuristic assumption into a testable condition of rank-deficiency within the cFIM. By defining the Information Capture Ratio, we provide a rigorous method for estimating intrinsic dimensionality in high-dimensional data. In short, our work bridges the gap between abstract information geometry and the demand of explainable AI, by providing a tractable path for revealing the statistical coverage and the efficiency of non-parametric models.
[LG-49] Dynamic Attention (DynAttn): Interpretable High-Dimensional Spatio-Temporal Forecasting (with Application to Conflict Fatalities)
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21435
作者: Stefano M. Iacus,Haodong Qi,Marcello Carammia,Thomas Juneau
类目: Applications (stat.AP); Machine Learning (cs.LG)
*备注:
Abstract:Forecasting conflict-related fatalities remains a central challenge in political science and policy analysis due to the sparse, bursty, and highly non-stationary nature of violence data. We introduce DynAttn, an interpretable dynamic-attention forecasting framework for high-dimensional spatio-temporal count processes. DynAttn combines rolling-window estimation, shared elastic-net feature gating, a compact weight-tied self-attention encoder, and a zero-inflated negative binomial (ZINB) likelihood. This architecture produces calibrated multi-horizon forecasts of expected casualties and exceedance probabilities, while retaining transparent diagnostics through feature gates, ablation analysis, and elasticity measures. We evaluate DynAttn using global country-level and high-resolution PRIO-grid-level conflict data from the VIEWS forecasting system, benchmarking it against established statistical and machine-learning approaches, including DynENet, LSTM, Prophet, PatchTST, and the official VIEWS baseline. Across forecast horizons from one to twelve months, DynAttn consistently achieves substantially higher predictive accuracy, with particularly large gains in sparse grid-level settings where competing models often become unstable or degrade sharply. Beyond predictive performance, DynAttn enables structured interpretation of regional conflict dynamics. In our application, cross-regional analyses show that short-run conflict persistence and spatial diffusion form the core predictive backbone, while climate stress acts either as a conditional amplifier or a primary driver depending on the conflict theater. Subjects: Applications (stat.AP); Machine Learning (cs.LG) Cite as: arXiv:2512.21435 [stat.AP] (or arXiv:2512.21435v1 [stat.AP] for this version) https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2512.21435 Focus to learn more arXiv-issued DOI via DataCite (pending registration)
[LG-50] Deep learning-enhanced dual-mode multiplexed optical sensor for point-of-care diagnostics of cardiovascular diseases
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21389
作者: Gyeo-Re Han,Merve Eryilmaz,Artem Goncharov,Yuzhu Li,Shun Ye,Aoi Tomoeda,Emily Ngo,Margherita Scussat,Xiao Wang,Zixiang Ji,Max Zhang,Jeffrey J. Hsu,Omai B. Garner,Dino Di Carlo,Aydogan Ozcan
类目: Medical Physics (physics.med-ph); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Applied Physics (physics.app-ph); Biological Physics (physics.bio-ph)
*备注: 32 Pages, 6 Figures, 2 Tables
Abstract:Rapid and accessible cardiac biomarker testing is essential for the timely diagnosis and risk assessment of myocardial infarction (MI) and heart failure (HF), two interrelated conditions that frequently coexist and drive recurrent hospitalizations with high mortality. However, current laboratory and point-of-care testing systems are limited by long turnaround times, narrow dynamic ranges for the tested biomarkers, and single-analyte formats that fail to capture the complexity of cardiovascular disease. Here, we present a deep learning-enhanced dual-mode multiplexed vertical flow assay (xVFA) with a portable optical reader and a neural network-based quantification pipeline. This optical sensor integrates colorimetric and chemiluminescent detection within a single paper-based cartridge to complementarily cover a large dynamic range (spanning ~6 orders of magnitude) for both low- and high-abundance biomarkers, while maintaining quantitative accuracy. Using 50 uL of serum, the optical sensor simultaneously quantifies cardiac troponin I (cTnI), creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) within 23 min. The xVFA achieves sub-pg/mL sensitivity for cTnI and sub-ng/mL sensitivity for CK-MB and NT-proBNP, spanning the clinically relevant ranges for these biomarkers. Neural network models trained and blindly tested on 92 patient serum samples yielded a robust quantification performance (Pearson’s r 0.96 vs. reference assays). By combining high sensitivity, multiplexing, and automation in a compact and cost-effective optical sensor format, the dual-mode xVFA enables rapid and quantitative cardiovascular diagnostics at the point of care.
[LG-51] Sensitivity Analysis of the Consistency Assumption
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21379
作者: Brian Knaeble,Qinyun Lin,Erich Kummerfeld,Kenneth A. Frank
类目: Methodology (stat.ME); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Optimization and Control (math.OC)
*备注:
Abstract:Sensitivity analysis informs causal inference by assessing the sensitivity of conclusions to departures from assumptions. The consistency assumption states that there are no hidden versions of treatment and that the outcome arising naturally equals the outcome arising from intervention. When reasoning about the possibility of consistency violations, it can be helpful to distinguish between covariates and versions of treatment. In the context of surgery, for example, genomic variables are covariates and the skill of a particular surgeon is a version of treatment. There may be hidden versions of treatment, and this paper addresses that concern with a new kind of sensitivity analysis. Whereas many methods for sensitivity analysis are focused on confounding by unmeasured covariates, the methodology of this paper is focused on confounding by hidden versions of treatment. In this paper, new mathematical notation is introduced to support the novel method, and example applications are described.
信息检索
[IR-0] Frozen LVLMs for Micro-Video Recommendation: A Systematic Study of Feature Extraction and Fusion
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21863
作者: Huatuan Sun,Yunshan Ma,Changguang Wu,Yanxin Zhang,Pengfei Wang,Xiaoyu Du
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Multimedia (cs.MM)
*备注: 10 pages, 4 figures
Abstract:Frozen Large Video Language Models (LVLMs) are increasingly employed in micro-video recommendation due to their strong multimodal understanding. However, their integration lacks systematic empirical evaluation: practitioners typically deploy LVLMs as fixed black-box feature extractors without systematically comparing alternative representation strategies. To address this gap, we present the first systematic empirical study along two key design dimensions: (i) integration strategies with ID embeddings, specifically replacement versus fusion, and (ii) feature extraction paradigms, comparing LVLM-generated captions with intermediate decoder hidden states. Extensive experiments on representative LVLMs reveal three key principles: (1) intermediate hidden states consistently outperform caption-based representations, as natural-language summarization inevitably discards fine-grained visual semantics crucial for recommendation; (2) ID embeddings capture irreplaceable collaborative signals, rendering fusion strictly superior to replacement; and (3) the effectiveness of intermediate decoder features varies significantly across layers. Guided by these insights, we propose the Dual Feature Fusion (DFF) Framework, a lightweight and plug-and-play approach that adaptively fuses multi-layer representations from frozen LVLMs with item ID embeddings. DFF achieves state-of-the-art performance on two real-world micro-video recommendation benchmarks, consistently outperforming strong baselines and providing a principled approach to integrating off-the-shelf large vision-language models into micro-video recommender systems.
[IR-1] KG20C KG20C-QA: Scholarly Knowledge Graph Benchmarks for Link Prediction and Question Answering
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21799
作者: Hung-Nghiep Tran,Atsuhiro Takasu
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注: Extracted and extended from the first author’s PhD thesis titled “Multi-Relational Embedding for Knowledge Graph Representation and Analysis”
Abstract:In this paper, we present KG20C and KG20C-QA, two curated datasets for advancing question answering (QA) research on scholarly data. KG20C is a high-quality scholarly knowledge graph constructed from the Microsoft Academic Graph through targeted selection of venues, quality-based filtering, and schema definition. Although KG20C has been available online in non-peer-reviewed sources such as GitHub repository, this paper provides the first formal, peer-reviewed description of the dataset, including clear documentation of its construction and specifications. KG20C-QA is built upon KG20C to support QA tasks on scholarly data. We define a set of QA templates that convert graph triples into natural language question–answer pairs, producing a benchmark that can be used both with graph-based models such as knowledge graph embeddings and with text-based models such as large language models. We benchmark standard knowledge graph embedding methods on KG20C-QA, analyze performance across relation types, and provide reproducible evaluation protocols. By officially releasing these datasets with thorough documentation, we aim to contribute a reusable, extensible resource for the research community, enabling future work in QA, reasoning, and knowledge-driven applications in the scholarly domain. The full datasets will be released at this https URL upon paper publication.
[IR-2] CEMG: Collaborative-Enhanced Multimodal Generative Recommendation
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21543
作者: Yuzhen Lin,Hongyi Chen,Xuanjing Chen,Shaowen Wang,Ivonne Xu,Dongming Jiang
类目: Information Retrieval (cs.IR)
*备注:
Abstract:Generative recommendation models often struggle with two key challenges: (1) the superficial integration of collaborative signals, and (2) the decoupled fusion of multimodal features. These limitations hinder the creation of a truly holistic item representation. To overcome this, we propose CEMG, a novel Collaborative-Enhaned Multimodal Generative Recommendation framework. Our approach features a Multimodal Fusion Layer that dynamically integrates visual and textual features under the guidance of collaborative signals. Subsequently, a Unified Modality Tokenization stage employs a Residual Quantization VAE (RQ-VAE) to convert this fused representation into discrete semantic codes. Finally, in the End-to-End Generative Recommendation stage, a large language model is fine-tuned to autoregressively generate these item codes. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CEMG significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines.
[IR-3] Dynamic Cooperative Strategies in Search Engine Advertising Market: With and Without Retail Competition
链接: https://arxiv.org/abs/2512.21501
作者: Huiran Li,Qiucheng Li,Baozhu Feng
类目: Computer Science and Game Theory (cs.GT); Information Retrieval (cs.IR); Systems and Control (eess.SY)
*备注: 60 pages, 17 figures,6 tables
Abstract:In search engine advertising (SEA) market, where competition among retailers is intense and multifaceted, channel coordination between retailers and manufacturers emerges as a critical factor, which significantly influences the effectiveness of advertising strategies. This research attempts to provide managerial guidelines for cooperative advertising in the SEA context by modeling two cooperative advertising decision scenarios. Scenario I defines a simple cooperative channel consisting of one manufacturer and one retailer. In Scenario II, we consider a more general setting where there is an independent retailer who competes with the Manufacturer-Retailer alliance in Scenario I. We propose a novel cooperative advertising optimization model, wherein a manufacturer can advertise product directly through SEA campaigns and indirectly by subsidizing its retailer. To highlight the distinctive features of SEA, our model incorporates dynamic quality scores and focuses on a finite time horizon. In each scenario, we provide a feasible equilibrium solution of optimal policies for all members. Subsequently, we conduct numerical experiments to perform sensitivity analysis for both the quality score and gross margin. Additionally, we explore the impact of the initial market share of the competing retailer in Scenario II. Finally, we investigate how retail competition affects the cooperative alliance’s optimal strategy and channel performance. Our identified properties derived from the equilibrium and numerical analyses offer crucial insights for participants engaged in cooperative advertising within the SEA market.
附件下载